Solar Equations
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Q: What is the solar constant E0 and its typical value?
A: Solar constant ≈ 1360–1367 W/m² at 1 AU, measured perpendicular to rays, outside atmosphere
Q: Why is irradiance on Earth lower than in space?
A: Due to atmospheric reflection, absorption (O₃, H₂O, O₂, CO₂), Rayleigh scattering (small particles), and Mie scattering (large particles).
Q: Define air mass ratio (AM) and give its formula.
A: Relative optical path length through atmosphere; m=1/cosψ, where ψ is solar zenith angle.
Q: What is AM 1.5 and why is it important?
A: Standard spectrum for PV testing; represents sunlight at 1.5× vertical path length, typical of mid-latitudes.
Q: What is the declination angle (θd)?
A: Angle between Sun’s rays and Earth’s equatorial plane; ranges from –23.5° to +23.5° annually.
Q: Formula for irradiance normal to a tilted plane (α)?
A: En = Ecosθdsin(θ+α)sinϕ + Esinθdcos(θ+α)
Q: State the Hottel equation for direct beam irradiance at surface.
A: E=E0(b0+b1e−km)E=E0(b0+b1e−km), where m = air mass ratio and b0,b1,kb0,b1,k depend on visibility.
Q: Condition for optimal fixed panel tilt at noon on a given day?
A: θ+α+θd = 90∘ ; where θ is the solar zenith angle and α is the panel tilt angle.
Q: Formula for minimum row spacing to avoid shading at noon?
A: Dmin= Lcosα+(Lsinα)cotβ, with β=θ−23.5∘ (NH).
Q: What happens when photon energy < semiconductor band gap?
A: No electron–hole pairs; photon passes through or is reflected.
Q: How does doping change silicon for PV?
A: n-type (Group V) adds electrons; p-type (Group III) creates holes; p–n junction forms depletion region. Doping introduces charge carriers in silicon.
Q: Name the four key PV I–V curve parameters.
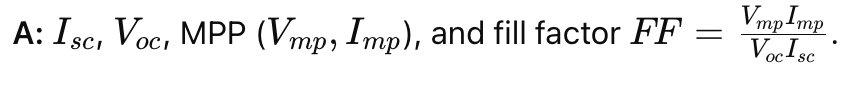
: Effect of increasing irradiance on I–V curve?
A: Isc increases; MPP shifts upward; Voc increases slightly.
Q: Formula for PV module efficiency.
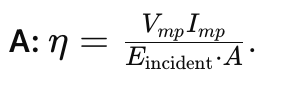
Q: How to split energy in a PV-T system?
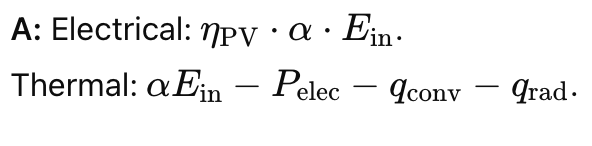
Q: Formula for power through a vertical window.
A: P= τAEn , with α = 90∘
Q: Why can tracking underperform fixed on overcast days?
A: Diffuse radiation is isotropic; tracking panels may be steep at morning/evening, capturing less diffuse light.