PT 713: Week 3 Pedi Review
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Developmental screening assessment
Brief overview exam to evaluate need for further, more in-depth testing
- Used for early identification with deviations from typical development
Examples of developmental screening tools
1. Harris Infant Neuromotor Test (HINT)
2. Denver Developmental Screening Test II
3. New Bayley III Screening Test
4. New screening version of TIMP called TIMPSI
What is the Harris Infant Neuromotor Test (HINT)?
Screens for developmental delays (motor and/or cognitive)
- Used for ages 3-12 months
- Short time to administer (15-20 mins)
What is the Denver Developmental Screening Test II?
Screens for developmental delays across several milestone based domains (GM, FM, language, social)
- Poor specificity and high over-referral rates
What is the purpose of using standardized assessments in pediatrics?
- Diagnose developmental delays and extend of delay
- Establish eligibility for services
- Document func. status, developmental level or progress
- Determine intervention targets and monitor progress with treatment
Types of standardized assessments
1. Measurement-based (comparisons)
2. Performance-based (quality and outcomes)
Types of measurement-based standardized assessments
1. Norm-referenced
2. Criterion-referenced
Types of performance-based standardized assessments
1. Process-oriented
2. Product-oriented
Norm-referenced assessments
Based on child's performance compared to a reference group (i.e. children of the same age/sex)
Criterion-referenced assessments
Based on child's performance compared to a predetermined criteria of performance/skill mastery
Process-oriented assessments
Assessments measuring the process or quality of movement (i.e. measuring wind-up, hip/shoulder rotation, foot placement during a ball throwing activity)
Product-oriented assessments
Assessments measuring the movement output (i.e. # of successful catches of a ball)
Examples of standardized assessments for INFANTS
1. Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS)
2. Peabody Developmental Motor Scales (PMDS-2)
3. Test of Infant Motor Performance (TIMP)
4. Bayley Scale of Infant Development (BSID)
5. Mullen Stage of Early learning (MSEL)
and a few more..
What is the AIMS assessment?
Purpose: Observational screen and track early motor and postural development
Type: Norm-referenced and process-oriented
- Used for ages 0-18 months
- Scored as 1- Observed or 0- Not observed
What is the Peabody assessment?
Purpose: Measure current motor skill level and acquisition of skill over time
Type: Norm-referenced and product-oriented
- Used for ages 1-72 months (6 yrs)
- Scored as 2- Complete, 1- Partial, 0- Fail
What is the TIMP?
Purpose: Early identification of developmental delays in high-risk infants
Type: Norm-referenced, elicited and observed
- Used from 0-4 months corrected (for high risk infants w <32 weeks GA)
Examples of standardized assessments for CHILDREN
1. Test of Gross Motor Development (TGMD-3)
2. Bruininks Oseretsky test of Motor Proficiency (BOT-2)
3. Movement Assessment Battery for Children (M-ABC)
What is the TGMD?
Purpose: Determine quality of gross motor skills, typically used in schools
Type: Norm-referenced and process-oriented
- Used for ages 3-10 years old
- Quick admin of 12 GM skills and object control (15-20 mins)
What is the BOT-2?
Purpose: Assess motor skill performance across variety of domains (GM, FM skills)
Type: Norm-referenced, product-oriented
- Used for ages 4-21 years old
- Full version can take 45-60 mins, short form optional if needed
What is the M-ABC?
Purpose: Able to identify "clumsy children" who may not be able to keep up with peers
- Used for ages 2-16 years with mild mvmt disorders
- Used often in schools
How to calculate corrected/adjusted age for infants born prematurely
Corrected age = CA in weeks - (40 - EGA in weeks)
- CA= Chronological Age in weeks
- EGA= Estimated gestational age in weeks
At what age do you not have to adjust age on testing for infants born prematurely?
For children older than 2, no need to adjust for prematurity
What is considered premature birth?
<40 weeks of gestation
What is the SFA?
Purpose: Used to identify needs and develop IEP
Type: Criterion-referenced (compares scores to grade-level norms)
- Used for ages K-6 with disabilities
- Admin can take up to 2 hours
Stroke Volume is lower or higher in children than adults?
SV lower in children (d/t smaller heart size)
Heart Rate is lower or higher in children than adults?
HR is higher in children
Tidal Volume is lower or higher in children than adults?
TV is lower in children
Respiratory Rate is lower or higher in children than adults?
RR is higher in children
For a 16-month old, which of the following standardized assessments could be used to assess motor skills (Poll-ev)?
a. AIMS
b. TGMD
c. PEDI
d. M-ABC
a. AIMS
Physical fitness tests for pediatric cardiopulmonary fitness
- 20-m PACER
- 1 mile walk/run
- Rockport walk test
- Targeted aerobic movement test
Physical fitness tests for pediatric muscular strength and endurance
- Dynamometers
- Curl-ups/sit ups
- 90 degree push ups
- Trunk lift extremity
Physical fitness tests for pediatric flexibility
- Back saver sit & reach
- Shoulder stretch
- Lateral side bending test
What is Down Syndrome?
A chromosomal disorder caused by errors in cell division
Types of DS
1. Trisomy 21 (extra chromosome on chromosome pair 21)- 90% of cases
2. Translocation (one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome pair)
3. Mosaic disorder (some cells typical, others trisomy 21)
What is "Chaplinesque gait"?
Gait pattern of hip ER, knee flexion/valgus and ER tibia, seen in patients w/DS often
T/F: Increased incidence of DS seen in older moms
T
Prenatal testing for DS
Screening: at 12-14 weeks with blood test and ultrasound
Diagnostic testing: Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS)
- Only recommended in conj. w/positive screening tests
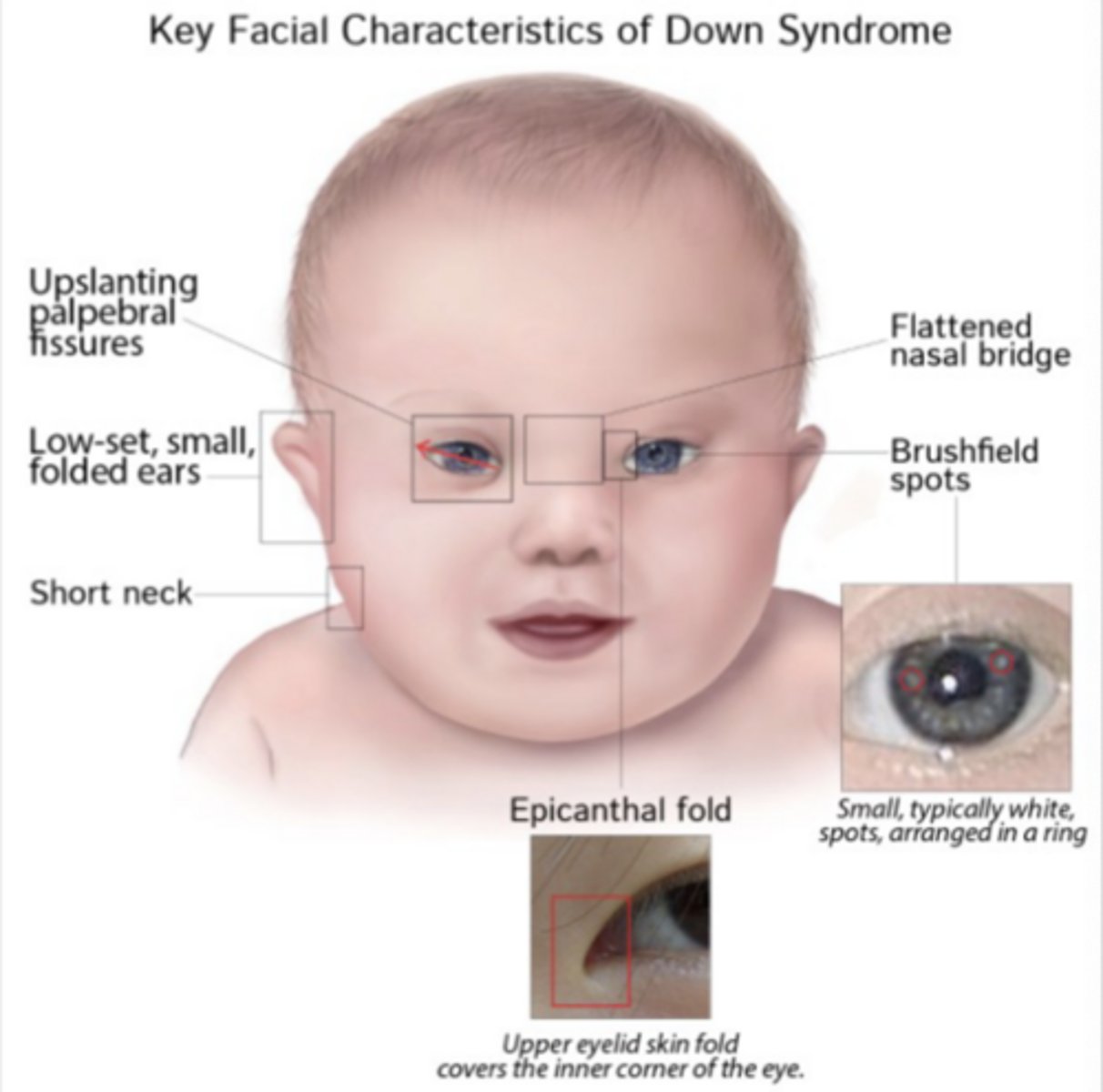
Craniofacial features of DS
- Inner epicanthal folds
- Upward slant of eyes
- Low nasal bridge
- Altered ear shape
- Flat facial profile
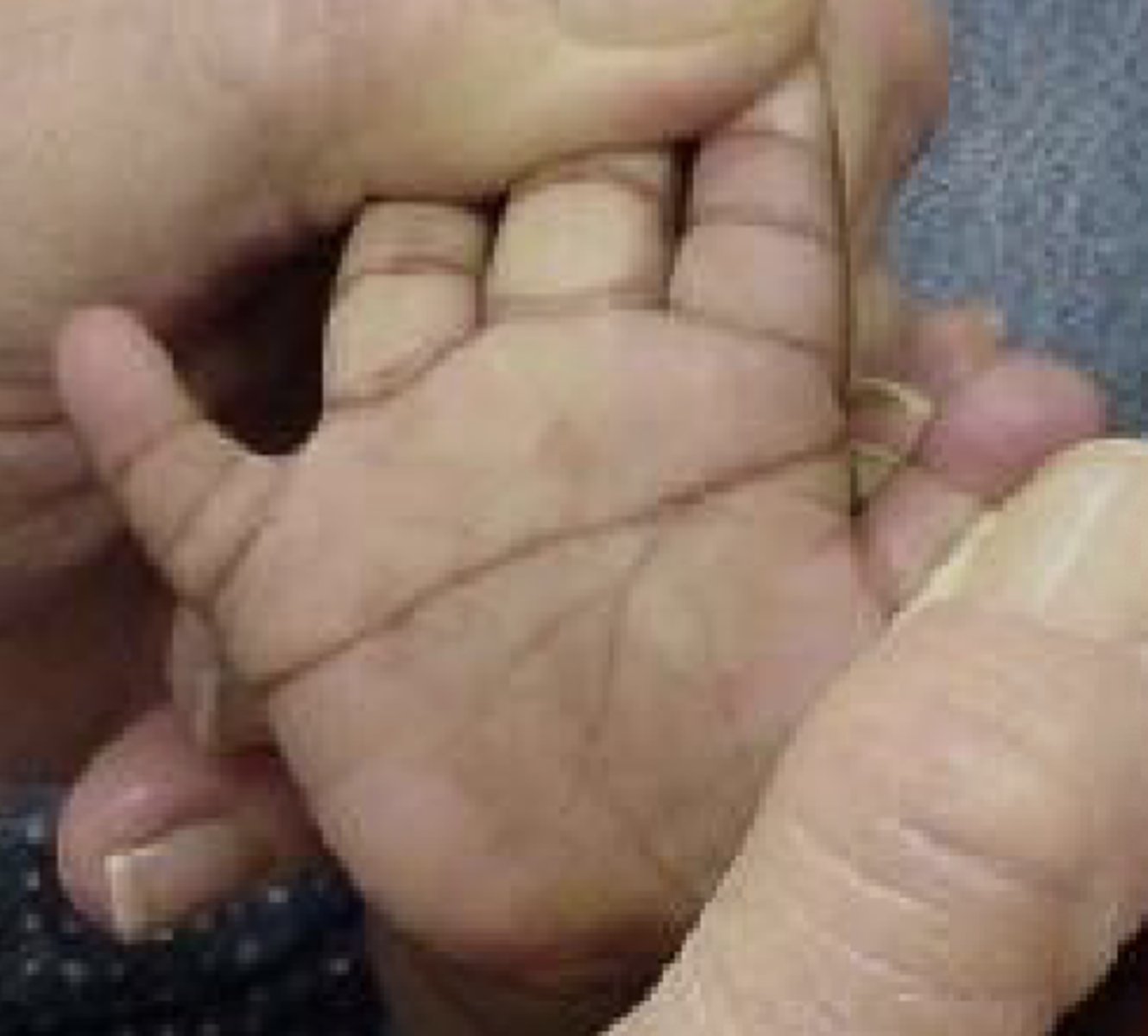
Other phenotypic features of DS
- Simian crease (palm)
- Short neck
- Clinodactly (curving) of 5th finger
- Wide gap between 1st and 2nd toe
Delays in gross motor milestones with DS
Usually rolling by 6 months, sitting by 12 months, crawling by 18 months, and independent walking by 24 months
- Note: Very variable!!
Neuromuscular impairments of DS
- Hypotonia
- Delayed postural development and alignment
- Slowed postural reactions
- Decreased balance and coordination
Early musculoskeletal impairments of DS
- Joint hypermobility (due to hypotonia and ligament laxity)
- Low muscle force production
- Atlantoaxial instability
- Scoliosis
- Altered body proportions
Warning signs of spinal cord compression as a result of atlantoaxial instability (seen in DS)
Gait changes, urinary retention, torticollis, reluctance to move neck, increased DTR
Language impairments seen in DS
Receptive language > Expressive language
Sensory impairments seen in DS
Vision changes
- Myopia (70%)
- Nystagmus
- Strabismus
Hearing loss (80-90%)
- Vestibular deficits
How are structural birth defects detected?
Ultrasound
How are genetic syndrome birth defects detected?
Carrier screening
How are chromosomal disorder birth defects detected?
Amniocentesis or CVS
What is DCD?
Developmental coordination disorder, categorized by gross and fine motor impairments that affect child's ability to perform everyday tasks including self care and academic tasks
What is dyspraxia?
Refers to those who have problem planning, organizing or carrying out movements in the right order
Etiology of DCD
Unknown however risk factors include low birth weight, prematurity, genetics, poor childhood nutrition, etc.
Screening for DCD usually is done after what age?
5 years
4 diagnostic criteria for diagnosis of DCD
1. Motor performance deficits
2. Participation and ADL deficits
3. Early onset
4. No exclusionary conditions
Typical presentation of the spine for someone with DCD
Usually stiff with a flattened/increased lumbar lordosis, thoracic kyphosis and hyperextension of the neck
What standardized assessment(s) is most commonly done with children with DCD
M-ABC and COPM
What is the primary focus of a PT providing services in a school-based setting under the IDEA act?
To assist a student in achieving educational goals and accessing the academic curriculum
Which of the following is NOT one of the 4 essential diagnostic criteria for DCD? (pollev)
a. The motor skills deficits significantly and persistently interferes with ADLs and school productivity
b. The presence of hypotonicity, joint laxity or being overweight
c. Motor skill deficits are ot better explained by an intellectual disability
d. The acquisition and execution of coordinated motor skills are substantially below what is expected for that age
b. The presence of hypotonicity, joint laxity or being overweight
Which of the following standardized assessment tools could be used to help establish DCD diagnosis for one of the DSM-V criteria, motor performance deficits? (pollev)
a. DCDQ
b. MABC
c. COPM
d. GAS
b. MABC
What is ASD?
Autism spectrum disorder, characterized by social communication impairments and presence of restricted/repetitive behaviors
3 Levels of ASD
Level 1: Require support
Level 2: Require substantial support
Level 3: Requires very substantial support
Describe ASD Level 1
- Child is usually verbally fluent but might have difficulty in back-and-forth meaningful conversations.
- Could have trouble moving from one activity to another.
- Difficulty in planning and organizing tasks/actions

Describe ASD Level 2
- Difficulty communicating/socializing with others.Shows specific interests or repetitive behaviors (e.g., stimming, head banging).
- Difficulty focusing on tasks for extended period of time

Describe ASD Level 3
Significant difficulty with daily living tasks, social interactions, shifting focus from one task to another.

Average age of ASD diagnosis
3-4 years old
Two most common proposed theories for the neurophysiology of ASD
1. Neuro-connectivity theory
2. Impaired mirror neurons
Children with ASD could show greater deficits in which types of PC?
All but primarily anticipatory
What is the TUDS?
Timed Up and Down Stairs
Scoring:
6-8 years old: M- 6.2s, F- 6.6s
9-11 years old: M- 5.2s, F- 5.6s
12-14 years old: M- 4.8s, F- 5.3s
Causes of toe-walking
- MSK (equines contracture, muscle tightness)
- Neurological (clonus)
- Sensory (visual or vestibular system
- Idiopathic
Common in ASD (9-20%)
PT management of toe-walking
Stretching, serial casting, AFOs, surgical correction
What is movement synchrony?
Ability to synchronize movement with a social partner
Types:
1. Joint
2. Turn taking
Early motor signs of ASD
- Delayed acquisition of milestones
- Poor PC (head lag)
- Deficits in motor anticipation/planning
- Poor FM skills
- Reduced tone
Early social/communication markers of ASD
- Lack of or delay in spoken language
- Poor response to name
- Falls to point or show joint attention
- Little to no eye contact
- Lack of interest in other children
Most common behavioral intervention in children with ASD
ABA (Applied behavior analysis)
Considers 3 components:
1. Antecedent (prompt that leads to behavior)
2. Behavior (response)
3. Consequence
How can the ABA inform us as PTs for patients with ASD?
Be aware of antecedents (triggers) like certain settings, events, situations that can result in a disrupting behavior. Also, avoid unintentional reinforcement of child's behaviors.
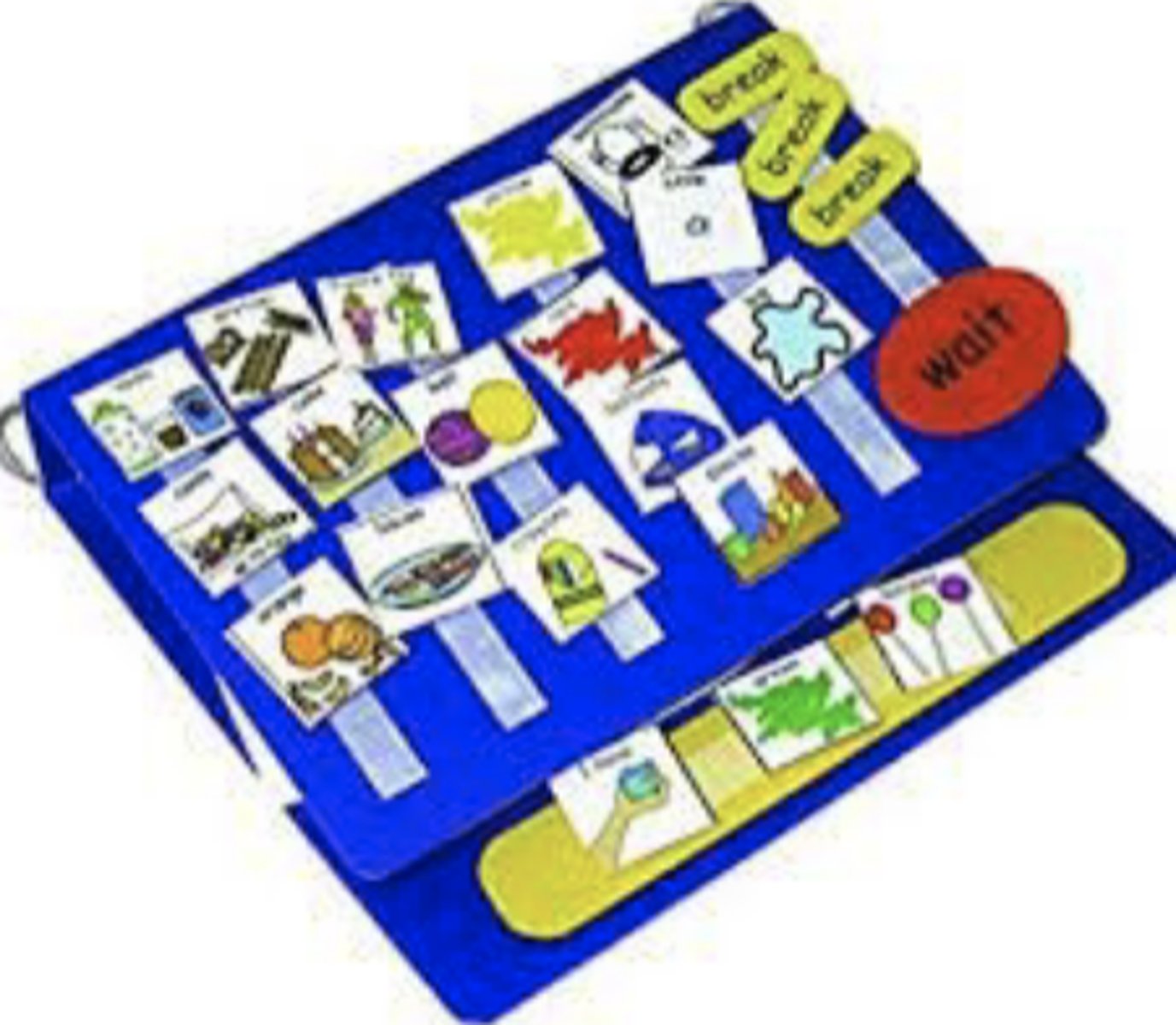
What is PECS?
Picture Exchange Communication System
- Commonly used for ASD as an alternative communication approach for non-verbal needs

What is a social story and how can we use it to help us interact with ASD patients?
Helps teach how to navigate common social situations.
- Use it prior to PT to outline session including:
1. What will happen
2. Expected participation/behavior
3. Outcome

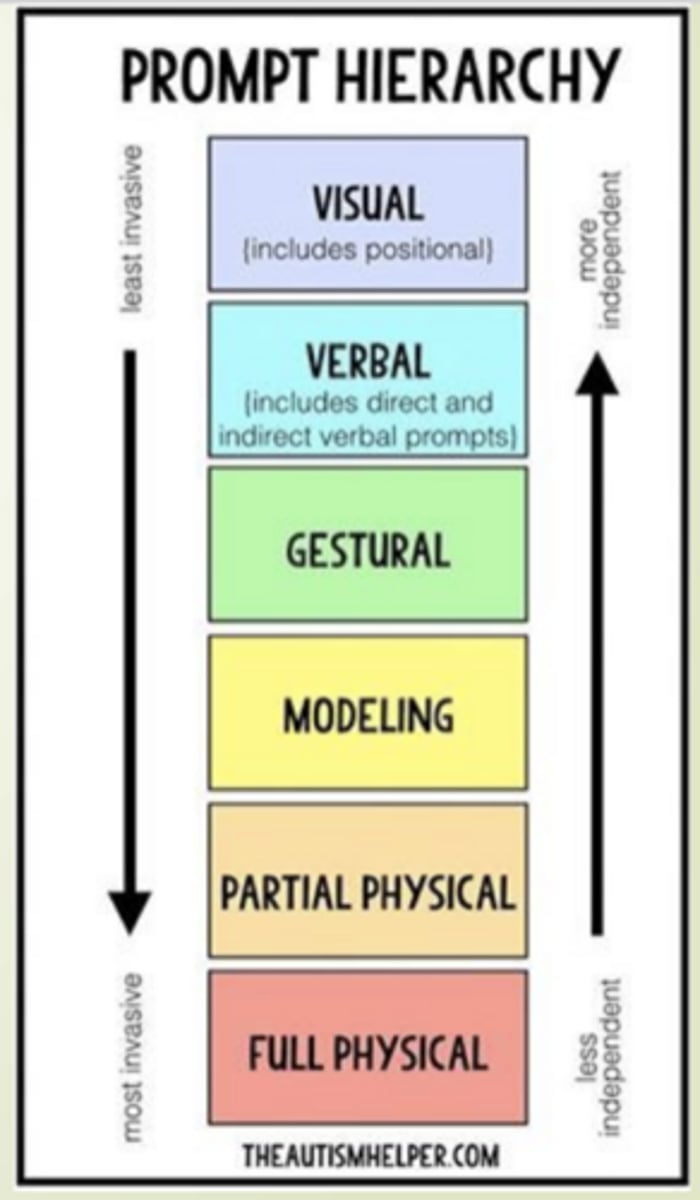
Types of "prompts" to note for patients with ASD
- Visual: Show picture of task
- Verbal: Continuous prompting during testing
- Gestural: Pointing towards goal
- Modeling: Demonstration
- Physical: Hands-on guidance
What is DMD?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a genetic disorder characterized by a progressive loss of muscle
- Muscle cell destruction d/t missing or abnormal dystrophin (Xp21 gene)
Pattern of muscle weakness seen in DMD
Proximal > distal muscle weakness
What is dystrophin?
A protein that is essential to proper functioning muscles.
- Provides stability and structure to the muscle membrane
When the body has no dystrophin, what will occur?
Lead to muscle tissue breakdown
- Muscle is replaced with scar and adipose tissue
- Results in loss of strength, function and eventual joint contractures
Muscular dystrophy continuum
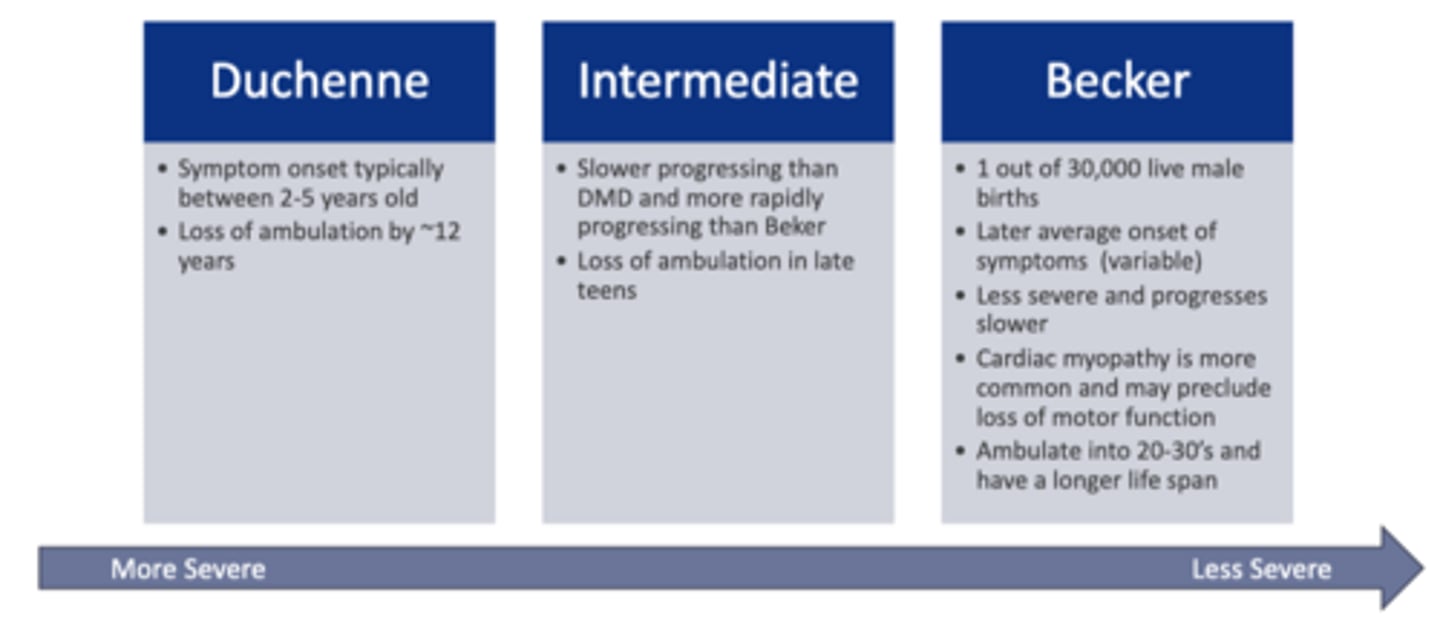
What age do typical DMD sx onset?
sx onset between 2-5 years old
What is common age for loss of ambulation with DMD?
~12 years old
Red flags for prompt referral to DMD specialist
- Creatine kinase levels >3x normal vis blood labs
- Tongue fasciculations
- Absent DTRs
- (+) Gower's sign
- Lack of development in major milestones
- Loss of motor milestones
- Calf pseudohypertrophy
Medical tx for DMD
NO curative treatment
- Oral corticosteroids (help prolong ambulation)
Stages of DMD
1. diagnosis
2. early ambulatory
3. late ambulatory
4. early non-ambulatory
5. late non-ambulatory
Diagnosis stage of DMD

Characteristics of early ambulatory stage of DMD

Characteristics of late ambulatory stage of DMD

Characteristics of early NON-ambulatory stage of DMD

Characteristics of late NON-ambulatory stage of DMD

Postural impairments seen in DMD
- Increased lumbar lordosis
- Calf pseudohypertrophy
- Scapular winging
- Mild out-towing
Typical progression of decreased ROM throughout DMD stages
Early: Limited PF, hip flexion, hamstring length
Transitional stages: Progression from above + forearm pronators and long finger flexors
Late: Progression from above + elbow flexors, cervical and worsening of scoliosis
Typical progression of muscle weakness throughout DMD stages
Early: Weak core, hip flexors/extensors/ABD, quads, PF/DF
Transitional stages: Progression from above + proximal UE
Late: Progression from above + distal UE, respiratory muscles, head control, chewing/swallowing
What is gower's sign?
Indicator of muscular dystrophy; to stand, the child has to "walk" hands up legs
What intensity of exercise should be prescribed for DMD?
Sub-max (Avoid high resistance and eccentric exercises)
- Examples: Swimming, walking, biking, standing (in late phases)
Cutoff scores that suggest loss of ambulation and functional decline over next 12 months
- 10mWT: >10-12 secs
- 6MWT: <325 m
- Floor to stand: >30 secs
- Time to climb 4 stairs: >8 secs
- NSAA: <9
What is the NSAA?
17 item scale assessing motor function in ambulatory patients with DMD
- Admin time 10-20 mins
- Scoring: 0 (lowest) - 34 (highest), each can receive score 2, 1, or 0
What is the Performance Upper Limb Test?
DMD disease specific scale which is best used for late ambulatory and non-ambulatory phases, when UE weakness becomes more prominent
- Scoring: 0 (lowest) - 42 (highest), each can receive 2, 1, or 0