Developmental Defects
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
April 2, 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
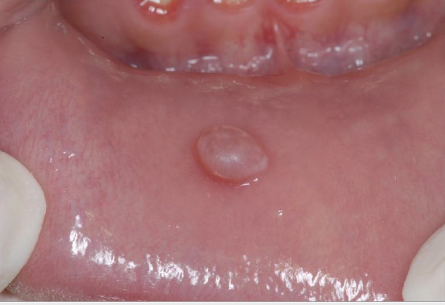
Sessile
Flat base
Polypoid
Between sessile and pedunculated
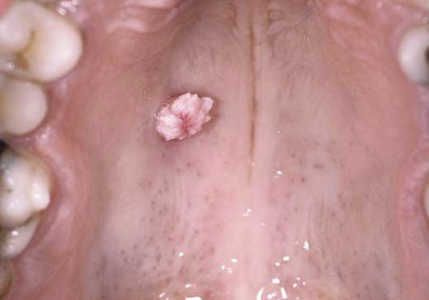
Pedunculated
Stalk like
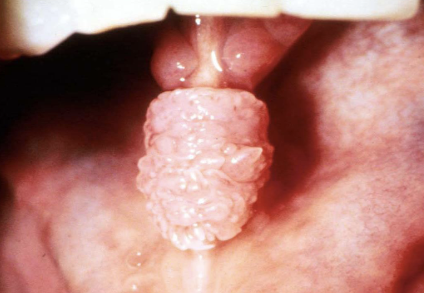
What does corrugated mean?
Wrinkled
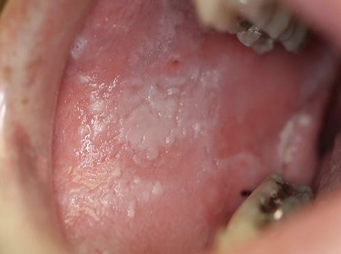
What is a fissure?
A cleft or groove, normal or otherwise, showing prominent depth
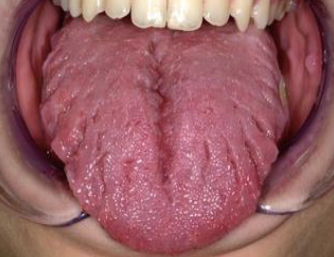
What is papillary
Resembling small projections or elevations found in clusters
What is smooth, rough, folded, ulcer
Terms used to describe the surface texture of a lesion
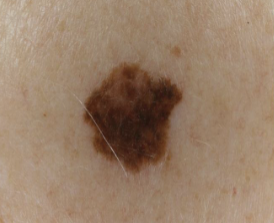
Define macule
An area that is usually distinguished by a color different from that of the surrounding tissue; it is flat and does not protrude above the surface of the normal tissue (freckle is an example of a macule)
Define papule
A small, circumscribed lesion usually less than 1cm in diameter that is elevated or protrudes above the surface of normal surrounding tissue
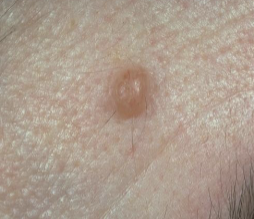
Define nodule
A palpable solid lesion up to 1cm in diameter found in soft tissue; it can occur above, level with, or beneath the skin surface
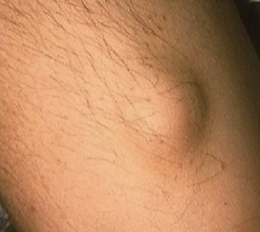
Define lobule
A segment or lobe that is a part of the whole lesion; these lobes sometimes appear fused together
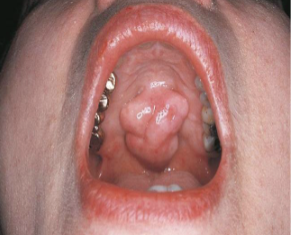
Define a vesicle
A small, elevated lesion less than 1cm in diameter that contains serous fluid
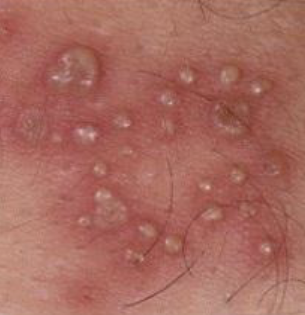
Define a pustule
Variously sized circumscribed elevations containing pus
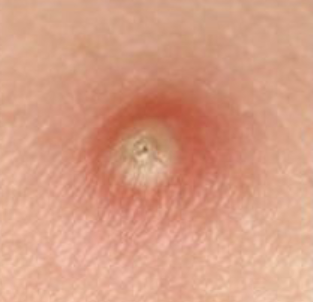
Define a bulla
A circumscribed, elevated lesion that is more than 5mm in diameter, usually contains serous fluid and looks like a blister
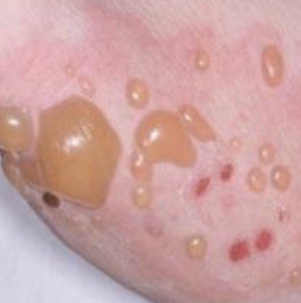
What is a well circumscribed border
borders that are defined and in which one can clearly see the exact margins and extent
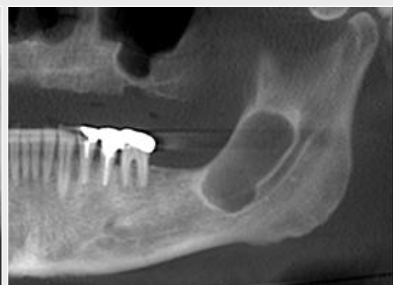
What is an ill defined border
Borders that are not well defined, making it difficult to detect the exact parameters of the lesion; this may make treatment more difficult and, depending on the biopsy results, more radical
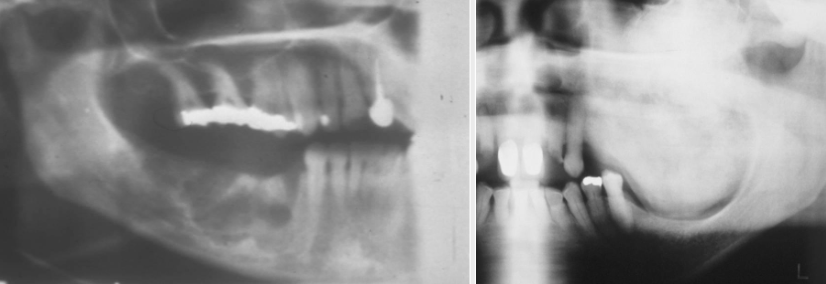
Define radiolucent
less dense tissue (e.g. pulp, periapical lesions)
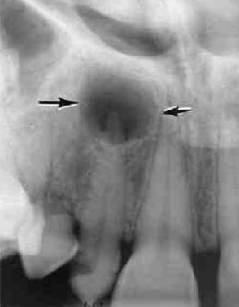
Define radiolucent and radiopaque
A mix of dense tissue (e.g odontogenic lesions, fibro-osseous lesions)
Define radiopaque
Highly dense structure (calcifications, bone, tooth)
What is a unilocular shape?
Having one compartment or unit that is well defined or outlined
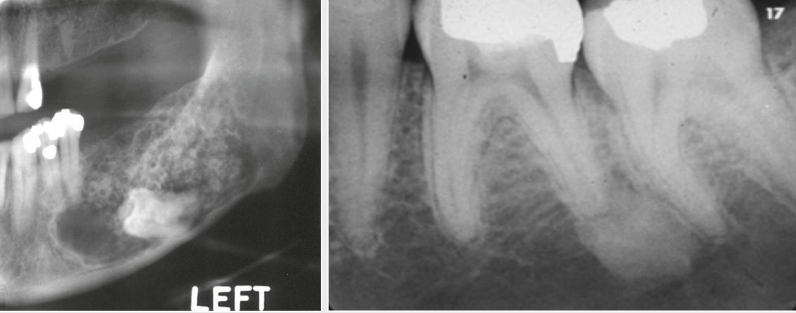
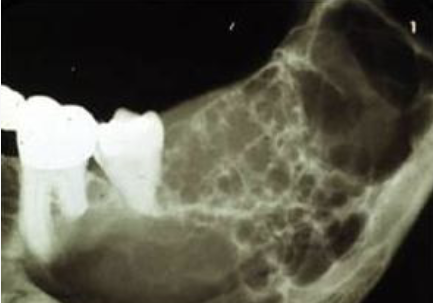
What is a multilocular shape?
Multiple unilocular lesions that are somewhat fused together, making up the entire lesion, sometimes described as resembling soap bubbles
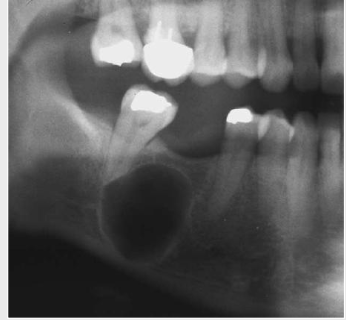
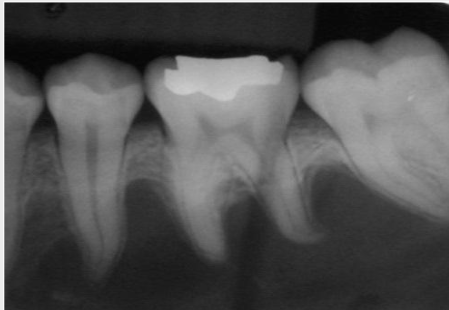
What is root resorption
Observed radiographically when the apex of the tooth appears shortened or blunted and irregularly shaped; occurs as a response to stimuli, which can include a cyst, tumor, trauma, malignancy
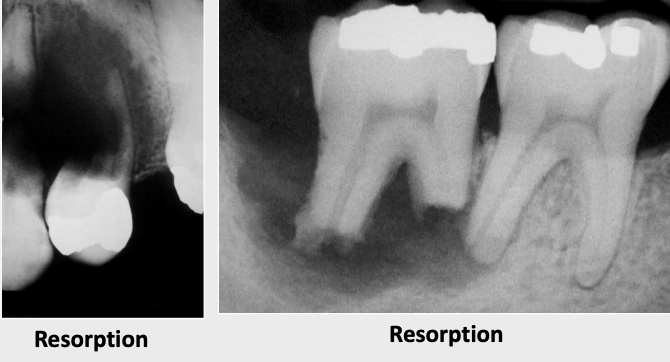
Define scalloping
A radiolucent lesion that extends between the roots, as seen in a traumatic bone cyst (TBC)
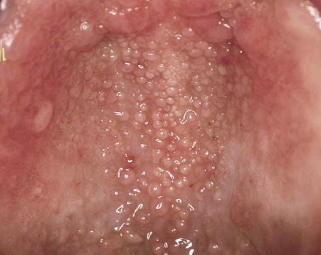
What are fordyce granules?
Clusters of “ectopic” sebaceous glands
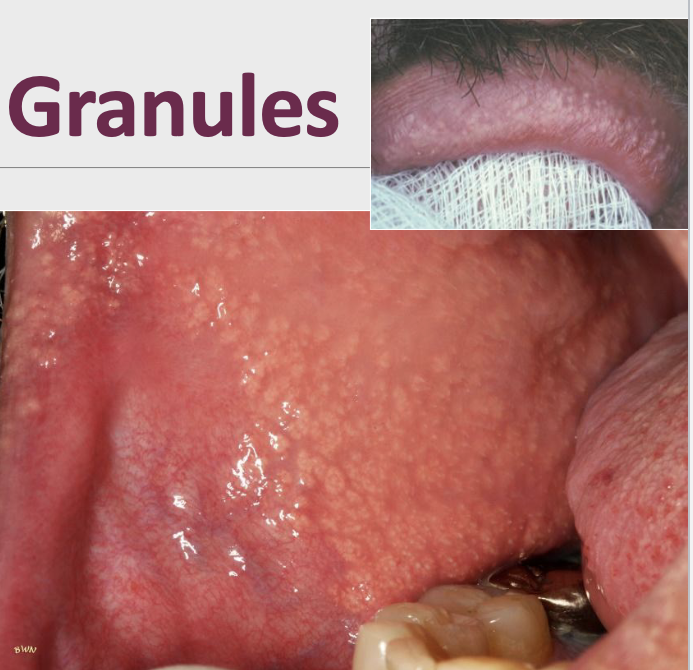
What percent of the population have fordyce granules?
80% of the population
How do fordyce granules appear clinically?
Yellow or yellow-white papular lesions
In which populations do you mostly see fordyce granules?
More commonly seen in adults; puberty appears to stimulate development
What is the clinical presentation of leukoedema?
Diffuse, gray-white, milky, opalescent lesions found bilaterally on buccal mucosa
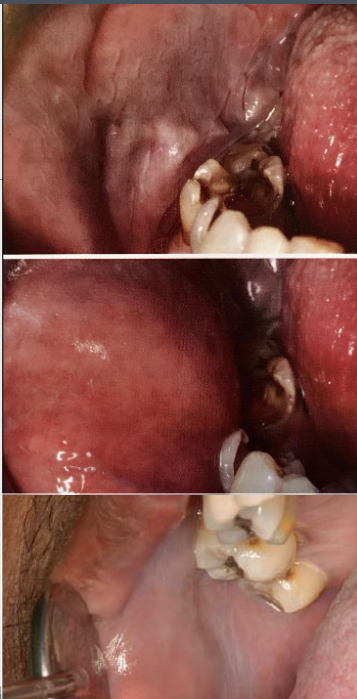
Does Leukoedema rub off?
No
In which populations do you see leukoedema?
Up to 90% of African American adults and 50% children
How would you clinically diagnose leukoedema?
White appearance disappears when the cheek is stretched
Is there any treatment for leukoedema?
No
In which populations would you see Linea Alba?
In patients who have clenching or bruxing habit
What is the clinical presentation of linea alba?
“white” line that extends anteroposteriorly on the buccal mucosa along the occlusal plane, bilaterally
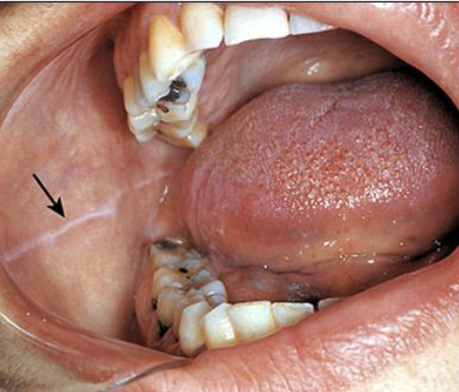
In which populations would you see physiological pigmentation
Melanin pigmentation of the oral mucosa or gingiva is most commonly observed in dark-skinned individuals
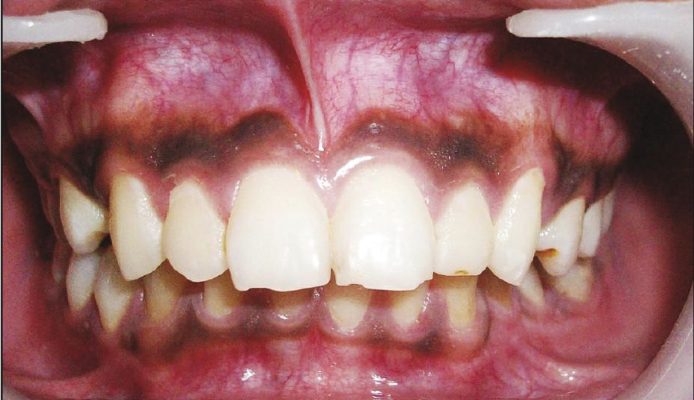
Where would you find lingual varicosities?
On the ventral and lateral surfaces of the tongue
What is the clinical presentation of lingual varicosities?
Red-to-purple enlarged vessels or clusters
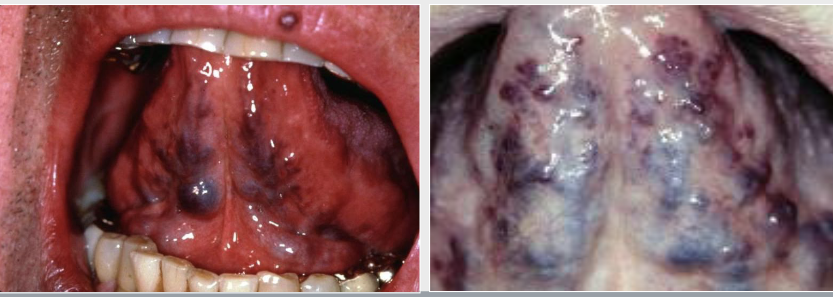
In which populations would you see lingual varicosities?
In individuals older than 60 years of age. It is thought to be related to the aging process
Diascopy
A technique where you use a glass slide, add pressure on a vascular lesion. If it is coming from the artery or vein, it should blanch. Vs. a hematoma (spillage of blood inside the tissue) so you’d see no blanching
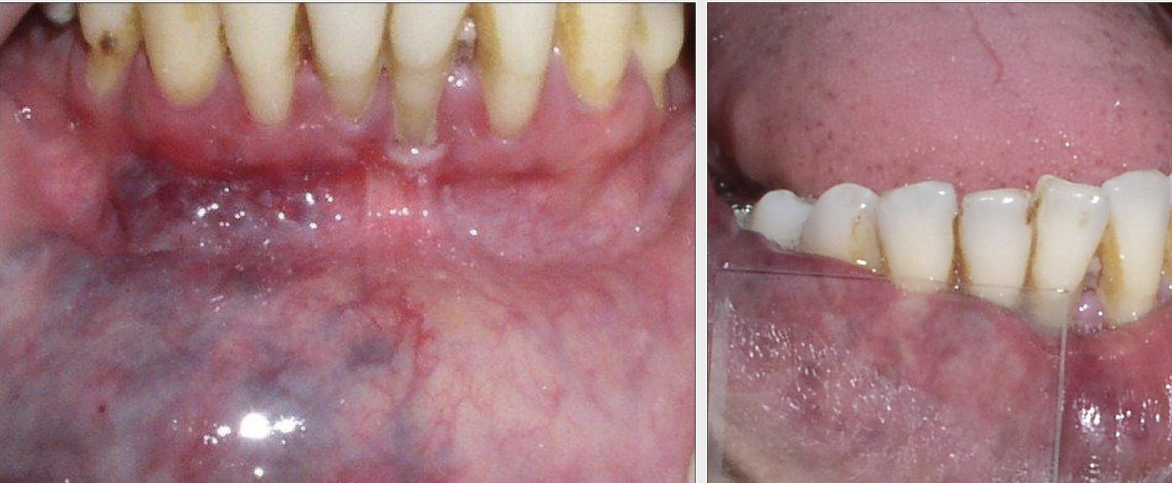
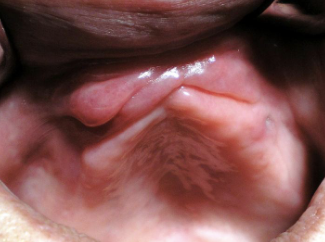
Define a retrocuspid papilla
A sessile nodule on the gingival margin of the lingual aspect of the mandibular cuspids
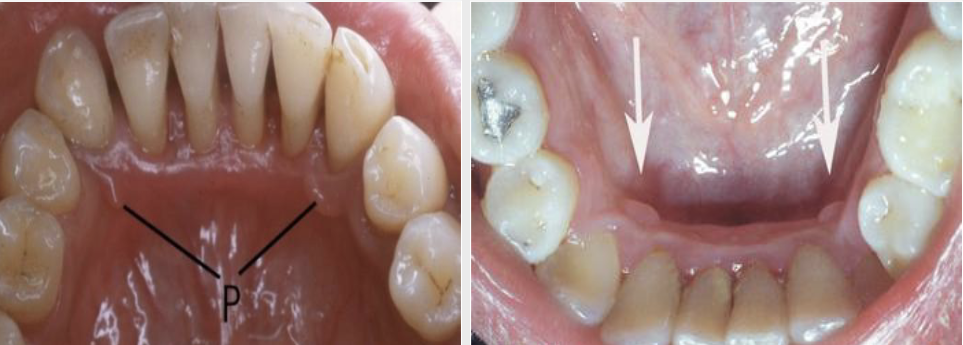
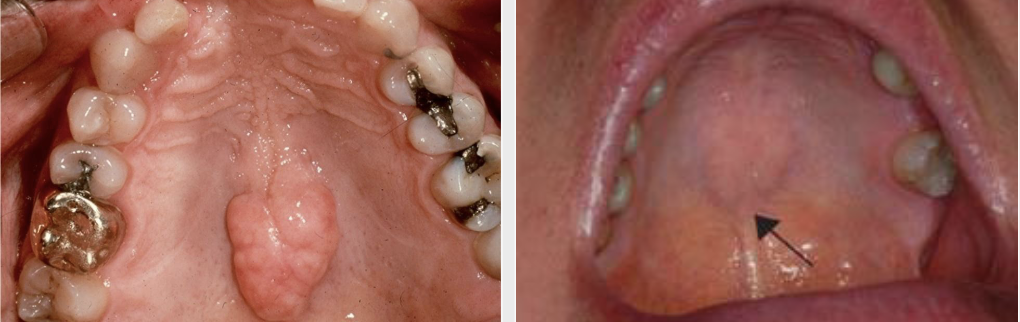
What are Torus Platinus?
Exophytic growth of normal compact bone on hard palate
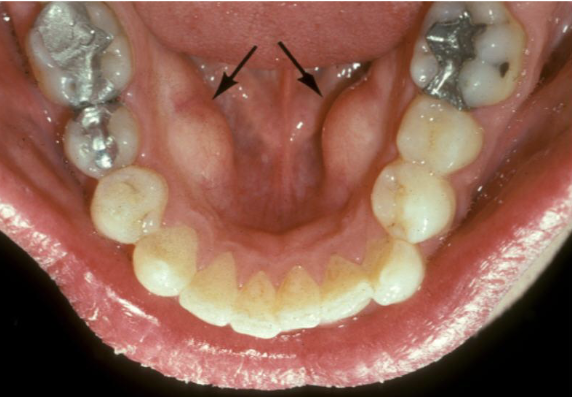
What is a mandibular tori?
Outgrowths of normal dense bone found on the lingual aspect of the mandible premolar area
By 3-4 weeks of life, what develops?
Lingual thyroid
By which week does the lingual thyroid descend into the neck?
7th
Where is the lingual thyroid located?
normal thyroid on posterior midline dorsum of the tongue posterior to the circumvallate papillae in the area of the foramen cecum
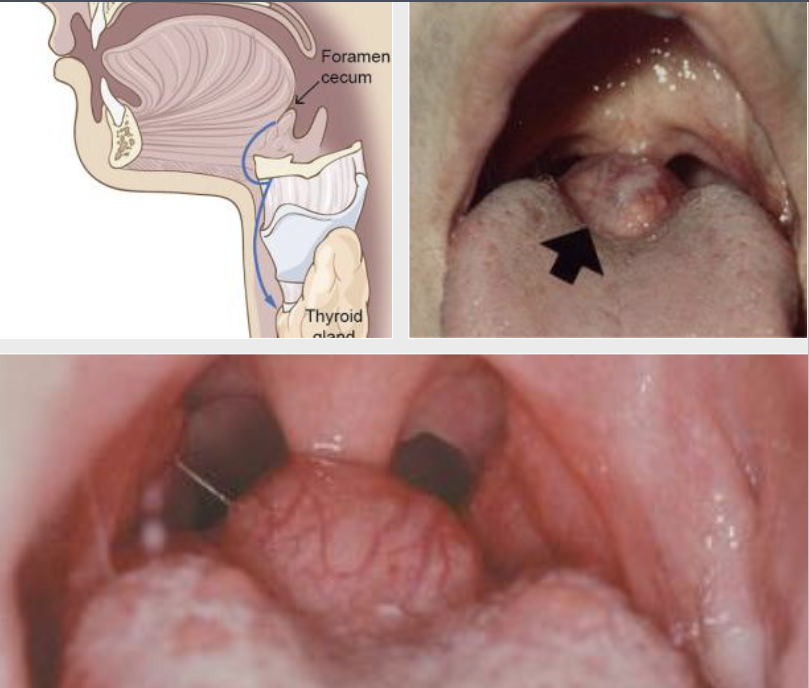
In which populations do you see more lingual thyroid?
Females > males (7:1)
What percent of ectopic thyroids are in the lingual thyroid position
90%
Lingual thyroid may develop
Adenoma or adenocarcinoma
WHat is the treatment?
70% of the time, this is the only thyroid tissue, use radioactive iodine, it all goes to tyroid gland, notx required unless problem develops
What is geographic tongue
Benign migratory glossitis; erythema migrans
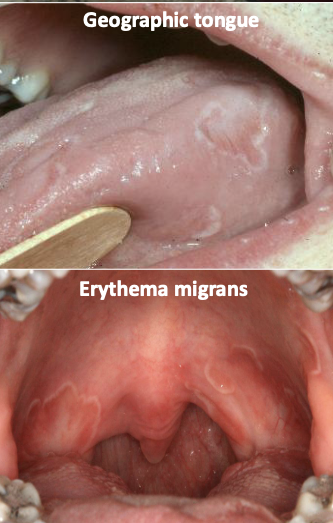
What is the clinical presentation of geographic tongue?
erythematous patches surrounded by white/yellow serpentine borders (changes location)
What is hairy tongue?
Excess keratin on surface of filiform papillae
What is the cause of hairy tongue?
Could be due to smoking, drugs, xerostomia, hx or radiotherapy to head and neck, poor oral hygiene
What is the clinical presentation of hairy tongue?
Starts white, may become black, brown, orange, green or yellow. The stain is from food/drink stains, chromogenic bacteria
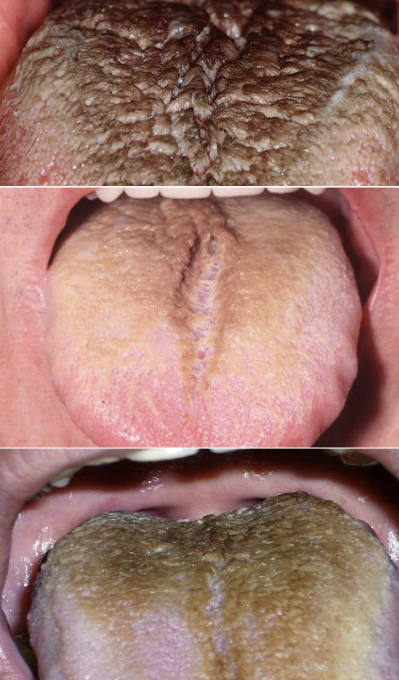
What is the treatment for hairy tongue?
Maintain good oral hygiene
Comes with halitosis
Remove the offending agent
Brush the tongue
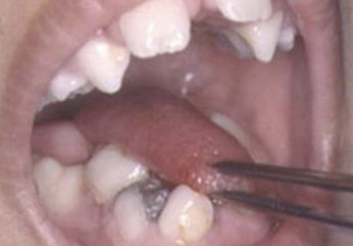
What is microglossia?
Abnormally small tongue, commonly associated with hypoplasia of the mandible. Oromandibular- limb hypogenesis syndromes
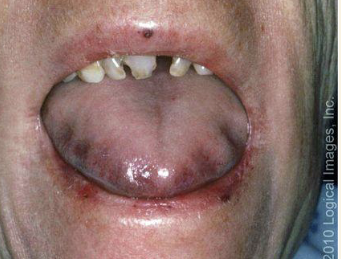
What is macroglossia?
Abnormally large tongue, most frequently caused by:
Vascular malformations
Muscular hypertrophy
Other etiologies: Down syndrome,
amyloidosis, angioedema, tumors
What is Ankyloglossia?
Abnormally short, thick lingual frenum resulting in limitation of tongue movement. May cause problems with speech and breastfeeding. You’d need a frenectomy
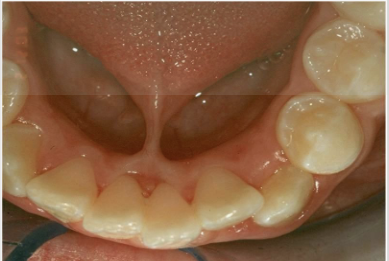
What are commissural lip pits?
Mucosal invaginations that occur at the corners of the mouth on the vermilion border
NOT associated with facial or palatal clefts
No treatment required
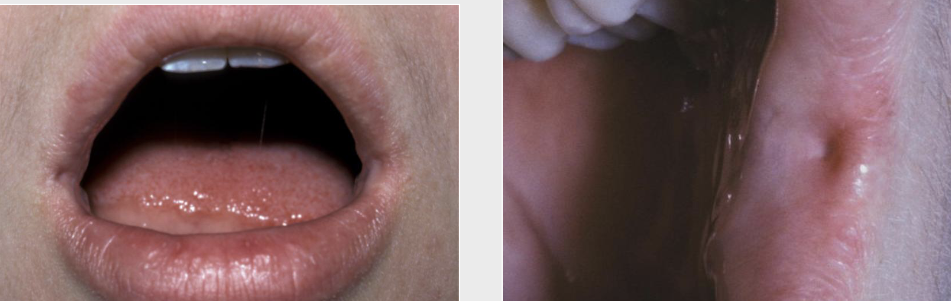
What is a caliber persistent artery?
Common vascular anomaly seen in adults
Main arterial branch extends up into the superficial submucosal tissue
Almost exclusively on upper lip
Elevated linear or arcuate lesion
Stretching the lip usually causes the artery to become inconspicuous
Unique feature is pulsation
No treatment, brisk bleeding
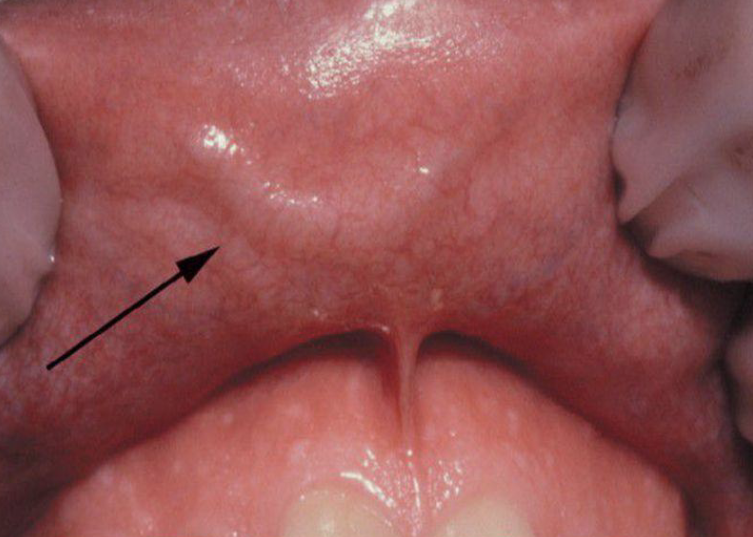
What is exostosis?
Localized bony protuberance that arise from the cortical plate
Maybe due to stress placed on the bone
Buccal, palatal, torus
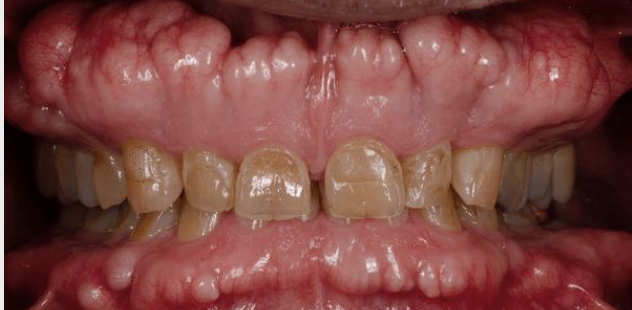
What is condylar hypoplasia?
Underdeveloped condyle due to congenital or acquired
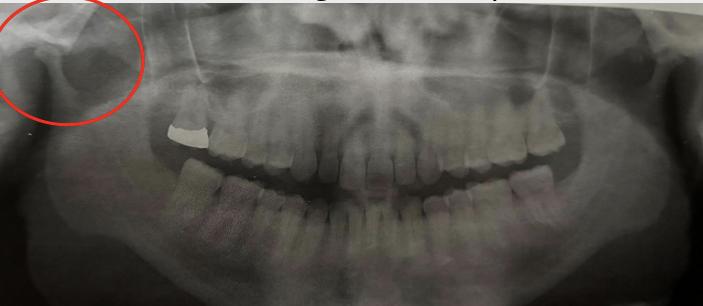
What is condylar hyperplasia?
Excessive growth of condyle due to neoplasm, endocrine disturbances
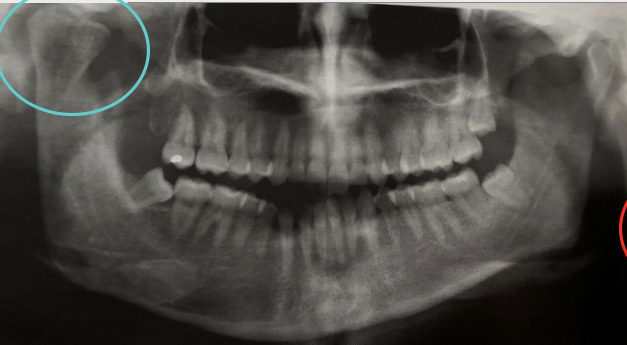
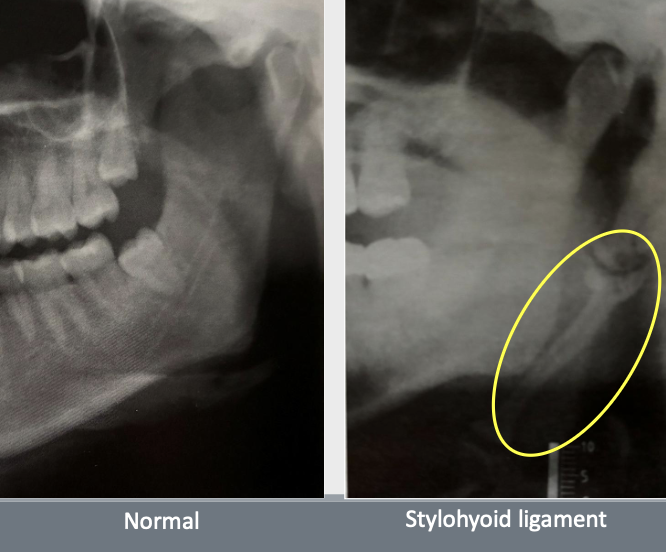
What is eagle syndrome?
Elongation of styloid process or mineralization of the stylohyoid ligament
Sometimes pain during opening mouth, swallowing, turning head sideways
Usually bilateral but can be unilateral
Treatment depends on severity
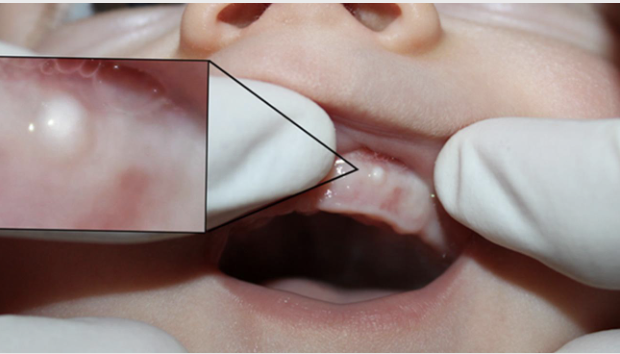
Cysts of Newborn: what is epstein’s pearls?
Occur along the median palatal raphe due to epithelial entrapment by palatal fusion
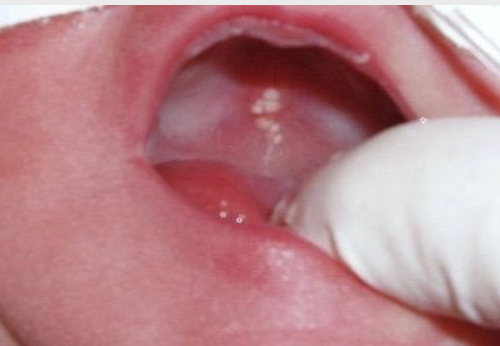
Cysts of Newborn: what is Bohn’s Nodule?
Occur along the buccal and lingual aspects of the alveolar ridge
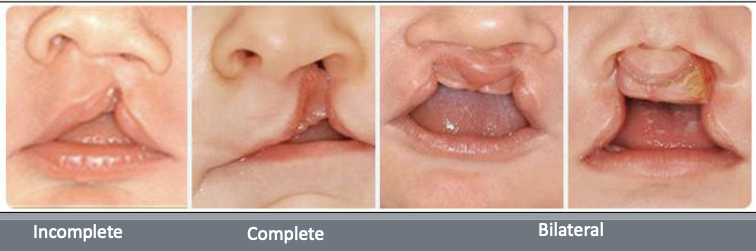
What are orofacial clefts?
One of the most common major congenital defects
What is the prevalence of orofacial clefts?
Prevalence
Native Americans: 1 in 250
Asians: 1 in 300
Caucasians: 1 in 700
African American: 1 in 1500
Which orofacial cleft is more common in males?
CL ± CP
Which orofacial cleft is more common in females?
CP
___% of CL is unilateral, (_____% is on the left side), ____% are bilateral
80, 70, 20
A complete CL extends to
The nostril
An incomplete CL does not involve
The nose
Complete clefts involving the alveolus usually occur between which teeth?
The lateral incisor and canine
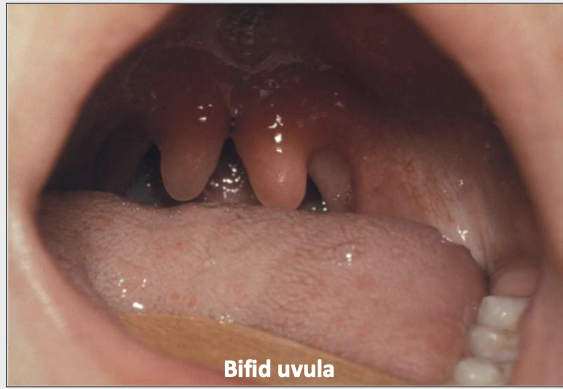
The cleft palate: what is a bifid uvula?
Minimal manifestation of CP
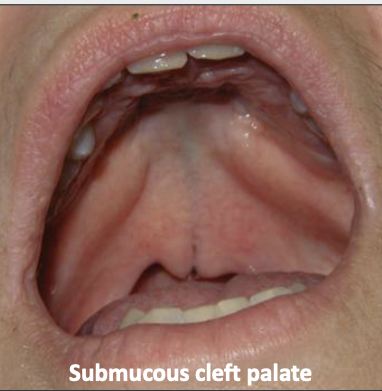
The cleft palate: what is a submucosal palatal cleft?
Surface is intact, but defect exists in the underlying musculature of the soft palate
What is Pierre Robin Syndrome (sequence)?
Cleft palate (CP), mandibular micrognathia, glossoptosis- posterior portion of tongue
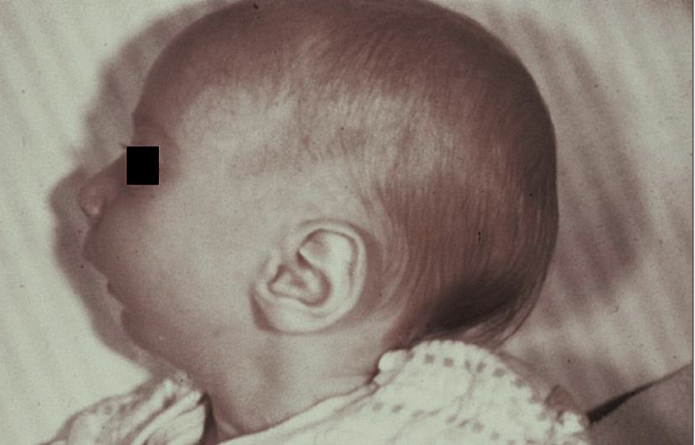
What is Van der Woude Syndrome?
Paramedian lip pits
Congenital invaginations of the lower lip
Usually bilaterally located
No tx except evaluate for syndrome (or for esthetics)
Autosomal Dominant
CL + CP or CP only
Paramedian lip pits
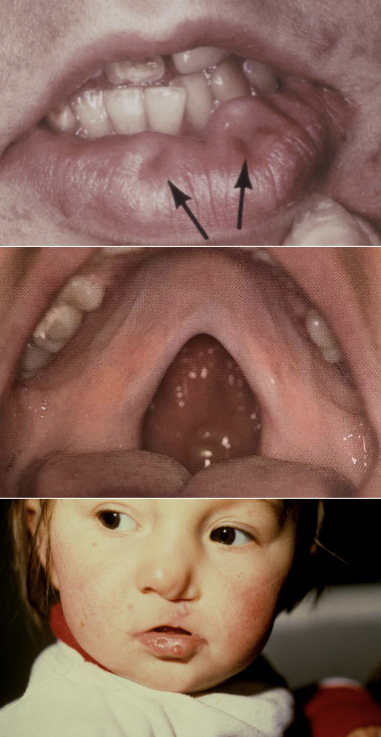
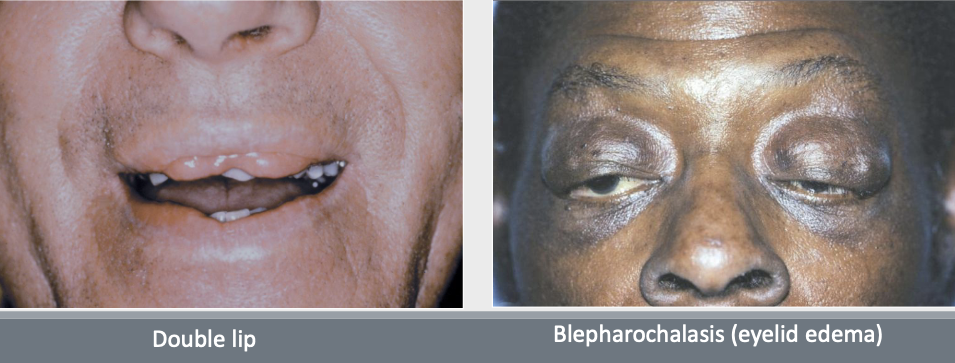
What is Ascher Syndrome?
Double lip (usually acquired), blepharochalasis (eyelid edema), nontoxic thyroid enlargement, congenital/sporadic (some are AD)
What is the clinical presentation of Crouzon Syndrome (craniofacial dysostosis)?
Ocular proptosis (Bulging of the eye)
Abnormal skull shapes: Clover leaf (kleeblattschädel)
Intra-oral: Maxillary hypoplasia, crowded teeth
Radiograph: “beaten metal” pattern
Clover leaf “kleeblattschädel”
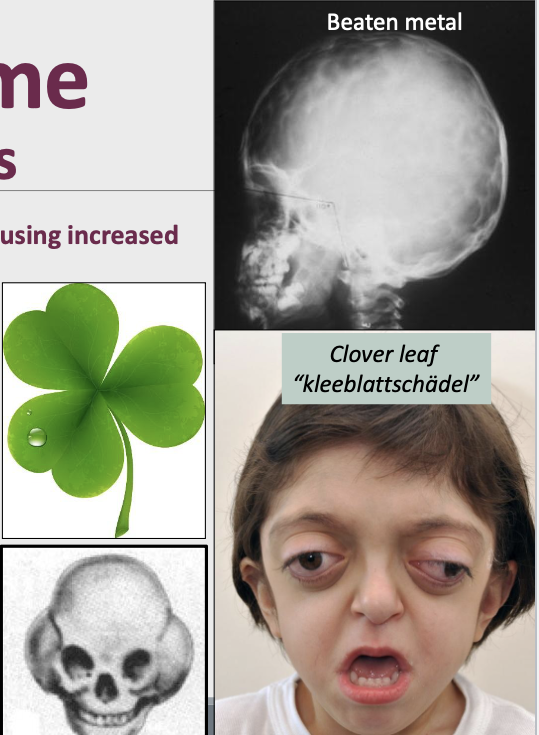
What is craniosynostosis?
Premature closing of the cranial sutures causing increased cranial pressure
What kind of disease is crouzon syndrom?
Autosomal dominant (AD) / mutation in FGFR2
What is Apert Syndrome (Acrocephalosyndactyly)
It is craniosynostosis increasing cranial pressure, also an autosomal dominant condition leading to a mutation in FGFR2
What is the clinical presentation of Apert Syndrome?
Ocular proptosis (Bulging of the eye)
Hypertelorism
Intellectually challenged
Always syndactyly (fused digits)
Abnormal skull shapes:
Acrobrachycephaly (tower head)
Clover leaf (kleeblattschädel)
Intra-oral: Maxillary hypoplasia, mand prognathism, v-arched palate, pseudocleft, gingival enlargement, trapezoid lip
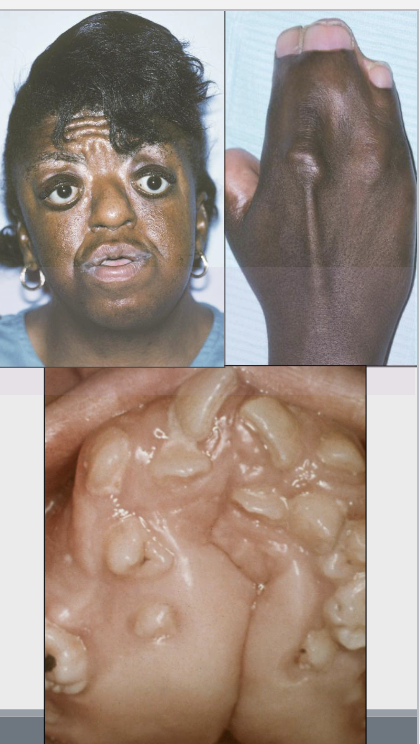
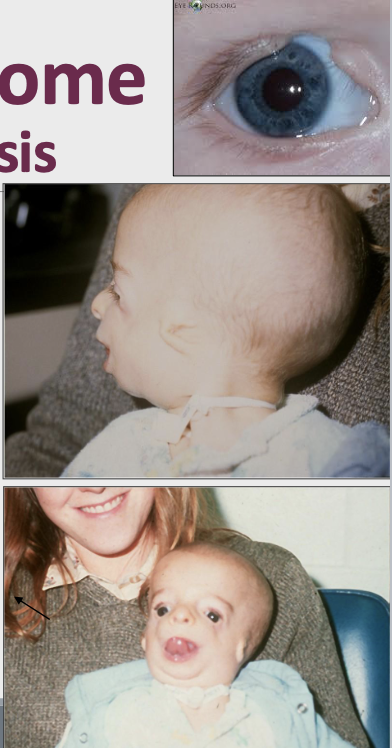
What is the cliinical presentation of Treacher Collin Syndrome?
Hypoplastic zygoma (depressed face)
Narrow face
Downward slanting of palpebral fissure
Coloboma (notched lower eyelid) in 75 %
Ear defect
Intra-oral: Microstomia, hypoplastic mandible
What kind of genetic condition is Treacher Collin Syndrome?
Autosomal Dominant with a defect in the 1st and 2nd branchial arches