Geography Case Study + Certain Key Facts
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Constructive Plate Boundrary
←→ Hot molten magma rises between plates, tectonic plates move away using ridge push and slab pull, magma cools forming new plate, on land rift valleys form.
Destructive
→← When tectonic plates converge, pressure builds between them. The rock eventually fractures, causing earthquakes. When oceanic and continental plates collide, the denser oceanic plate is subducted under the continental plate in to the mantle, where it melts. Hot magma can rise through the lithosphere and erupt as lava through volcanoes.
Conservative
^v Pressure builds at the margin of the tectonic plates as they are pulled along behind a plate being subducted elsewhere (slab pull). As friction is overcome, the rock fractures in an earthquake
Slab pull
Plate tectonics sink into the mantle at a subduction zone
Crossrail
£19BN, completed in 2023 after several delays
140+ million customers journeys
Complaints about crowding and reliability
Raised property values 25% around stations along crossrail route.
£42BN benefit to wider uk economy
55,000 full time jobs generated
Commonwealth
2.7 billion people, 56 countries.
Combined GDP of US$13.1 Trillion, estimated to reach 19.5 trillion by 2027
Many commonwealth countries have low ecological footprint.
In sub-saharan africa, 7/10 top performing countries for gender equality are members of commonwealth.
North/south divide
Lower life expectancy (75.2 male in Manchester VS 82.4 male in Chelsea)
South pupils 40% more likely to get good gcse grades
Average house price NE is 193,200 VS 471,286 in SE
10% unemployment in NE (highest in UK)
Fixing North/South divide
Improved transport links (HS2, which reduces london brum journeys by an hour, £10bn added to economy, 41,000 new homes, 30,000 new jobs)
LEPs 38 LEPs in england, lancanshire lep created 50,000 new jobs, and they are planning a £62 million BT investment to make wifi better for 97% of region
Enterprize Zones, enterprize zones in salmesbury and watson will create 6000 highly skilled jobs in advanced engineering and manufacturing sector
Changing transport infrastructure
40+ million vehicles on road in 2023 (25 million in 80s)
Heathrow and gatwick opening new runways; heathrow expansion plan to generate £12bn. But they will destroy rivers, homes and have to reroute the M25.
Outer Hebrides
50% population decline since 1901 as the main industry on the island doesn’t need that much work. (crofts)
Impacts of textile industry
Account for 10% of global carbon emissions
70 million oil barrels used annually to produce polyester
20% of industrial water pollution comes from textiles and dyes
90% of Mongolia is facing desertification due to breeding of cashemere goats
30% decrease in food production due to degraded soil in next 20-50 years if nothing changes.
1.5 trillion litres of water used annually
Celtic and Co
All materials biodegradable + recyclable
Offcuts that are too small to work with given away to schools and charities
75% of clothes made in Newquay, Cornwall
Repair and resole service for their boots
Customers can give used clothes to be recycled by the company
M&S
100% of cotton sourced from renewable sources, leading to 40% higher revenue for convential farmers, 30% less water use and 10% yield improvement
Cambridge Science Park
Connected to London on M11
35 miles from stanstead airport
170 companies based there (Microsoft, Toshiba)
Has lead to a congested city, higher house prices and no connections to cities that aren’t london tbh
152 acres of mature parkland, bicycle storage, 7,200 employees, nursery, health and fitness centre, etc
Cobalt business park
Provides recreation, fitness centre, cycleways, green space
20 minutes from international airport, close to A1 road
Business in cobalt qualify for gov assistance
Deindustrialisation
3,500 coal mines in 1913, 0 now.
Iron and steel industry got cooked when shipyards got cooked. Last steelworks closed in 2015
Easington colliery devasted local town when it closed in 1993, making 1000 men in the area unempluzzed, unemployment is still high in the area.
Post-deindustrialisation
IT in UK worth 58bn/year
100,000 software companies in UK
LARGEST mobile device market in europe
Nigeria’s Importance?
Largest economy in Africa
Predicted to be top 20 economies by 2050
Largest country in africa (224 million), very young population
Supplies 2.75% of world’s oil
Other facts of Nigeria
Oil makes up 98% of Nigeria’s export value
70% of pop lives in poverty
250 ethnic groups
In 2013, nigeria contributed 5th largest number of troops to UN
Tourism in Tunisia
Since 1960 life expectancy rose from 42 to 76
7 UNESCO sites, the starwars building too
Tourism industry provided 370,000 jobs
2015 tourist attacks leading to a 40% decrease in visitors.
Strategies to reduce development gap
Aid, Economic Invest, Intermediate Technology, Microfinance Loans, Fair Trade, Debt relief, Industrial development.
Case studies for certain strategies to reduce development gap.
Intermediate Technology
Solar powered bulbs in Nepal
Economic Invest
More than 2000 Chinese companies have invested billions into Africa.
Microfinance Loans
Phones for Women with Grameen Bank, they lend $200 to woman to buy a phone, then the woman charge other people to use the phone
They’ve lent 9 million people money, 97% of whom are WOMEN!
Typhoon Haiyan
6000 people reported dead
1,000,000 homes damage
Oil barge spilled 800,000L of oil, affecting 10 hectares of mangrove trees.
8 people died in Tacloban raiding a rice building.
£20 billion cost (5% of its GNP)
£1.5 billion in foreign aid
Wind speeds up to 314km/h
15 feet storm surge, flooding attracted snakes.
HMS Illustrious provided aid and 8 helicopters.
How do storms form?
Tropical storms form in areas of low pressure between 5 and 30 degrees north and south of the Equator.
For a tropical storm to form the ocean temperature needs to be least 27 for a period of several weeks.
Warm, moist air rises creating low pressure.
Air is drawn in to fill the low pressure from the surrounding area creating strong winds.
The winds spiral inwards due to the curvature of the earth. This is known as the Coriolis effect.
As the warm air rises is cools and clouds form, causing torrential rain.
Condensation releases latent heat which helps power the storm.
Storms in northern hemisphere spin anti-clockwise, clockwise in southern hemisphere
Also needs to be 60-70m deep IIRC
BEAST FROM THE EAST WAzuuh
1000 flights cancelled
7,000 schools closed in the UK
£1 bn lost every day of beast from the east
30 deaths
Insolation
Incoming solar radiation (basically heat from sun), intensity of it varies depending on latitude (curvature of the earth)
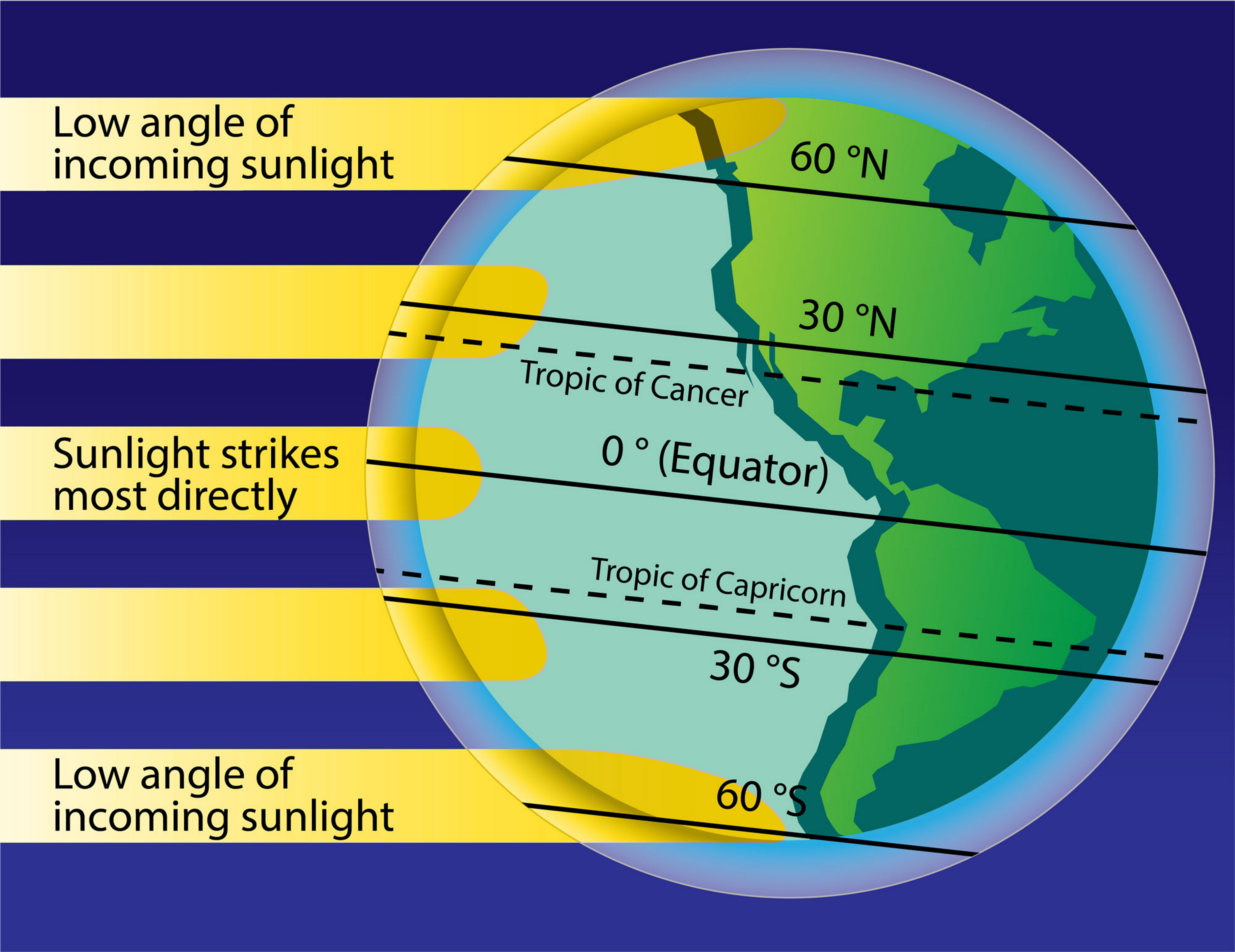
Global atmospheric circulation
Hot air rises at the Equator creating low pressure and heavy rain.
This leads to the growth of rainforests at the Equator (hot, wet conditions)
The air travels along the top of the atmosphere and begins to sink back down at 30N and 30S.
This lead to high pressure as the air sinks, resulting in dry conditions and desert formation.
High pressure = Cool air, gets dense and sinks to ground, leading to clear skies and dry conditions
Low pressure = Warm air, gets less dense and rises. Creating evaporation leading to clouds, wetness, windyness
Managing Climate Change
Alternative energy
Planting trees
Carbon capture & storage (muy expensive) (we could handle 10-50% of CO2 emissions until 2100 if we did this)
International Agreements (e.g. Paris Agreement)
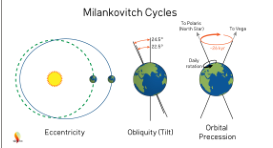
Milankovitch Cycles
Eccentricity (path of earth’s orbit)
Precession (natural wobble of earth), varies on 19,000-24,000 years cycle
Obliquity/Axal Tilt, every 41,000 years varies between 21.5-24.5 degrees. 23.5 degrees rn
Basically when these aspects line up, earth can get HOT, or cold
Solar Activity
Cyclical changes in solar energy linked to the presence of sunspots. 11 year changes in sun’s sunspot activity, more sunspots, more hot.
Volcanic Activity
Short term decrease in temperature as ash blocks out solar rays; long-term increase due to increased CO2 in atmosphere.
How we know earth’s climate has changed?
When you get a U-shape in a valley, that means it used to be ice, the very slow movement of ice carves this U-Shaped valley, and when it melts you get this landform.
Back in the day (1810), you could skate across the Thames, this has not happened in our lifetime.
You can study the rings of old trees.
Study the width, can tell you about rainy seasons, avalanches, etc.
Measure the greenhouses gases storied in ice cores extracted from the Antarctic.
Tools of measurement we used in comp 3
Calipers - rocky rocky measure
clinometer - angle gun
Freiburg Traffic
400km cycle paths
70% of population lives next to a tramline, tram every 8 minutes
any tickets for events are valid for public transport
Has lead to:
25,000 more tram journeys in 1 year, 30,000 less car journeys in 1 year.
Low car density (<500 cars per 1000 residents)
Singapore Traffic
High petrol prices
Electronic road pricing on major roads
Lead to:
45% less traffic,
2/3 of all daily journeys by public transport
Beijing
Cars banned from city one day a week based on a number-plate system
Non-residents can’t bring a car in to city.
Expansion of public transport, (30 new metro lines and a BRT)
Lead to:
20% drop in car use, but 5 million cars still and congestion gna get worse.
UK WASTE
Produces 30 million tonnes (UK) every year
400 million if you include mining+quarrying waste
20% of household waste culd be composted
in last 10 years, recycling increased from 11% to 40%
London stats
9 mil population, 300+ languages spoken
Notting hill carni shows multiculturalness
By 2040 it is estimated POC’s will outnumber white ppl.
35.6 avg age, compared to 40.3 nationally
Immigrants
8 million immigrants in UK; 6/10 come here to work.
26% of doctors born outside UK
Shoreditch
Good links to City of London (CBD)
Got gentrified, formally lots of bangladeshi’s in brick lane.
In 1980s, home owernship 60% (this is higher than today)
Greenbelt
If we used 1% of available greenbelt land, we could create 600,000 homes.
London waste
4000 premature deaths per year due to pollution
Most of central London is above EU limit of 40mg/m
¼ of London’s waste goes to landfill outside of London
Solutions to London waste
Cycle superhighways
Cyclists risen from 1% of road users to 15%
1/8 cars electric in 2020, compared to 1/16 in 2019. Rapidly increasing.
Government goal of 0 landfill waste by 2030, 61% of waste is recycled.
Lagos water supply
10% have access to treated piped water.
People dig bore holes, but bore holes often get contaminated.
In 2012, Lagos officials started policing use of boreholes and giving out permits for water vendors.
Cholera
3604 deaths in 2021 from Cholera in Nigeria.
820,000 infected after Haiti earthquake
Traffic in Lagos
3h+/day in traffic for average Lagosian.
28 per 100,000 fatal accident rate
Air pollution 5x higher than recommend limit
LAMATA introduced a BRT; 200,000+ people use service every day, still not enough, buses often over capacity.
Makoko
60% of people live in squatter settlements (like Makoko) in Lagos
55% use a pit latrine
Live on less than $2/day
250,000 population, people happy to be here.
Lagos Importance
Diverse economy (50% of Nigeria’s non-oil industry is located in Lagos)
GDP of >$136 BILLION (2017)
7th Fastest growing city in the world
80% of foreign trade flows through Lagos (next to atlantic coastline)
Megacities
In 2015, 28, by 2050 there will be 50.
Urbanization
56% of population lived in urban areas compared to 34% in 1960.
Why Haiti Earthquake was so bad
34th Highest population density in the world
53% adult literacy rate
Gdp per person of $659
Last major earthquake was in 1770
7.1 magnitude, 5 mile deep focus.
Haiti Effects
220,000 deaths
1.5 million homeless
£10 billion cost of damage (practically their entire GDP)
Haiti response
£5.8Bn pledged, only half materialized.
NGOs set up camps
20 million cubic metres of rubble generated, only 5% cleared within next few months.
USA, UK sent 10,000 troops
Damaged water supply lead to cholera outbreak (10,000 deaths)
Christchurch, New Zealand Earthquake
14,000 earthquakes/year
6.3 magnitude
185 death toll
£12Bn cost damage
Effects of Christchurch earthquake
80% of City lost power - waste and water services also disrupted.
30million tonnes of Ice tumbled into Tasman lake, hitting boats with 3.5m high waves
185 death toll
£12Bn cost damage
Response to Christchurch Earthquake
NZ government declared state of national emergency.
Redcross appealed internationally, raising millions.
Power companies constructed new lines within 2.5 days.
£12 billion cost of insurance claims.
Medical staff from Australia
Saguaro Cactus Adaption
Spikes instead of leaves minimize surface area, leading to less water loss through transpiration + deter animals from eating it.
Shallow root systems cover lots of area, allowing maximum absorption of water
Pleats between the ribs allow stem to swell when water in absorbed. (Able to absorb 95% of its total body weight in water)
Managing TRF’s strategies
Eco tourism ($7Bn USD/YEAR), site along the Rio Negra that does this, allows families to stop surviving off deforestation, but this instead. Dolphins no longer seen as a nuisance, but as an economic boon.
International Agreements, countries threaten to cut country’s funds unless they fix deforestation, e.g. Norway (since 2008) has donated £1.1Bn to Brazil, but threatened to cut if deforestation was not reduced.
Selective logging + replanting; mimic nature in how you cut trees, mark long term residual trees to not be harvested, collect saplings of trees, grow them in nurseries and then replant. Clear cuts are beneficial as it’s natural and helps forests develop.
Rainforest Importance
Home to 2/3 of world’s plant species and 30 million species in general
20% of worlds O2
2000-3000mm of rainfall, 25-30C temps
400+ indigenous groups
4,100 miles of rivers in rainforest
25% of medicine comes from rainforest plants
Deforestation
Forest loss contributes 12-17% of greenhouse gas emissions
4000-6000 species go extinct every year due to deforesation
At current rate of deforestation rainforests could be lost in 100 years (half already lost)
Why does deforestation happen?
Cattle ranching - 70%
Small-scale agriculture - 19%
Logging - 3%
Large-scale agriculture - 6%
Other (H.E.P, roadbuilding, etc) - 2%
Further negative effects of deforestation
Makes soil fertility bad - top part of forest cover is cleared leads to thin topsoil being removed by heavy rainfall, these bare slopes are prone to soil erosion, silting up rivers and messing up fertility.
Gold mines cause deforestation and then the mercury used to separate gold from the ground enters nearby rivers, poisoning fish and local populations
330 indigenous tribes in 1900, only 240 now.
Creatures that have evolved in TRF.
Red-eyed tree frog has evolved sticky pads on its feet allowing it to grip on to leaves and branches high up. Bright red eyes startle predators, lives in canopy layer.
Liana are woody vines that grow up trunks of larger trees so they don’t have to waste energy building their own trunks to access the sunlight above.
Some trees grow buttress roots (large, wide instead of deep), as nutrients in soil are bad so this way they can access a lot of the surface-nutrients, and also effectively support the tree stable in soft, wet ground.
Restoring an eco-system case study
Yellowstone got rid of wolves by 1926 due to fears it would scare away tourists, eco-system got done terribly (overflow of like deers or something), so in 1995 they brought them back and it saved the ecosystem, increasing vegetation population, allowing tree roots to fortify ground, stopping rivers from meandering.
River Tees
85 miles
High force waterfall, highest waterfall in England, formed due to dolerite, laying over limestone (limestone gets eroded quicker)
Meanders in river in SE-darlington
Floodplains + levees formed due to repeated flooding
Dorset Coast
Contains a stack called old harry - chalk headland eroded to form caves, arches, and a stump called Harry’s wife.
Chesil Beach is an 18-mile-long pebble tombolo (spit that joins island to mainland)
Studland bay and Swanage bay have a headland of harder chalk in between called ‘The Foreland’
Nepal energy case study
84% rural population
They have no coil, oil or gas reserves.
98% generated through hydropower, many of which are microhydros.
RUMA-KHOLA Microhydro, provides electricity for 6 villages, made using world-bank funds, it lead to a decrease in deforestation (as they don’t have to burn wood for energy)