lipids part 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
major classes of membrane lipids(polar)
phospholipids, glycolipids, and archaebacterial ether lipids
sub classes of phospholipids
glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids( this one is sphingosine+fatty acid+ PO4+choline)
sub classes of glycolipids
sphingolipids and galactolipids
What makes up a glycerophospholipid
a glycerol, 2 fatty acid chains, a phosphate, and an alcohol
what makes up a sphingolipid that us under a PHOSPHOLIPID
sphingosine, fatty acid, phosphate, and a choline
Under glycolipids, what are the sphingolipids made of
sphingolipid, fatty acid, and mono- or oligosaccharide(sugar)
What are galactolipids made of
a glycerol, 2 fatty acids, mono- or oligosaccharide, and a sulfate group(SO4)
What kind of bond binds diacylglycerols( glycerol backbone in common glycerophospholipids) to their alcohol head groups?
phosphodiester bond- the -OH on C3 is bound to a phosphate group, this phosphate group is esterfied to an -OH head group
phosphatidic acid
glycerophospholipid linked to an alcohol
phosphatidylethanolamine
glycerophospholipid linked to an ethanolamine
phosphatidylcholine
glycerophospholipid linked to a choline
plasmalogens have a what chain while most glycerophospholipids have what
ether linked alkenyl chain/ ester linked fatty acids
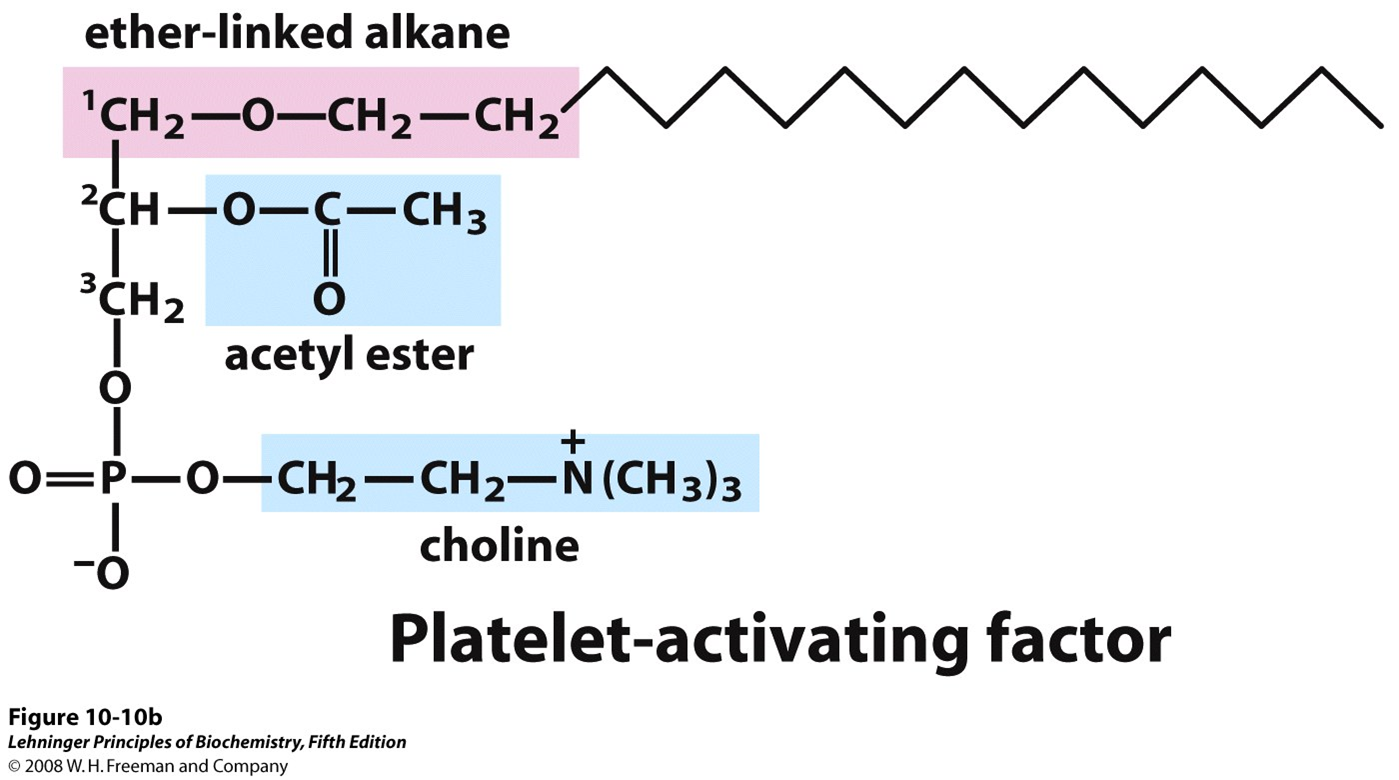
What makes the platelet activating factor more water soluble than most glycerophospholipids and plasmalogens?
While it also has the ether linked alkyl chain at C-1, but C-2 is ester-linked to acetic acid, which makes the compound much more water-soluble
galactolipids predominates in what
plants
which lipids are phosphate free
galactolipids
Three glycolipids of chloroplast thylakoid membranes
MGDG, DGDG, and sulfolipid
What do MGDG and DGDG’s head groups have in common
almost all their acyl groups are derived from linoleic acid and they’re head groups are uncharged
in sulfolipid, sulfonate carries a what
fixed negative charge
Archaebacteria
have lipids that span the entire membrane and are more stable than glycerophospholipids to heat and pH due to ether linkages rather than ester linkages
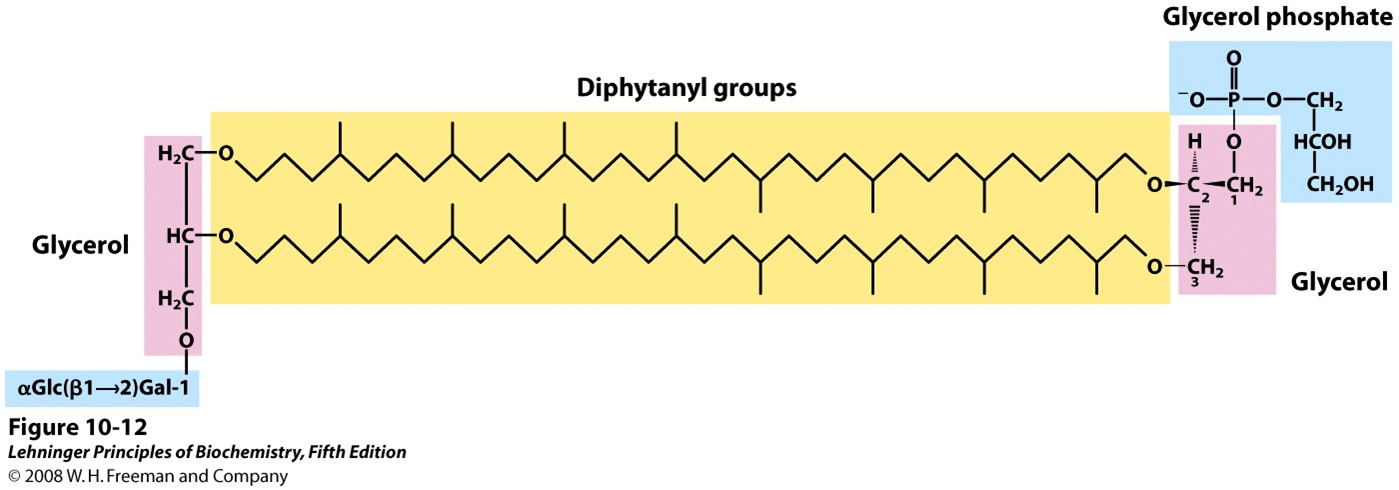
what is the yellow portion composed of?; the glycerol moieties in the archaeal lipids are in what configuration(contrary to those in bacteria and eukaryotes)?;
Long hydrocarbons composed of 8 five-carbon isoprene groups condensed end to end.
R configuration
In the molecule shown here, one glycerol is linked to the disaccharide α-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-galactofuranose; the other glycerol is linked to a glycerol phosphate head group.
Sphingolipids are derivatives of what
sphingosine
3 subclasses of sphingolipids
sphingomyelins, glycosphingolipids, gangliosides
where do you find most phingolipids
in the plasma membrane of animal cells
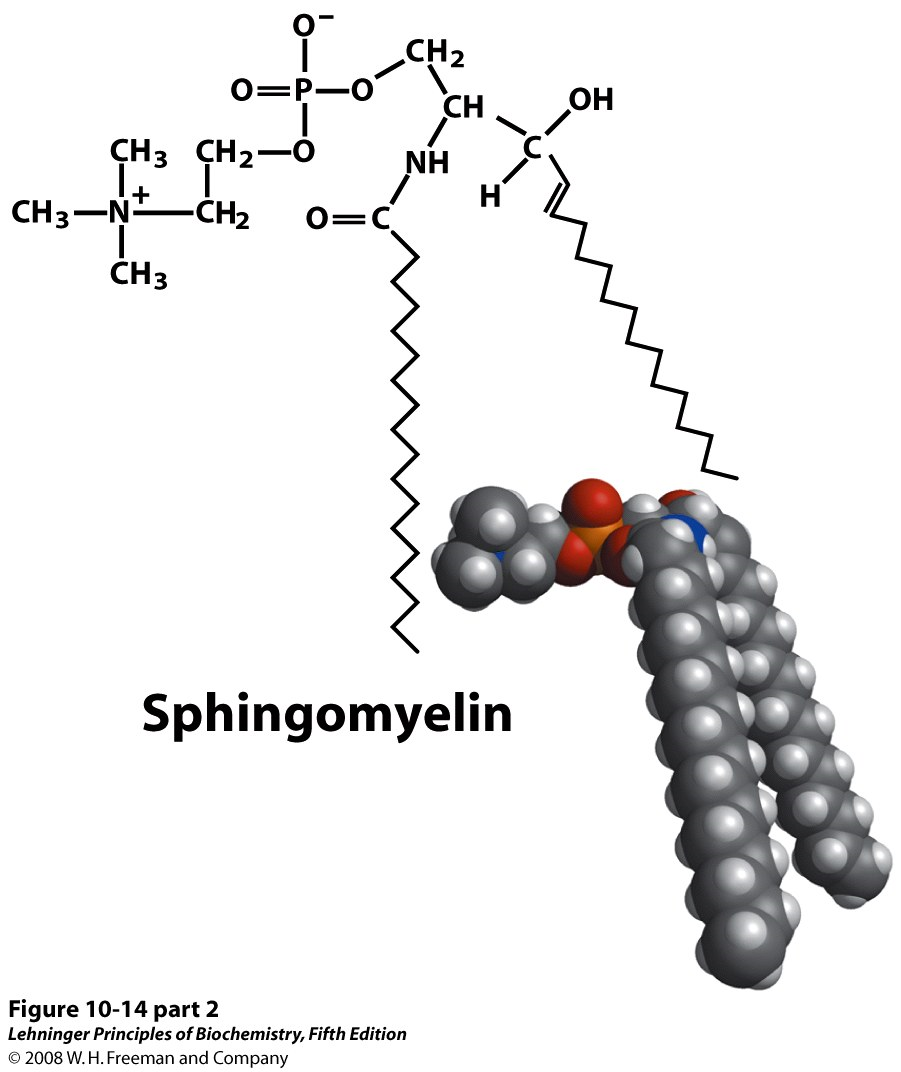
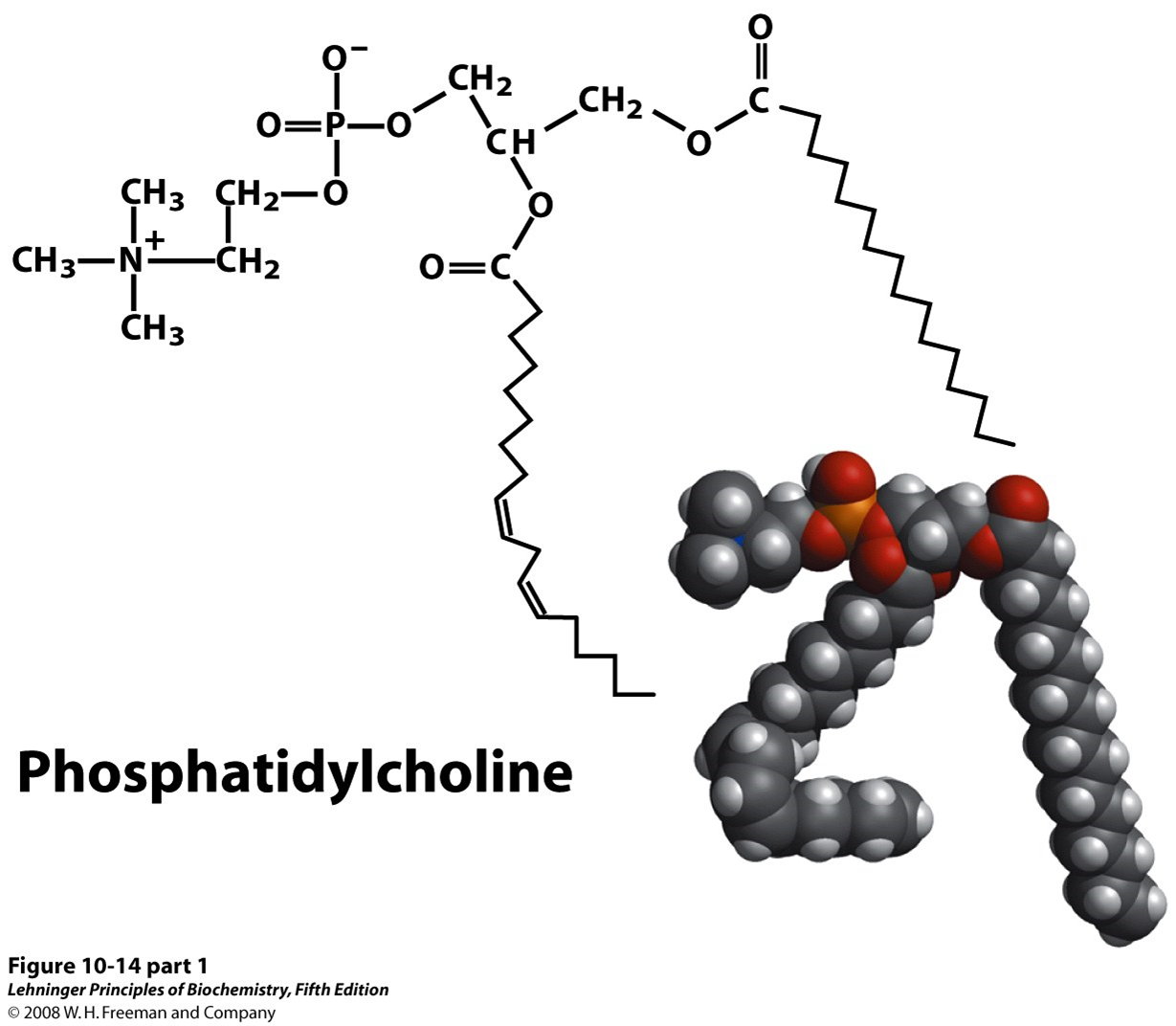
What do these two have in common in structure and shape
polar, + charged phosphocholine head group
amphipathic lipids
has two long fatty acyl chains that bend at unsaturated bonds.
What do phospholipases do and where does it take place
it cleaves phospholipids at specific locations and it takes place in the lysosomes
Sterols:structure
contain steroid nucleus of 4 fused rings, 3 six carbon and one 5 carbon ring
Cholesterol
major sterol found in animal tissue
Purpose of sterols
serve as biological precursors for steroid hormones and some bile acids
5 main classes of structural lipids
glycerophospholipids, glycolipids, GDGTs, sphingolipids, sterols
purposes of lipids
signaling molecules, cofactors, and pigments
function of phosphatidylinositols(glycerophospholipid+ inositol head group)
help regulate cell structure and metabolism
eicosanoids
several signaling functions including injury recovery
steroids
signal carriers between cells
vitamin D
steroid precursor, vital in the regulation of calcium reuptake
vitamin A
steroid precursor, important in vertebrate eye