Its all about those drugs
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Start with this
Pls don't bully me if I misspell some things, goodluck

What are commonly used inhalation anesthetics?
1. Isoflurane
2. Sevoflurane
3. Desflurane
Less commonly used inhalant anesthetics:
1. Methoxyflurane
2. Nitrous oxide
3. Halothane
New: xenon
Considerations of selecting an inhalation agent:
❀ metabolic
❀ Anesthetic potency
❀ Rate of induction, recovery, and rate of recovery
❀ Cardioplumonary consideration
❀ moniiiiii $$$
Major elimination route of inhalation anesthetics are done through the _________
respiratory tract
Isoflurane %
❀ 0.17%
(metabolized by the liver and kidneys)
Sevoflurane %
❀ 3.0%
(metabolized in the liver and kidneys
Why do we not use nitrous oxide?
❀ not spare other inhalant much
❀ requires higher fresh gas (02) flow
❀ Diffusion hypoxia
What does MAC stand fo foolll?
Minimum alveolar concentration
What does MAC mean?
The concentration of a vapor in the alveoli of the lungs that is needed to prevent movement (motor response) in 50% of subjects in response to surgical (pain) stimulus
Clinically surgical plane of anesthesia is __________ times of MAC
1.5-2
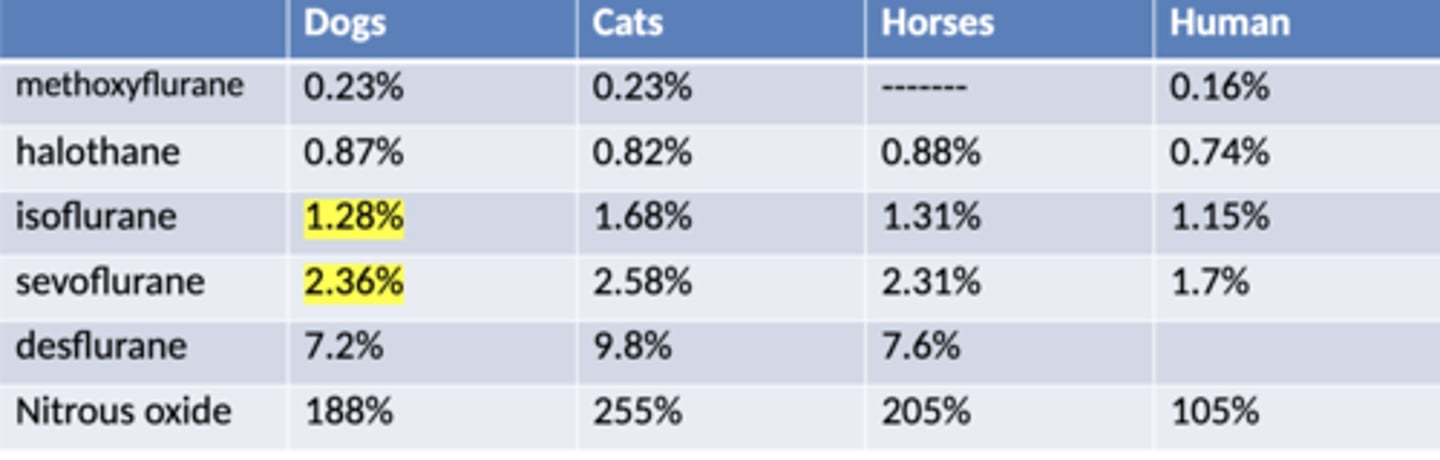
Anesthetic Potency %'s
Isoflurane:
Dog- 1.28%
Cats- 1.68%
Sevoflurane
Dog- 2.36%
Cats- 2.58
The ________ the MAC, the _________ potent the anesthetic agent
less, MORE
True or false: Isoflurane is less potent than sevoflurane
false, Sevoflurane is less potent requiring higher % meaning more $$$
As anesthetic dose increases, mean arterial pressure is _______
decreased= most potent vasodilator
Decreasing MAC factors
❀ Hypotension (ex) hemorrhage intra-op
❀ Hypothermia
❀ Metabolic acidosis
❀ Extreme hypoxia (PaO2 <38 mmHg)
❀ Age
❀ Premedication (opioids, sedatives, tranquilizers)
❀ Pregnancy
Increasing MAC factors:
All your hypers!
❀Hyperthermia
❀Hyperthyroidsm
(increased release of thyroid hormones)
❀Hypernatremia
(sodium concentration is too high)
❀ Drugs increase CNS catecholamines (the good stuff aka cocaine, tricyclic antidepressants)
NOT increasing MAC factors
❀ type of stimulation
❀ duration of anesthesia
❀ species
❀ sex
❀ PaCO2 or PaO2
The higher the blood/gas solubility, the _____ the induction and recovery rates
slower
Rate of induction, Rate of change in anesthetic depth and Rate of recovery CHART
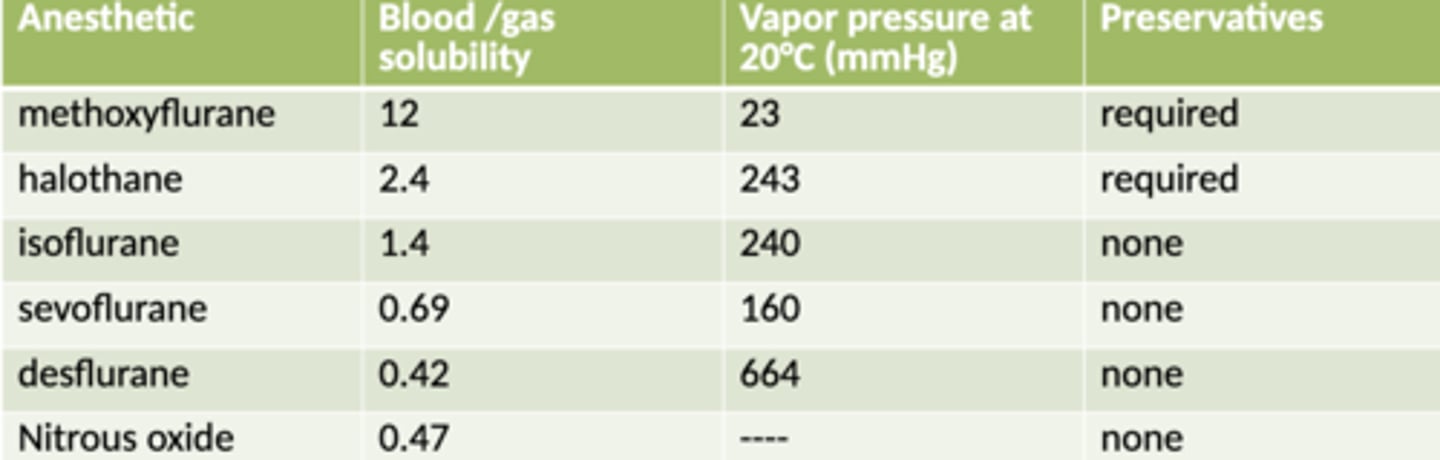
During anethesia, which inhalant can be changed faster when it comes to depth of anesthesia
sevoflurane
Whats one disadvantage of using inhalant anesthetics?
Patients hold breaths due to the pungent smell
Debilitating patients require reduced or increased inhalant anesthetic %?
reduced
Nasotracheal intubation is suitable for?
foals and calves calves are more difficult to be nasotracheal intubated
Lets talk money, whats the ranking of which ones more expensive
Most expensive: desflurane
to...
sevoflurane -> isoflurane -> halothane (least expensive)
Anesthesia maintenance
❀Methoxyflurane: 0.5 - 1.5%
❀ Isoflurane: 1 - 2.5%
❀ Sevoflurane: 2.5 - 4.0%
What can recovering from an inhalant cause?
Dysphoria
(how i feel everyday)

Once you turned off the inhalant vaporizer, keep the patient....
on oxygen for at least 5 mins
General anesthesia process:
1. pre-medications
2. Induction (injectable anesthetics)
3. Maintenance (inhalant/ injectable anesthetics)
Why do we give premeds?
to decrease stress/anxiety
What should you remember when patient is under sedation?
☆ NEVER EEEVAAAAAAA trust a sedated animal
☆ Support spine/muscle
(use transport table)
Why use chemical restraint?
To provide proper restraint and to decrease the chance from getting injury for both your patient and yourself
Pre-emptive analgesia
☆ before pain occurs, control and treat pain
☆ recovery from surgery is faster
☆ control pain, decrease other drug dosage
What are the pre-medication drugs?
1. Phenothiazine (major tranquilizers)
2. Benzodiazepines (minor tranquilizers)
3. Alpha 2 agonists
4. Opioids
5. Anticholinergics
Phenothiazines
Acepromazine
Butyrophenones
☆ droperidol (innovar-vet)
☆ azaperone (Stresnil)
Mechanism of action of major tranquilizers
☆ dopamine antagonists
☆ high doses have negative effects: tremor, rigidity, catalepsy
Acepromazine: concentration
Phenothiazine
(10 mg/ml)
Note: bottle dose is 10 times the recommended dose!
Acepromazine: dosage
Dog: 0.01-0.05 mg/kg
Cat: 0.02-0.1 mg/kg
Horse: 0.005-0.02 mg/kg
3 multiple choice options
Acepromazine: injection sites
Dog and Cat: IM, SQ, IV
Horse: IV, IM
Acepromazine: clinical uses
☆ decrease anxiety
☆ NO ANALGESIA
☆ Dose dependent: use at low doses
☆ chaaa epppp
Acepromazine- 3 "anti-"
☆ antiarrythmogenic
☆ antiemetic
☆ antihistamine
Acepromazine: cardiovascular effects
☆ HYPOTENSION
(due to alpha 1- adrenergic blockade)
Acepromazine: other effects
☆ minimal respiratory effects
☆ mild H-1 antihistaminic properties
☆ extrapyramidal signs at a high dose (rigidity, tremors, catalepsy)
Controversial: lower seizure threshold
Why don't we use phenothiazine in breading stallion?
Can cause penile prolapse (ouch!)
Acepromazine: duration
NOT REVERSIBLE
☆ last for several hours (long acting)
Acepromazine: method of elimination
☆ hepatic metabolism
(effects may be prolonged with hepatic disease/ neonate/ geriatric patients
Butyrophenones:
☆ droperidol (similar to phenothiazine)
☆ azaperone (use in swine primary) This can be used with other drugs like butorphanol, azaperone, and medetomidine
Benzodiazepines:
- diazepam
- midazolam
- zolazepam
- flumazenil
Which one is an antagonist?
flumazenil
3 multiple choice options
Benzodiazepines: mechanism of action
agonists at benzodiazepine receptor sites in the CNS; these receptors potentiate the effects of GABA (an inhibitory neurotransmitter) in the CNS
Benzodiazepines: Clinical uses:
☆ mild sedation effects (not dependable)
☆ central muscle relaxant properties
☆ useful sedatives in debilitated animals or neonates
☆ good sedative in camelids, small rumiants
☆potent anticonvulsants (prevents seizures)
Benzodiazepines: Cardiopulmonary effects
NONE!
☆ maybe some mild hypotension and respiratory depression
☆ if given a bolus, may see apnea
Benzodiazepines: adverse effects
☆ may see excitement/agression when given alone
☆usually only used if patient is pediatric/ geriatric or debilitated
do NAWT give ________ Benzodiazepines!!!!
cats

Which is water soluble
midazolam
2 multiple choice options
Which IS irritating to the tissue:
diazepam
2 multiple choice options
Diazepam site
IV or rectally
Midazolam site
IM or SQ
Benzodiazepines: duration
In general: relatively short!
Up to an hour: diazepam/midazolam
D: antiseizure effects may be shorter, duration effects may be greatly prolonged in geriatrics
M: little change with geriatric
Species dependent:
zolazepam
Benzodiazepines: dosage
Diazepam and: 0.2-0.4 mg/kg
What is benzodiazepine reversible with?
flumazenil
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists
Main ones:
-dexmedetomidine (Dexdomitor)
-xylazine (Rompun)
-detomidine (Dormosedan)
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: reversals
-yohimbine (yo... he fine) (yobine)
-tolazoline (priscoline)
-atipamezole (antisedan)
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: mechanism of action
☆ agonist activity at alpha-2 adrenergic receptors
☆ results in decrease in release of norepinephrine from adrenergic nerve terminals in CNS and periphery
☆ cases sedation, decreased sympathetic activity, analgesia
Why use alpfhufuej (cat stepped on keyboard) alpha- 2 adrenergic
☆ great sedation
☆ excellent analgesia
☆ muscle relaxation
REVERSIBLE
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: cardiopulmonary effects
☆ SEVERE bradyarrythmias (slow heart rate)
-do NAWT treat w atropine-
☆ negative inotropic effect: decrease cardio output
☆ Biphasic effect on blood pressure
☆ mild respiratory depression alone
☆ stridor & dyspnea in horses + brachycephalic dawgz
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: other effects
☆RUMINANTS ARE EXTREMELY SENSITIVE
-least sensitive is swine)
☆ decrease GI activity
☆ cause vomiting in cats and dogs
☆abortion in cattle
☆increased urination
☆sweating
☆hyperglycemia
☆horses may kick
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: duration of action
ALL DOSE DEPENDENT
Xylazine: up 30 mins
Detomidine: up to 2 hrs
Dexmedetomidine: up to 1 hr
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: xylazine
Dogs/cats: 0.1-0.5mg/kg IM, SQ, IV
Horse: 1.0 mg/kg, IV or IM
Ruminants: 0.44- 0.1 mg/kg IV or IM
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: detomidine
ONLY FOR HORSES
0.01-0.02 mg/kg IV
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: dexmedetomidine
3-30 mcg/kg IV, IM
Alpha-2 Adrenergic Agonists: reversals dosage
☆yohimbine: (0.1 - 0.15 mg/kg, IM)•
☆tolazoline: (1 - 1.5 mg/kg, IM) - do not use in llama andalpaca
☆atipamezole: (0.1 mg/kg, IM or IV) - usually give same volume of dexmedetomidine
What is Zenalpha?
☆ Medetomidine + Vatinoxan
☆ vatinoxam works in the periphery
☆ medetomidine: sedation and analgesia
☆Improved cardiac output
☆ONLY FOR DAWGGGSS IM
☆less bradycardia and not induced vasocontriction compared to dexmedetomidine
Name me some opioids or else
☆ morphine
☆ hydromorphone
☆ fentanyl
☆ methadone
☆ meperidine
☆ buprenorphine
☆ butrophanol
☆ nalbuphine
☆ naloxone
Full agonist opioids
☆ morphine
☆ hydromorphone
☆ fentanyl
☆ methadone
☆ oxymorphone
☆ meperidine
(produces good sedation and analgesia- treats moderate to severe pain)
Partial mu agonist
buprenorphine
(produces good analgesia but NOT good sedation- treats mild to moderate pain)
Agonist (kappa) & Antagonist (mu)
☆ butorphanol
☆ nalbuphine
(NOT good analgesia but good sedation- treats mild pain)
Its used for partial reversal of full agonist opioid
Full antagonists
☆ naloxone
☆ naltrexone
(reverses sedation and analgesia completely)
Opioids: Clinical uses
☆ sedation
☆ analgesia
Opioids: cardiopulmonary effects
☆ bradyarrhythmia (easy to correct with anticholinergics)
☆ respiratory depression (decrease tidal volume and increase panting)
☆minimal effect on blood pressure
☆Histamine release for morphine, meperidine --> vasodilation hypotension
Opioids: other effects
☆ 3P: poop, pee, puke
☆ #addictive
Hydromorphone dosage
2mg/ml
Dose: 0.05 ~ 0.2 mg/kg, IM, SQ or IV
(usually 0.1 mg/kg as premed)
Hydromorphone duration
Long acting: 2-4 hours (dose dependent)
Hydromorphone why do we use
☆ produces good sedation and analgesia
☆ treats moderate to severe pain
☆ less likely to cause histamine release
☆Bradyarrhythmia
Morphine: dosage
15 mg/ml or 1 mg/ml
☆ 0.5-1 mg/kg IM or SQ
☆ 0.1 mg/kg (epidural)
Morphine: duration
2-4 hours
Morphine: why do we use
☆ treats moderate to severe pain
☆ sedation and analgesia
☆ cheap
☆ Histamine release- give IV injection (CRI)!!!!
Cat: morphine mania
Fentanyl dosage
50 mcg/ml
wtf idek what to say
☆2-5 mcg/kg IV bolus
☆5-50 mcg/kg/hr IV CRI
☆ 2-5 mcg/kg/hr IV CRI
Fentanyl duration
Short: 10-15 mins use CRI
Fentanyl why do we use
☆ produces good sedation/ analgesia
☆ treat moderate to severe pain
Fentanyl dermal patch
☆good for home pain control
☆not great choice for anesthesia protocol
☆Long duration: 72 hours
Over dosage... sedation & bradyarrythmias
Methadone dosage
10 mg/ml dawgs and kats
☆ full agonist opioid
0.1-0.2 mg/kg SQ,IM, IV
Methadone duration
2~4 hours (redoes 2 hrs)
Methadone why we use
☆ good sedation/ analgesia
☆ treat moderate to severe pain
Buprenorphine dosage
0.3 mg/ml kats
0.005- 0.04 mg/kg
IV,IM, SQ, transmucosally
Buprenorphine duration
6-8 hours, onset can be slow (~30 mins)
Buprenorphine why we use
☆ mild sedation/ moderate analgesia
SIMBAadol
1.8 mg/ml
lol get it. SIMBA cus like cats... yeah ok
Duration: 24 hrs
Dosage: 0.24 mg/kg SQ
Causes: hypotention, hyper/hypothermia, tachycardia
Zoribum
☆only for cats
☆ up to 4 days
☆ apply 1-2 hours before surgery