BIOL 4004 Exam 2
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
The ER lumen and golgi are topologically equivalent to the ________________
extracellular space
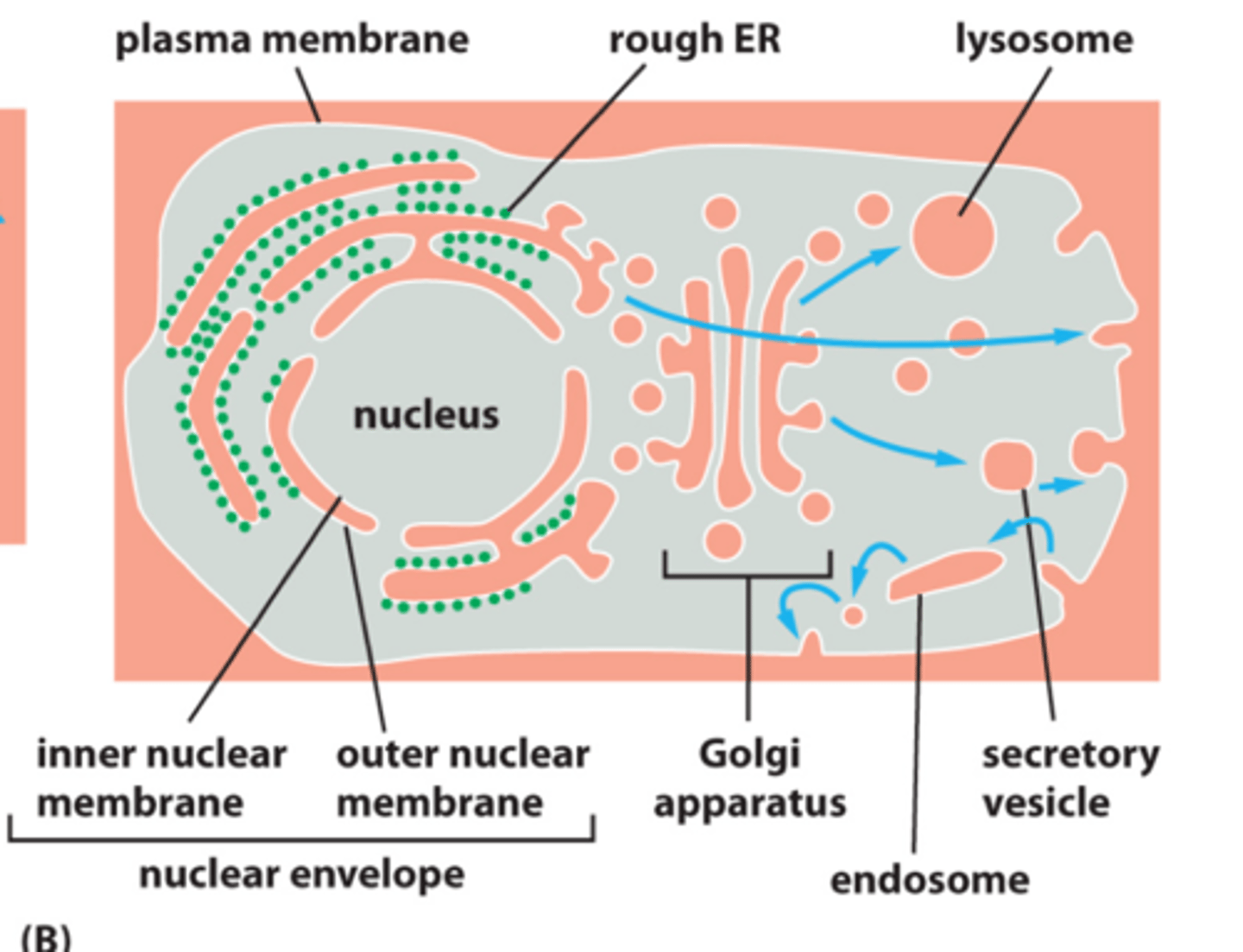
the nucleus is continuous with the ___________
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
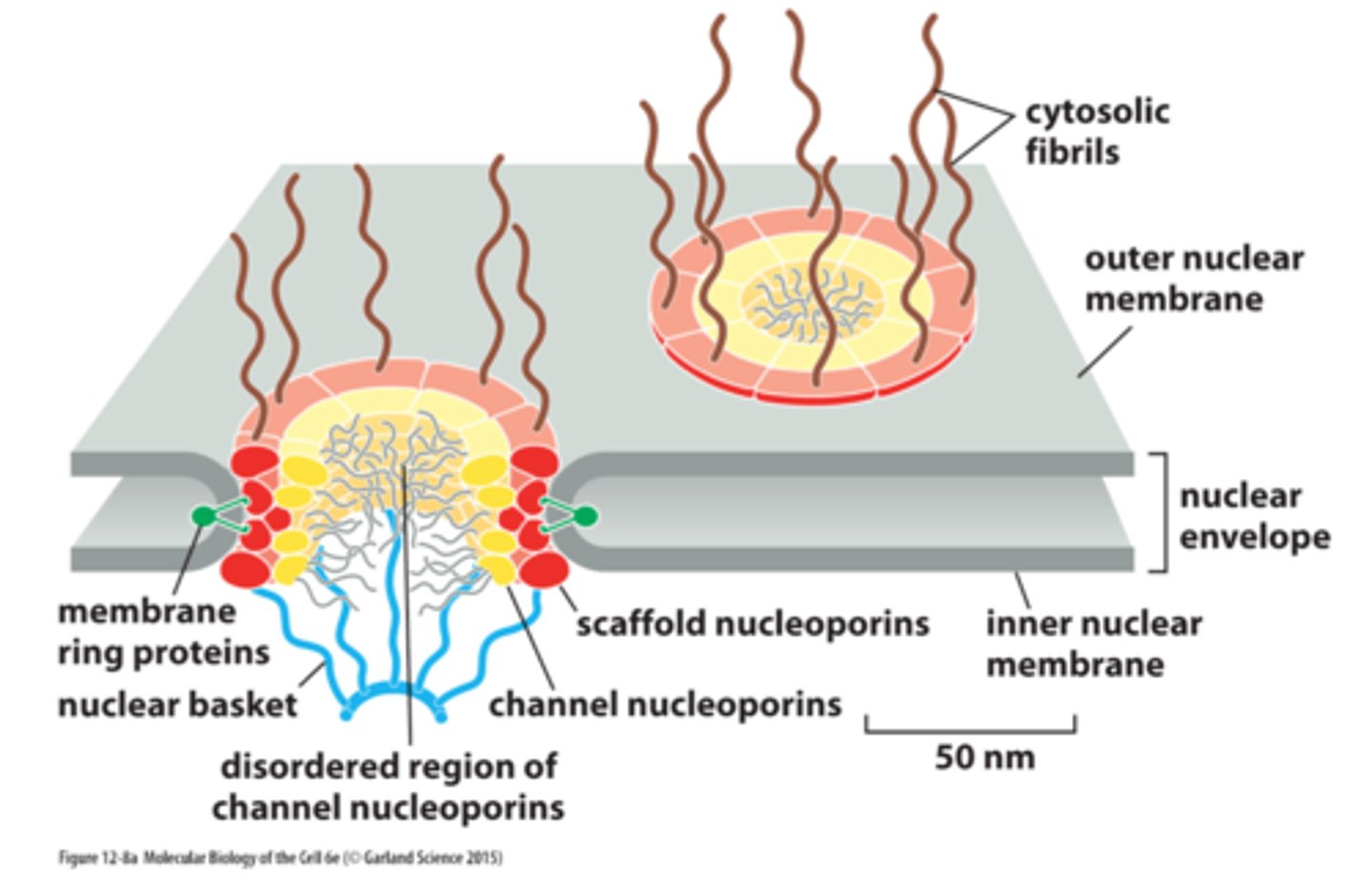
how many proteins is each nuclear pore complex (NPC) made up of
20-30 proteins
the localization of T-antigen containing its normal nuclear import signal
T-antigen will be localized to the nucleus as normal
localization of T-antigen containing a point mutation in the nuclear import signal
the sequence will no longer function as a NLS and the protein will remain in the cytosol
T or F: the mitochondria is part of endomembrane communication and vesicular traffic
F
All eukaryotic cells have the same basic set of _____1_____ that are functionally ______2______, and have __________3_________ compartments.
1. organelles
2. distinct
3. membrane-enclosed
What did the evolution of internal membranes accompany?
the specialization of membrane function
prokaryotes use their plasma membrane for ________
everything
2 distinct evolutionary origins of organelles:
1. progressive formation of an endocytosis system
2. endosymbiotic relationship
progressive formation of an endocytosis system
1. ancient prokaryotic cell
2. invagination
3. ancient eukaryotic cell
4. endomembrane system formation
What 2 special functions did the cell membrane of the ancient prokaryotic cell have in the formation of the endocytosis system?
1. It could anchor the DNA
2. ribosomes attached to it (so protein synthesis could occur by membrane)
endosymbiotic relationship
1. anaerobic pre-eukaryotic cell (from progressive formation of endocytosis system) engulfed an aerobic prokaryotic cell
2. initially both lived in symbiosis
3. aerobic eukaryotic cell with multiple mitochondria
3 benefits of forming an aerobic eukaryotic cell
1. cell became more functionally independent
2. contains their own genome
3. nuclear compartment surrounded by a double membrane (protects the chromosomes)
Where does protein synthesis begin?
on ribosomes in the cytosol
sorting cells
direct protein delivery to specific locations from cytoplasm
3 mechanisms used to move proteins from one compartment to another
1. gated transport
2. transmembrane transport
3. vesicle transport
gated transport
movement of proteins into and out of the nucleus

transmembrane transport
membrane bound protein translocates proteins across a membrane FROM the cytosol TO either the mitochondria or the ER lumen
vesicle transport
membrane-enclosed transport vesicles move proteins between compartments
example of vesicle transport
ER lumen --> golgi --> secretory vesicles --> cell exterior --> endosome --> lysosome (back into cell)
2 amino acids that the nuclear localization signal (NLS) is rich in
1. Lys
2. Arg
nuclear import receptor is a ___________ protein
cytoplasmic
what does the nuclear import receptor bind
NLS and NPC proteins
what does the nuclear import receptor have an affinity to
NPC
nuclear export occurs in a similar/different way from nuclear import
similar
2 things nuclear export requires
1. nuclear export signal
2. nuclear export receptors
what provides directional transport through nuclear pore complexes
Ran GTPase
T or F: nuclear transport is passive transport and requires no energy
F; it is active transport and requires energy
process that provides energy for nuclear transport
energy is provided by the hydrolysis of GTP by Ran GTPase
GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs)
triggers GTP hydrolysis and in effect inactivates Ran
Guanine Exchange Factor (GEF)
promotes the exchange of GDP for GTP (exchange reaction) on Ran GTPase
Ran-GTP binds to ____________________
nuclear import/export receptors
Ran-GDP does not bind to ______________
nuclear import/export receptors
Where is RanGDP localized?
cytosol
Where is RanGTP localized?
nucleus
Where is Ran-GAP located?
cytosol
Where is Ran-GEF located?
anchored to chromatin and is therefore in the nucleus
What drives nuclear transport in the appropriate direction?
the gradient of the two conformational forms of Ran
Steps of nuclear import
1. Nuclear import receptor (R) binds to cargo
2. R/Cargo complex binds to NPC proteins
3. R/Cargo moves to nucleus side of NPC
4. Ran-GTP binds to R, releasing cargo
5. R/Ran-GTP is transported back through NPC to the cytosol
6. GTP is hydrolyzed by Ran-GAP
7. Ran-GDP dissociates from receptor
Nuclear export occurs by a similar mechanism except that?
Ran-GTP (nucleus) promotes cargo binding to the export receptor
Mitochondrial proteins are transported into the mitochondria (MT) by a _______-___________________ mechanism
post-translational
what are mitochondrial proteins synthesized as?
as mitochondrial precursor proteins in the cytosol
T or F: mitochondrial proteins do not require a signal sequence for transport
F: they do require a signal sequence
How do mitochondrial proteins remain unfolded in the cytosol?
interact with chaperone proteins via binding
What family of chaperone proteins do mitochondrial proteins interact with?
Hsp70 family
____________________________ mediate protein transport across MT membranes
Protein translocators
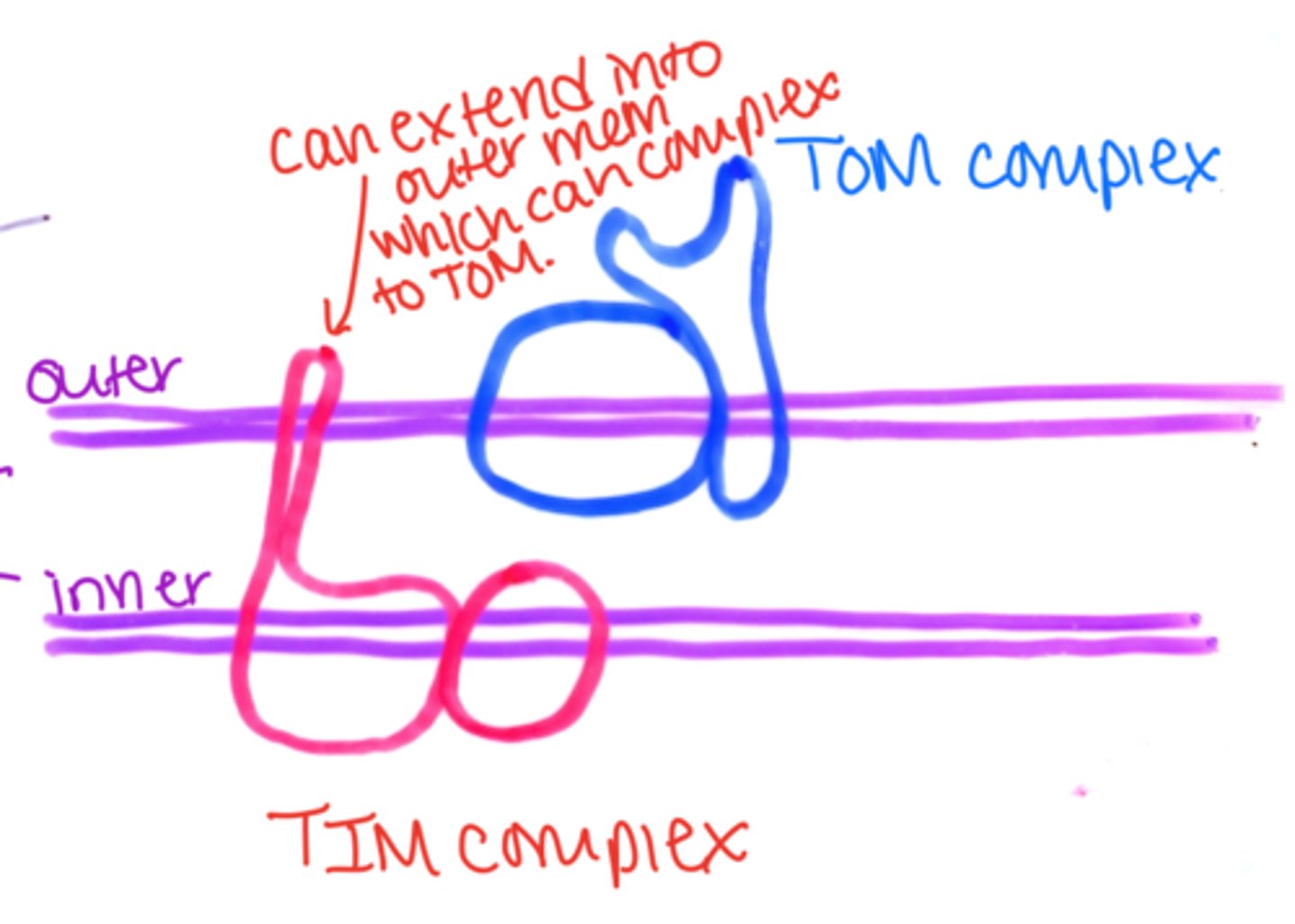
2 mitochondiral protein translocators
1. TOM complex
2. TIM complex
TOM complex
translocase of the outer MT membrane
TIM complex
translocase of the inner MT membrane
T or F: the TIM complex can extend slightly into the outer membrane
T: this allows it to complex with TOM
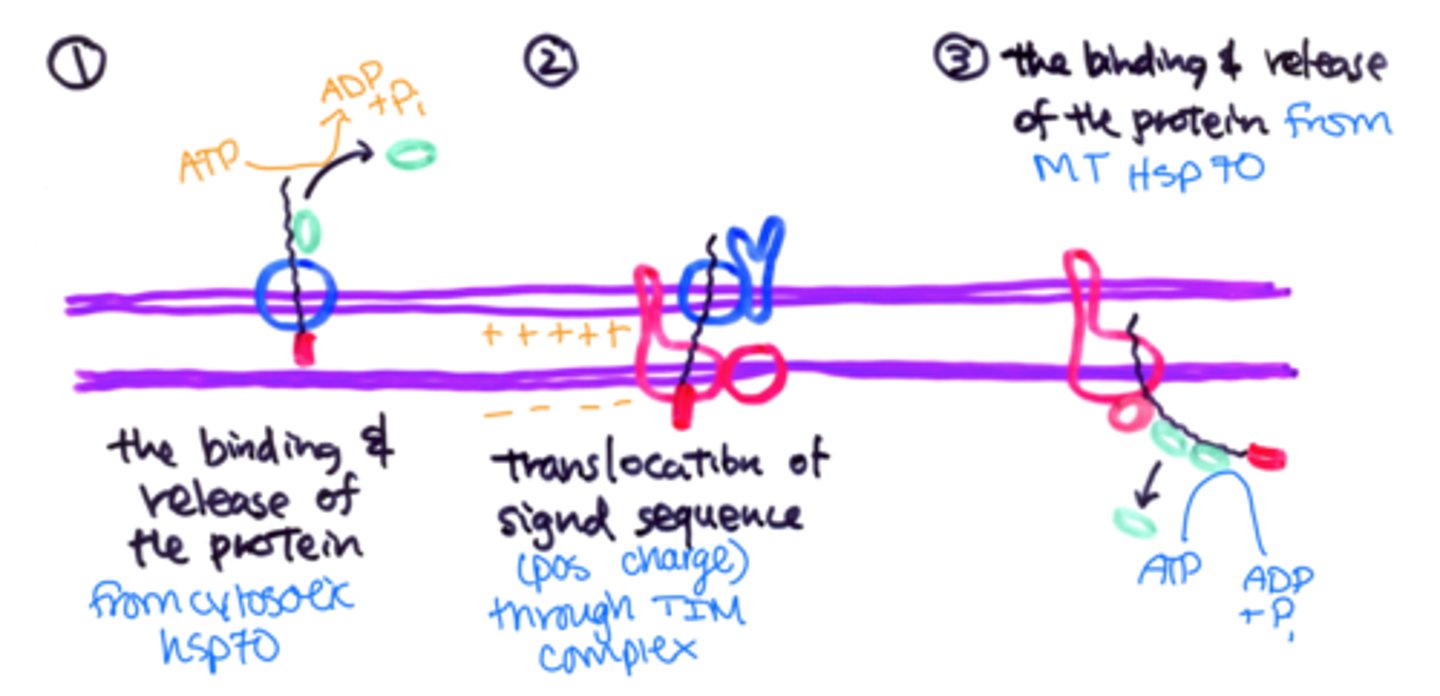
Steps of protein transport into mitochondria
1. precursor protein remains unfolded by binding Hsp70
2. signal sequence on N-terminus of protein binds to import receptor of TOM complex
3. translocation into matrix while still unfolded via binding of signal sequence to TIM complex
4. As soon as protein is in matrix, MT Hsp70 keep it unfolded until translocation is complete
5. signal sequence cleaved by signal peptidase
6. Hsp70 proteins leave and mature folded MT protein is formed
What 2 things drives protein import in to the matrix space?
1. ATP hydrolysis
2. membrane potential
Protein import into the mitochondria (MT) requires energy at what 3 steps?
1. ATP hydrolysis in the cytosol
2. Electrical H+ gradient (generated by H+ from the matrix to the intermembrane space)
3. ATP hydrolysis in the matrix space
5 vital cellular functions of ER
1. Protein synthesis and sorting
2. lipid biosynthesis
3. glycolsylation
4. attachment of lipid anchors to proteins
5. intracellular storage of calcium ion
glycolsylation
- attachment of sugars to proteins
- forms glycoproteins
Where does lipid modification occur?
golgi
T or F: ER is a closed vesicular space
T
transmembrane proteins end up going to the __________
membrane
secreted proteins end up _________________?
being secreted outside of the cell
proteins can be destined for the lumen of the ER and other organelles such as ______1______ and ______2_____
1. golgi
2. lysosome
import of proteins into the ER lumen is a ____-____________________ process
co-translational process
T or F: import of proteins into ER requires chaperone proteins
F: no, because this transport is co-translational
T or F: Import of proteins into ER lumen requires additional energy
F
Where does the translation of all proteins start?
cytosol (from there it can be directed to the mitochondria or ER lumen, etc)
Signal recognition particle (SRP)
directs ER signal sequences to a specific receptor in the rough ER membrane
the ER signal sequence is highly hydrophillic/hydrophobic (1) because of its _____-_____ (2) nonpolar amino acid stretch
1. hydrophobic
2. 15-20
Steps of protein translocation to rough ER membrane
1. translation starts in cytosol
2. SRP binds to signal sequence and ribosome blocking translation
3. SRP-ribosome complex binds to SRP receptor in ER membrane
4. SRP-ribosome complex binds to protein translocator
5. re-initiation of translation
model for translocation of a soluble protein across the ER membrane
1. re-initiation of translation
2. co-translational insertion into ER lumen
3. translation "pushes" polypeptide into ER
4. growing polypeptide forms a loop
5. ribosome is released after translation is finished
6. signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase
7. mature folded protein
model for insertion of a single-pass transmembrane protein into the ER membrane
1. signal sequence serves as a start-transfer signal
2. hydrophobic stretch of amino acids in polypeptides acts as a stop-transfer signal
3. stop-transfer signal anchors protein into the membrane (does not stop translocation)
4. stop-transfer signal is released into the membrane by the translocator and becomes membrane spanning segment of membrane
What is different about the transmembrane protein utilized for single-pass insertion into the ER membrane?
there is an additional hydrophobic region on the peptide that is NOT the signal sequence
What happens when you have multiple pairs of start and stop sequences?
you can use multiple translocators at the same time and have multiple transmembrane domains
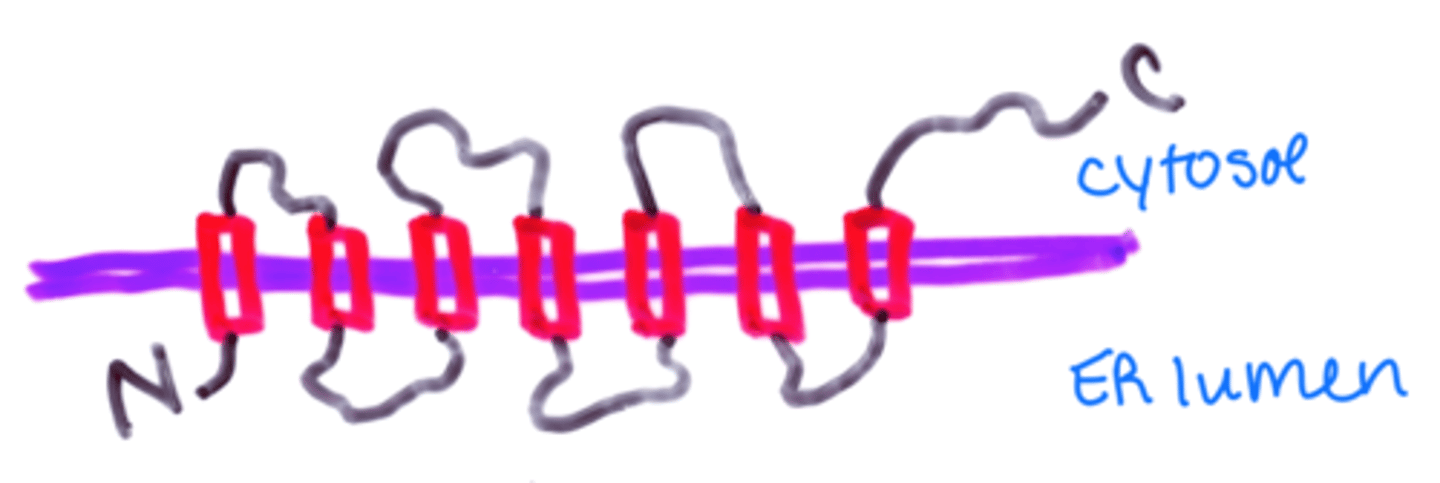
multiple start/stop-transfer signals direct each TM sequence into the ____1_____ and each region will be inserted into the ____2____ membrane
1. translocator
2. ER
What are most proteins in the ER?
glycoproteins
preformed precurser oligosaccharides
made in the ER but not linked to translation, there is always a pool of them
preformed precursor oligosaccharides are transferred to what?
proteins
dolichol
lipid molecule that holds the precursor oligosaccharide in the ER membrane
the precursor oligosaccharide is transferred to what amino acid residues?
Asn (N)
oligosaccharyl transferase
Enzyme that transfers a precursor oligosaccharide from membrane-bound dolichol to certain N residues of proteins imported into the ER.
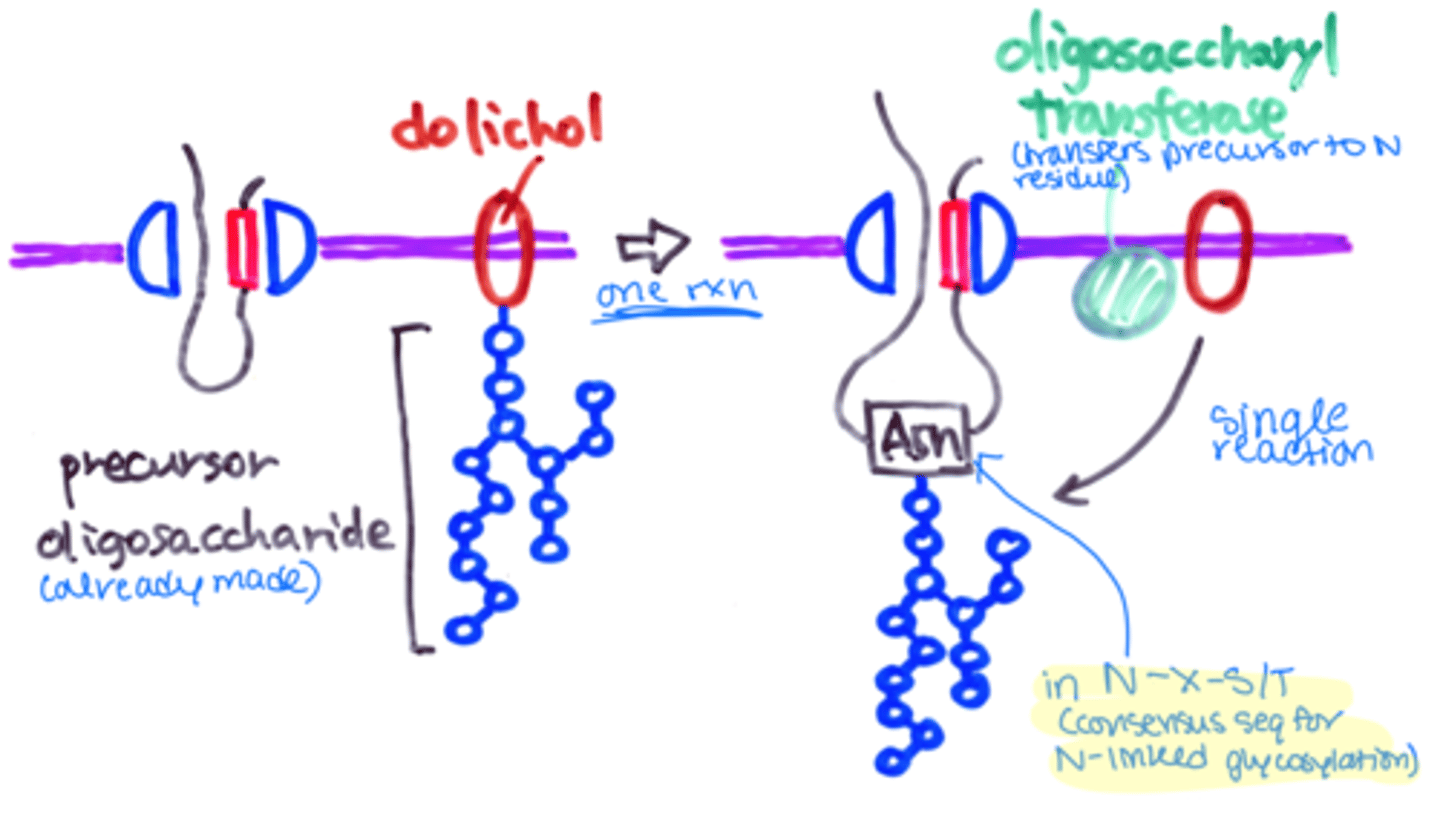
consensus sequence for N-linked glycosylation
N-X-S/T
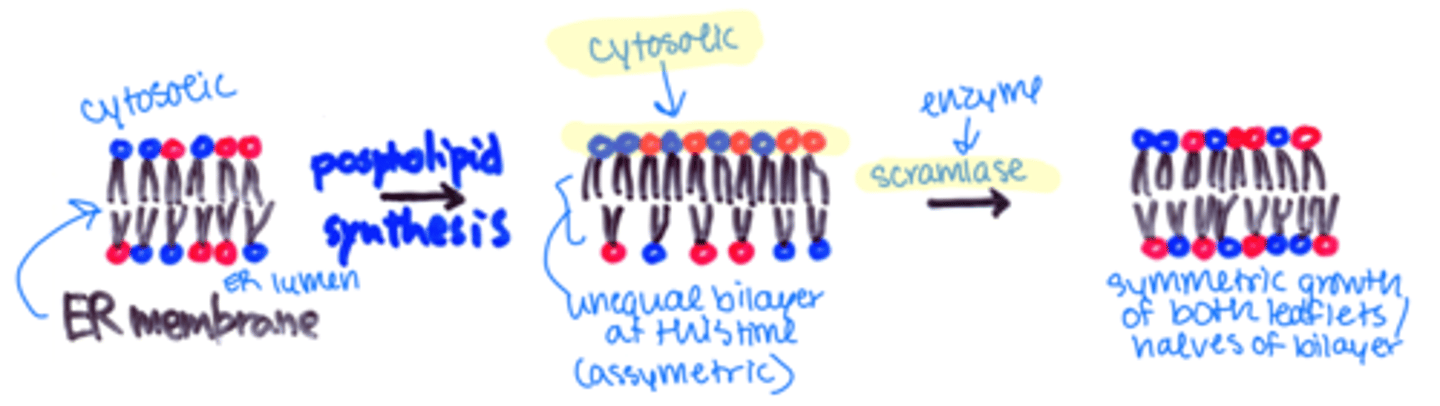
Where are most membrane lipid bilayers assembled?
ER
What does the ER membrane synthesize?
most of the major classes of lipids
where does the synthesis of phospholipids occur?
exclusively in the cytosolic leaflet of the ER membrane
Scramblase
phospholipid translocator that equilibrates between 2 leaflets
transport vesicles
transfer lipids and proteins between some organelles
5 organelles that transport vesicles work between
1. plasma membrane
2. ER
3. golgi
4. lysosomes
5. endosomes
microsomes
- artificial organelles derived from the ER (not naturally in mammalian cells)
- fragments of ER but still functional (can do everything ER can do)
Microsome formation
Cells are homogenized (crushed) making cells unviable, but still leaving some organelle function
In vitro-translation without microsomes
ribosomes are isolated and translation occurs without microsomes

In vitro translation with microsomes
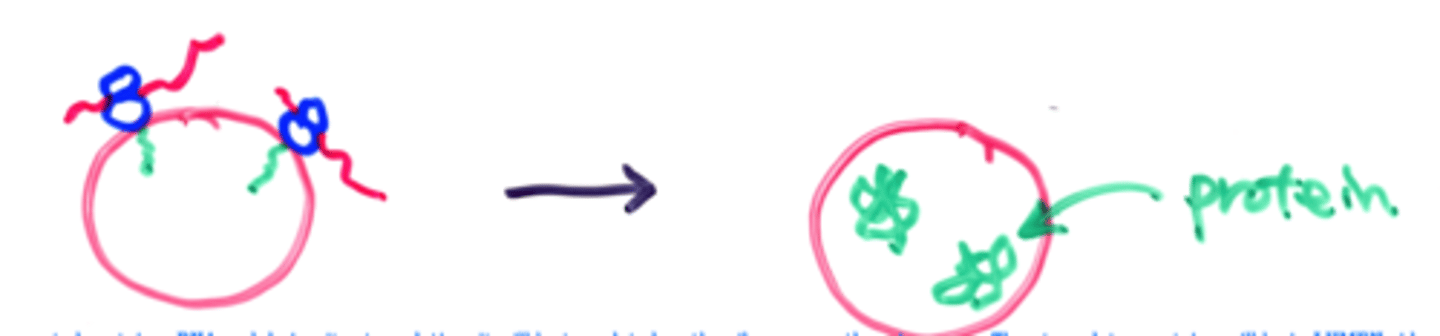
What happens when you add a small amount of protease to experiment with in vitro translation without microsomes?
the proteins will be degraded since there is no protection by a membrane
What happens when you add secreted mRNA to experiment of in vitro translation with microsomes?
mRNA will be translated on the ribosome on the microsome and the translated proteins will end up on the lumen side of the microsome
What happens when you add a small amount of protease to experiment with in vitro translation with microsomes?
it will degrade the protein outside of the ER membrane but the protein below the membrane will be protected
What happens when you add detergent and protease to experiment with in vitro translation with microsomes?
detergent will disrupt the microsome membrane allowing entire protein to be susceptible to degradation
What happens when you run a gel with the same polypeptides from the experiment of in vitro translation without microsomes?
there will be one band because the protein segments will be the same size (no modifications)
What happens when you run a gel with the same polypeptides from the experiment of in vitro translation with microsomes?
there will be multiple segments (ladder) because signal sequences could be cleaved and sugars could be added on via microsome method
1 out of 500 individuals has one defective _______1______ R which gives them a high risk of heart attack by ___________2___________
1. LDL
2. atherosclerosis
transport vesicles ______ 1________ from one compartment and ____2___ with another
1. bud off
2. fuse
what do transport vesicles carry?
materials as cargo
2 major pathways utilized by transport vesicles
1. biosynthetic secretory pathway
2. endocytic pathway