BSC2085L Practical 2
1/270
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
271 Terms
The axial skeleton
skull, vertebral column, bony thorax
Skull is composed of the
cranium and facial bones
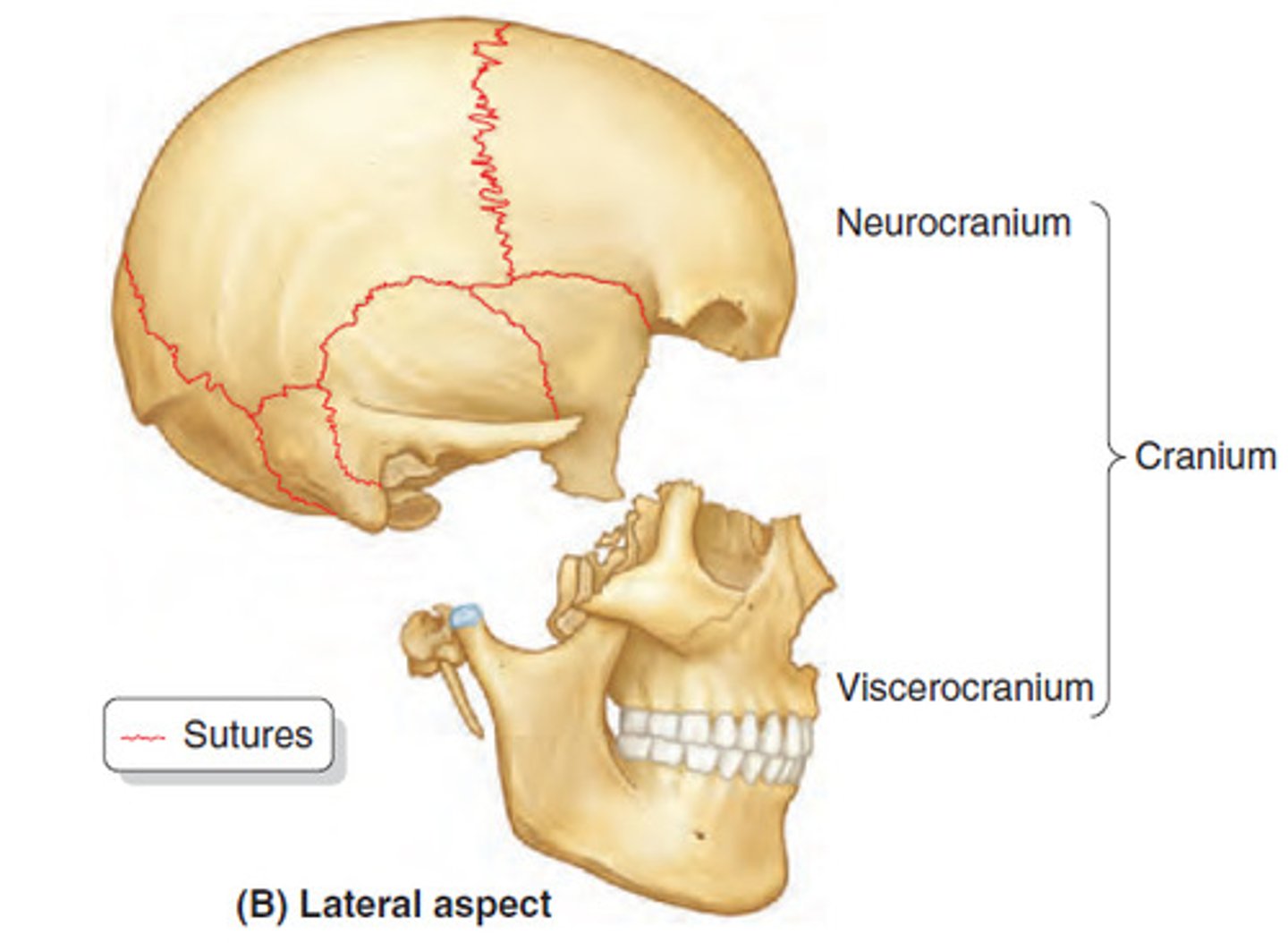
2 Major areas in the cranium
cranial vault and cranial floor
cranial vault
superior, lateral, and posterior walls of skull
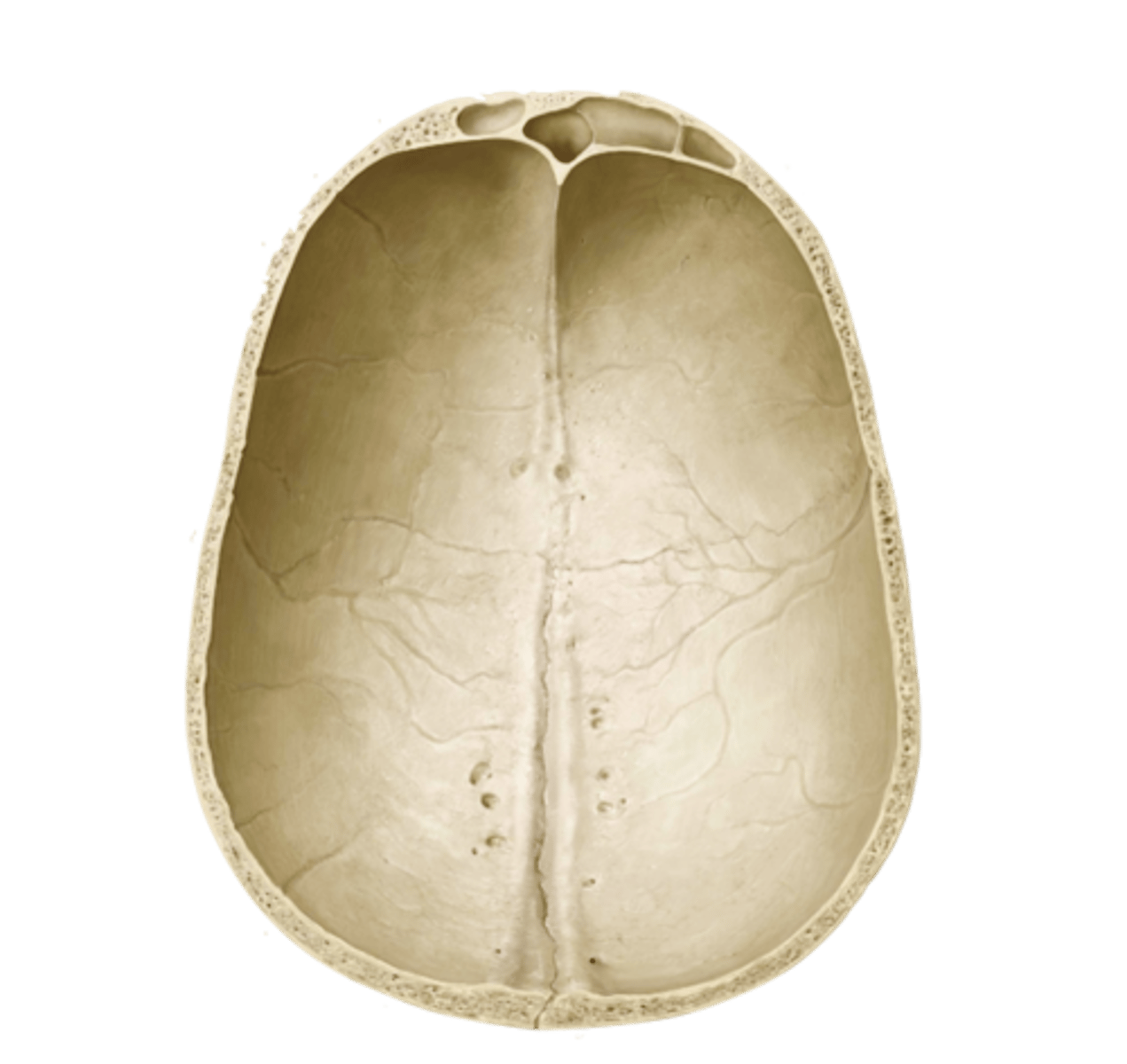
cranial floor
3 concavities; anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossae

Cranium major sutures
coronal, lambdoid, sagittal, squamous
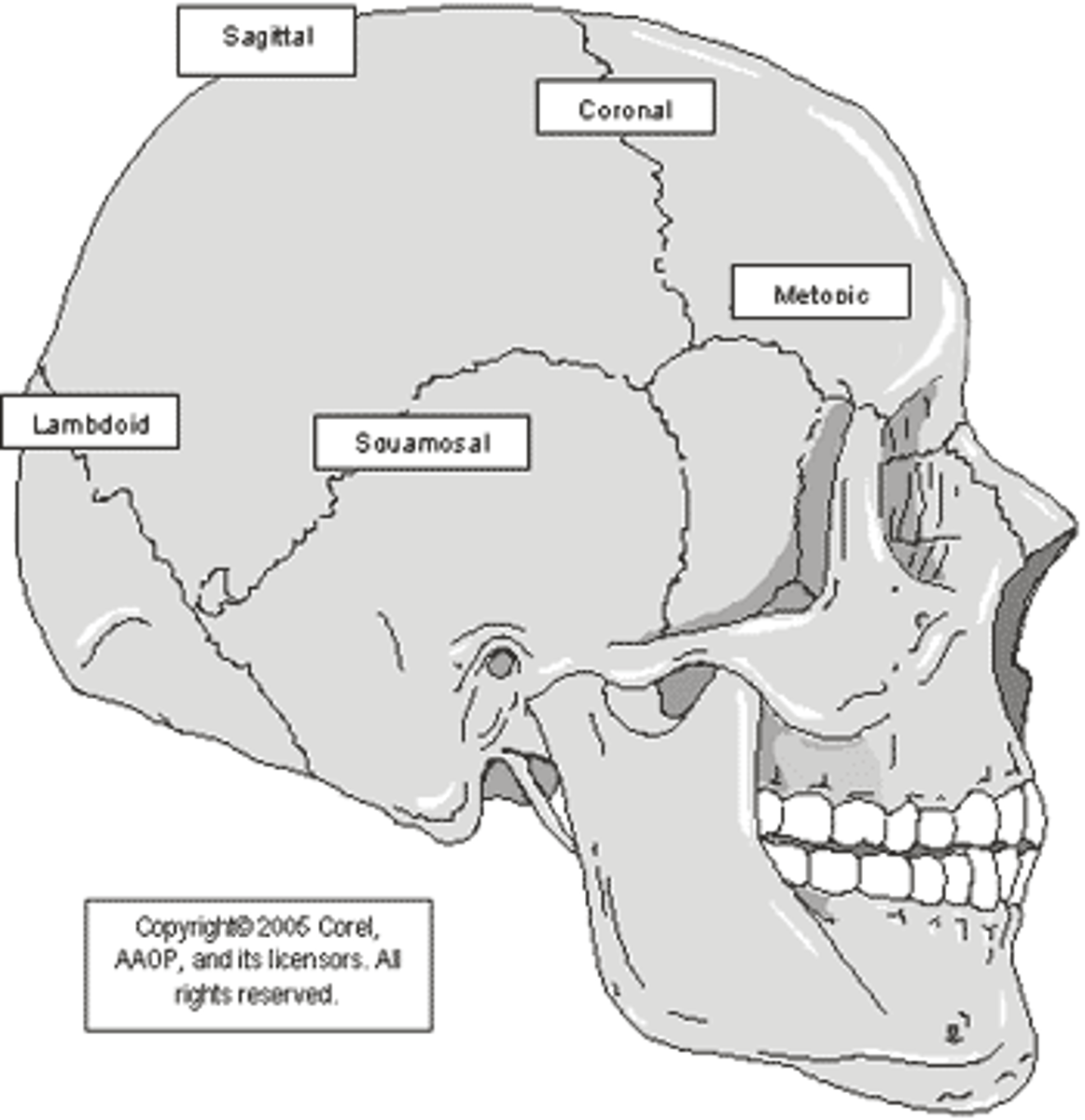
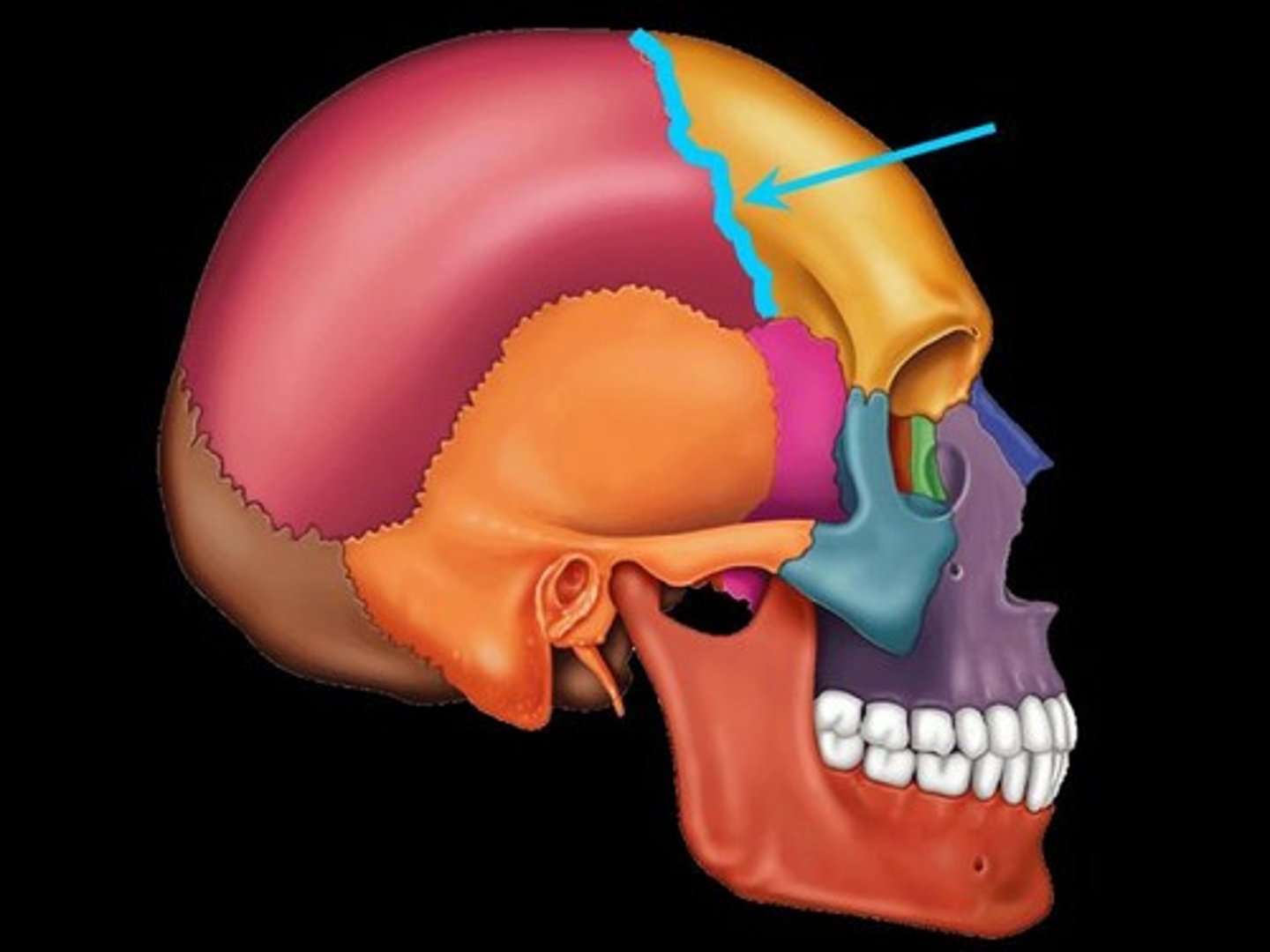
Coronal suture
connects the frontal bone to the parietal bone
Lambdoid suture
connects the parietal bone to the occipital bone
Sagittal suture
connects the left and right parietal bones
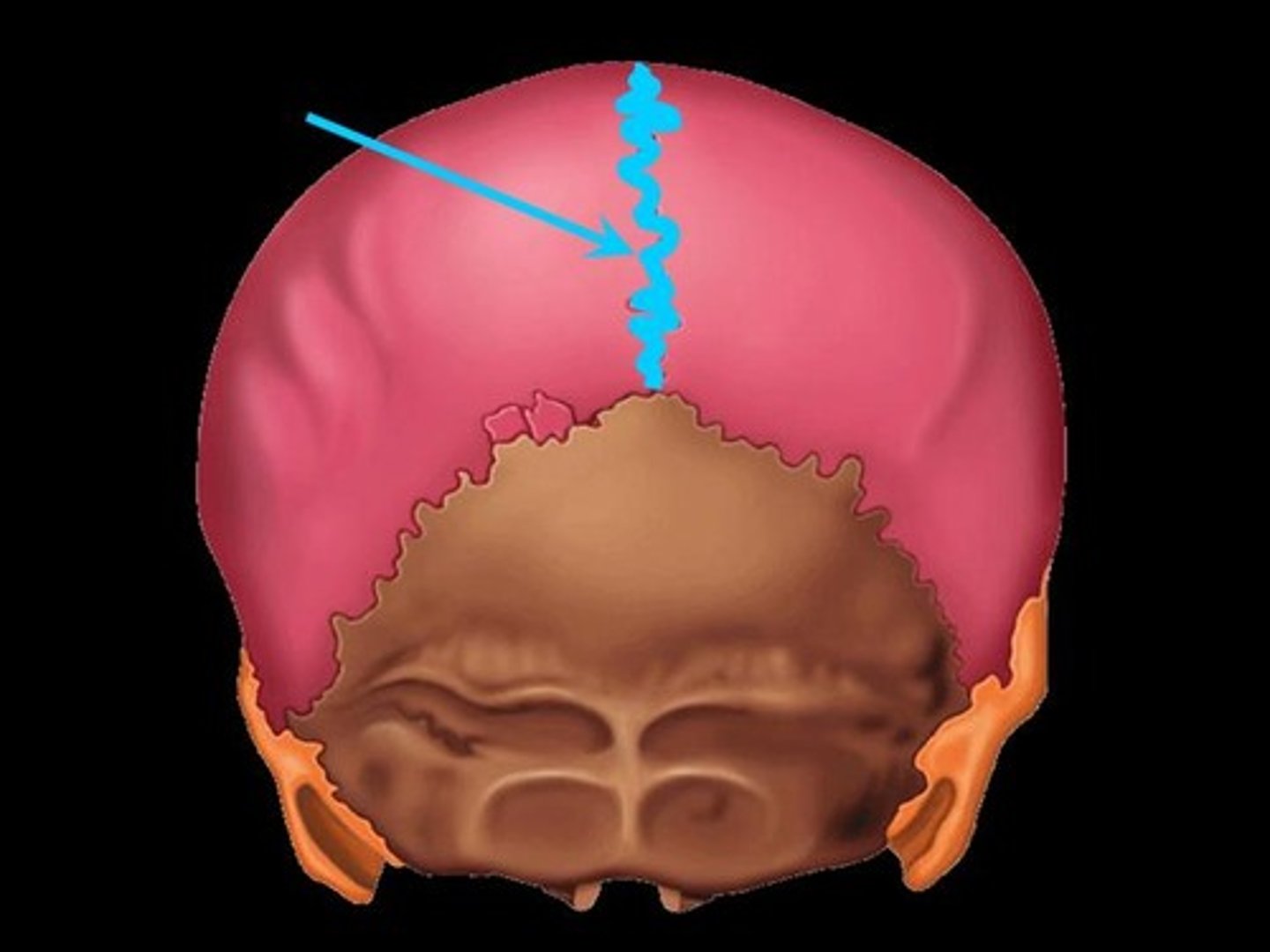
Squamous suture
connects the parietal bone to the temporal bone

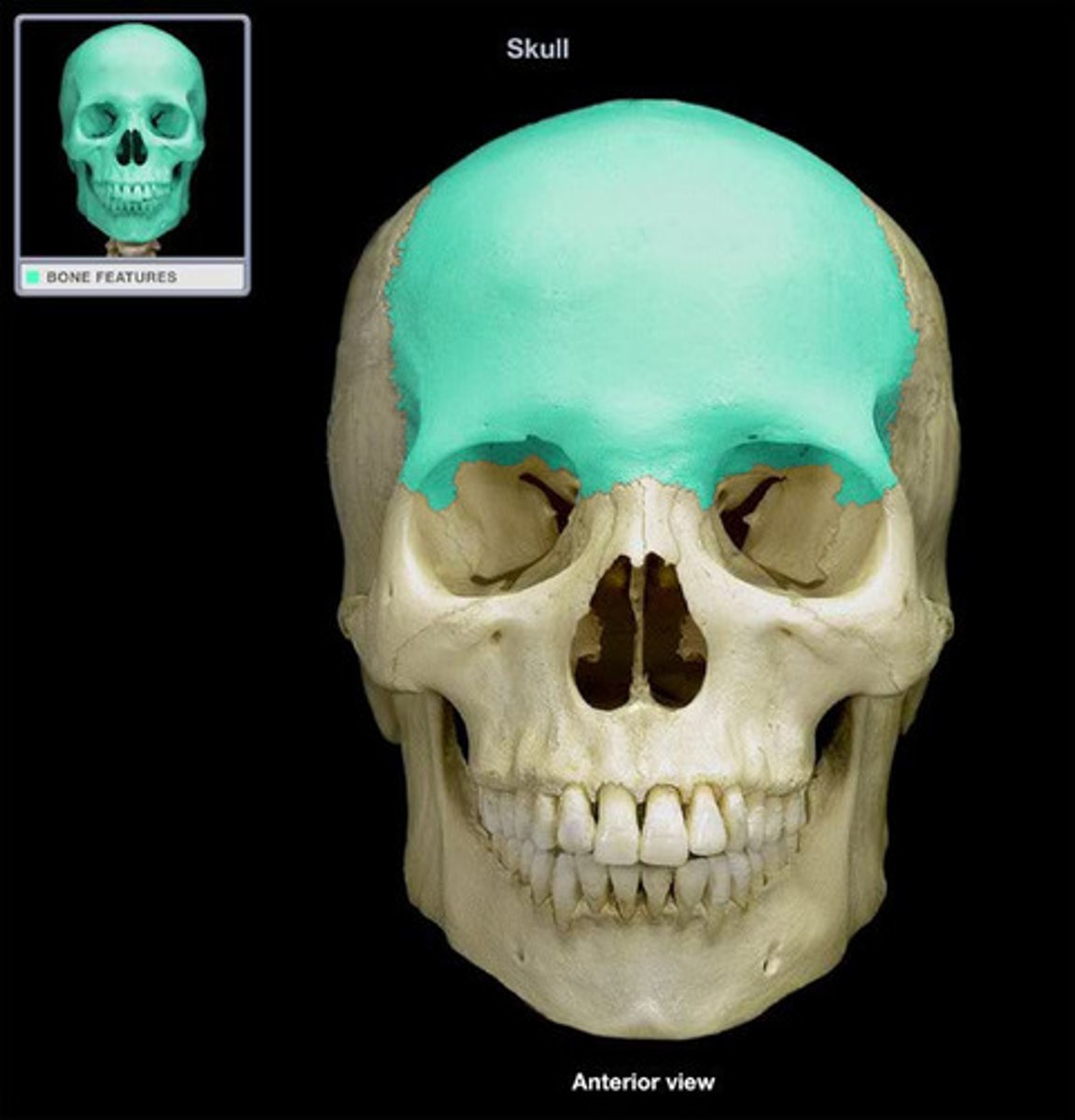
Frontal bone structures
Glabella, Supraorbital foramen (notch)
Glabella
located between the orbital cavities
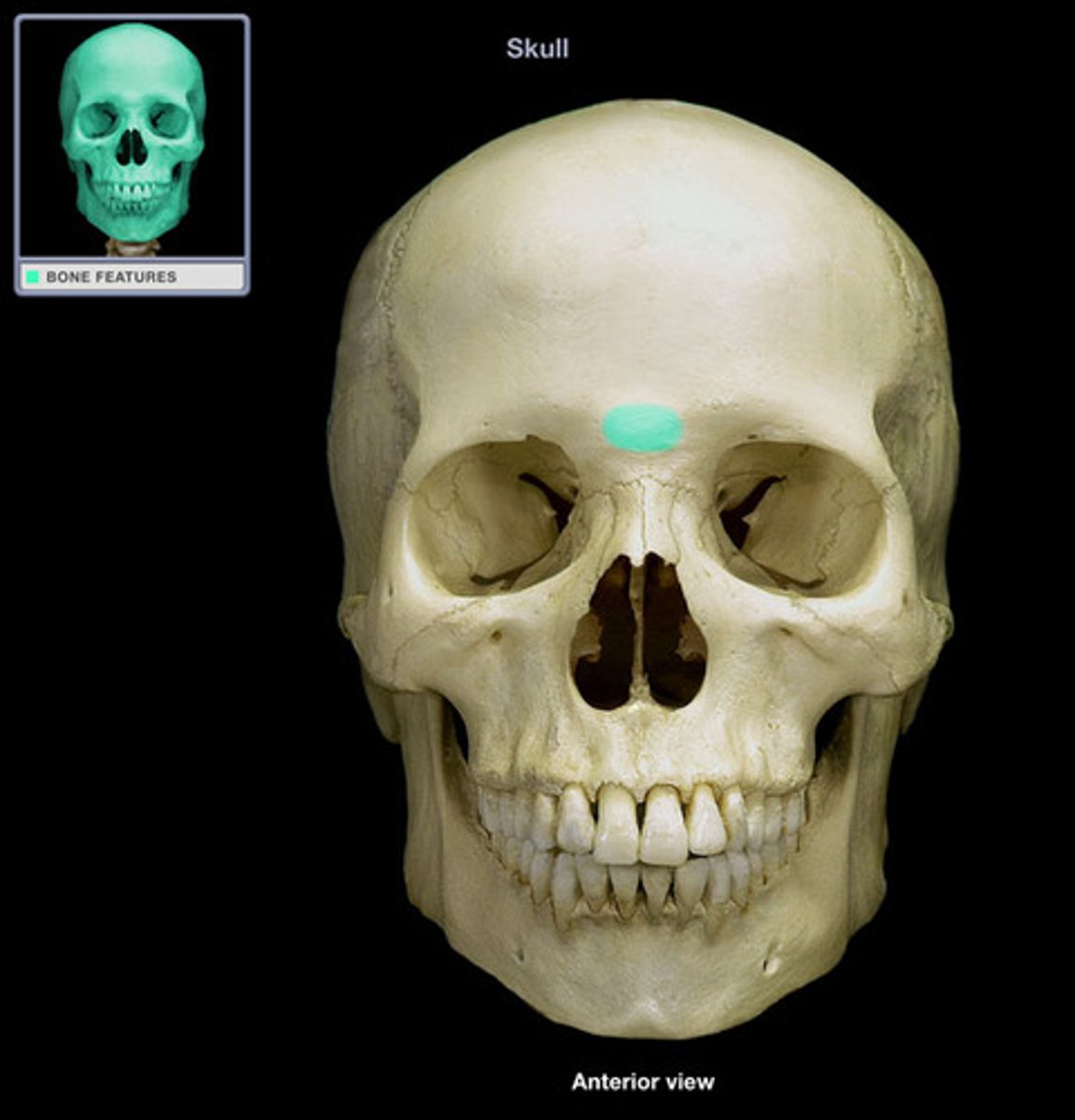
Supraorbital foramen (notch)
opening above each orbit, passageway for blood vessels and nerves

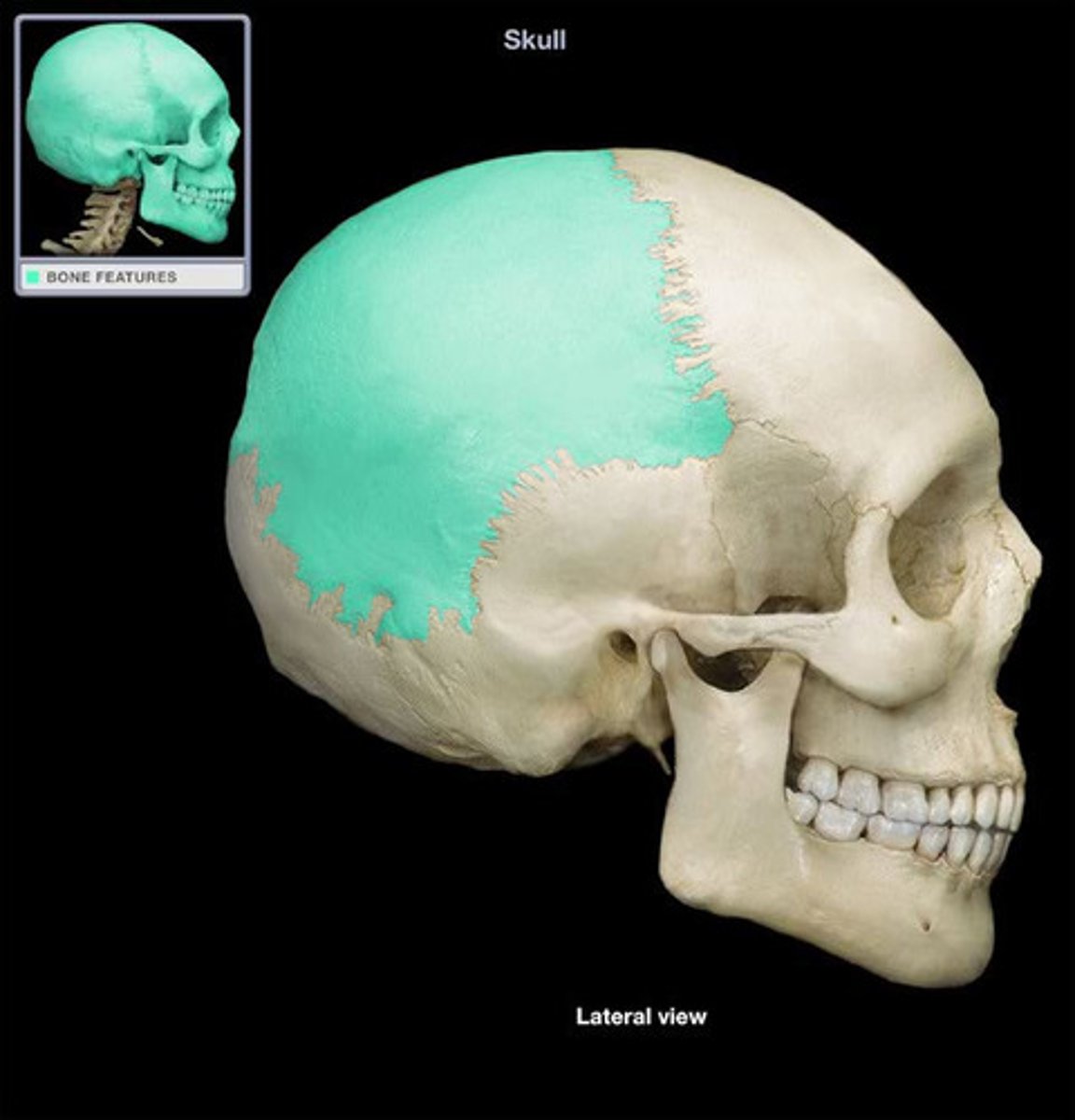
Parietal bone structures
sagittal suture, coronal suture
Temporal bone structures
Squamous region, tympanic region
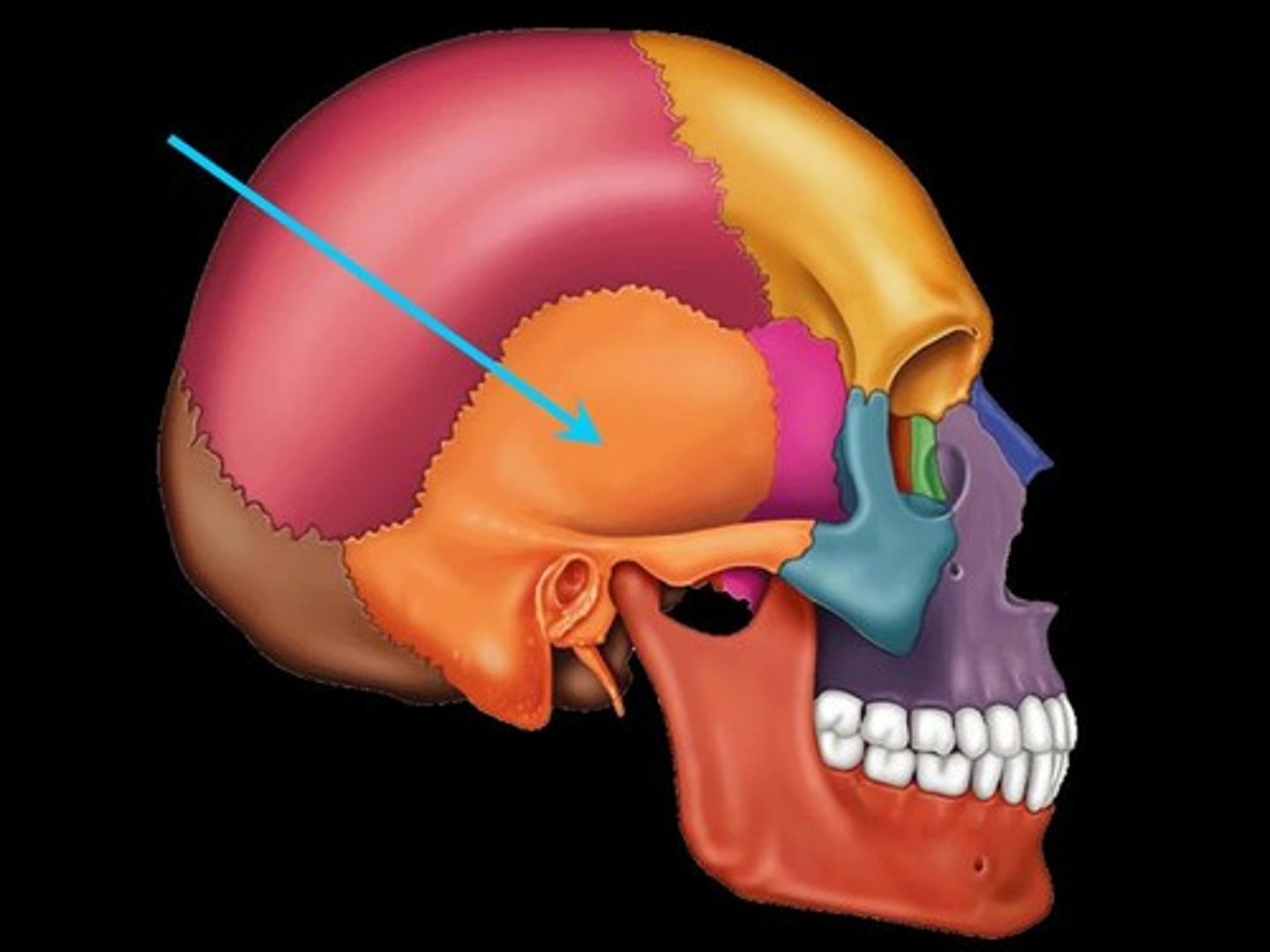
Squamous region
Zygomatic process
Tympanic region
External acoustic meatus, styloid process, mastoid region, petrous region

External acoustic meatus
ear canal
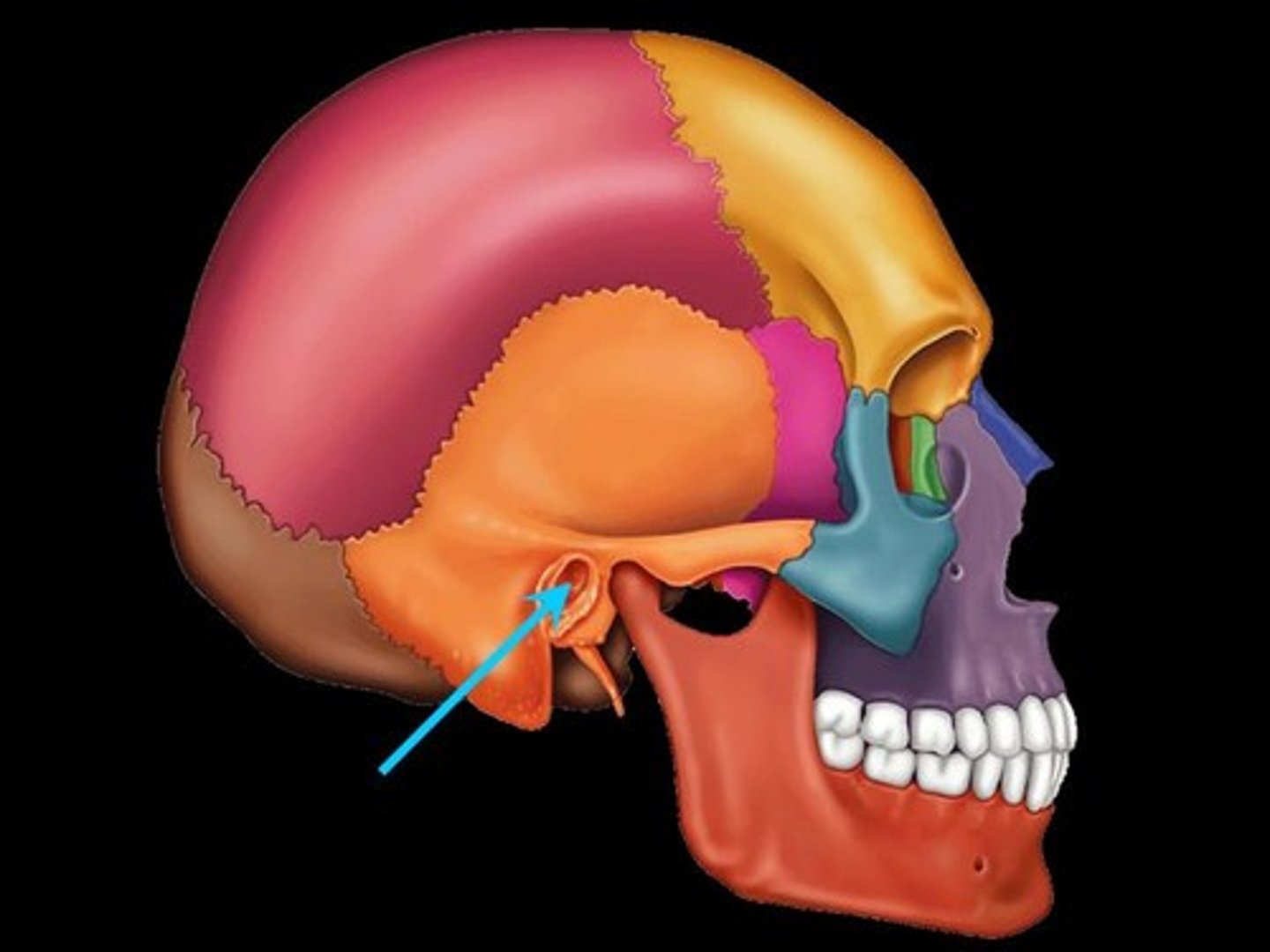
Styloid process
muscle/ligament attachment site
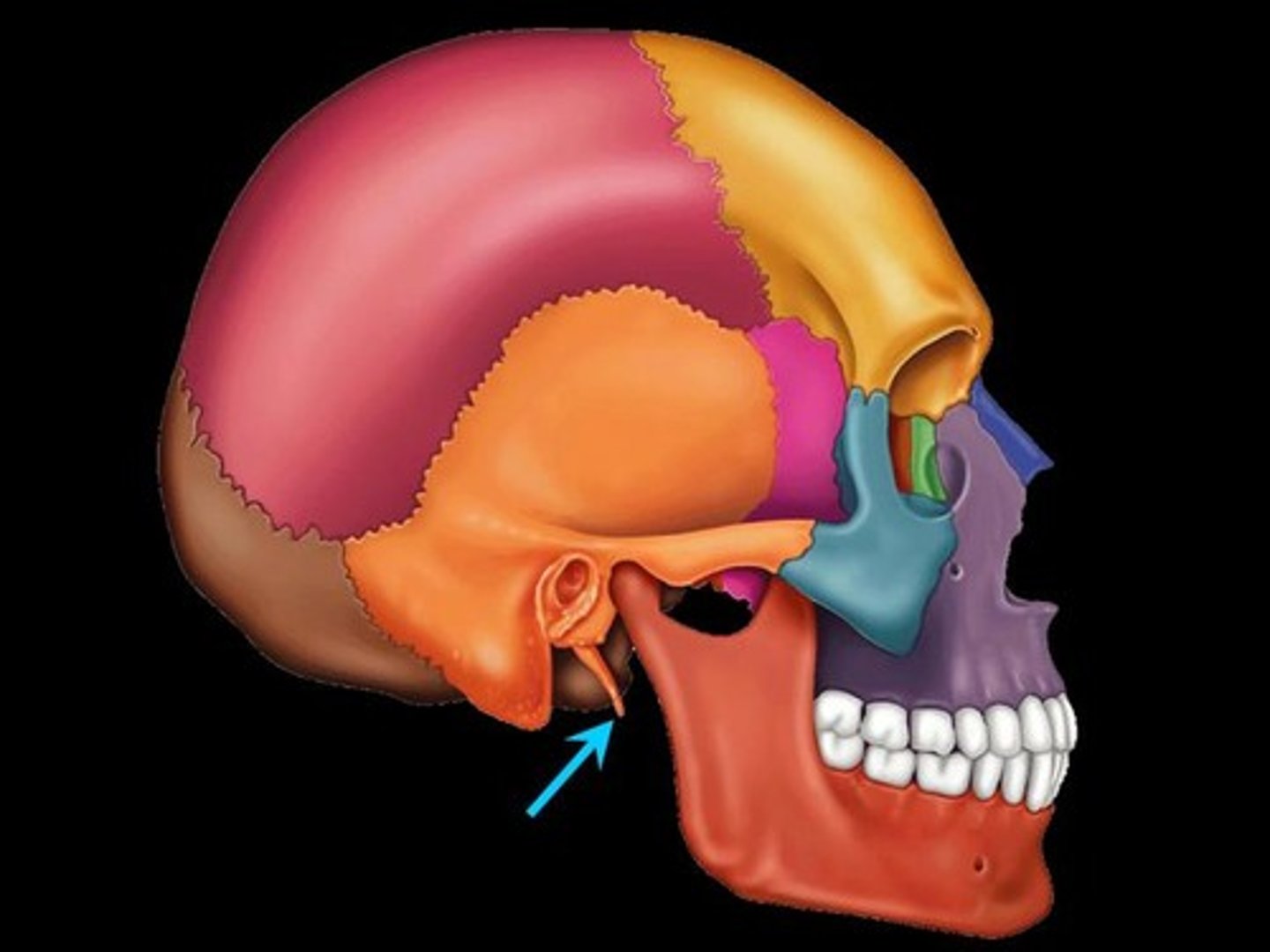
Mastoid region
muscle attachment site (mastoid process)
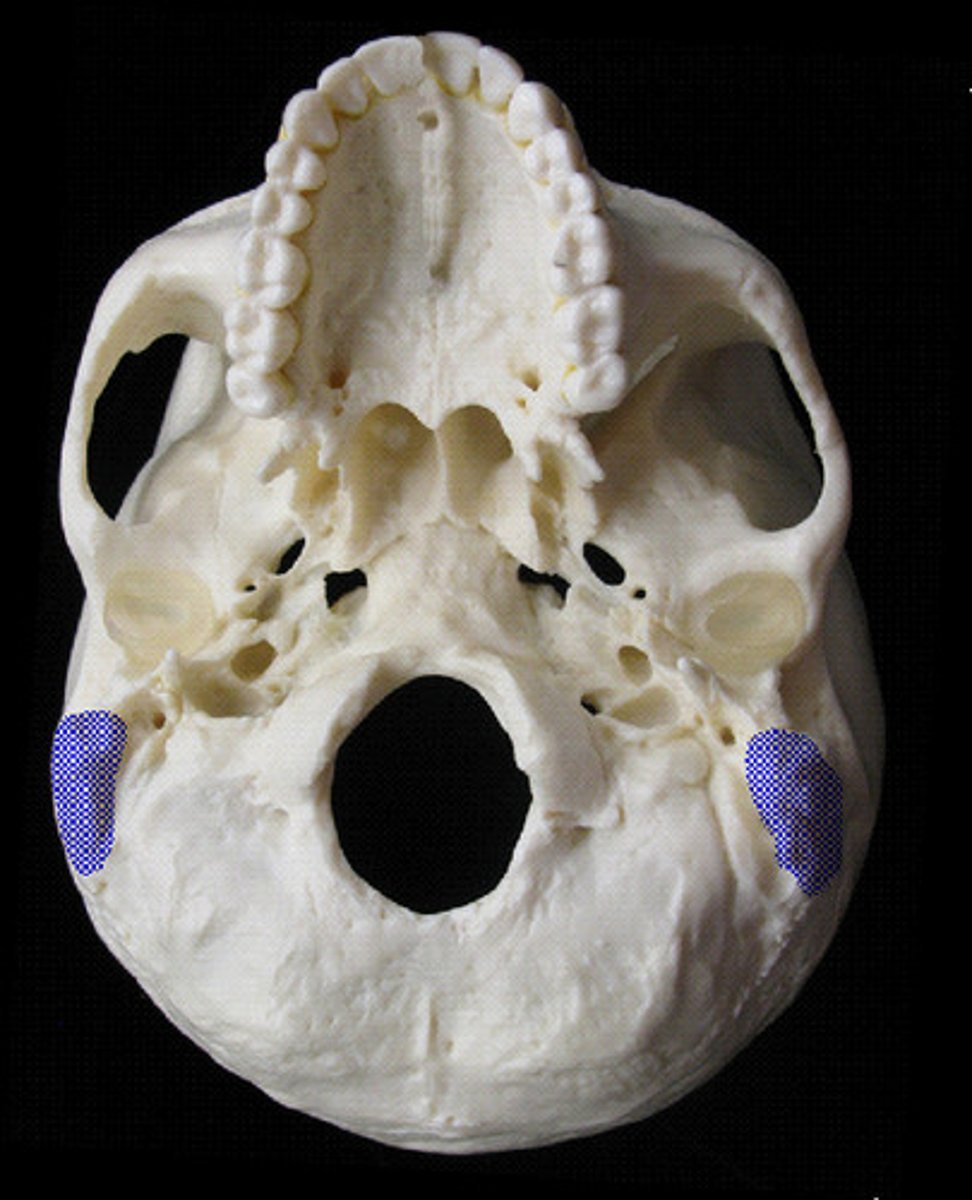
Petrous region
jugular foramen, carotid canal, internal acoustic meatus
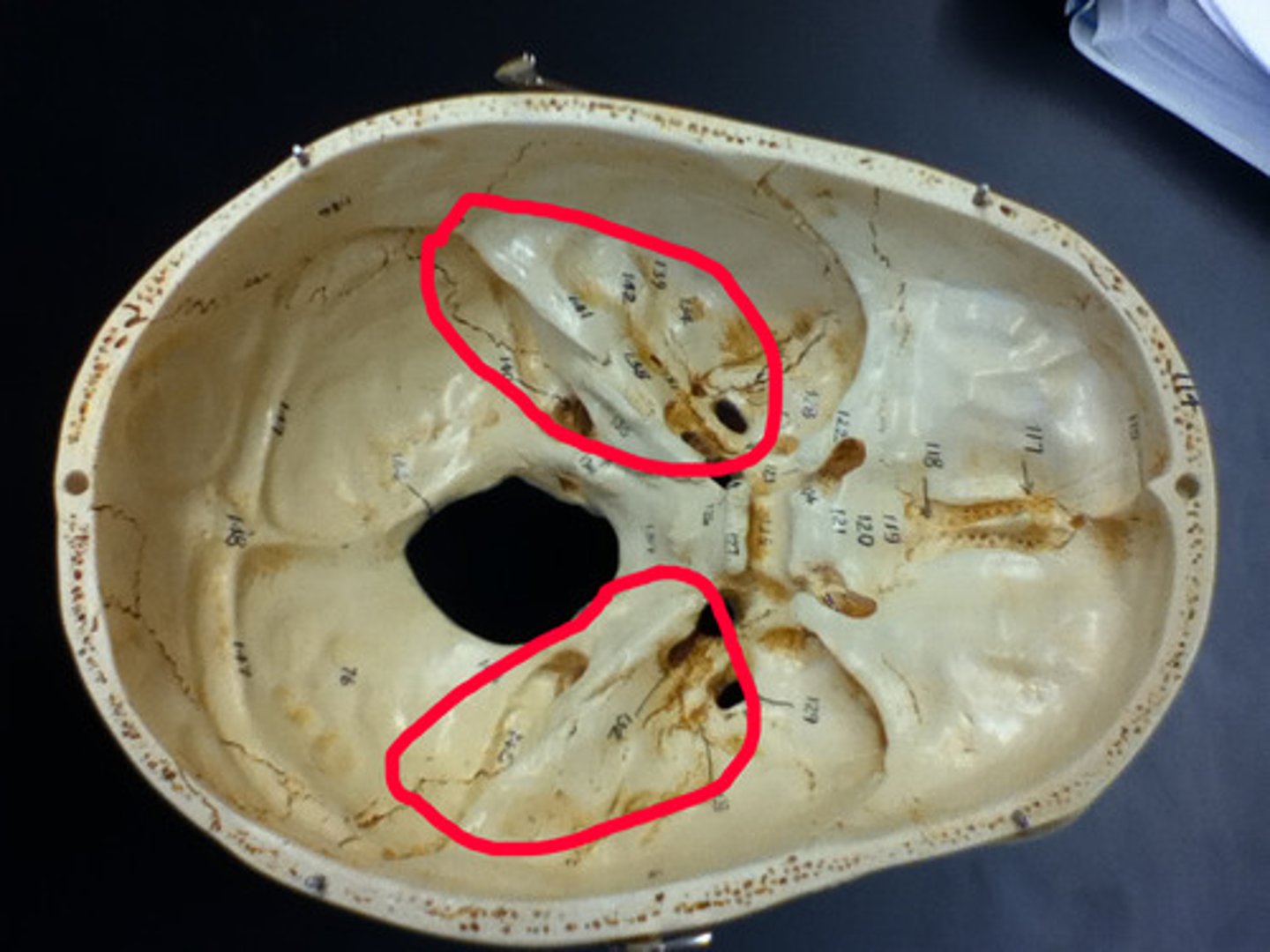
Jugular foramen
passage for internal jugular vein, cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory)

Carotid canal
passage for internal carotid artery
Internal acoustic meatus
passage for cranial nerves VII (facial) & VIII (vestibulocochlear)
Occipital bone structures
Foramen magnum, occipital condyles, hypoglossal canal
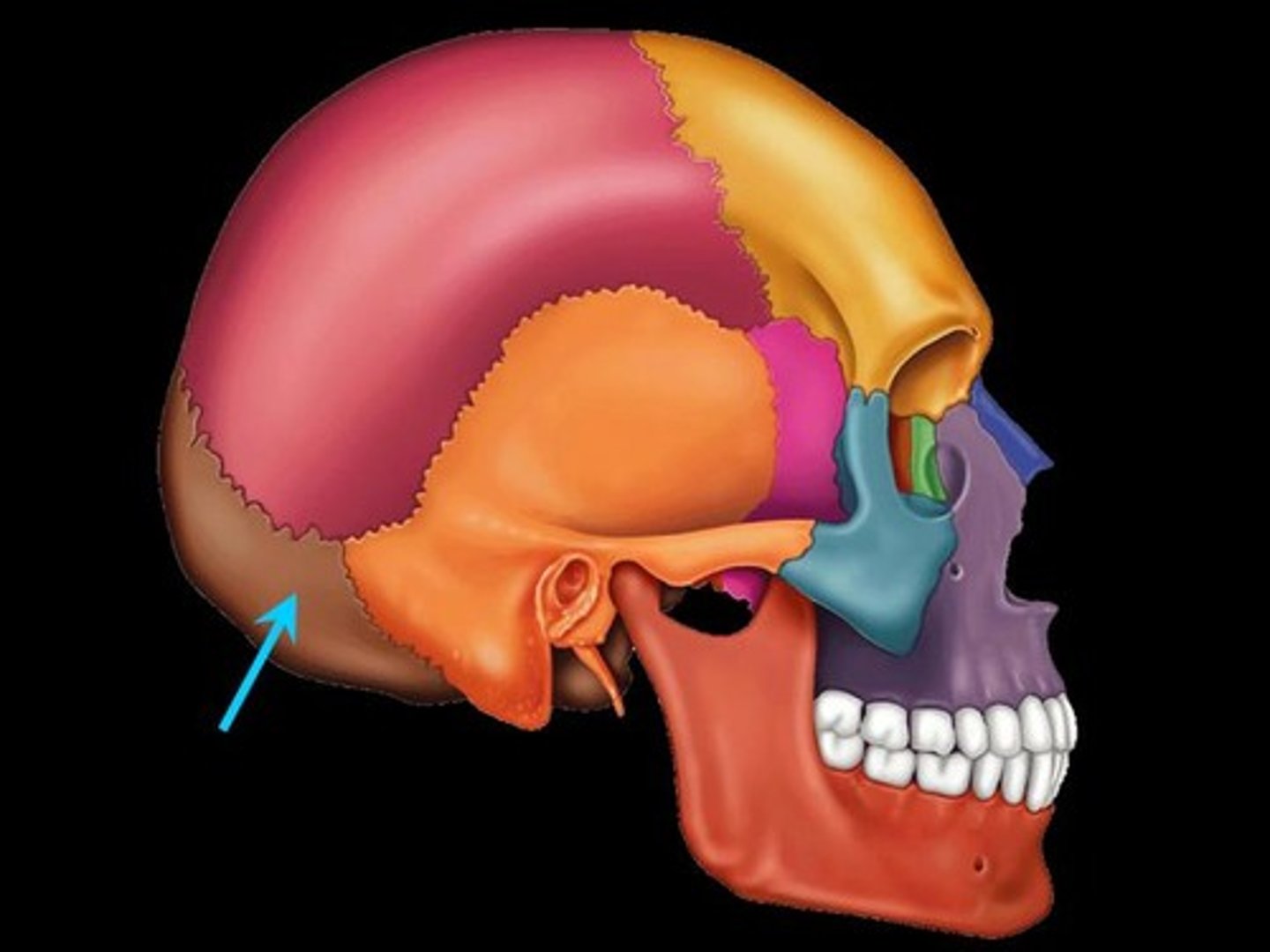
Foramen magnum
where the spinal cord enters the cranium to connect to the brain
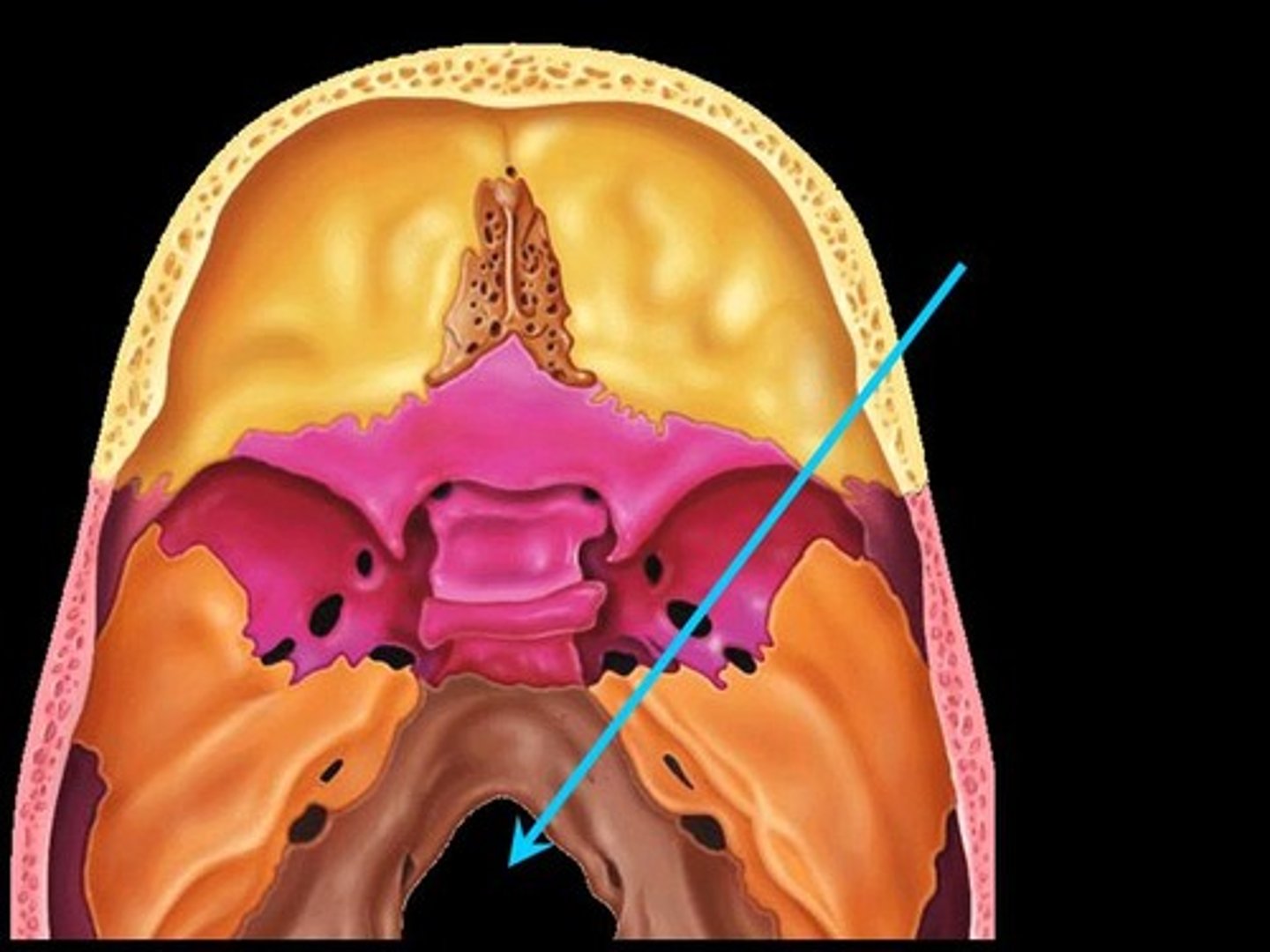
Occipital condyles
articulation site with 1st cervical vertebra (atlas)
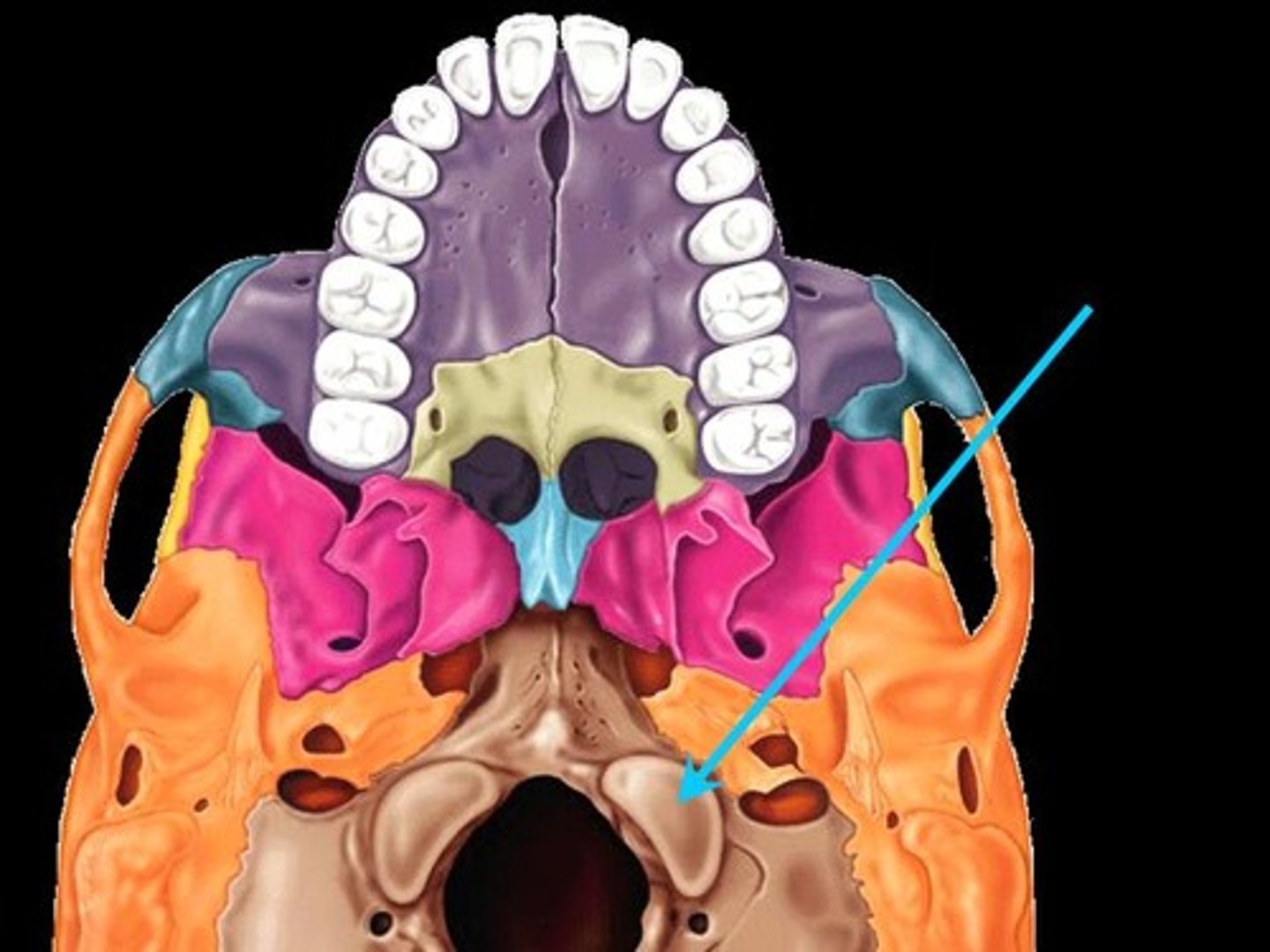
Hypoglossal canal
passage for cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal nerve)
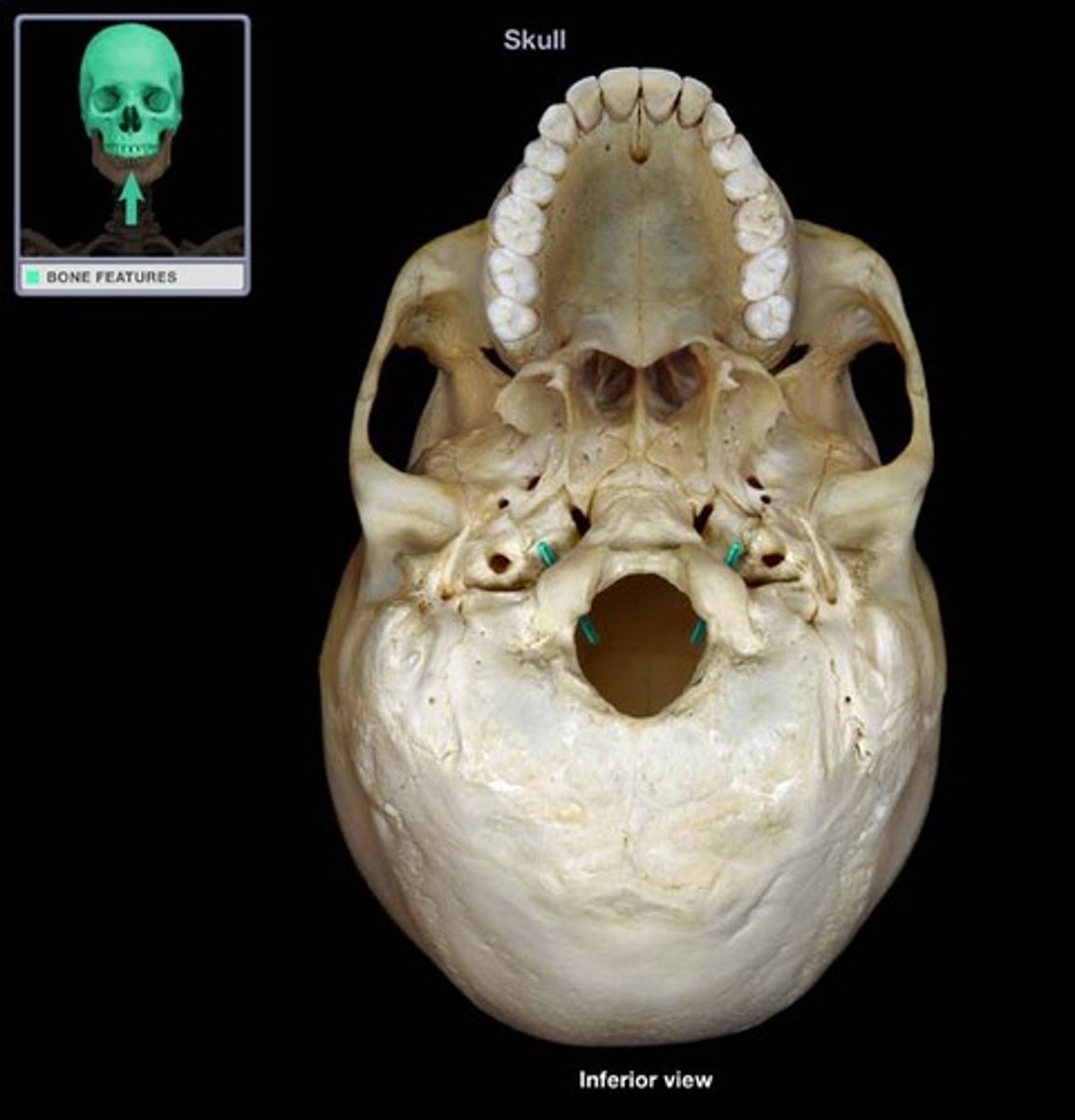
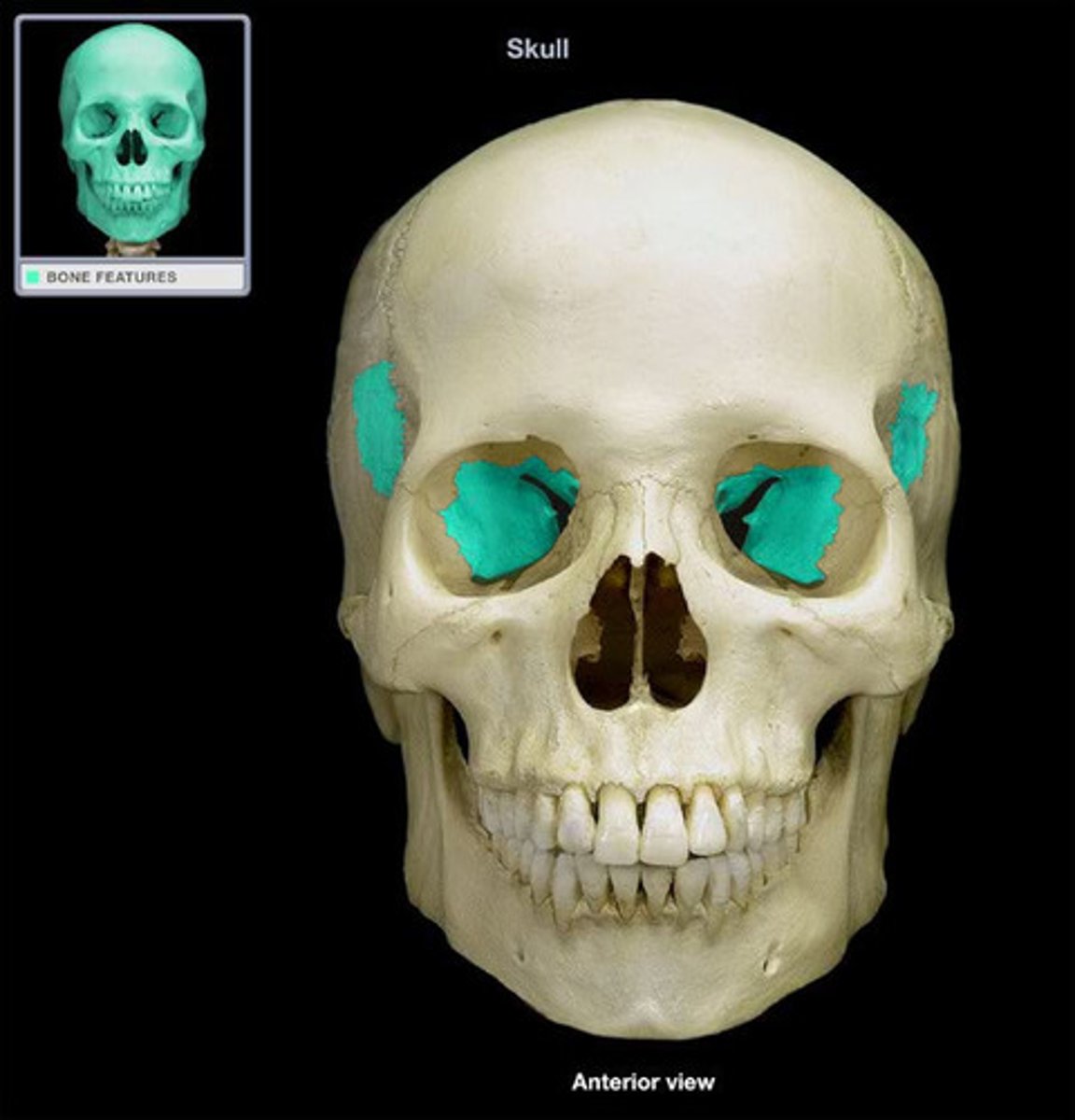
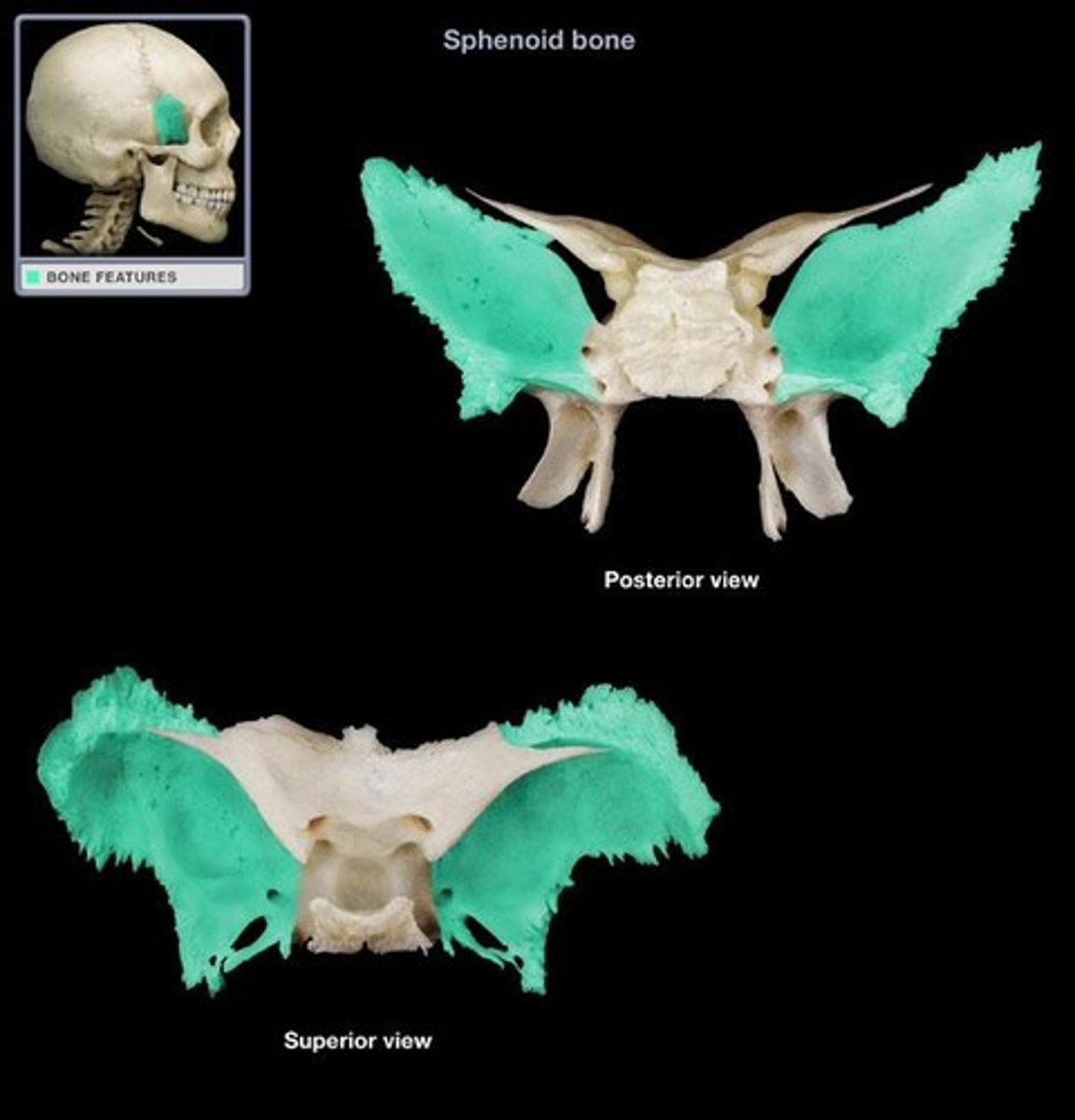
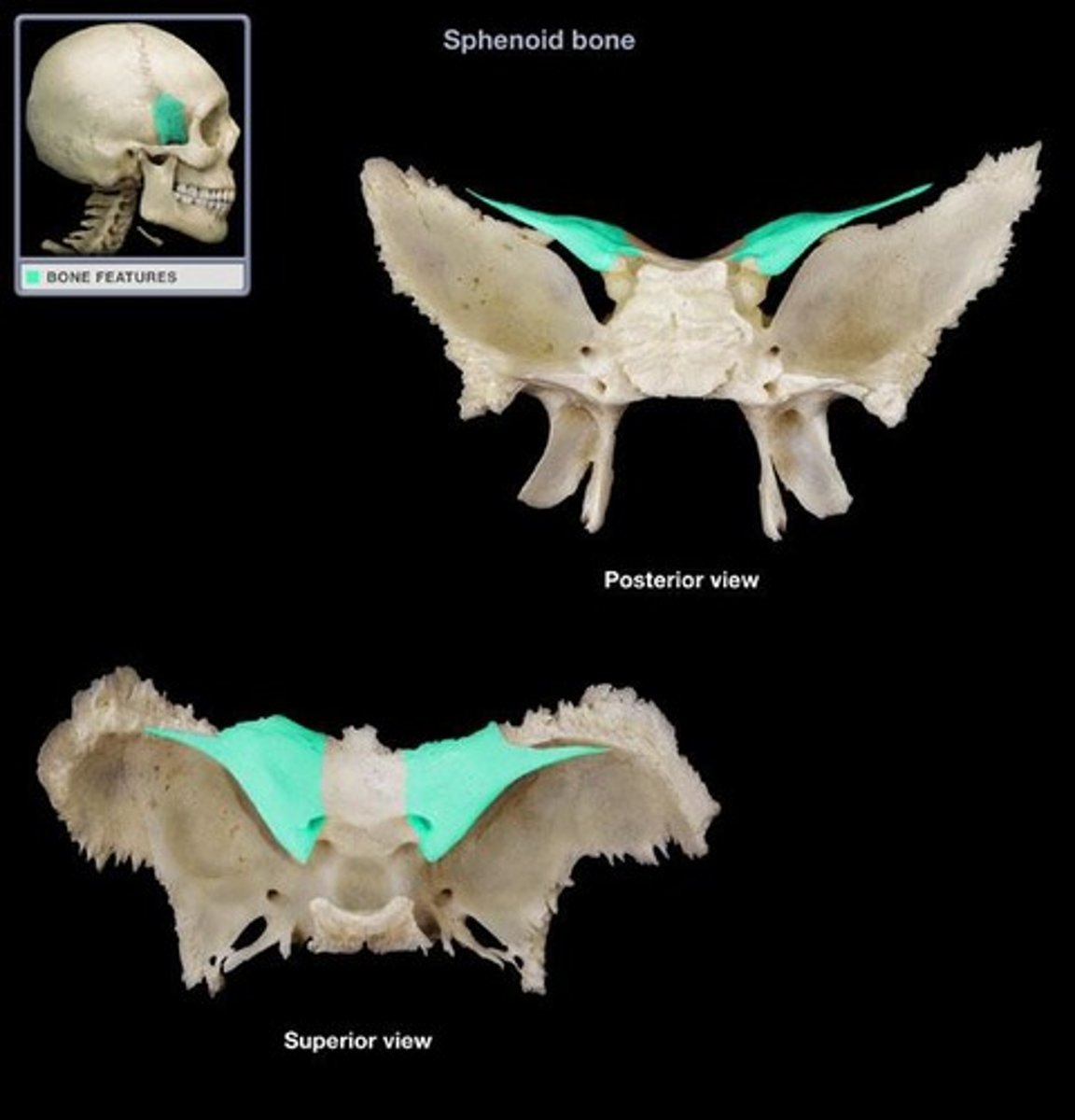
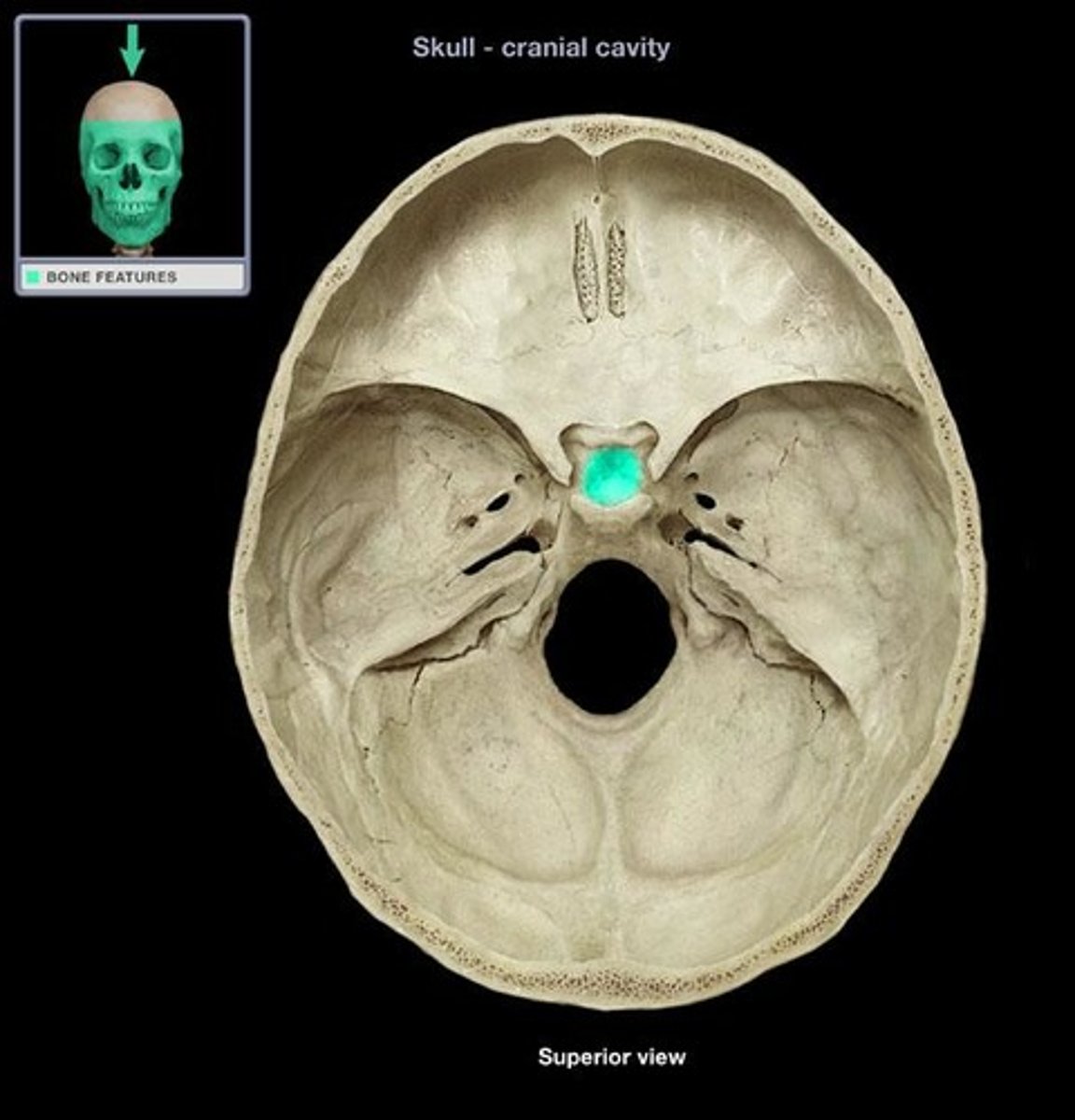
Sphenoid bone structures
Greater wings, lesser wings, sella turcica, optic canals
Greater wings of sphenoid
part of orbital cavity
Lesser wings of sphenoid
-anchors dura mater (covering that encloses the brain)
Sella turcica
midline of sphenoid bone, hypophyseal fossa here
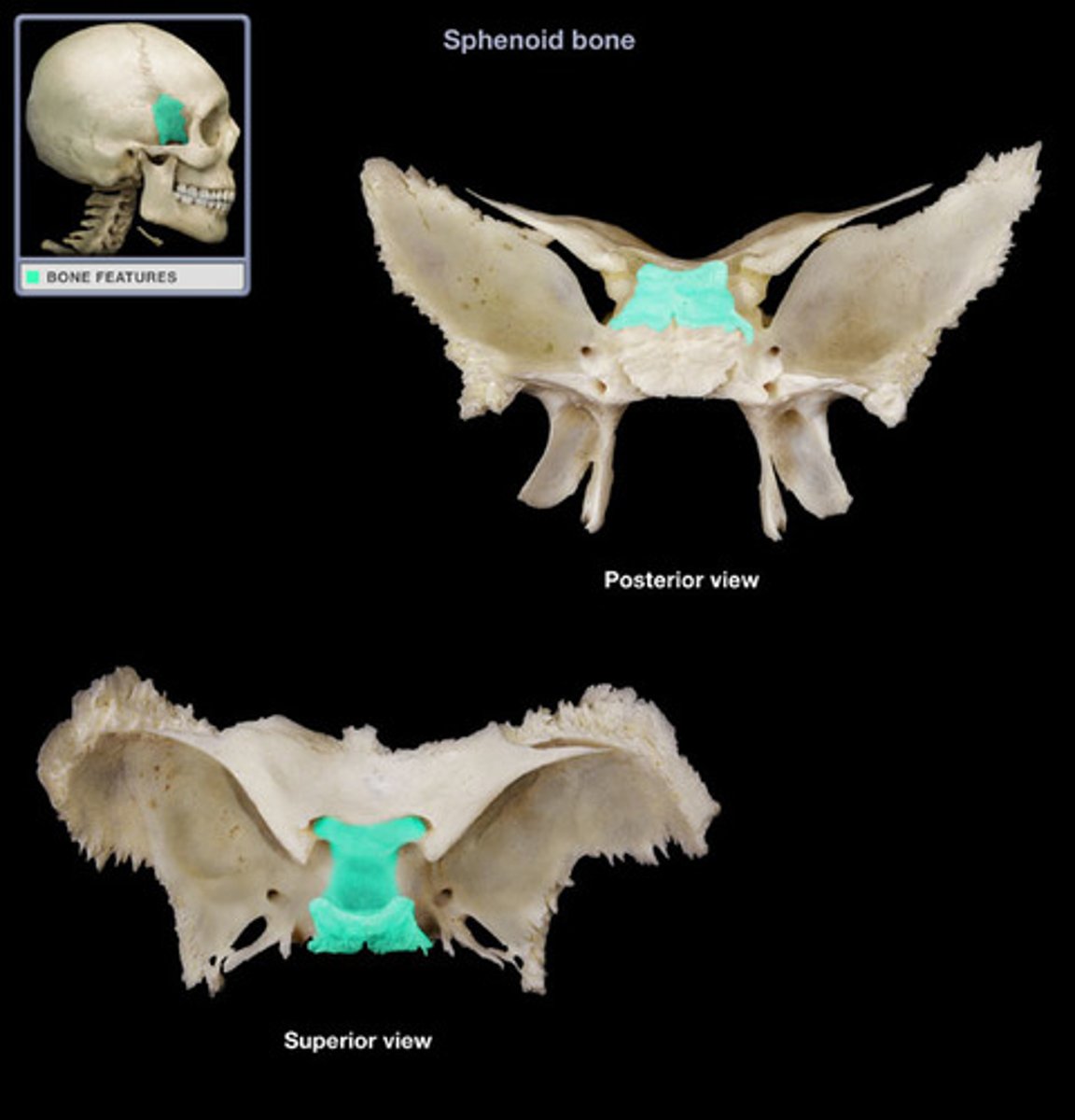
Hypophyseal fossa
houses the pituitary gland
Optic canals
openings at base of lesser wings for cranial nerve II (optic nerve)
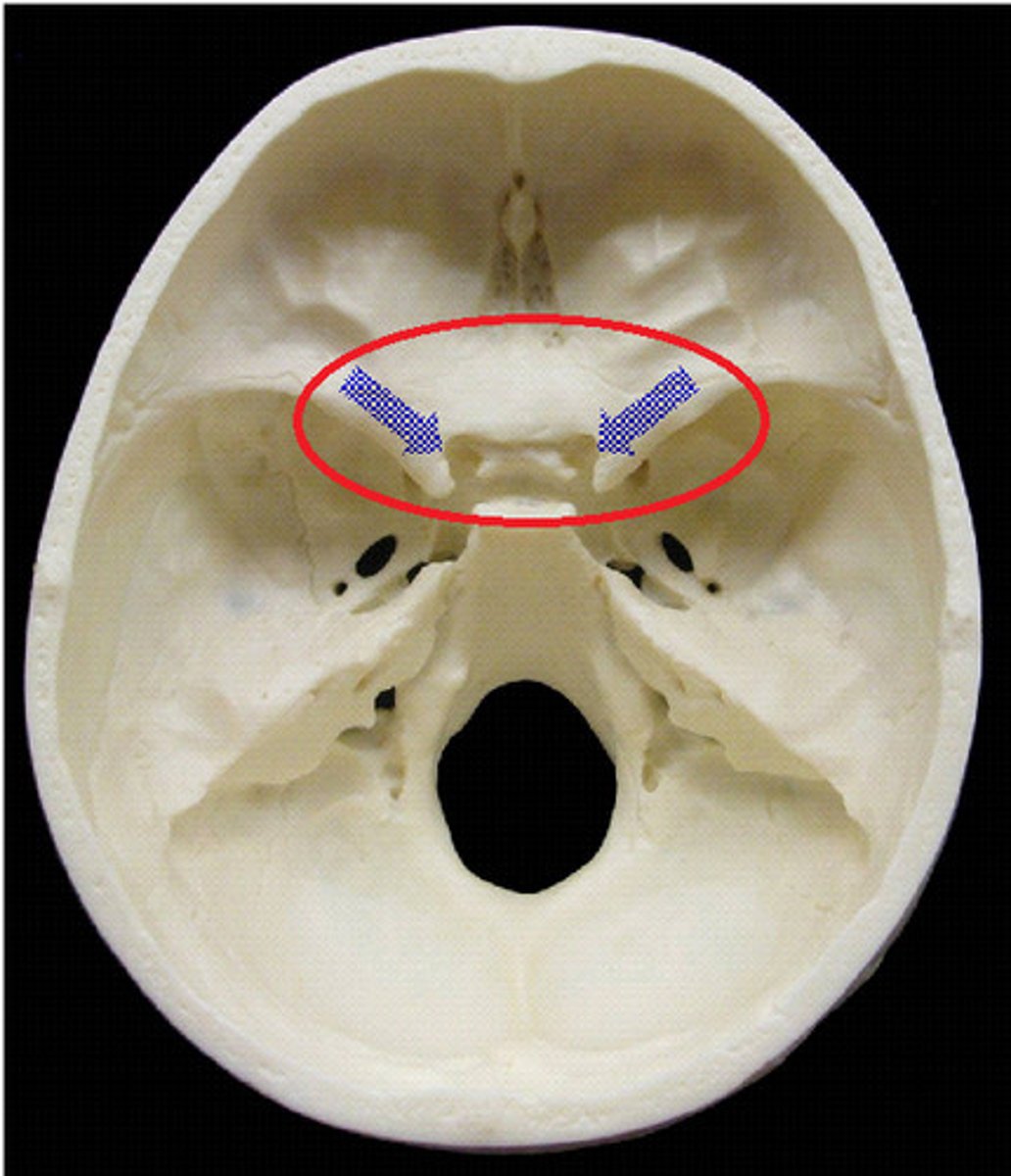
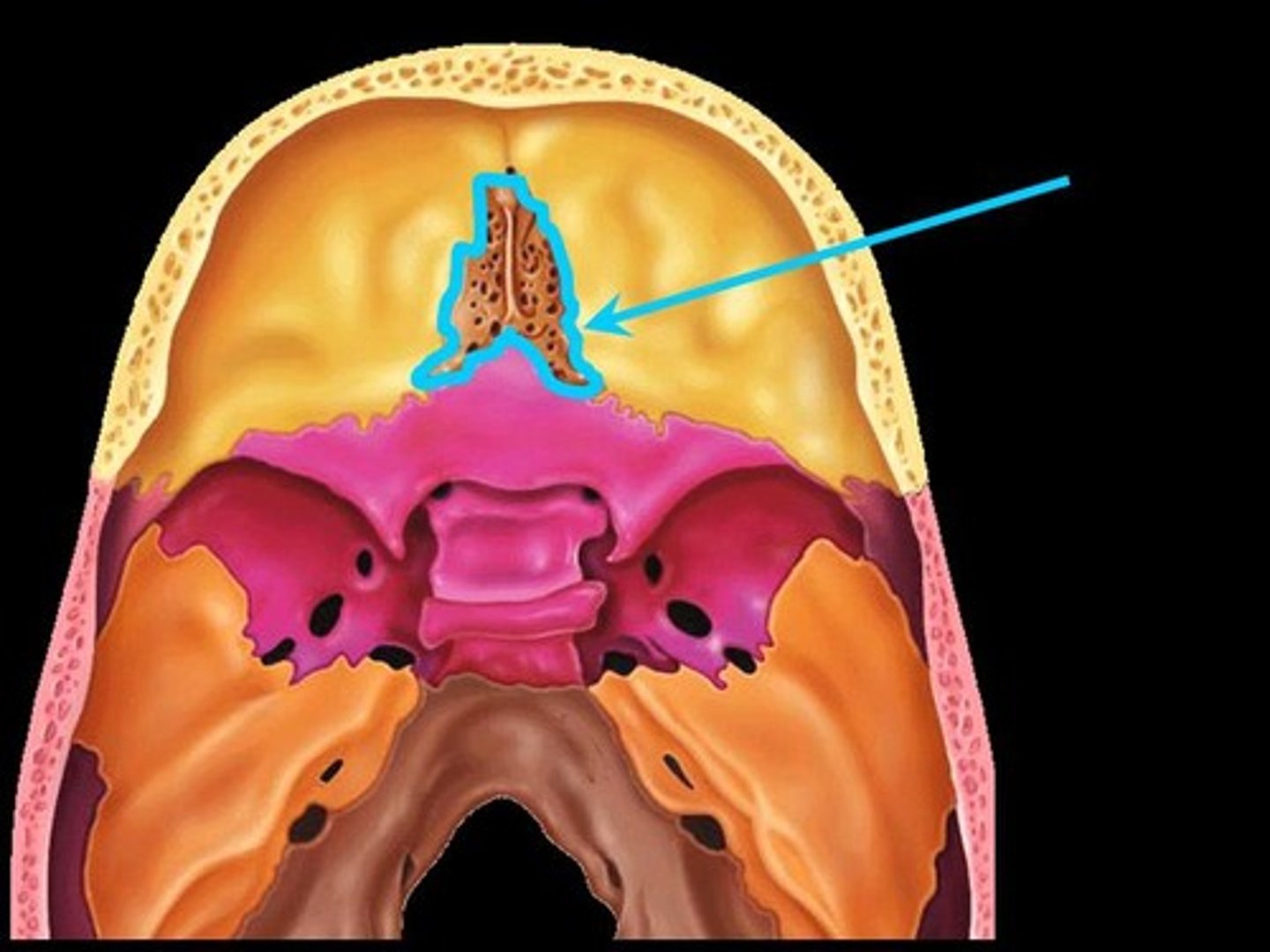
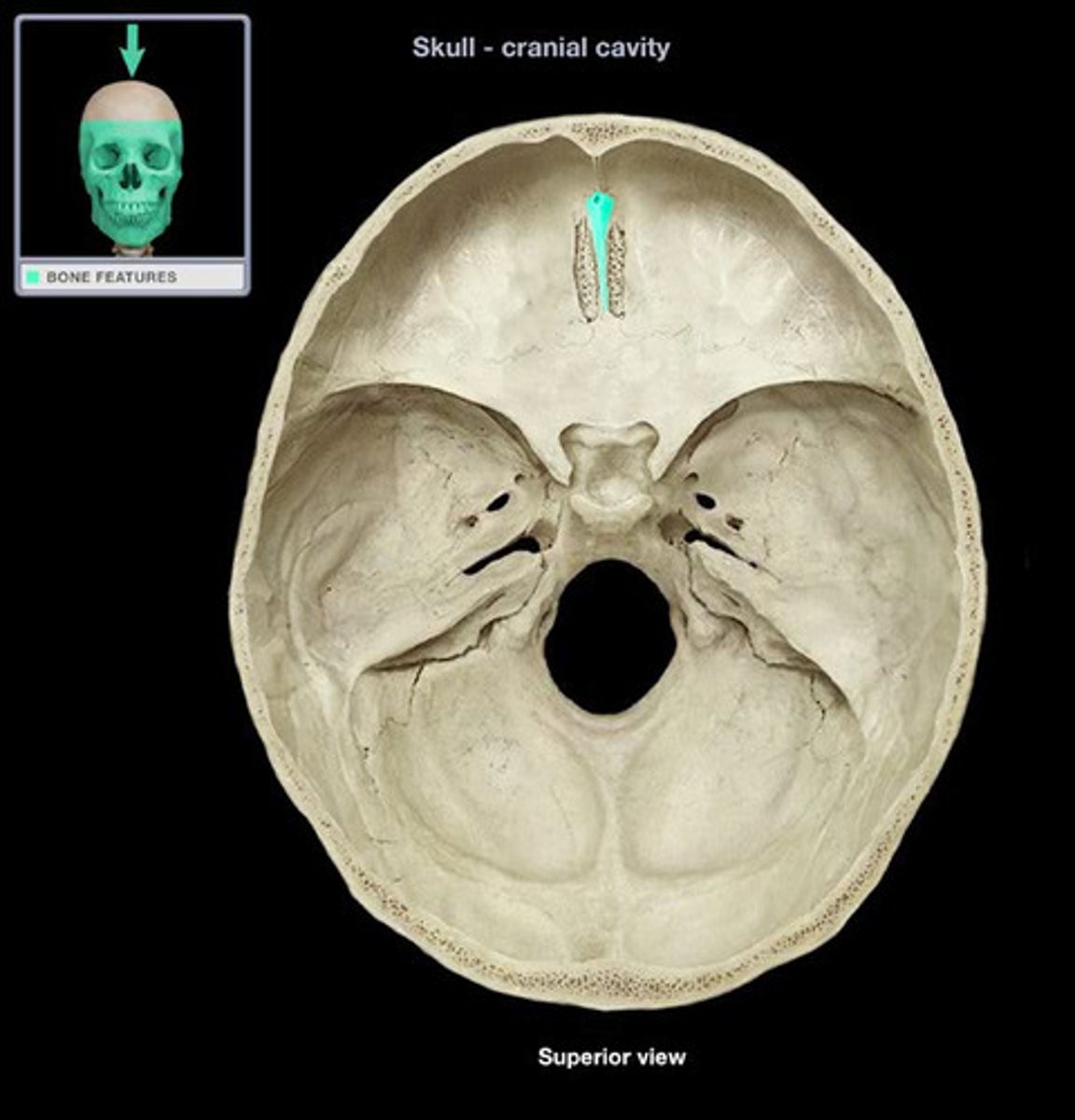
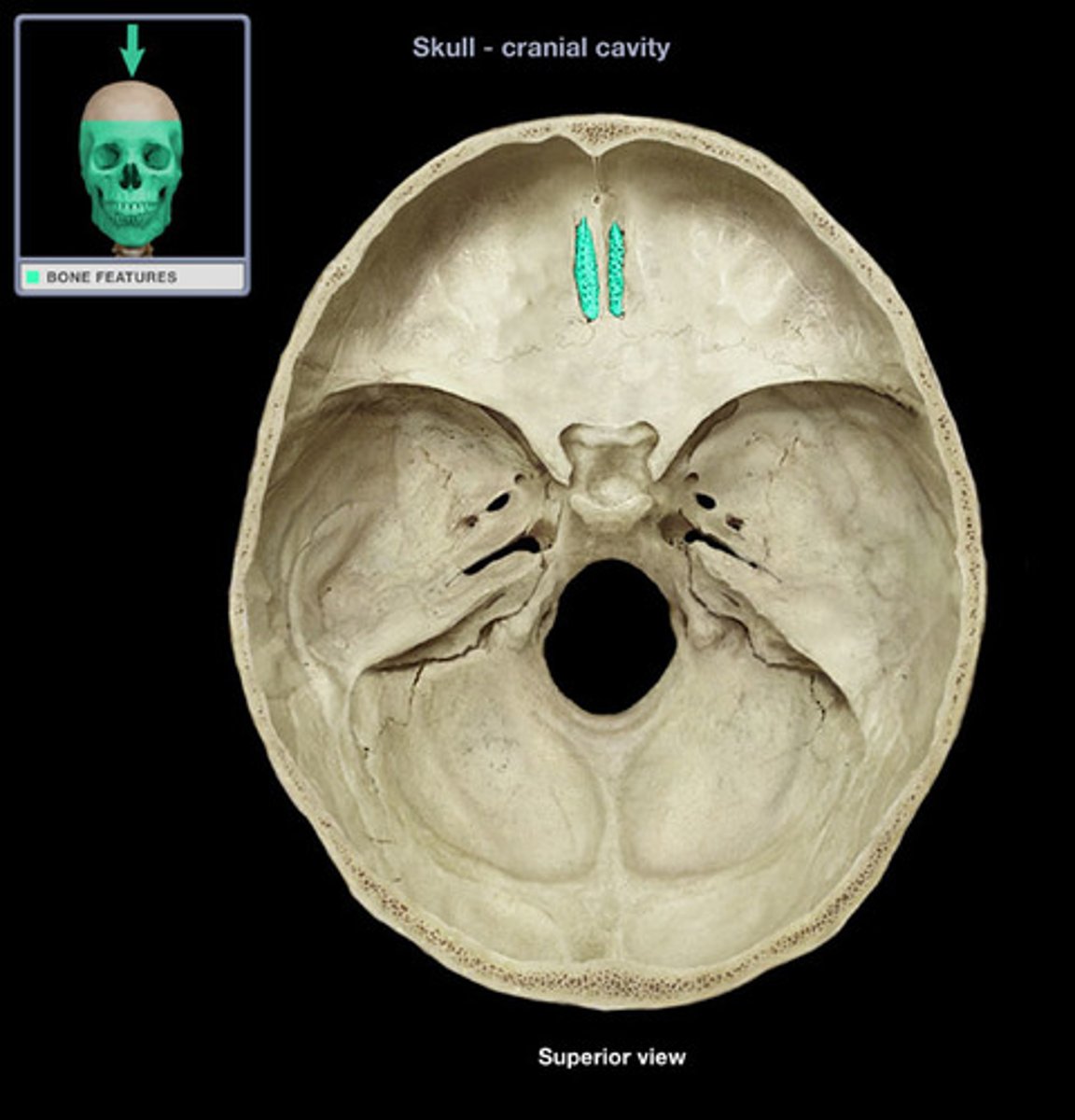
Ethmoid bone structures
Cribriform Plate, crista Galli
Crista galli
anchors dura mater (leathery connective tissue membrane that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord)
Cribriform plate
allows olfactory fibers (cranial nerve I) from nasal mucosa to enter the brain
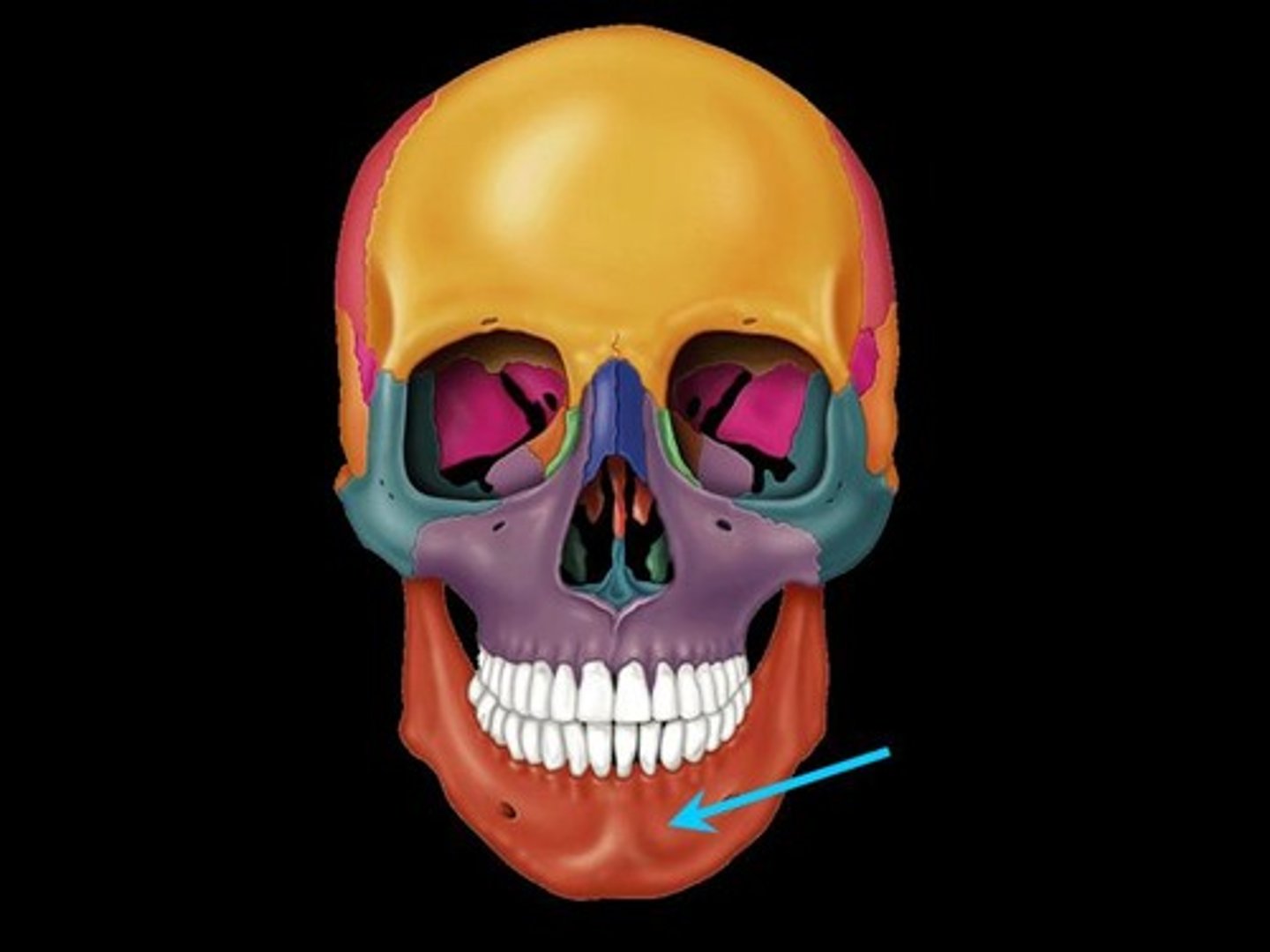
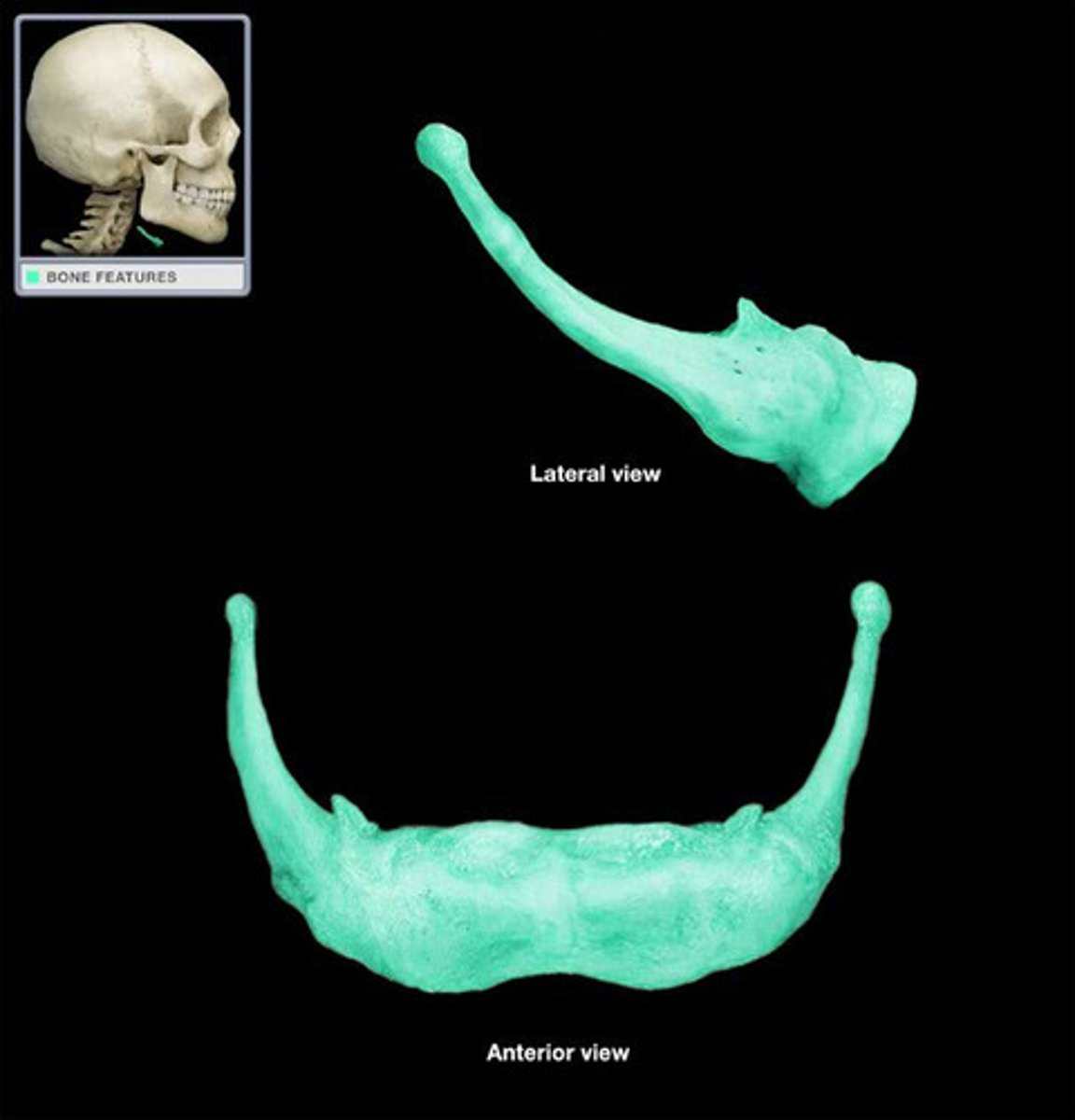
Mandible structures
Body of mandible, Mandibular ramus, Mandibular angle, Coronoid process, Mandibular notch, Condylar process
Maxilla structures
Palatine process (anterior part of the hard palate)

Facial bones
mandible, maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, lacrimal, nasal, vomer, inferior nasal conchae
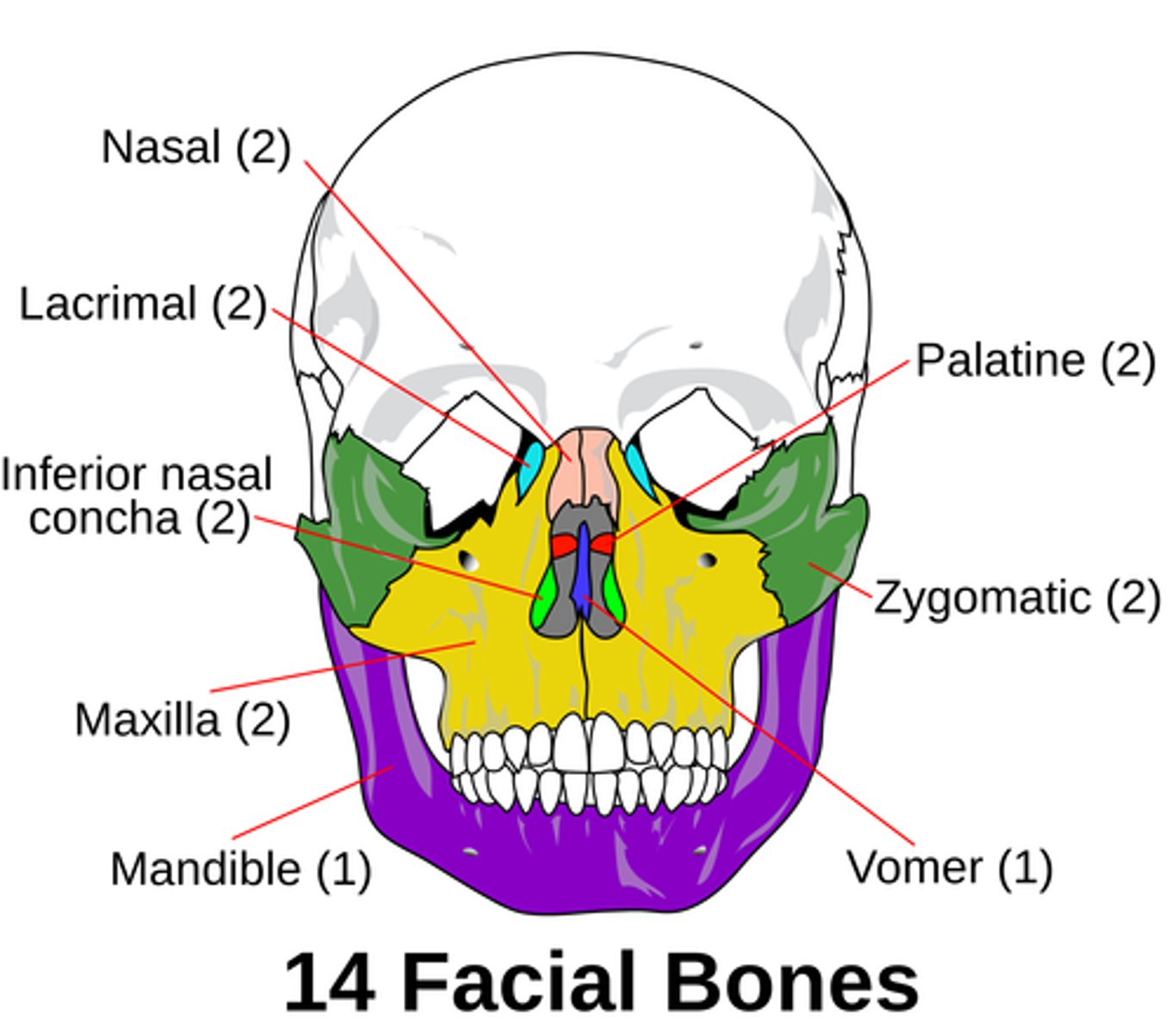
The hard palate is composed of...
BOTH the palatine process of the maxilla AND the palatine bone.

Hyoid bone
serves as a point of attachment
for many tongue and neck muscles.
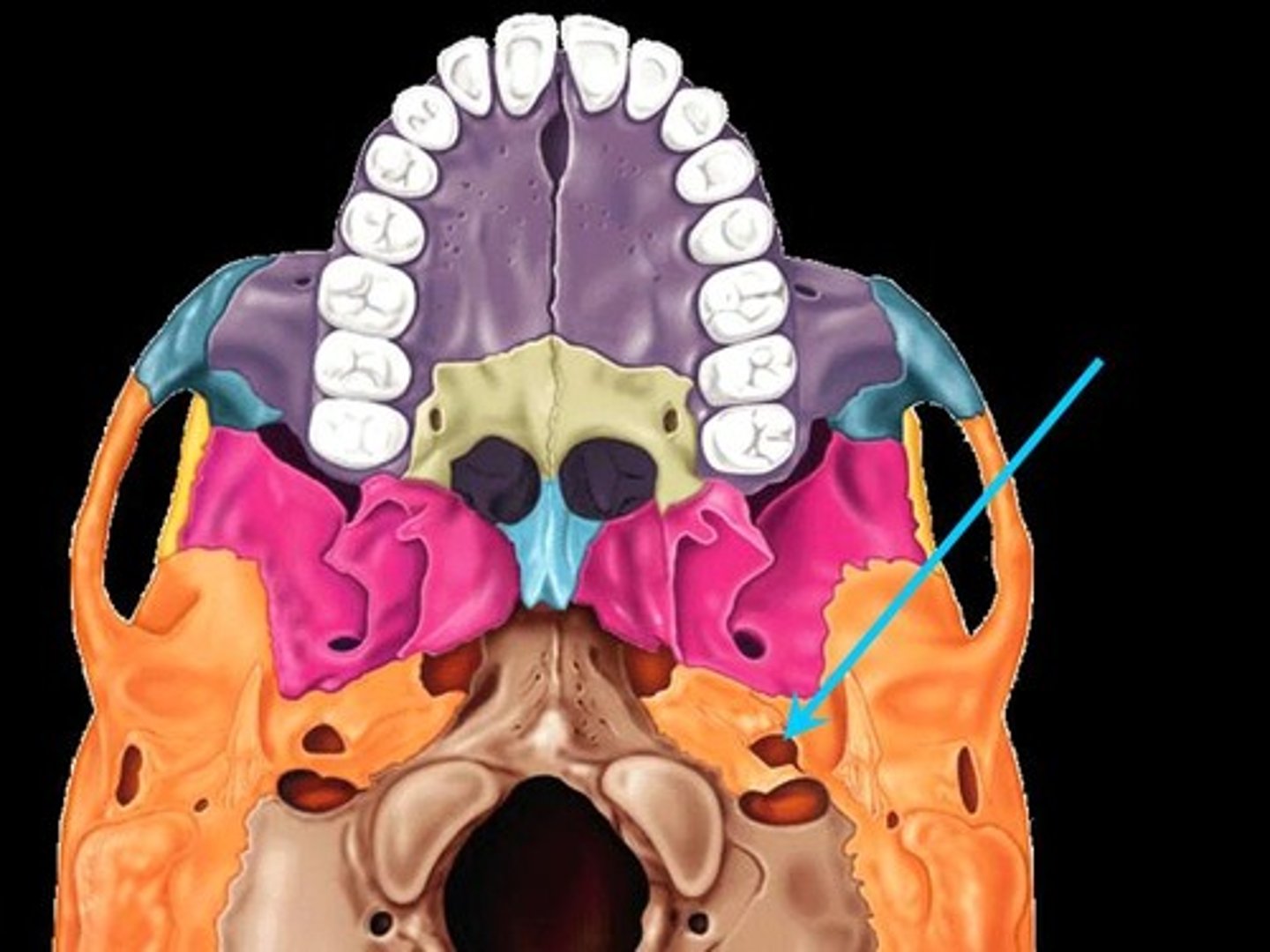
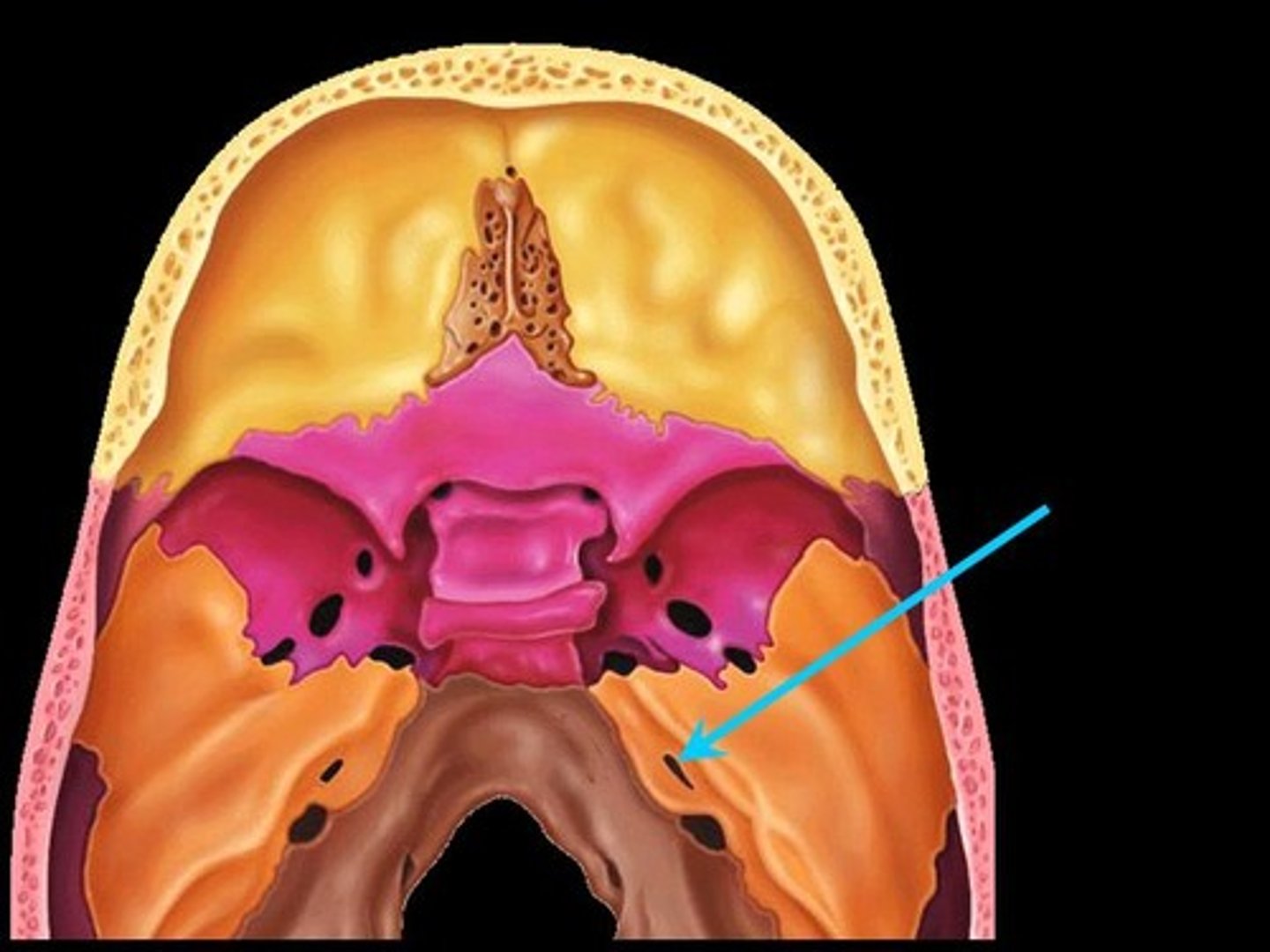
Paranasal Sinuses
Four skull bones (maxillary, sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal) contain sinuses (mucosa-lined air cavities); lighten the skull; may act as resonance chambers for speech
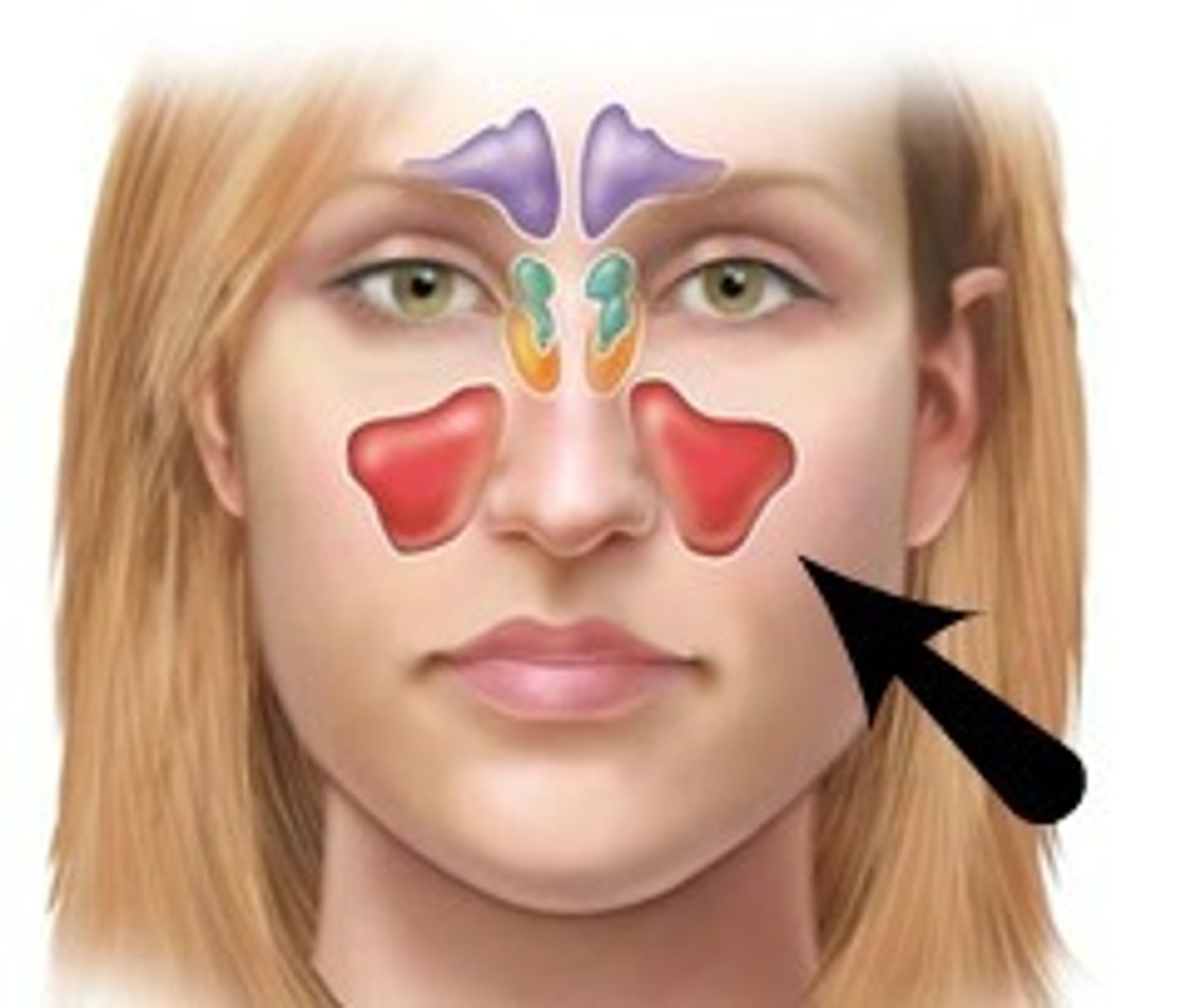
Sinusitis
inflammation of sinuses (from bacterial infection or allergy); as air in sinus cavity is absorbed, partial vacuum forms causing sinus headache; severe infections may require surgery to drain
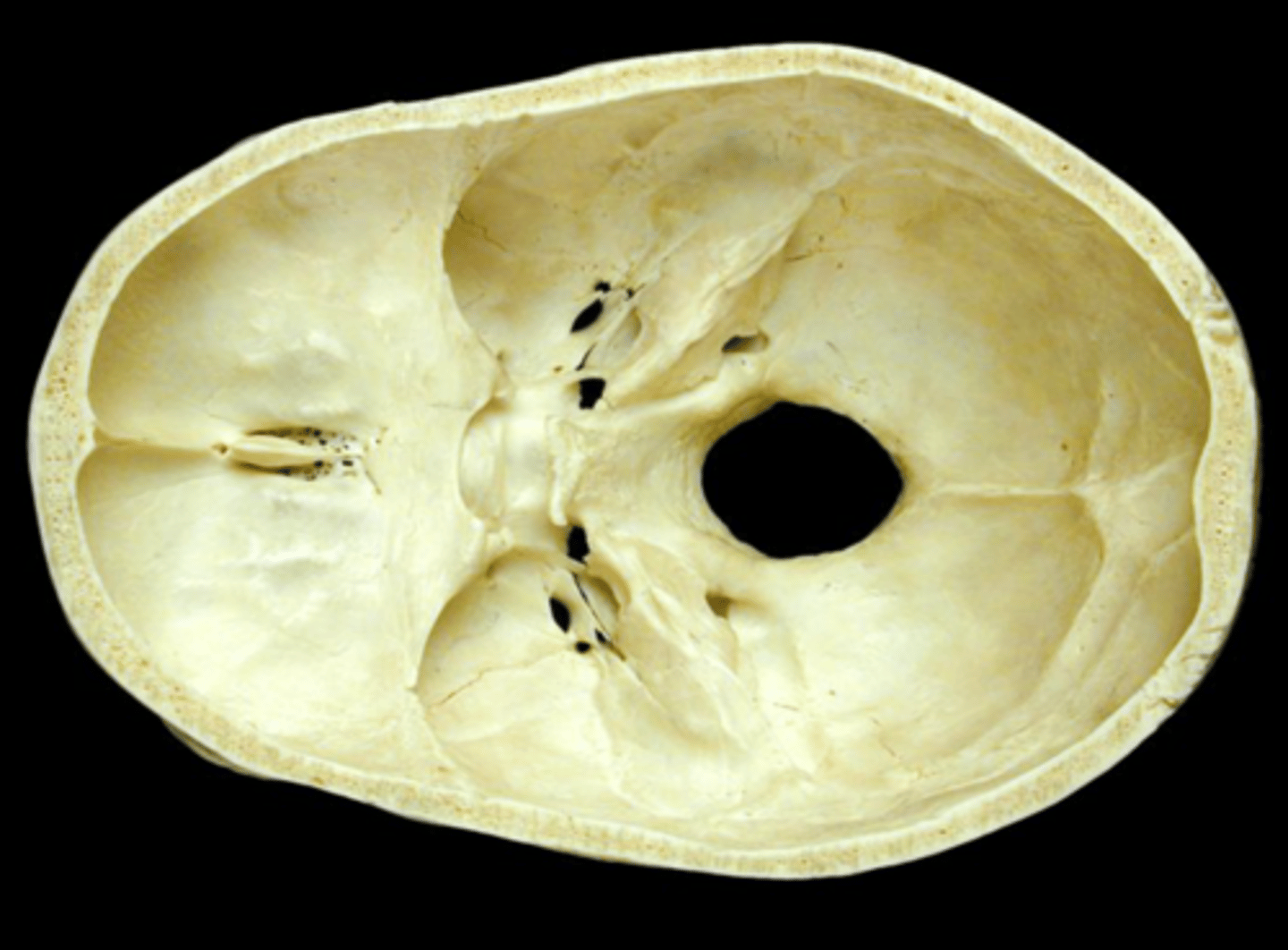
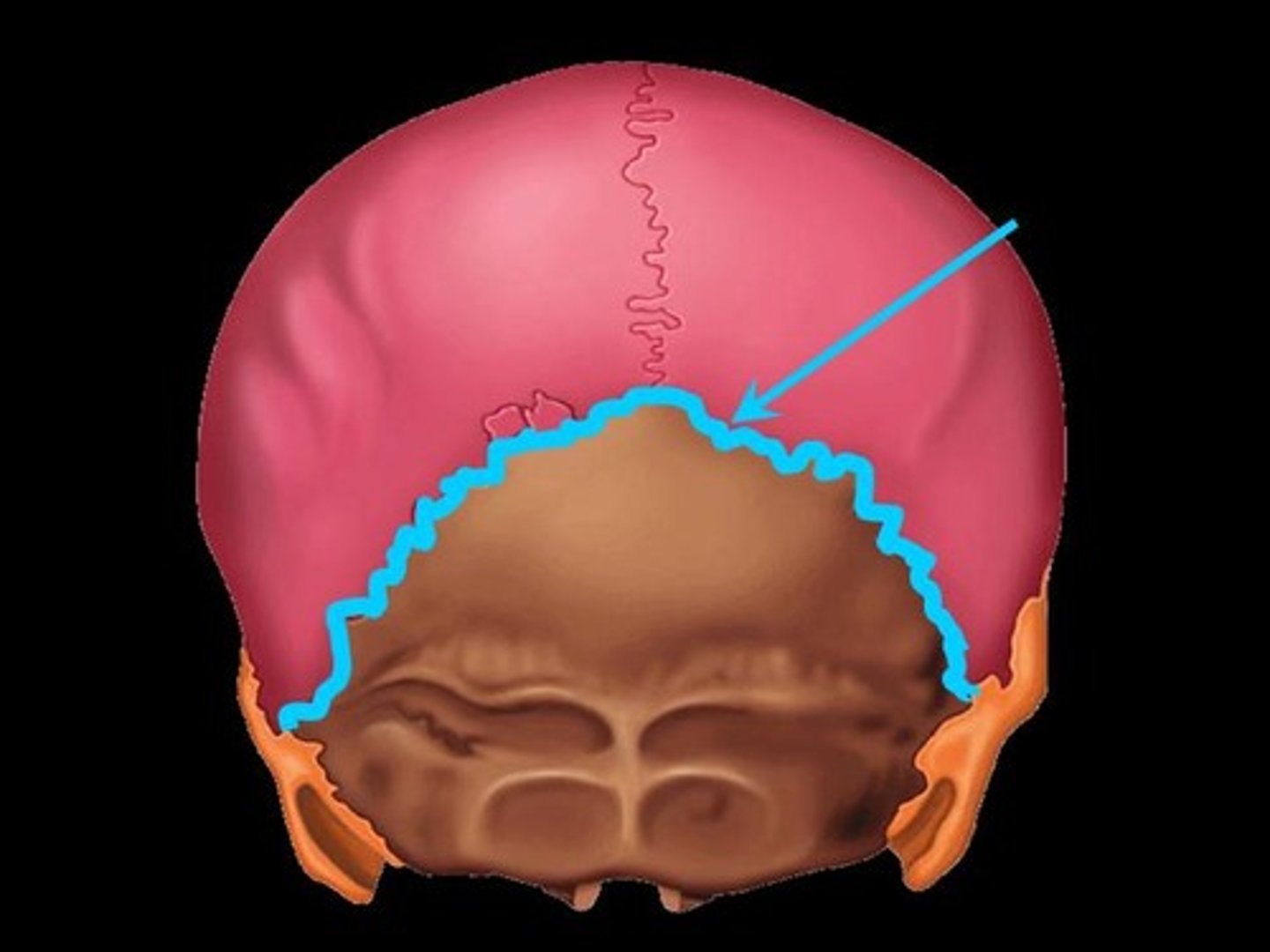
Fetal Skull
contain fontanelles to allow the skull to compress slightly during birth; allows for brain growth during late fetal life
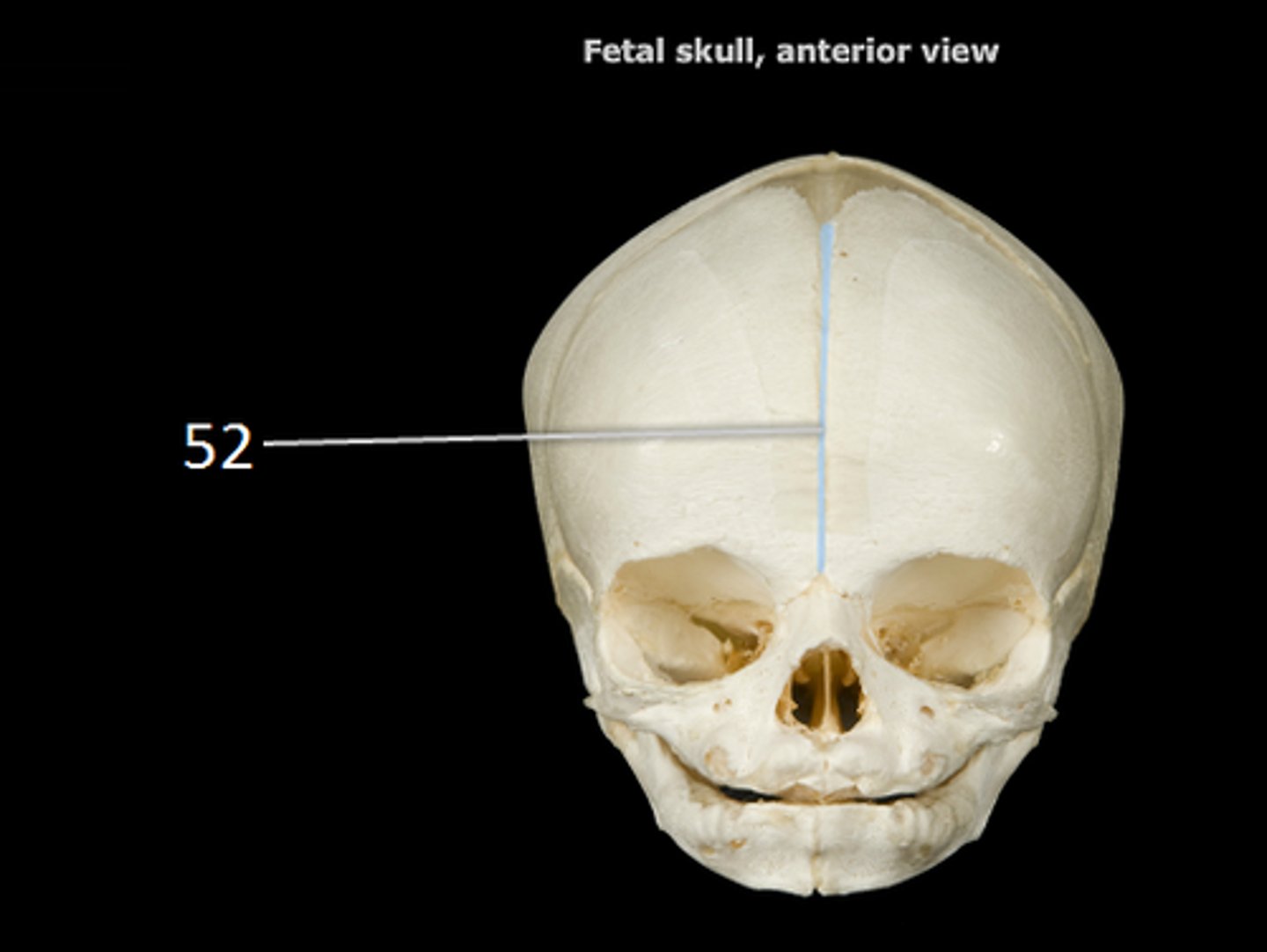
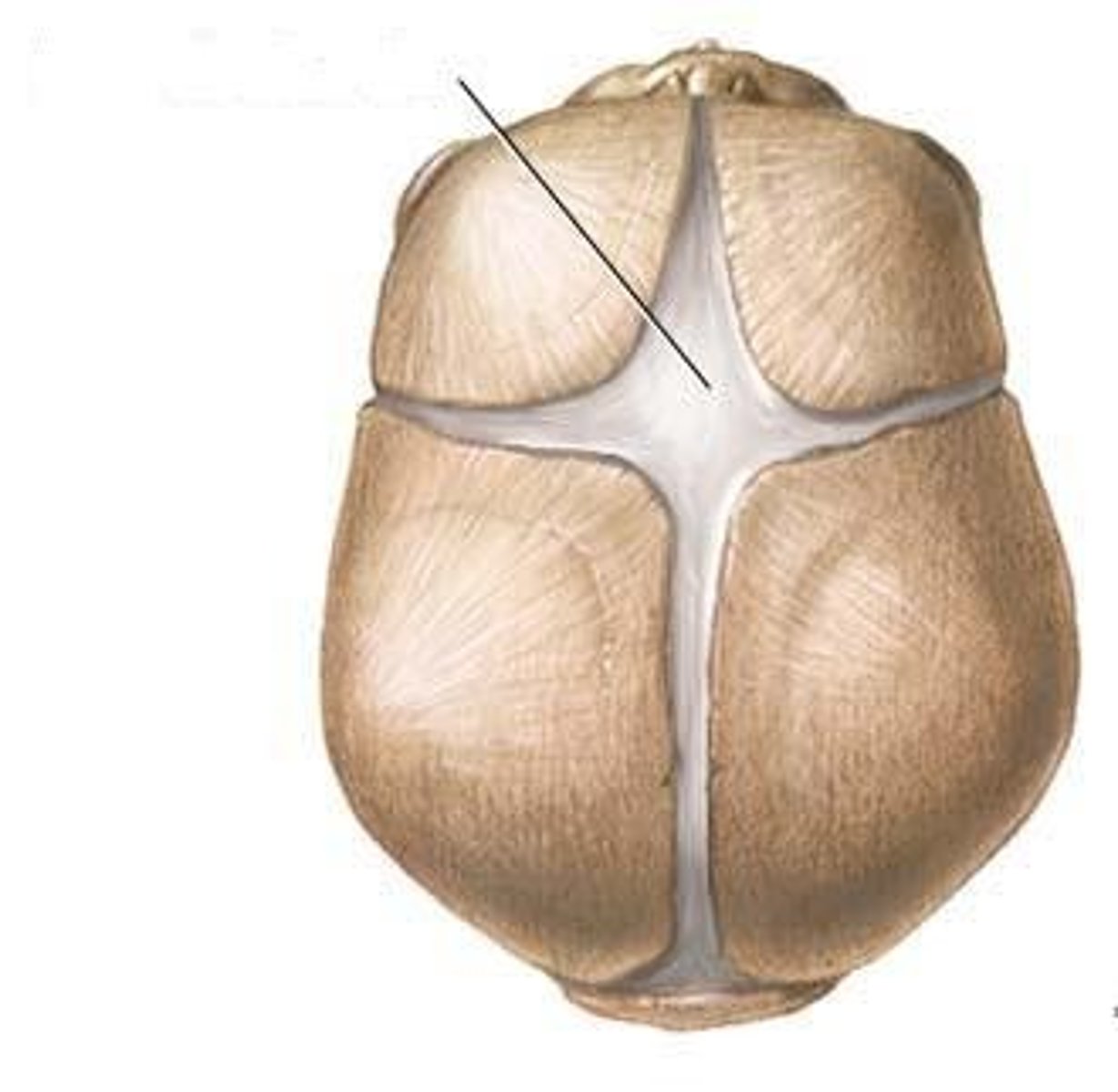
Fontanelles
Areas of fibrous membranes; completely ossify (become bone) by the time the child is 1.5-2 years old
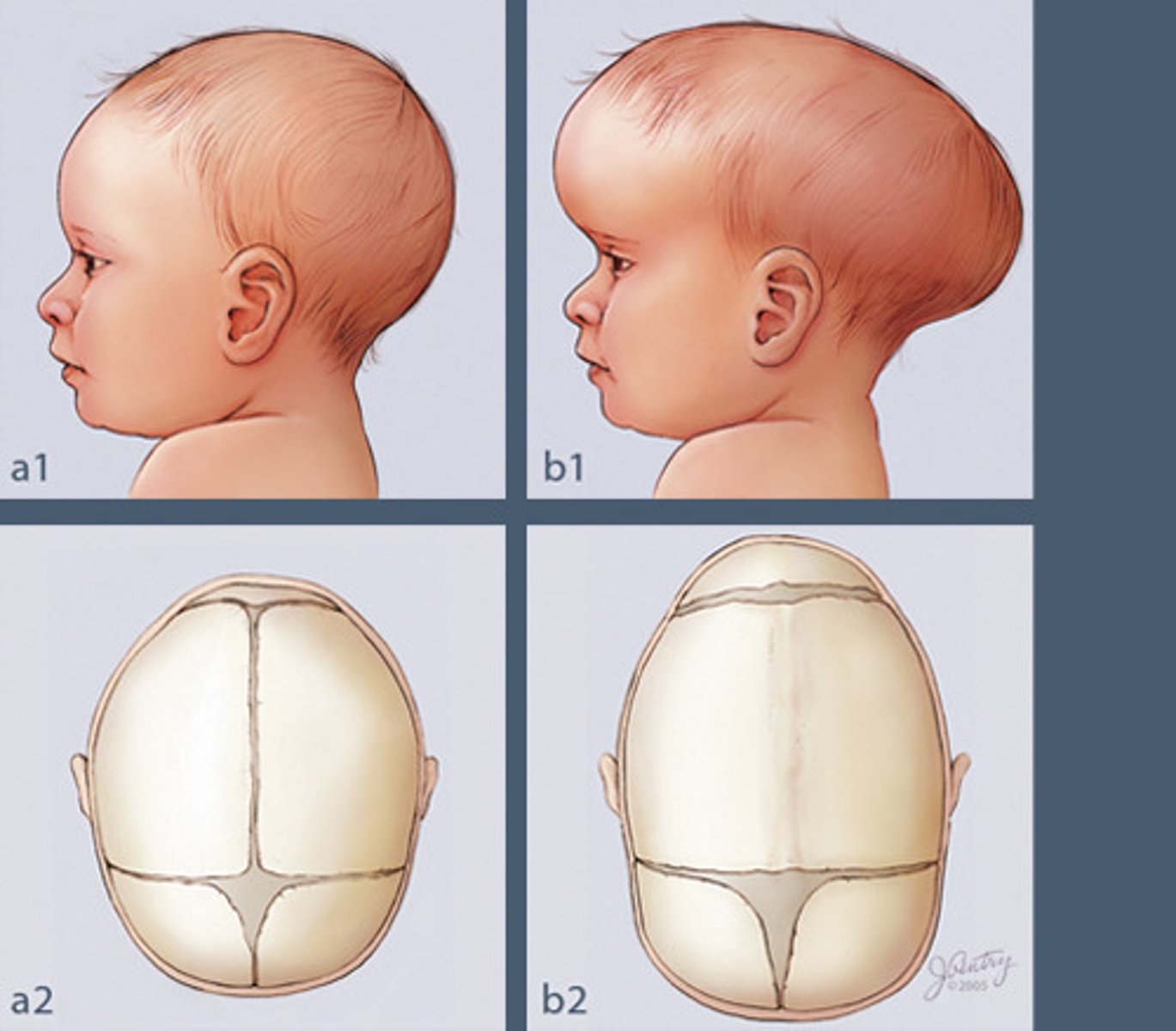
Craniosynostosis
birth defect that causes one or more of the sutures on a baby's head to close earlier than usual; cause: unknown, may be genetic; symptoms: abnormally shaped head, no fontanelles, slow or no increase in head size as baby grows
Vertebral column
24 vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
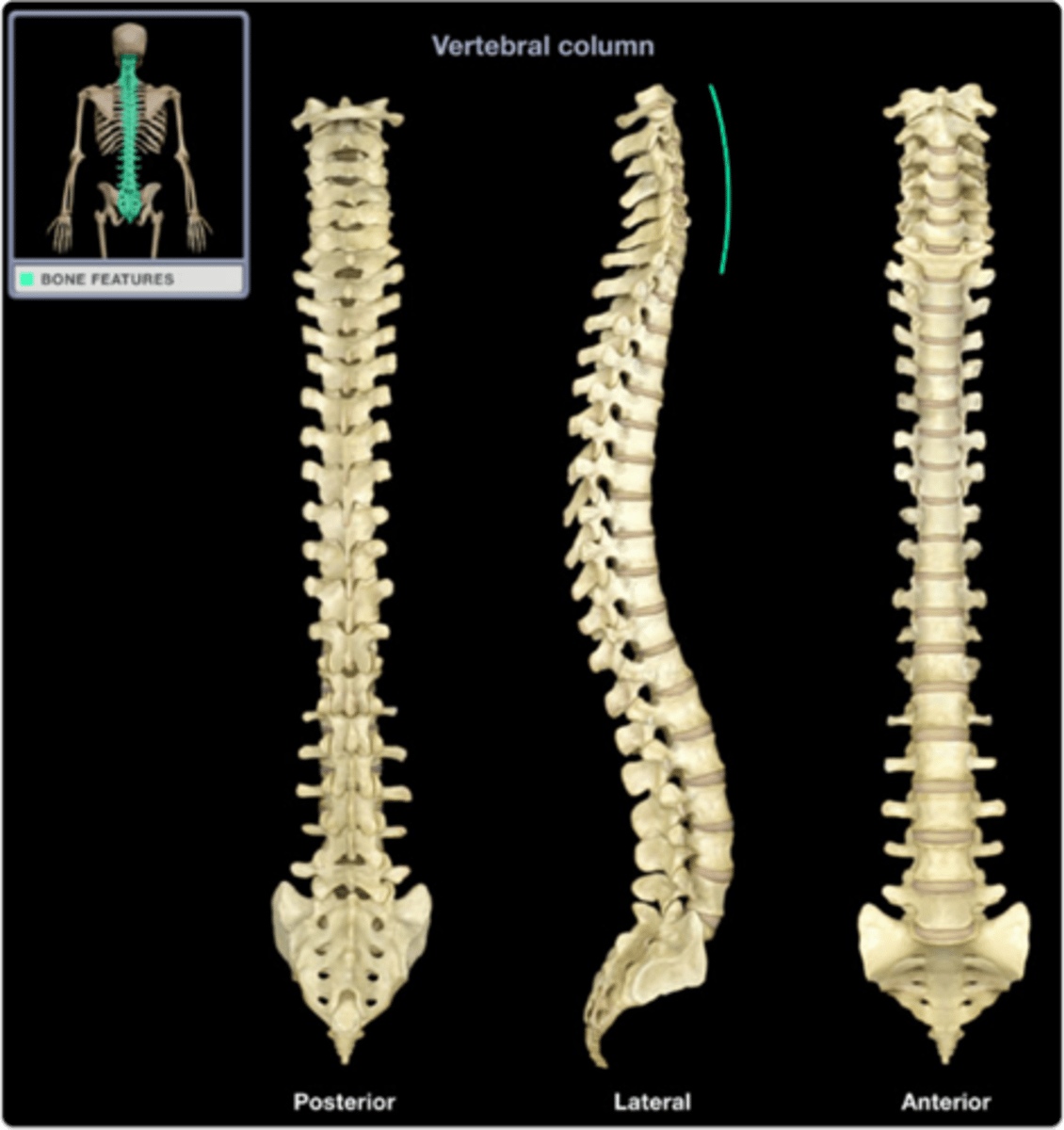
24 vertebrae
7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar

Cervical vertebrae
C1-C7
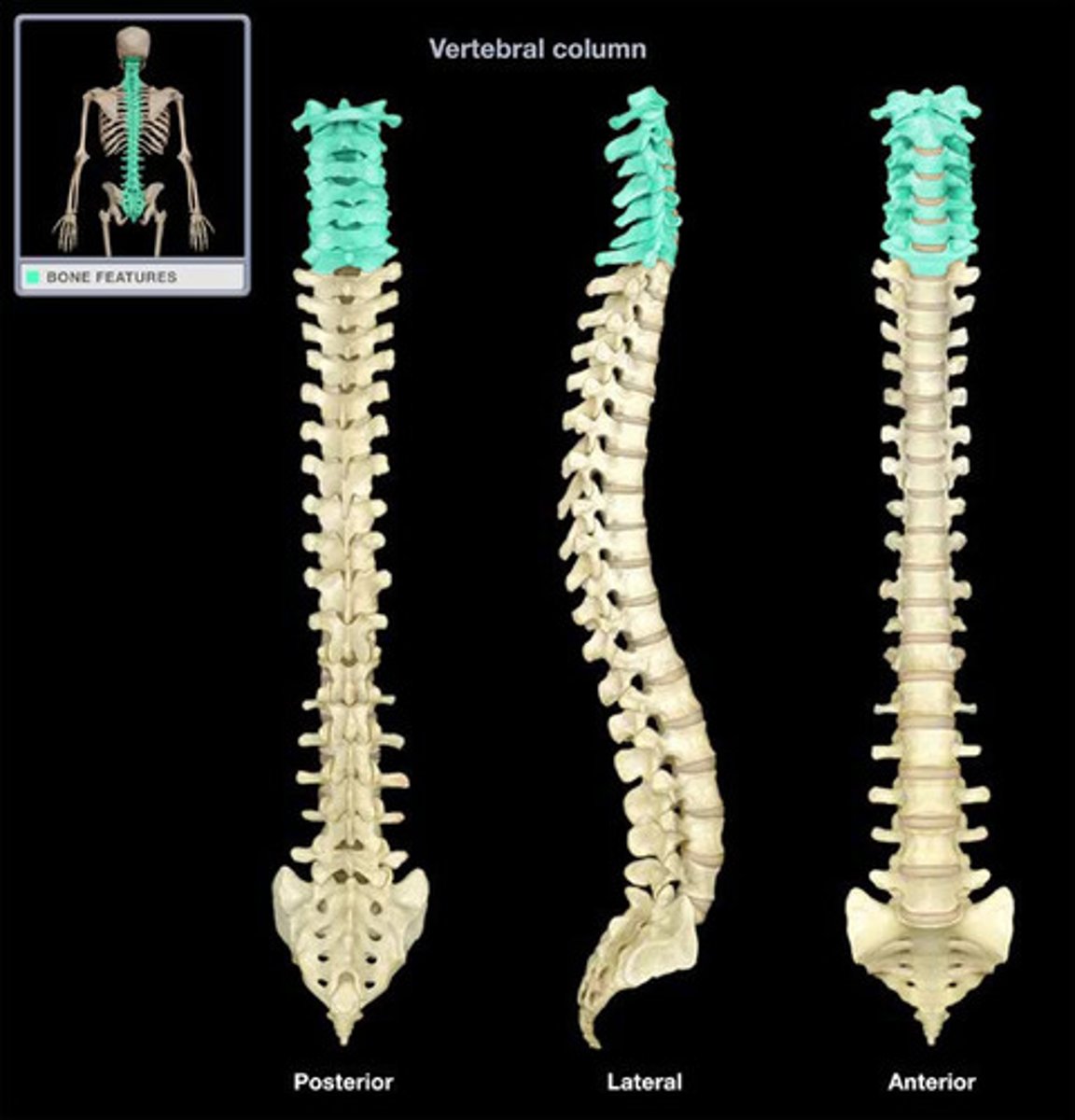
Cervical 1 (C1/atlas)
lacks body and spinous process, allows head to nod

Cervical 2 (C2/axis)
has dens (odontoid process) for head rotation

Cervical 1-7 (C1-C7) distinguishing features
triangular vertebral foramen, transverse processes contain foramen/foramina for vertebral arteries traveling to brain, C7 (vertebra prominens) is a landmark for counting vertebrae
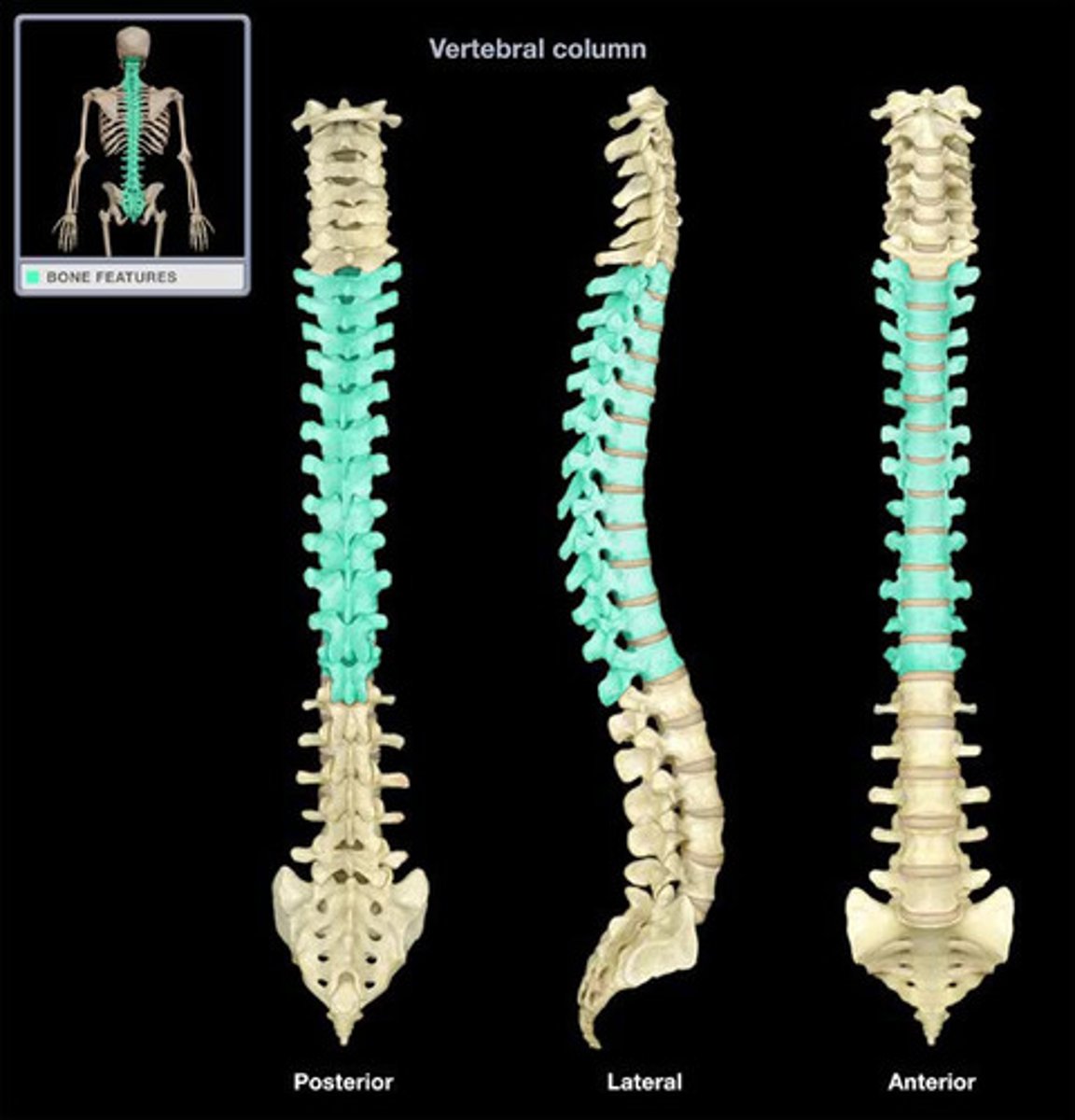
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12) distinguishing features
heart shaped body, small articulating surfaces/costal facets (superior and inferior) articulates with head of rib, round/oval vertebral foramen, transverse costal facets (on transverse process) articulate with rib tubercles
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5) distinguishing features
block-like body & short thick spinous process, superior articular process pointing posteromedial, inferior articular process pointing anterolateral, spinal cord ends at superior area of L2
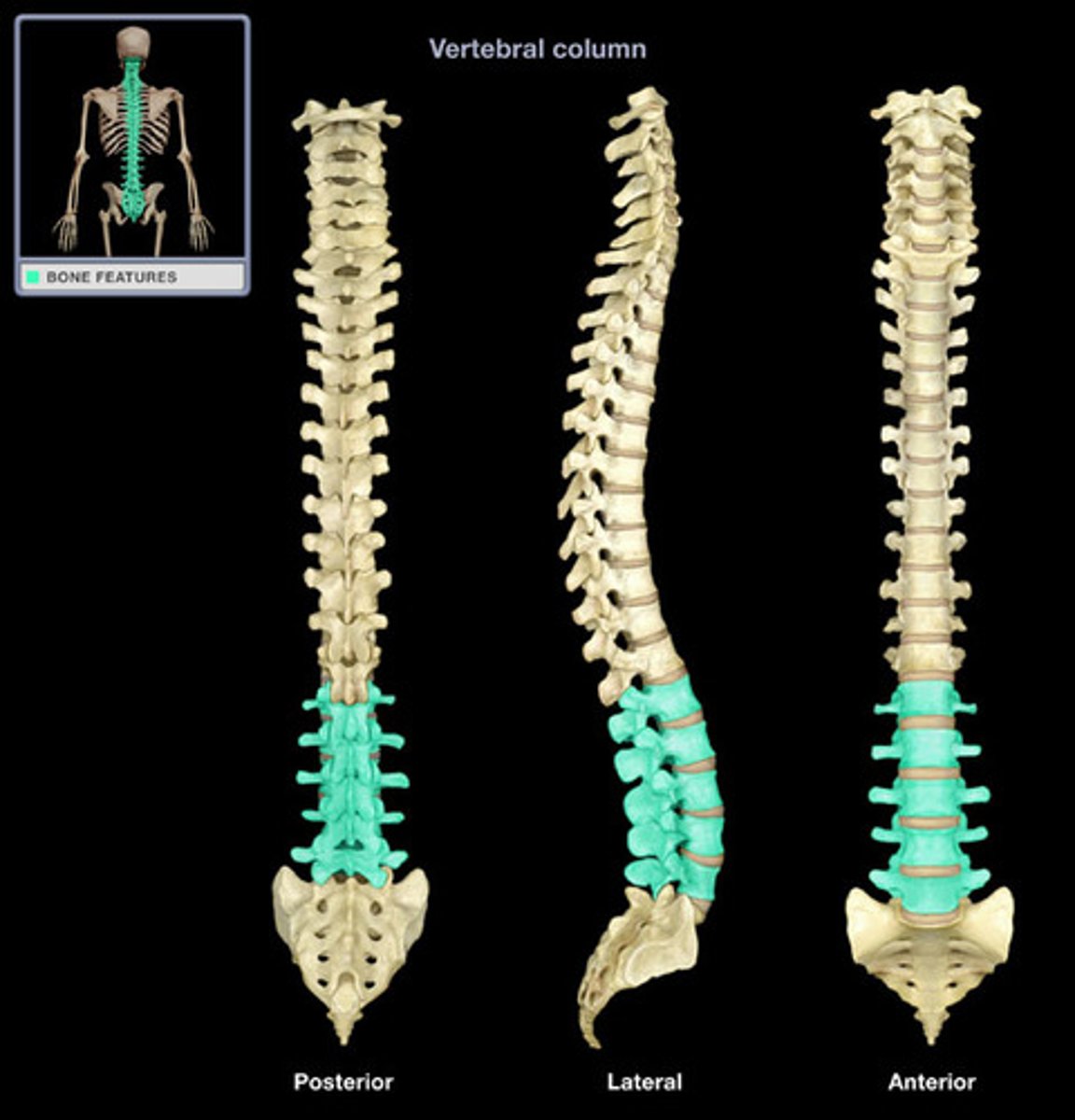
Spinal/lumbar 'tap' performed between...
between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5 to minimize injury to spinal cord. Administration of anesthesia for childbirth also performs in these regions
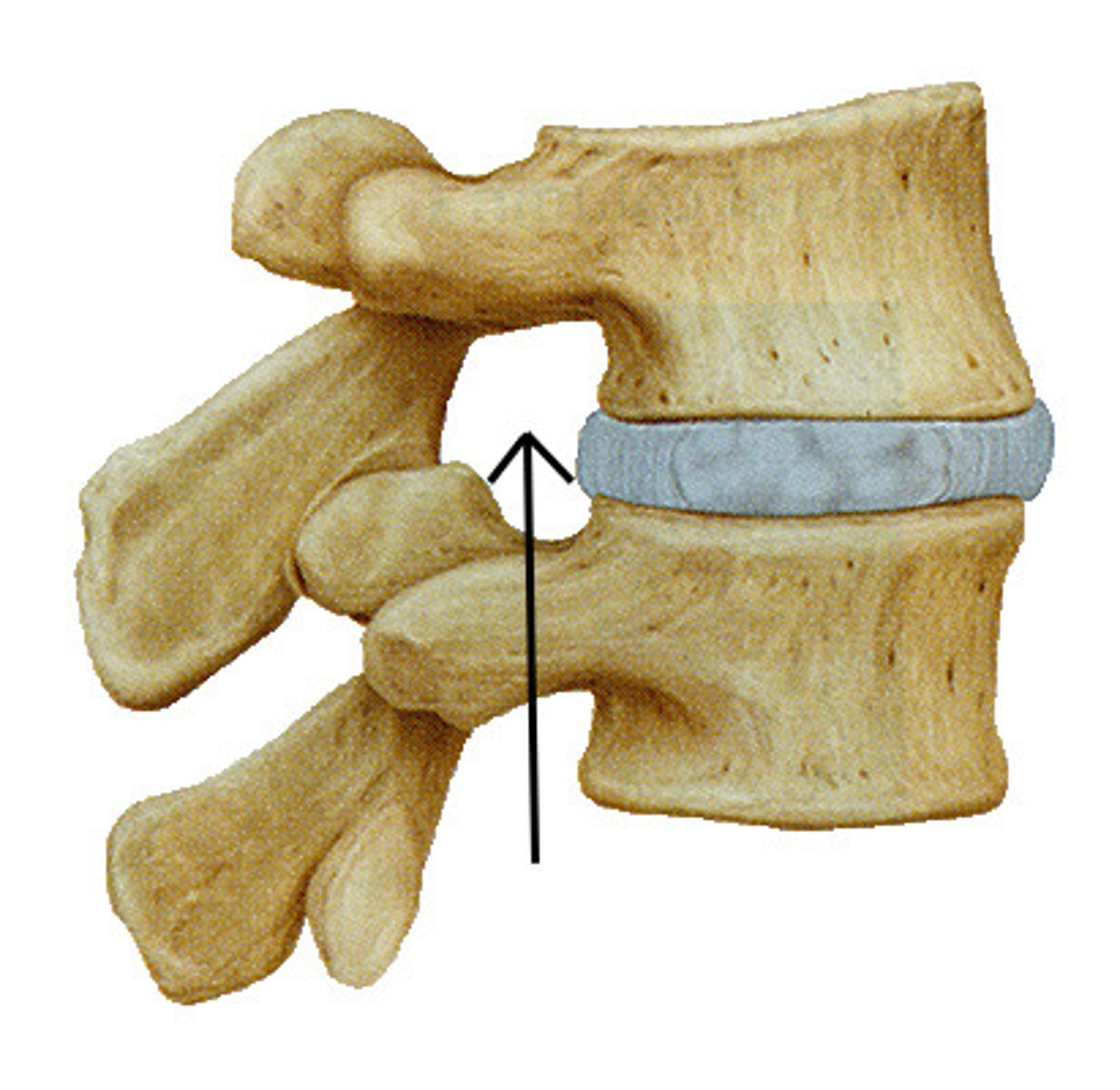
Intervertebral Foramen
A foramen exists between the inferior notch of a superior vertebra and the superior notch of an inferior vertebra; for nerves to enter or exit the spinal cord
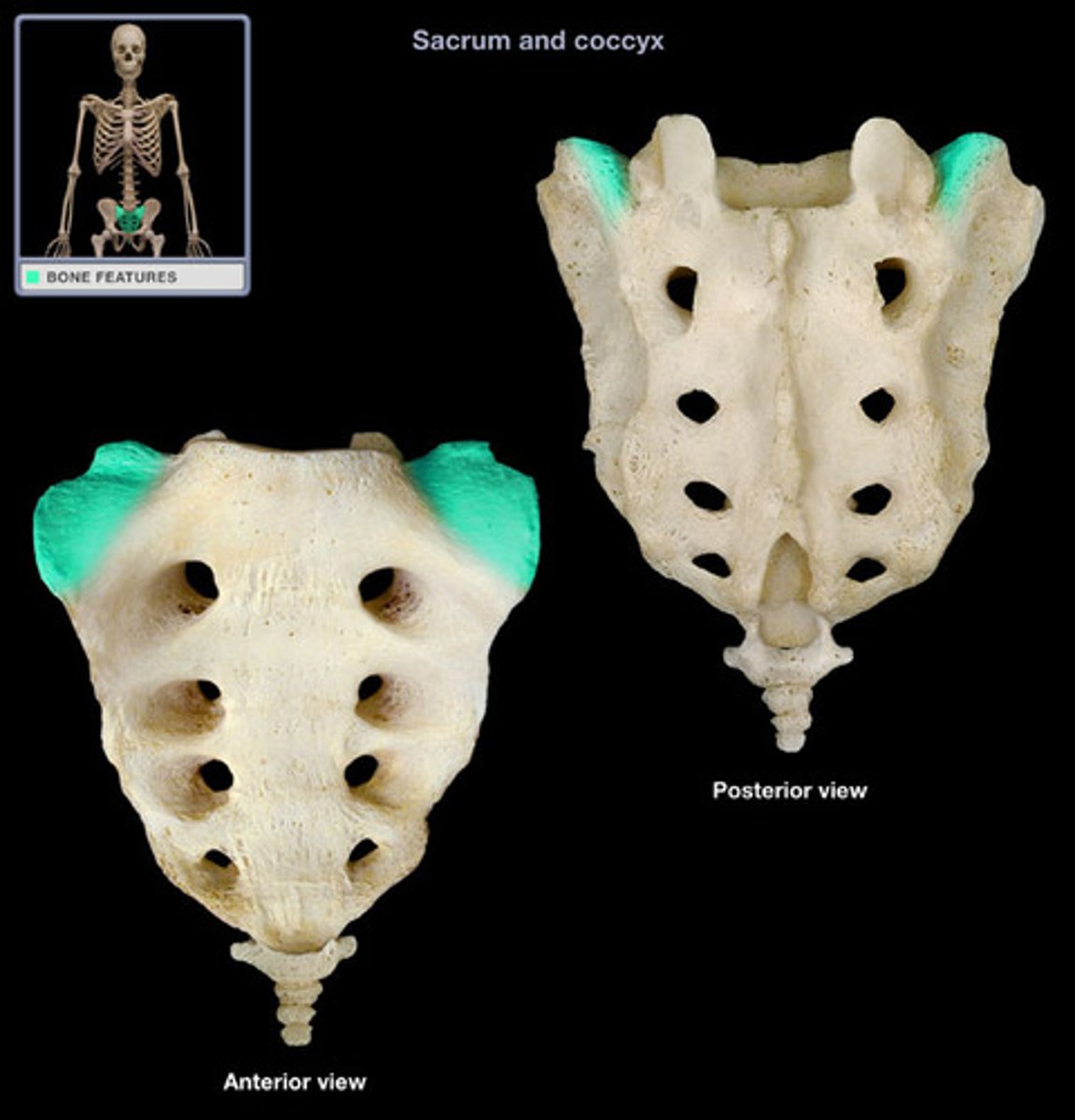
Sacrum
Formed by fusion of 5 bones
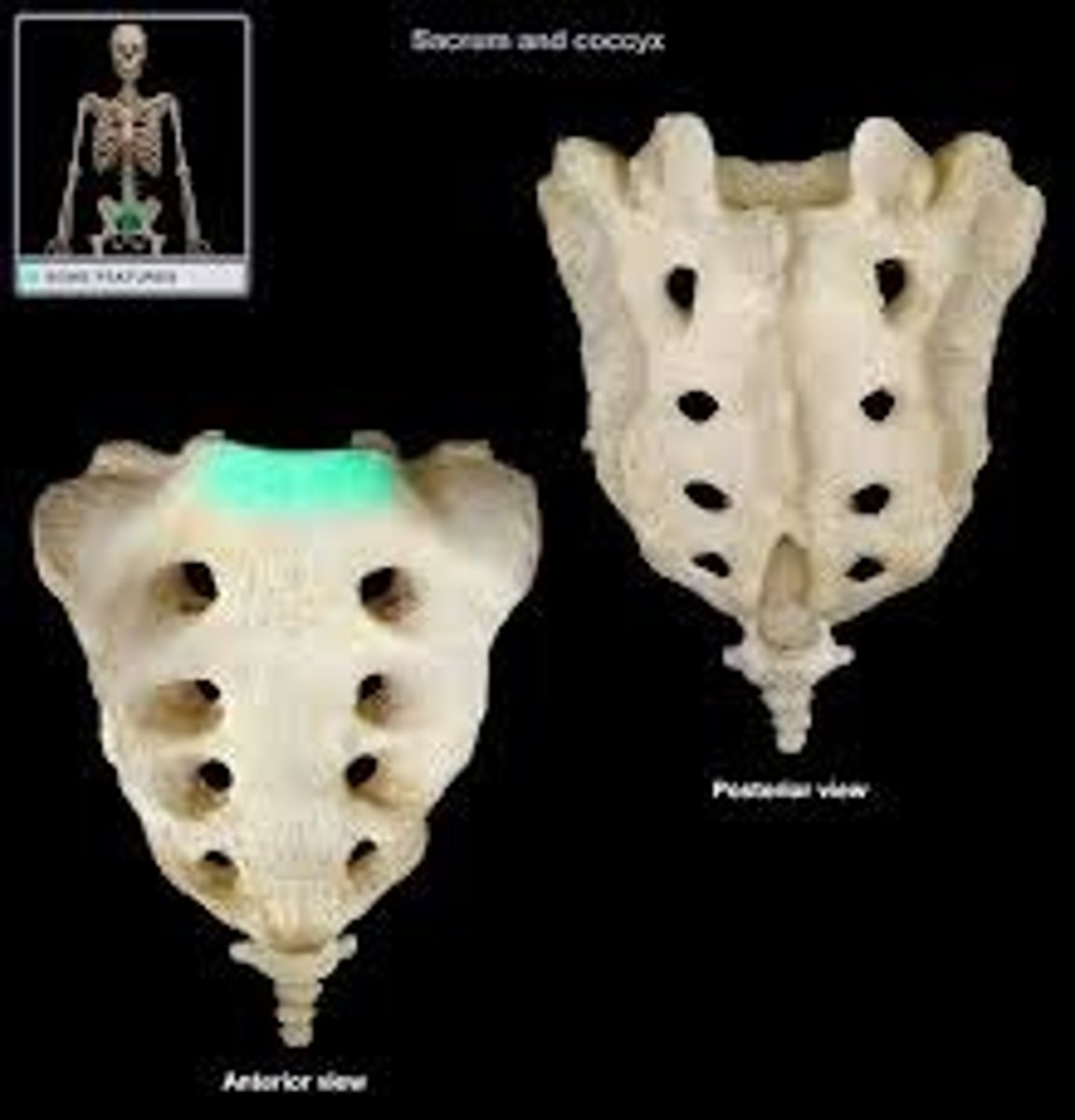
Sacrum prominent features
Sacral promontory, median sacral crest, ala, transverse ridges, anterior/posterior sacral formina
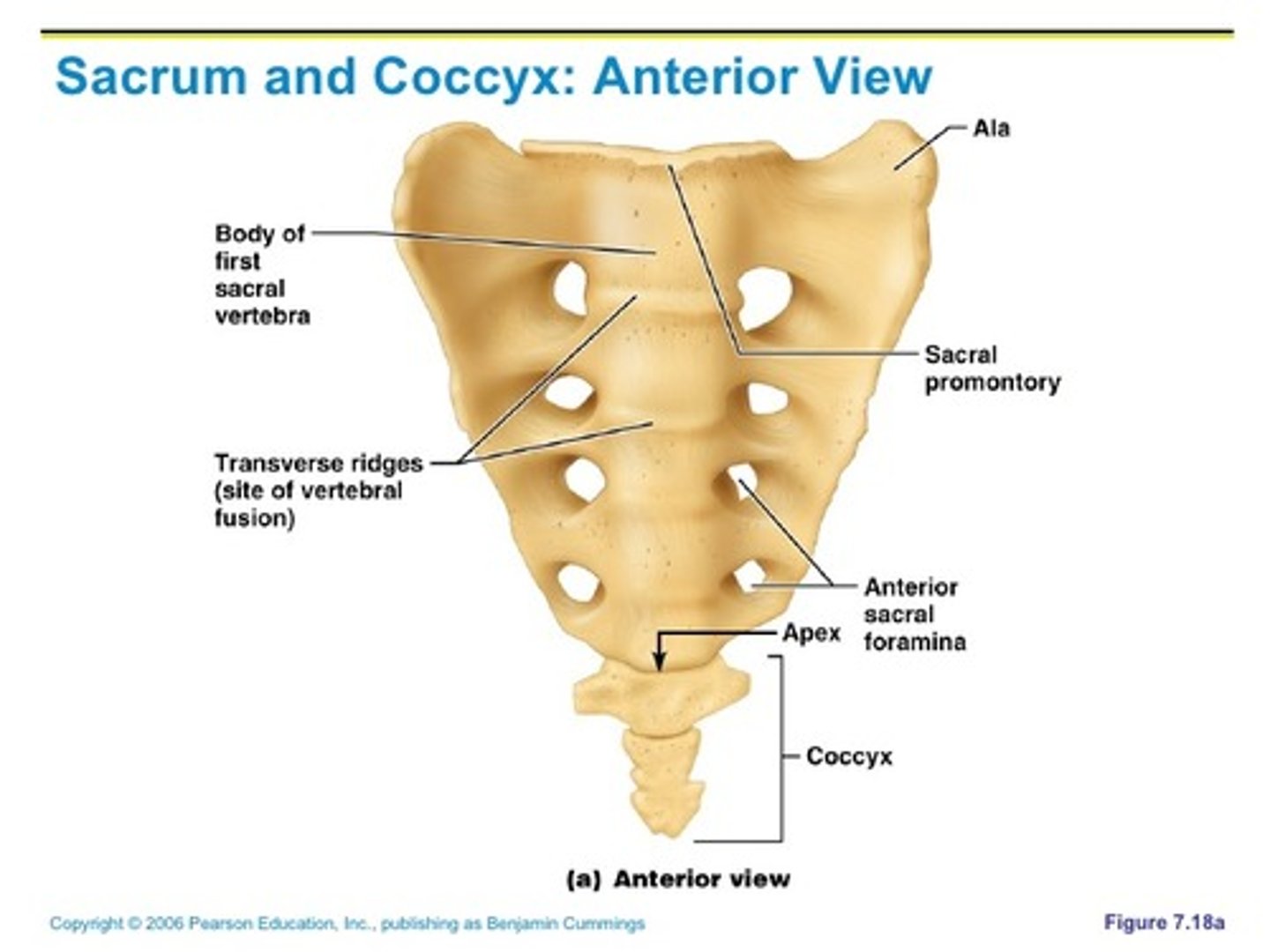
Sacral promontory of sacrum
at anterior border of S1
Median sacral crest of sacrum
remnant of fused spinous processes

Ala of sacrum
formed by fusion of transverse processes
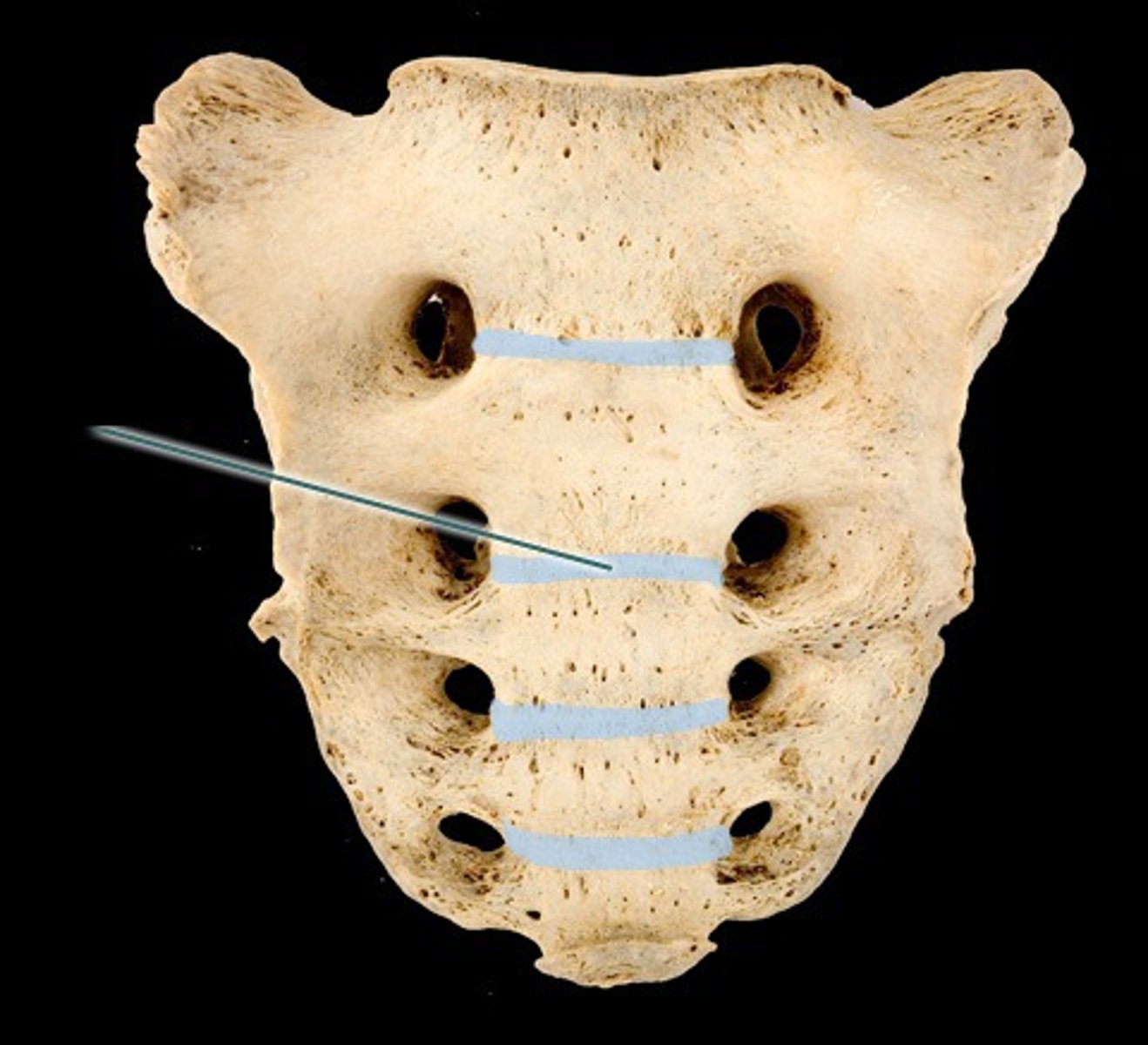
Transverse ridges of sacrum
site of vertebral fusion
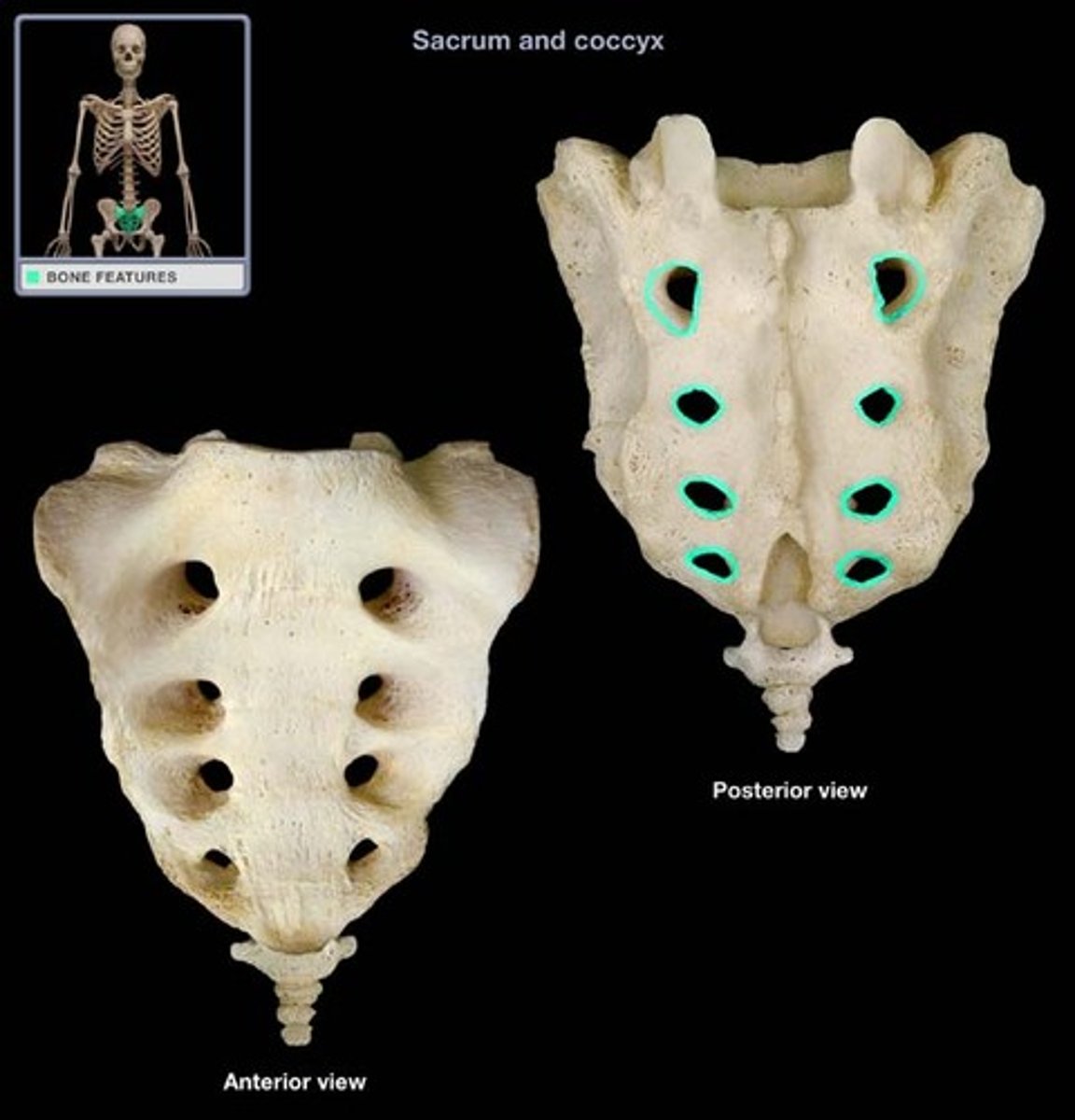
Anterior/Posterior sacral foramina of sacrum
passage for blood vessels and nerves
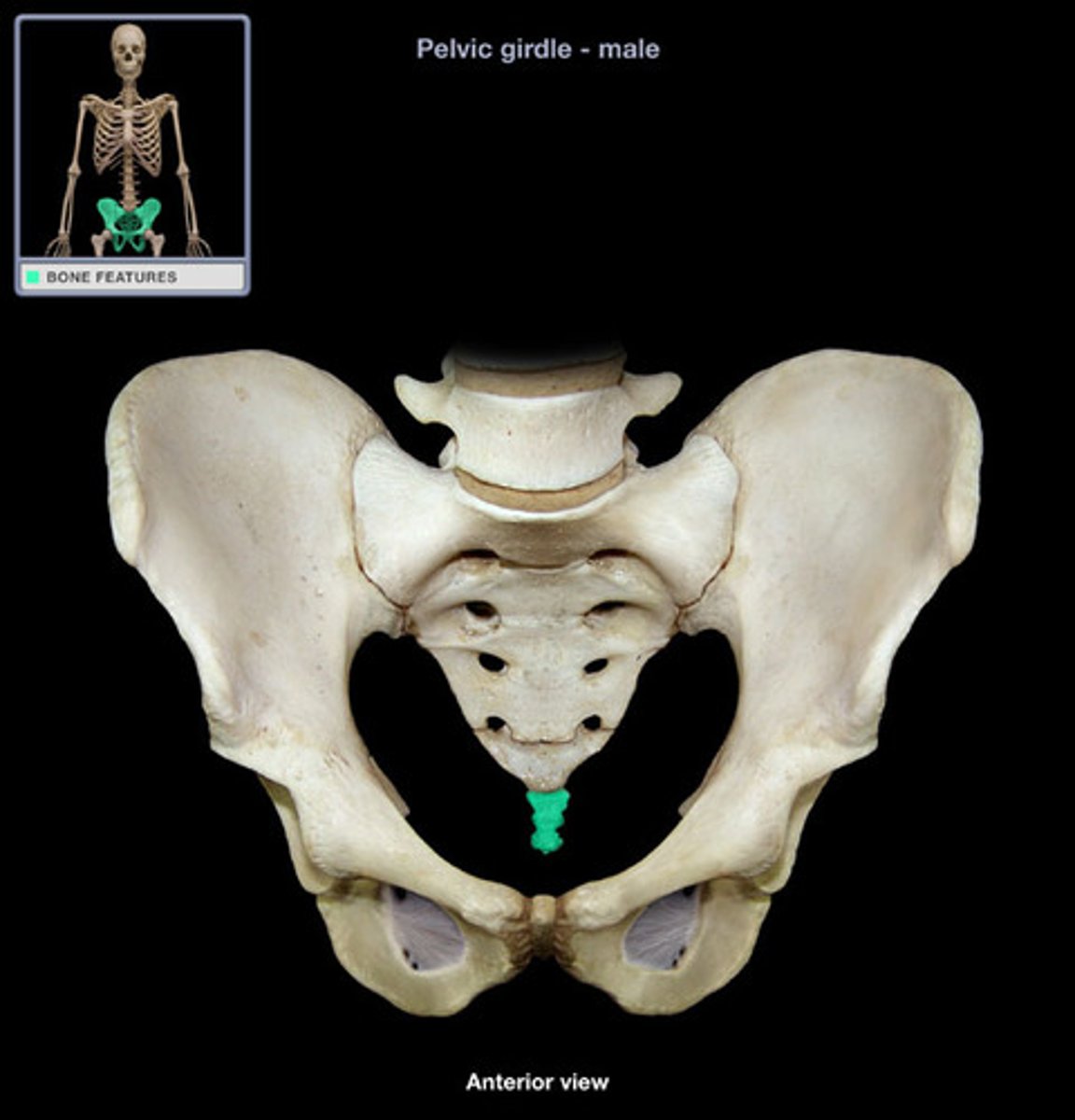
Coccyx
Commonly known as the "tailbone"; It is formed by fusion of 3-5 irregularly shaped vertebrae; Attached to sacrum by ligaments
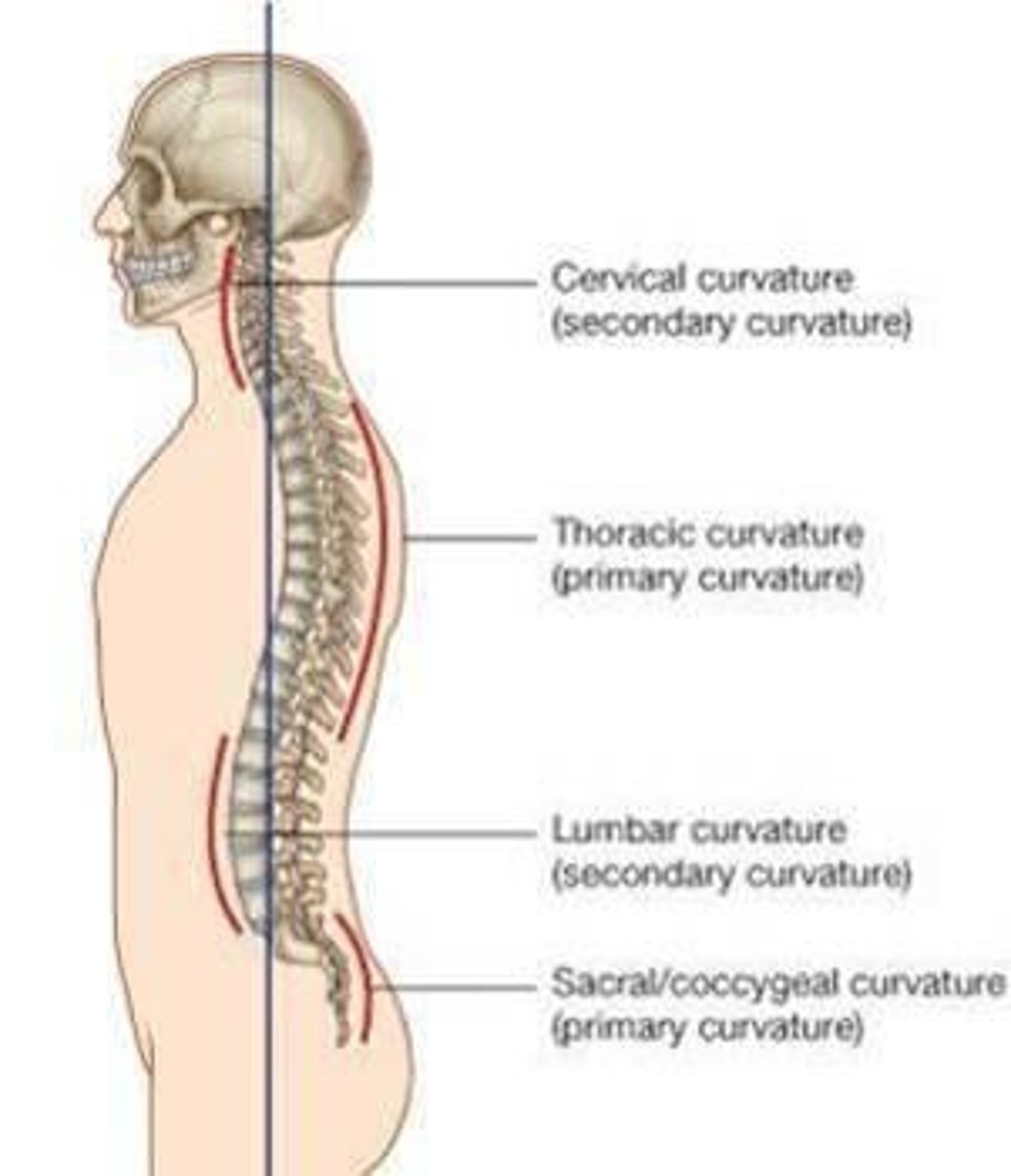
Spinal Curvatures
Primary and secondary curvatures

Primary curvatures
present at birth (thoracic & sacral curvatures)
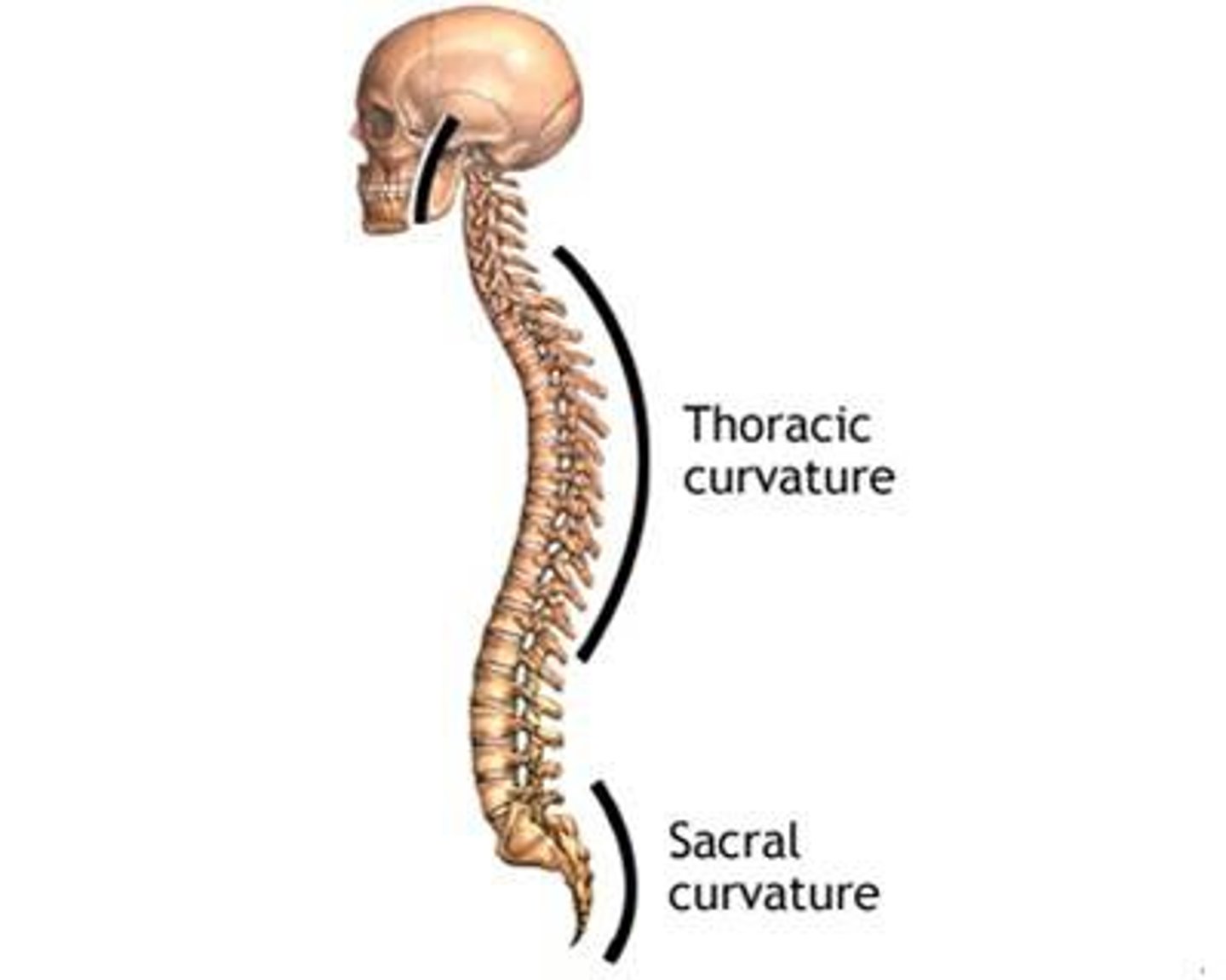
Secondary curvatures
develop after birth (cervical & lumbar curvatures)
Cervical curvature allows...
baby to hold head up
Lumbar curvature allows...
baby to walk

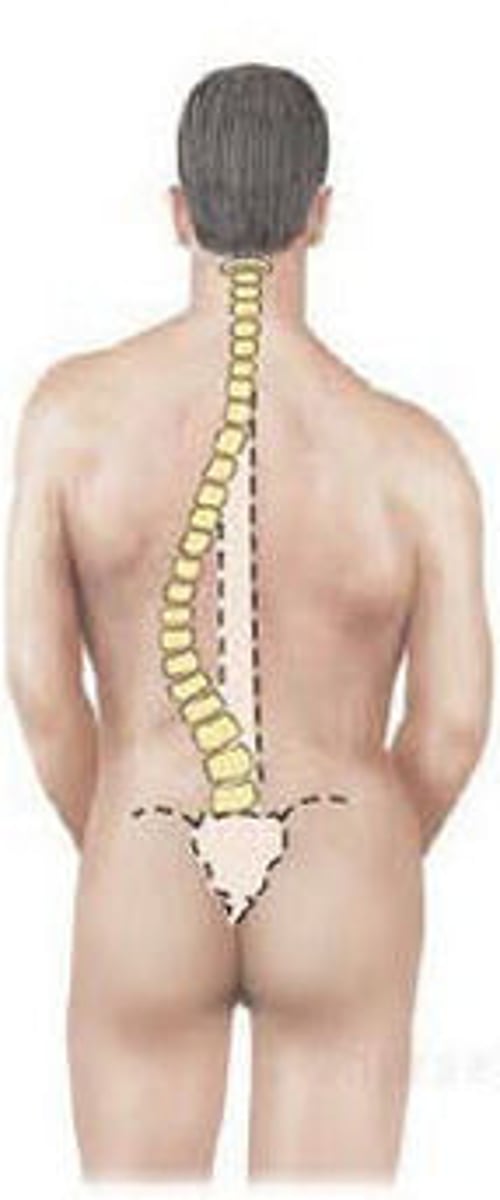
Abnormal curvatures
scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis

Scoliosis
lateral thoracic spine curvature
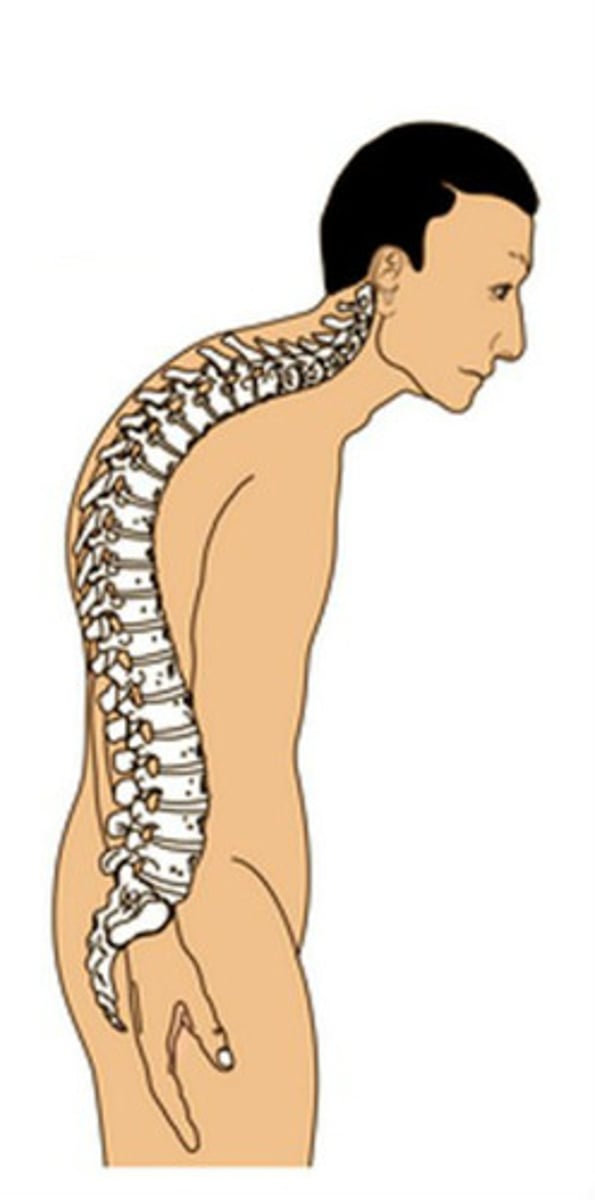
Kyphosis
excessive posterior thoracic curvature
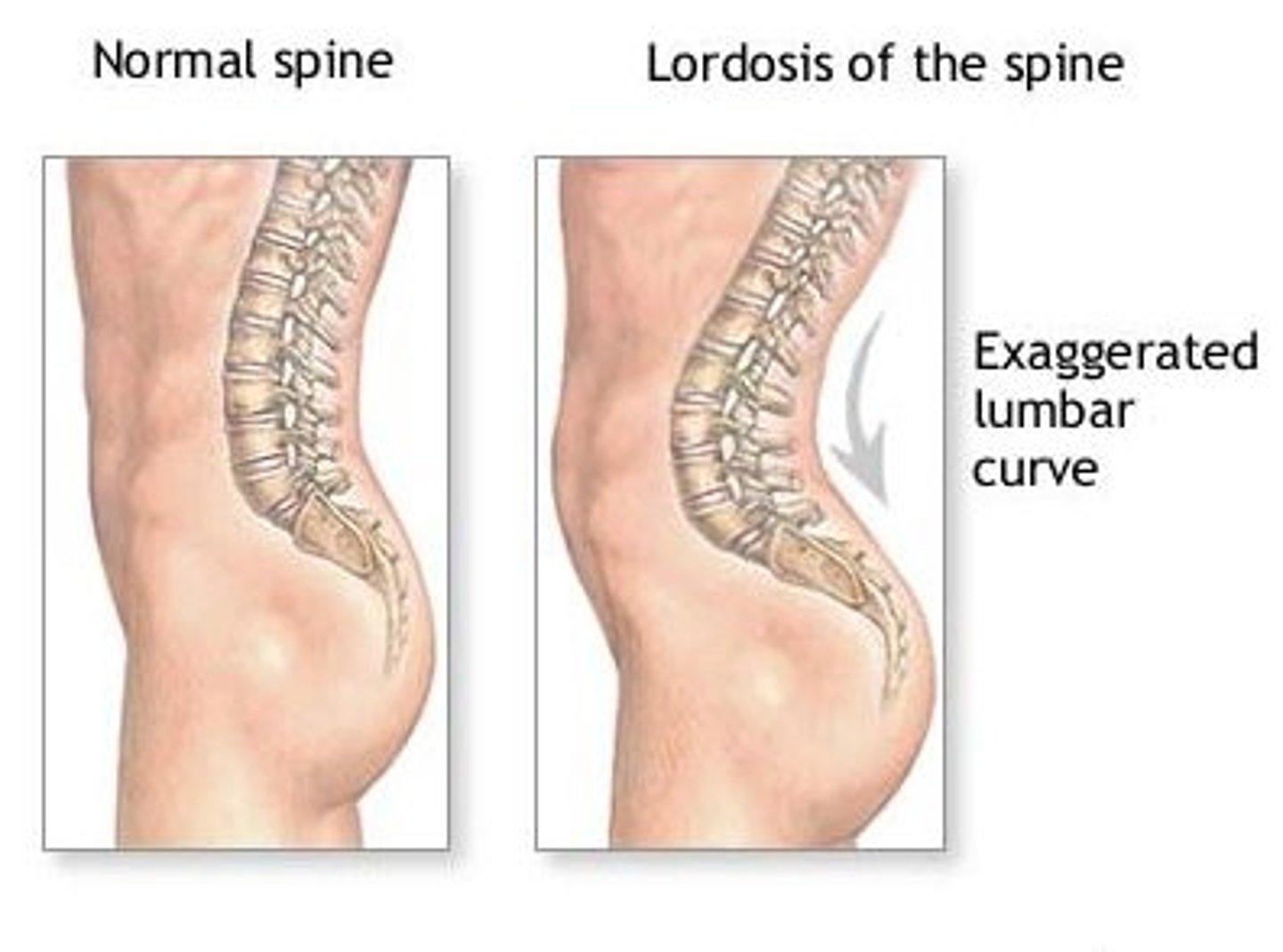
Lordosis
excessive lumbar curvature
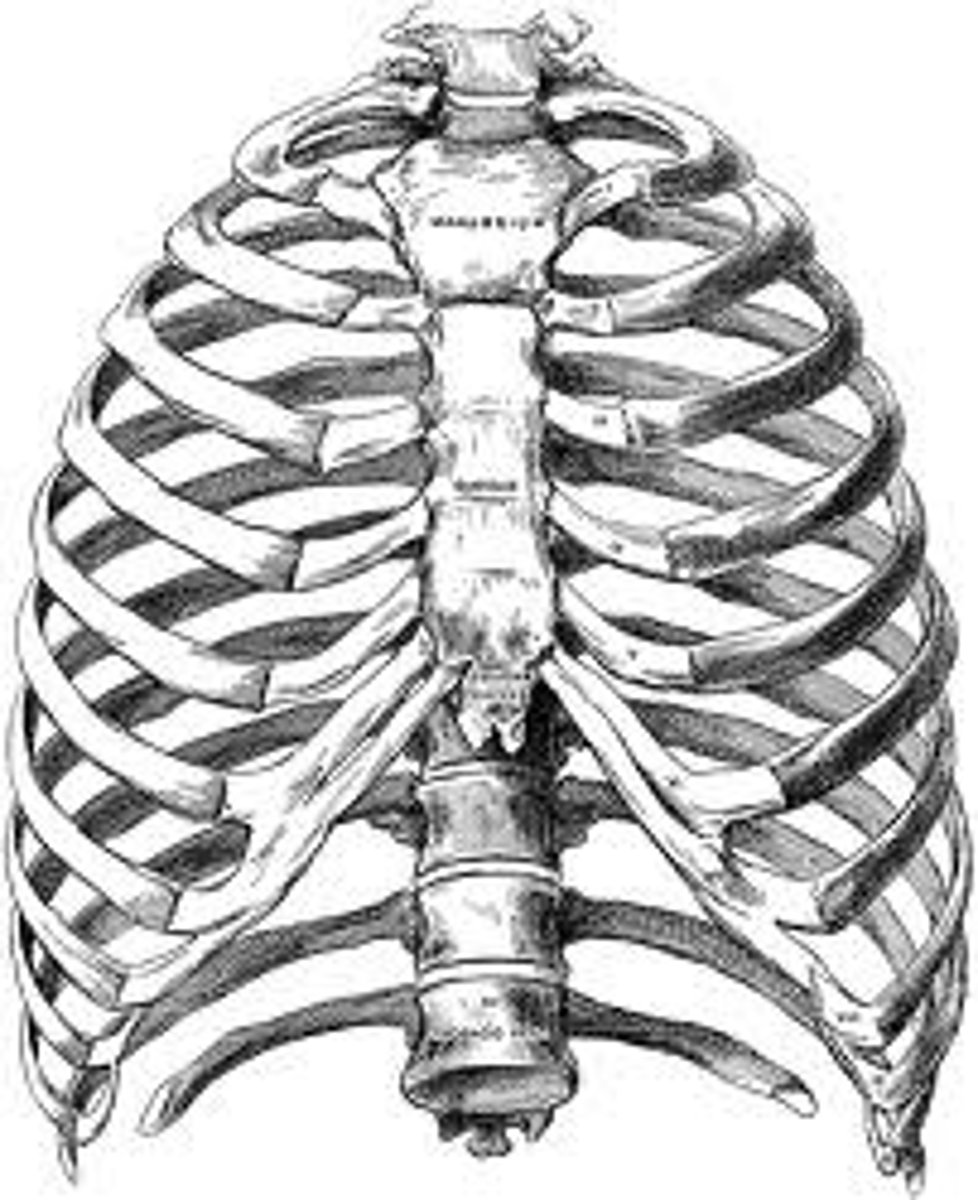
Bony Thorax Composed of...
sternum, ribs, thoracic vertebrae
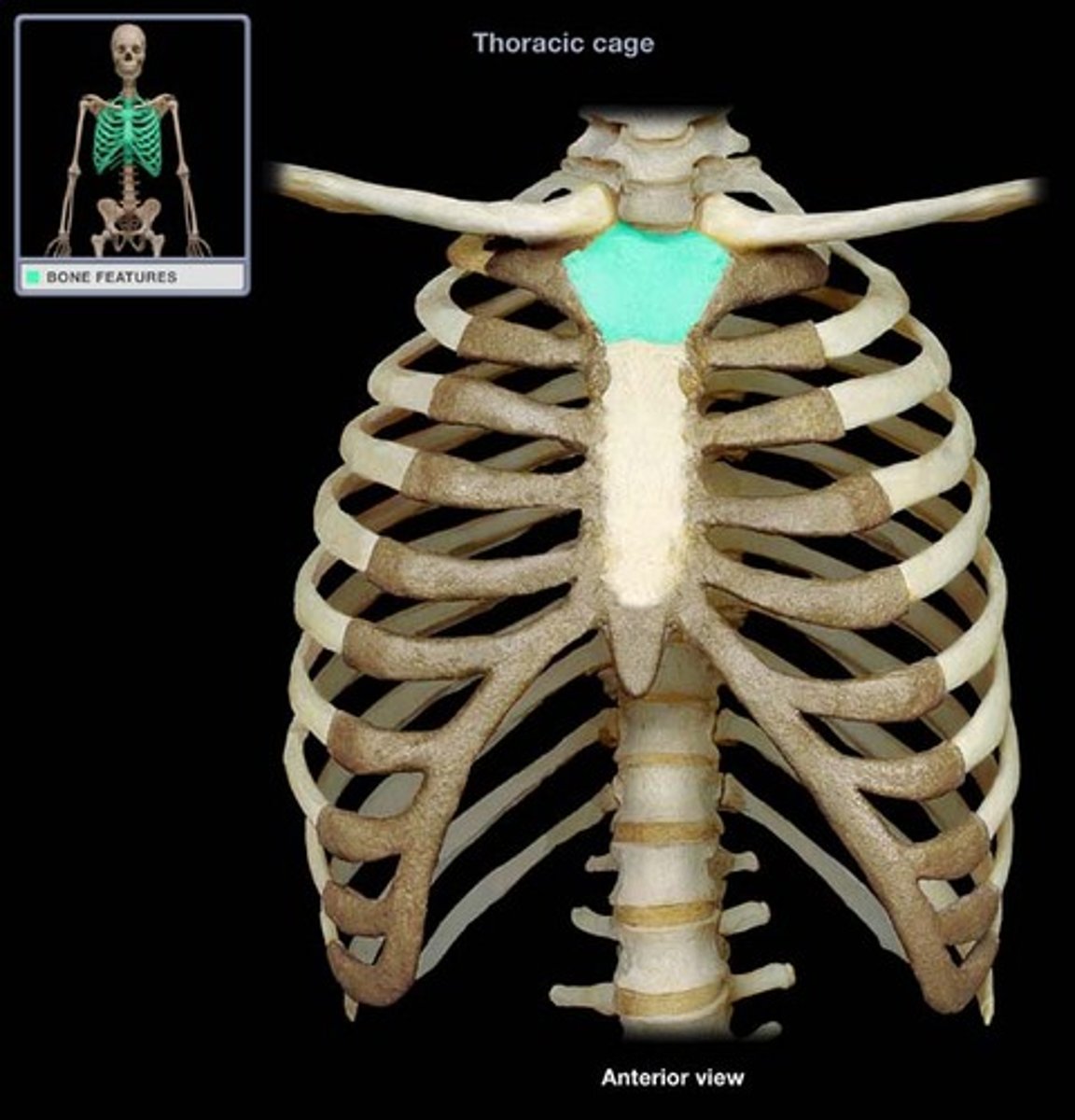
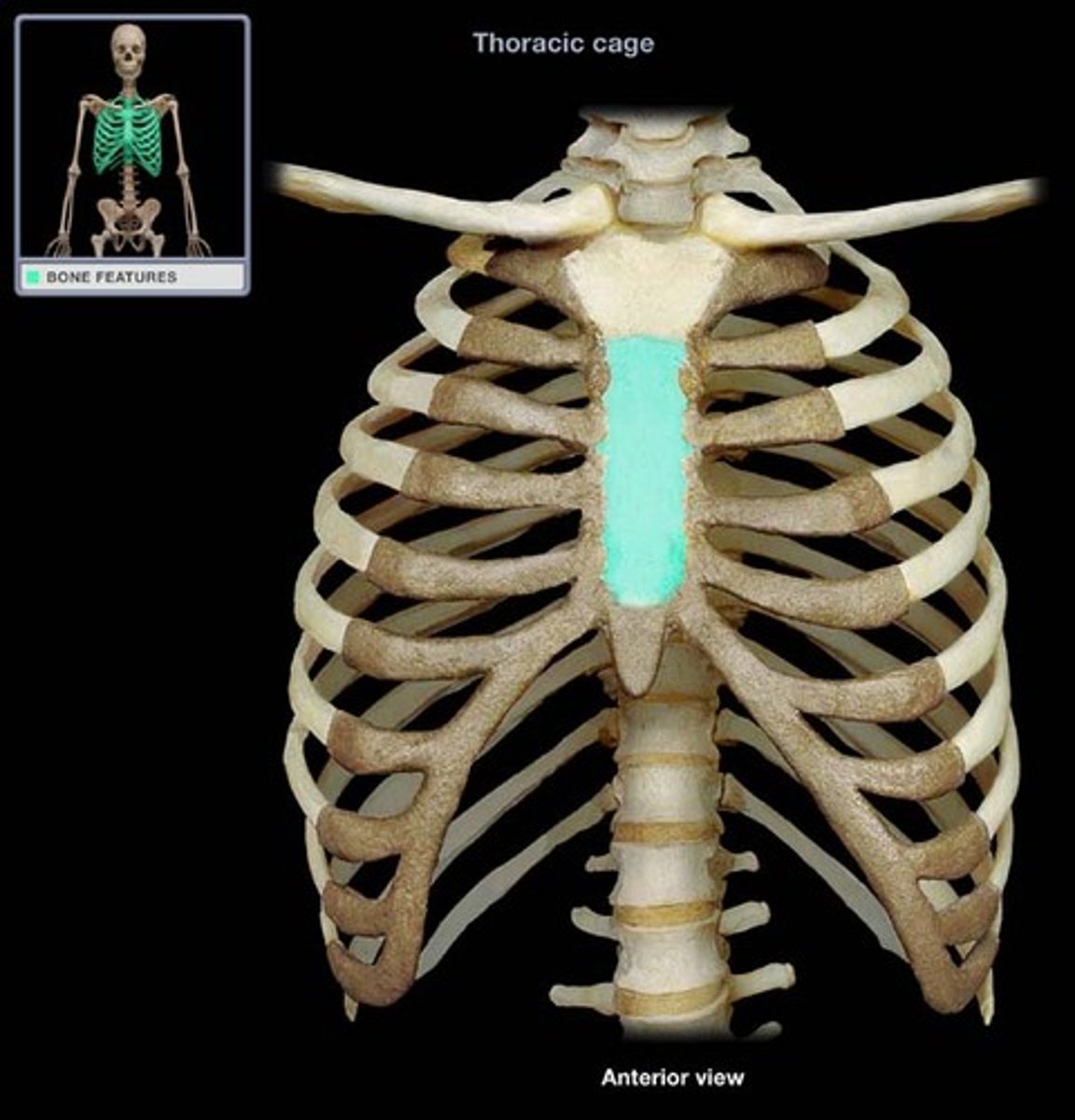
Sternum
Attaches to 1st seven pairs of ribs. The sternum is formed by fusion of 3 bones

Three bones of the sternum
manubrium, gladiolus, xiphoid process

Manubrium of sternum
articulates with clavicle
Gladiolus (body) of sternum
bulk of sternum
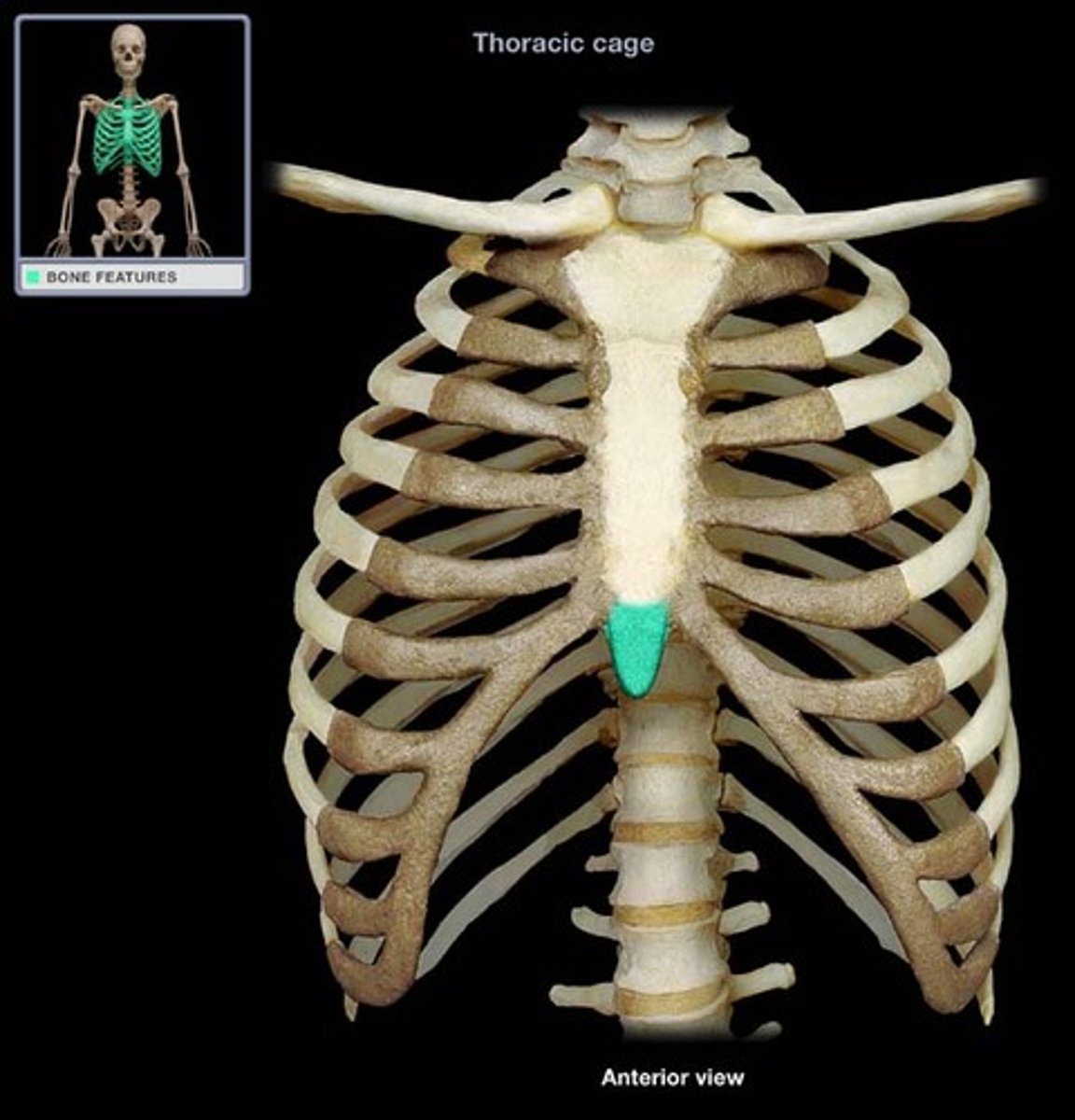
Xiphoid process of sternum
located at the inferior end
(made of hyaline cartilage in children,
usually ossified in adults)
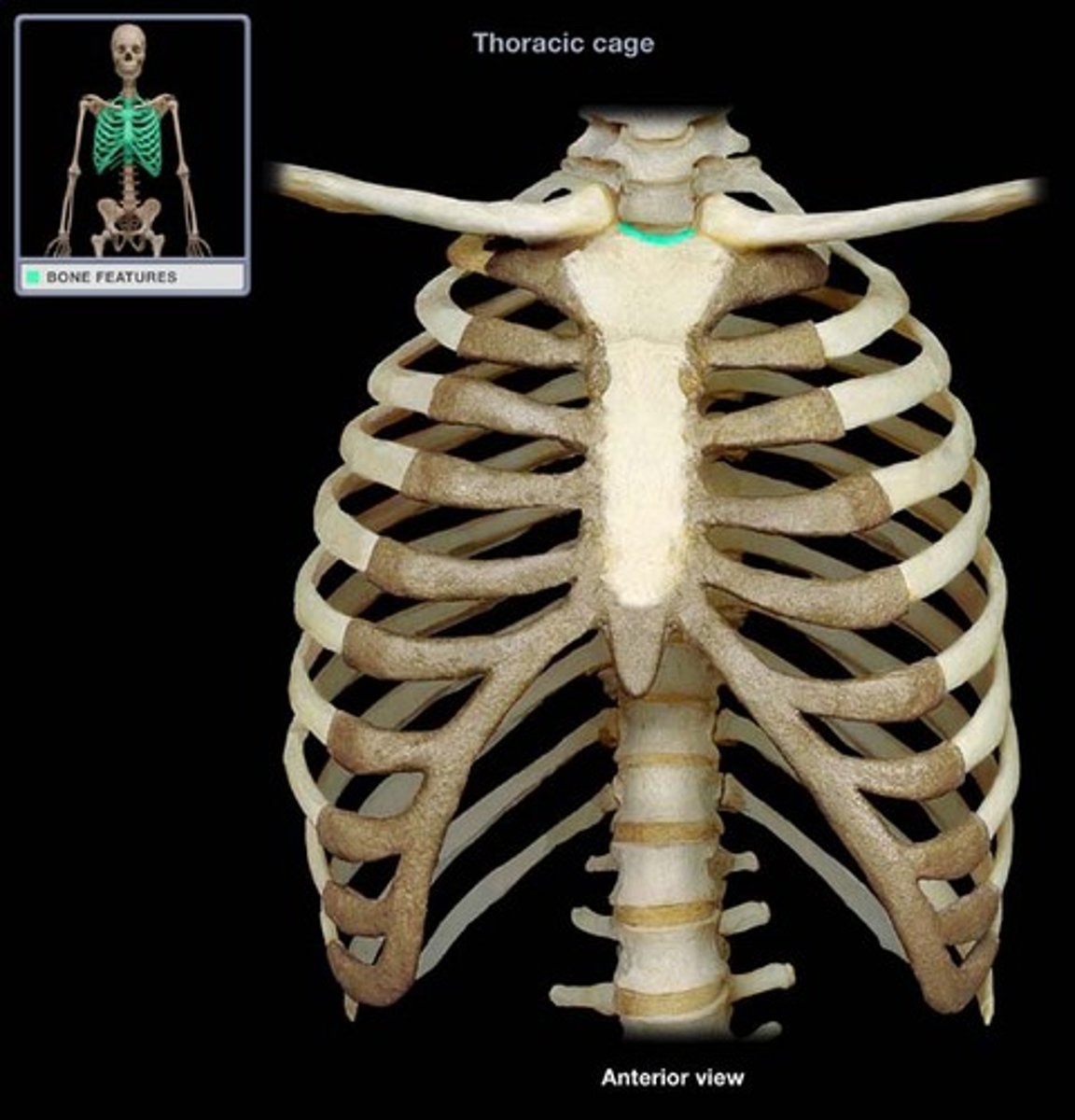
Landmarks of the sternum
jugular notch, sternal angle, xiphisternal joint
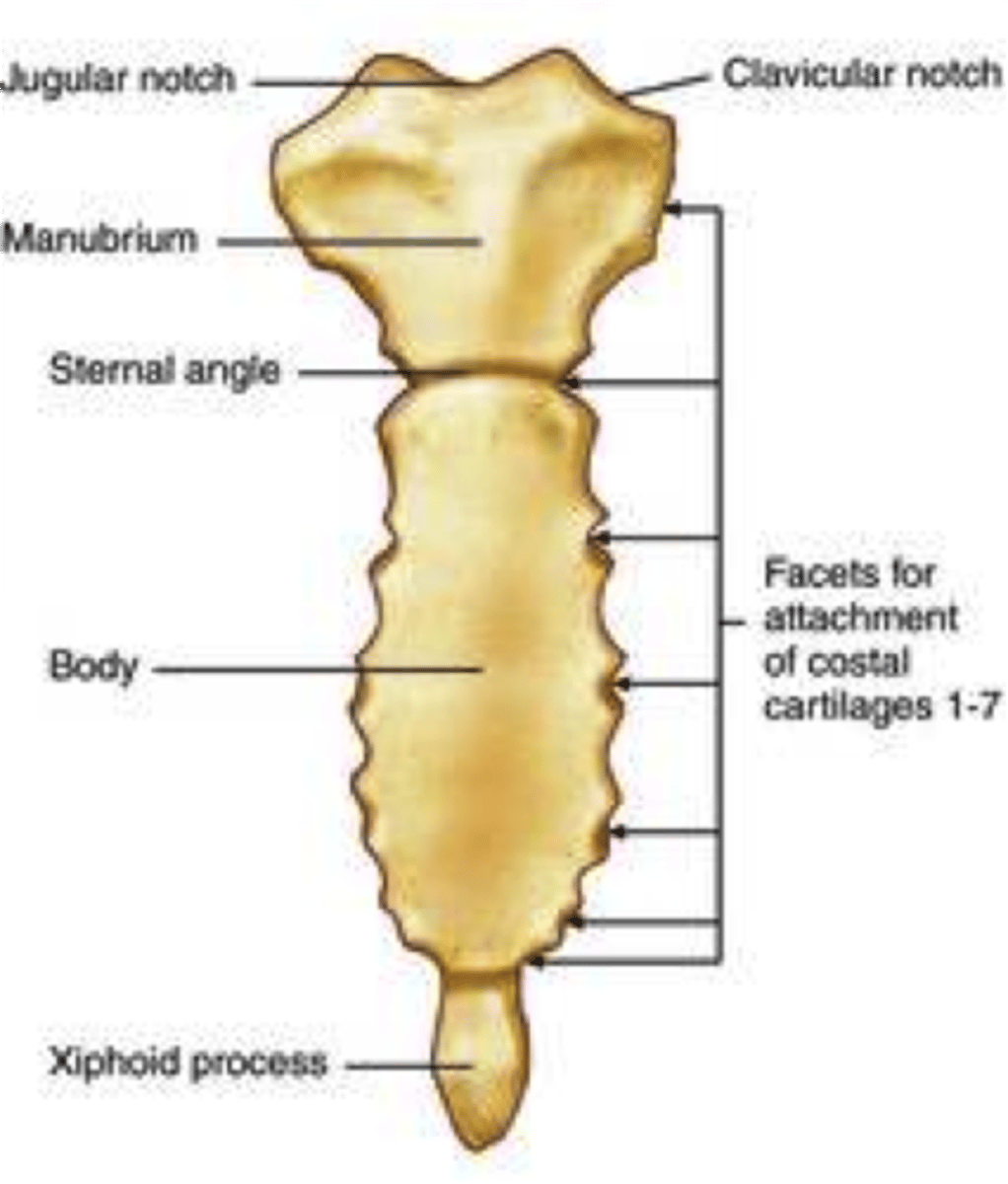
Jugular notch of sternum
at the level of the 3rd thoracic vertebra
Sternal angle of sternum
at the level of the 2nd ribs and 5th thoracic vertebra
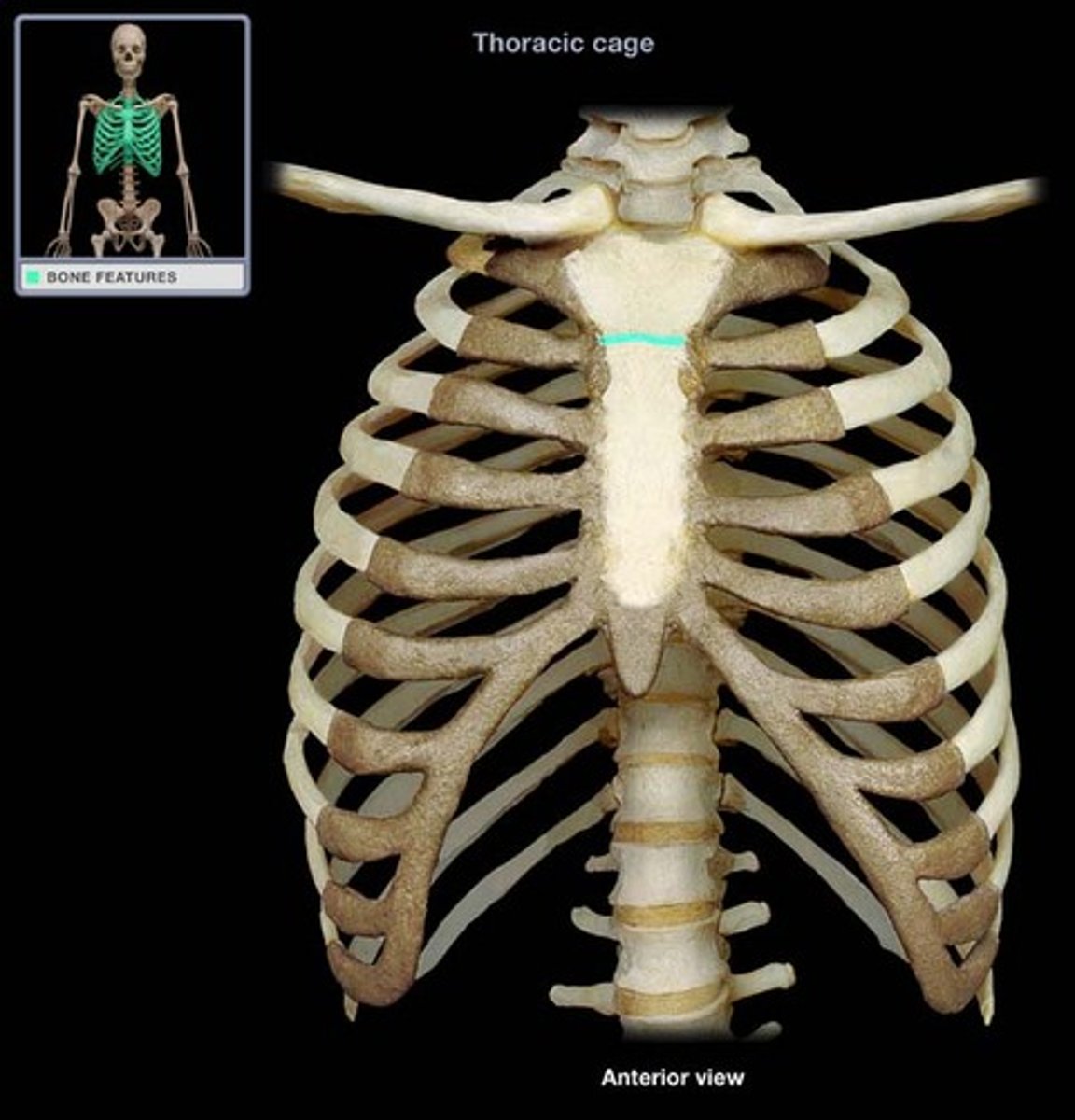
Xiphisternal joint of sternum
at the level of the diaphragm and 9th thoracic vertebra

Ribs
We have 12 pairs of ribs; Ribs interact with the thoracic vertebrae. The facets on the head of the rib interacts with the inferior costal facet AND superior costal facet of adjacent thoracic vertebrae. The facet on the tubercle of the rib interacts with the transverse costal facet
Vertebrosternal ribs (1-7)
true ribs, attach to the sternum thru their own costal cartilage
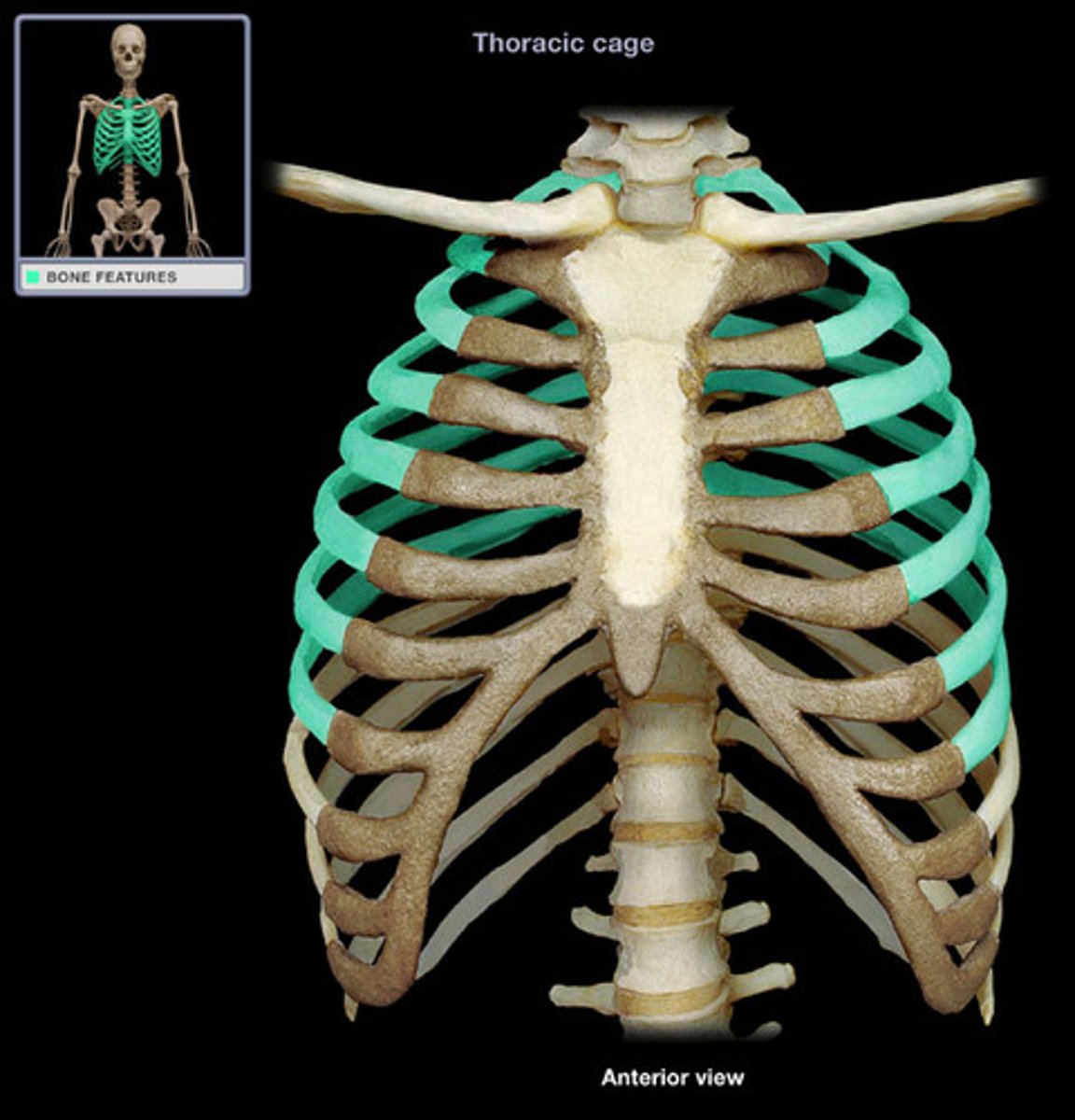
Vertebrochondral ribs (8-12)
false ribs; ribs 8-10 attach to sternum thru costal cartilage of rib 7; ribs 11-12: floating/vertebral ribs do not attach to sternum

The Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, appendages/limbs

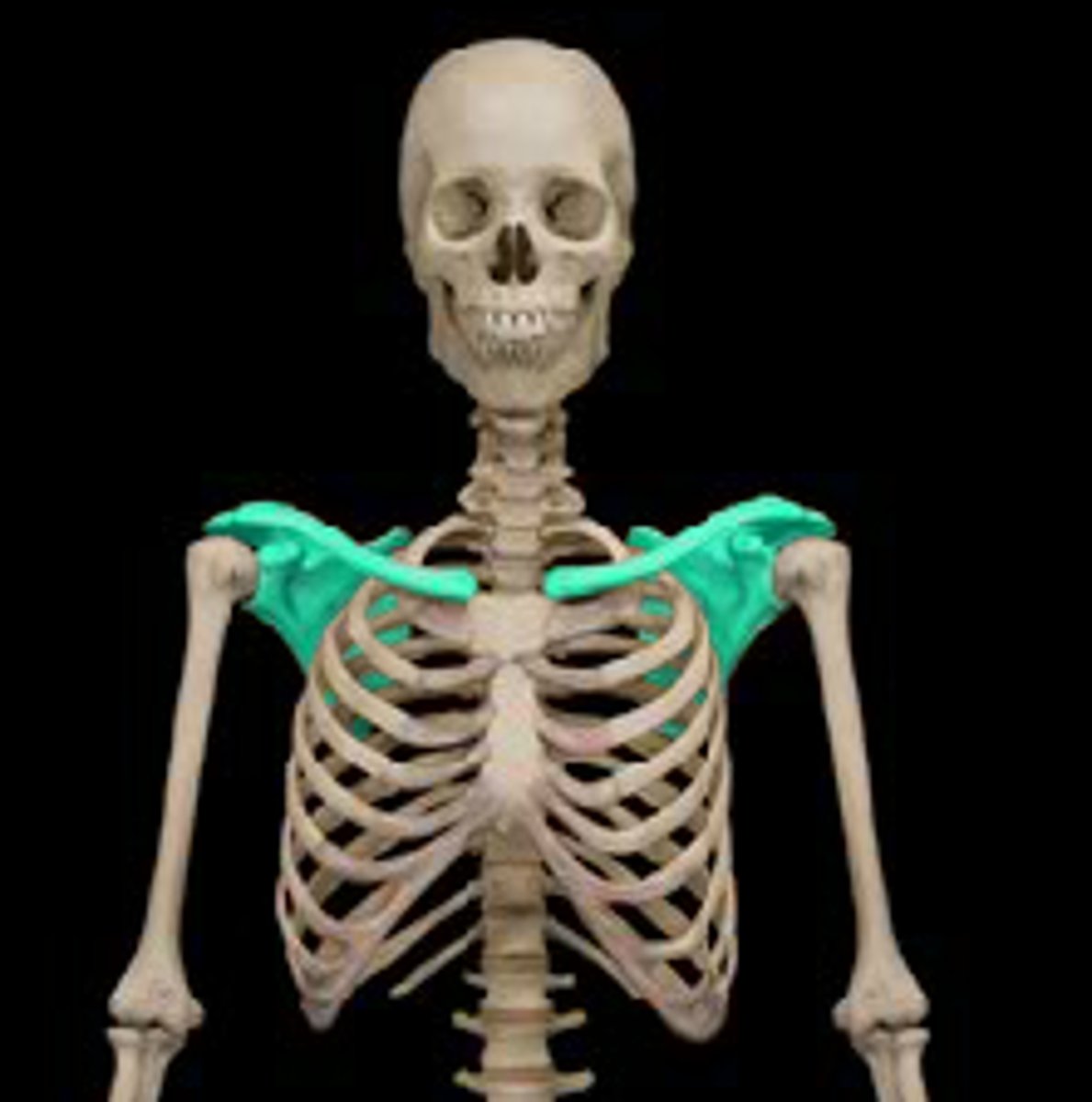
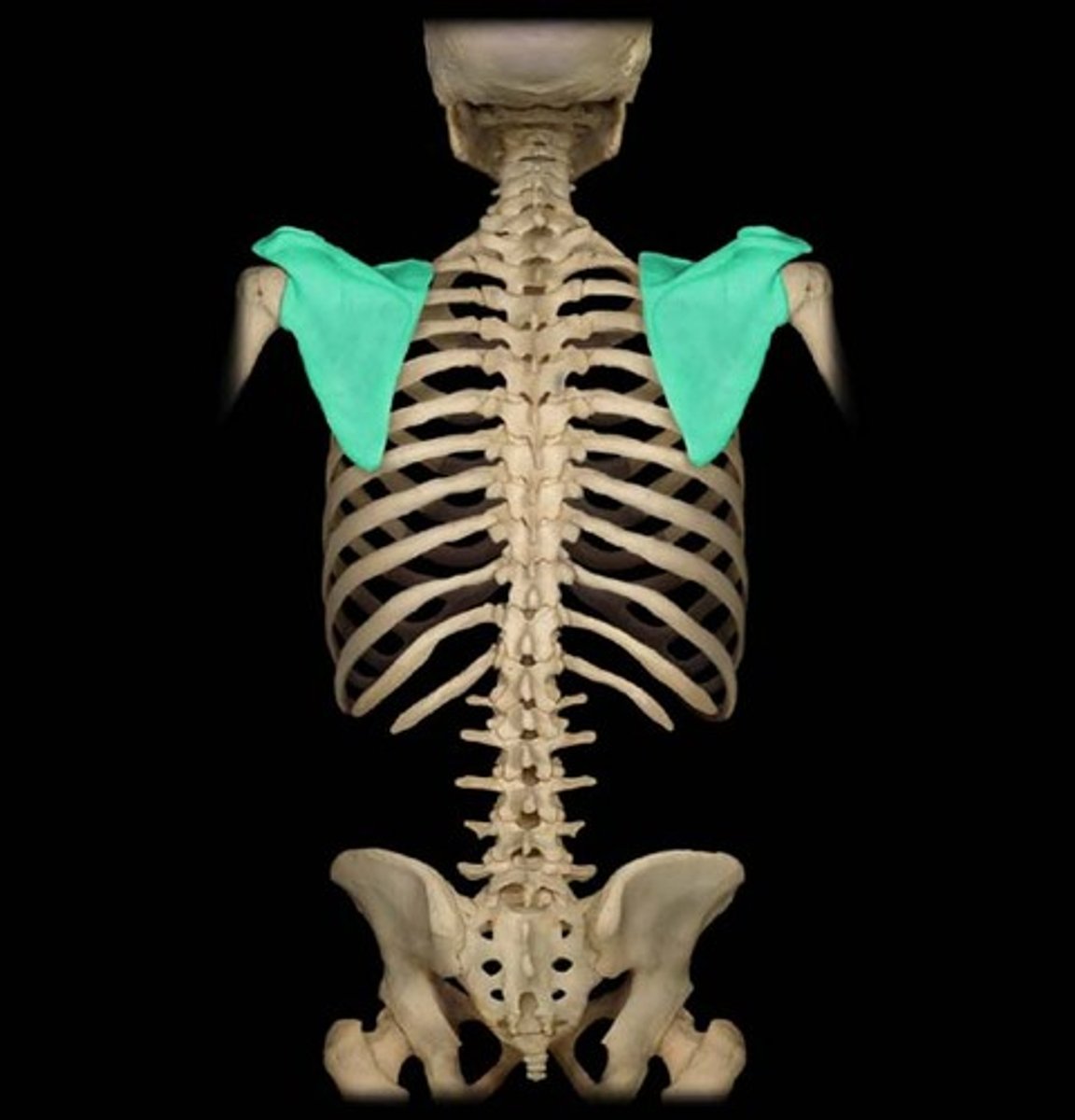
Pectoral Girdle
clavicle and scapula
Clavicle (anterior)
convex forward & concave lateral
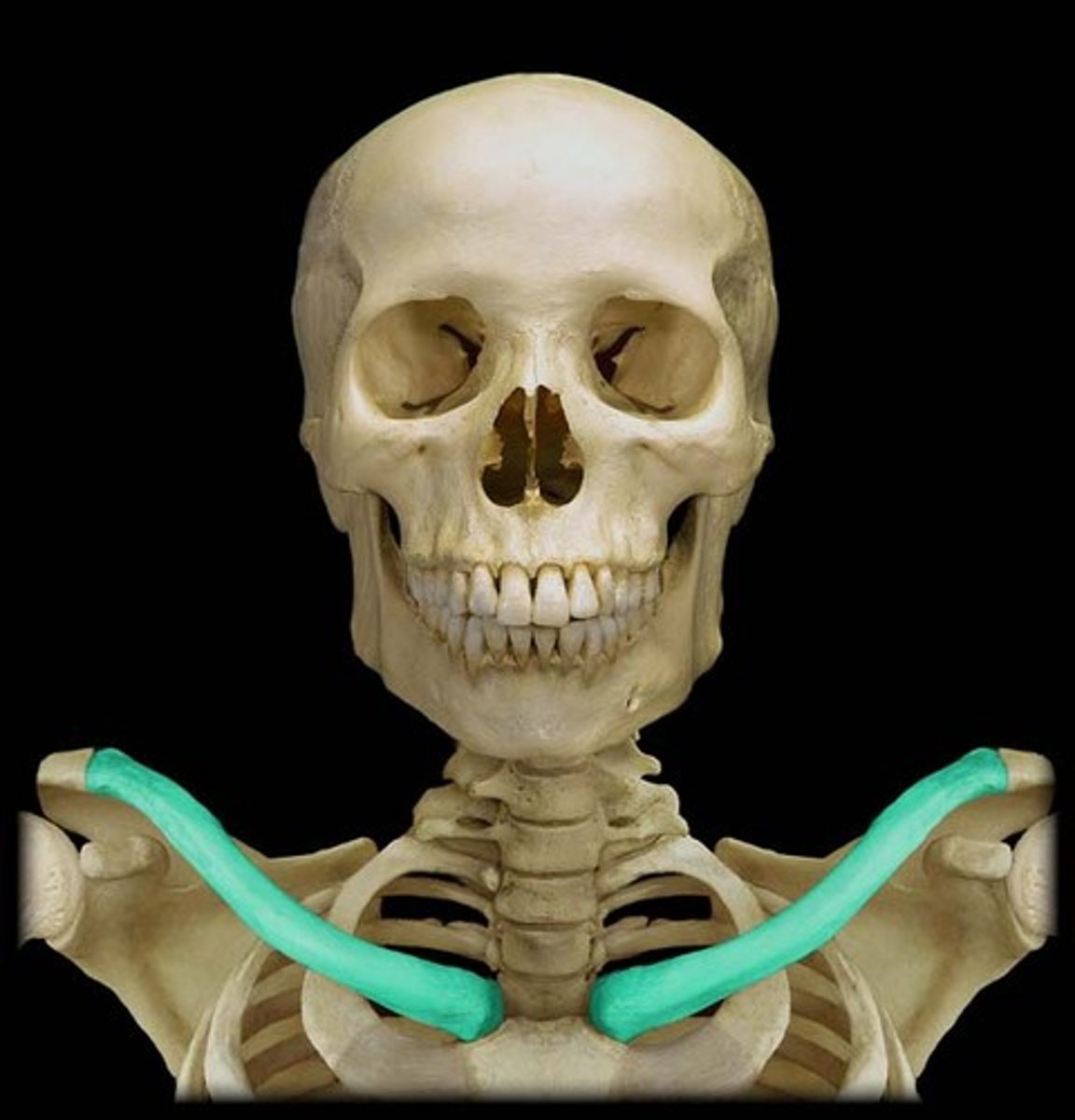
Clavicle important structures
acromial end, sternal end, conoid tubercle
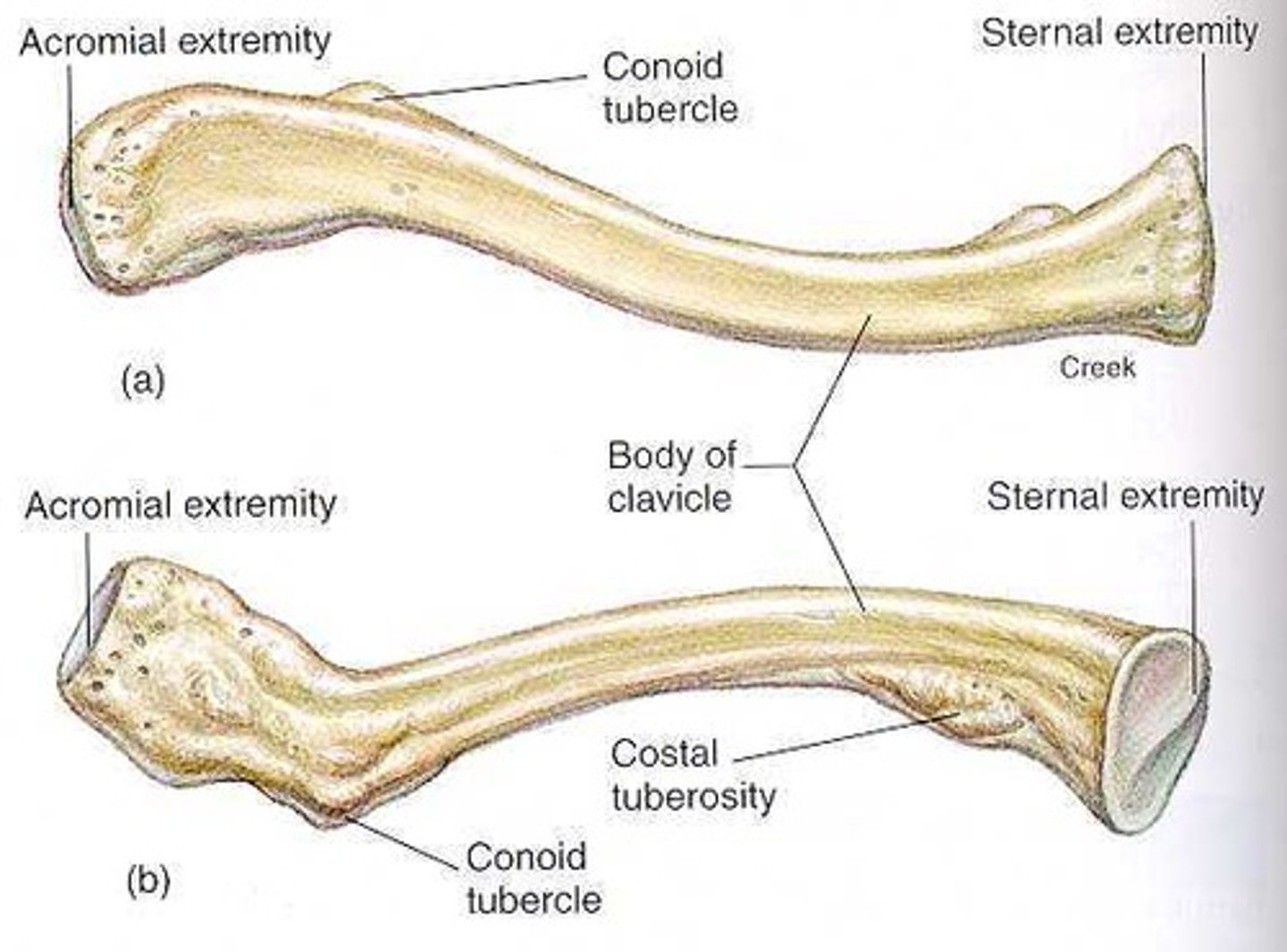
Acromial end of clavicle
articulates with scapula

Sternal end of clavicle
attaches to sternum
Conoid tubercle of clavicle
ligament attachment site
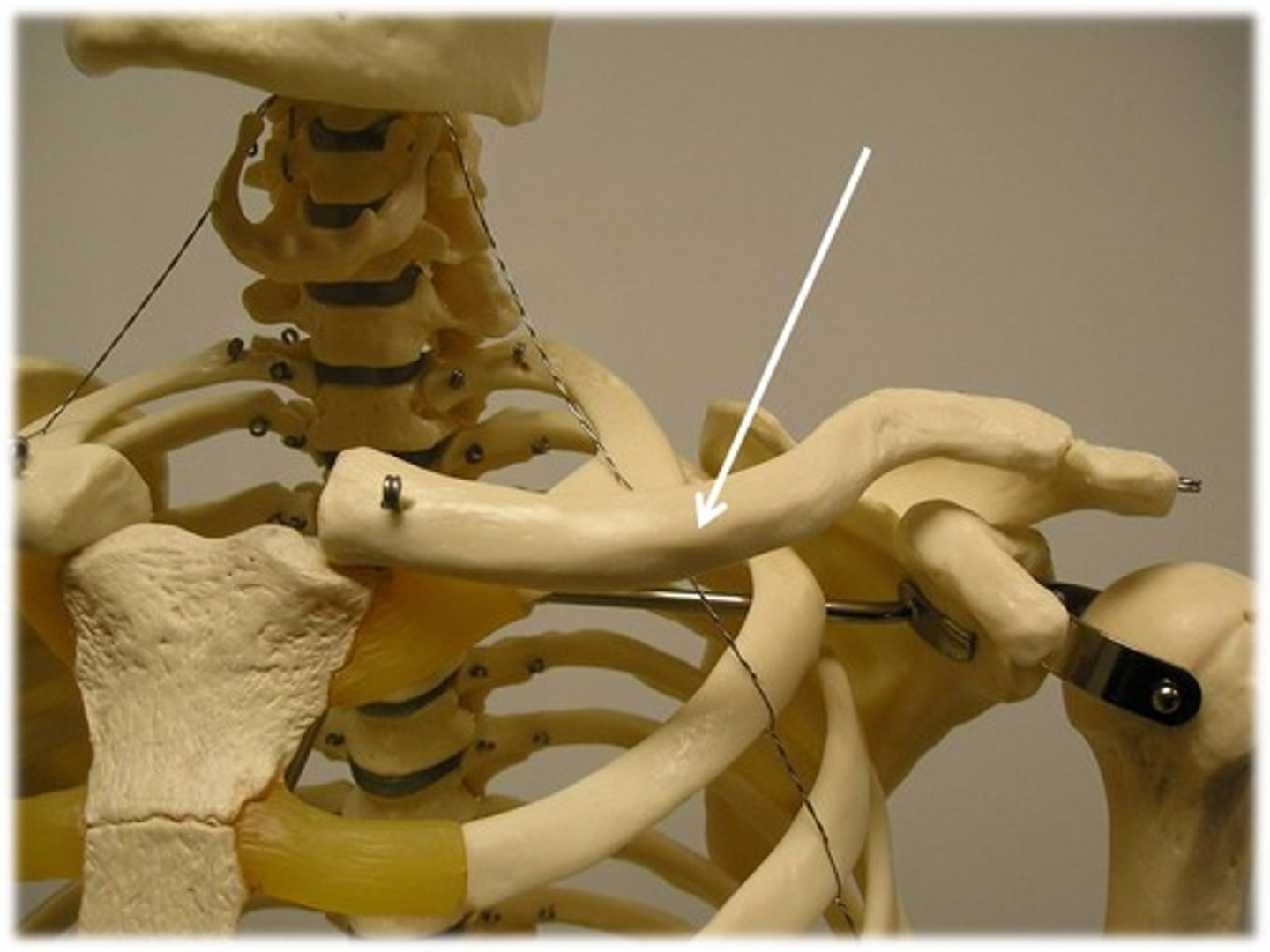
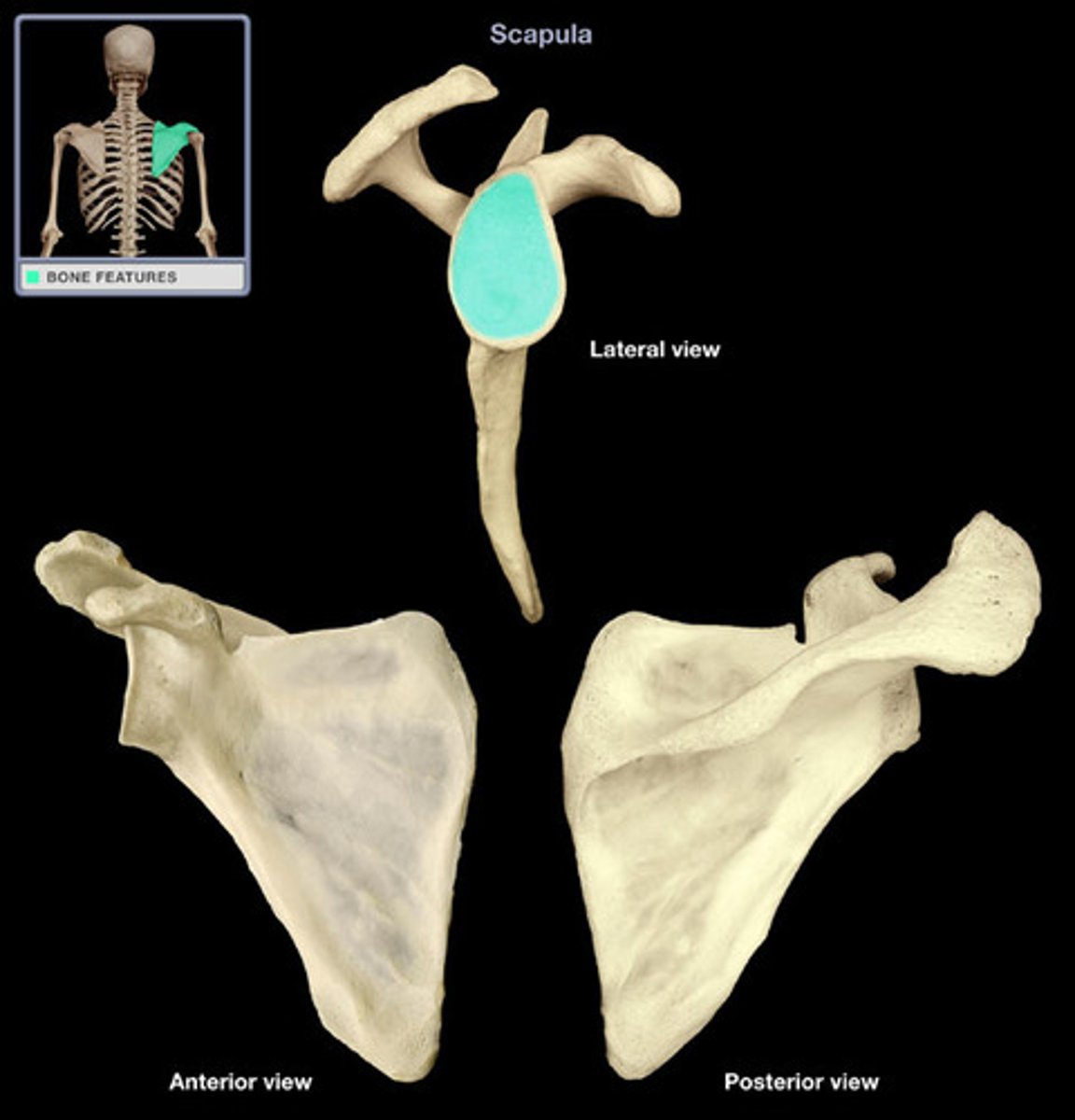
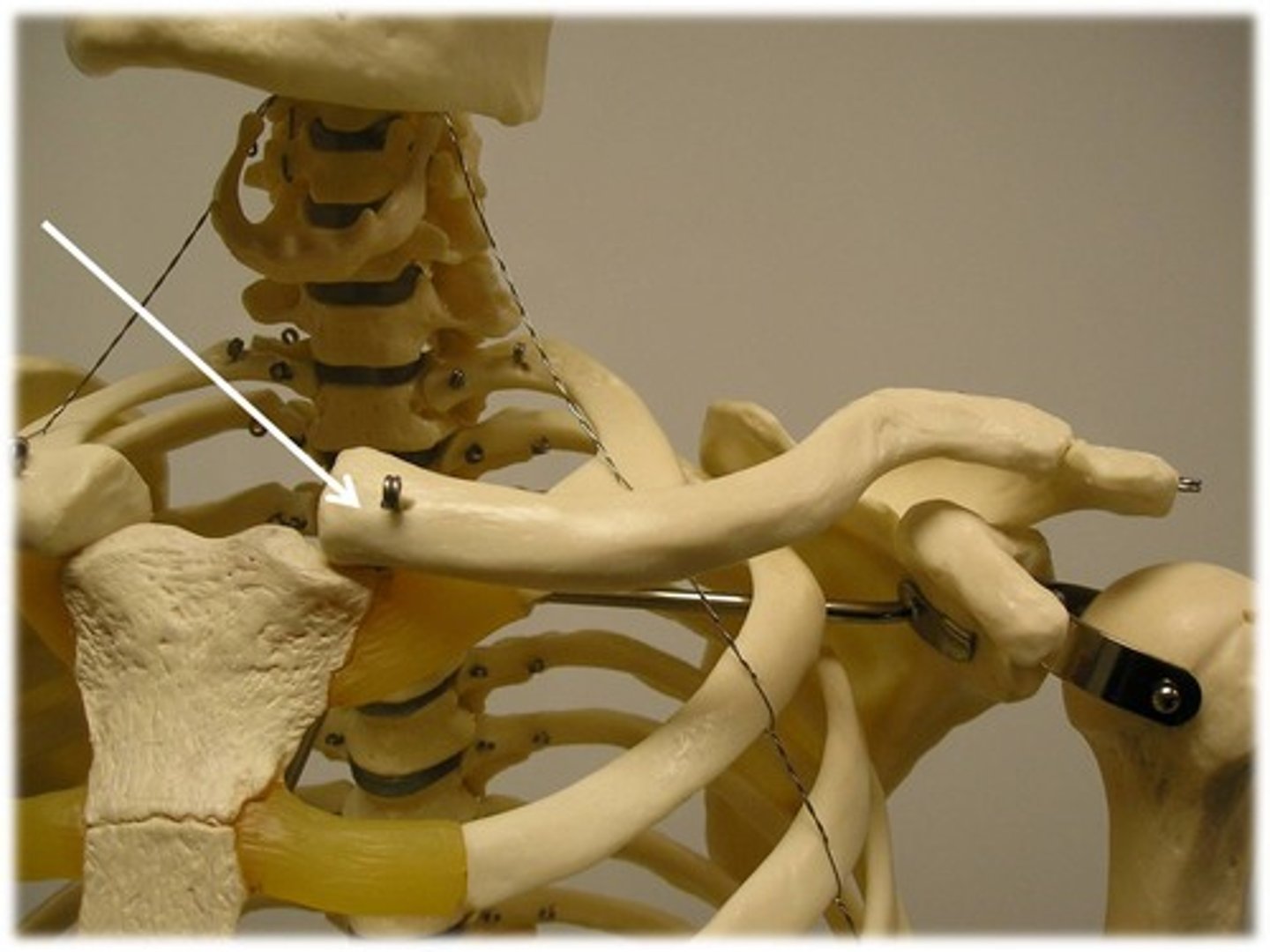
Scapula (posterior)
acromion superior & lateral
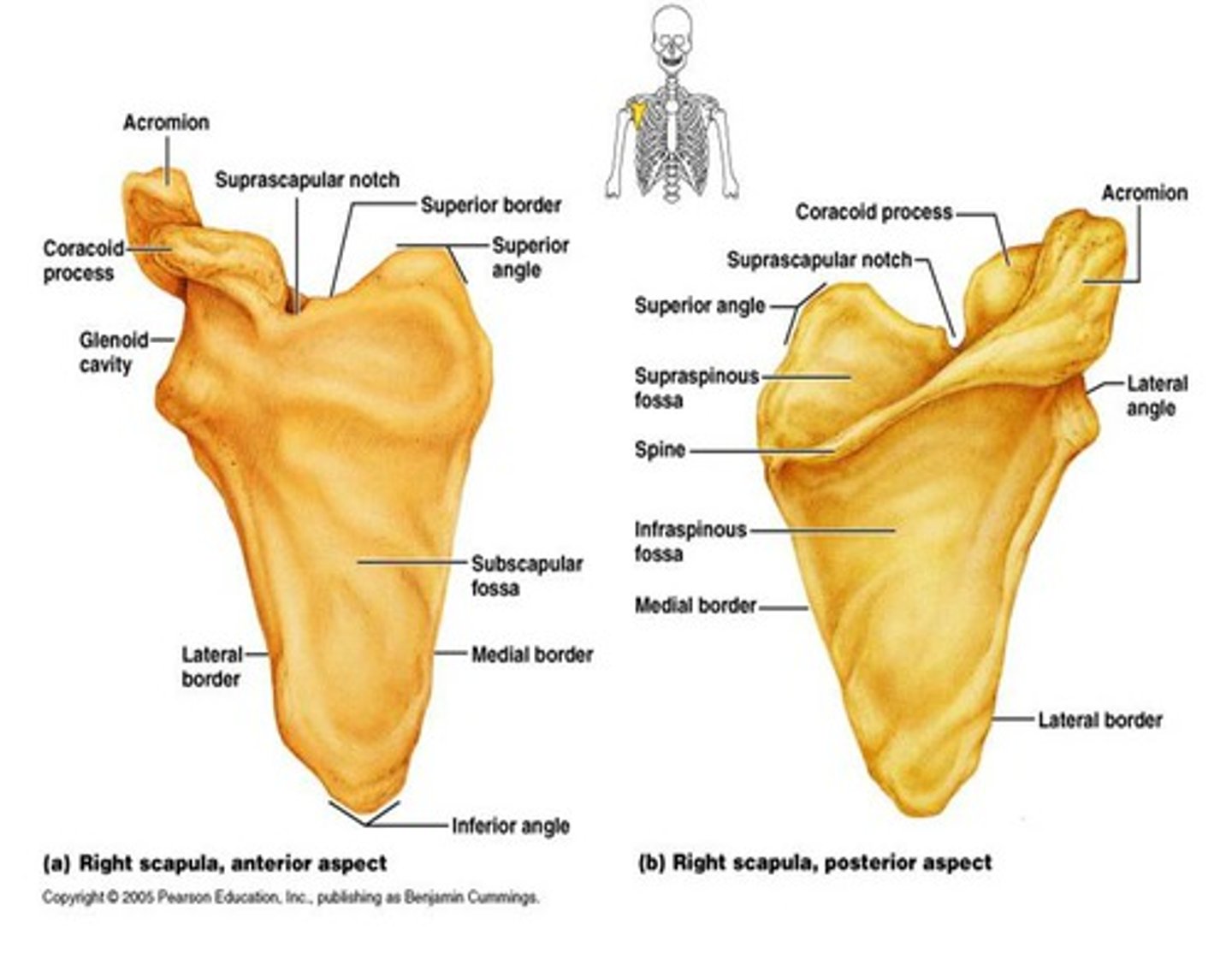
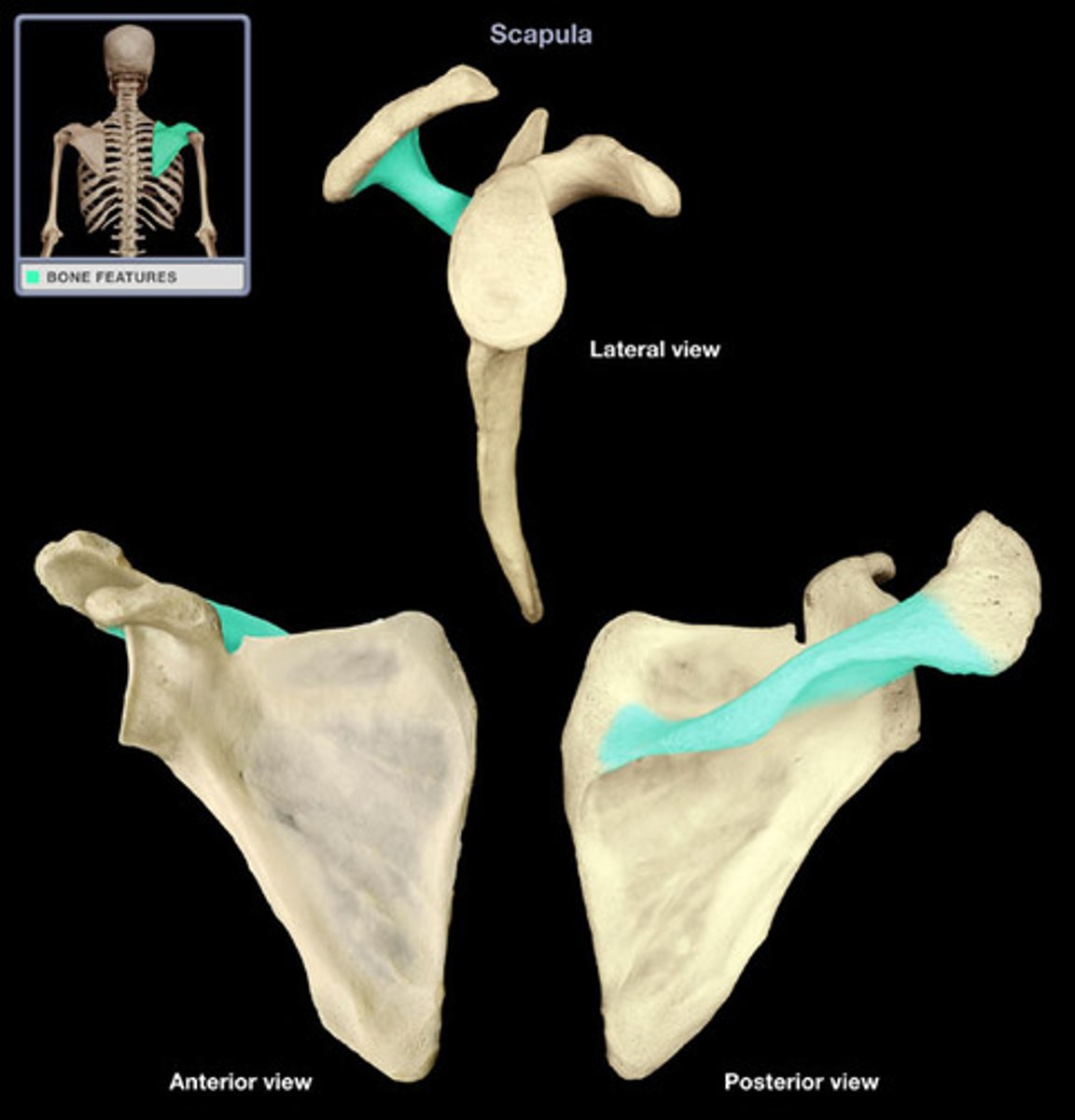
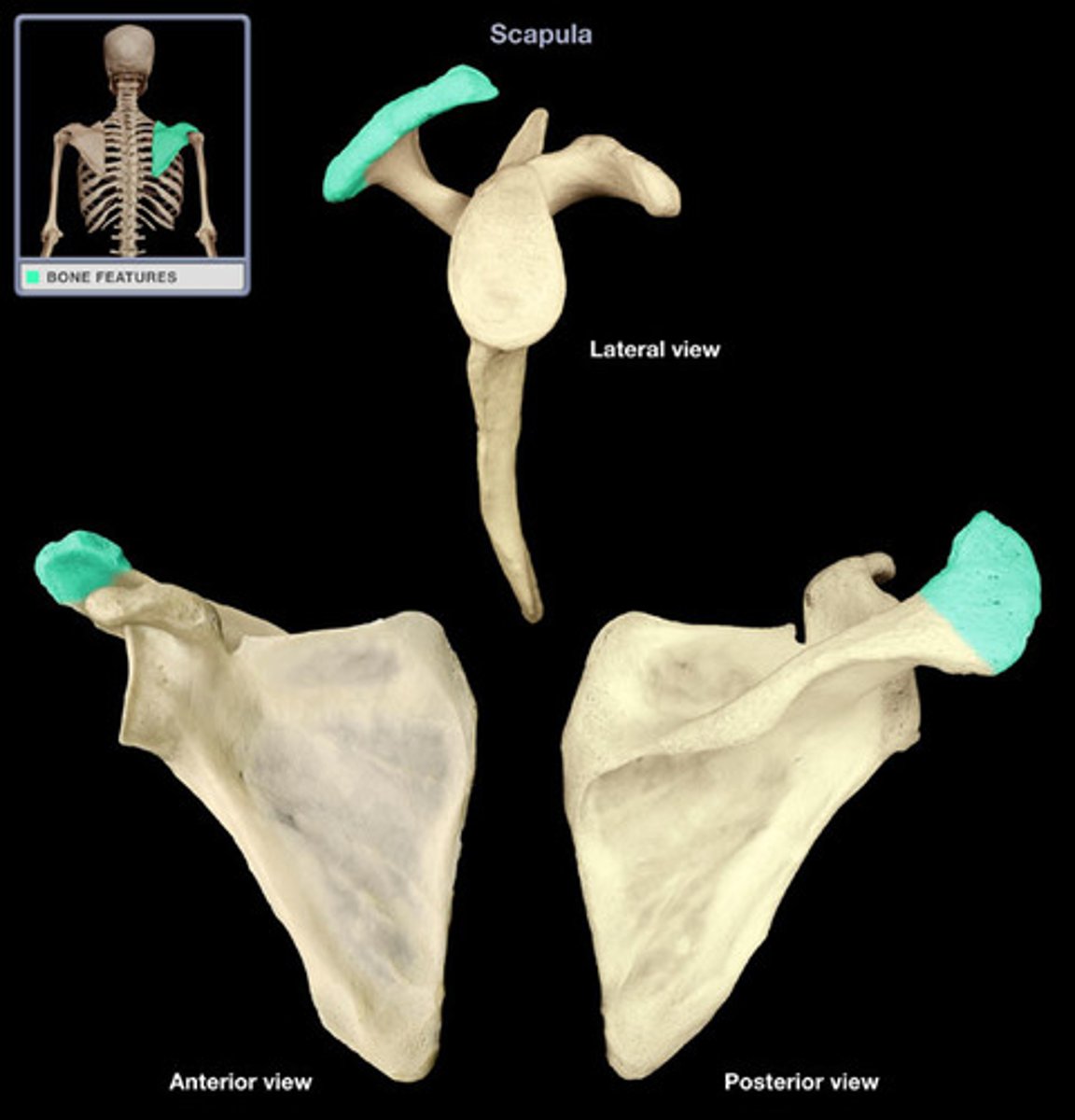
Scapula important structures
spine, acromion, coracoid process, glenoid cavity, suprascapular notch, superior/lateral/medial borders, supraspinous fossa, superior angle, inferior angle
Spine of scapula
extends into the acromion
Acromion of scapula
connects with clavicle
Coracoid process of scapula
muscle attachment

Glenoid cavity of scapula
socket for humerus