Parotid, Temporal, Infratemporal Fossae, and TMJ
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Parotid region
Posterolateral part of the facial region
Includes:
parotid gland and duct
parotid plexus of the facial nerve (CN VII)
retromandibular vein
external carotid artery
masseter muscle
Zygomatic arch
Superior boundary of the parotid region
External ear, anterior border of SCM
Posterior boundary of the parotid region
Ramus of the mandible
Medial boundary of the parotid region
Anterior border of masseter
Anterior boundary of the parotid region
Angle and inferior border of mandible
Inferior boundary of the parotid region
Parotid gland
Largest salivary gland
approx. weight: 15g
enclosed within a parotid sheath
occupies the parotid bed
irregularly shaped/triangular
Irregularly shaped/triangular
Shape of parotid gland
Anteroinferior to the EAM, between ramus and mastoid process/SCM
Location of the parotid gland
Anterior to EAM
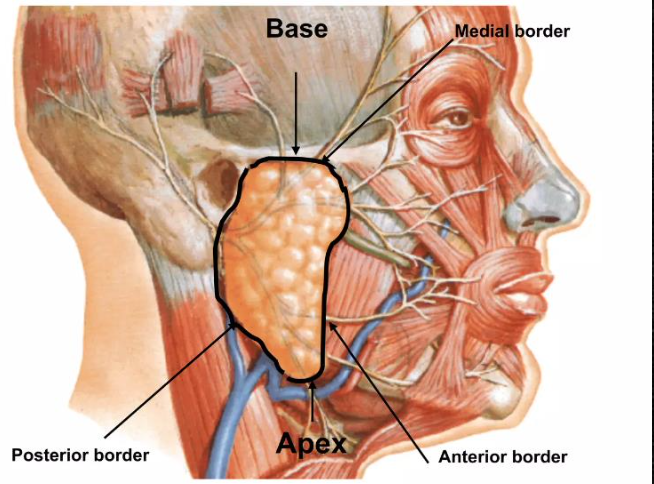
The base of the parotid gland is located _____
Posterior to the angle of the mandible
The apex of the parotid gland is located _____
Parotid sheath
Parotid fascia/fascial sheath
Tough, unyielding fascial capsule
Continuation of cervical fascia
Attaches to the deep surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible
Encloses the parotid space (entirely closed)
cervical fascia
The parotid sheath is a continuation of the _____
Stensen’s duct
Another name for parotid duct
Parotid duct
Passes horizontally from the anterior edge of the gland
Pierces the buccinator and enters the oral cavity through a small cavity opposite the 2nd maxillary molars (17 or 27)
Buccinator
What muscle does the parotid duct pierce?
2nd maxillary molars
The parotid duct pierces the buccinator and enters the oral cavity through a small cavity opposite the _____
Anterior, posterior, medial
Borders of the parotid gland
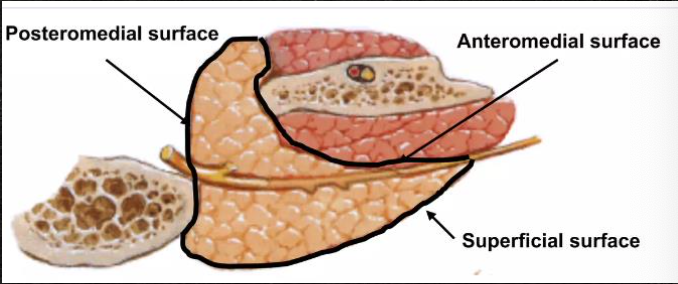
Superior, superficial, anteromedial, posteromedial
Surfaces of the parotid gland
Apex of the parotid gland
Contains:
Cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII)
Divisions of retromandibular veins
Base of the parotid gland
Contains:
EAM
Superficial temporal vessels
Auriculotemporal nerve
Facial nerve
Facial nerve
Retromandibular vein
External carotid artery
Structures passing through the parotid gland
Retromandibular vein
Drains structure of face
Drainage of parotid gland
Deep
Auriculotemporal nerve (general pain sensation)
Greater auricular nerve (branch of cervical plexus)
Sensory innervation of parotid gland
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Parasympathetic innervation of the parotid gland
Secretion of thin, watery saliva
Parasympathetic stimulation of parotid gland
CN IX → tympanic plexus (in middle ear) → lesser petrosal nerve → otic ganglion → post-ganglionic parasympathetics (auriculotemporal nerve) → parotid gland
Parasympathetic pathway of the parotid gland
Carotid plexus
Sympathetic innervation of the parotid gland
Reduce saliva secretion
Sympathetic stimulation of parotid gland
Posterior auricular artery
Superficial temporal artery
Blood supply of the parotid gland
Parotid node
Jugulodigastric node
Lymphatic drainage of the parotid gland
Temporal region
Lateral area of the scalp and the deeper soft tissues overlying the temporal fossa of the cranium, superior to the zygomatic arch
Temporal fossa
Lateral depression of the skull
Occupied by the temporalis muscle
Boundaries:
Post & sup: temporal lines
Ant: frontal and zygomatic bones
Lat: zygomatic arch
Inf: infratemporal crest
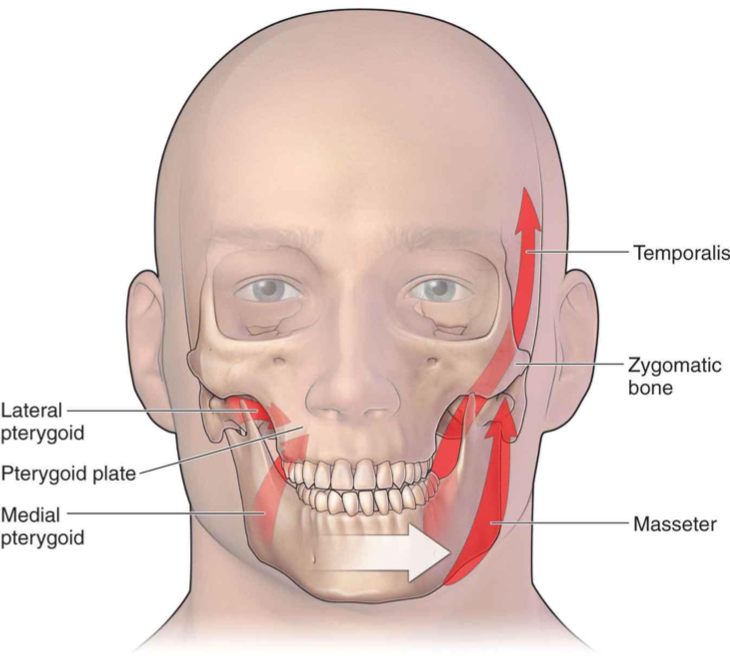
Temporalis
Large, fan-shaped muscle
Arises from the bony floor and overlying temporal fascia
Attaches to the skull between the superior and inferior temporal lines
Temporal fascia
Forms the roof of the temporal fossa
Inferiorly splits into 2 layers
Tethers the zygomatic arch superiorly
Resists downward pull when masseter contracts
Temporalis fascia
Superior attachment of temporalis
Floor of temporal fossa, deep surface of temporal fascia
Proximal attachment of temporalis
Coronoid process, anterior border of ramus of mandible
Inferior attachment of temporalis
Deep temporal branches of CN V3
Innervation of temporalis
Elevation of mandible - anterior & superior fibers
Retraction - posterior/horizontal fibers
Actions of temporalis
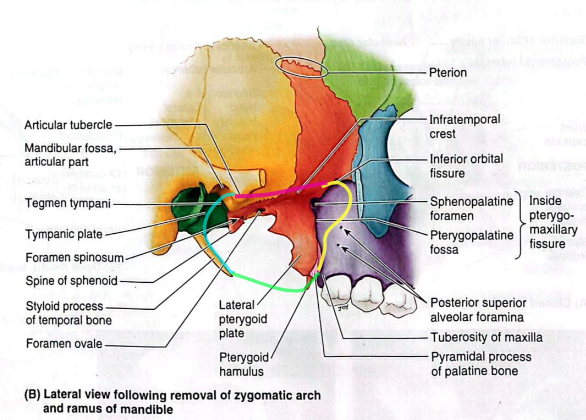
Infratemporal fossa
Irregularly-shaped space deep and inferior to the zygomatic arch, deep to the ramus of the mandible, and posterior to the maxilla
Communicates with temporal fossa
Boundaries:
Lat: ramus of mandible
Med: lateral pterygoid plate
Ant: post. aspect of maxilla
Post: tympanic plate and mastoid and styloid processes of the temporal bone
Sup: inferior (infratemporal) surface of the greater wing of sphenoid
Inf: where the med pterygoid muscle attaches to the mandible near its angle (imaginary)
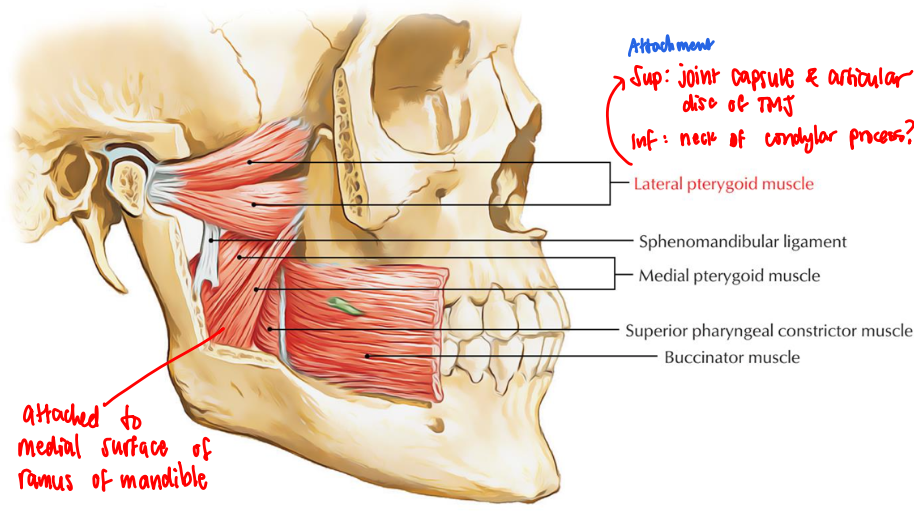
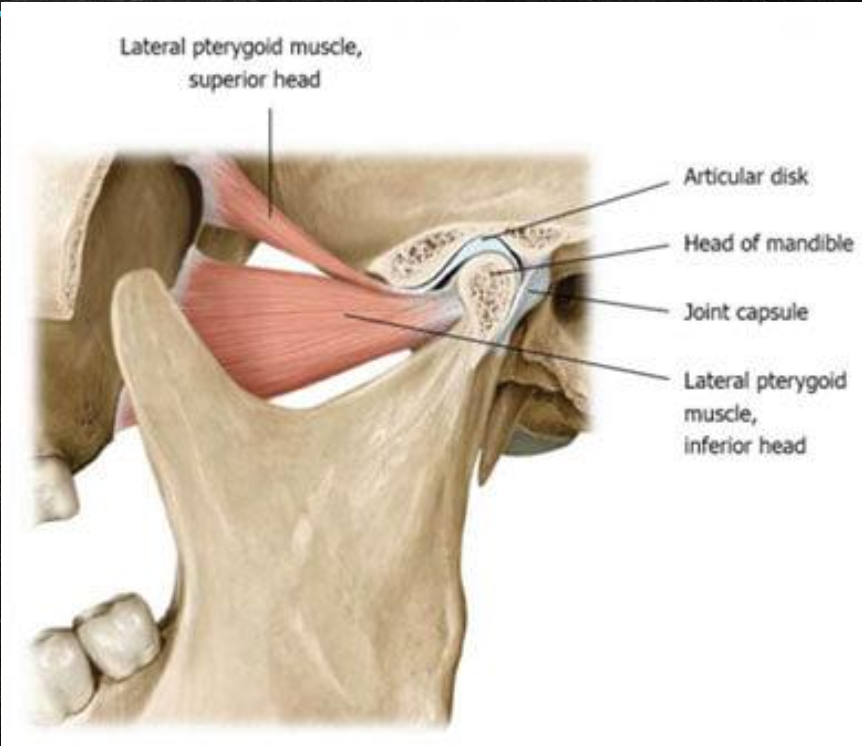
Lateral pterygoid muscle
All muscles of mastication elevate the mandible EXCEPT the _____
Inferior part of temporalis
Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
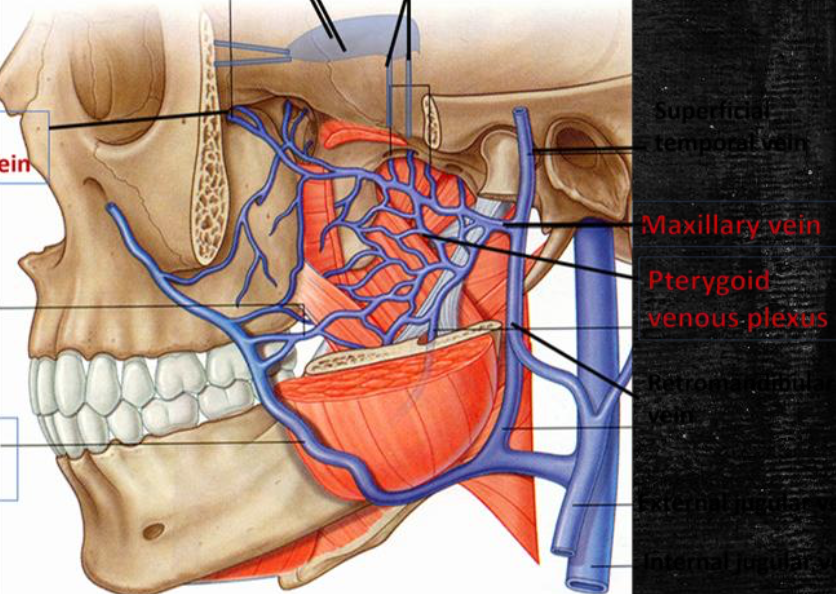
Maxillary artery
Pterygoid venous plexus
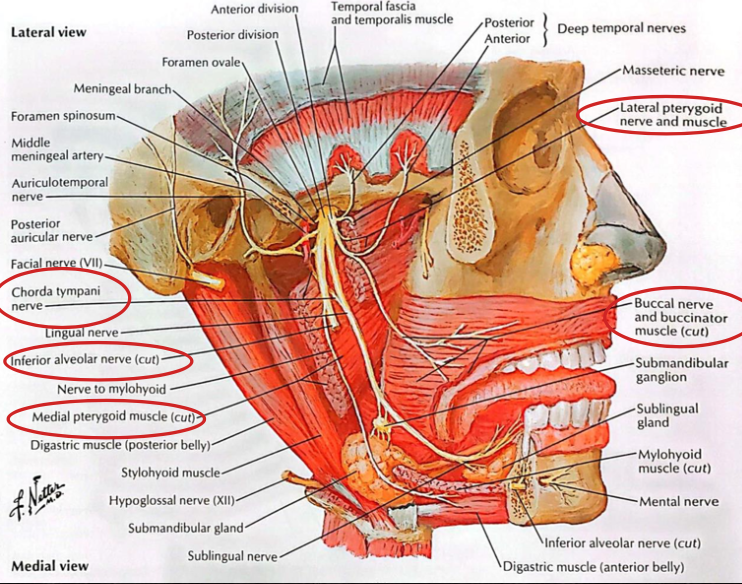
Mandibular, inferior alveolar, lingual, buccal, chorda tympani nerves
Otic ganglion
Contents of infratemporal fossa
Masseter
Temporalis
Lat pterygoid
Med pterygoid
Muscles of mastication
Lateral and medial pterygoid muscles
Quadrangular, 2-headed muscles of mastication
Deep auricular
Anterior tympanic
Middle meningeal
Accessory meningeal
Inferior alveolar
Branches of the 1st part of the maxillary artery
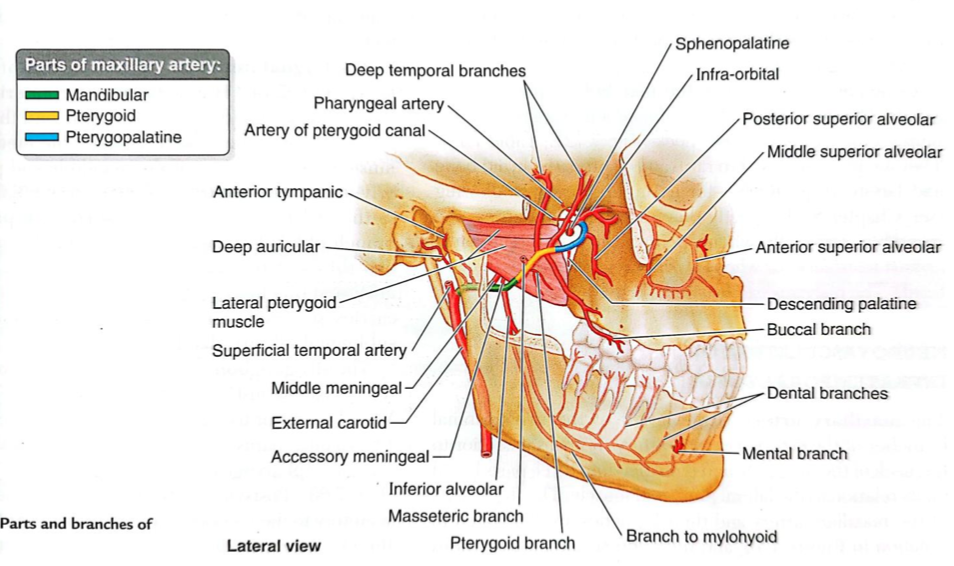
Branches to muscles of mastication
Buccal artery
Branches of the 2nd part of the maxillary artery
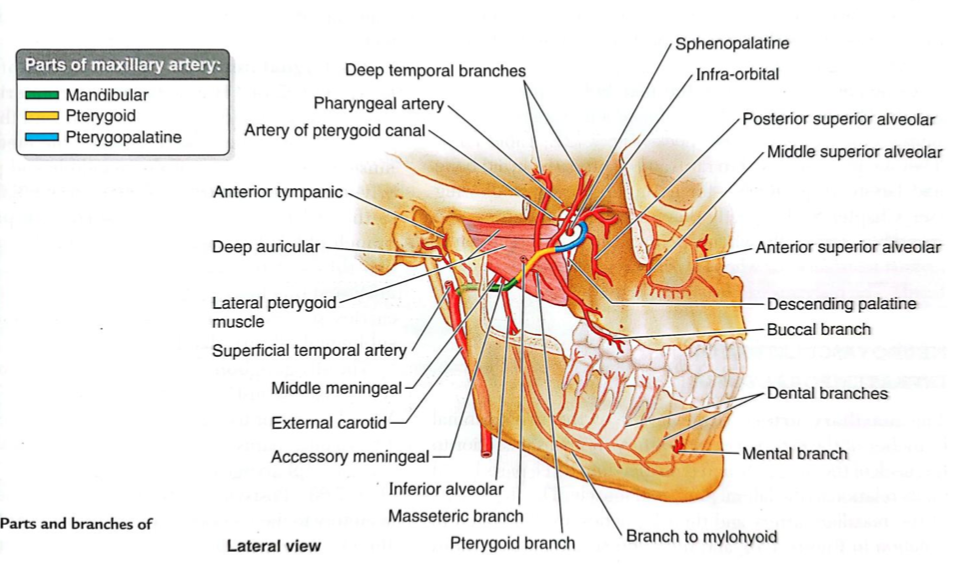
Infraorbital
Descending palatine
Artery of pterygoid canal
Sphenopalatine
Anterior, middle, posterior superior alveolar
Pharyngeal
Artery of pterygoid canal
Branches of the 3rd part of the maxillary artery
Deep auricular artery
Lies within parotid gland
Supplies:
TMJ
EAM
outer surface of ear drum
Anterior tympanic artery
Arises within parotid gland
Supplies tympanic cavity and inner surface of ear drum
Middle meningeal artery
Enters cranial cavity via foramen spinosum
Supplies skull and dura mater
Foramen spinosum
The middle meningeal artery enters the cranial cavity via _____
Accessory meningeal artery
Enters cranial cavity via foramen ovale
Supplies semilunar ganglion (CN V) and dura mater
Foramen ovale
The accessory meningeal artery enters the cranial cavity via _____
Inferior alveolar artery
Enters mandibular foramen
Supplies lower teeth and gums
Passes through mental foramen and becomes mental artery
Mandibular foramen
The inferior alveolar artery enters _____
mental foramen ; mental artery
The inferior alveolar artery passes through _____ and becomes _____
Posterior superior alveolar artery
Runs with superior alveolar nerve (CN V2)
Supplies upper molars and premolars
Infraorbital artery
Enters orbit via inferior orbital fissure
Runs with infraorbital nerve
Supplies lower eyelid, side of nose, upper lip, oral mucosa
Gives rise to anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries
Infraorbital artery
Which artery gives rise to anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries
Inferior orbital fissure
The infraorbital artery enters orbit via _____
Descending palatine artery
Supplies soft and hard palates
Terminal branch
Artery of pterygoid canal
Supplies pharynx and auditory tube
Pterygoid venous plexus
What is the venous counterpart of maxillary arteries?
Chorda tympani
Provides taste sensation from anterior 2/3 of tongue
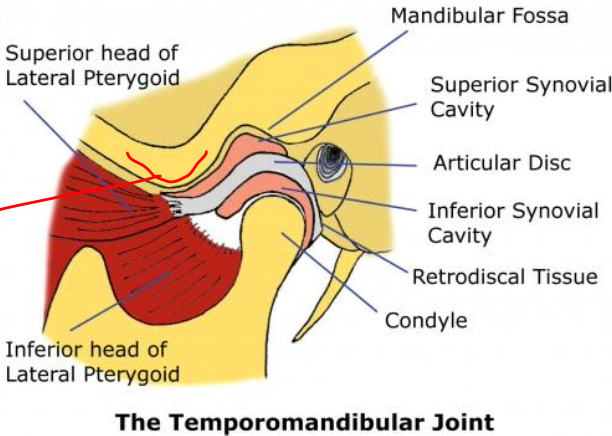
Temporomandibular joint
A modified hinge type of synovial joint, permitting translation and a small degree of pivoting in addition to elevation and depression movements
Ginglymoarthrodial joint
ginglymus — hinge
arthrodial — gliding
An example of diarthrosis (freely movable)
The only mobile joint of the skull
Fibrocartilage
Articular surface of TMJ is covered by _____
Occlusal contact of teeth
Rigid endpoint of closure of TMJ
TMJ
Last joint to start to develop
Articular tubercle of temporal bone
Mandibular fossa
Condyloid process of mandible
Articular disc
Superior articular cavity
Inferior articular cavity
Parts of the TMJ
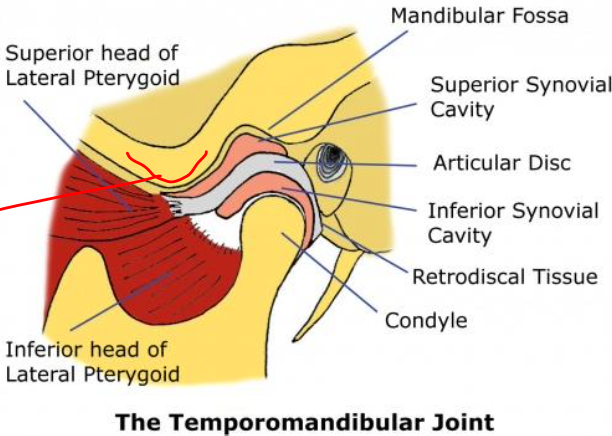
Mandibular fossa
Where condylar head is articulated (TMJ)
Fibrous capsule
▪ Capsule that encloses the TMJ
▪ Attached at the borders of the articulating surfaces of the mandibular fossa and eminence of the temporal bone and to the neck of the mandible
Articular disc
▪ Fibrocartilaginous disc dividing joint cavity in upper and lower compartments
▪ Sagittal section: a thin intermediate zone with thickened anterior and posterior bands
▪ Posteriorly: attached to a region of loose vascular nervous tissue
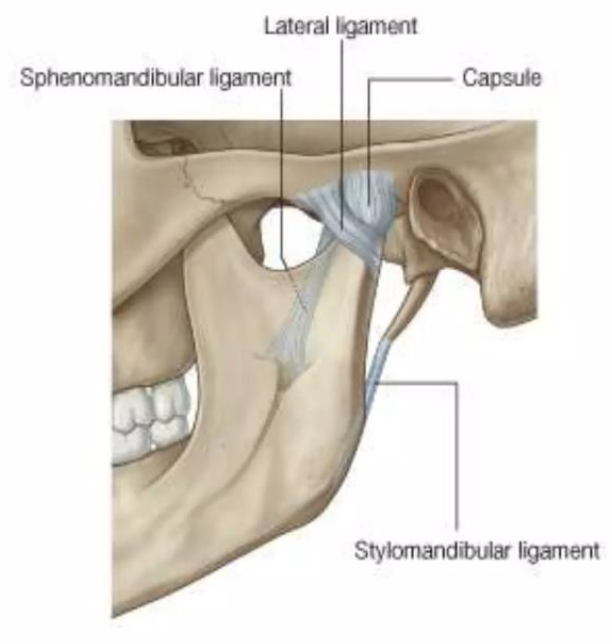
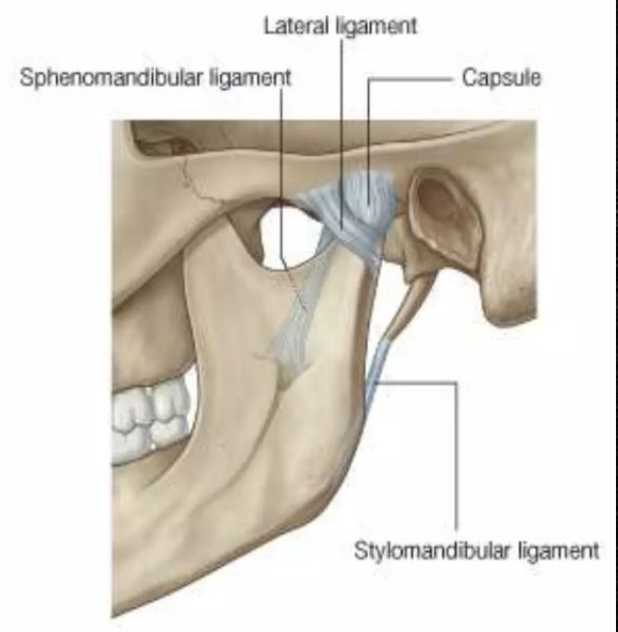
Lateral ligament
Ligament of TMJ
Formed by the thickened part of the joint capsule
Attached above the articular tubercle
Extends downwards and backwards at angle of 45º to the horizontal
Strengthens the joint laterally
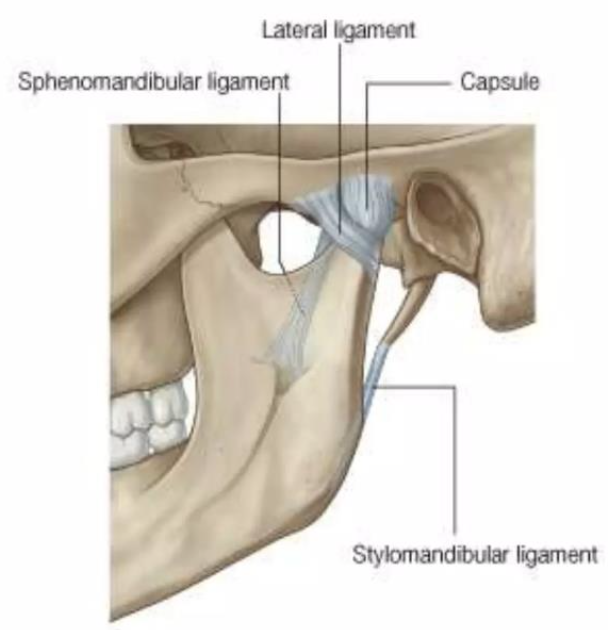
Sphenomandibular ligament
A flat, thin band that descends from the spine of the sphenoid
Runs from the spine of the sphenoid to the lingula of the mandible
Widens at the lingula of the mandibular foramen
Medial to and normally separate from capsule
Primary passive support of the mandible
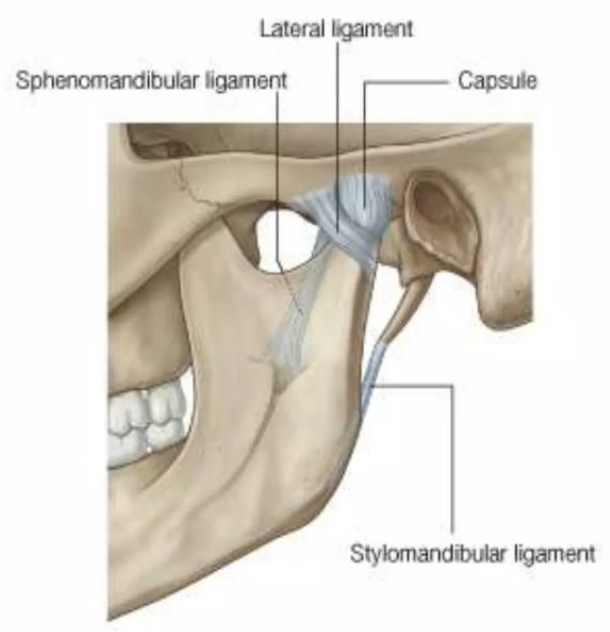
Stylomandibular ligament
A thickened band of deep cervical fascia that stretches from apex and adjacent anterior aspect of the styloid process to the angle and posterior border of the mandible
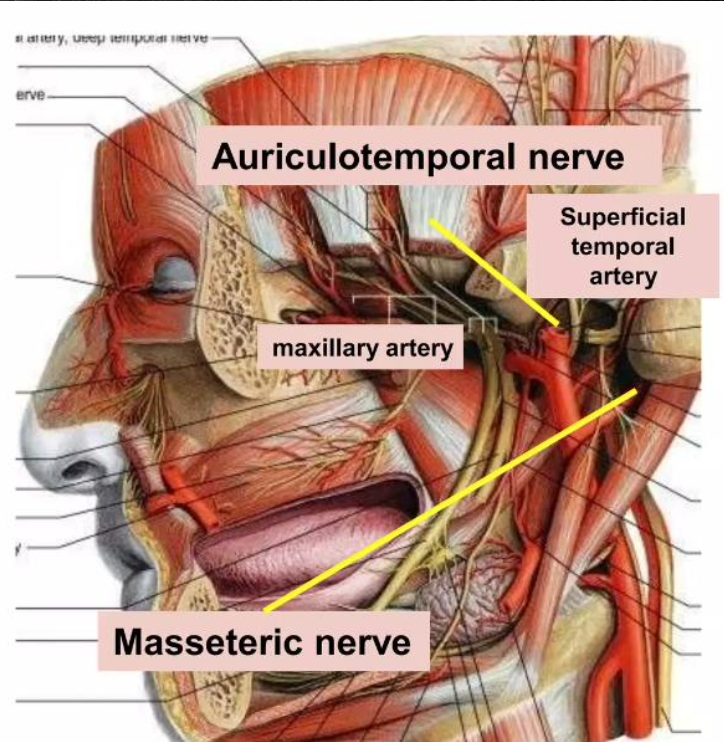
Superficial temporal artery
Maxillary artery
Blood supply of TMJ
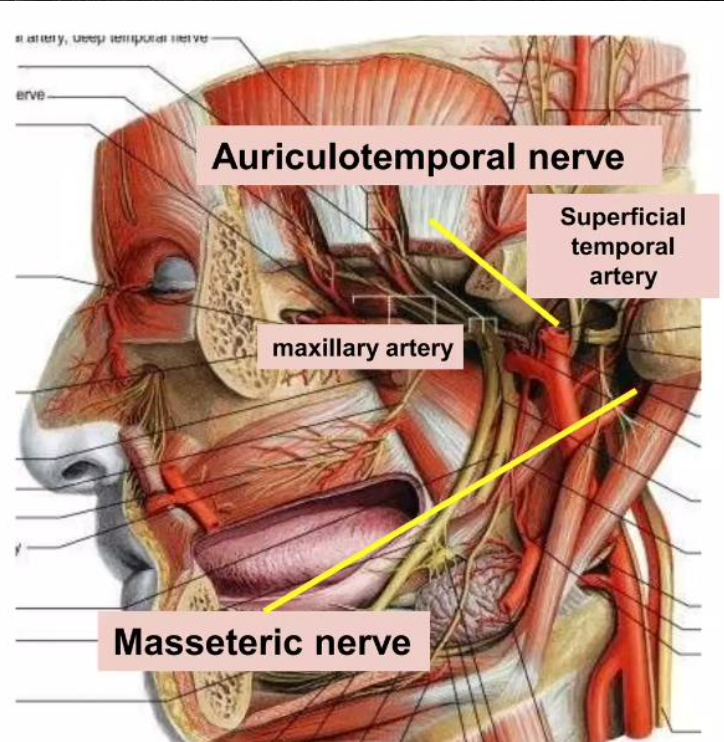
Masseteric
Auriculotemporal nerves
Nerve supply of TMJ
Rotational/hinge movement
TMJ movement in the first 20-25 mm of mouth opening
Translational movement
TMJ movement when mouth is excessively opened (disc glides to articular tubercle)
Elevation
Action of:
Temporalis
Masseter
Medial pterygoid
Depression
Action of:
Lateral pterygoid
Suprahyoid
Infrahyoid
Protrusion
Action of:
Lateral pterygoid
Masseter
Medial pterygoid
Retrusion
Action of:
Temporalis (posterior oblique and near horizontal fibers)
Masseter
Lateral movements
Action of:
Temporalis of same side
Pterygoids of opposite side
Masseter
Symmetrical jaw opening
Start: Each mandibular condyle rotates in the lower joint compartment.
After a few degrees of opening: The condyle continues rotating; both slide forward
50-60 mm
Maximum mouth opening
Eccentric jaw opening
Condyle on the non-working side slide back and forth during lateral movements.
Temporomandibular and sphenomandibular ligament keep condyle firmly against articular eminence
Temporomandibular and sphenomandibular ligament
They keep condyle firmly against articular eminence
Eccentric and symmetric jaw closing
▪ Jaw closing muscles
▪ Joint tissues compressed, ligaments shortened
▪ Non-working condyle moves further