Energy Flow In Ecosystems Study Island
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
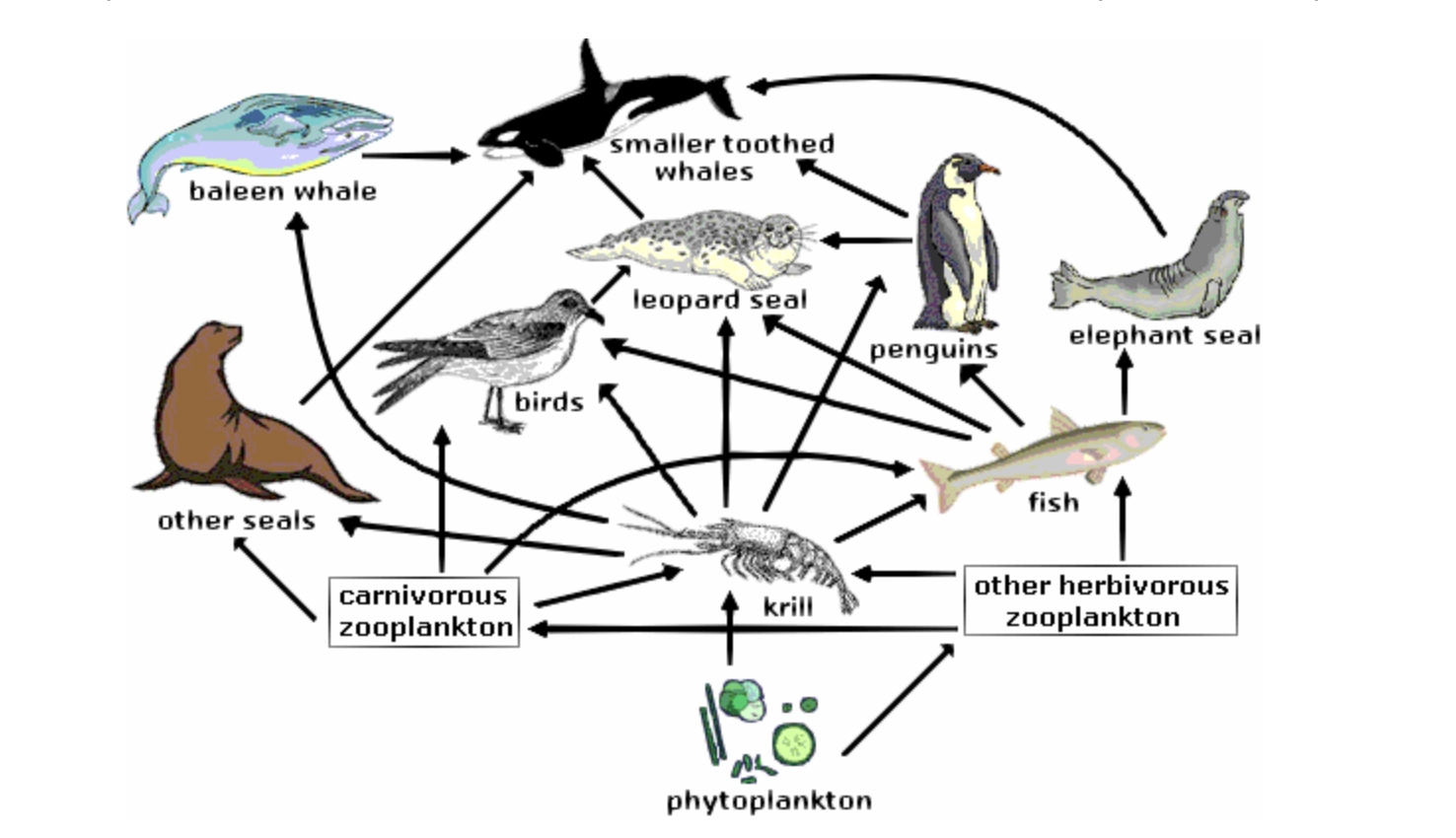
The Antarctic food web is less complex than other food webs around the world. There are fewer different species that are part of it. However, there are more of each species.
\
(photo)
\
According to the food web shown, which organism is both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer?
\
(photo)
\
According to the food web shown, which organism is both a primary consumer and a secondary consumer?
krill
2
New cards
The energy pyramid for an ecosystem is pictured below.
\
(photo)
\
Which type of organism can be found in all levels of the energy pyramid except the first (bottom) level?
\
(photo)
\
Which type of organism can be found in all levels of the energy pyramid except the first (bottom) level?
consumers
3
New cards
Food chains show how living organisms obtain their food, while food webs show how multiple food chains are interrelated. \n \n Which of the following is a true statement regarding food webs?
Matter and energy are conserved as they pass through a food web.
4
New cards

What does the following diagram illustrate?
an energy pyramid
5
New cards
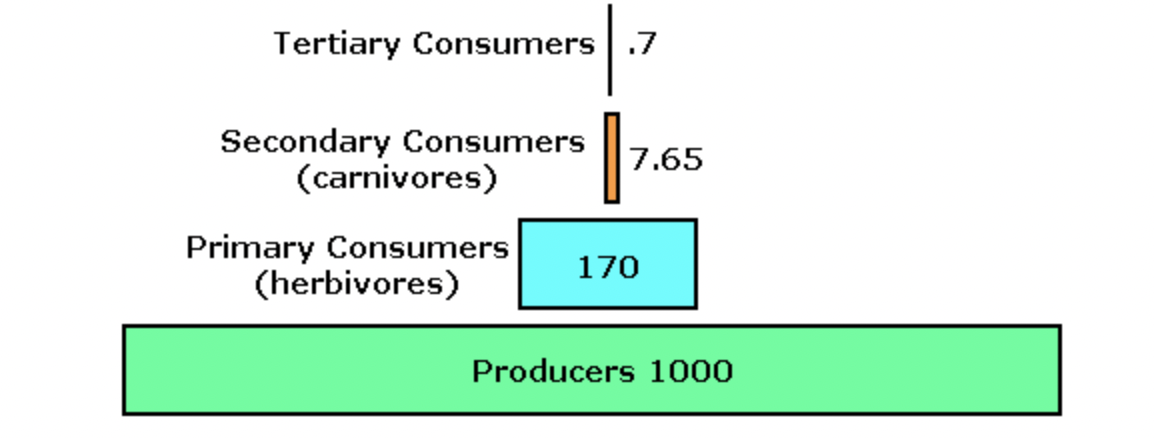
The energy pyramid below shows a possible amount of energy, in kilocalories, available in the organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
\
(photo)
\
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor destroyed. If this is true, why is there less energy in the top of the energy pyramid than there is in the bottom of the energy pyramid?
\
(photo)
\
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor destroyed. If this is true, why is there less energy in the top of the energy pyramid than there is in the bottom of the energy pyramid?
Energy is lost between each trophic level as heat.
6
New cards
The food chain below shows an example of how energy flows through an ecosystem.
\
PLANT → MOUSE → SNAKE → HAWK
\
What is the ultimate source of all of the energy that flows through this food chain?
\
PLANT → MOUSE → SNAKE → HAWK
\
What is the ultimate source of all of the energy that flows through this food chain?
the Sun
7
New cards
What happens to the chemical elements that make up the molecules of living things as they pass through a food web?
Some of their energy is stored in newly made structures.
8
New cards
Which type of organism generates oxygen and makes up the lowest trophic level in an energy pyramid?
producers
9
New cards
Which of the following living things would be found closest to the beginning of a food chain?
caterpiller
10
New cards
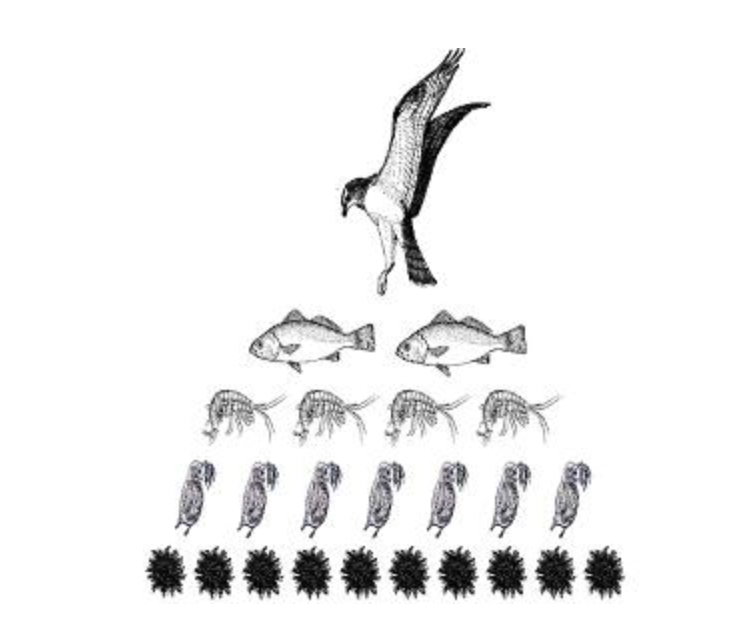
The diagram below shows an energy pyramid.
\
(photo)
\
Which of the following best explains why the number of organisms at each level decreases while moving up the energy pyramid?
\
(photo)
\
Which of the following best explains why the number of organisms at each level decreases while moving up the energy pyramid?
The animals at each level use energy, so only a small amount of their energy is available to the next level.
11
New cards
Examine the following food chain and choose the organism that would best fill in the blank portion.
Wheat → Mouse → ? → Hawk
Wheat → Mouse → ? → Hawk
snake
12
New cards
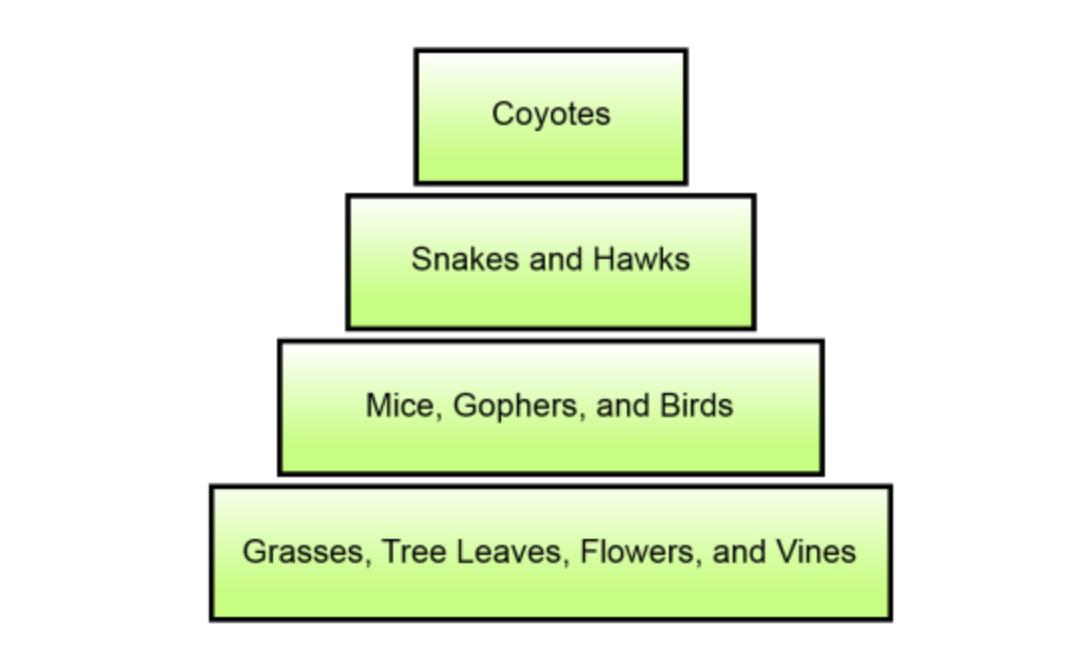
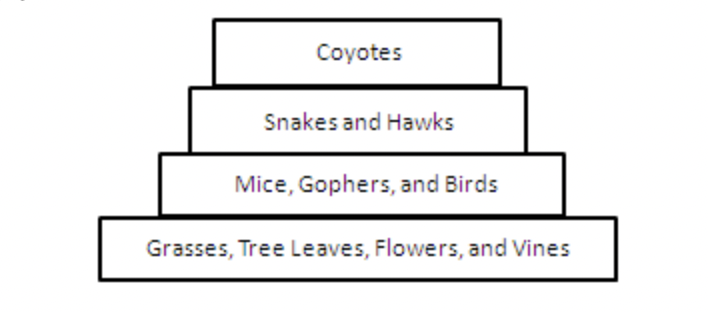
An energy pyramid representing a forest ecosystem is shown below. Which level of the energy pyramid represents the forest's producers?
Grasses, Tree Leaves, Flowers, and Vines
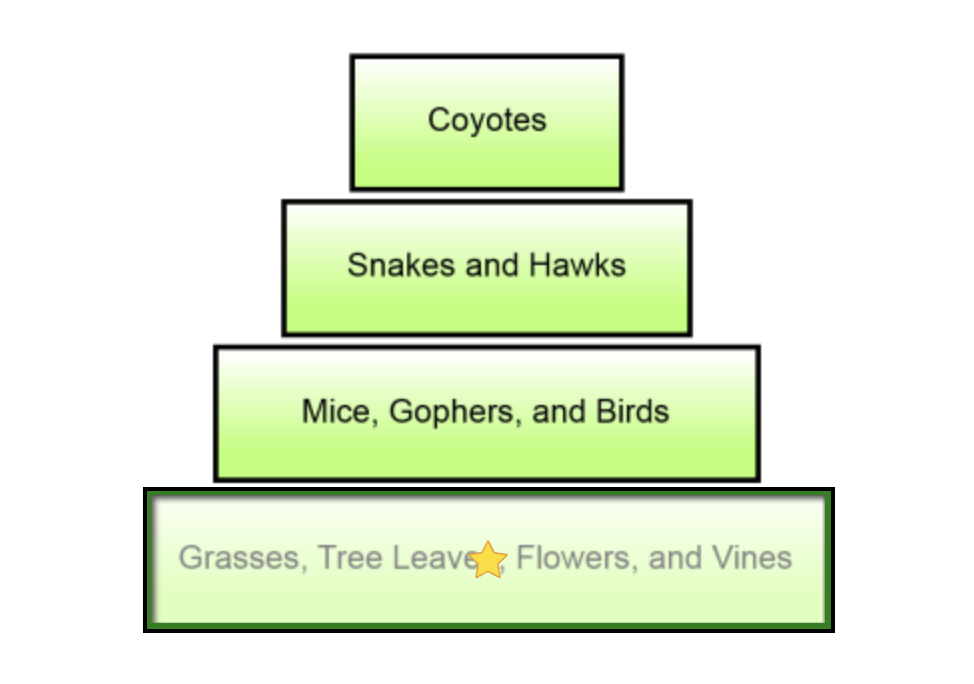
13
New cards
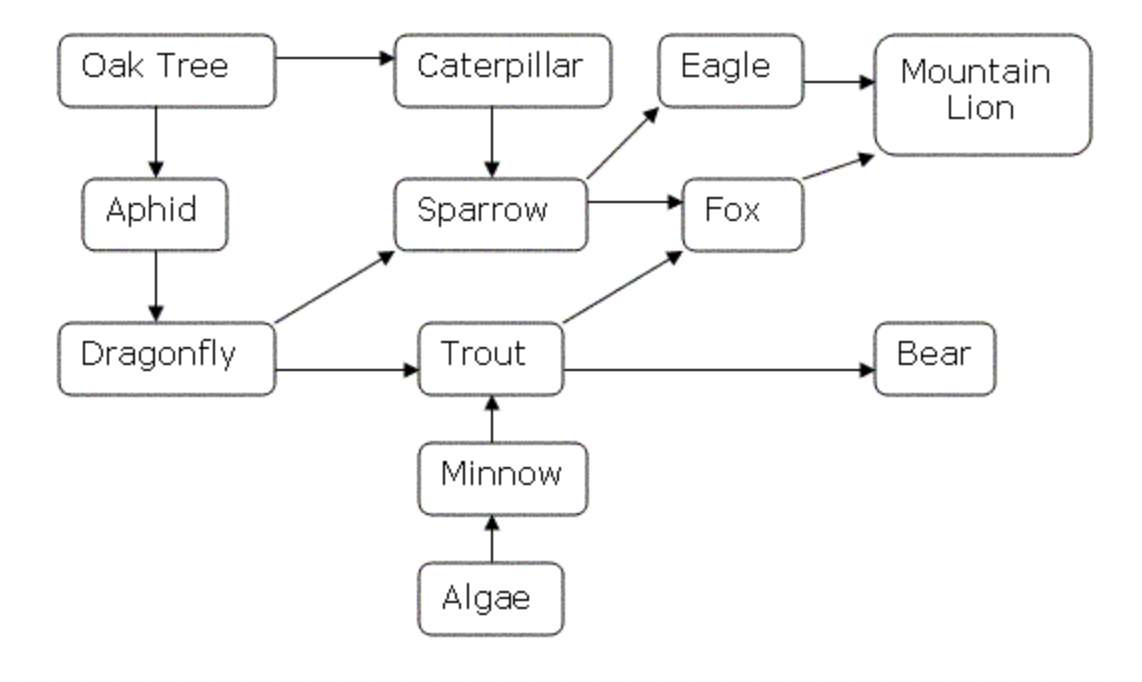
What does the following diagram illustrate?
a food web
14
New cards
An energy pyramid representing a forest ecosystem is shown below. Which level of the energy pyramid represents the forest's tertiary consumers?
coyotes
15
New cards
In the following desert food web, what do scorpions consume?
Spiders, Moths, Lizards, Scorpions
16
New cards
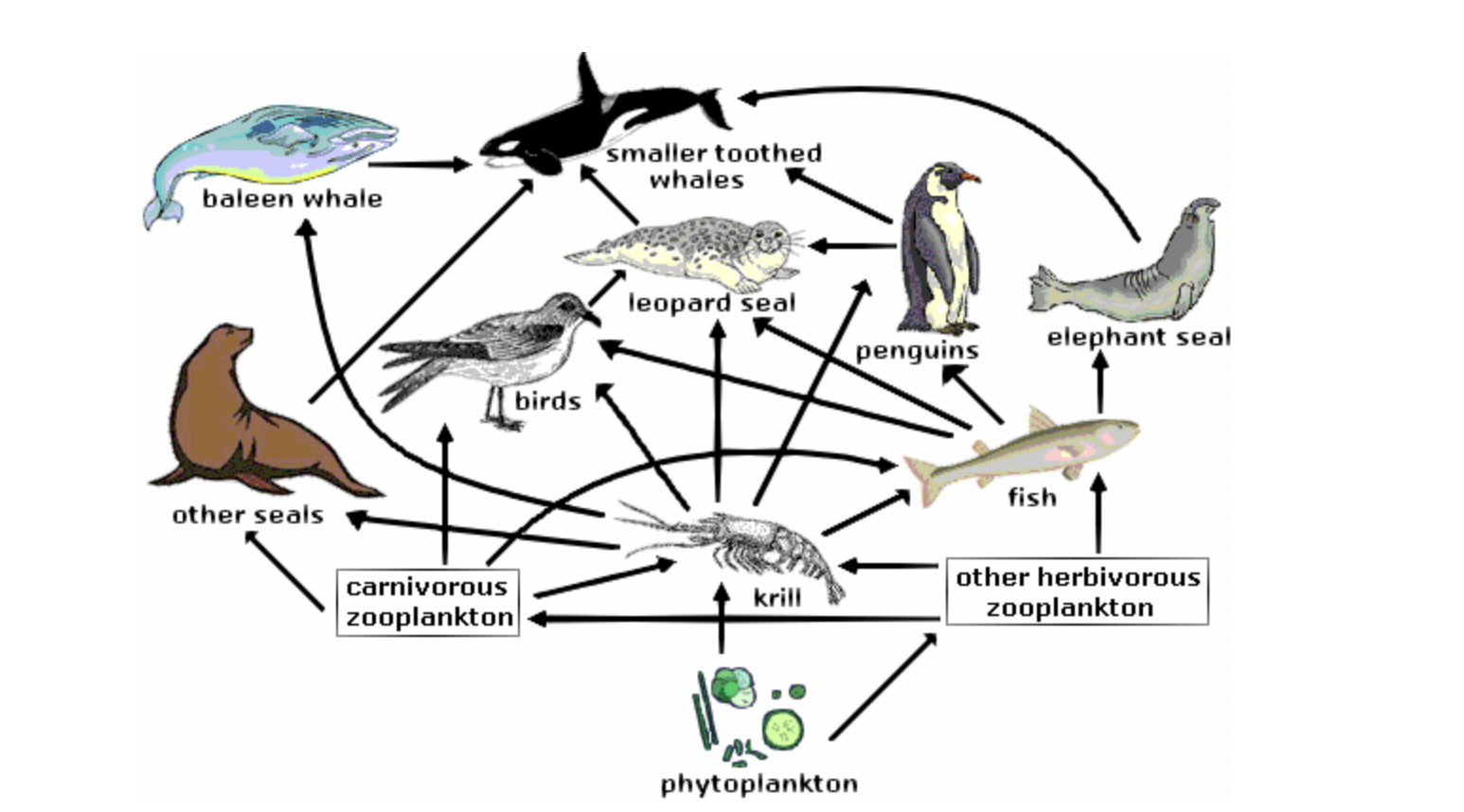
According to the food web shown, which group below lists only secondary consumers?
fish, carnivorous zooplankton, birds
17
New cards
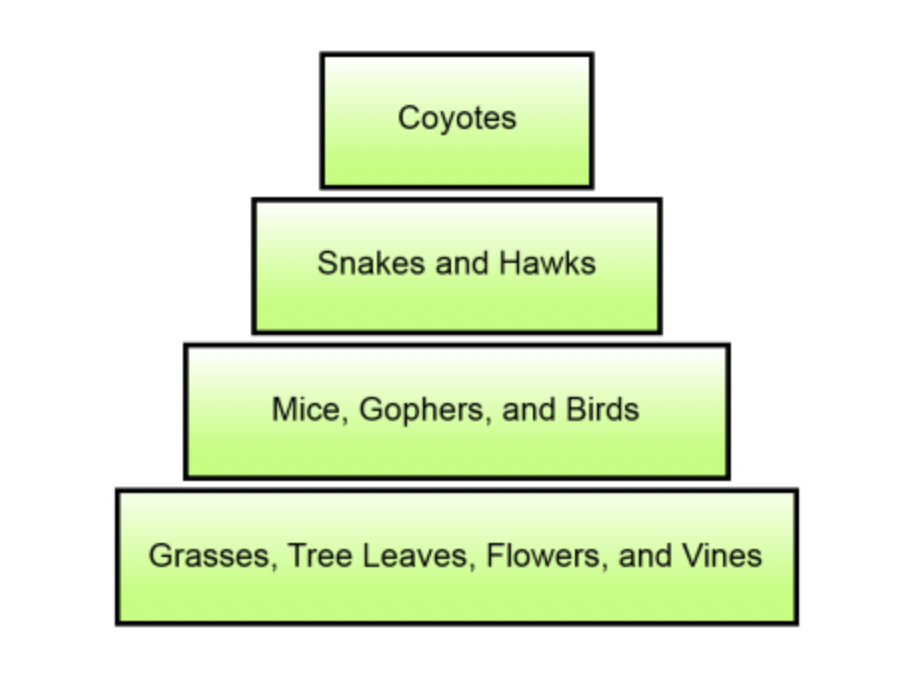
An energy pyramid representing a forest ecosystem is shown below. Which level of the energy pyramid represents the forest's secondary consumers?
Snakes and Hawks
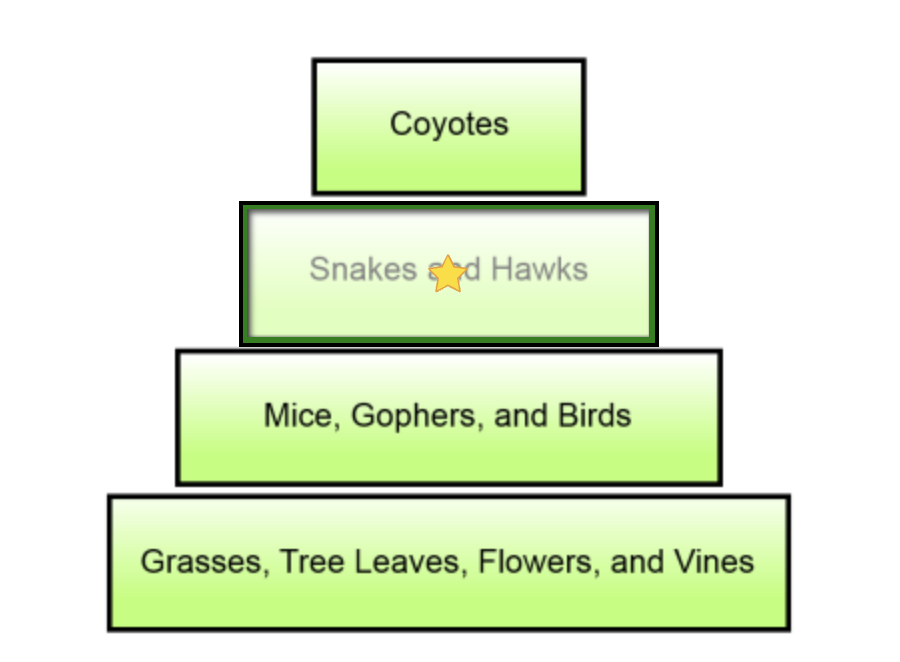
18
New cards
An organism makes glucose using energy from the Sun. The organism is a
producer
19
New cards
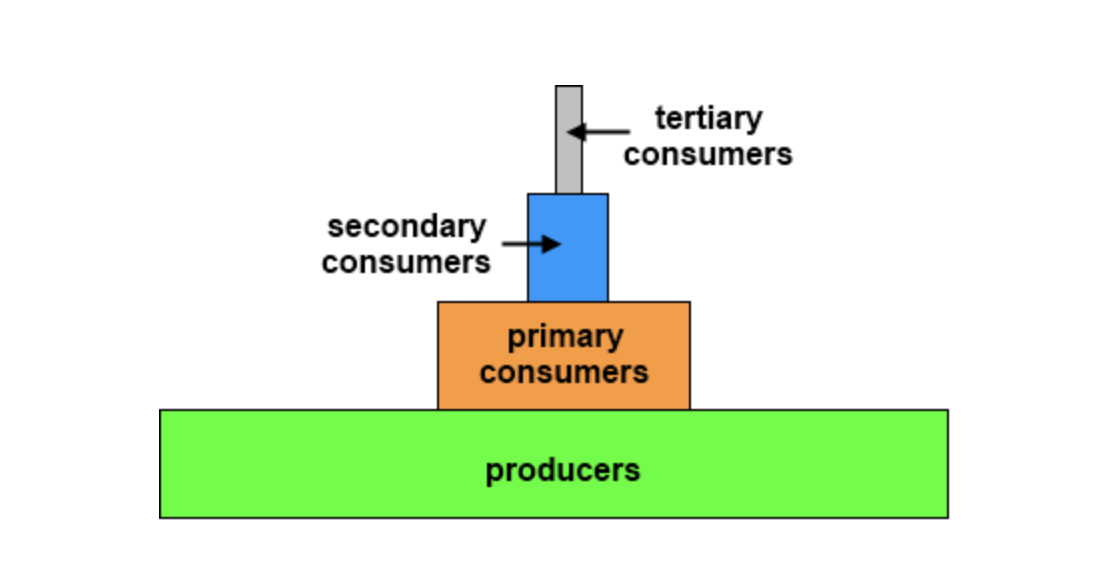
Examine the energy pyramid below.
\
(photo)
\
Is it possible for the top level to be wider than the level before it?
\
(photo)
\
Is it possible for the top level to be wider than the level before it?
No, it is not possible for an ecosystem to support more predators than prey.
20
New cards
What is the ultimate source of energy for all ecosystems?
the Sun
21
New cards
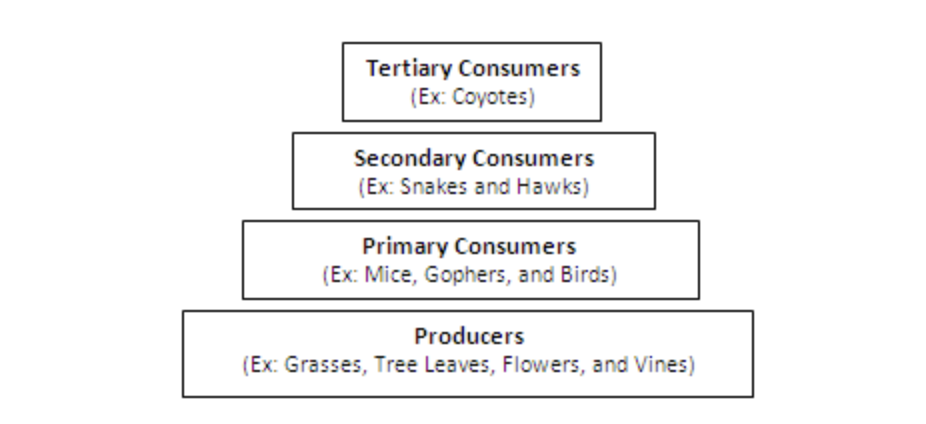
An energy pyramid is shown below.
\
(photo)
\
What does the energy pyramid demonstrate?
\
(photo)
\
What does the energy pyramid demonstrate?
A great amount of energy is lost traveling up the energy pyramid.
22
New cards
Producers are autotrophic. That is, they are able to feed themselves by converting carbon dioxide from the air and light energy from the Sun into food. \n \n Consumers and decomposers are heterotrophic. This means that these organisms must obtain their food by eating other organisms or organic matter. \n \n The relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers carrying out either autotrophic or heterotrophic nutrition are identified through
food webs
23
New cards
Green plants are the first living organism in a food chain. Where do plants get the energy that they pass along to the primary consumers in their food chains?
from the sun
24
New cards
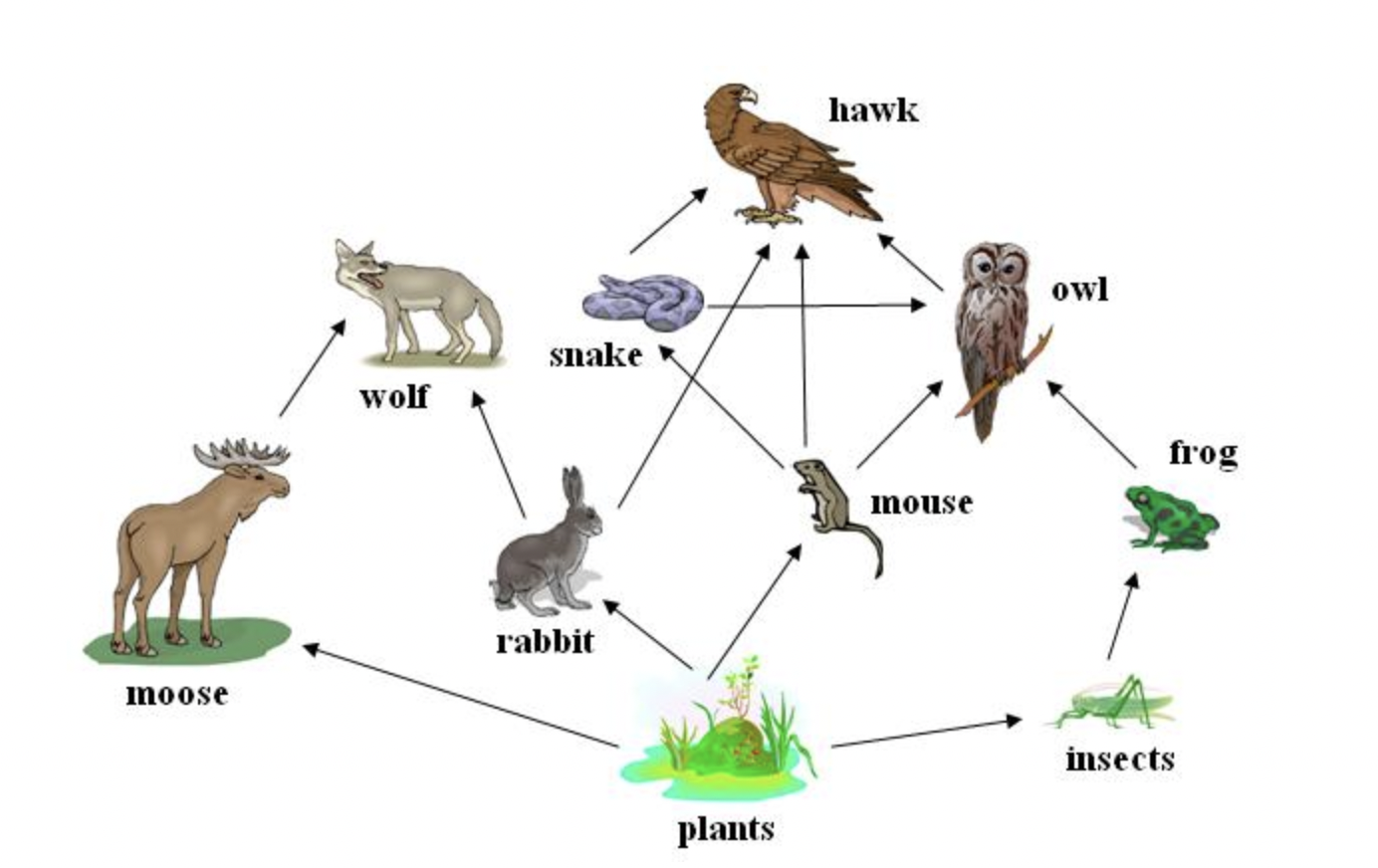
Examine the food web below.
\
(photo)
\
If plants were removed from this ecosystem, which of the following organisms would be affected?
\
(photo)
\
If plants were removed from this ecosystem, which of the following organisms would be affected?
all of these
25
New cards
n a marine ecosystem, phytoplankton perform photosynthesis. Krill eat the phytoplankton, and seals, whales, and sea birds feed on the krill. Finally, great white sharks hunt and eat the seals. \n \n Which of these organisms are consumers?
sharks, krill, seals, whales, and sea birds
26
New cards
Which level in a food web contains the highest amount of total available energy?
producer
27
New cards
Food webs and food chains are two different ways that ecologists illustrate the interrelatedness of organisms in an ecosystem. What is the relationship between a food web and food chain?
Food webs illustrate multiple interrelated food chains.
28
New cards
PLANT → MOUSE → SNAKE → HAWK
\
Based on the food chain shown above, energy in this ecosystem flows from
\
Based on the food chain shown above, energy in this ecosystem flows from
the mouse to the snake.
29
New cards
An energy pyramid representing a forest ecosystem is shown below. Which level of the energy pyramid represents the forest's primary consumers?
mice, gophers, and birds
30
New cards
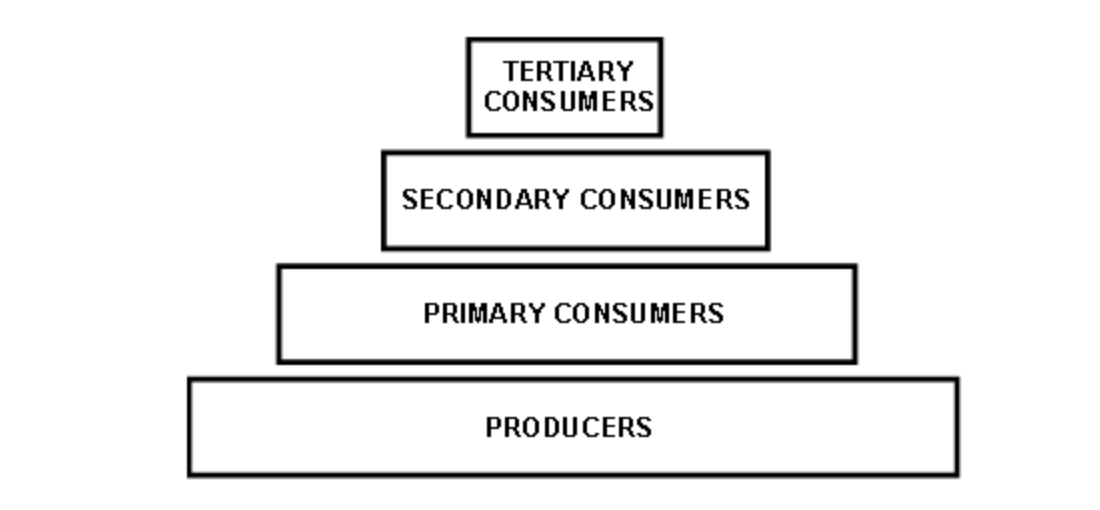
An ecological pyramid is a type of graph that can represent the amount of biomass, the amount of energy, or the number of organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
\
(photo)
\
If each block in the above diagram is proportional to the number of organisms that it represents, which of the following statements is true?
\
(photo)
\
If each block in the above diagram is proportional to the number of organisms that it represents, which of the following statements is true?
There are fewer tertiary consumers than there are secondary consumers.
31
New cards
What does the following diagram illustrate?
Algae → Minnows → Salmon → Bear
Algae → Minnows → Salmon → Bear
a food chain
32
New cards
The diagram below shows a food chain.
Grass → Rabbit → Weasel → Fox → Fungi
Which population would most likely increase if the weasel was removed from the food chain?
Grass → Rabbit → Weasel → Fox → Fungi
Which population would most likely increase if the weasel was removed from the food chain?
Rabbit
33
New cards
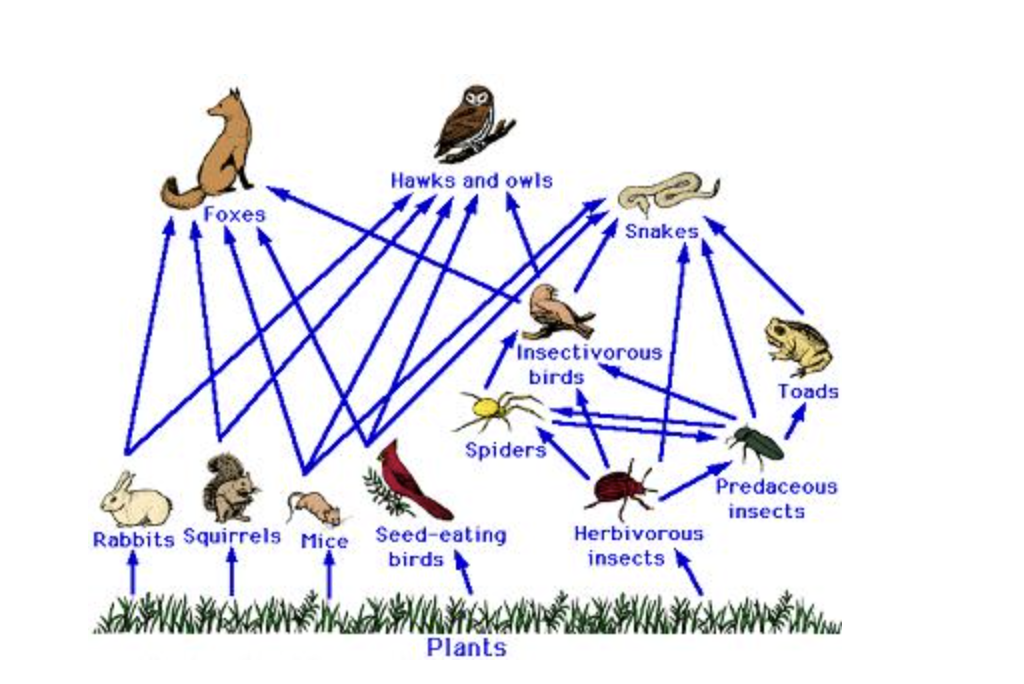
The diagram below shows a food web.
\
(photo)
\
Which of the following is true about the food web?
\
(photo)
\
Which of the following is true about the food web?
Squirrels provide foxes and owls with energy.
34
New cards

Examine the energy pyramid below. Why is the first block containing the plants the widest block?
\
(photo)
\
(photo)
This block represents the trophic level with the most stored energy.
35
New cards
As energy flows through ecosystems, atoms and molecules cycle among
both the living and nonliving components of the biosphere.
36
New cards
Food chains show how living organisms obtain their food, while food webs show how multiple food chains are interrelated. \n \n Which of the following is a true statement regarding food webs?
Matter and energy are conserved as they pass through a food web.
37
New cards
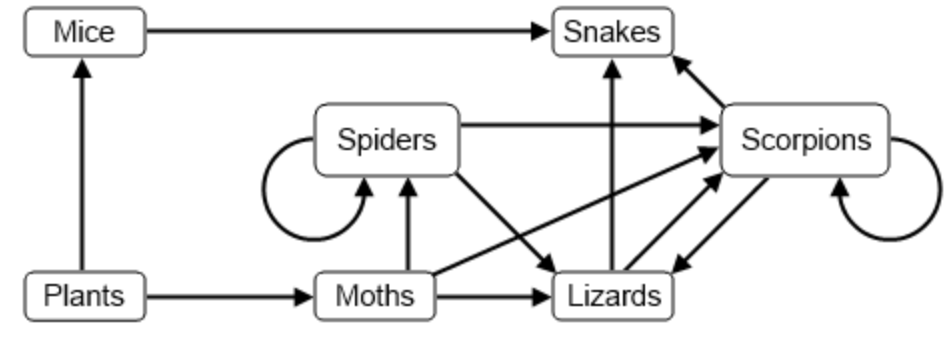
Examine the following desert food web.
\
(photo)
\
What would happen to the flow of energy if all the mice were removed?
\
(photo)
\
What would happen to the flow of energy if all the mice were removed?
Snakes would have to eat more lizards and scorpions.
38
New cards
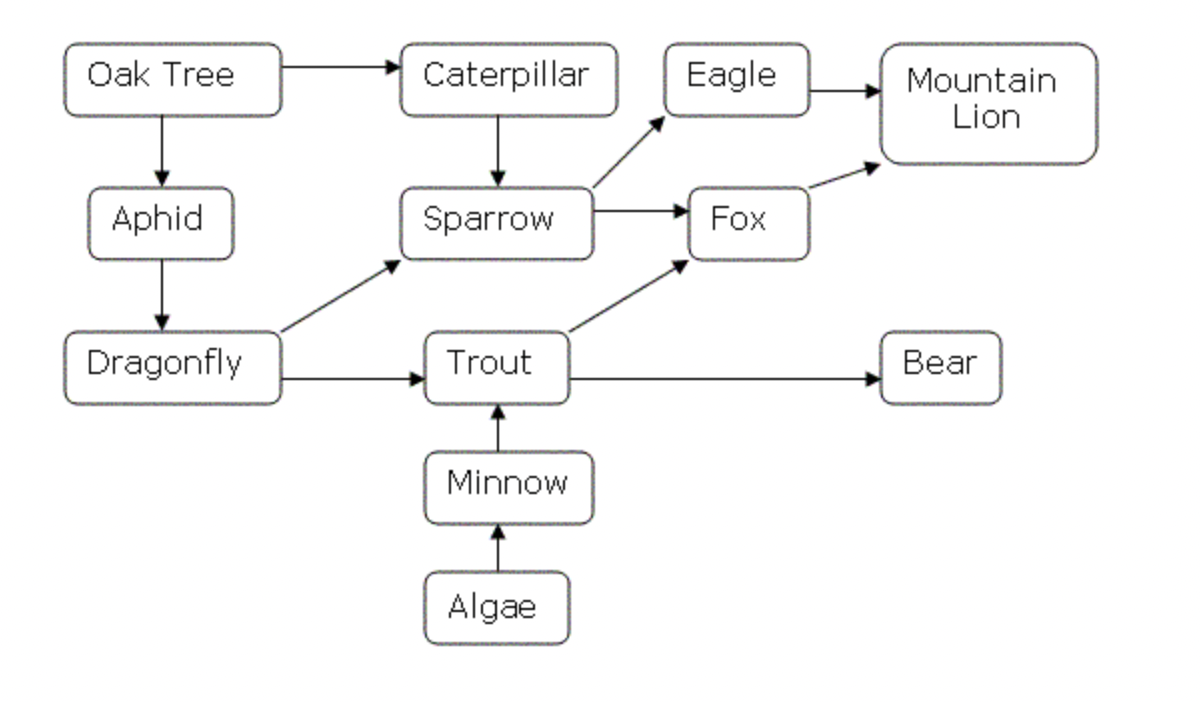
Examine the food web below.
Which organisms in the food web are primary consumers?
Which organisms in the food web are primary consumers?
39
New cards
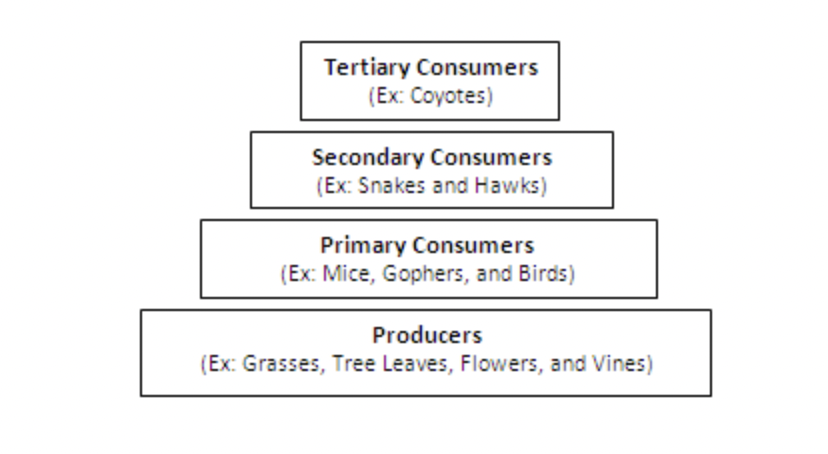
Examine the energy pyramid below. At what level would you add a population of rabbits?
primary consumer