Group 7
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Iodine’s solubility
It’s not soluble in water.
However, if iodide ions are present, then it is soluble and reacts to form triiodide ions, which gives the solution it’s brown colour.
I2 + I- → I3-
Trends down group 7
Melting and boiling points increase because larger molecules and larger number of v.d.ws.
Electronegativity decreases down the group because increased atomic radius and shielding.
Ionisation energy decreases because of shielding and increased atomic radius which weakens the forces of attraction between valence electrons and nucleus.
Chlorine reacting with water
Reacts with water in a disproportionation reaction, meaning the chlorine is simultaneously oxidised and reduced.
Cl2 (g) + H2O → ← HCl (aq) + HClO (aq)
HClO is chloric acid. It’s a mild oxidising agent and effective at killing bacteria without harming humans so it’s used in swimming pools and water treatment for sterilisation.
Chlorine reacting with cold dilute alkali
Disproportionates again to form chloride, chlorate ion and water.
Cl2 + 2OH- (aq) → Cl- (aq) + ClO- (aq) + H2O(l)
The chlorate ion is an important oxidising agent and is used in domestic bleach, NaClO
Appearance and properties of fluorine
Yellow gas
Very reactive
Very toxic
Appearance and properties of chlorine
Green gas
Very reactive
Very toxic
Appearance and properties of bromine
Brown liquid
Very easily form orange vapour.
Orange when dissolved in water.
Very reactive and toxic.
Appearance and properties of iodine
Grey crystalline solid/
Very easily forms purple vapour.
Solution in water is brown.
2 more reactions of chlorine with water
2Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (l) → 4HCl (aq) + O2 (g)
NaClO (s) + H2O (l) →← Na+ (aq) +OH- (aq) + HClO (aq)
Oxidising power of halogens
Oxidising agents get reduced easily in order to oxidise another substance, meaning it can gain electrons quickly which they can do because they are very electronegative.
Oxidising power decreases down a group due to increased shielding and atomic radius.
Fluorine is the best oxidising agent so it’s ignored because it’s too strong.
Out of Cl, Br and I, the oxidising power decreases.
Reducing power of the halides
Reducing agents are oxidised easily, meaning they lose electrons.
This increases down halides due to decreased electronegativity, making it easier to lose electrons.
Iodide= fairly good
Bromide= Fairly poor
Chloride= Poor
Fluoride= Very Poor
Identifying halide ions
Add dilute nitric acid (to ensure carbonates and hydroxides are removed as CO2 or water and do not interfere with the precipitates, producing false positives.
Add silver nitrates
Chloride= white
Bromide= cream
Iodide= yellow
Chloride dissolves upon addition of dilute NH3
Bromide (and chloride) dissolves upon addition of concentrated NH3. (solubility decreases down the group)
Addition of chlorine water to potassium chloride solution
No reaction
Addition of bromine water to potassium chloride solution
No reaction
Addition of iodine solution to potassium chloride solution
No reaction
Addition of chlorine water to potassium bromide solution
Orange solution as Br2 is made
Cl2 + 2Br- → 2Cl- +Br2
Bromide is displaced by chlorine as it’s less reactive than chlorine.
Addition of bromine water to potassium bromide solution
No reaction
Addition of iodine solution (doesn’t dissolve in water) to potassium bromide solution
No reaction
Addition of chlorine and bromine water to potassium iodide
Brown solution made as I2 is formed.
This is because iodide is displaced.
Drinking water
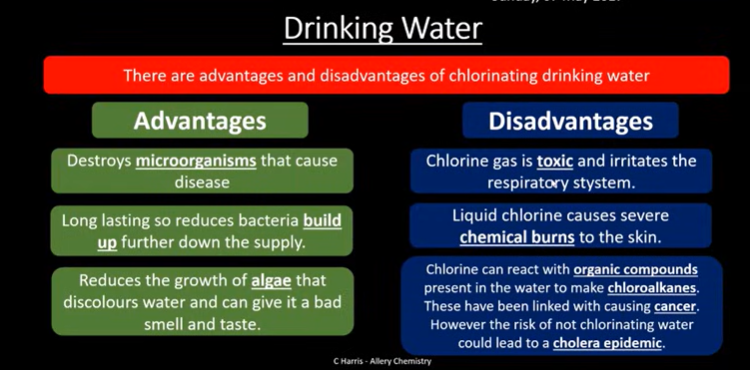
Halides as reducing agents: F- and Cl-
Fluoride and chloride suck and don’t undergo a redox reaction.
NaCl + H2SO4 → HCl + NaHSO4
same with fluoride
Bromide as reducing agent
Lowkey an amazing reducing agent
First undergoes acid-salt step
NaBr + H2SO4 → HBr + NaHSO4
Then redox reaction in which sulfuric acid is reduced to sulfur dioxide.
2NaBr + 3H2SO4→Br2 + SO2 + 2H2O + 2NaHSO4
2Br− → Br2 + 2e−
H2SO4 + 2H+ +2e− → SO2 + 2H2O
Iodide as reducing agent
NaI +H2SO4 → HI +NaSO4
Then redox
2NaI + 3H2SO4 → I2 + SO2 + 2H2O+ 2NaHSO4
2I−→I2+2e−
H2SO4 + 2H+ +2e− → SO2 + 2H2O
6NaI + 7H2SO4 → 3I2 + S + 4H2O + 6NaHSO4
6I− → 3I2 + 6e−
H2SO4 + 6H+ +6e−→S + 4H2O
8NaI + 9H2SO4 → 4I2 + H2S + 4H2O + 8NaHSO4
8I−→4I2+8e−
H2SO4 + 8H+ +8e− → H2S + 4H2O