o-chem 2 chapter 13 Ethers Epoxides Thiols
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
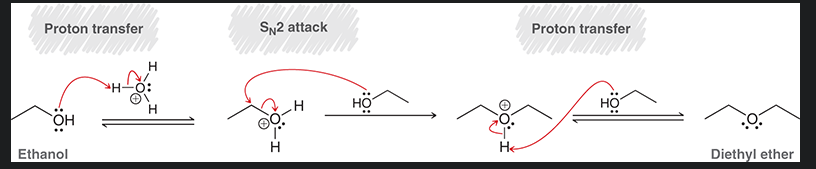
mechanism for industrial production of diethyl ether.
start with ethanol.
3 limitations of this mechanism?
SN2 mechanism, so it only works on primary alcohols
1st and last steps are in equilibrium
can only make symmetrical ethers
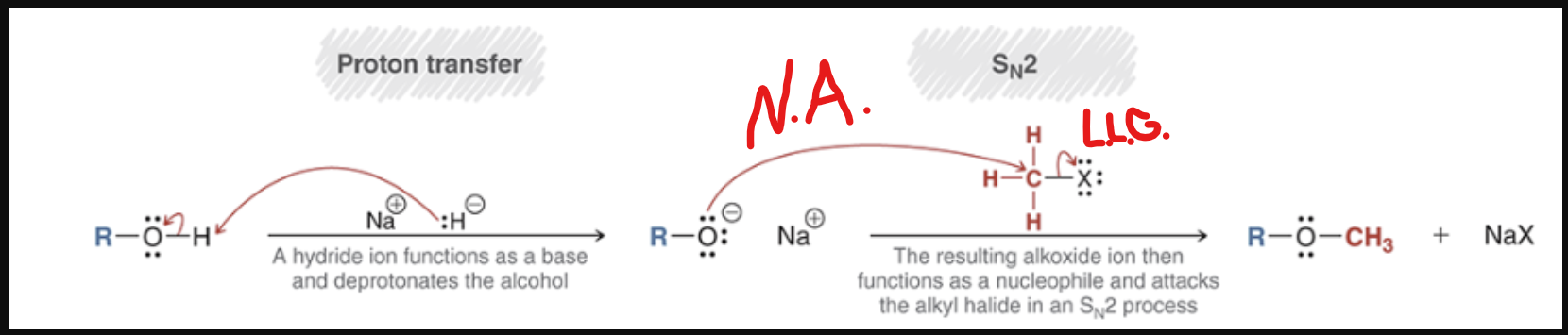
Williamson Ether Synthesis mechanism
R-OH—-?—> R-O-R
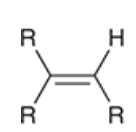
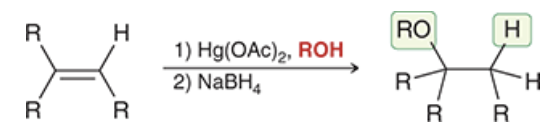
alkoxymercuration-demercuration to create ethers (show rxn using the shown alkene)
additon of alkoxy group and H across a pi bond With no carbocation rearrangements
markivnikov
Anti
involves formation of a bridged intermediate (mercurinium ion)
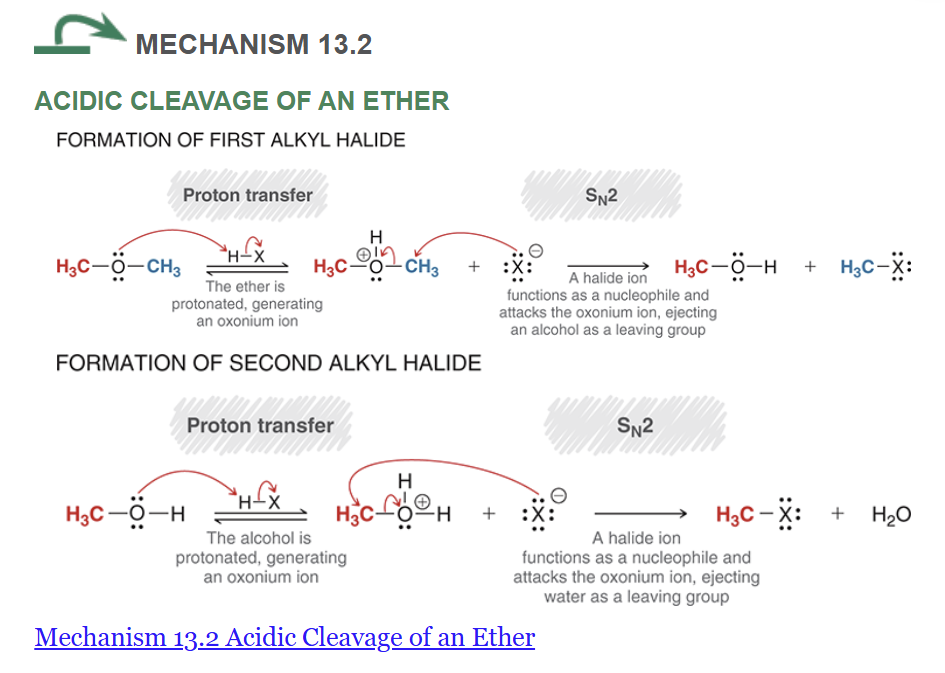
acidic cleavage of an ether (using dimethyl ether)
what conditions cause only one alkyl halide to form?
when a tertiary chiral carbon is attached to the O of the ether, what mixture is made?
remember, the arrows for SN2 are a NA and LLG arrow
if there is only one equivalent HX, only the first alkyl halide is made (major and minor products may form)
additionally, certain groups (such as phenol) prevent the second alkyl halide from being formed
when there is a tertiary chiral carbon attached to the O of the ether, a racemic mixture is made as it undergoes a SN1 mechanism instead
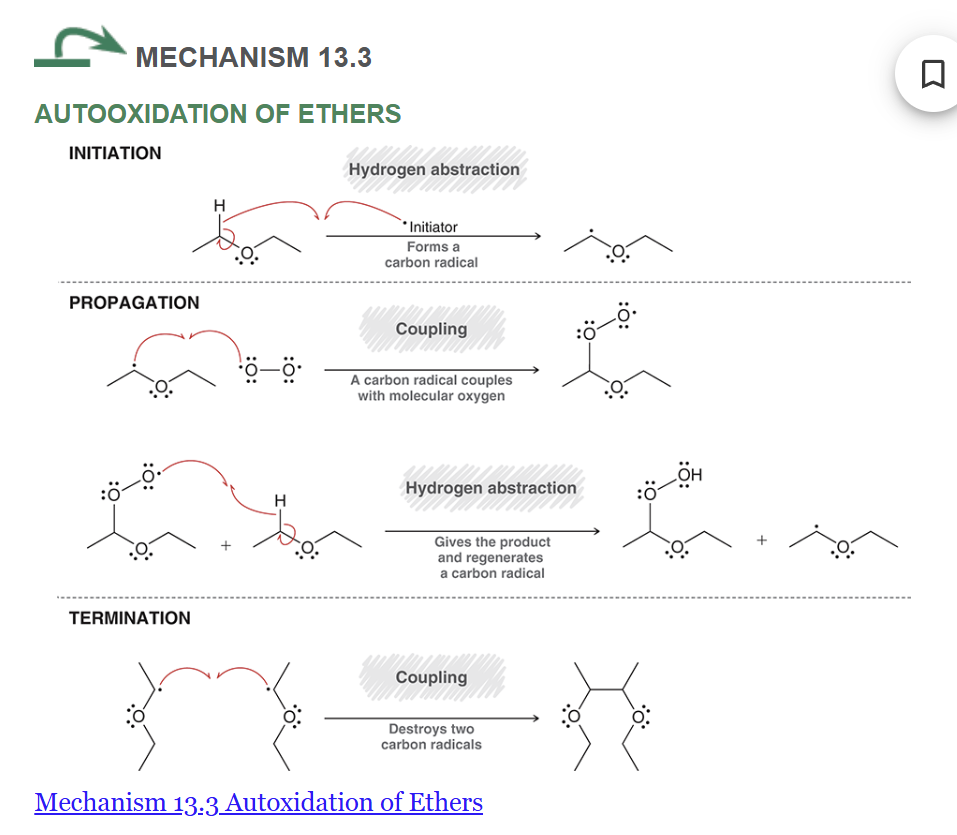
mechanism of autoxidation of ethers
start with diethyl ether
3 membered epoxide
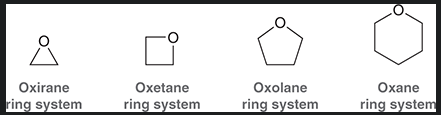
4 membered epoxide
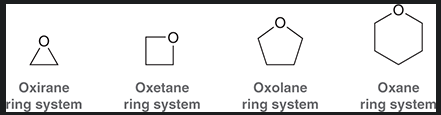
5 membered epoxide
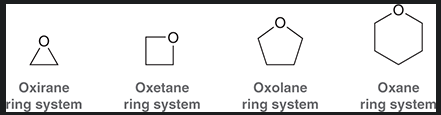
6 membered epoxide
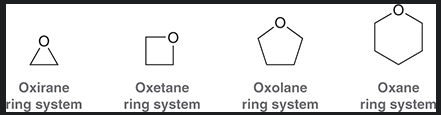
why is oxirane more reactive then other epoxides?
significant ring strain
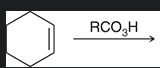
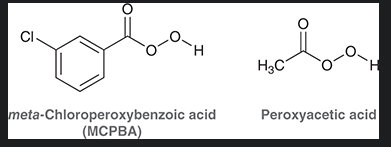
what is this reagent on the arrow called?
a peroxy acid
two commonly used peroxy acids
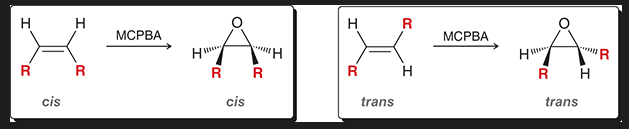
is this process stereospecific or stereoselective?
stereospecific
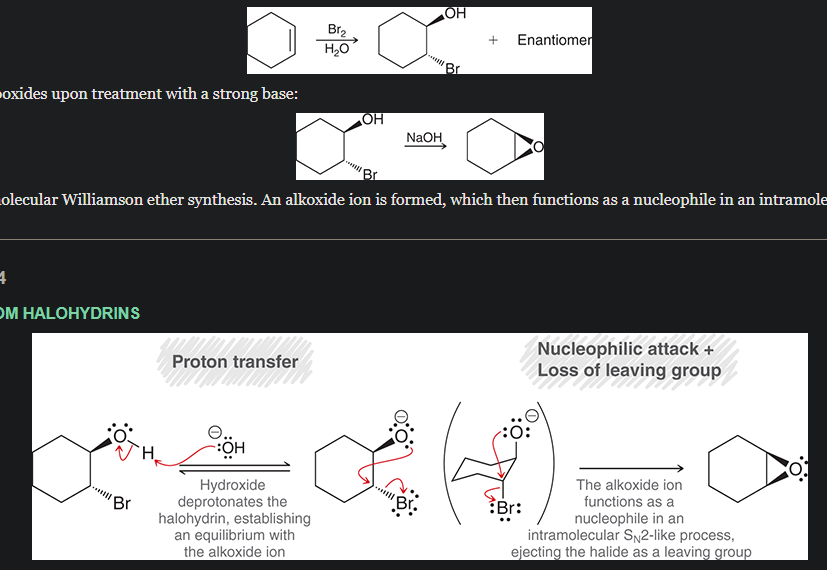
mechanism of epoxide formation from halohydrin formation.
start with cyclopentene, convert that into a halohydrin, then show the mechanism with that.
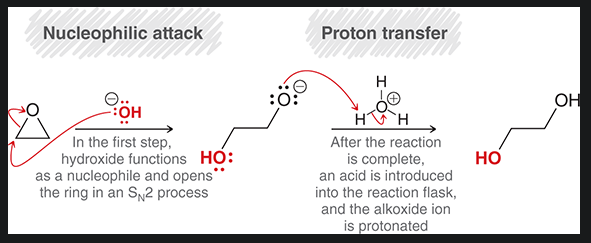
epoxide ring opening with a strong nucleophile
start with oxirane
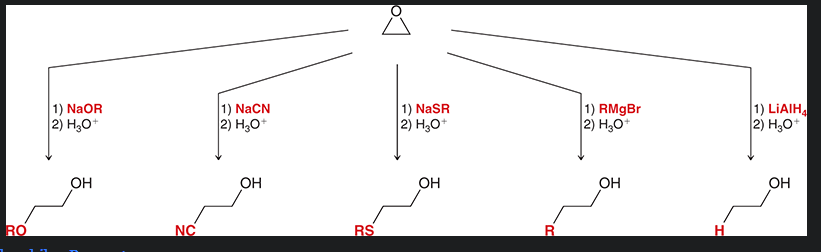
strong nucleophiles that can be used for epoxide ring opening?
not show: NaX where X= Cl, Br, or I
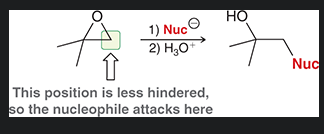
in a nucleophilic ring opening rxn, the nucleophile attacks the (more/less) substituted postion? why?
less substituted
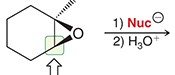
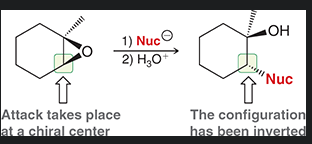
mechanism of acid catalyzed ring opening with oxirane and hydro halic acids
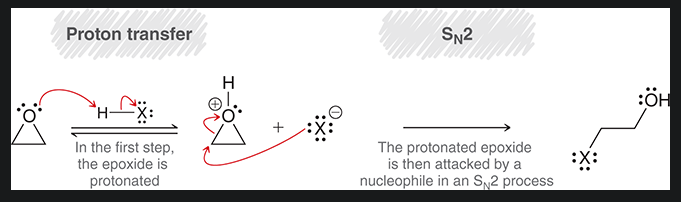
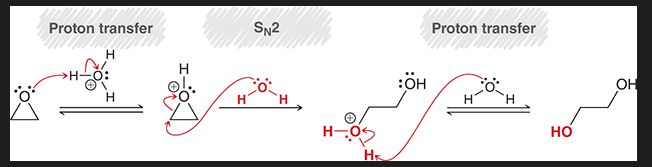
mechanism of acid catalyzed ring opening with oxirane and water under acidic conditions
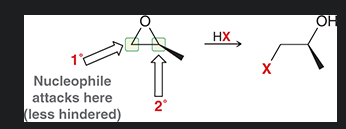
when there is a primary carbon and secondary carbon in a oxirane where would a nucleophilic attack take place in a acid catalyzed ring opening? why?
nucleophile attacks the primary carbon as the dominant factor is steric effect (the primary carbon is less sterically hindered)
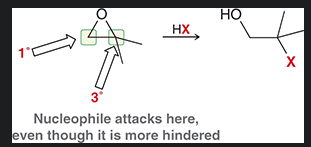
when there is a primary carbon and tertiary carbon in a oxirane where would a nucleophilic attack take place in a acid catalyzed ring opening? why?
nucleophile attacks the tertiary carbon as the dominant factor is electronic effect (the tertiary carbon can hold a partial positive charge much better than the primary )
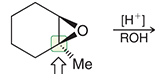
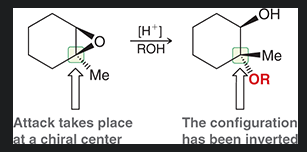
why are thiol groups called “mercapto” in naming?
thiols where once called mercaptans
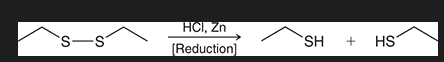
mechanism for oxidation of thiol/ formation of disulfides. start with R—SH
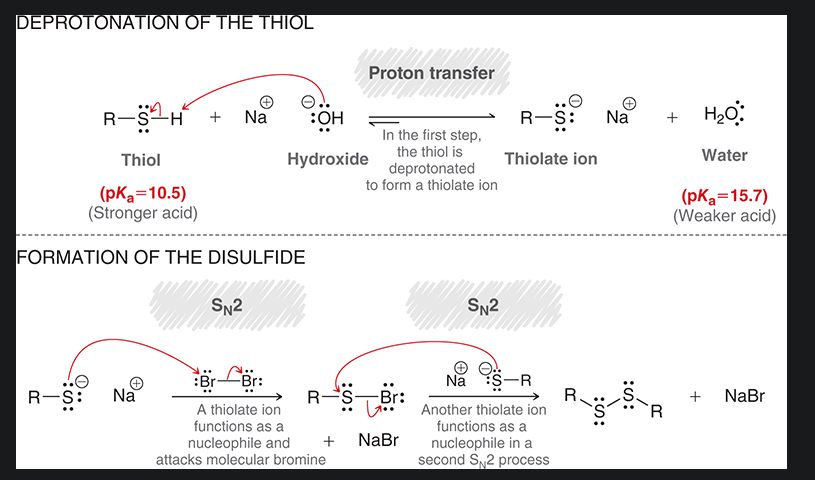

what is the reagent covered by red? what type of rxn is this?
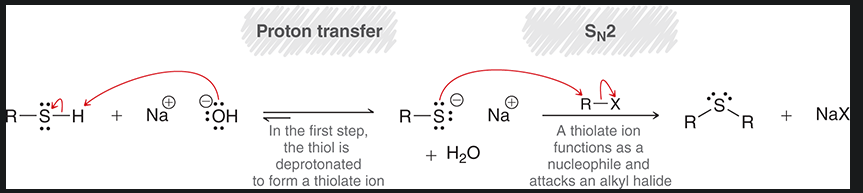
mechanism for sulfide creation from thiols
start with R-SH
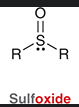
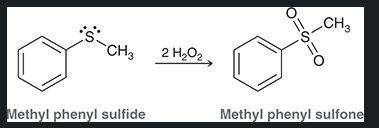
sulfoxide
molecule containing a S=O flanked by two R groups
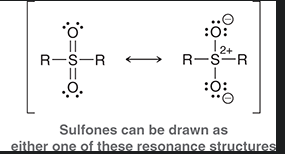
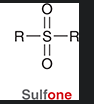
sulfone
molecule containing a Sulfur double bonded to two oxygens and single bonded to two R groups
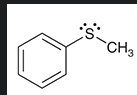
how do you make a sulfoxide from this?
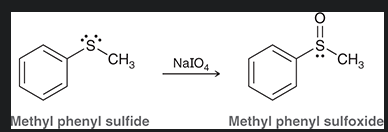
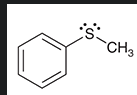
how do you make a sulfone from this?
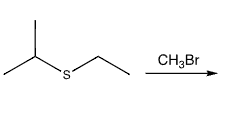
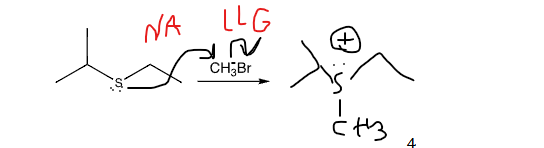
show mechanism arrows as well. what is special about theproduct?
the product can act as an alkylating agent, adding the CH3 to a nucleophile
show sulfoxide resonance
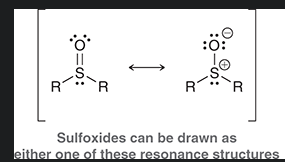
show sulfone resonance