Chapter 23, Lesson 1: Functions of the Urinary System
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 23, Lesson 1 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
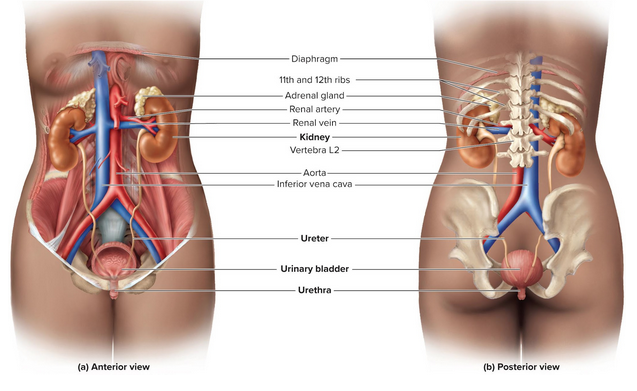
Urinary system organs
Two kidneys
Two ureters
Urinary bladder
Urethera
Kidney functions
Metabolic wastes, hormone filtration from blood
Blood volume, pressure, osmolarity regulation
Electrolyte, acid-base balance
Erythropoietin for red blood cell production
Calcium regulation
Free radical detoxification
Glucose synthesization in starvation
Waste
Any substance useless to or present in excess in the body
Metabolic waste
Waste substance produced by the body
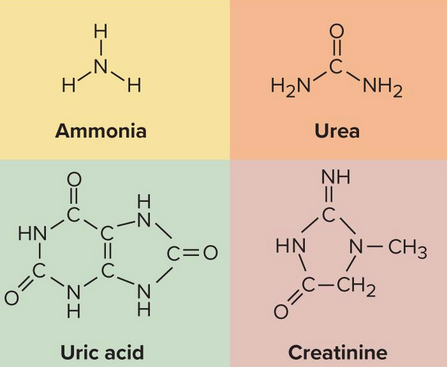
Nitrogenous waste
Type of metabolic waste that contains nitrogen
Urea
Uric acid
Creatinine
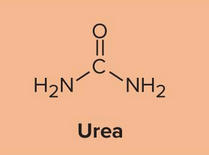
Urea
Type of nitrogenous waste from protein catabolism
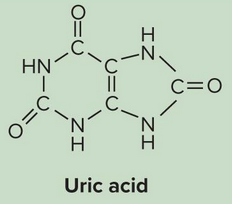
Uric acid
Type of nitrogenous waste that is a product of nucleic acid catabolism
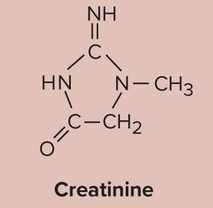
Creatinine
Type of nitrogenous waste that is a product of creatine phosphate catabolism
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
The level of nitrogenous waste in the blood; normally around 10 to 20 mg/dL
Excretion
The separation of wastes from body fluids for elimination, carried out by the respiratory, integumentary, digestive, and urinary systems