Oligopoly
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the terms of an oligopoly?
The market is dominated by a few large sellers
High barriers to entry/exit: so it’s hard for new firms to enter the market
is differentiated goods. All goods must be similar but slightly different.
interdependence: one firm’s actions will directly affect another firm
Explain two possible sunk costs involved in entering the fizzy drinks market. (4 marks)
Sunk costs are costs that cannot be recovered.
Like advertising. Pepsi-co and Coca Cola spend millions advertising their fizzy drinks, but once paid, they can’t recover the money spent on billboards or TV ads, so advertising is a huge sunk cost.
Secondly, R&D. There’s no way to recover the costs of researching and developing a new fizzy drink recipe - so R&D is also a sunk cost.
When demand is inelastic, an increase in price will:
increase total revenue.
(QD has fallen by a smaller % in comparison to the price)
When demand is inelastic, a decrease in price will:
decrease total revenue.
(QD has increased a smaller % in comparison to the price)
Why are different fizzy drinks both priced the same?
The fizzy drinks market is oligopolistic so firms are interdependent: one firm’s action will directly affect another firm.
If Pepsi-so undercuts Coca Cola with a lower price, a price war will break out and they’ll both compete away their profits.
If Pepsi-co increases its price, it will lose its consumers to Coca Cola.
So firms have no reason to change their price.
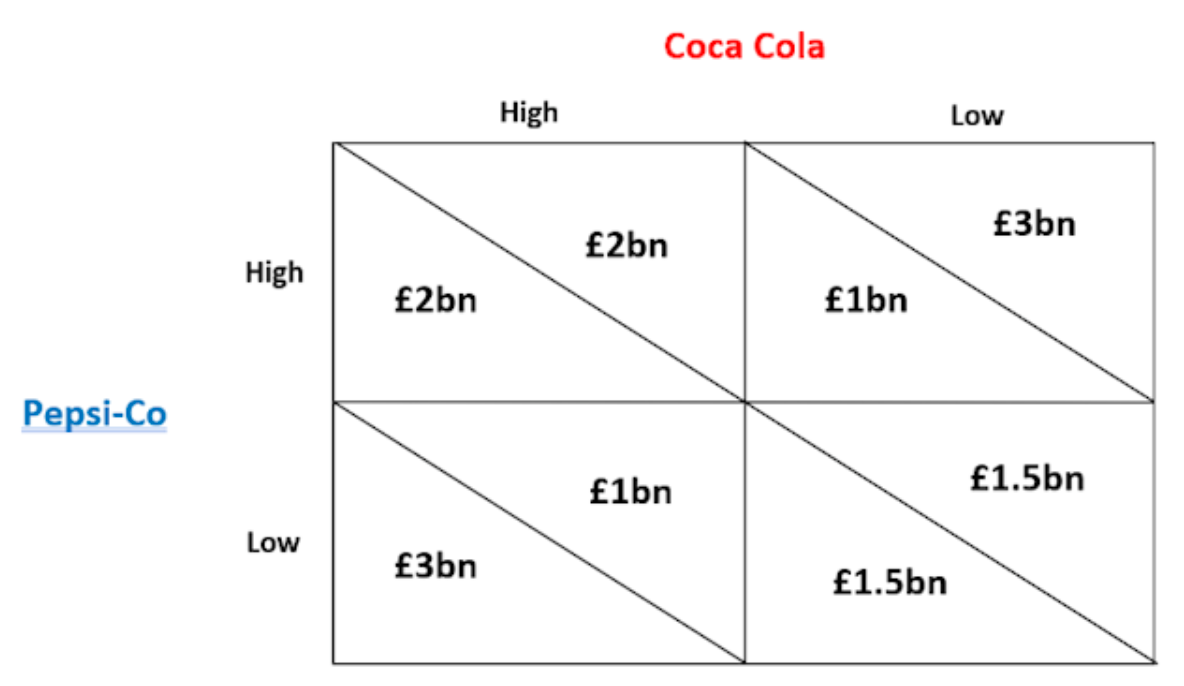
we have our two firms, their strategies: high price and low price, and then their payoffs - the payoff on the left represents:
Pepsi’s payoff
if we wanted to work out Pepsi and Coca Cola’s payoff when Pepsi play low price and Coca Cola play high price:
Pepsi= 3
Coca Cola= 1
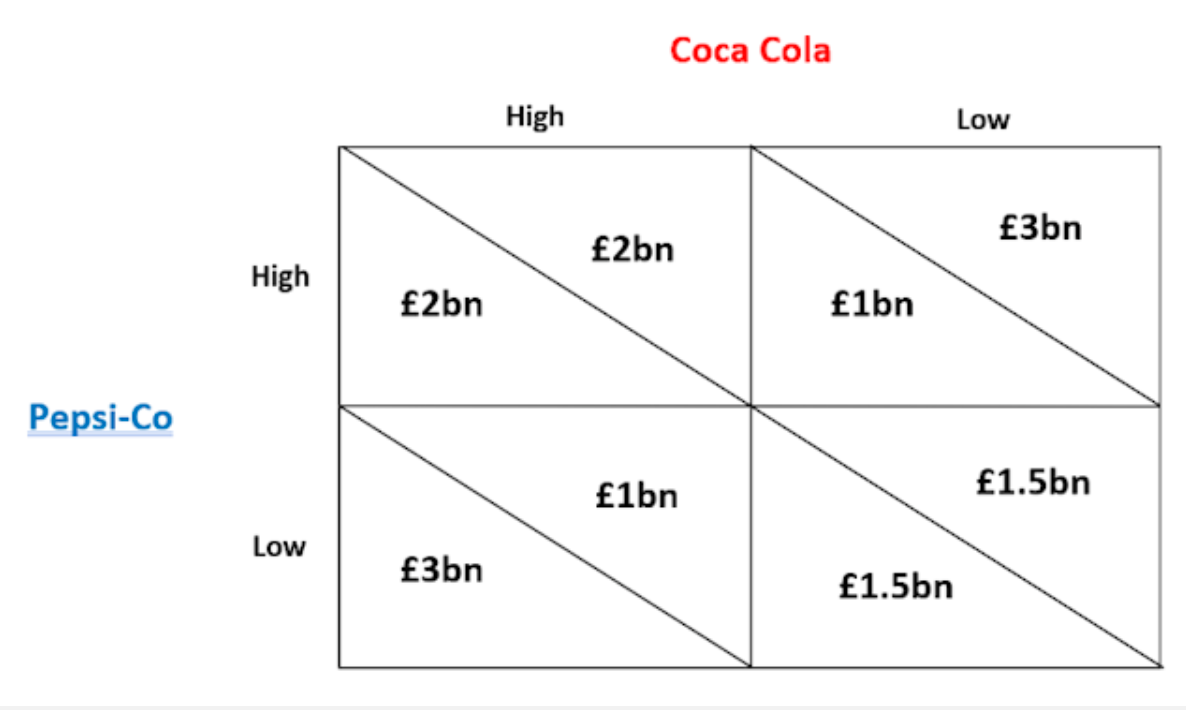
What are price wars?
when firms try to undercut each other with lower prices to steal the other firms’ consumers.
How can firms prevent price wars with other dominating firms?
Collusion- where two or more firms agree to limit competition
What is overt collusion?
when there’s a formal agreement between firms to collude which is kept hidden, because the CMA fines companies who are found overtly colluding
What is tacit collusion?
when there’s an unspoken agreement between firms to collude.
how might a firm compete on price?
1. Price wars: when firms try to undercut each other with lower prices to steal the other firms’ consumers.
Price wars can be very dangerous! As firms cut their prices lower and lower, any supernormal profit will be competed away.
2. Predatory pricing: when a firm aggressively cuts its prices below AVC to force out competitors from the market.
So in the short run, by pricing below shutdown point, a firm incurs a loss. But in the long run, the firm forces out its competitors, so they can put prices back up and take over the entire market.
3. Limit pricing: when an incumbent firm uses its economies of scale to set a price low enough to limit new firms from entering.
Small new firms without any economies of scale, won’t be able to compete or make a profit so they’ll stay out of the market.
What are the non price competition strategies?
When firms compete without changing price:
Advertising
branding
quality
loyalty cards