m4 tuts pcol p4
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Network of glands and organs that produce and release hormones via blood circulation
Growth Hormones
Somatotropin
A peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals.
GH agonists
Examples:
Somatotropin
Somatrem (Somatomedin C, IGF1)
Mecasermin
Somatropin
Achondroplasia
Growth failure due to IGF1 deficiency: Laron syndrome
Achondroplasia
Most common “dwarfism” in children
Mecasermin
Growth failure due to IGF1 deficiency: Laron Syndrome. Tx is ?
GH antagonists
Examples:
Somatostatin - Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH)
Pegvisomant
Octreoride & Lanreotide
Octreotide
Used in:
Gigantism (Acromegaly)
Pancreatic tumor (insulinoma - B cells & glucagonoma - a cells)
Carcinoid tumor
MOA:
It decreases the secretion of hormones
Pegvisomant
Pegylated (increased DOA); Used in acromegaly
HPA axis (Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal axis)
Hypothalamus → secretes CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone)
Anterior pituitary → releases ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) in response to CRH
Adrenal cortex → stimulated by ACTH to produce corticosteroids (mainly cortisol)
Positive feedback - switch on
Negative feedback - switch off
Adrenal Steroids
Mineralocorticoids
Glucocorticoids
Adrenal androgen
Mineralocorticoids
Glomerulosa; salt
Aldosterone - most common
Fludrocortisone ⭐
Glucocorticoids
Fasciculata; sugar
Low potency: Cortisone, Hydrocortisone (cortisol)
Medium potency: Prednisone, Methylprednisolone, Triamcinolone
High potency: Dexamethasone, Betamethasone
Adrenal androgen
Reticularis; sex
DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
Corticosteroids Antagonists
Receptor blockers
Spironolactone
Mifepristone
Synthesis inhibitors
Metyrapone
Ketoconazole, Fluconazole (ANTI-FUNGAL) ⭐
Salt Retaining Property
Highest salt retention: Aldosterone
No salt retention: Dexamethasone, Betamethasone
Aldosterone
Highest salt retention
Conn’s disease
Hyperaldosteronism (↑ Aldosterone)
↑ Na, H2O
↓ K+ = ↑ HCO³- = Metabolic alkalosis
Tx: Spironolactone
SE: Gynecomastia - alt: Eplerenone
Dexamethasone, Betamethasone, Triamcinolone
No salt retention
Betamethasone, Dexamethasone
Hasten fetal lung maturation in premature babies - Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) ⭐
Spironolactone
Drug for Conn’s Disease (hyperaldosteronism)
Cushing Syndrome
Hypercortisolism = ↑ cortisol = ↑ sugar
Drugs for Cushing Syndrome (Hypercortisolism)
1. Endogenous Cushing Syndrome
Due to adrenal adenoma, pituitary tumor
Tx: Surgery (During surgery, stress dose using Hydrocortisone to prevent adrenal crisis)
2. Exogenous Cushing Syndrome
Chronic or prolonged use of steroids causing HPA axis suppression
Management: gradual dose reduction
If inoperable:
(-) steroid synthesis: Ketoconazole, Metyrapone
(-) steroid receptor: Mifepristone (to control hyperglycemia)
Endogenous Cushing Syndrome
Due to adrenal adenoma, pituitary tumor
Tx: Surgery (During surgery, stress dose using Hydrocortisone to prevent adrenal crisis)
Exogenous Cushing Syndrome
Chronic or prolonged use of steroids causing HPA axis suppression
Management: gradual dose reduction (dose tapering)
NO abrupt withdrawal → adrenal crisis
True
Cushing syndrome - If inoperable:
(-) steroid synthesis: Ketoconazole, Metyrapone
(-) steroid receptor: Mifepristone (to control hyperglycemia)
Addison’s Disease (Adrenal insufficiency)
Destruction of adrenal gland (low cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenal androgen)
Mx: HRT - Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hydrocortisone - preferred agent
Addisonian Crisis (Acute adrenal crisis)
Chronic use and suddenly stopped taking their corticosteroids
Low cortisol and androgen, normal aldosterone
Mx: Do not abruptly stop!
Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal (HPG) axis
Hypothalamus → secretes GnRH (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone) in a pulsatile manner
Anterior Pituitary → responds to GnRH by releasing LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone)
Ovary →
FSH → stimulates follicle growth and estrogen production
LH → triggers ovulation and formation of corpus luteum (which produces progesterone and estrogen)
Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal (HPG) axis
Hypothalamus → secretes GnRH (pulsatile)
Anterior Pituitary → releases LH and FSH in response to GnRH
Testis →
LH → stimulates Leydig cells → produce testosterone
FSH → stimulates Sertoli cells → support spermatogenesis and produce inhibin
LH only
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
Detect pregnancy
Detect prostate cancer
Lutropin
FSH only
Follitropin (a/B)
Urofollitropin
LH and FSH
Menotropin
Pulsatile
Physiological GnRH
Pattern → transient, rapid bursts of GnRH (~60–90 min)
Effect on pituitary → stimulates LH and FSH secretion
Outcome → normal reproductive function (ovulation in females, spermatogenesis in males)
Non-Pulsatile
Continuous GnRH
Pattern → sustained, non-transient GnRH release
Effect on pituitary → desensitization → ↓ LH and FSH
Suppression of sex hormones (used in breast cancer, prostate cancer, endometriosis)
GnRH Agonists
suffix: -relin, leuprolide
Pulsatile: treatment of infertility
Nonpulsatile: treatment of prostate cancer, breast cancer, endometriosis
GnRH Antagonists
Binds GnRH receptors on the pituitary → blocks GnRH action
Effect on pituitary → rapid suppression of LH and FSH
Outcome → ↓ gonadal sex hormones (testosterone in males, estrogen/progesterone in females)
GnRH Antagonists
suffix: -relix
Treatment of precocious puberty, endometriosis
Treatment of:
Women: Breast cancer
Men: Prostate cancer
Estrogens and Progestins
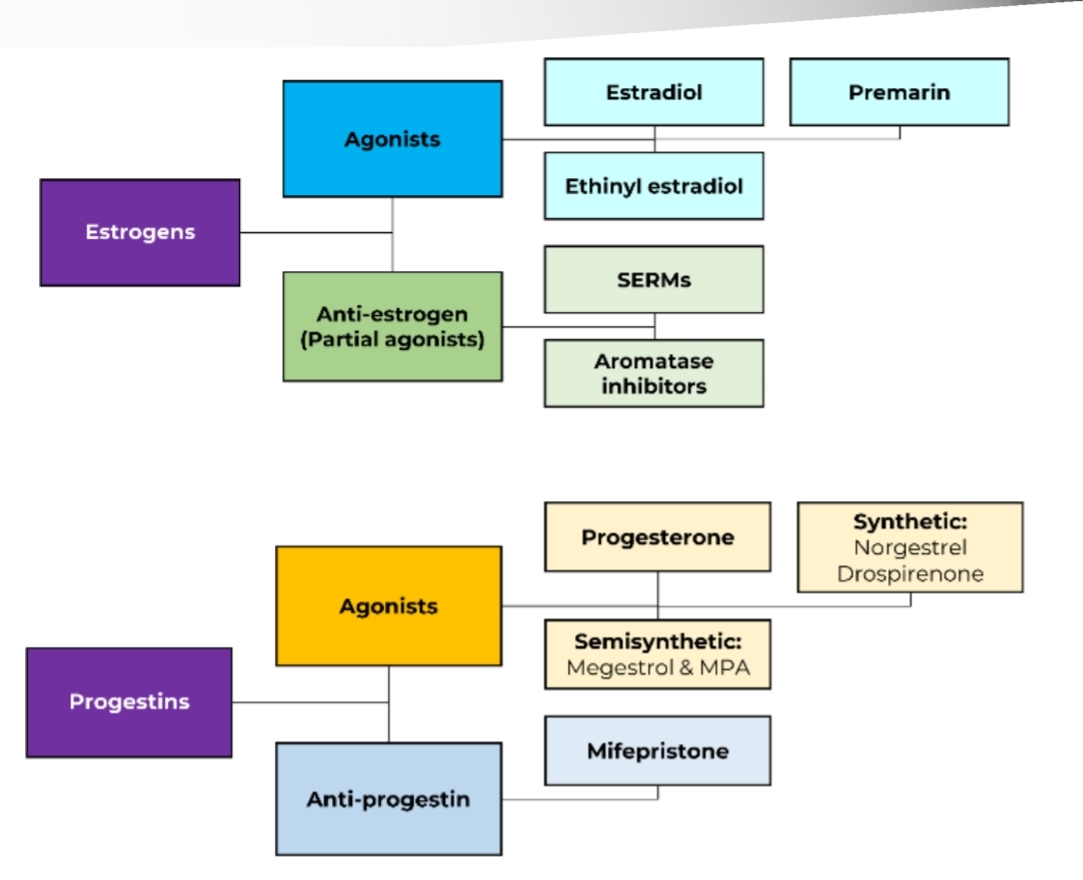
Estradiol
Most potent; pre menopausal estrogen
Estriol
Pregnancy estrogen
Estrone
Postmenopausal estrogen
Premarin
Pregnant mare’s urine
True
Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs): Work by stopping estrogen from being produced in the first place by inhibiting the aromatase enzyme.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Work by blocking the estrogen receptor on cancer cells, preventing estrogen from binding and stimulating growth.
Estrogens
Major natural estrogen: Estradiol
Rationale for synthetics:
Increase oral bioavailability, half-life, and feedback inhibition of FSH and LH
Estrogens
Estrogen increases cancer risk
Endometrial cancer (unless progestins are added)
Risk factor: Endometrial hyperplasia
Prevention: Estrogen + Progestin
Diethylstilbestrol (DES) during breastfeeding → vaginal cancer
Endometriosis
Growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus (e.g., ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic cavity)
Pathophysiology →
Ectopic endometrial tissue responds to hormonal cycles → proliferates and bleeds
Causes inflammation, scarring, and adhesions
First-line drugs for endometriosis
Combined OCPs (+ NSAID)
Progestins (Medroxyprogesterone acetate - Depo-provera®) ⭐
Others: Danazol, GnRH agonists (-relin), GnRH antagonists (-relix)
Anti-estrogens (SERMs)
Clomiphene ⭐
Treatment of anovulatory infertility
A/E: multiple births
Tamoxifen
Treatment of breast cancer in premenopausal women
A/E: Endometrial hyperplasia
If resistant to tamoxifen: Fulvestrant
Raloxifene
Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
Clomiphene
Treatment of anovulatory infertility
Female infertility where a woman doesn't release an egg from her ovary during a menstrual cycle, which prevents pregnancy
A/E: multiple births
Tamoxifen
Treatment of breast cancer in premenopausal women
A/E: Endometrial hyperplasia
If resistant to tamoxifen: Fulvestrant (full antagonist)
Partial agonist
Raloxifene
Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
Aromatase inhibitors
Anastrozole
Letrozole
Exemestane
Treatment of:
Anovulatory infertility
Breast cancer in postmenopausal women
Androgens
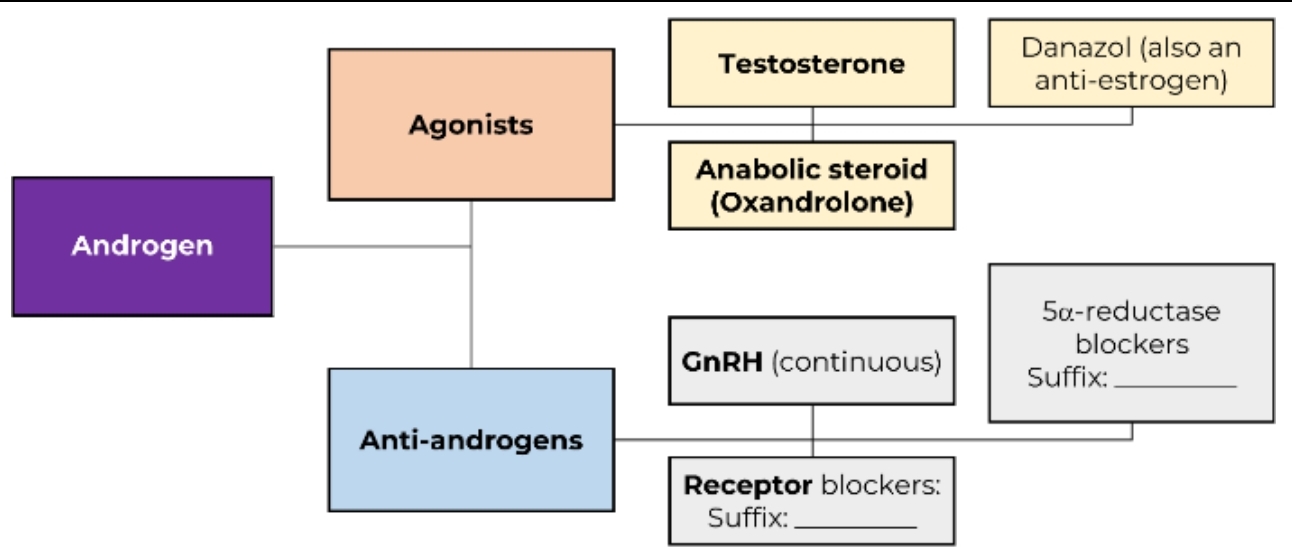
Androgens
Major androgen: Testosterone
Anabolic steroids: Oxandrolone, Fluoxymesterone
Anti-androgens
GnRH analogs
Administered in continuous or non-pulsatile fashion
Use: Inoperable prostate cancer
Androgen Receptor Blockers
Suffix: -tamide
Flutamide, Bicalutamide
Combined with GnRH analogs for prostate cancer
5α-reductase blockers
Suffix: -asteride
Reduce prostate volume and can retard progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
GnRH analogs
Administered in continuous or non-pulsatile fashion
Use: Inoperable prostate cancer
Androgen Receptor Blockers
Suffix: -lutamide
Flutamide, Bicalutamide
Combined with GnRH analogs for prostate cancer
5α-reductase blockers
Suffix: -steride
The enzyme 5α-reductase converts testosterone into DHT.
DHT is a potent male sex hormone linked to prostate growth and hair loss.
By blocking this enzyme = reduced DHT levels in the body.
Finasteride, Dutasteride
Reduce prostate volume and can retard progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Decreased chances of male pattern baldness
Finasteride + Tamsulosin
Finasteride works by reducing the size of the prostate, which relieves pressure on the urethra (the tube that empties the bladder).
Tamsulosin works by relaxing muscles in the prostate and bladder, improving urine flow.
Thyroid Hormones
Hypothalamus → secretes TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone)
Anterior Pituitary → responds to TRH by releasing TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone)
Thyroid Gland → stimulated by TSH to produce:
T4 (Thyroxine) → mostly a prohormone
T3 (Triiodothyronine) → active form, converted from T4 in peripheral tissues
Thyroid Hormones
Positive Feedback:
TSH stimulates thyroid gland → Enhances production of T3 and T4. This is a feed-forward stimulation (as long as the body needs thyroid hormones).
Negative Feedback:
High levels of T3 and T4: Inhibit TRH release from hypothalamus Inhibit TSH release from pituitary → Prevents overproduction of thyroid hormones.
Hypothyroidism
Most common: Hashimoto’s disease, thyroiditis
Others: Cretinism, Myxedema
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism → Low T4, Low T3; High TSH
Primary hypothyroidism
Most common
Cause → Underactive thyroid gland
Secondary hypothyroidism
Cause → Thyroid hormone deficiency from pituitary gland dysfunction
Tertiary hypothyroidism
Cause → Thyroid hormone deficiency from hypothalamic disorder
Cretinism
Congenital hypothyroidism / Infantile hypothyroidism
Myxedema
Adults with long-standing untreated hypothyroidism
Severe form → Medical emergency
Hypothyroidism
DOC: Levothyroxine (L-thyroxine)
Liothyronine (or T3)
L-thyroxine (or T4)
Hyperthyroidism
Most common: Grave's disease
Others: Plummer's disease, thyrotoxicosis, thyroid storm
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism → ↑ T4, ↑ T3; Low TSH
Primary hyperthyroidism
Most common
Cause → Overactive thyroid gland
Secondary hyperthyroidism
Cause → Overproduction of TSH
Tertiary hyperthyroidism
Cause → Overproduction of TRH
Grave's Disease
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism
Plummer's Disease
Toxic multinodular goiter
Thyroid Storm
Rare but life-threatening complication of untreated hyperthyroidism
Thyrotoxicosis
Elevated levels of thyroid hormone in the body, regardless of cause
Hyperthyroidism
DOC: Methimazole (preferred)
S/E: Aplsia cutis - CI to pregnancy in first trimester
If pregnant: Propylthiouracil (PTU) (lower risk of birth defects)
A/E: Liver damage, agranulocytosis (PTU is 2x riskier)
Symptom controller: Beta-blockers (propranolol)
Hyperthyroidism
Thiamides - methimazole, carbimazole, and propylthiouracil
Iodides - radioactive I-131
Beta blockers (propranolol)
Prolactin
Milk production
Prolactin-inhibiting hormone: Dopamine
Hyperprolactinemia
Causes: Infertility
Acromegaly: ↑ GH, ↑ Prolactin
Treatment: + Octreotide
Bromocriptine - dopamine R agonist
Cabergoline - dopamine R agonist
Dopamine
Prolactin-inhibiting hormone
Hyperprolactinemia
Causes: Infertility
Acromegaly
Treatment: + Octreotide
Bromocriptine - dopamine R agonist
Cabergoline - dopamine R agonist
Vasopressin
AKA Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
V1 = Blood vessels = Vasoconstriction
V2 = Kidneys = Anti-diuresis
Vasopressin Agonist
Indication:
Central Diabetes Insipidus = ↓ ADH (polyuria - increased urination)
Nonselective (V1, V2):
Vasopressin
Selective:
Desmopressin - selective in D2 (DOC FOR Central Diabetes Insipidus) - synthetic ADH/Vasopressin
Desmopressin
Selective in D2 ⭐
DOC FOR Central Diabetes Insipidus
Synthetic ADH/Vasopressin
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Kidneys unresponsive to ADH → polyuria, polydipsia
Treatment:
Amiloride (K-sparing)
Blocks lithium entry in collecting ducts
Reduces polyuria
Thiazides (HCTZ)
Paradoxical effect: normally a diuretic but reduces urine output
Mechanism:
Causes mild extracellular volume depletion
↑ Proximal tubule water reabsorption
Less water reaches collecting duct → ↓ urine volume
Vasopressin Antagonist
Indication:
↑ ADH, SIADH (Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone)
Fluid retention, Hyponatremia
Nonselective (V1, V2):
Conivaptan
Selective V2:
Tolvaptan (preferred)
Additional info: Demeclocycline is also used for SIADH
Desmopressin
Used in:
Hemophilia A
↓ Clotting Factor VIII → impaired coagulation → prolonged bleeding
X-linked recessive
Related to vWF → CF VIII normally stabilized by vWF
Von Willebrand Disease
↓ von Willebrand Factor → impaired platelet adhesion and ↓ CF VIII
Symptoms → Mucocutaneous bleeding
Overlaps with Hemophilia A → low CF VIII contributes to bleeding
Nocturnal Enuresis
In children with bleeding disorders (Hemophilia A or vWD) → urinary tract bleeding may worsen enuresis
Definition → involuntary urination at night (≥5 years old)
Oxytocin
Milk ejection
Oxytocin agonist
For labor
Synthetic oxytocin (Pitocin®)
Oxytocin Antagonist
Labor suppressant (for premature labor)
-siban (atosiban)
Diabetes Mellitus
Group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels.
DM Type 1
Cause: No insulin due to pancreatic β-cell destruction
Also known as: IDDM (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus)
DOC (treatment) → Insulin
DM Type 2
Cause: Not enough insulin or insulin does not work properly
Also known as: NIDDM (Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus)
1st-line treatment: Metformin and oral hypoglycemic drugs
Insulin → Used as adjunct if needed
Gestational DM
Cause: Affects pregnant women, usually disappears after delivery
DOC (treatment) → Insulin (the only FDA approved for pregnancy)
Insulin
Insulin stimulates glycogenesis (synthesizing glycogen from glucose for storage)
Mechanism:
↑ Glucose uptake into liver and muscle
Activates glycogen synthase → converts glucose-1-phosphate to glycogen
Inhibits glycogenolysis (breaking down stored glycogen into glucose)
Key effect
Stores excess glucose as glycogen → lowers blood glucose levels
Insulin
Storage
Promotes glycogen storage in liver and muscle (glycogenesis)
Uptake
Increases glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue via GLUT4 transporters
Utilization
Stimulates glycolysis → glucose converted to pyruvate → ATP production
Energy
Enhances fatty acid and protein synthesis
Key effect
Lowers blood glucose by facilitating cellular glucose utilization (glycolysis) and storage (glycogenesis)
Diabetes Mellitus
Hyperglycemia (High blood sugar)
↓ Insulin (Type 1) or ↓ insulin effectiveness (Type 2) → impaired glycogenesis → less glucose stored as glycogen
↓ Glucose uptake → impaired glycolysis → cells have less energy
More glucose in the blood
Clinical effects
Polyphagia → increased hunger because cells are energy-deprived
Polyuria → excess glucose filtered by kidneys → osmotic diuresis
Polydipsia → excessive thirst due to fluid loss from polyuria
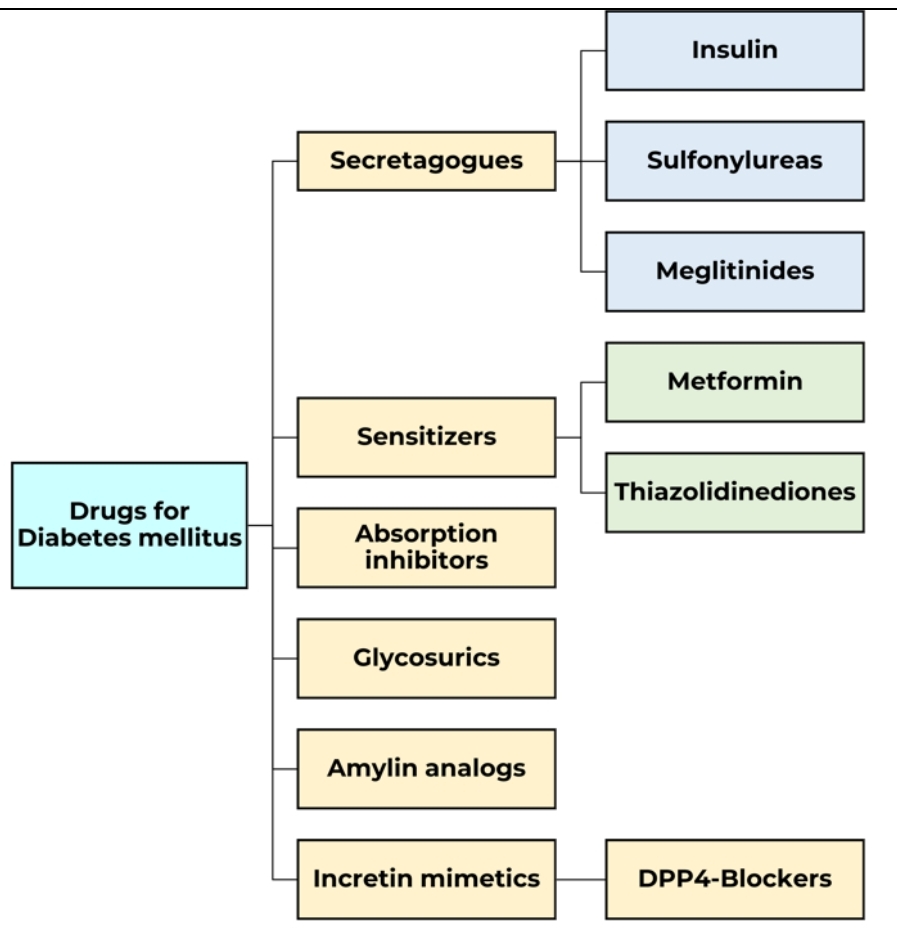
Secretagogues, Sensitizers
Problem: Absent or insufficient insulin
Solution: ?
True
Problem: High blood glucose
Solution:
Decrease glucose absorption
Decrease glucose reabsorption
Decrease cravings (carbohydrates)
Secretagogues
Augment insulin secretion = ↑ storage and uptake & utilization of glucose
S/E: hypoglycemia, weight gain (because of enhanced glycogenesis)
Insulin, Sulfonylureas (g drugs)
Insulin
Types:
Ultra-rapid: Afrezza®
Rapid: Glulisine, Aspart, Lispro
Short: Regular, Semilente
Intermediate: NPH or Isophane, Lente
Long: Ultralente, Glargine, Detemir
Ultra-long: Degludec, Icodec
Insulin
Most common route: Subcutaneous ⭐
Use: DM type 1 & Gestational (DOC), DM Type 2 (Adjunct)
Hexamer
Storage form of insulin
Monomer
Active form of insulin
Glargine
Peakless insulin
Regular Insulin
The only IV route insulin
Preferred agent for Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Lente (Intermediate)
Insulin Zinc Suspension
Amorphous Insulin Zinc Suspension
Type: Short-acting
Also called: Semi-lente
Onset/Action:
Faster absorption
Controls postprandial blood glucose
Crystalline Insulin Zinc Suspension
Type: Long-acting
Also called: Ultralente
Onset/Action:
Slow, extended absorption
Provides basal insulin control over 24 hours
Sulfonylureas
MOA
Close ATP-sensitive K⁺ channels on pancreatic β-cells
Membrane depolarization → triggers opening of voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels
↑ Intracellular Ca²⁺ → stimulates insulin secretion
1st gen: -amides
Chlorpropamide, Tolbutamide, Acetohexamide
No selectivity
2nd gen: Gly, Gli
Glibenclamide (Glyburide) Glimepiride, Glipizide, Gliclazide