Topic 1A - Key concepts in biology (copy)
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 Core Practical: 1) Investigate biological specimens using microscopes (1.6)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1.3 What can light microscopes be used to see?
Images of cells and large subcellular structures (like nuclei and vacuoles).
1.3 What is the maximum magnification of a light microscope? (aprox)
2000x
1.3 What is often used on the specimen on light microscopes to have a clearer representation?
A stain
1.3 What century was the first light microscope developed in?
17th century
1.3 What century was the first electron microscope developed in?
20th century
1.3 What do electron microscopes use to form an image?
beams of electrons
1.3 What do light microscopes use to form an image?
light and lenses
1.3 Which type of microscope has a higher resolution and magnification? And why is this useful?
electron
They can therefore be used to study cells in much finer detail
Enabling biologists to see and understand more subcellular structures such as mitochondria, chloroplasts and ribosomes.
They have also helped develop better understanding of the nucleus and cell membrane
1.3 What is the definition of magnification?
How many times larger the image is than the object
1.3 What is the pathway of light through a light microscope?
light source → stage → object / specimen → objective lens → body tube → eyepiece lens → eye
1.3 What is the formula to calculate magnification?
magnification = Image size / Actual size
1.3 An image of an animal cell is 30mm in size and it has been magnified by a facto of x3000. What is the actual size of the cell?
0.01 mm = 10μm
1. 3 How do you calculate the total magnification of a light microscope?
Magnification of a light microscope = Magnification of eyepiece lens x Magnification of objective lens
1.3 Light vs electron microscope
-light microscopes are cheaper
-light microscopes are easier to use (so are used in schools)
-electron microscopes are used to study sub-cellular structures
-electron microscopes have a better resolution
1.1 what are the 5 kingdoms
animals, plants, protoctists, prokaryotes and fungi
1.1 which of the 5 kingdoms are eukaryotes?
fungi, animals, plants and protoctists
1.1 are eukaryotic cells single or multicellular?
they can be both
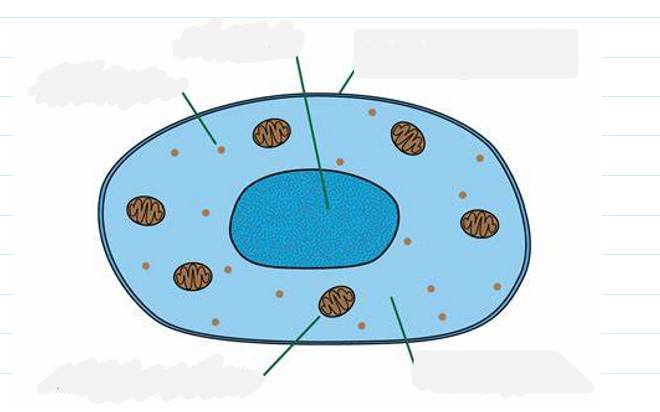
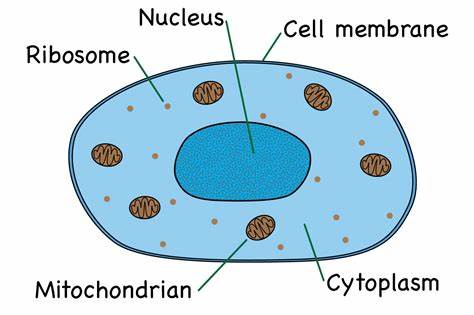
1.1 label this diagram of an animal cell
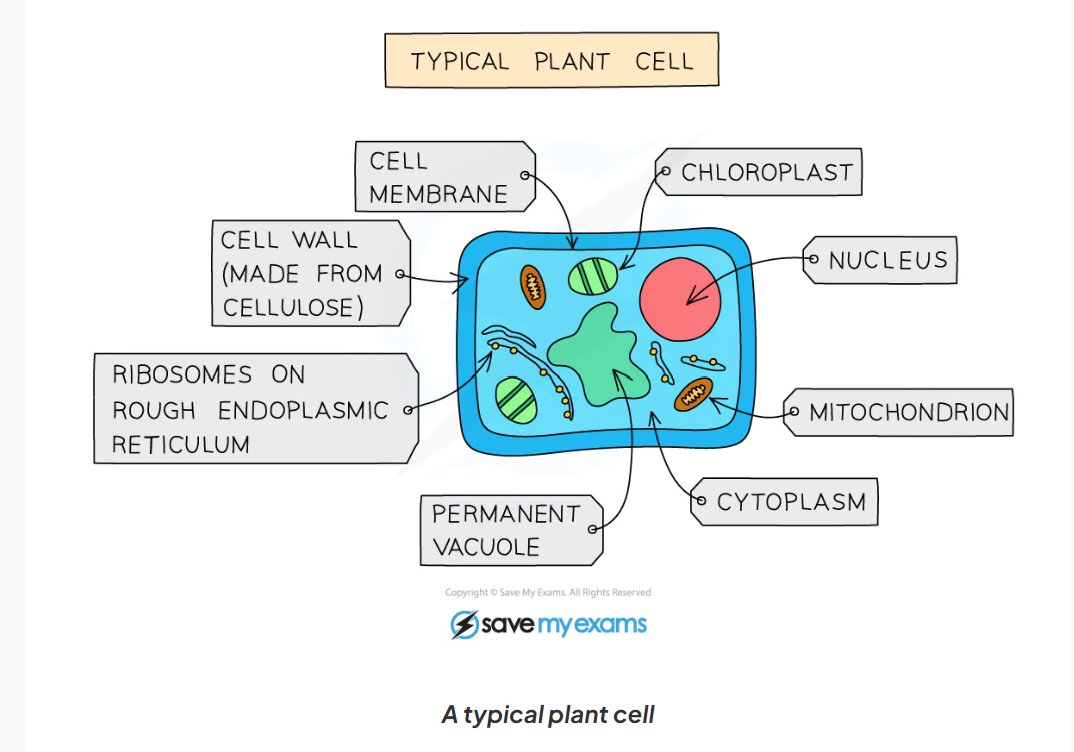
1.1 label this diagram of a plant cell
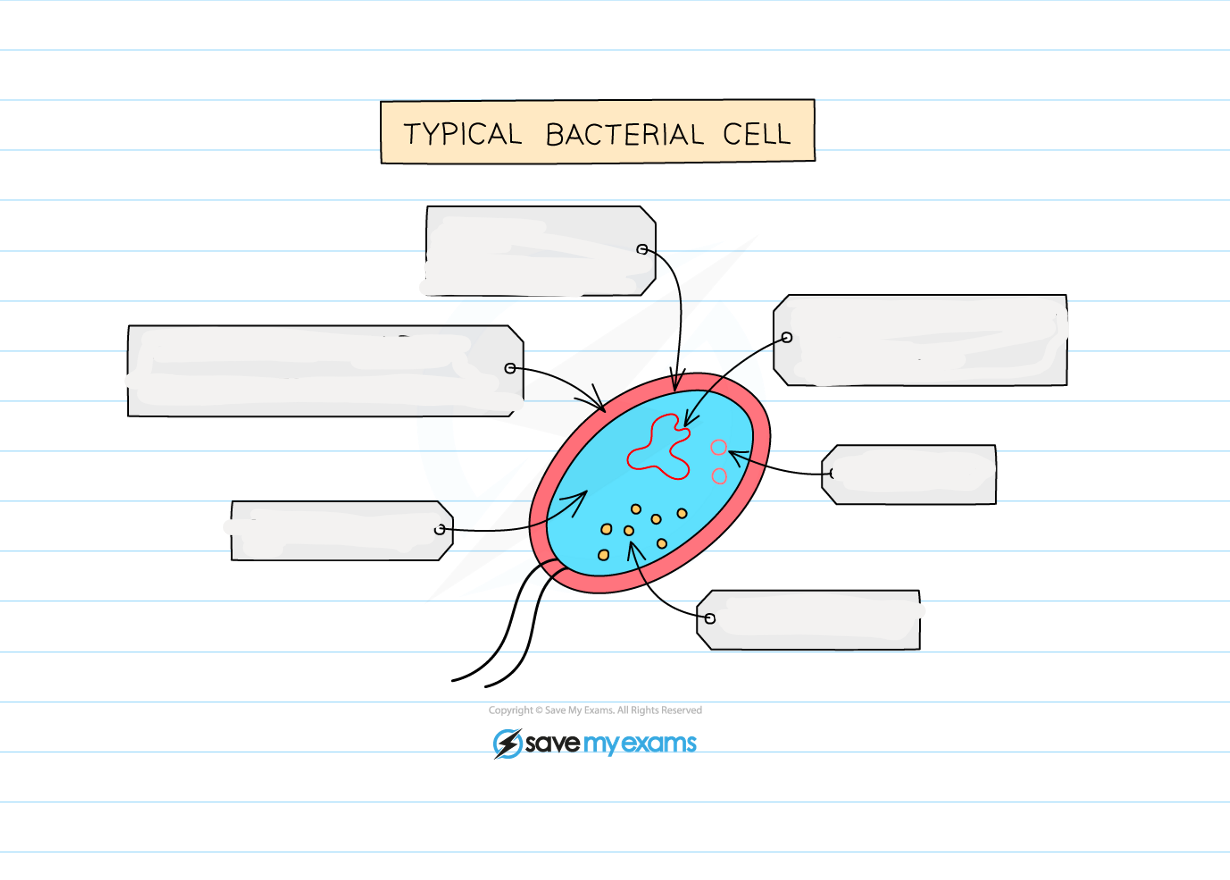
1.1 Label this diagram of a bacteria cell
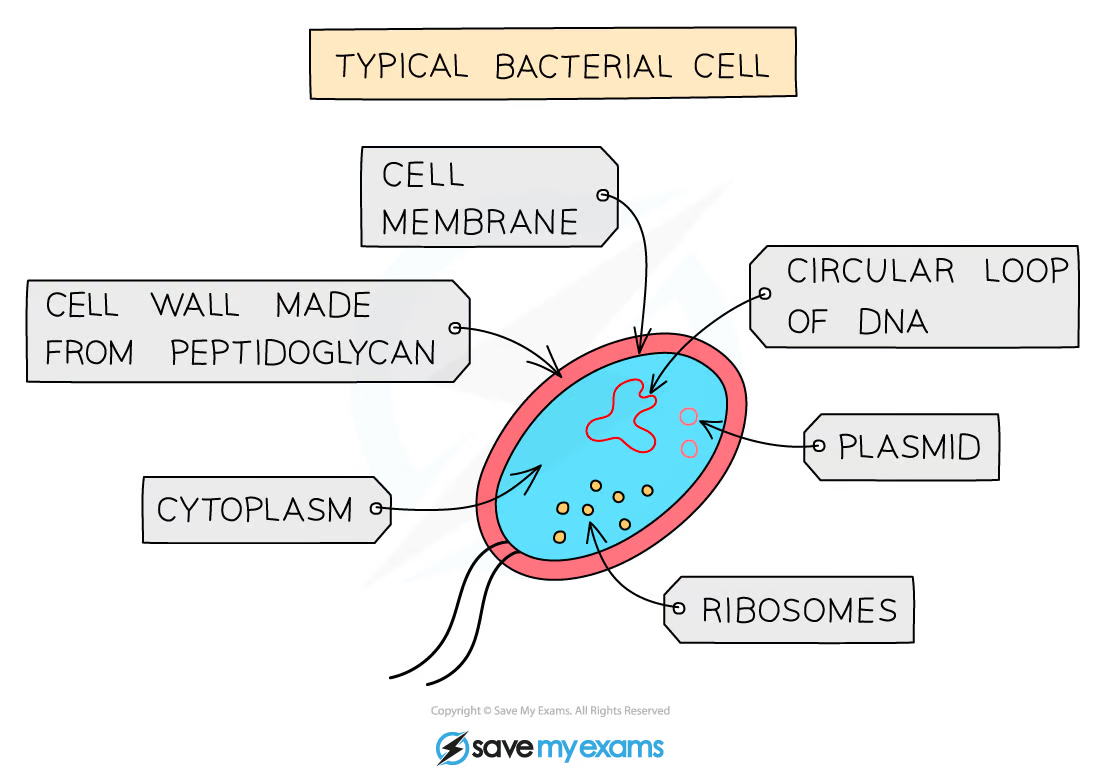
1.1 what are prokaryotic cells?
they are always single-cellular and do not contain a nucleus (instead their genetic material is found in the cytoplasm)
1.1 Give an example of a prokaryotic cell?
bacteria cell
1.1 what are the main features of animal cells?
-they are multicellular
-their cells contain a nucleus with a distinct membrane
-they do not have cellulose cell walls
-they do not contain chloroplasts (unable to carry out photosynthesis)
1.1 nucleus function
contains the genetic material (DNA) which controls the activity of the cell
1.1 Cytoplasm function
-where chemical reaction take place such as anaerobic respiration
-jelly-like substance
1.1 Cell membrane function
controls what goes in and out of the cells
1.1 Ribosome function
-where protein synthesis take place
-found in the cytoplasm
1.1 Mitochondria function
-where aerobic respiration takes place
-releases energy for the cellular processes
-cells with high rates of metabolism (carrying out many different cell reaction) have significantly higher numbers of mitochondria than cells with fewer reactions taking place.
1.1 cell wall function
-made of cellulose ( a polymer of glycose)
-give the cell extra support and its shape
1.1 Permanent vacuole function
-contains sap; solution was sugars and dissolved salts in water
-used for storage of certain materials
-also helps support the cell
1.1 Chloroplast function
-site of photosynthesis
-contains a green pigment called chlorophyll which absorbs light energy
-contains the enzymes needed for photosynthesis
1.1 what are the main features of fungi? (7 things)
-usually multicellular but some are single cellular
-their cells contain a nucleus with a distinct membrane
-made of thread like structures known as hyphae that contains many nuclei and are organised into a network known as mycelium
-don’t contain chloroplasts (no photosynthesis)
-they feed by secreting extracellular digestive enzymes onto food and absorbing the digested molecules.
-some fungi are parasitic and feed on living things
-some store carbs as glycogen
-examples of fungi are moulds, mushrooms, yeast
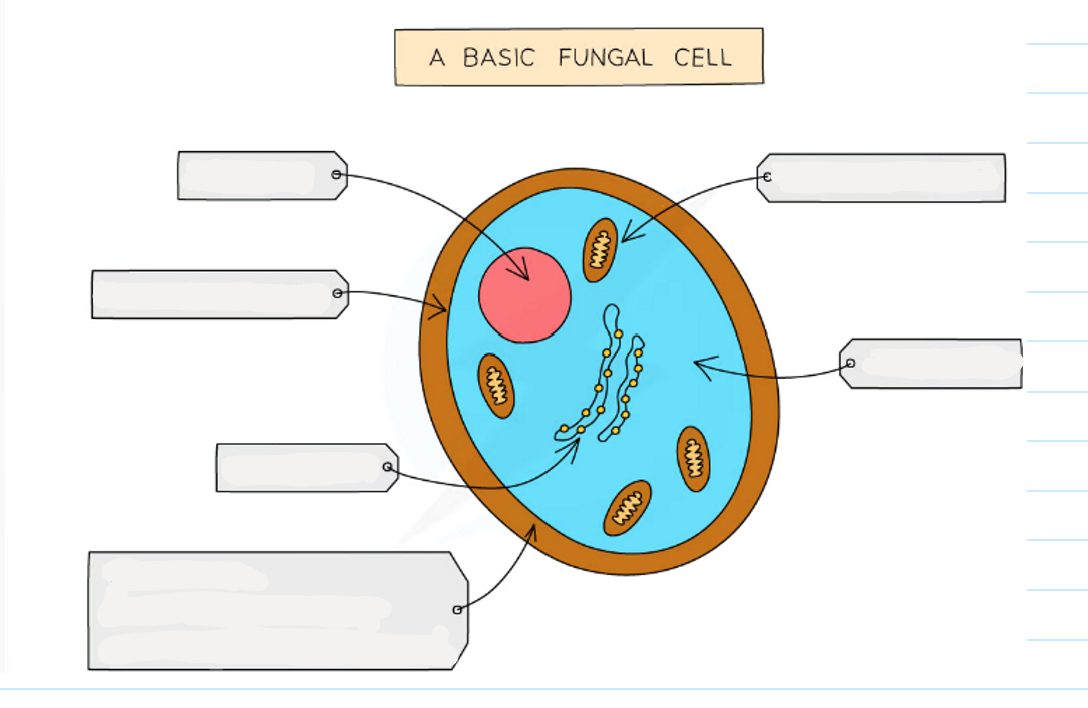
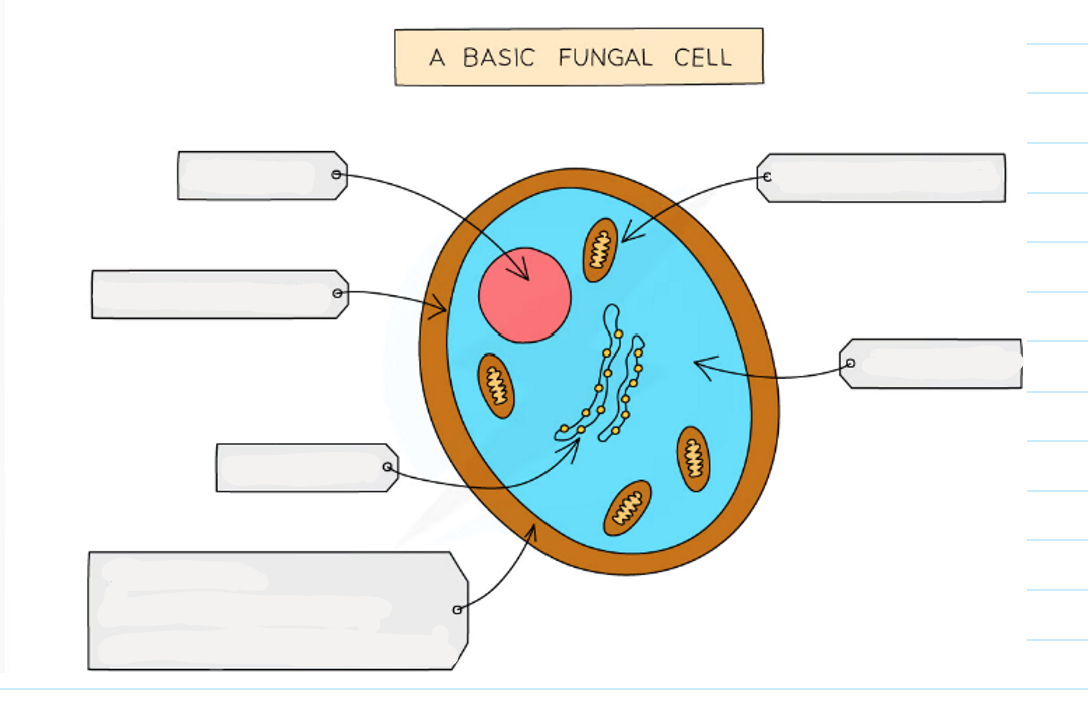
1.1 label this diagram of a fungi cell
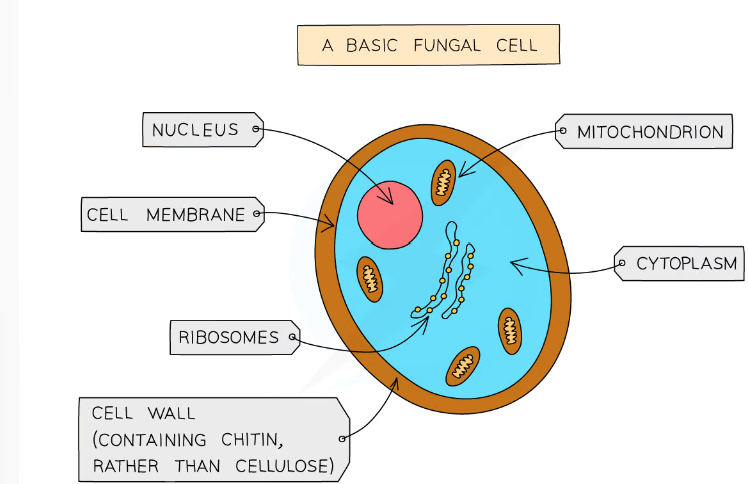
1.1 what are the main features of protoctists?
-mainly microscopic and single-celled but some group together to form larger forms
-their cells contain a nucleus with a distinct membrane
-some have cell walls and chloroplasts soe photosynthesis, others feed on organic living things
examples: chlorella, plasmodium (malaria), paramecium
1.1 here are some examples of protoctist cells
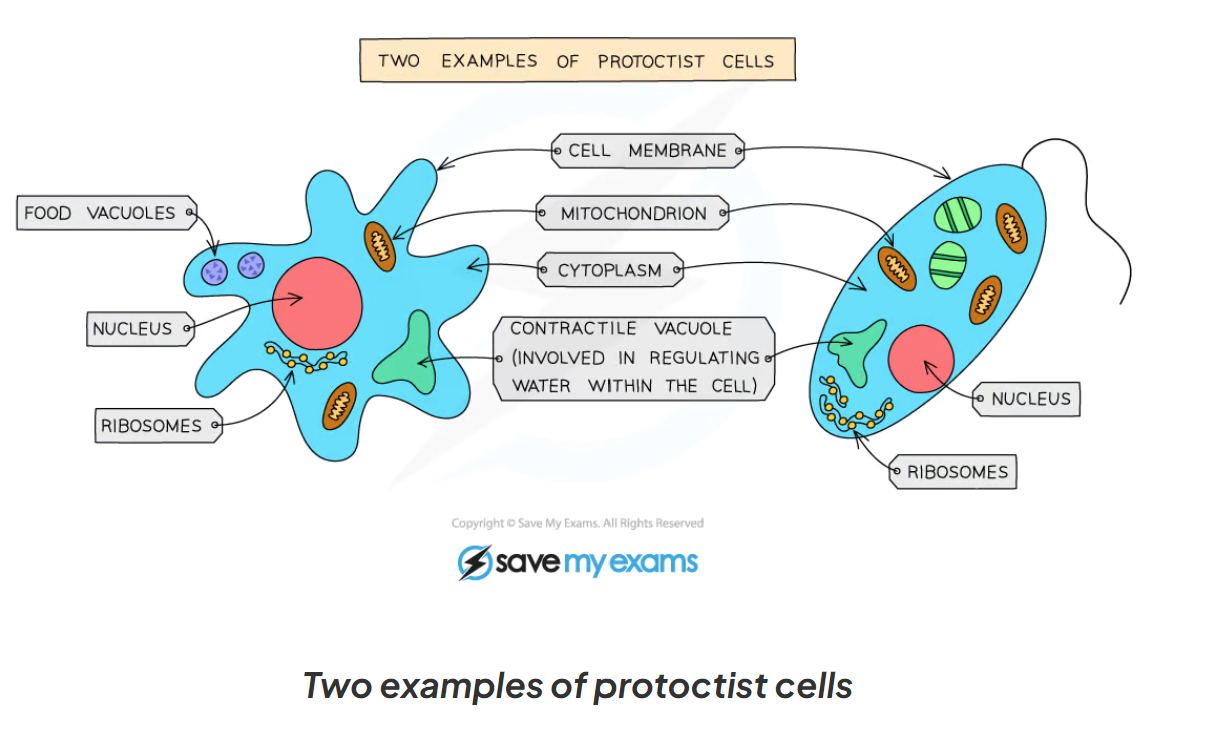
1.1 what are the main characteristics of bacteria?
-they are microscopic and single-cellular
-have a cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and ribosomes
-no nucleus, but have circular chromosomes of dna that float in the cytoplasm
-have plasmids - small rings of dna (also floating in the cytoplasm) that contain extra genes to those found in the chromosomal dna
-no mitochondria, chloroplasts and other membrane bound organelles
-some have a flagellum
-examples: pneumococcus (pathogen causing pneumonia), lactobacillus (used to produce yoghurt)
1.2 what is a specialised cell?
cells which have developed certain characteristics (adaptations) in order to perform particular functions
1.2 How do cells speciallise?
By undergoing differentiation
1.2 what is differentiation?
the process by which cells develop the structure and characteristics needed to be able to carry out their functions.
1.2 examples of specialised animals cells
sperm cell, egg cell, ciliated cell
1.2 sperm cell function
needed in reproduction to carry the DNA of the male to the female egg cell (ovum)
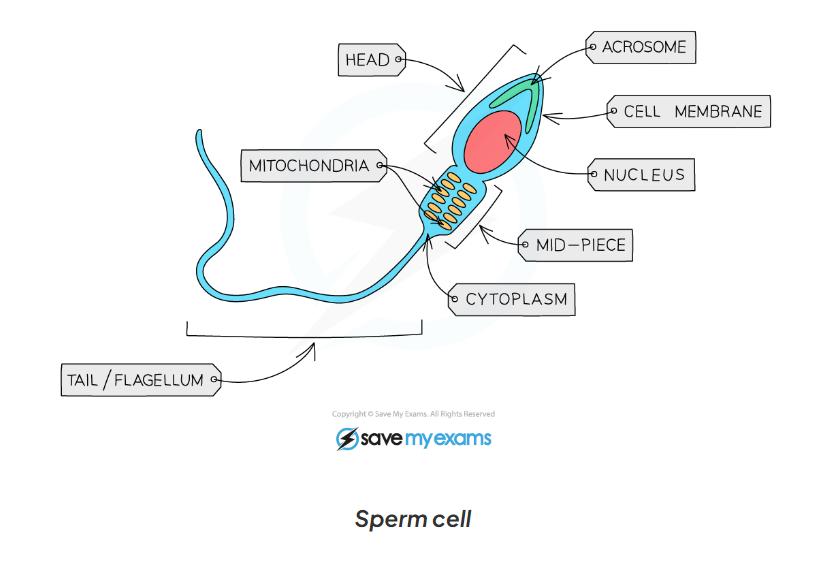
1.2 sperm cell adaptations
-head contains the genetic material for fertilisation in a haploid nucleus ( containing half the number of chromosomes)
-the acrosomes in the head contains digestive enzymes to penetrate the egg
-the mid piece is packed with mitochondria to release energy needed to swim and fertilise the egg
-the tail enables the sperm to swim
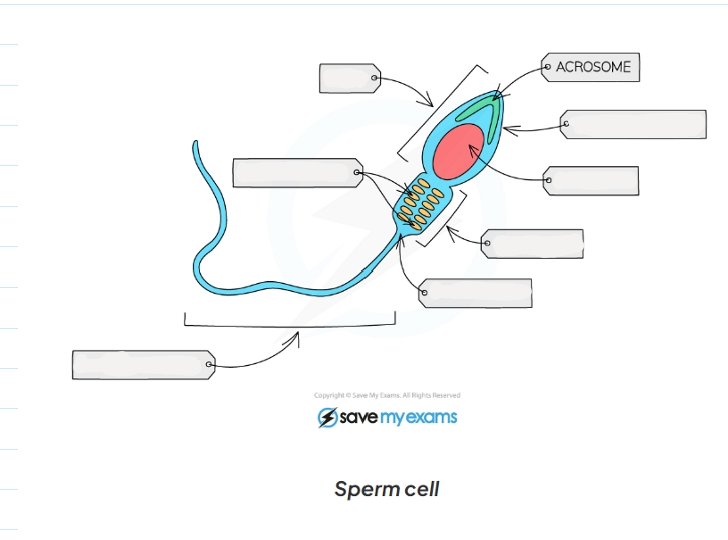
1.2 label this diagram of a sperm cell
1.2 role of an egg cell?
key in reproduction to be fertilised by a sperm cell to develop an embryo
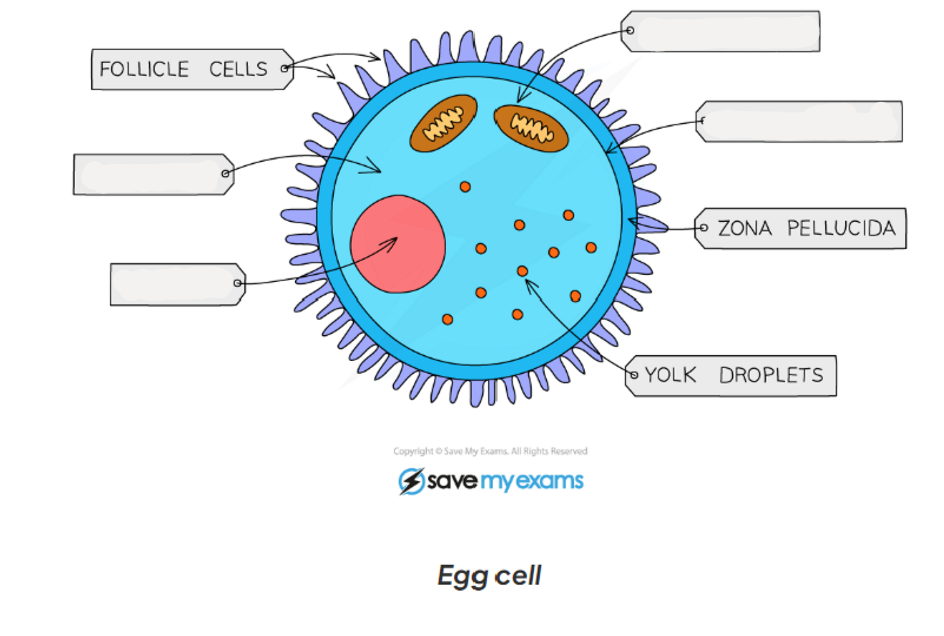
1.2 label this diagram of a egg cell
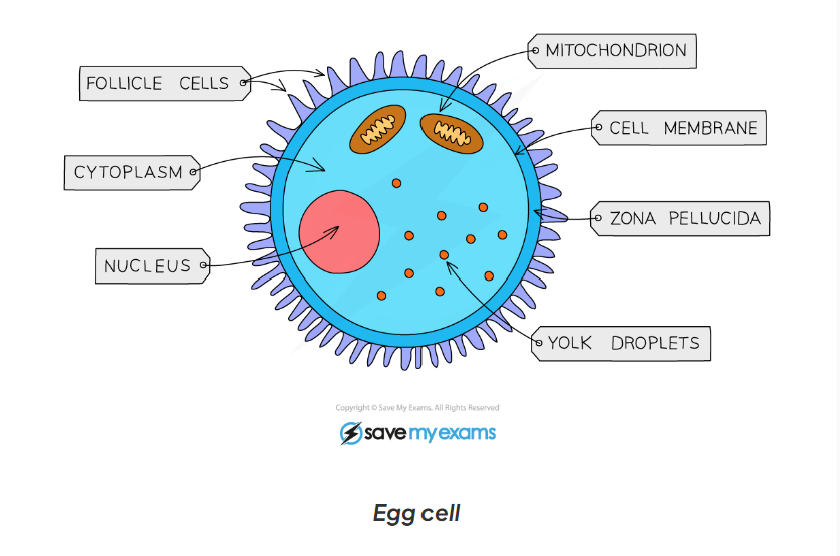
1.2 egg cell adaptations
-contains lots of cytoplasm which has nutrients for the growth of the early embryo
-haploid nucleus contains the genetic material for the fertilisation
-cell membrane changes after fertilisation by a sperm cell so that no more sperm can enter
1.2 what are ciliated epithelial cells
they are highly specialised for their role of wafting bacteria and other particles (trapped by mucus) up to the throat (to be coughed out) or to be swallowed to the stomach (to be digested)
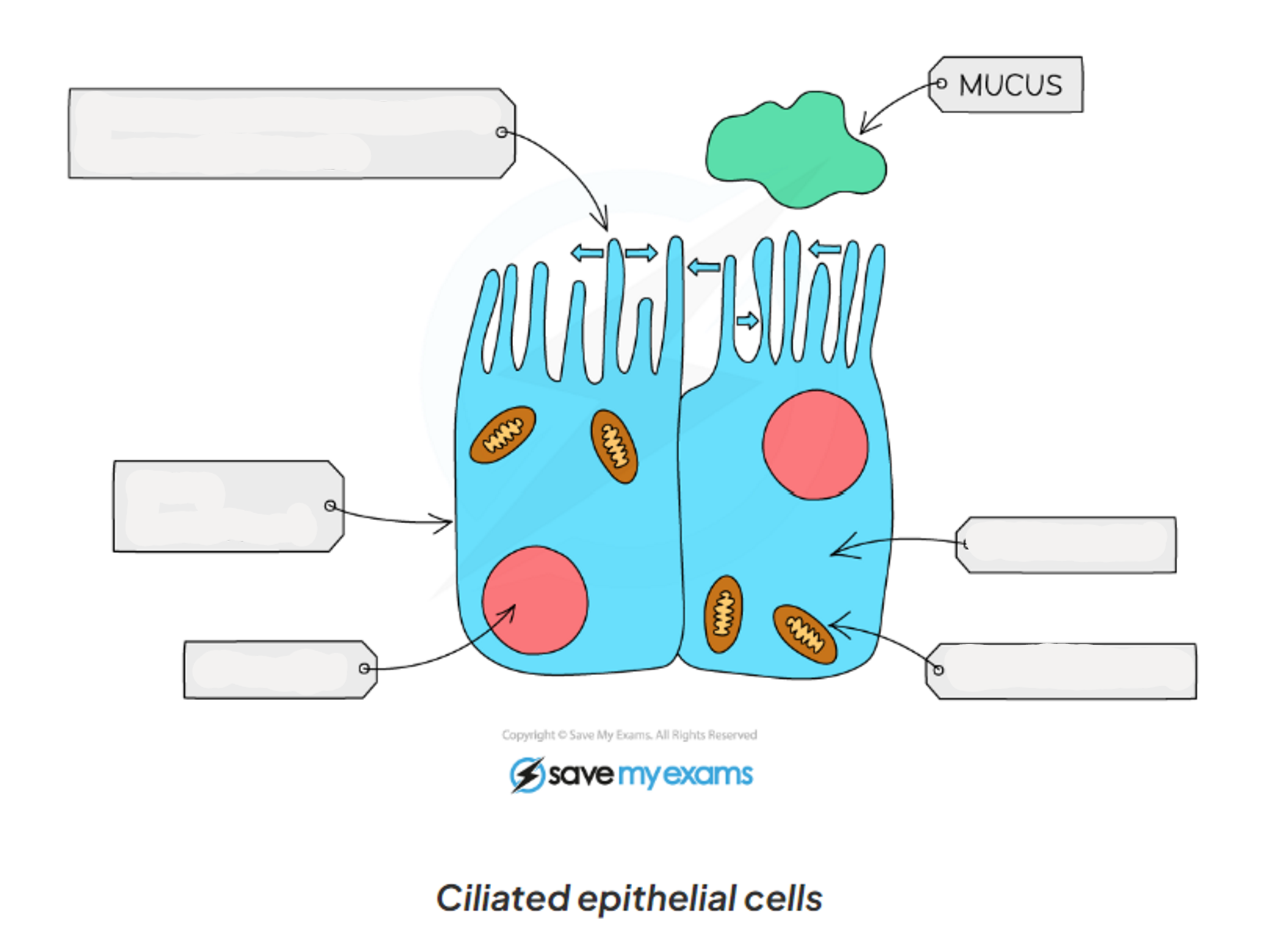
1.2 label this diagram of a ciliated cell
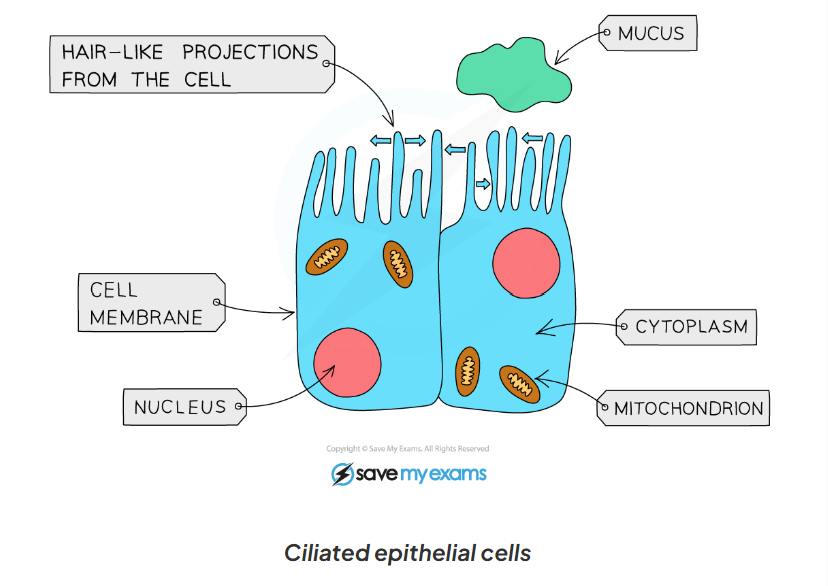
1.2 ciliated cell functions
-extension of the cytoplasm increases the surface area from hair - like structures(cilia)
-have cilia which beat to move mucus and trapped particles up to the throat
1.4 what are the 4 main units used, and what are their relative sizes in standard form?
mµ (picometer 10^-12), nm (nanometre 10^-9), μm (micrometre 10^-6), mm (millimetre 10^-3), m (metre 10^-2)
1.4 how do you convert from nm to μm, and in standard form
divide by 1000
1 μm = 1 × 10-3 mm
1.4 how to convert μm to mm and in standard form
divide by 1000
1 μm = 1 × 103 mm
1.4 convert from mm to m, and in standard form
divide by 1000
1 mm= 1 × 10-3 m
1.4 convert from μm to nm, and in standard form
multiply by 1000
1 μm = 1 × 10-3 nm
1.4 convert from m to μm, and in standard form
multiply by 1000, then multiply by 1000 again
1 m = 1 × 106 μm
1.4 convert from mm to nm, and using standard form
multiply by 1000, then multiply by 1000 again
1mm =1 × 106 nm
1.4 convert from mm to μm, and using standard form
multiply by 1000
1mm = 1 × 103 μm
1.4 convert from nm to m, and using standard form
multiply by 1000, then by 1000, then by 1000
1nm = 1 × 10-6 mm
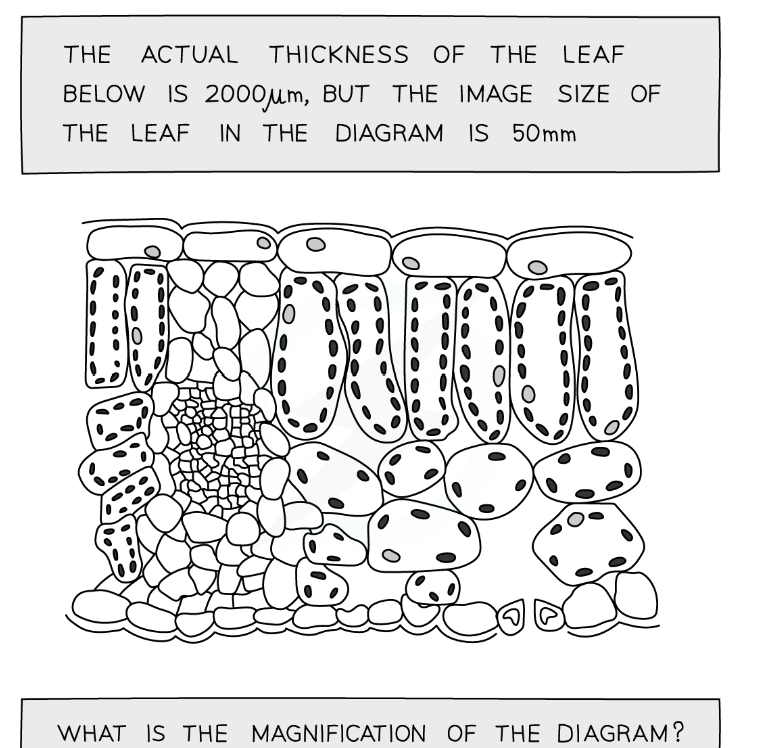
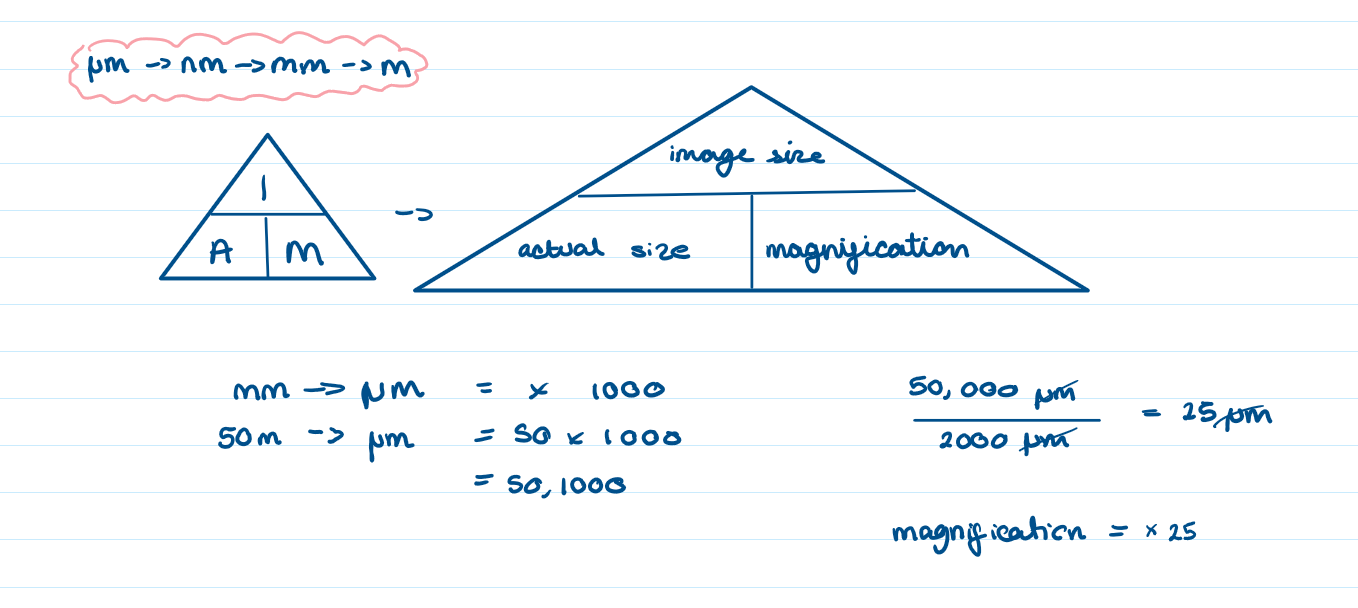
1.4 the actual thickness of the leaf below is 2000μm, but the image size of the leaf in the diagram is 50mm.
What is the magnification of the diagram?
magnification= x25
1.4 what is standard form?
a way of writing very big and very small number using powers of 10
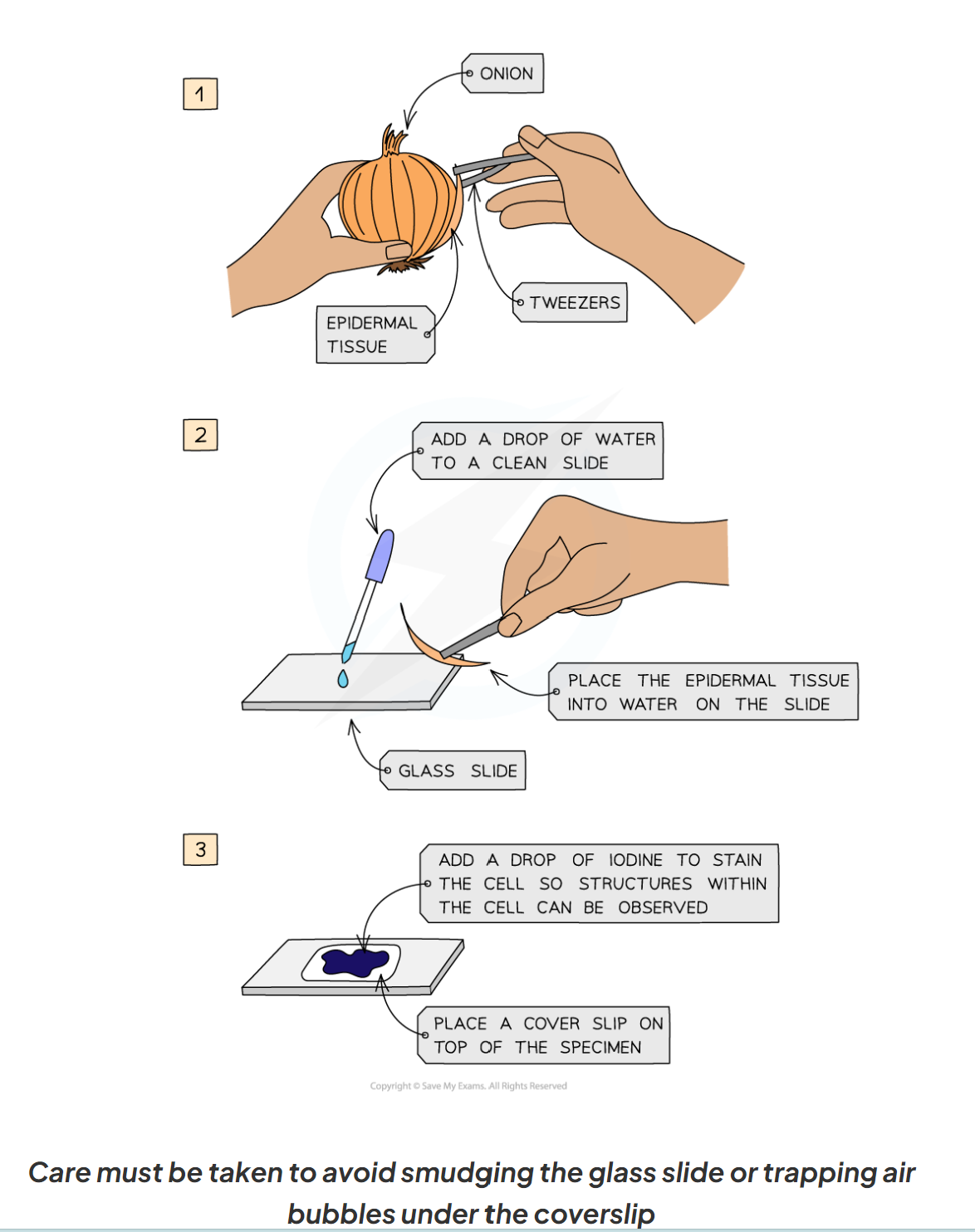
1.6 what are the apparatus needed for the core practical to investigate biological specimens using microscopes. (7 things)
microscope, forceps, scissors, scalpel, coverslip, slide and a pipette
1.6 is the method to investigate biological specimens using microscopes
the specimen must be prepared on a microscopic slide to be observed under a light microscope.
this must be done carefully to avoid damaging the biological specimen and the structures within it
prepare the slide: use a scalpel to cut a tin layer of cells from the onion cell, then place on the slide
gentle place the cover slip on top and carefully press down to remove air bubbles
a stain may be required to make the structures visible
1.6 Why is it important to always use the lowest power objective lens?
-helps to prevent damage to the lens or coverslip in case the stage has been raised too high
-it is easier to find what you are looking for in the field of view
1.6 What is used to measure the size of an object when viewed under a microscope?
a calibrated graticule and a stage micrometre
1.6 results
draw what u see under the microscope
1.6 how do you calculate the size of a single cell?
-clip a ruler or eyepiece graticule on top of the slide
-view the ruler and slide under the x100 objective lens and adjust focus to obtain a clear image
-line the cells along 1mm and count the number of cells that fit across that length
1.6 limitations of this experiment?
-cell structures are 3D and the different tissue samples will have been cut a different planes resulting in inconsistencies when viewed on a 2D slide.
-treatment of specimen when preparing slides could alter the structure of cell