Economics Unit 1 Review
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Economics
The study of how society uses limited resources to satisfy unlimited desires

Scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants

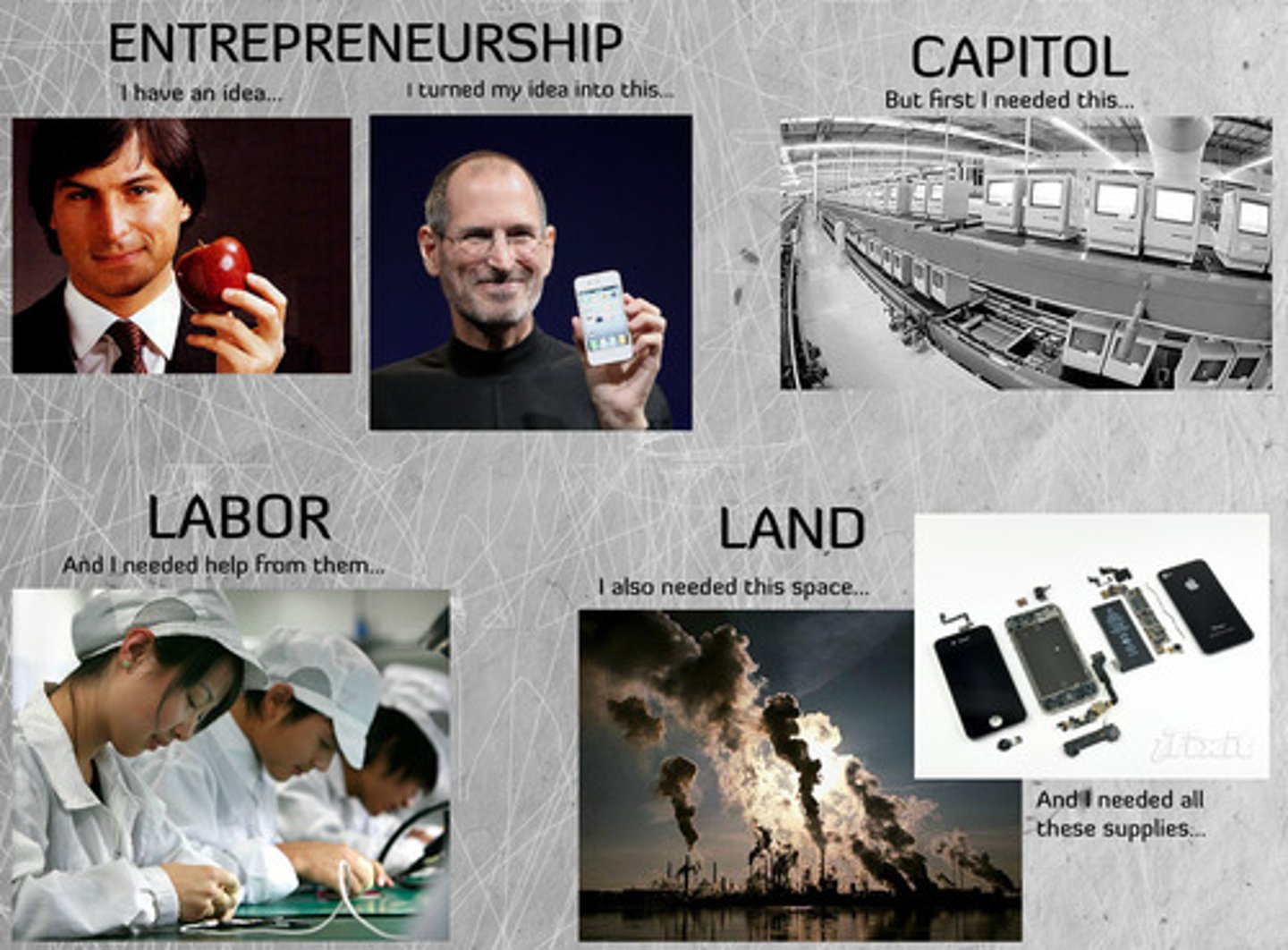
Entrepreneur
A person who organizes, manages, and takes on the risks of a business.

opportunity cost
Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another

service
work that is performed for someone

Factors of production
Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship
(CELL)
Want
An item that we desire but that is not essential to survival

Capital
any human-made resource that is used to produce other goods and services
Resource
Anything that can be used to produce something else

Division of labor
the assignment of different parts of a manufacturing process or task to different people in order to improve efficiency.
3 economic questions
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?
Efficiency
using resources in such a way as to maximize the production of goods and services
Underutilization
the use of fewer resources than the economy is capable of using
competition
the struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers
marginal cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
free enterprise
resources are privately owned, competition is welcome, little government control
5 characteristics of free enterprise
Economic Freedom-choice
Private property rights
voluntary exchange
Profit motive
competition
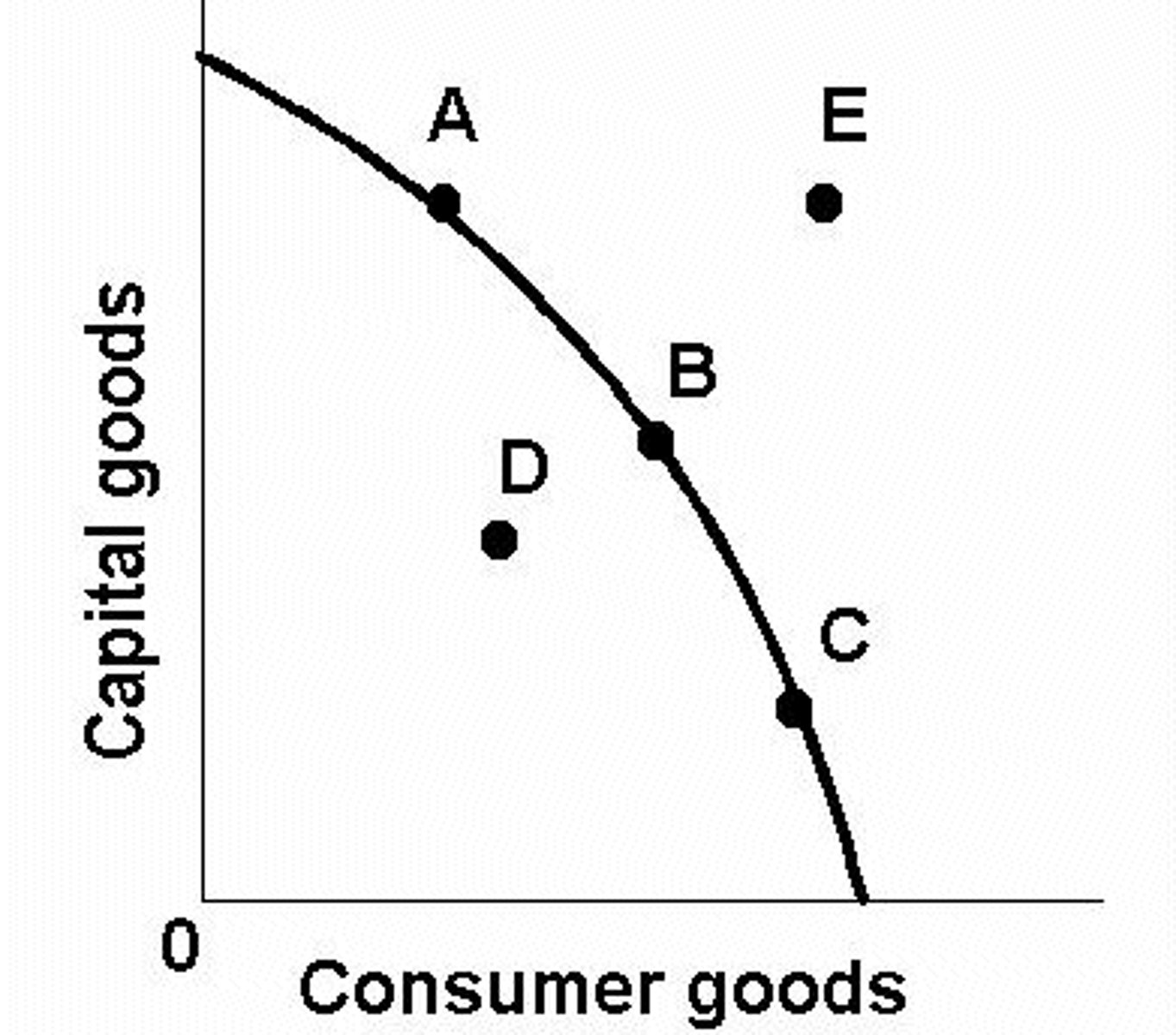
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)/curve
a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that may be produced with available resources and current technology
How can a PPF shift?
changes in resources and/or tech
service
work that is performed for someone

Utility
The capacity to be useful and provide satisfaction
Need
Basic requirement for survival

Invisible hand
A term coined by Adam Smith to describe the self-regulating nature of the marketplace

Resource
Anything that can be used to produce something else

shortage
a situation in which a good or service is temporarily unavailable

free market economy
individuals decide what is made, how it is made, and how much is made

Karl Marx
Founder of communism

Adam Smith
Economist who wrote Wealth of Nations; Laissez-Faire economics, invisible hand
John Maynard Keynes
British economist who thought deficit spending would create jobs and stimulate the economy.

3 economic questions
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?
Economic Security
plans set up for unemployment problems solve worry over loss of jobs, sickness, or injury
Social Security-federal program
free enterprise
resources are privately owned, competition is welcome, little government control
5 characteristics of free enterprise
Economic Freedom-choice
Private property rights
voluntary exchange
Profit motive
competition
Role of Consumer
Decide what to be produced by casting their dollar votes.
Role of Government
protector , provider, regulator, consumer
marginal cost
the cost of producing one more unit of a good
Externality
an economic side effect of a good or service that generates benefits or costs to someone other than the person deciding how much to produce or consume
positive externality
beneficial side effect that affects an uninvolved third party (education, neighbor fixing a fence, neighbor painting their house)
Factor market (resource market)
A market which factors of production are bought and sold
product market
the market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce
circular flow diagram
a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms
mixed economy
An economy in which private enterprise exists in combination with a considerable amount of government regulation and promotion.
free market economy
an economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets and the government plays a small role in the economy.
Command Economies
economic systems in which the government largely decides what goods and services will be produced, who will get them, and how the economy will grow
Law of Marginal Utility
states that a consumer will only buy so much of a given product even though the price is low
law of diminishing returns
the principle that, at some point, adding more of a variable input, such as labor, to the same amount of a fixed input, such as capital, will cause the marginal product of the variable input to decline
thinking at the margin
deciding whether to do or use one additional unit of some resource
PPF curve--
it always slopes down and to the right (has a negative slope) because resources are used differently.
individual mandate (ACA)
Required healthy people to join the risk pool and purchase an insurance plan. Removed by Congress.
Bismarck Model of Healthcare
The Bismarck model uses an insurance system and is usually financed jointly by employers and employees through payroll deduction. Unlike the U.S. insurance industry, Bismarck-type health insurance plans do not make a profit and must include all citizens. Doctors and hospitals tend to be private in Bismarck countries. This model is found in Germany, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Switzerland, and Japan.
Beveridge Model of Healthcare
Health care is provided and financed by government through tax payments, patients never receive a medical bill, many hospitals and clinics are owned by the government, i.e. Britain. Single payer.
National Health Insurance
A plan to provide universal health insurance under which the government provides basic health insurance to all citizens. In most such plans, the program is funded by taxes on wages or salaries.
out of pocket
medical bill that is not covered by insurance and must be paid by the patient
Premium
Amount you pay monthly, quarterly, semiannually or annually to purchase different types of insurance