BSCI 170 Final 2025
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
please let me pass this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
About 2.6 billion years ago, prokaryotic cells started photosynthesizing—making oxygen from CO2, water, and sunlight—directly contributing to about 50% of the oxygen in our atmosphere, and paving the way for the evolution of aerobic metabolism. These prokaryotic cells are called:
cyanobacteria
What are the three shared properties f all living things?
Reproduction, Homeostasis, Growth and Development
What are the 4 classes of macromolecules (the monomers from which they are made)
Protein (Amino Acids), Lipids (fatty acids), Nucleic Acid (nucleotides), carbohydrates (sugar)
Water is essential to life. Which property of water has the least impact on life compared to the others?
Near-colorless appearance

How many covalent bonds does sulfur need to form to have a full valence shell
2

How many electron shells does sulfur have?
3

How many s and p orbitals contain paired electrons in sulfur’s valence shell?
1 s orbital and 1 p orbital
For a covalent bond to be nonpolar, the two atoms that form the bond must have
similar electronegativites
-OH
Hydroxyl
C=O
Carbonyl
-COOH or COO-
Carboxyl
-NH2 or -NH3-
Amino or Amines
-OPO32
Phosphate
-CH3
Methyl
-SH
Sulfydryl
-COH (c=o)
Aldehyde group
what is implied about charged functional groups?
polar
Components of a Nucleotide
a pentose (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine, or Uracil)
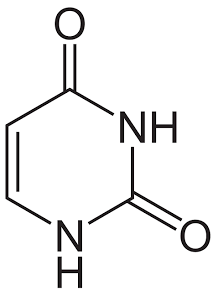
what is this?
uracil
how can you tell the difference between deoxyribose and ribose?
deoxyribose has OH and H while ribose has two OH
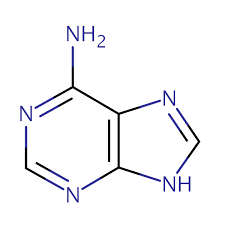
what is this
Adenine
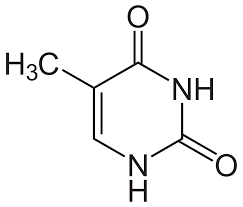
what is this
thymine
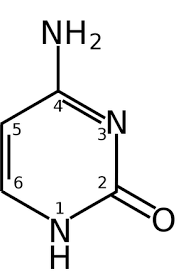
what is this
cytosine
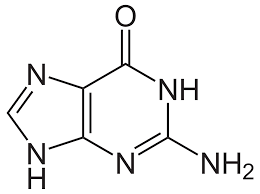
what is this
guanine
what is the combination of a pentose sugar and a base called?
nucleoside
Phospholipids differ from triglycerides in that phospholipids ______
are amphipathic (have both nonpolar and polar parts)
what is the complementary RNA sequence for the DNA sequence of 5’ TAC ACC GCA TAG GAT 3’
3’ AUG UGG CGU AUC CUA 5’
Triglycerides (fats/oils) are composed of _____ and _______.
3 fatty acids; 1 glycerol
Identify the true statement applicable to ALL carbohydrates from the options
They follow the general formula (CH2O)n
Complementary base pairing _____
takes place between purine and pyrimidine bases
what are adenine and guanine
purines
what are cytosine, thymine, and uracil
pyrimidines
The Central Dogma dictates that in cells, _____, the intermediary molecule between _____ and _____, is synthesized in a process called _______.
RNA; DNA; Proteins; Transcription
Which solution has the lowest [H+}
pH=10
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different covalent arrangements
structural isomers
Which of the following statements best describes the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in triglycerides?
Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds, while saturated fatty acids do not.
Phospholipids form a bilayer that _____
has a hydrophobic core
A storage polysaccharide composed of glucose monomers in plants
Starch
Bond connecting a carbohydrate molecule to another group, formed through dehydration
Glycosidic bond
Three-dimensional structure of polypeptide
Tertiary structure of proteins
Distance-dependent interaction between nonpolar functional groups
van der Waals interactions
Type of interaction between two water molecules
Hydrogen bond
Structure of polypeptide maintained by hydrogen bonding interactions between amino acid backbone atoms
Secondary structure of proteins
Interaction between positively charged and negatively charged ions
Ionic bonds
linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
Primary structure of proteins
Protein structure level involving more than one polypeptide
Quaternary structure of proteins
Chemical bond that occurs when two atoms share a pair of electrons
Covalent bond
A monosaccharide found in milk
Galactose
Covalent bond made by sidechain atoms of cysteine
Disulfide bond
are nonpolar molecules hydrophobic or hydrophilic
hydrophobic
are polar molecules hydrophilic or hydrophobic
hydrophilic
A protein that changes shape in response to binding two molecules in the same direction is an example of a:
symporter carrier protein
what is the y-axis on endergonic and exergonic graphs
Free Energy
what is the x-axis on endergonic and exergonic graphs
time of reaction
endergonic
positive ΔG
exergonic
negative ΔG
Ea
activation energy; the difference between the reactions or products (whichever is higher) and the top of the curve
ΔG
free energy; the difference between the reactants and products; id products are lower than reactants than its negative
Explain why adding an enzyme is not enough to make an endergonic reaction proceed?
Endergonic reactions require an input of energy to proceed, and while enzymes can speed up reactions, they cannot provide the energy needed to drive the reaction forward. This requires reaction coupling, which is when one reaction borrows energy from another.
Which statement about diffusion is false?
During diffusion, the cell membrane becomes increasing less permeable to the diffusing substance
Osmosis is _____
the movement of water across selectively permeable membranes
A cell with an interior concentration of 25% salt is placed in a solution, Solution X, with a 5% salt concentration. Which statement accurateky describes about solution X relative to the cell?
Solution X is hypotonic to the cell
Three types of endocytosis in bult transport are
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and receptor mediated endocytosis
Which specific type of bulk transport involves the formation of small vesicles to ingest fluid and tiny dissolved solutes from the extracellular environment?
Pinocytosis
The cell engulfs large solid particles by surrounding them with the cell membrane to form a vesicle
Phagocytosis
The cell takes in extracellular fluid and dissolved substances by forming small vesicles
Pinocytosis
The cell selectively internalizes specific molecules when they bind to receptors on the cell membrane
receptor mediated endocytosis
Tay-Sachs disease is a genetic disorder that results in the destruction of neurons due to a buildup of sphingolipids in the cells. Which organelle in malfunctioning in Tay-Sachs?
lysosome
Which of the following sequences correctly lists in order the steps involved in the incorporation of a proteinaceous molecule within a cell
synthesis of the protein on the ribosome; modification in the endoplasmic reticulum; tagging in the Golgi; distribution via the vesicle; distribution via the Golgi; tagging in the endoplasmic reticulum
An allosteric inhibitor does which of the following
Binds to an enzyme away from the active site and changes the conformation of the active site, decreasing its affinity for the substrate
Who is the measure of the available energy in a system that can do work, ΔG, is named after?
Gibbs
Uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to move ions/compounds against their concentration gradient. (channel proteins, carrier proteins, both neither)
Neither
Moves compounds across the membrane, down their concentration gradient, by binding to the compound on one side of the membrane
carrier proteins
facilitates diffusion of ions/compounds across the cell membrane
carrier and channel proteins
Forms a very selective pore in the cell membrane that allows for one type of ion/compound to cross the cell membrane via diffusion
channel proteins
The sodium-potassium pump establishes and maintains both concentrations and electrical gradients across the plasma membrane. Which statement best explains the difference between sodium’s and potassium’s respective gradients in the cell?
Sodiums electrochemical gradient drives Na+ into the cell because both the electrical and concentration forces favor its entry, while potassium concentration gradient drives K+ out of thecell despite an opposing electrical gradient
ATP is relatively _____, allowing it to undergo hydrolysis which ____ energy, which then forms ADP
Unstable, releases
Which of the following is true of enzymes
The same enzyme can speed up the same reaction over a thousand times
Lactose —> Glucose + Galactose; catabolic or anabolic
catabolic
Lactose —> Glucose + Galactose; positive or negative ΔG
negative ΔG
using facilitated diffusion?
Large, Polar, Charged
what type of molecules cross the membrane using simple diffusion?
small, nonpolar, uncharged
what type of molecules cross the membrane using active transport?
against concentration gradient
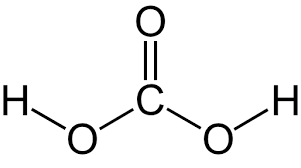
Would you expect the molecule below to cross the membrane down its concentration gradient via diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport?
facilitated diffusion
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only transferred or transformed
Briefly and concisely explain how the events illustrated in the figure above demonstrate the first law of thermo dynamics.
for the H+ to be pumped across the membrane ATP is required as it is moving against its concentration gradient. This allows the secondary transporter to take that energy and pump H+ down its concentration gradient and sucrose against its concentration gradient
What is the second law of thermodynamics? Briefly and concisely explain how the events illustrated in the figure above demonstrate the second law.
The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of the universe increases. In the figure, ATP hydrolysis drives the pumping of H⁺ against its gradient and the cotransport of sucrose against its gradient, which decreases entropy locally by creating order. However, the entropy increase from ATP hydrolysis in the surroundings is greater than the entropy decrease in the system, so the total entropy of the universe increases.
When ATP is broken down to release energy, it forms:
ADP and one phosphate
During the second half glycolysis, what occurs?
ATP is made
What is the main transformation that occurs during glycolysis?
Glycolysis produces ATP, pyruvate, and NADH by oxidizing glucose
Which product of pyruvate oxidation enters the Citric-Acid Cycle
Acetyl-CoA
Select the true statement about fermentation
results in the formation of lactic acid or alcohol
How many ATP is generated from oxidizing all 10 NADH during oxidative phosphorylation?
25 ATP
Which of the following process(es) generate NADH?
Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
ATP synthase during the oxidative phosphorylation consists of two primary components, the proton channel (F0) and the ATP synthesis enzyme (F1). Which of the following best describes the roles of these components and the overall process of ATP synthesis?
F0 creates a proton gradient, while F1 uses the energy from the gradient to phosphorylate ADP, forming ATP
Which of the following processes will be impacted by low NAD+ and FAD levels?
All of the above
how to know highest oxidation state?
highest H:O, low C:H ex. carbon dioxide is highly oxidized while methane is not
Identify the oxidized and reduced products in the following reaction: Cr++Sn4+ —> Cr3+ +Sn 2+
Cr3+: oxidized; Sn2+:reduced
Oxidized form of NAD
NAD+
Reduced form of NAD
NADH