Institutions and Development
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Definition of Institutions
\
* We will use broad definitions
* North - „rules of the game in society“
* Lin and Nugent - set of humanly devised behavioural rules that govern and shape the interaction of human beings, in part by helping them to form expectations of what other people do
* We will use broad definitions
* North - „rules of the game in society“
* Lin and Nugent - set of humanly devised behavioural rules that govern and shape the interaction of human beings, in part by helping them to form expectations of what other people do
2
New cards
Informal Institutions
\
* Informal institutions – norms, customs, ethics – often may be related to culture
* „Carriers of history“ – go through generation to generation
* Reflect current set of values
* Sanction are not by the state (private enforcement, moral condemnation, ostracism, loss of reputation)
* Role of tribal chiefs, religious leaders…
* Meaning of the institutions – shaping human behavior
* Informal institutions – norms, customs, ethics – often may be related to culture
* „Carriers of history“ – go through generation to generation
* Reflect current set of values
* Sanction are not by the state (private enforcement, moral condemnation, ostracism, loss of reputation)
* Role of tribal chiefs, religious leaders…
* Meaning of the institutions – shaping human behavior
3
New cards
Formal Institutions
\
* Formal ones – typically for example constitution, laws, regulation in general
* They determine political, economic and enforcement system
* They are being formed and enforced by the state – sanctions, fines, executions
* Formal ones – typically for example constitution, laws, regulation in general
* They determine political, economic and enforcement system
* They are being formed and enforced by the state – sanctions, fines, executions
4
New cards
Relation between formal and informal institutions
\
* Informal institutions play very significant role in shaping formal ones
* Formal ones may in a long term shape informal ones
* Informal institutions play very significant role in shaping formal ones
* Formal ones may in a long term shape informal ones
5
New cards
Role of the Institutions
\
* They structure incentives for human behavior
* They raise certainty in the world of imperfect knowledge and different perceptions
* As they shape behavior, they influence whole-society outcomes – the form of democracy and economic performance
* They structure incentives for human behavior
* They raise certainty in the world of imperfect knowledge and different perceptions
* As they shape behavior, they influence whole-society outcomes – the form of democracy and economic performance
6
New cards
Impact of institutions on development
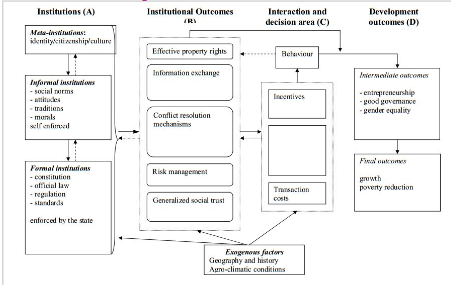
7
New cards
Origin of Institutions
\
* Institutions are never neutral, they have a „political origin“
* They reflect ideas, values and interests of those who had created them (rational actors)
* They are often outcome of a political bargain and compromises
* In practice they may function differently from what was intended
* Institutions are never neutral, they have a „political origin“
* They reflect ideas, values and interests of those who had created them (rational actors)
* They are often outcome of a political bargain and compromises
* In practice they may function differently from what was intended
8
New cards
Institutional History
\
* Current institutions in developing countries are often influenced by the institutions imposed by former colonial powers
* Different types of settlement = different institutions?
* Difference between North and South America
* Current institutions in developing countries are often influenced by the institutions imposed by former colonial powers
* Different types of settlement = different institutions?
* Difference between North and South America
9
New cards
Institutional Change
\
* Institutions do not have a fixed character
* Rapid changes are not usuall (unless there is a revolution)
* Internal or external threats
* Change of ideas or interests of the key players in society
* Institutions are subjects to a long-lasting political struggle – the winner is able to change them
* Some actors are more powerful to change institutions than others (poor, low-caste are weak)
* Institutions do not have a fixed character
* Rapid changes are not usuall (unless there is a revolution)
* Internal or external threats
* Change of ideas or interests of the key players in society
* Institutions are subjects to a long-lasting political struggle – the winner is able to change them
* Some actors are more powerful to change institutions than others (poor, low-caste are weak)
10
New cards
Virtuous vs. Vicious Circles
\
* Acemoglu-Robinson – theory of institutional change
* Virtuous circle – a positive change tends to bring more positive changes and brings new interests into play
* Vicious circles – there are forces that keep the old system together
* Interplay of political and economic institutions
* Acemoglu-Robinson – theory of institutional change
* Virtuous circle – a positive change tends to bring more positive changes and brings new interests into play
* Vicious circles – there are forces that keep the old system together
* Interplay of political and economic institutions
11
New cards
Governance
\
* Set of traditions and institutions that create rules for performing of autority in a given country
* 1) Processes by which the government is created, monitored and changed
* 2) The capacity to govern – to formulate and implement politics
* 3) Respect of the citizens to the government
* Set of traditions and institutions that create rules for performing of autority in a given country
* 1) Processes by which the government is created, monitored and changed
* 2) The capacity to govern – to formulate and implement politics
* 3) Respect of the citizens to the government
12
New cards
Separation of Powers
\
* First made up by Montesquieau
* Legislative, executive and judiciary branch
* Several principles
* Division of powers
* Indipendence of powers
* Balance of powers
* None of the powers is accountable to the others
* First made up by Montesquieau
* Legislative, executive and judiciary branch
* Several principles
* Division of powers
* Indipendence of powers
* Balance of powers
* None of the powers is accountable to the others
13
New cards
Rule of Law
\
* The state has to obbey its own laws – it has to act in accordance with the law
* States gives the guarantees for justice
* Judiciary branch oversees the executive one
* Principle of legal certainty
* The state has to obbey its own laws – it has to act in accordance with the law
* States gives the guarantees for justice
* Judiciary branch oversees the executive one
* Principle of legal certainty
14
New cards
Constitution
\
* Basic law of the country
* Sets „rules of the game“
* Creates a basic legal framework, divides the powers between various actors
* Rules of the competition for pover, its use, distribution and control over it
* There are rigid constitutions and more changeable ones
* Informal institutions like political culture play an important role in keeping the consensus on the basic rules
* Basic law of the country
* Sets „rules of the game“
* Creates a basic legal framework, divides the powers between various actors
* Rules of the competition for pover, its use, distribution and control over it
* There are rigid constitutions and more changeable ones
* Informal institutions like political culture play an important role in keeping the consensus on the basic rules
15
New cards
Type of State and its organization
\
* Unitary vs Federal – more centralized or less centralized organization
* Presidential vs Parliamentary democracy – tips of the balance to one side or the other one
* Unitary vs Federal – more centralized or less centralized organization
* Presidential vs Parliamentary democracy – tips of the balance to one side or the other one
16
New cards
Political Parties
\
* Most common are mass based parties that try to agregate large number of votes
* Free political competition legalizes their governance
* Political parties serve as stabilizators of the regimes
* Ethnic or regional parties might undermine the integrity of the state
* Participation in the excersise of political power – either form government or opposition
* Multiparty, two-party and single-party systems
* Phenomenon of the pro-poor parties
* Most common are mass based parties that try to agregate large number of votes
* Free political competition legalizes their governance
* Political parties serve as stabilizators of the regimes
* Ethnic or regional parties might undermine the integrity of the state
* Participation in the excersise of political power – either form government or opposition
* Multiparty, two-party and single-party systems
* Phenomenon of the pro-poor parties
17
New cards
Function of State
\
* Security
* Clean and efficient bureaucracy necessary
* Protection of property rights
* Guarantee of the rule of law
* Protection against economic shocks and provision of basic social security
* Fight against corruption
* Security
* Clean and efficient bureaucracy necessary
* Protection of property rights
* Guarantee of the rule of law
* Protection against economic shocks and provision of basic social security
* Fight against corruption
18
New cards
Worldwide Governance Index
\
* Created by World Bank
* Voice and Responsibility
* Political Stability and Absence of Violence
* Effectiveness of the Government
* Quality of the Regulation
* Rule of Law
* Control of Corruption
* Created by World Bank
* Voice and Responsibility
* Political Stability and Absence of Violence
* Effectiveness of the Government
* Quality of the Regulation
* Rule of Law
* Control of Corruption
19
New cards
Protection of property rights
\
* One of the basic functions of the state
* Property rights are an incentive to investment and inovation
* De Soto – inadequate property rights are slowing down development
* In some states there is a problem with expropriation
* One of the basic functions of the state
* Property rights are an incentive to investment and inovation
* De Soto – inadequate property rights are slowing down development
* In some states there is a problem with expropriation
20
New cards
International Country Risk Guide (IRCG)
\
* Measures the quality of the investment climate
* It composes of 22 indicators:
* Government Stability
* Quality of Bureucracy
* GDP Growth
* Risk of Exproptiation
* Measures the quality of the investment climate
* It composes of 22 indicators:
* Government Stability
* Quality of Bureucracy
* GDP Growth
* Risk of Exproptiation
21
New cards
22
New cards
Corruption Perception Index
\
* Created by Transparency International
* Index made up by polls, opinions of experts
* Why only perception – hard data are missing
* Poor countries typically have highest CPI
* Created by Transparency International
* Index made up by polls, opinions of experts
* Why only perception – hard data are missing
* Poor countries typically have highest CPI