NR 442 Community Health Nursing Exam 2 Study Set questions and answers + rationales for student success
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Types of Disasters:
- Natural (eg. tornado, diseases, droughts, wildfires, hurricane, or earthquake)
- Man-made (e.g. plane crash, terrorism, riots, fires, bridge collapse, toxic spill, pollution, or wars)
- Combination (natural/technological) - natural disaster that creates or results in a widespread technological problem
What is a Natural Disaster?
- A natural event such as a flood, earthquake, or hurricane that causes great damage or loss of life

Mass Casualty Incident (MCI)
- A disaster situation that results in a large number of victims who need the response of multiple organizations; according to Dr. Lewis >100 people affected for a mass casualty incident
What is multiple casualties range?
- 1 to 99 individuals
What is terrorism?
- The use of violence and intimidation in the pursuit of political or social aims; unlawful use of force according to the FBI
What are weapons of mass destruction?
- Weapon designed to cause death or serious bodily injury; e.g. toxins, chemicals, explosives, biological agents, etc.
What is Anthrax?
- Spore-forming gram + bacterium Bacillus antracis; through inhalation is esp deadly
- S/S: Fevers + chills, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, confusion, dizziness, cough, N/V, stomach pains, headaches, fatigue, body aches are common primarily through inhalation methods
Bioterrorism
- The deliberate spread of pathogenic organisms into a community to cause widespread illness, fear, and panic
- E.g. small pox, anthrax, Ebola are category A agents
- E.g. Typhus, ricin toxin, west Nile virus, E.coli, and food safety threats are category B
- Influenza, TB, or rabies are category C and the third highest priority
Characteristics of Disasters
- Frequency, predictability, preventability, imminence-speed of onset, scope, and intensity
Prevention in Disasters
primary - aimed at preventing the occurrence of a disaster/limiting consequences
- during nondisaster/predisaster stages
secondary - search, rescue, triage of victims
- assessment of destruction and devastation
- implemented once disaster occurs
tertiary - focus on recovery and restoring community to previous levels of function
- aimed at preventing a recurrence/minimizing effects of future disasters
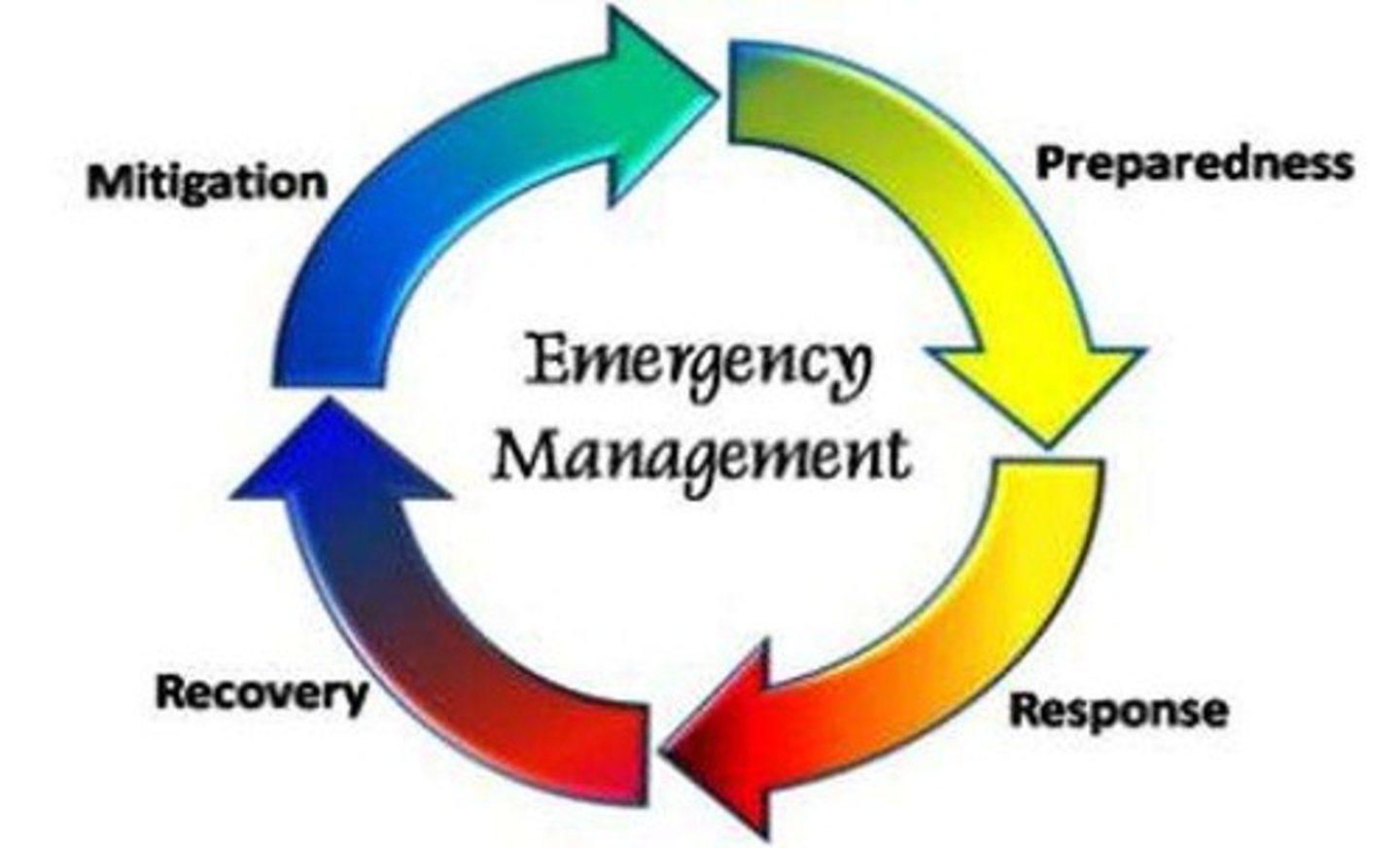
Disaster Management
- The plans that are in place designating the community's response to a disaster
- Respond more quickly, more effectively, and less confusion
- Ensures resources are available
- Basic Disaster Supply Kit - BOB (Bug Out Bag)
- Important papers, antiseptics, food, clothing, etc.
Governmental Responsibilities
- Local government (first responders) responsible for safety and welfare
- State government involved when disaster overwhelms local community resources
- Federal government through Department of Homeland Security, CDC, FEMA
U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
- Federal agency that is an umbrella for several existing agencies that was designed to bring together all the functions related to emergencies, immigration, border security, and antiterrorism efforts
FEMA - Federal Emergency Management Agency
- Agency charged with providing assistance to communities hit by natural disasters; Mission is to support citizens and first responders to ensure that, as a nation, everyone works together to build, sustain, and improve the capacity to prepare for, protect against, respond to, recover from, and mitigate all hazards
Disaster Management Stages
1. prevention
2. preparedness
3. response
4. recovery

Prevention Stage
- Identify potential disaster risks.
- Create risk maps
- Educate citizens regarding what actions to take to prepare for disasters.
- Individual, family, and community level
- Develop a plan for meeting the potential disasters identified.
Preparedness Stage
- Training in first aid
- Assembling a disaster emergency kit
- Establishing a predetermined meeting place
away from home
- Making a family communication plan
Response Stage
- Response stage begins
immediately after the disaster incident occurs
• May include:
• Shelter in place
• Evacuation
• Search and rescue
• Staging area
• Disaster triage
Disaster Triage
- START triage system- Nurses and other
emergency personnel such as physicians,
EMTs, and paramedics are responsible for
performing triage duties
• "Simple Triage And Rapid Treatment"-
Goal:
- Used in multicasualty or mass casualty
incident
- Triage of injured person should occur in
less than 1 minute based on:
• Respirations
• Perfusion
• Mental status
• Uses people with minor injuries to assist
• Person is tagged with a colored triage tag
• Victims moved to the treatment area
START Color-Coded Triage Tag
- Green = walking wounded
- Yellow = systemic but not yet life-threatening complications
- Red = life-threatening conditions that can be stabilized and have a high probability of survival
- Black = deceased or injuries so extensive that nothing can be done to save them
- Hazmat tag = contaminated

Psychological Triage
- Four keys to gauging mental health impact:
- Extreme and widespread property damage
- Serious and ongoing financial problems
- High prevalence of trauma in the form of injuries, threat to life, and loss of life
- When human intent caused the disaster
-In addition, panic during the disaster, horror, separation from family, and relocation or displacement may play a part
Public Health Activities
- Can take place at any level (e.g. individual, organization, community)
Responses to Disasters
- Community: heroic phase, honeymoon phase gratitude reliving the experience, disillusioned phase responders feel depression and exhaustion, and reconstruction when counseling may be needed
- Individual: cognitive, emotional, physical, behavioral, and PTSD
Recovery Stage:
- Begins when the danger from the disaster
has passed.
- All local, state, and federal agencies are
present in the area.
• Help victims rebuild their lives
• Restore public services
• Cleanup of damage and repair begins
• Evaluation and revision of the disaster
plans
• Understand the financial impact
Home Health Nursing
- "a specialized area of nursing practice, rooted in community health nursing, that delivers care in the residence of the client"

Purpose of Home Health Nursing
- Provide nursing care to individuals and families in their home
- Referrals: Physician, NP, hospital discharge planner, school teacher, clinical health care provider, or patient/patient family
Home Health - Balanced Budget Act of 1997
- Significantly changed the way Medicare pays for home health services
- No longer reimbursed using retrospective payment system for services rendered
- Now prospective payment system (PPS)
- HHS receive a fixed amount of money based on cost of client's given diagnosis
Types of Home Health Agencies
- Official (i.e., public)
- Nonprofit
- Proprietary/private corporate company
- Hospital-based agencies
Reimbursement for Home Care
- Medicare benefits under Title XVIII of the Social Security Act
- Individual over 65
- Homebound and under the care of a physician
- Requires medically necessary skilled nursing care or therapy services
- Exceptions for Medicare Hospice Benefit
- Medicaid benefits under Title XIX if eligible
- Private health insurance
OASIS
- The Outcome and Assessment Information
Set (OASIS) is a data set determines
Medicare pay rate and measures outcomes
of adult home care patients to monitor
outcome-based quality improvement -CMS,
2008
• Includes sociodemographic,
environmental, support system, health
status, and functional status attributes
of an adult patient.
• Is mandatory for all Medicare and
Medicaid patients receiving skilled care.
Nursing Standards for Home Health
- Baccalaureate-level education required
because of the autonomy and critical
thinking skills necessary in home care
• Care based on ANA standards and QSEN
competencies
• Patient centered care
• Teamwork and collaboration
• Evidence-based practice
• Quality improvement
• Safety
• Informatics
Conducting a Home Health Visit
- Visit preparation:
- Review the referral form
- Contact client and establish a trust
relationship
- Referral:
- Formal request for home visit from
clinician, communicable disease
service, hospital, client, or client's
family
- Contains info on current medications,
diet, physicians' orders, care plan
goals, other disciplines involved in care
Conducting a Home Health Visit (Part 2)
- Initial telephone contact
- Exchange of essential information
- Environment
- Observe drive to client home
- Surrounding neighborhood
- Accessibility of the home in
regards to client's condition
- Railings, lighting, etc.
Documentation/Assessment Home Health
- Obtain subjective information from
client and family.
- Obtain client health knowledge.
- Collect information through
observations and questions.
- Include information of functional
status, ADL for Medicare
reimbursement and individualized
care plan
- Develop a plan for the client and
family.
- Nursing diagnoses to address
client's problems and identifies
actual or potential
Hospice Home Care
- Improves end of life care
- Relieves suffering
- Supports the patient and family/caregiver through the dying process
- Provides grief support to the family after the patient has died

Caring for the Caregiver
- Careful assessment of the caregiver's mental and physical health is important
- All decisions regarding care are made considering the health of the caregivers
- Caregivers need constant reassurance for the care they provide
- Interventions to prevent decline in caregiver's health; respite care is important!
Pain Control & Symptoms Management
- Remember: The patient's pain is whatever he
or she says it is, regardless of the nurse's
objective evaluation of the situation
- Meds are given in doses sufficient to
keep patient free of pain; administered
on a regular schedule
- Help in managing other symptoms
(nausea and vomiting, constipation,
diarrhea, fatigue, decreased appetite)
- Provide emotional support to
patient/family as they adjust to patient's
impending death
- The main issue is pain management
and tolerance not addiction
- Breakthrough pain should not be a big
problem if the RN is using good
assessment, documentation and
knowledge about medications.
True/False: You can perform chest compressions if the patient is noted as a DNR
False, the patient has elected to not receive chest compressions for resuscitation check patient status before performing this!!!
Durable Power of Attorney
A durable power of attorney is another type of advanced directive that allows an individual to designate a healthcare proxy or surrogate to make decisions about medical treatment if the person is unable to make those decisions for themselves. Without those documents, state law may define who can legally make those decisions, which may vary by state.
Correctional Nursing
- Nursing that occurs in correctional facilities and is defined by the location of the work or the legal status of the patient, rather than by the role functions performed
- Recognize safety and security issues for the nurse; always maintain an escape rote
- Understand that: inmates manipulate nurses, environment is heavily isolated
Health Issues in Prison Populations
- Daily operations of a correctional clinic includes management of acute and chronic illness
- HIV, hepatitis, and TB
- Health care issues recognized during screenings
- Screen inmate upon entry
- Triage process includes physical and mental health history
Further Health Issues in Prison Populations:
- Women in prison: impact of drug use and victimization and stress associated with separation from children
- Adolescents: Often incarcerated in adult facilities that are ill-equipped with challenges of adolescent development
Mental Health Issues in Correctional Settings:
- Adjustment to incarceration is extremely difficult for many mentally ill individuals.
- Deinstitutionalization led to what amounts to "criminalization of the mentally ill."
- Access to mental health treatment and medication is a right for prison inmates.
- Nurses must always be aware of the vulnerabilities of people with mental illness who are incarcerated.
Education & Forensic Nursing
- Specialty education needed to obtain a certificate in forensic nursing, a minor or concentration, or a graduate degree
- Specialized curriculum:
- Fundamentals of forensic nursing
- Forensic law
- Forensic science
- A minimum number of supervised clinical hours
- A clinical internship may also be required
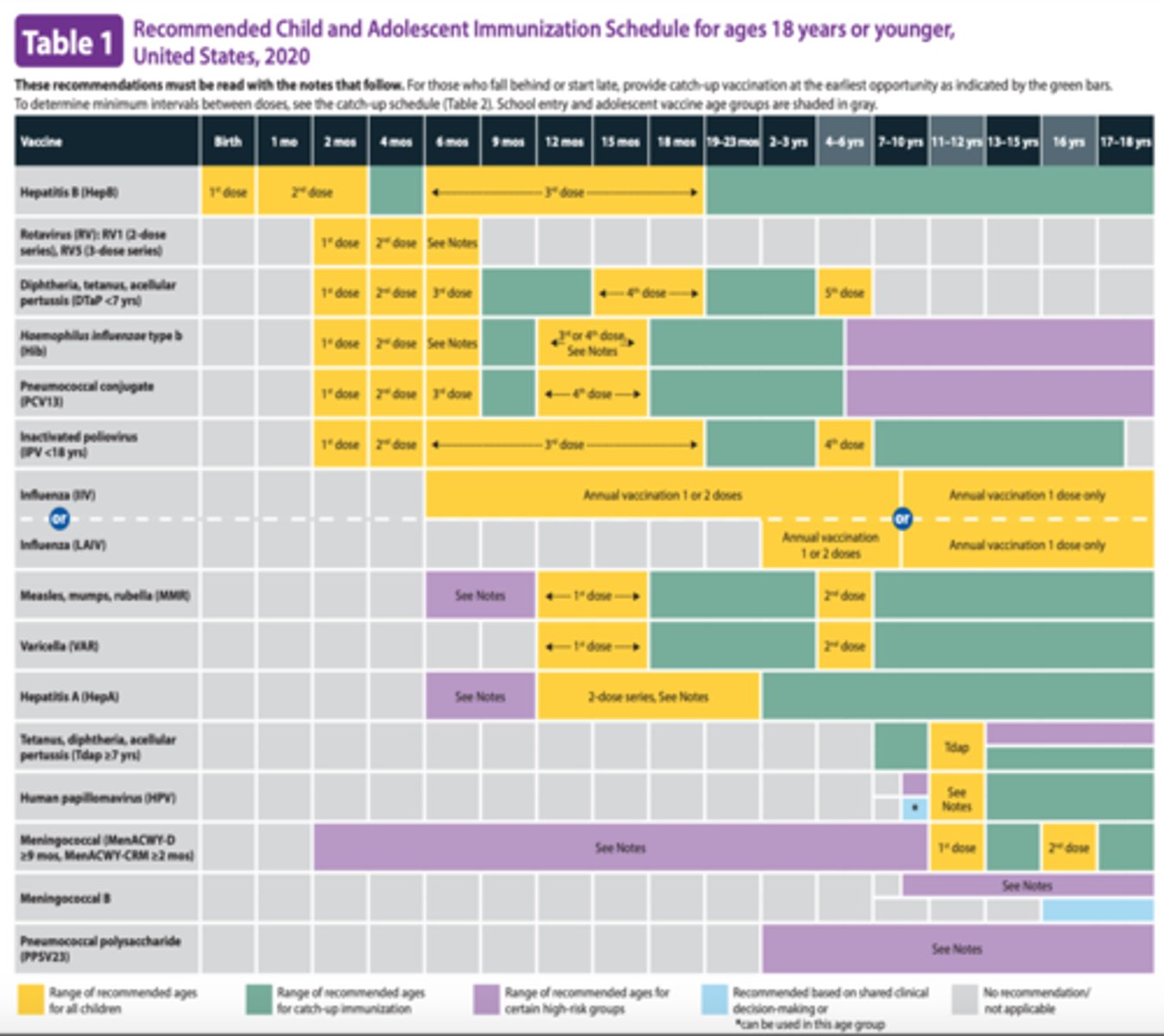
Immunization Schedule (Birth to 12 Months)
- Hep B
- Dtap
- IPV
- PVC
- HiB
- Influenza vaccine is appropriate at >6 months old
True/False: MMR, Varicella, Zoster, & HepB are live attenuated vaccines
False, while most of these are, HepB is inactivated
True/False: When considering administration of vaccines, fever, allergies are contraindications to administering live vaccines; in addition DO NOT administer if immunocompromised or pregnant
True
What is HIPAA?
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act; protects patient's private health information to being disseminated without consent
What is OSHA?
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration; a federal agency that sets standards for staff and patient safety.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
- Medicare is a federal program that provides health coverage if you are 65+ or under 65 and have a disability, no matter your income.
- Medicaid is a state and federal program that provides health coverage if you have a very low income.
Chaplains & Hospice
- During the end-of-life process, a hospice chaplain honors and nurtures a patient's spiritual needs. They are an important part of a hospice care team
Why are key informant interviews important?
- It is used for direct conversations with individual community members for the purpose of obtaining ideas and opinions
What is the difference between chronological and functional age?
- Actual age in years versus functional ability and the ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs)
True/False: Older adults generally prefer "aging in place" instead of living in nursing homes
True, older adults report wanting to age in their own homes instead of a facility
Sources of Income for Older Adults
- Four sources for population aged 65 and over:
o Social security
o Earnings
o Pension
o Assets
True/False: A large portion of older adults income is spent on groceries
False, the largest portion of income is spent on healthcare
Widowhood
- A label applied to both men and women who survive the death of a spouse...
o Seen more in women
• Loss of companionship and intimacy
• Loss of one's sexual partner
• Feelings of grief
• Loneliness and less efficient financial management
• Changes in relationships with children, married friends, and other family members
• Possibly raising their grandchildren
o Increase of number of children under 18 years living in households maintained by
grandparents
Healthy People 2020
- Attain high-quality, longer lives free of preventable disease, disability, injury, and premature death.
- Achieve health equity, eliminate disparities, and improve the health of all groups.
- Create social and physical environments that promote good health for all.
- Promote quality of life, healthy development, and healthy behaviors across all life stages.
True/False: The purpose of screenings is for early detect of disease not prophylaxis
True
Poor diet and physical activity leads to:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes
- Osteoporosis
- Some types of cancer
Common Health Concerns
• Chronic Illness
o Arthritis
o Hypertension
o Diabetes
• Medication use
o High prevalence of chronic diseases = large numbers of medication
o Older adults responsible for more than a third of total outpatient spending on
prescription medications
o Polypharmacy makes older adults vulnerable to drug interactions and dangerous
adverse reactions.
Elder Safety and Security Needs
1. Risk of falls
2. Physiologic changes
3. Chronic illness
4. Medications
5. Osteoporosis
6. Orthostatic Hypotension
7. Generalized weakening
8. Environmental hazards (home assessment), Cold Stress - Hypothermia
Elder Abuse and Neglect
- Any knowing, intentional, or negligent act by a caregiver or other person that causes harm to people age 65 and older
- Types include: physical, psychological/emotional, financial, and neglect
What is generalized anxiety disorder?
= An anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal; > 6 months in this state
What is Depression?
• Depression is a condition that interferes with daily life
such as the ability to work, sleep, concentrate, eat,
and enjoy life; hopelessness
o Can lead to suicide
• Maybe overlooked as older adults experience death
of loved ones, retirement, stressful life events
• Treatment may consist of medication alone or in
conjunction with psychotherapy.
What is the CAGE test?
- The CAGE questionnaire asks the following questions:
i. Have you ever felt you needed to Cut down on your drinking?
ii. Have people Annoyed you by criticizing your drinking?
iii. Have you ever felt Guilty about drinking?
iv. Have you ever felt you needed a drink first thing in the morning (Eye-opener) to steady your nerves or to get rid of a hangover?
- Two "yes" responses indicate that the possibility of alcoholism should be investigated further
Suicide in Older Adults:
As age increases, so does the rate of suicide
- Passive suicide: refusal to eat, drink or cooperate with care.
- Older adults tend not to communicate their intentions unless directly asked; thus suicidal attempts in older adults are more successful
- Associated with"
o Depression
o Chronic illness
o Physical impairment
o Medical conditions that significantly limit functioning or life expectance
o Unrelieved pain
o Financial stress
o Loss and grief
o Social isolation
o Alcoholism
Alzheimer's Disease (AD):
- A progressive disease that destroys the brain's neurons, gradually impairing memory, thinking, language, and other cognitive functions, resulting in the complete inability to care for oneself; the most common cause of dementia
- Assessment tools include:
o Mini-Cog
o Mini-Mental State Examination
o Clock drawing test
- No cure and limited treatment options are available.
End of Life Issues:
- Issues pertaining to management of the final phase of life, after-death disposition of the body and memorial services, and distribution of assets
- Patient Self-Determination Act (PSDA) of 1990
o Requires health care facilities that receive Medicare and Medicaid funds to ask
patients on admission if they possess advance directives.
• Living will
• Durable power of attorney
• DNR (do-not-resuscitate) order
• Physician Orders for Life Sustaining Treatment (POLST)
Nurse's Role End of Life Care
- Use therapeutic communication
- Provide psychosocial care
- Manage symptoms
- Promote dignity & self esteem
- Maintain a comfortable & peaceful environment
- Promote spiritual comfort & hope
- Facilitate mourning
Disabilities Overview:
- Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 and the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 define having a disability by how it limits carrying out a major life activity such as the ability to:
• Breathe
• Walk
• See
• Hear
• Speak
• Work
• Care for oneself
• Perform tasks
• Learn
- Disability is an umbrella term covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions
True/False: At age four, the nurse should plan to administer the following vaccines: IPV, MMR, Varicella, HepB, and Dtap
False, HepB is not administered at this age, but every other vaccine is correct
True/False: Children can receive the influenza vaccine at 3 months
False, children may receive the vaccine at 6 months
Parent Education for Flu Vaccines:
- S/S: pain, swelling, redness at injection site, mild fever, chills, fatigue, muscle ache, and headache
True/False: Educational pamphlets are required to be provided and educated on prior to vaccine administration
True
True/False: Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance companies can no longer discriminate against kids with preexisting conditions.
True
Eligibility Requirements Medicare:
- >65 years of age
- Disabled
- ESRD
- ALS
Essential Items for a Go Bag:
- Whistle, flashlight
- Bleach
- Insurance cards, ID
- Pen/paper
- Medications
- Other important legal docs
- Snacks/water
Phases of Emotional Reaction During Disaster:
- Heroic - intense excitement and concern for survival. Rush for assistance.
- Honeymoon- affected individuals begin to bond and relive their experiences.
- Disillusionment - responders may experience depression and exhaustion. Delays in receiving aid.
- Reconstruction- involves adjusting to a new reality and continued rebuilding of the area. Counseling may be needed.
True/False: S/S of Anthrax exposure include flu-like S/S
True

Primary v Secondary v Tertiary Prevention for Disasters:
- Primary e.g. tornado, hurricane, tsunami warning or evacuation
- Secondary e.g. Determining if roads are safe before completing a search and rescue
- Tertiary e.g. Restore the community after the disaster
True/False: Ciprofloxacin is used to treat anthrax.
True
Correctional Nursing Key Point Review:
- Primary goal is safety!
- Prevent manipulation from inmates
- Anticipation of actions is a key skill to learn and maintain
What is a living will?
- a written statement detailing a person's desires regarding their medical treatment in circumstances in which they are no longer able to express informed consent, especially an advance directive.
What is a DNR order?
- For terminally ill
- Signed when no resuscitation wanted in the event of a respiratory or cardiac arrest
- Patient or health care surrogate/proxy make this decision
- Must be signed by physician
Priorities with Hospice:
- Dying with dignity
- Comfort
- Pain Management
- Family Support
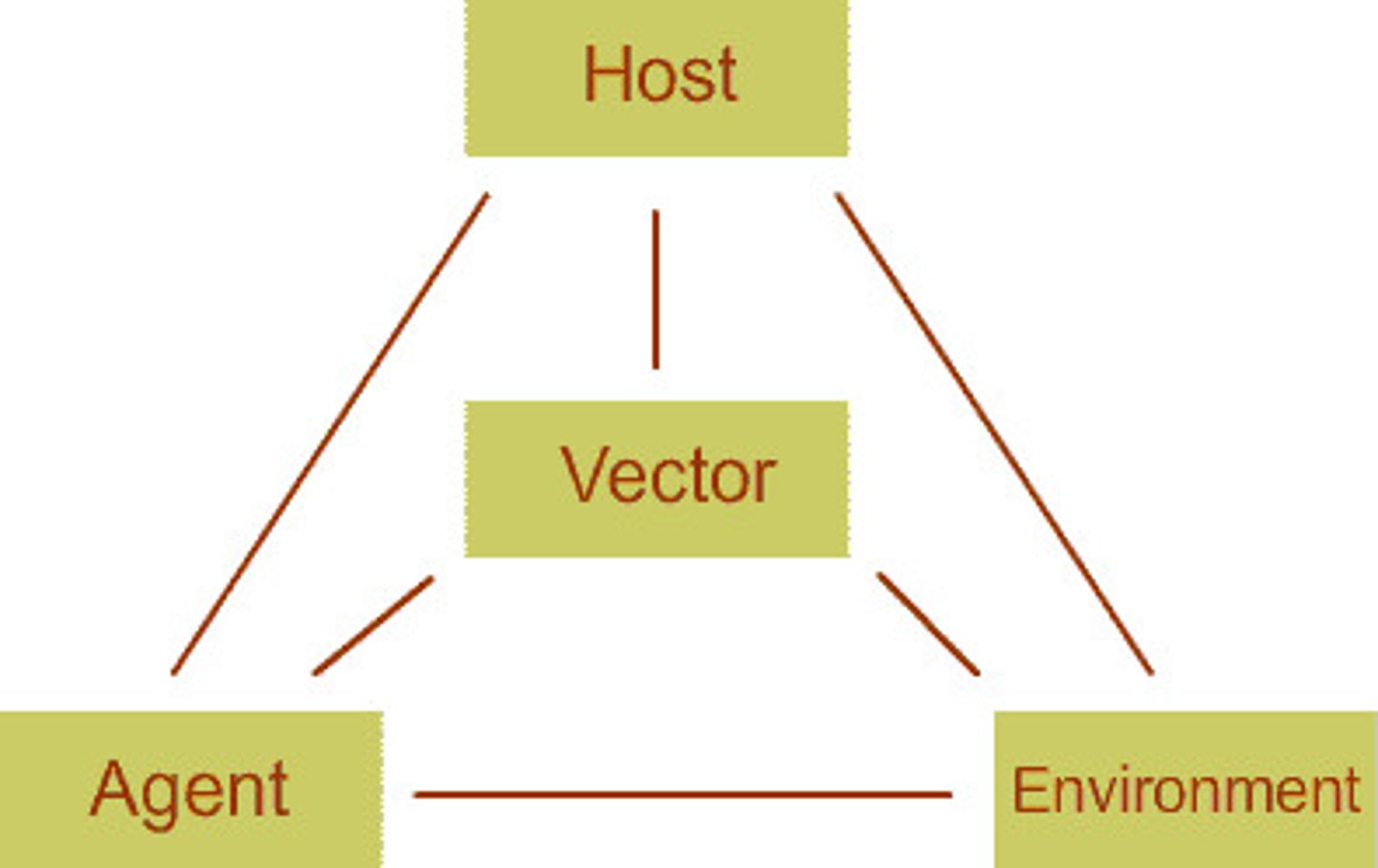
Epidemiologic Triad:
- Host, agent, environment
Rural Healthcare Issues:
- Lack of tertiary care
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Lack of access to HCP on regular basis or ability to afford
- ETOH abuse or other drugs

Migrant Worker Issues in Healthcare:
- Lack of insurance
- Lack of HCP
- Language barrier
- Dental care
- TB
- Fear

True/False: Vitamin K is given to infants post birth to aid in clotting
True
Portals of Entry & Exit:
1. Skin & Mucous Membranes
2. Respiratory tract
3. Digestive tract
4. Genito-urinary tract
5. Placenta
True/False: A pt. newly diagnosed with methylene-resistant staphylococcus aureus should be placed on airborne precautions
False, contact precautions is indicated
A man that drinks 5 beers and smokes a pack of cigarettes a day is known as a ___ risk factor:
- Modifiable
What does it mean when two families live under the same roof?
- Doubling up; common with single parents /w children
True/False: Kale, spinach, and parsley are rich in vitamin K
True
True/False: Willowbark may cause gastric bleeding and is thus contraindicated with Warfarin therapy
True
True/False: The primary role of a nurse is documentation
False, the primary role of a nurse is advocacy
Vector-Borne Modes of Transmission:
- Malaria
- West Nile Virus
- Lyme Disease
Vulnerable Populations Include:
- Immigrant population
- Poverty & homelessness
- Substance abusers
- Mentally ill
- Older adults
- Abused patients
A plane carrying 275 passengers that has a potential to crash land would result in a ___ casualty event
- Mass