Topic 16- Nervous System Organization
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the primary function of the nervous system?
To sense and react to the environment, improving survival and reproduction.
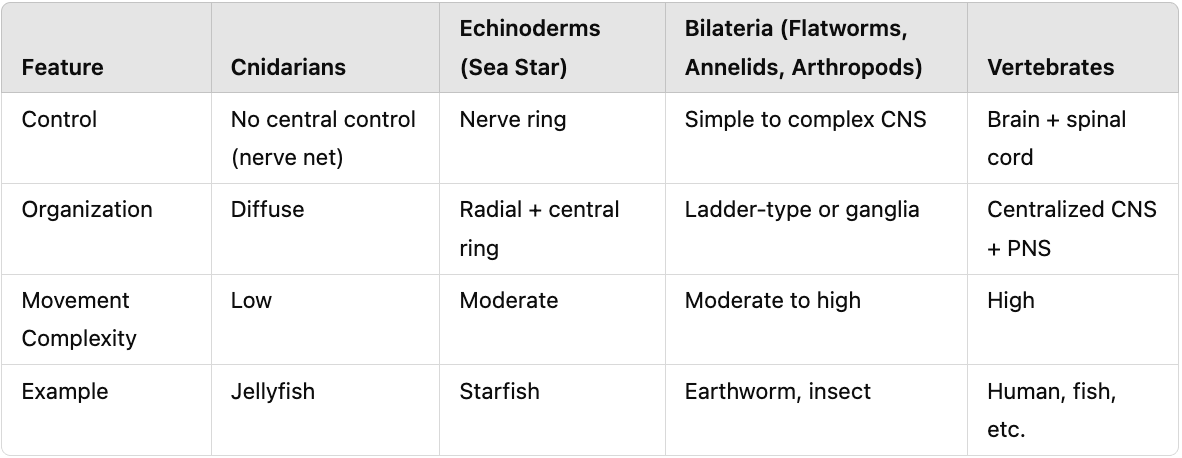
What type of nervous system do cnidarians have?
A nerve net with no central control.
What structure allows central control in sea stars?
A nerve ring that signals muscles.
What is the simplest bilaterian with a central nervous system?
Platyhelminthes (flatworms) with a brain, eyespot, and ladder-type CNS.
How do annelids and arthropods differ in their nervous system from flatworms?
They have more complex brains and ganglia.
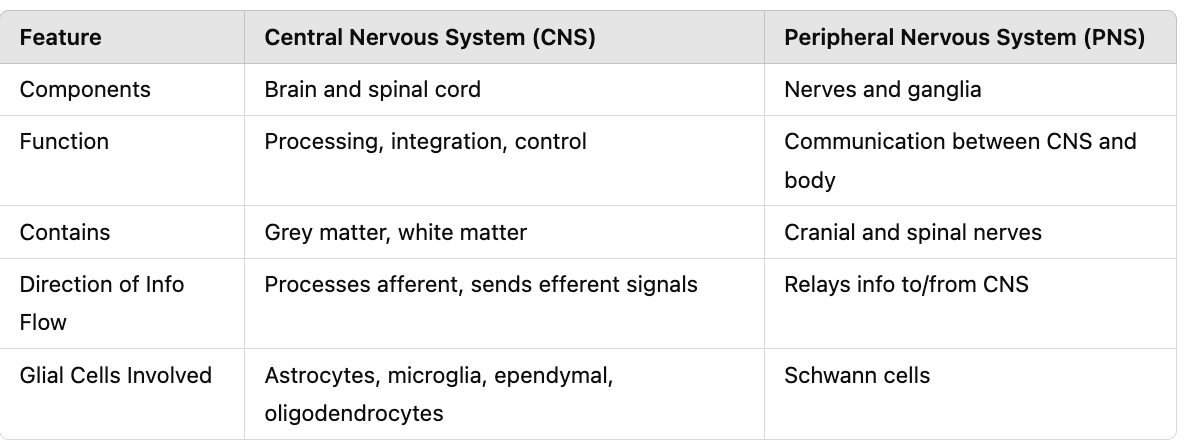
What are the two main parts of the vertebrate nervous system?
CNS (brain and spinal cord) and PNS (nerves and ganglia).
What is the difference in nervous systems between chitons and squids?
Chitons have simple nervous systems (slow), squids have complex systems (fast).
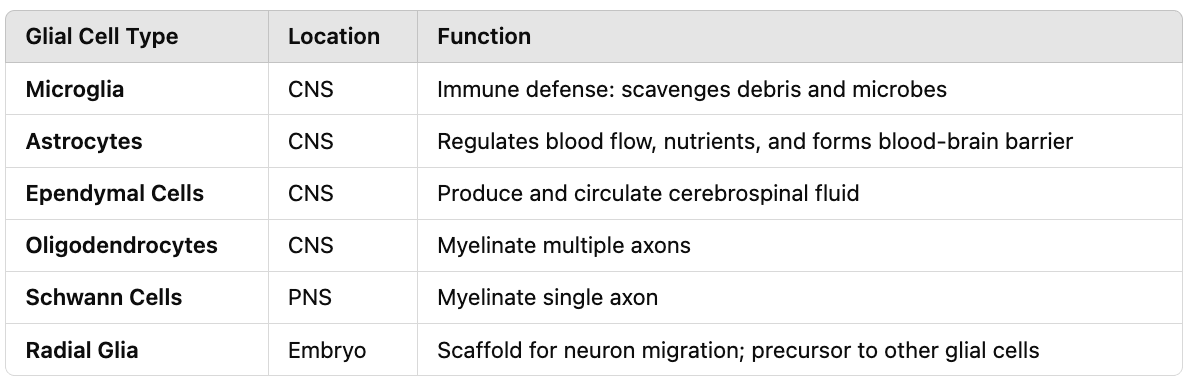
What do microglia do?
Scavenge dead cells and protect the brain from microorganisms.
What is the role of astrocytes?
Regulate blood/nutrient flow to neurons and form the blood-brain barrier.
What do ependymal cells produce and support?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Which glial cell myelinates axons in the CNS?
Oligodendrocytes.
Which glial cell myelinates axons in the PNS?
Schwann cells.
What is the function of myelin?
Insulates axons and prevents signal loss.
What do radial glia do in the embryo?
Form tracks for neuron migration.
What is the main function of the brain in the CNS?
Central control of the body.
What surrounds the ventricles in the brain?
Grey matter surrounds white matter (myelinated axons).
What are the functions of the spinal cord?
Transmits impulses and controls reflexes.
What does the grey matter in the spinal cord surround?
The central canal with cerebrospinal fluid.
What is a reflex action?
A rapid, involuntary response (e.g., knee jerk).
What do sensory receptors do in the PNS?
Detect stimuli and transmit information to and from the CNS.
Where do cranial nerves originate and what do they serve?
Originate in the hindbrain; serve head and upper body.
Where do spinal nerves originate and what do they serve?
Originate in spinal cord; serve the entire body.
What does the afferent division of the PNS do?
Brings sensory input to the CNS.
What are visceral vs. somatic sensory inputs?
Visceral: unconscious (e.g., blood pressure); Somatic: conscious (e.g., vision).
What does the efferent division of the PNS do?
Sends motor signals from the CNS to effectors.
What does the motor system control?
Voluntary and reflex movements via skeletal muscle.
What does the autonomic nervous system control?
Involuntary functions like digestion, heart rate, and gland activity.
What are the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
Enteric (digestive), Parasympathetic ('rest and digest'), Sympathetic ('fight or flight').
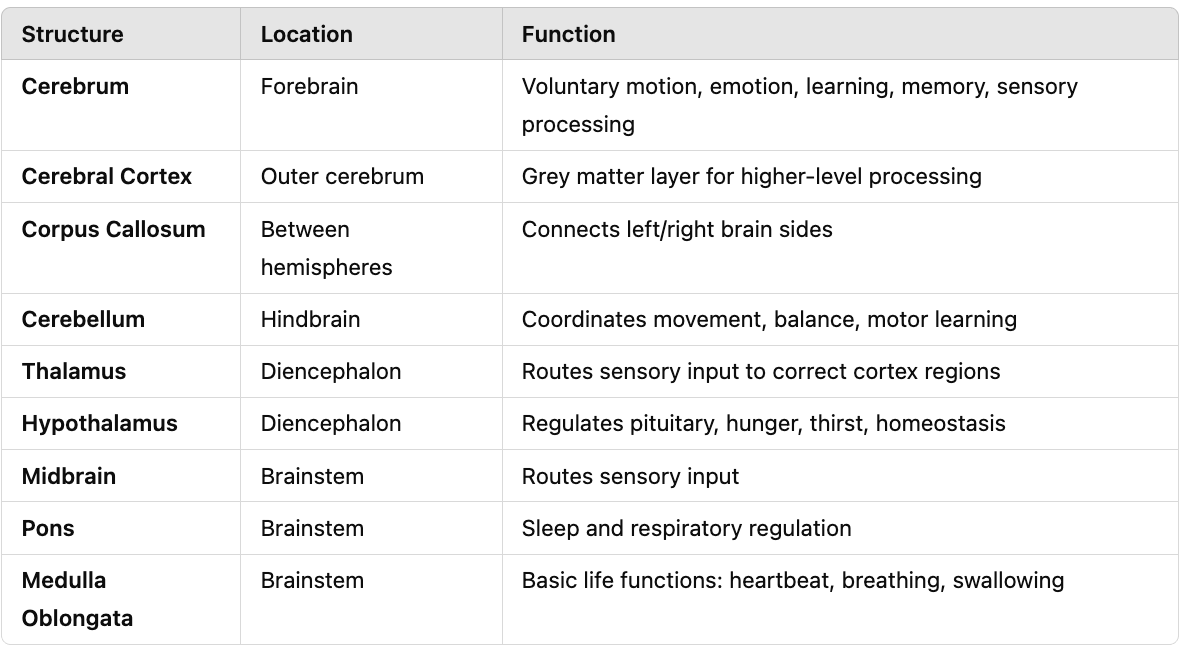
What structure does the vertebrate brain develop from?
The anterior portion of the neural tube.
What are the three primary brain regions in vertebrates?
Forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain.
What connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain?
The corpus callosum.
What is the cerebral cortex responsible for?
Voluntary movement, learning, emotion, memory, sensory processing.
What does the cerebellum control?
Coordination of movement and balance.
What is the role of the thalamus?
Routes sensory input to the correct part of the cerebrum.
What does the hypothalamus regulate?
Pituitary gland, hunger, and thirst.
What are the functions of the brainstem?
Basic life functions like breathing, heart rate, and swallowing.
Which parts make up the brainstem?
Midbrain, pons, and medulla.
Compare and contrast animal nervous systems between cnidarians, echinoderms (sea stars), bilateral (flatworms, annelids, anthropoids), and vertebrates in terms of control, organization, movement complexity, and example.
Compare and contrast the types of glial cells (microglia, astrocytes, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells, and radial glia) in terms of their location and function.
Compare and contrast the central and peripheral nervous systems (CNS vs. PNS) in terms of components, function, direction of information flow, glial cell involvement, and organization.
Sequence the flow of information in a nervous system signaling pathway, starting from stimulus detection and ending in a response, including the roles of afferent neurons, interneurons, and efferent neurons.

Sequence the stages of vertebrate brain development from the neural tube to the differentiation of forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain structures.

Compare and contrast major brain structures (cerebrum, cerebral cortex, corpus callosum, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, pons, medulla) in terms of their location and function.