Display and Image Processing, Harmonics, and Contrast Imaging
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
what goes on in the back end?
(1) scan converter changes the format of the data
(2) scan converter converts the images received from the body to a video format
(2) scan converter provides a means of displaying acquired echo information
functions of the scan converter
(1) pre-processing
(2) memory storage
(3) post-processing
(4) digital to analog (D/A) conversion
pre-processing
(1) manipulation of image before storage in the scan converter
(2) controlled in the scan converter by the sonographer
(3) can be reversed before or inside the scan converter
(4) cannot be reversed once stored
(5) can only be done on active or unfrozen images
post-processing
(1) manipulation of the image after storage
(2) occurs after A to D conversion
(3) all post-processing can be reversed
(4) any changes done after the image is frozen
(5) can be controlled by the sonographer
(6) newer machines now have more post-processing functions
scan converter/memory storage
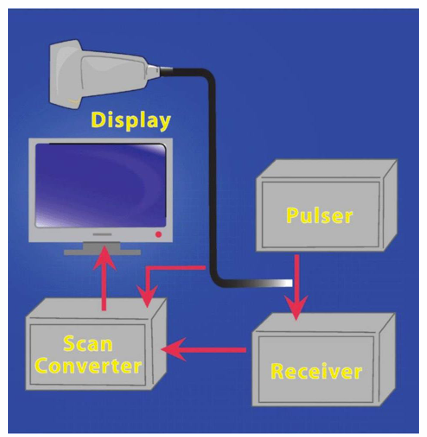
scan conversion
(1) makes grayscale displays and real-time imaging possible by storing image data
(2) scan converter accepts image information in one scan mode (B-scan) and sends it to the display unit in another scan mode (raster scan)
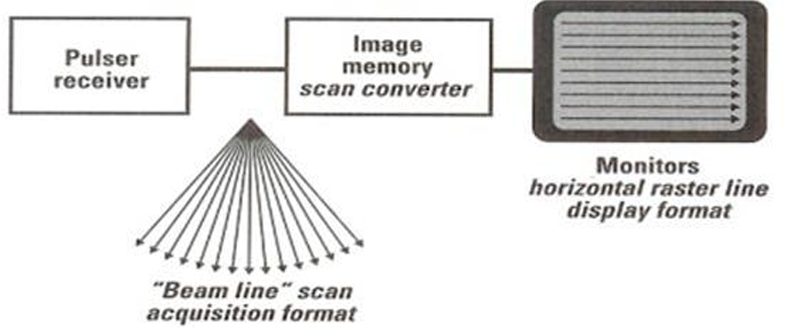
raster scan
series of horizontal raster lines

other back-end functions
(1) patient identification
(2) measurements
(3) analysis
(4) data storage to external devices
(5) cine loop review
(6) patient reports
(7) post-processing techniques, conversion of signal into video format for display
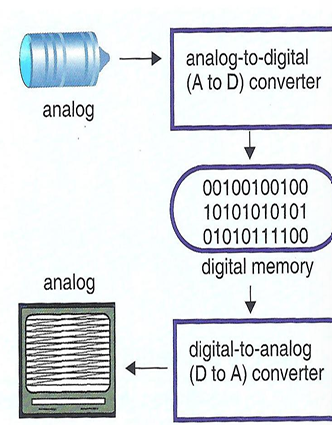
digital scan converter
(1) uses computer technology to convert images into numbers (digitizing)
(2) images stored as zeroes and ones (binary numbers)
(3) these numbers are processed, stored in memory, and retrieved from memory for reconversion into analog video signals for the display screen
advantages of the digital scan converter
(1) uniformity
(2) stability
(3) durability
(4) speed
(5) accuracy
analog to digital conversion
(1) electrical signals created by the TDR during reception are converted from analog to digital using the ADC
(2) contains zeroes and ones
(3) each signal during reception is assigned a numeric value
when an image is stored in memory, each ___ of that image is given a storage location
pixel
the gray shade of each pixel is determined by the ___ of the echo
amplitude
cine loop and freeze frame
(1) formatted data is temporarily stored in the large bank of digital memory
(2) allows temporal storage of the last several frames
benefits of the cine loop
(1) ability to review complicated images in slow time
(2) comparison of frames and changes with time
(3) ability to go back and find the best images for measurement
bistable display
(1) first US systems
(2) narrow dynamic range
(3) composed of only two shades (black and white)
(4) produce high-contrast image
gray scale display
(1) multiple levels of brightness
(2) different shades of greys are assigned to different amplitudes
(3) images are either stored (written) into a scan converter OR displayed (read) onto a display monitor
(4) is possible with the help of a scan converter
after signals are amplified and demodulated in the receiver and TGCs are applied, the resulting range of echo amplitudes is called ___ ___
dynamic range
dynamic range (DR) values
(1) DR = 40 dB → 100 different echo amplitudes → 100 shades of gray needed to display the image
(2) the human eye cannot distinguish that many shades of gray
(3) thus, the range of amplitudes is compressed to 64, 32, or 16 shades of gray
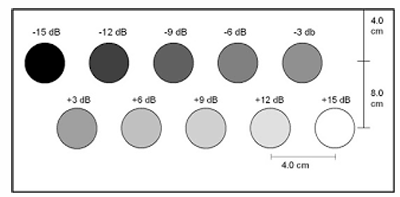
gray scale shades
(1) the top row has the smallest DR
(2) the middle row has a DR in the middle
(3) the bottom row has the largest DR
basic digital nomenclature
(1) binary number is a group of bits and is a series of zeroes and ones
(2) digital numbers are binary
(3) on = 1; off = 0
bit
(1) derived from binary digit
(2) smallest amount of digital memory
(3) the smallest digital output from an A/D converter
(4) it is bistable (value of 0 or 1)
byte
(1) group of 8 bits of computer memory
(2) bytes are sued to represent many types of data
(3) 8 bits = 1 byte
(4) natural grouping of bits (8 bits is a power of 2)
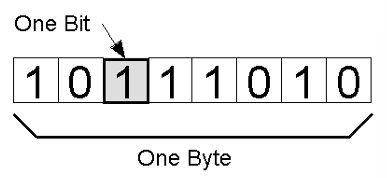
a 3-bit byte is stored in 3-plane memory
(1) each pixel of image will have 3 bits determining its shade of gray
(2) 23 or 8 shades may be represented
___ ___ is controlled by the number of bits in the system controls
contrast resolution
T/F: the greater the number of shades, the better the contrast resolution
true
memory storage in US systems use 4, 5, or 6-bit bytes to represent 16, 32, or 64 shades of gray
(1) # of memory planes (bits in each byte) = x → 2x shades are respresented
(1) 24 = 16 → 25 = 32 → 26 = 64
if the number of bits is low,
(1) fewer shades of gray
(2) higher contrast
(3) good for cardiac and vascular exams
if the number of bits is high,
(1) more shades of gray
(2) less contrast
(3) good for abdominal, OB/GYN, and small parts exams
pre-processing functions include
(1) spatial compression
(2) spatial compounding
(3) panoramic imaging
(4) pixel interpolation
(5) persistence
(6) edge enhancement
(7) image update
(8) RES or write zoom
(9) 3D image acquisition
edge enhancement
sharpening of boundaries to make them more detectable
post-processing functions include
(1) image colorization
(2) 3D image presentation
(3) gray tone processing
(4) read zoom
(5) polarity switch (black and white inversion)
(6) display brightness and contrast variation
(7) speckle tracking
(8) measurements done on images (trace, ellipse tool)
what is the relationship between compression and dynamic range?
they are inversely related (as compression increases, dynamic range decreases)
compression is adjusted by the sonographer using the
dynamic range setting
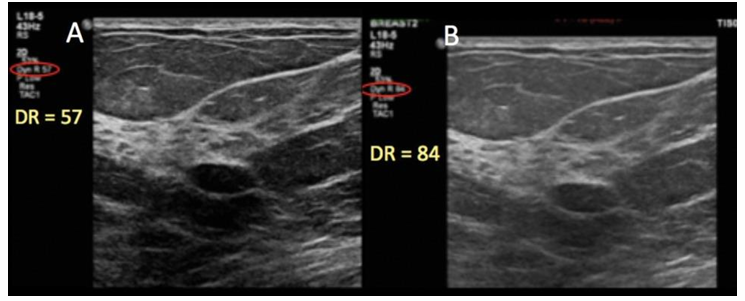
a ___ DR (60 dB) means more shades of gray, while a ___ DR (40 dB) means fewer shades of gray
wide; narrow
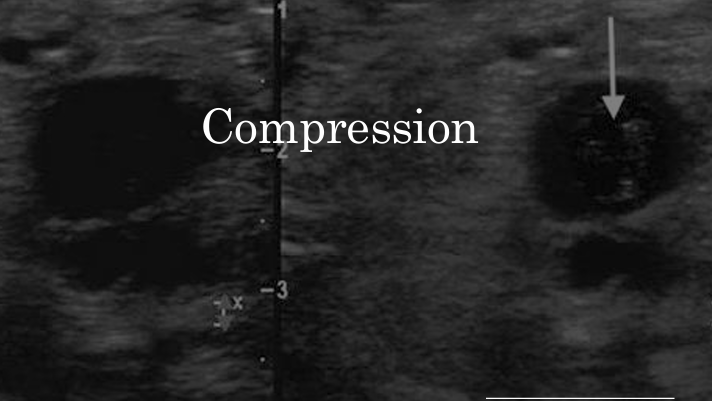
which image has more compression?
the image on the left has more compression (less grays), while the image on the right has less compression (more grays)
spatial averaging (AKA spatial smoothing)
(1) method used to reduce noise by smoothing
(2) image optimization by filling in missing pixels
(3) pixel regions are averaged together to reduce or eliminate areas of signal dropout
(4) improves spatial resolution
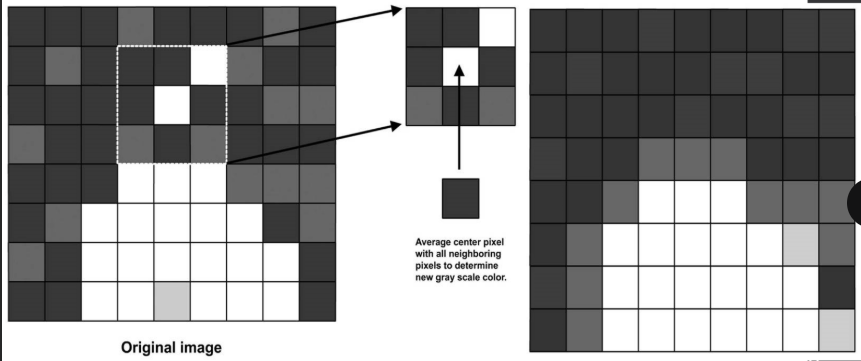
pixel interpolation
(1) fills in the gaps of undetected data due to increased space between lines
(2) needed with sector proves because scan lines separate more at increasing depths
(3) increases line density
(4) improves spatial resolution
persistence (AKA frame averaging)
(1) averaging technique of sequential frames to provide a smooth image
(2) reduces noise to improve SNR
(3) provides good contrast resolution
(4) reduces temporal resolution and frame rate
(5) controlled by the operator

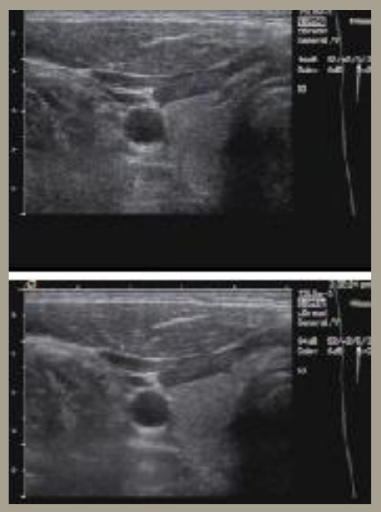
describe the persistence of the following thyroid images
(1) the top image has minimum averaging (note the image noise and contrast)
(2) the bottom image has maximum averaging (note the smoothness of the image)
edge enhancement
(1) filtering technique that makes pictures look sharper
(2) the machine identifies and emphasizes sharp edge boundaries in the image by increasing the image contrast
(3) left image = original, right image = enhanced edges
what is the purpose of zoom (AKA magnification) in US imaging?
the sonographer can optimize anatomic image details by enlarging a portion of the image to fill the screen
region of interest (ROI)
selected part of an image
what are the two forms of zoom?
(1) write (acoustic) zoom
(2) read (non-acoustic) zoom
write (acoustic) zoom is
(1) applied during data acquisition
(2) a pre-processing function applied before storage in the scan converter memory
(3) the image is converted from A to D form and stored in the scan converter
(4) performed on a live image
how does write zoom work?
(1) operator identifies the ROI to be magnified
(2) the system rescans only the ROI
(3) new data is written into the scan converter
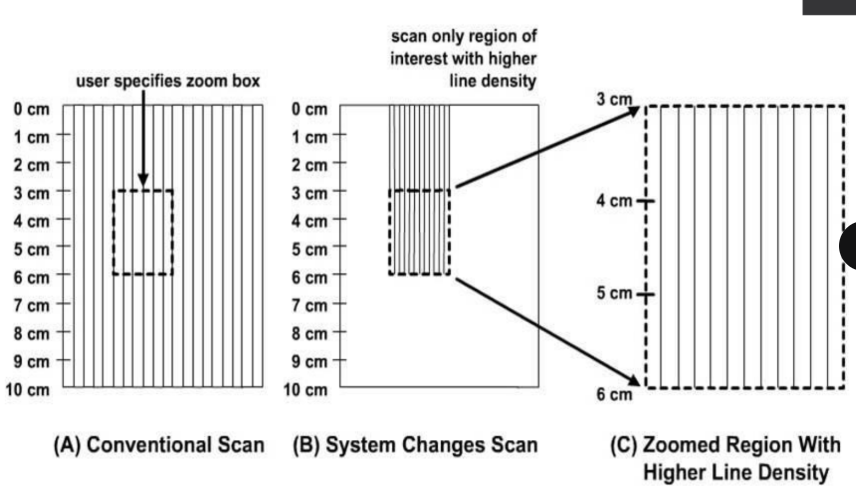
what happens to the image quality when write zoom is used?
(1) the number of pixels and scan lines in the ROI image is greater
(2) improved image detail
(3) increased spatial resolution
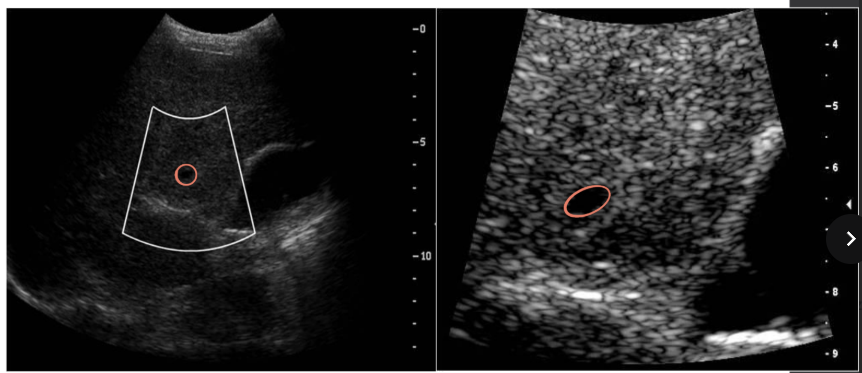
read (non-acoustic zoom)
(1) magnification after image data is stored in the scan converter memory
(2) image is converted from A to D form and stored in the scan converter
(3) performed on a frozen image
how does read zoom work?
(1) sonographer identifies the ROI
(2) system reads and displays only the original data
(3) ROI is not rescanned
what happens to the image quality when read zoom is used?
(1) the number of pixels remains the same, but the pixels are enlarged
(2) the number of scan lines remains the same
(3) does not improve spatial resolution
compound imaging (AKA crossbeam)
(1) multiple images formed at varying angles are created over time and then averaged to create one image
(2) the more frames averaged, the better the image quality
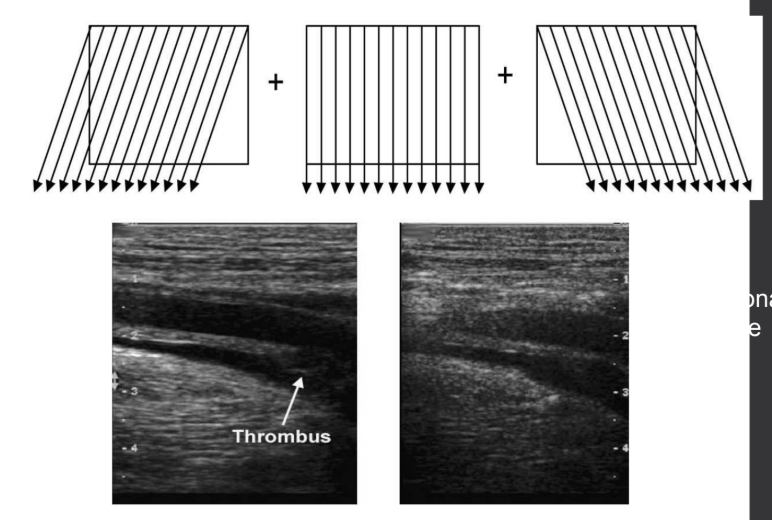
what are the benefits of using compound imaging?
(1) reduces speckle
(2) reduces shadowing artifacts
(3) improves spatial resolution
what are the limitations of using compound imaging?
(1) reduces temporal resolution
(2) reduces frame rate
panoramic imaging
(1) extends (widens) the field of view by physically moving the TDR across the patient to create a 2-D image over time
(2) echo data from previous planes are retained while new data is added from planes in other directions
tissue colorization
(1) using colorization maps to improve the visualization when DR must be preserved; used to extend visual dynamic range
(2) post-processing function that uses color hues with different levels of brightness
(3) does not always result in better visualization of signals, but it does provide some advantage at times
the human eye can see more ___ than ___
colors; gray
the human eye can see ___ shades of gray
64
trace/ellipse tool
(1) post-processing feature that is used to measure an image of interest
(2) “trace tool” allows area and circumference measurements on frozen 2D images
(3) “ellipse tool” is also used to measure area and circumference
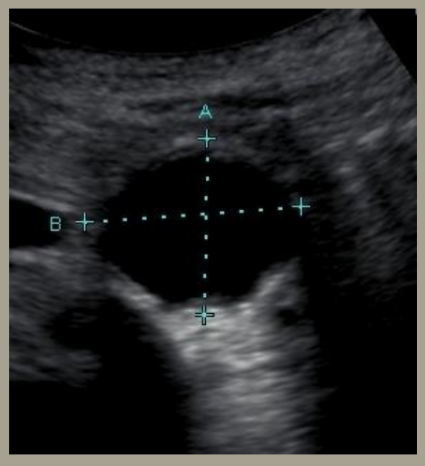
what tool is this image showing?
calipers
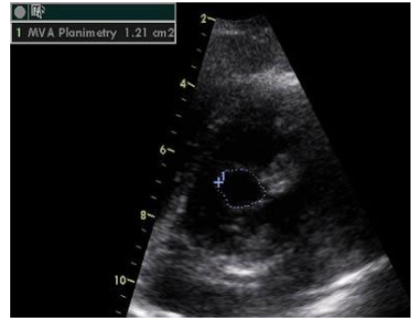
what tool is this image showing?
image trace
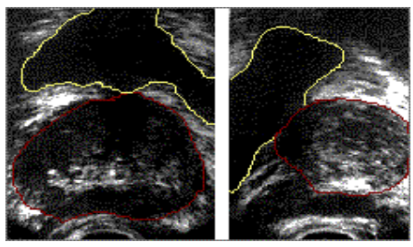
what is the red tool used in this image?
ellipse tool
3-D image presentation
(1) converts 2-D grayscale US images into a volumetric data set
(2) utilized in OB US imaging
(3) volume rendering (popular in OB US imaging)
(4) post-processing choices that present stored 3-D volume data in different ways on the display
(5) most systems still acquire multiple parallel 2-D scans and store them before processing into 3-D images
(6) taking multiple 2-D images allows you to make 3-D images
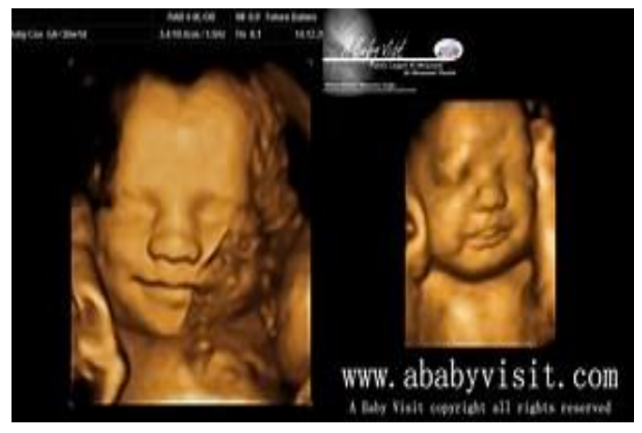
what does this image show?
3-D surface rendering
volumetric scanning
(1) 3-D imaging acquires and displays information in the axial, lateral, and elevation dimensions
(2) the beam is electronically steered in the lateral and elevation dimension
(3) early 3-D imaging was reconstructing 3-D images from 2-D slices, but modern 3-D imaging performs volumetric imaging
(4) requires many parallel 2-D scans (obtained manually or electronically)
2-D images typically refers to
(1) grayscale images
(2) electrical focusing in the axial and lateral dimensions
(3) mechanical focusing in the elevation dimension
voxel
(1) most common 3D volume reconstruction
(2) 3-D picture element (pixel) with a length, width, and thickness
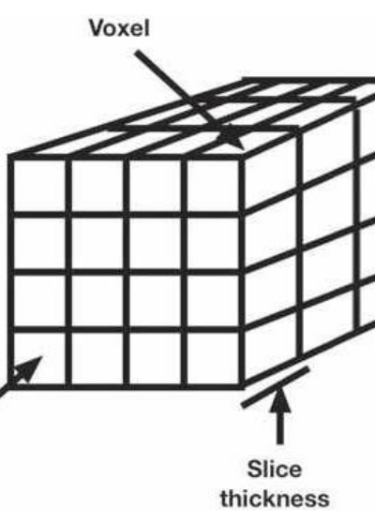
ways to show volumetric scan data
(1) surface rendering (OB scanning)
(2) 2-D slices through a 3-D volume
(3) transparent views
T/F: real-time presentation of a 3D image is called “4D”
true
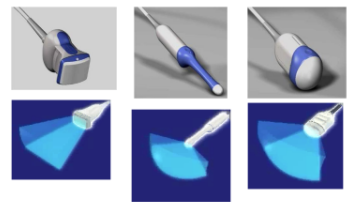
what kind of probes are these?
volumetric 3-D probes
harmonic imaging
(1) is the creation of an image from sound reflections at twice the frequency of the transmitted sound
(2) transmits at a lower frequency to allow for depth penetration, but receives at a higher frequency (harmonic) to allow for better resolution
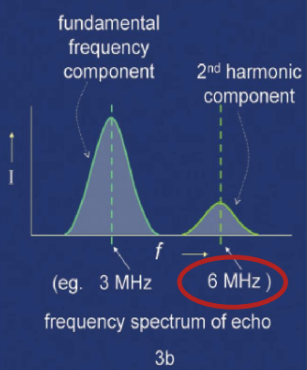
the higher the TDR frequency, the ___ the resolution
higher
how does harmonic imaging work?
(1) as US propagates through medium, it produces acoustic energy at multiples of the transmitted frequency
(2) energy from fundamental frequency is converted to harmonic frequency by non-linear behavior
(3) harmonics are not present as the sound leaves the TDR, they are created deeper in the tissues during transmission
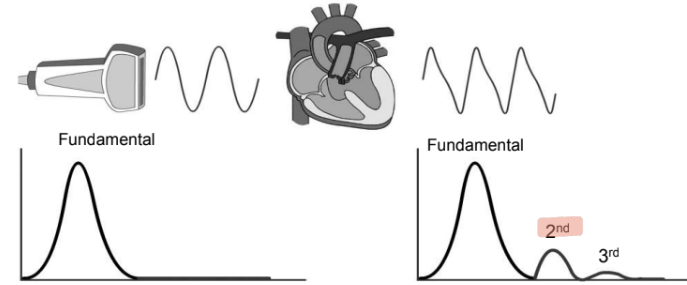
non-linear behavior
(1) sound travels at slightly different speeds through tissue
(2) increased speeds in areas of compressions and decreased in areas of rarefactions
(3) variation is speed alters the shape of the sound beam and small energy transferred from the fundamental frequency to the harmonic frequency
(4) strength of the wave grows as sound travels
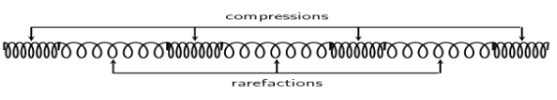
what is needed for harmonic imaging?
(1) wide bandwidth (AKA broad band)
(2) good dynamic range
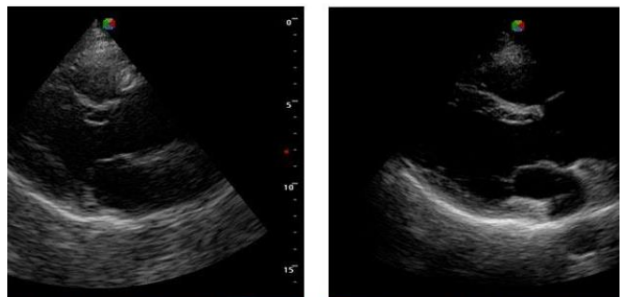
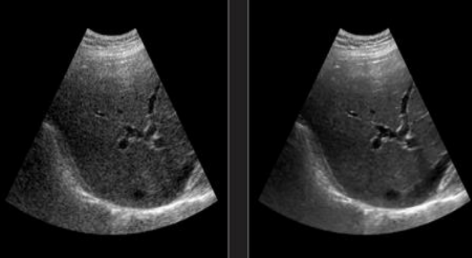
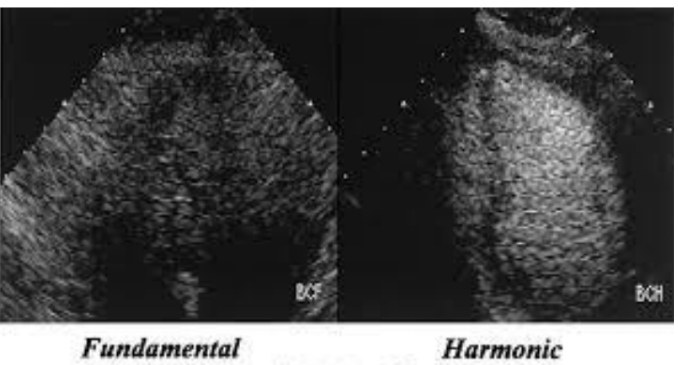
which image uses harmonics?
the image on the right (note that the overall resolution is better, but the valves appear thicker)
advantages of harmonic imaging
(1) improves lateral resolution
(2) reduces grating lobes
(3) reduces reverberation and clutter artifacts
(4) reduction in phase aberration
(5) cyst clearing
(6) improves SNR
(7) improves resolution in patients with large body habitus
disadvantages of harmonic imaging
(1) harmonic beams attenuate quicker than fundamental beams
(2) degradation of axial resolution (fixed with pulse inversion)
pulse inversion AKA phase inversion
(1) used to reverse/prevent axial resolution degradation caused by using harmonic imaging
(2) requires multiple acoustic lines to produce a single display line
(3) pulse inversion transmits two beams with inverted phases
the fundamental reflections add ___, eliminating the need for a longer SPL
destructively
the harmonic signals add ___
constructively
the harmonic signal increases in amplitude by a square root of two, leading to
a degradation in temporal resolution by a factor of two
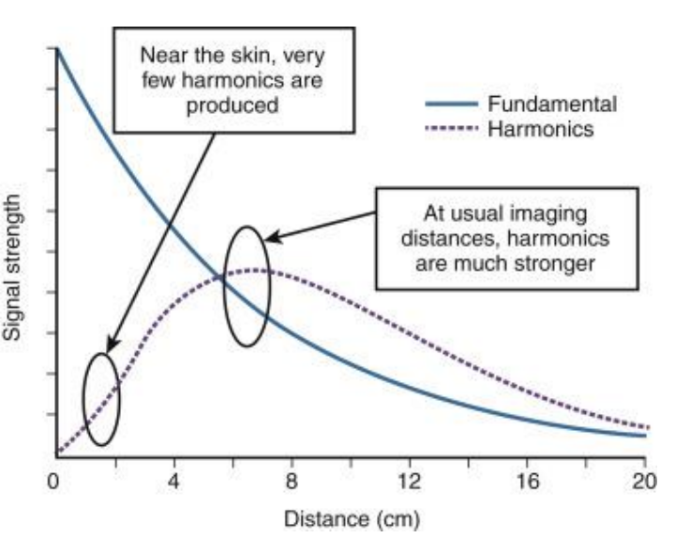
tissue harmonics ___ throughout the length sound beam
vary
describe the tissue harmonics in the near field
near the face of the TDR, there are no harmonics
describe the tissue harmonics in the focal zone
narrower beams = increased harmonic energy = increased acoustic pressure/beam intensities
describe the tissue harmonics in the far zone
increasing depth = increased attenuation = decreased pressure/acoustic pressure due to divergence
T/F: tissue harmonic imaging (THI) displays only the harmonic components of the transmitting signal
false - it displays the return signal
clinical applications of THI
(1) cardiac scanning
(2) difficult patient habitus
(3) further delineating or defining masses with an organ
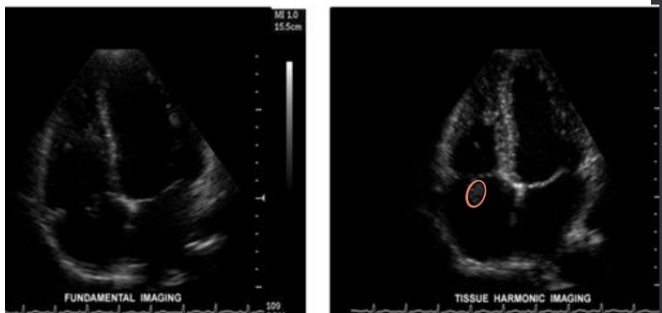
contrast harmonics
(1) lower frequency TDRs and increased beam strength are needed for good contrast harmonics
(2) accomplished during reception of the signal
microbubbles as a contrast agent
(1) gas-contained microbubbles are good contrast agents as gas is 100,000x less dense than blood
(2) blood, tissues, and gas have a huge impedance mismatch, causing increased brightness to the area of interest
(3) bubbles distort and create harmonic energy
(4) agitated saline microbubbles enhance blood echoes by introducing multiple liquid-gas interfaces
(5) microbubbles are dissolved rapidly in blood and lose echogenicity
(6) brands: optison, levovist, definity
microbubbles are commonly used as contrast agents for a specific kind of ___
echocardiogram
contrast helps overcome several US limitations, such as
(1) contrast resolution on grayscale
(2) detection of low blood flow
(3) detection of flow in very small vessels
the ___ ___ is the most important part of the contrast microbubble because it determines the echogenicity (increased echogenicity due to increased impedance)
gas core
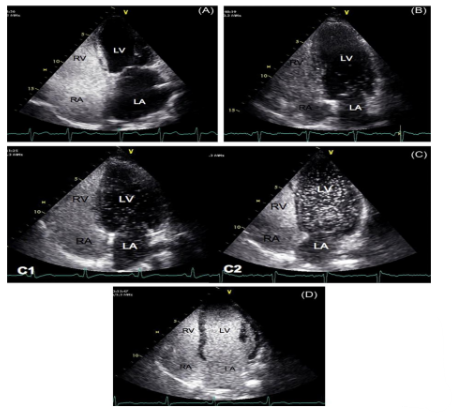
describe what is happening in this image
(1) this echocardiogram depicts a positive bubble study
(2) the bubbles start on the right side of the heart and flow into the left side of the heart over time
(3) demonstrates relevant pathologies such as a patent foramen ovale (PFO)
what does this image depict?
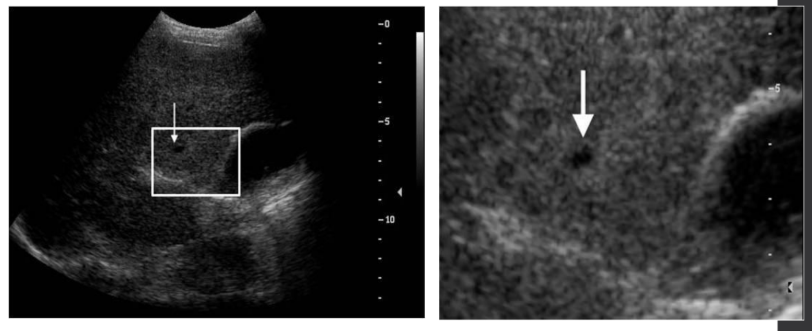
carotid US with contrast
contrast harmonic power doppler
using high MIs (mechanical indices) results in a contrast-to-tissue ratio improvement over standard MI B-mode harmonic imaging
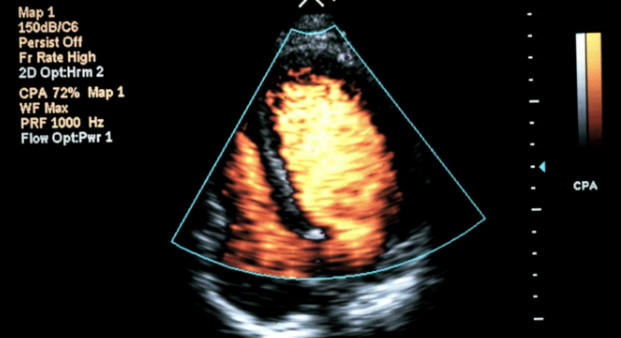
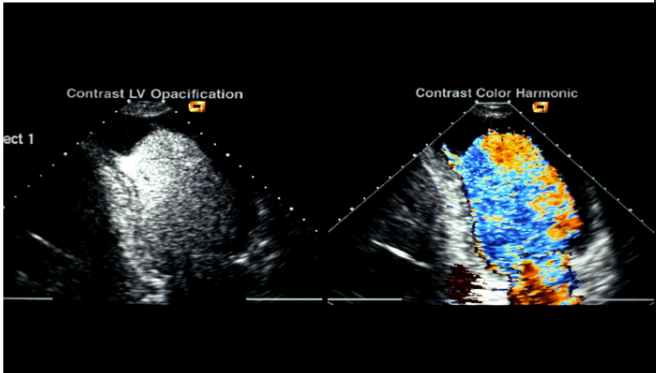
what does this image display?
contrast color harmonies
wall motion imaging
thorough evaluation of cardiac wall motion is difficult for some patients
power motion imaging (PMI)
improves evaluation of the cardiac wall
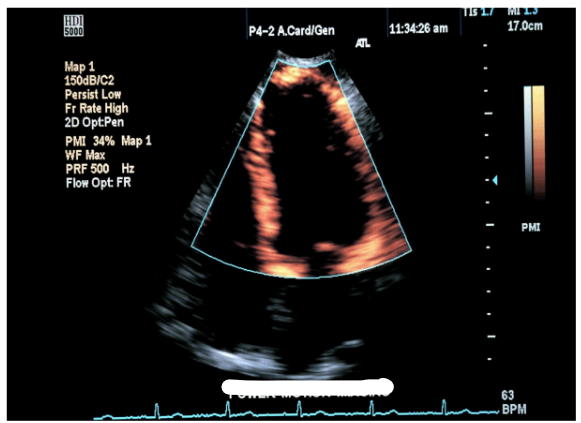
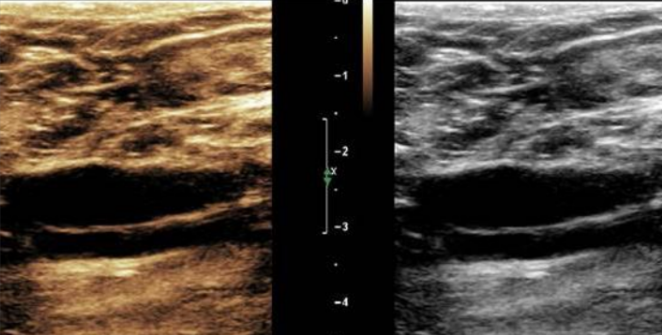
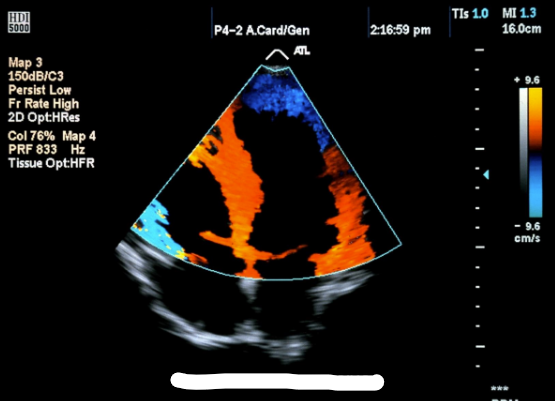
tissue doppler imaging (TDI)
uses color doppler (filter is set to low velocity, high amplitude
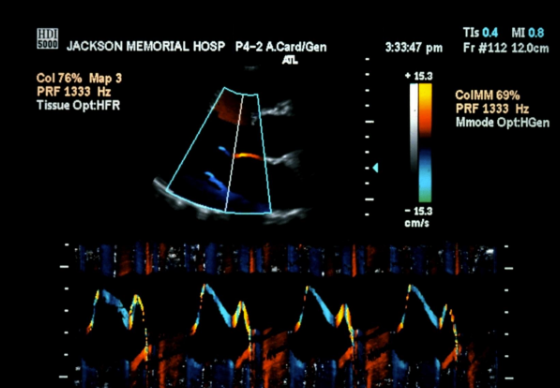
what does this image display?
M-mode TDI