General Chemistry 1 Exam 1
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Scientific Method
1) Identifying a question, developing a hypothesis 2) Perform experiment, make observations, record data 3) Interpret data, general hypothesis 4) Collect more data, maybe develop law or theory
Law
A statement that summarizes past observations and is used to predict future ones.
Theory
A possible explanation or a law
Solid
Fixed shape and volume
Liquid
Fixed volume, no fixed shape
Gas
No fixed volume or shape, Compressible.
Homogeneous Mixture
The composition of the mixture is the same throughout
Heterogeneous Mixture
The composition is not uniform
Pure Substance
A material that is composed of only one type of particle
Mixtures
A combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities
Decanting
To carefully pour off
Filtration
To separate using a physical boundary
Distillation
To separate via boiling point difference
Physical Change
Does not change composition
Chemical Change
Does change composition
Celsius to Fahrenheit
F=1.8C+32
Celsius to Kelvin
K=C+273.15
Significant Figures: Multiplication/Division
The total # of S.F in the answer is equal to the least # that appears in a measurement
tera (T)
10^12
mega (M)
10^6
kilo (k)
10^3
deci (d)
10^-1
centi (c)
10^-2
milli (m)
10^-3
micro (μ)
10^-6
nano (n)
10^-9
pico (p)
10^-12
Derived Unit
A unit derived from fundamental units of length, mass, and time.
(1cm^3=1mL)
Accuracy vs. Precision
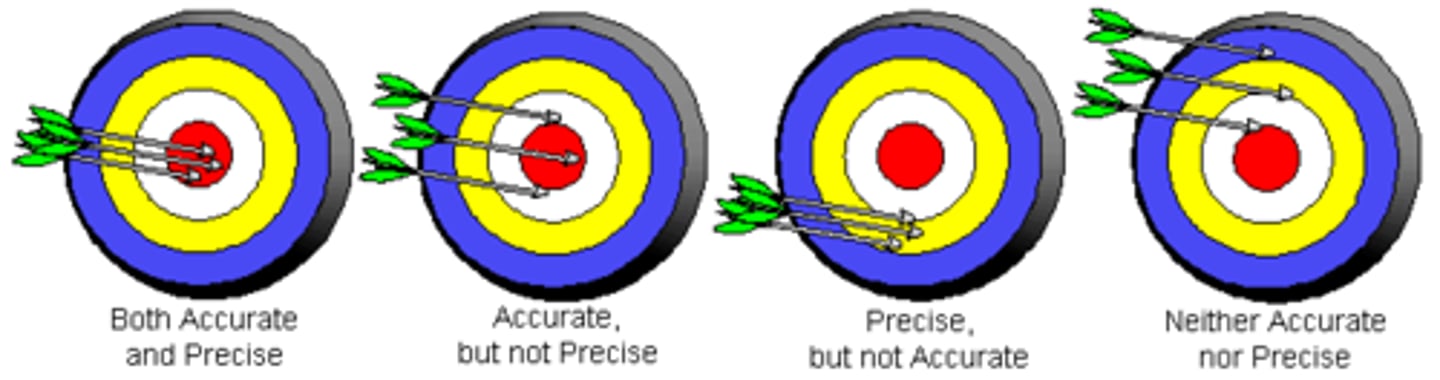
Random Error
Error that is not repeatable and lead to fluctuations in results.
Repetitions of the same experiment lead to different results.
Systematic Error
Error that is repeatable and means that the experimental measurements are centred on the wrong target
J.J. Thomson
Discovered the electron (cathode ray tube experiment)
Robert Millikan
Discovered the charge and mass of the electron
(negative, 0.00055 amu) Via oil drop experiment
Ernest Rutherford
Discovered nuclear model of the atom via gold foil experiment.
Atomic Theory Postulates
-Matter is composed of very tiny or microscopic particles called "Atom".
-Atom is an indivisible particle.
-Atom can neither be created nor it is destroyed.
-Atoms of an element are identical in size, shape, mass and in other properties.
-Atoms of different elements are different in their properties.
-Atoms combine with each other in small whole numbers.
-All chemical reactions are due to combination or separation of atoms.
Atomic Number
Same as number of protons
H
Hydrogen
He
Helium
Li
Lithium
Be
Beryllium
B
Boron
C
Carbon
N
Nitrogen
O
Oxygen
F
Fluorine
Ne
Neon
Na
Sodium
Mg
Magnesium
Al
Aluminium
Si
Silicon
P
Phosphorus
S
Sulfur
Cl
Chlorine
Ar
Argon
K
Potassium
Ca
Calcium
Sc
Scandium
Ti
Titanium
V
Vanadium
Cr
Chromium
Mn
Manganese
Fe
Iron
Co
Cobalt
Ni
Nickel
Cu
Copper
Zn
Zinc
Ga
Gallium
Ge
Germanium
As
Arsenic
Se
Selenium
Br
Bromine
Kr
Krypton
Rb
Rubidium
Sr
Strontium
I
Iodine
Xe
Xenon
Cs
Cesium
Ba
Barium
At
Astatine
Rn
Radon
Fr
Francium
Ra
Radium
Pt
Platinum
Hg
Mercury
Pb
Lead
Sn
Tin
Bi
Bismuth
Ag
Silver
Au
Gold
W
Tungsten
U
Uranium
Sb
Antimony
Isotopes are dependent on
The number of neurons
Cation
e-
Anion
e->p+
Avagadro's Number
6.022X10^23
1 amu=
1g/mol
Atomic Element
Pure substance
Molecular element
Two or more atoms together
Covalent Bond
-2 non metals
-metalloid/non metal