Neuropath: metabolic disease of periparturient ruminant
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Clinical presentation of hypomagnesaemia
Can be acute or gradual, depending on diet
Anorexia, isolation, hyperexcitability
Tetanic muscle spasms/tremors
Staggering, ataxia, recumbency
Convulsions, seizures, opisthotonos
Salivation, frothing at mouth
Snapping eyelids
Death occurs due to respiratory failure during seizure
Often occurs concurrently with hypocalcaemia in sheep.
Clinical presentation of Hypocalcaemia
Cattle:
Affects high-producing cows shortly after parturition.
Wobbly, trembling all over body, teeth grinding = early signs
Downer cow, head turned to flank
lethargic, weak rapid pulse, cool extremities, muscle fasciculations, no ruminal contractions
Progresses to lateral recumbency, flaccid paralysis.
Coma and death if left untreated
Sheep:
Affects older ewes in late gestation or early lactation
Depression, weakness, ruminal stasis, bloat, coma, death
Clinical presentation of ketosis in cattle (12)
Anorexia
Weight/condition loss
Drop in milk
Constipation
CNS signs = circling, staggering, licking, bellowing, hyperesthesia, headpressing, trembling
Acetone breath
Clinical presentation of ketosis in sheep (12)
1-3 weeks before parturition
Selective anorexia
Increased recumbency
Aimless walking, muscle twitching, fine muscle tremors
Opisthotonos
Grinding teeth
Blindness, ataxia
Sternal recumbency
Coma and death
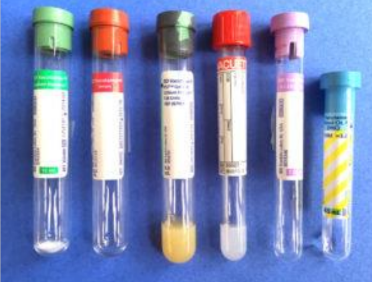
What do all these large animal tubes contain (left to right)
Heparin (plasma biochemistry)
Nothing (serum biochemistry)
Gel and heparin (rarely used)
Nothing
NaK-EDTA (haematology and cytology)
Sodium citrate (coagulation testing)
What samples do you get from: aqueous humour and vitreous humour?
Aqueous = Ketones/ BHBs, Calcium
Vitreous = Urea, Magnesium
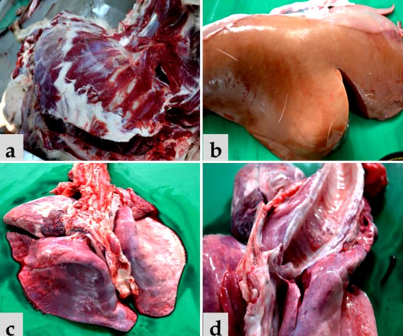
Post-mortem of heavily pregnant ewe found dead. Pregnant with 3 lambs. Diagnosis?
Ketosis/Pregnancy toxaemia/twin lamb disease. Causes hepatic lipidosis.
2 things to test for when determining ewes at risk of ketosis
Urine ketone concentration
Increased serum BHB concentrations
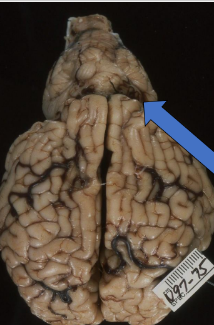
What is this in a calf?
Arnold-Chiari malformation
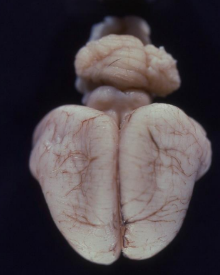
What is this condition in a cat?
Lissencephaly
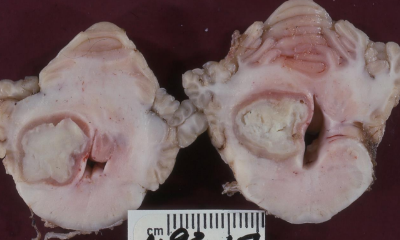
What is this in a goat?
Abscess
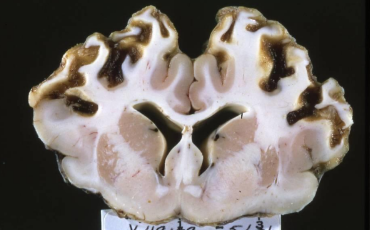
What is this in a cow? Diagnostic test.
Cerebrocortical necrosis
Autofluorescence under UV light
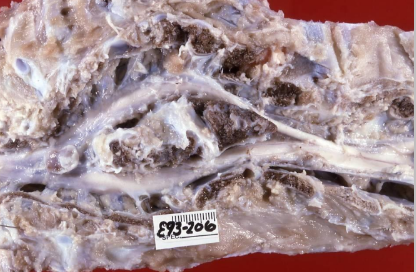
What condition has this calf got in its spinal cord?
Diastematomyelia
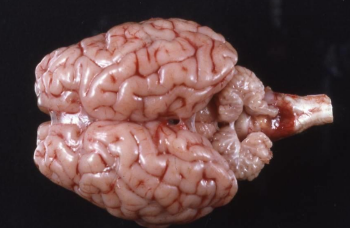
What condition has this lamb got?
Cerebellar hypoplasia

What is this structure called?
Cauda equina

What condition has this pig got?
Meningoceles
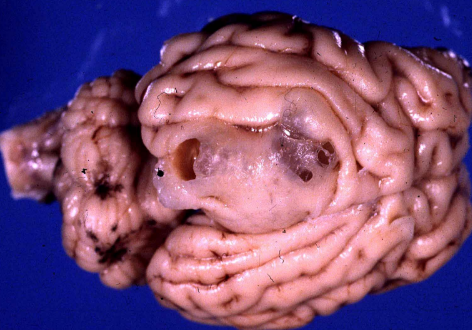
What condition does this sheep have? Causative agent?
Gid
Taenia multiceps causing cerebral coenurus
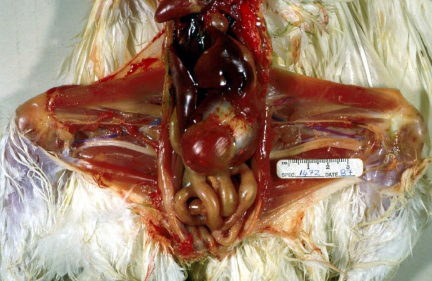
What disease does this chicken have?
Mareks disease
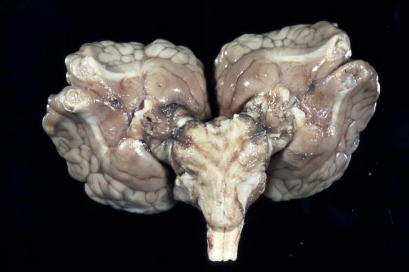
What condition has this calf got?
Diprosopus
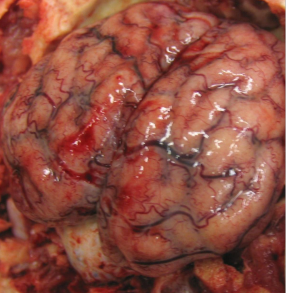
What type of pathogen?
Bacterial
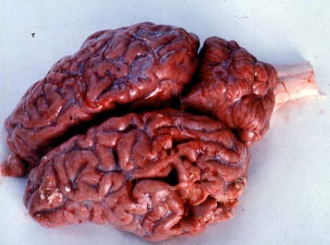
What causative agent of diffusely red brain in cow
Babesia bovis
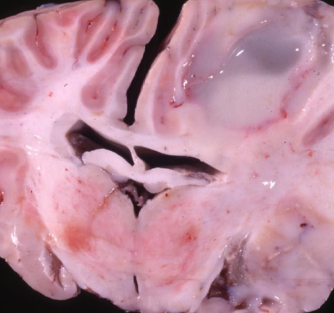
What does this horse have?
Abscess
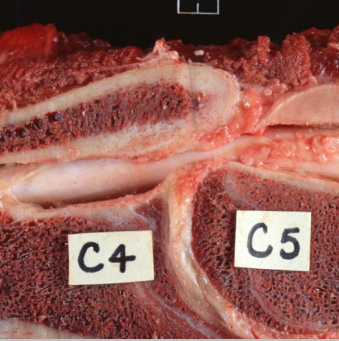
What condition has this horse got?
Cervical vertebral stenotic myelopathy
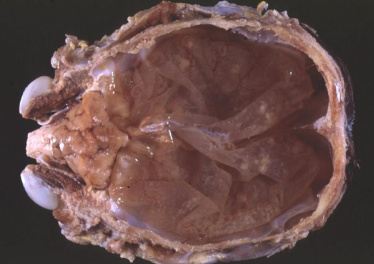
What is this condition in a cow?
Hydranencephaly