Ochem-Exam 1
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
terminology, EAS reactions, Substituents
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Electron donating group
substituents that have lone pairs on the atom adjacent to the pi system
Inductive effect
Withdrawal or donation of electrons by a sigma bond due to electronegativity
Kinetic control
when the product of an irreversible reaction depends only on relative rates and not on stability
Thermodynamic control
when the product of a readily reversible reaction depends only on stability and not on relative rates
Electron withdrawing group
Substituents that have atoms adjacent to the pi system containing several bonds to more electronegative atoms
Allylic carbocation
A resonance stabilized carbocation in each of the two resonance forms of which the formal charge of +1 is on a carbon adjacent to an alkene
Resonance effect
Withdrawl or donation of electrons through a pi bond due to the overlap of a p orbital on the substituent with a p orbital on the aromatic ring
Diene
A hydrocarbon chain that has two double bonds that may or may not be adjacent to each other
Dienophile
The olefinic or acetylenic component that is seeking a diene in the Diels-Alder reaction
Aromaticity
Recognized when a compound follows Huckel’s rule, resulting in unusual stability
Chloronation

Bromination

Nitration
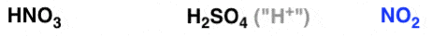
Sulfonation
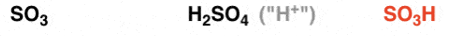
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation

Friedel-Crafts Acylation

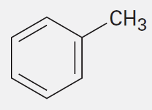
Toluene
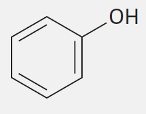
Phenol
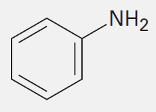
Aniline
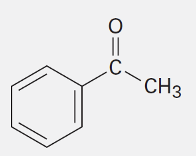
Acetophenone
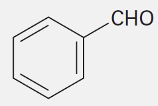
Benzaldehyde
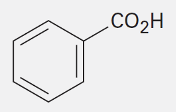
Benzoic Acid
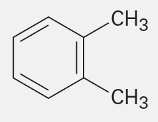
O-Xylene
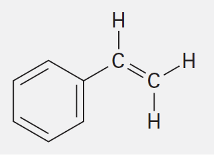
Styrene
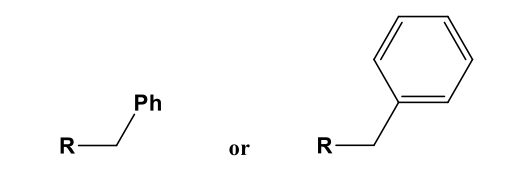
Benzyl
Phenyl
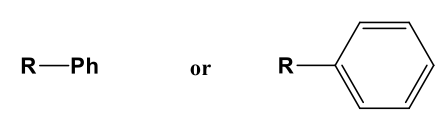
Nitro
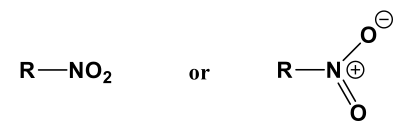
Formyl
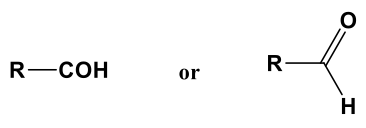
Acetyl
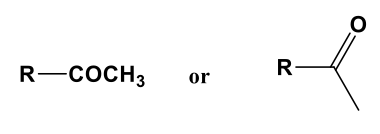
Carboxy
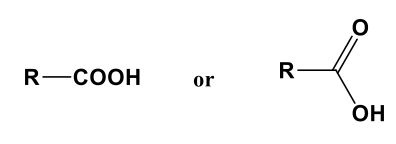
Amino

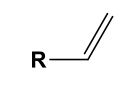
Vinyl
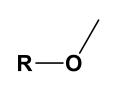
Methoxy
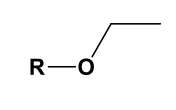
Ethoxy
Hydroxy
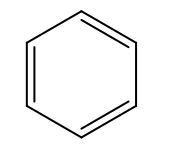
Benzene
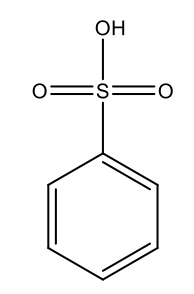
Benzenesulfonic Acid
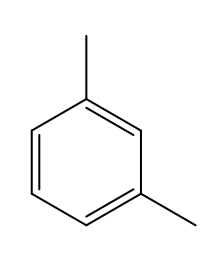
m-xylene
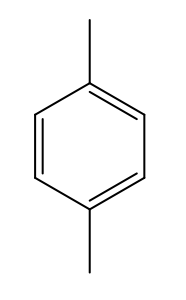
p-xylene