Micro Unit 4 - Monopoly
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Characteristics of Monopoly (4)
One large firm → The firm is the market
Unique product → No close substitutes
High barriers of entry due to economies of scale
Firms can not enter the industry
Monopolies are price setters
General Misconceptions About a Monopoly
All Monopolies Make a Profit
Monopolies are usually efficient
All monopolies are bad for the economy
All monopolies are illegal
Monopolies charge the highest price possible
The government never prevents monopolies from forming
Can a monopoly be good for the economy?
Economies of scale can make it impractical to have smaller firms → Monopoly sometimes good for the economy
Natural Monopoly
Industry where a single firm can produce at a lower cost than 2 or more competing firms
ONE firm can produce at the socially optimal quantity and lowest cost due to economies of scale
Better to have only ONE firm because ATC is falling at socially optimal quantity
Where do you produce in a monopoly?
Always Maximize Profit → MR=MC
If a monopoly wants to sell more units you need to ___
Lower the price
What is the main difference between a Monopoly and Perfect Competition
Marginal Revenue is ALWAYS LESS than demand
Where is Demand Elastic/ Inelastic?
Inelastic where price causes TR to increase
Elastic if price causes TR to decrease
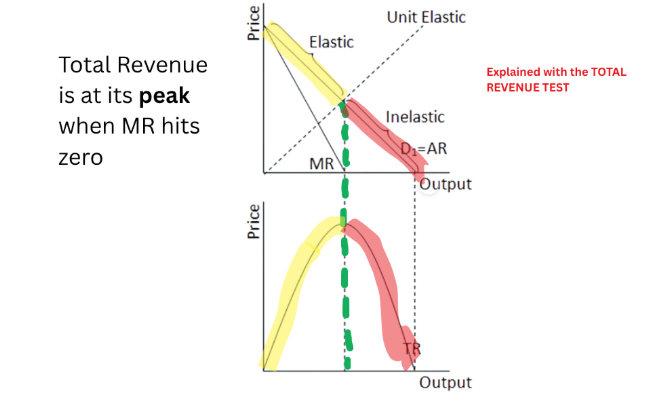
Where is a price set in a monopoly?
Price is set at Demand → Produces at MR=MC but sells at the price where it intercepts with D
When do you shutdown in monopoly?
Shutdown when the PRICE SOLD (D) is below AVC
Monopoly Efficiency
Monopolies are INNEFICIENT because they
Charge a higher price
Don’t produce enough (Not Allocatively Efficient)
Produce at higher cost (Not productively efficient)
Monopolies produce less and charge higher price
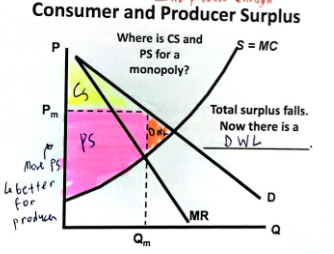
Where is CS and PS for a monopoly?
Economies of Scale role in Monopoly
Economies of Scale make it impractical to have smaller firms
Having one big company can keep costs low
Why/ how regulate monopolies?
Keeps prices low and tries to keep monopolies efficient
Regulates by using price controls → Price Ceiling (Max Price)
Socially Optimal Price
Where Demand = Marginal Cost → Place to set price ceiling
No deadweightloss but NOT PROFITABLE
Typically requires government subsidy
Fair Return Price (Break-Even)
Set at ATC=D (Normal Profit)
Firms breakeven but not at socially optimal price/ quantity
Price Discrimination
Practise of selling the same product to different buyers at different prices
EG. CHILD & ADULT MOVIE TICKETS, BUSINESS DISCOUNT
What are requirements of Price Discrimination
Having monopoly power, being able to segregate the market and consumers can NOT RESELL PRODUCT
Result of Price Discrimination
Results in MORE profit, MANY prices, and NO CONSUMER SURPLUS
Monopolistic Competition
Large numbers of sellers
SOME control over price
Different products
Low barriers to entry/ exit
A lot of ADVERTISING
Monopolistic Competition VS Perfect Competition
Monopolistic | Perfect Competition |
|
|
Differentiated Products
Goods are not identical and firms want to capture marketshare
Since the products have substitutes firms use non-price competition
Non-Price Competition
Competition within a market that is driven by things other than price
Brand Names/ Packaging, Product Quality/ Attributes, Service, Location and ADVERTISING
Advertising aims to Increase demand and make demand more ELASTIC
Monopolistic Competition Graph in Short Run
Same as a monopoly firm making profit → MR > D (SEE GRAPH)
Produce at D=MC and ATC Is below
Monopolistic Competition Graph in Long Run
Firms will enter the market and drives down CURRENT FIRM DEMAND for firms ALREADY IN MARKET
Demand will continue to fall until there is NO ECONOMIC PROFIT
Produce at D=MC and ATC also is that point
Monopolistic Competition Long Run Equilibrium
Quantity where MR=MC Moves up to P=ATC
D&MR CURVE ARE THE ONES THAT SHIFT NOT ATC → Shift up and down
Shifting Demand in Monopolistic Competition with PROFIT
New firms enter, and more firms = more close substitute and less market share
Demand for each firm decreases
Shifting Demand in Monopolistic Competition with LOSSES
Firms will exit → Less substitutes → More market share
Demand for each firm rises
Excess Capacity
Given current resources, the firm CAN produce at lowest costs but they decide not to
Gap between Minimum ATC and MR=MC is the excess capacity
Firms hold back production to maximize profit
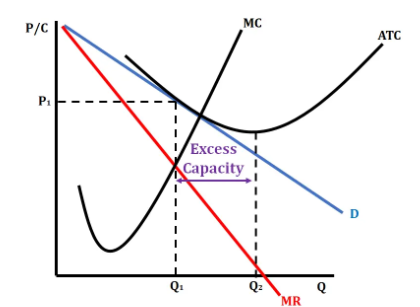
Why is Monoplistic Competition NOT Productivley Efficient?
Typically produce at MR=MC and sell at MR=D
BUT it is not at the lowest ATC so its not efficient
Characteristics of Oligopolies
Few Large Producers (less than 10)
Both identical OR differentiated products
High barriers to entry
Control over price (Price Maker)
Mutual Interdependence → Firms use strategic Pricing
What are the 3 Barriers to Entry for Oligopoly?
Economies of Scale → Hard to make cars bc only big firms make cheap cars
If others join, you lower price so you fuck them in the arse
High start-up costs (factory, infrastructure)
Ownership of raw materials → Control over raw materials
Game Theory
Study of how people behave in strategic situations
Helps oligopoly maximize profit
Interdependence (Oligopoly)
Oligopolies are interdependent since they compete with only a few other firms
Pricing and output decisions must be strategic to avoid economic loss
Game theory helps us analyze their strategies
Dominant Strategy
Best move to make regardless of what your opponent oes
You benefit no matter what your opponent does → Whatever opponent does, do same shit
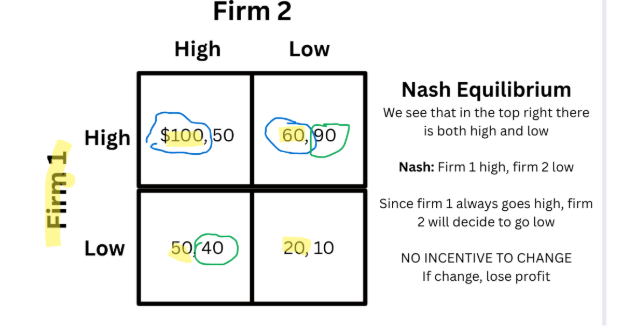
Nash Equilibrium
Optimal outcome that occurs when both firms make decisions simultaneously with no incentive to change
If they change their strategy they will be worse off
Dominant Strategy (On Matrix)
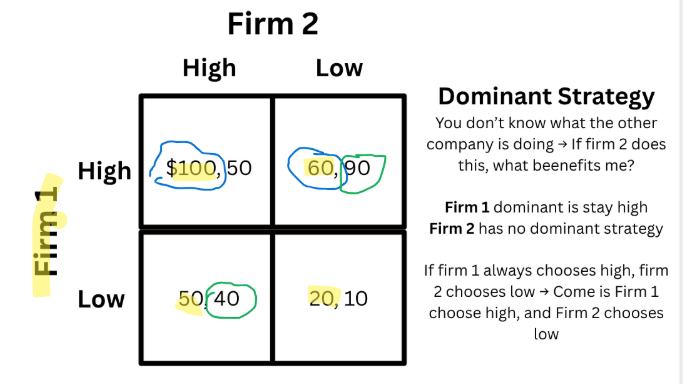
Nash Equilibrium (On Matrix)
3 types of oligopolies
price leadership - no graph
Colluding - monopoly geaph
non colluding - kinked deamdn