applied research methods and self reflective practitioner
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
reflective practice
an essential element of all applied psychology work
concept was introduced in the 80s for many different professions
what is reflective practice?
learning through and from experience towards gaining new insights of self and practice- Finlay
an active, dynamic action based and ethical set of skills, placed in real time and dealing with real, complex and difficult situations-Moon
Reflection is an active process by which knowledge can be developed from professional practice (Page, 2009)
It helps practitioners learn from experience and understand the nature of working as an applied psychologists within dynamic circumstances the require constant decision making (Page, 2009)
reflective practice skills
a way of examining your own experiences and actions
a learnt and developed skill
reflecting on what you did, how you did it and what you should do differently/ better next time
• Evaluating your first-hand experience of an event, process
or activity
• Analysing the reasons for things that you did well and less
well
• Learning from the experience to improve or refine your
performance in a similar situation in the future
what does reflective practice require?
conscious effort to examine, think and develop insight about our experiences and practice
develop critical, constructive and creative thinking
openness and willingness to examine and reexamine our ways of thinking, seeing and doing
Open ourselves and our practice/work to scrutiny of self and others
• Find new perspectives and approaches for our future practice
casual thinking vs reflective thinking
reflective thinking requires a conscious effort to think about event and to develop insight into the experience of this event
this requires critical, constructive and creative thinking
critical reflection in reflective practice
critical reflection is the process of looking back in order to enhance future personal development in our practice
also reflecting on how our actions impacted others-
what does critical reflection highlight?
Critical reflection should highlight what we have learnt and
how we will make constructive/productive action plan
moving forward
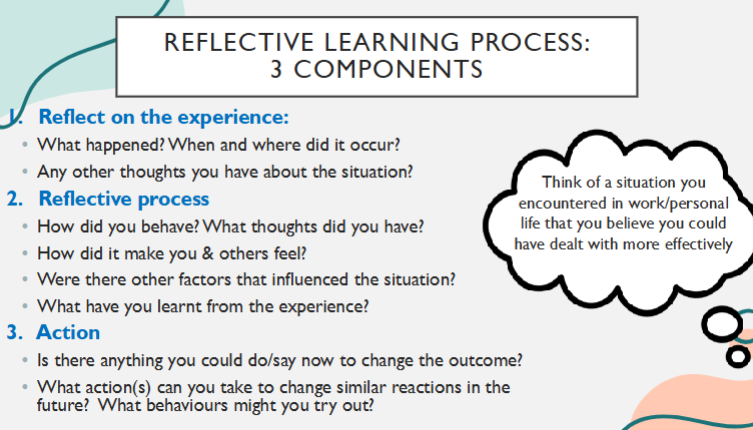
3 components of reflective learning:
reflect on the experience
reflective process
action
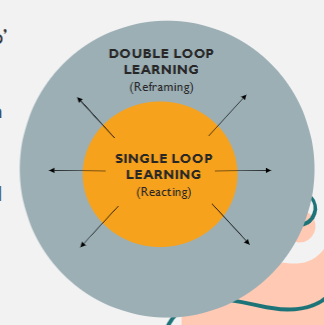
Prof Argyris
suggested "double loop learning"
helps us recognise a new paradigm and to reframe our ideas in order to improve them
single loop learning is reacting and double loop learning is reframing your thoughts

reflective practice as a skill
reflection = stepping out of single loop of changing actions to fix a problem and into second loop = help recognise a new paradigm and to reframe/modify our ideas to improve them
developing a reflective practice: Thomson (2015)
need critical, constructive and creative thinking
developed using Thompsons (2015) six steps: read, ask, watch, feel, talk, think
its not just thinking that is important but understanding the theory-how others practice, how to explore ideas with others-Thomson

benefits of reflective practice
helps to develop creative thinking skills, and encourages active engagement in work processes
theorists agree that reflective practice bridges the gap between theory and practice
encourages us to explore our own beliefs and assumptions and to find solutions to problems
helps to increase self awareness and develop a better understanding of others
FRAMEWORKS OF REFLECTIVE PRAC
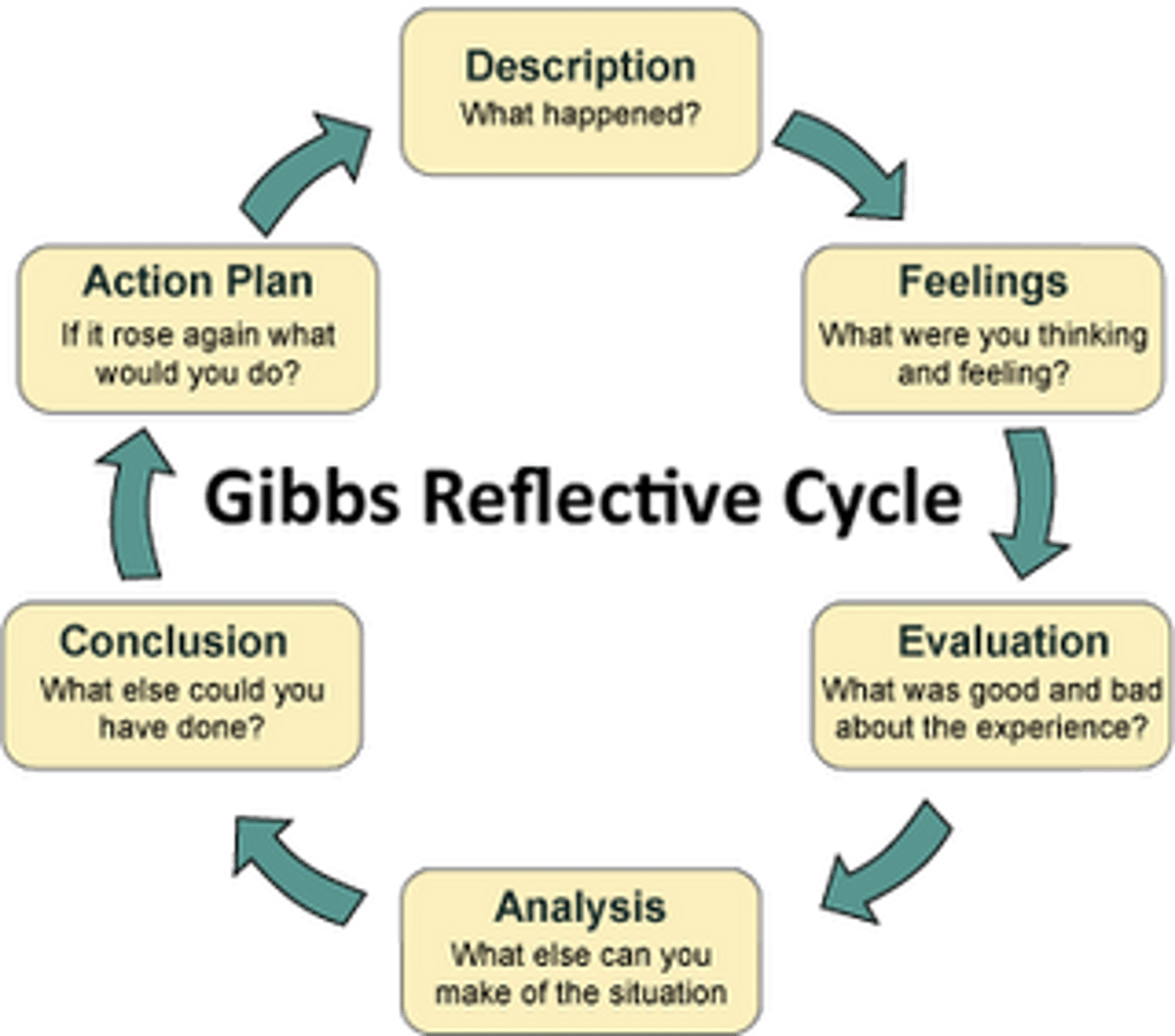
reflective learning cycle: learning by doing (Gibbs, 1988)
keep diary to record your experiences and how they made you feel at the time-use it to id patterns in ur way of working and compare your exp. to lit and plan to tackle similiar situations in the future -draw on what went well too
1. Description; what happened?
2. Feelings; what were you thinking and feeling?
3. evaluation; what's good and bad about the experience?
4. analysis: what sense can you make of this situation?
5. conclusion: what else could you have done?
6. action plan: if it arose again, what would you do?
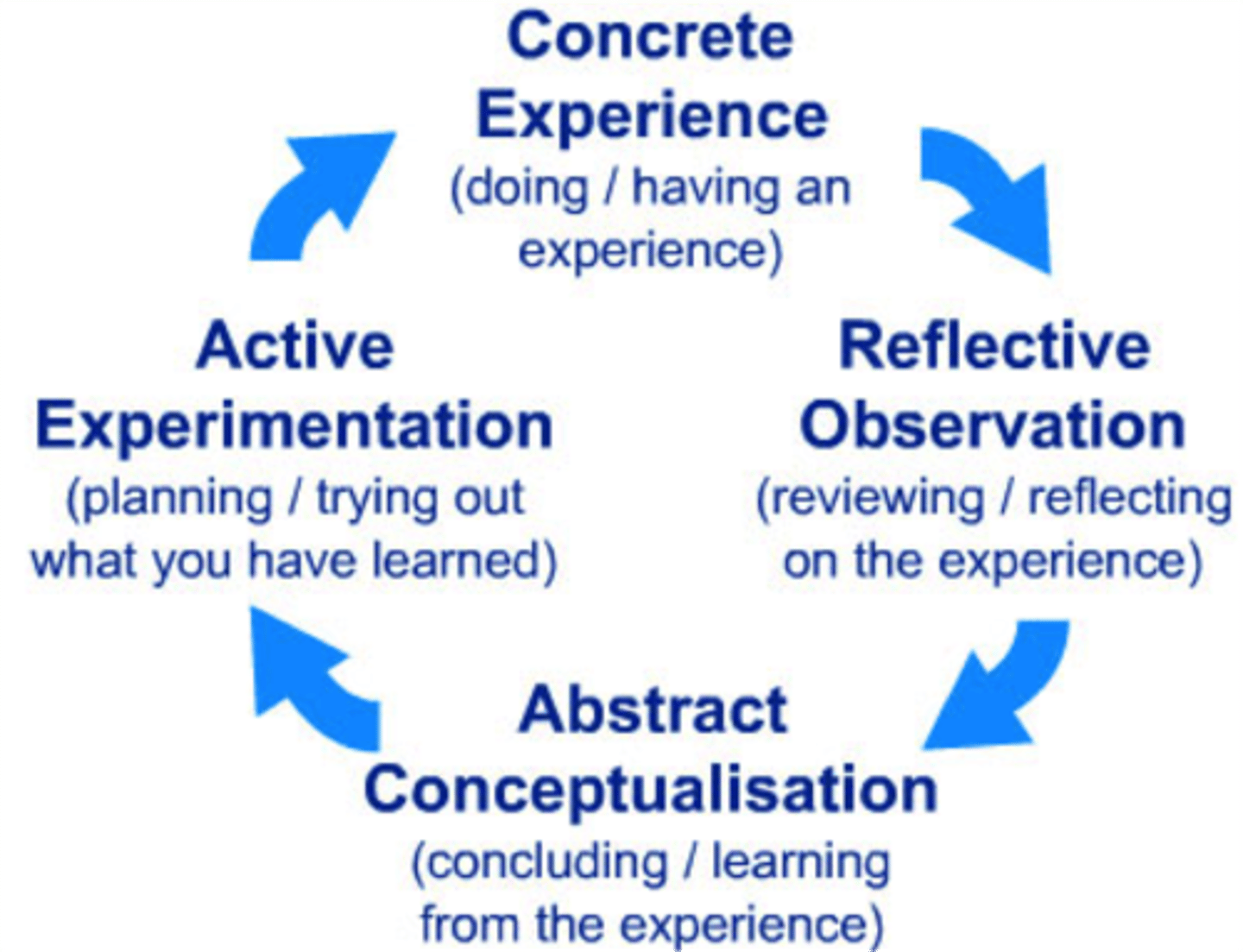
Kolb's learning cycle theory (1984)
proposes that we learn from our daily life experiences and reflection is an integral part of such learning
we can learn from any experience by going through the four stages:
-concrete experience (actually having an experience)
-reflective observation (reflecting on the experience)
-abstract conceptualisation (learning from the experience)
-active experimentation (trying out what you have learnt)
KOLB IN APPLIED PRACTICE
This cycle helps practitioners shape new ideas and conclusions about their future practice with the people under their care
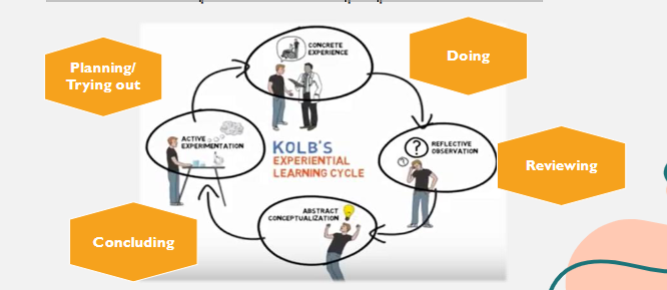
Kolb's learning cycle theory (1984) framework
helps us:
make sense of our experiences as practitioners
learn from them
work out different/ better ways of doing things in the future
can contribute to our professional knowledge and enhance our work practice
DEFEATISM IN REFLECTION
Reflecting and knowing your limitations is
the first step to improving


EVALUATION & ANALYSIS
Refocus our thinking about our existing knowledge, which can help us generate new knowledge and ideas
As a result, we can modify our actions, behaviour, treatments, and learning needs
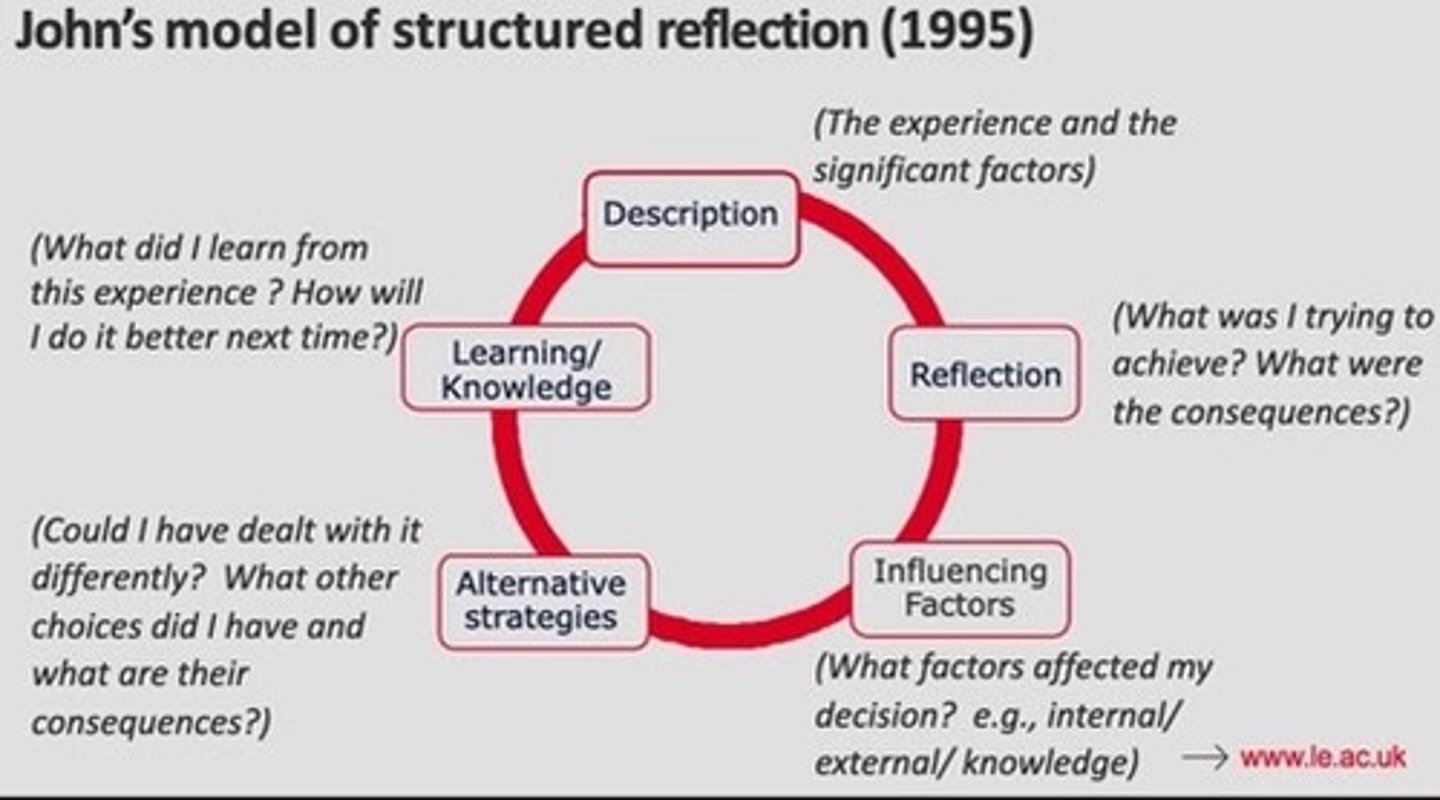
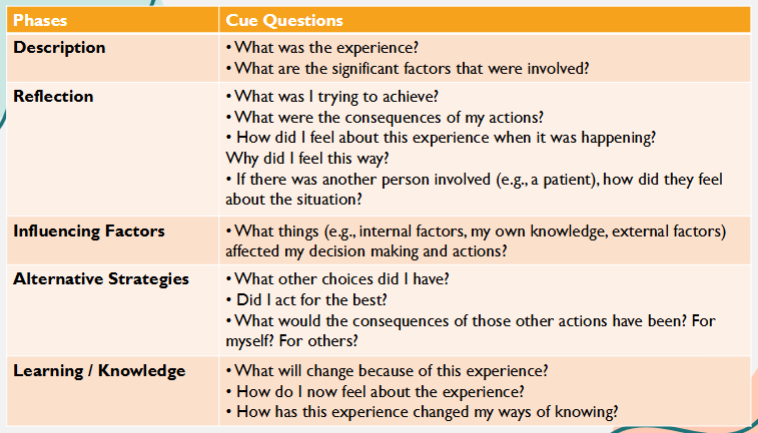
John's model of structured reflection (1994)
developed for nursing practitioners but is applicable to any field
offers a technique that is especially useful in the early stages of practitioners learning how to reflect
John advised using a structured diary and the model for analysing events and for general reflection on experiences
"look in" and "look out" of the situation ; challenges our natural tendency to judge ourselves too harshly
look out-write a description of the
situation around your thoughts and feelings; what you are
trying to achieve, why you responded in the way you did, how
others were feeling, did you act in the best/ethica
description, reflection, influencing factors, alternative strategies, learning/knowledge
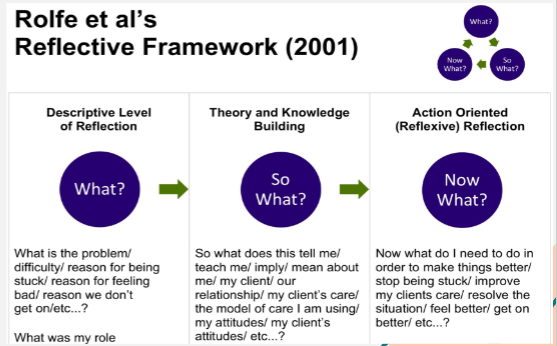
Rolfe's reflective practice (2001)
three simple questions to reflect on a situation
what?
so what?
now what?-thought this was a great contribution to practice