Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Compare/contrast the basic characteristics of the somatic and autonomic nervous system
somatic:
sensory & motor neurons
voluntary
autonomic:
receives input from sensory receptors located in organs, blood vessels, muscles, & nervous system
involuntary
Compare the sensory input of the SNS vs. ANS
SNS → somatic senses & special senses
ANS → interoceptors; some somatic & some special senses
Compare the control of motor output for SNS vs. ANS
SNS → voluntary; from cerebral cortex (contributions from corpus striatum, cerebellum, brainstem, spinal cord)
ANS → involuntary; from hypothalamus, limbic system, brainstem, & spinal cord
Compare the motor neuron pathway for SNS vs. ANS
SNS → one-neuron pathway; somatic motor neurons extending from CNS synapse directly with effector
ANS → usually two-neuron pathway; preganglionic neurons extending from CNS synapse with postganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglion, & postganglionic neurons extending from ganglion synapse with visceral effector
Compare the neurotransmitter & hormones of the SNS vs. ANS
SNS → all somatic motor neurons only release ACETYLCHOLINE (ACh)
ANS → all sympathetic/parasympathetic preganglionic neurons release ACh. Most sympathetic postganglionic neurons release NE; those to most sweat glands release ACh. All parasympathetic postganglionic neurons release ACh. Chromaffin cells of suprarenal medullae release epinephrine & norepinephrine (NE)
Compare the effectors of the SNS vs. ANS
SNS → skeletal muscle
ANS → smooth muslce, cardiac muscle, & glands
Compare the responses of the SNS vs. ANS
SNS → contraction of skeletal muscle
ANS → contraction/relaxation of smooth muscle; increased or decreased rate & force of contraction of cardiac muscle; increased or decreased secretions of glands
Which parts of the brain provide regulation for ANS reflexes?
hypothalamus & brain stem
What are interoceptors? Where are they located and what is their function? Provide two examples of an interoceptor
interoceptors
location: blood vessels, visceral organs, muscles, & nervous system
function: monitor conditions in the internal environment
example 1: chemoreceptors → monitor blood CO2 level
example 2: mechanorecepetors → detect the degree of stretch in walls of organs/blood vessels
How do autonomic motor neurons regulate visceral activities?
either increasing (Exciting) or decreasing (inhibiting) ongoing activities in thier effector tissues
Most autonomic motor pathways consist of two motor neurons in series. Name and briefly describe them
preganglionic neuron → cell body is in CNS & axon extends to an autonomic ganglion
postganglionic neuron → unmyelinated axon extending from ganglion to effector
What is dual ANS innvervation?
most body organs receive impulses from both sympathetic & parasympathetic neurons
What is the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
sympathetic → “flight-or-flight”; stimulation leads to increased alertness & metabolism
parasympathetic → “rest-and-digest”; stimulation slows down most body activity
Where are the cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons located in the sympathetic division?
lateral gray horns of the gray matter in the T1-L3 segments
List the ganglion of the sympathetic division
celiac ganglion
aorticorenal ganglion
superior mesenteric ganglion
renal ganglion
inferior mesenteric ganglion (?)
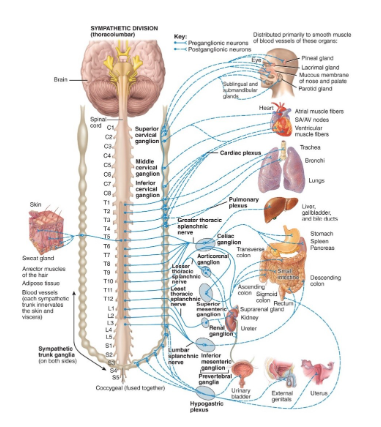
What is another name for the sympathetic division?
thoracolumbar
Name the 2 major types of sympathetic ganglia & briefly describe them
sympathetic trunk ganglia → lie in vertical row on either side of the vertebral column
prevertebral ganglia → lie anterior to vertebral column & close to large abdominal arteries
What does the sympathetic division stimulate that the parasympathetic division does not?
skin & kidney
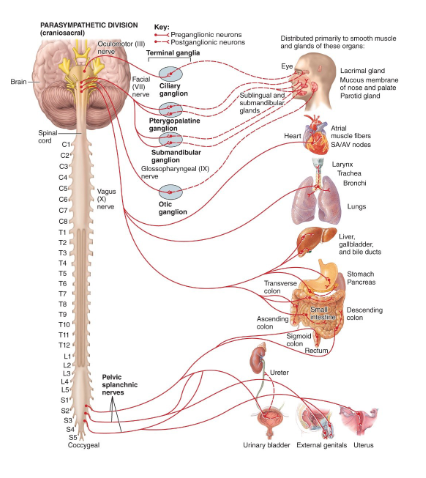
Where are the cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons in the parasympathetic division?
in the nuclei of 4 cranial nerves (III, VII, IX, X) in the brain stem & in lateral gray matter in S2-S4 segments of the spinal cord
__% of parasympathetic flow goes through the __ nerve
80%; vagus
What is another name for the parasympathetic division?
craniosacral
List the ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system
terminal ganglia
ciliary ganglion
pterygopalatine ganglion
submandibular ganglion
otic ganglion
List the 4 ways that axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons connect with postganglionic neurons
Axon may synapse w/ postganglionic neurons in the 1st ganglion is reaches
Axon may ascend or descend to a higher or lower ganglion before synapsing w/ postganglionic neurons
axon may continue w/o synapsing, thru the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion & synapse w/ postganglionic neurons
axon may pass w/o synapsing, thru the sympathetic trunk ganglion & a prevertebral ganglion, then extend to adrenal medullae
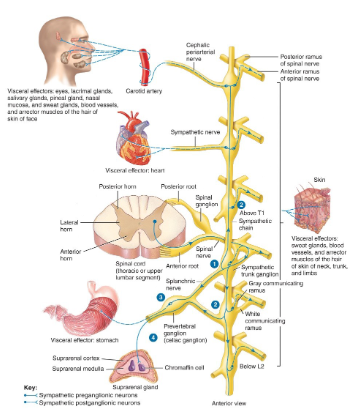
what is the adrenal medullae?
central part of adrenal gland, on top of kidneys; activates fight or flight
The abdomen & pelvis contain major autonomic plexuses which are often named after the artery along which they are distributed. Name them
celiac (solar) plexus
superior mesenteric plexus
inferior mesenteric plexus
renal plexus
hypogastric plexus
mnemonic → Cats Sleep More In Rainy Houses
Where are the sympathetic trunk ganglia?
anterior & lateral to vertebral column
2 cervical
11-12 thoracic
4-5 lumbar
4-5 sacral
1 coccygeal
Based on the neurotransmitter they produce and release, autonomic neurons are considered as either ___ or ___. What neurotransmitters does each release?
cholinergic → release acetylcholine (ACh)
adrenergic → release norepinephrine (noadrenalin)
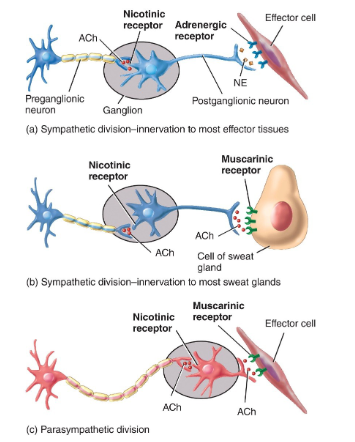
What are 2 cholinergic receptors?
nicotinic receptors
muscarinic receptors
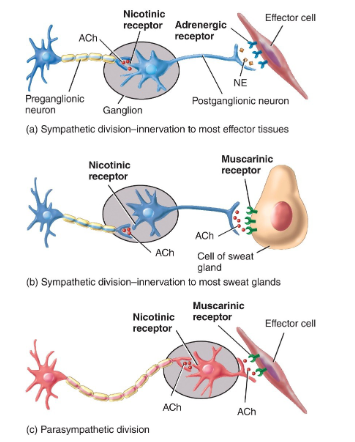
List the 3 major locations of nicotinic receptors and the effects of each
Plasma membrane of postganglionic sympathetic & parasympathetic neurons → excitation = impulses in postganglionic neurons
chromaffin cells of suprarenal medullae → epinephrine & norepinephrine secretion
sarcolemma of skeletal muscle fibers (motor end plate) → excitation = contraction
List the 3 major locations of muscarinic receptors and the effects of each
effectors innervated by parasympathetic postganglionic neurons → in some, excitation; in others, inhibition
sweat glands innervated by cholinergic sympathetic postganglionic neurons → increased sweating
skeletal muscle blood vessels innervated by cholinergic sympathetic postganglionic neurons → inhibition to relaxation to vasodilation
what are beta blockers? how do they work? provide an example.
AKA “beta-adrenergic blocking agents”
medications that reduce blood pressure
work by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline)
cause heart to beat slower & w/ less force → lowers BP
widens veins/arteries to improve blood flow
e.g. propanolol
Compare the distribution of sympathetic vs. parasympathetic division
symp → wide regions; skin, sweat glands, arrector muscles of hair, adipose tissue, smooth muscle of blood vessels
para → mainly to head & viscera of thorax, abdomen, & pelvis; some blood vessels
Compare the location of preganglionic neuron cell bodies & site of outflow for symp vs. para divisions
symp → lateral gray horns of spinal cord segments T1-L2 or L3.
para → nuclei of cranial nerves III, VII, IX & X (3, 7, 9, 10)
Compare the associated ganglia of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → sympathetic trunk ganglia & prevertebral ganglia
para → parasympathetic ganglia
Compare the ganglia locations of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → close to CNS & distant from visual effectors
para → typically near or within wall of vicsceral effectors
Compare the axon length & divergence of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → preganglionic neurons w/ short axons synapse with many postganglionic neurons with long axons that pass to many visceral effectors
para → preganlionic neurons w/ long axons usually synapse w/ 4-5 postganglionic neurons w/ short axons that pass to a single visceral effector
Compare the white & gray communicating rami of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → bost present; white contains myelinated preganglionic axons; gray contains unmyelinated postganglionic axons
para → neither present
Compare the neurotransmitters of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine (ACh) which is excitatory & stims postganglionic neurons; most postganglionic neurons release norepineprine (NE); postganglionic neurons that innervate mosr sweat glands & some blood vessels in skeletal muscle release ACh
para → preganglionic neurons release ACh, which is also excitatory and stims postganglionic neurons; postganglionic neurons release ACh
Compare the physiological effects of the symp vs. para divisions
symp → fight-or-flight
para → rest-and-digest
What is Autonomic Tone? What is it regulated by?
balance between sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous system activity
regulated by hypothalamus
effects body organs differently
when sympathetic input increases, parasympathetic input decreases & vice versa (equilibrium)
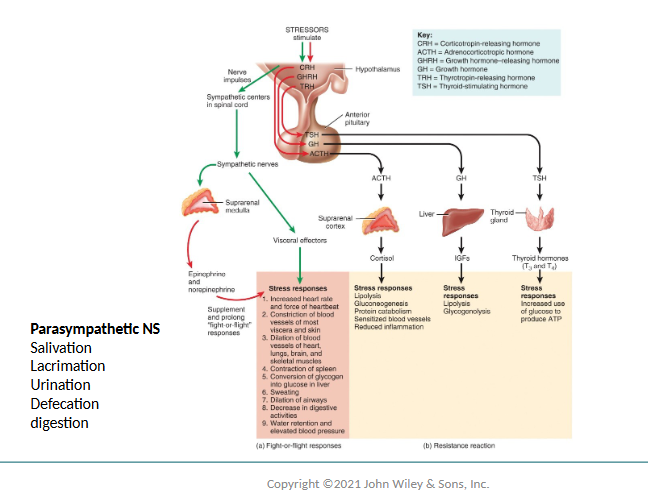
What does Sympathetic Stimulation lead to?
secretion of norepinephrine by adrenal glands
increase in rate & strength of the heartbeat
constriction of blood vessels of non-essential organs
dilation of vessels of essential organs (skeletal muscle & cerebral cortex)
increase in rate & depth of breathing
hepatic conversion of glycogen → glucose
decrease in GI activity
SLUDD is an acronym used to describe the responses of the prasympathetic nervous system. What does it stand for?
Salivation (increased)
Lacrimation (increased)
Urination (increased)
Digestion (increased)
Defecation (increased)
& 3 decreases (rate/force of heart beat, airway size, rate of breathing, & pupil size)
What is controlled when nerve impulses pass through an autonomic reflex arc?
heart rate & force of ventricular contraction
blood pressure & blood vessel diameter
What is the autonomic reflex arc composed of?
receptor
sensory neuron
integrating center
motor neurons
effector
What is Raynaud Phenomenon?
occurs due to excessive sympathetic stimulation of smooth muscle in arterioles of digits
vasoconstriction leads to numbness & ischemia in digits