Temporal and Infratemporal Regions
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the infratemporal fossa?
a deep facial region that contains two of the four muscles of mastication
the infratemporal fossa communicates with a more medial space known as what?
pterygopalatine fossa
what are the boundaries of the infratemporal fossa?
Lateral: ramus of the mandible & zygomatic arch
Medial: lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone
Anterior: posterior aspect of maxilla
Posterior: Temporomandibular (TMJ) joint
Superior: Greater wing of Sphenoid
what is located within the infratemporal fossa?
- medial pterygoid
- lateral pterygoid
- maxillary artery
- pterygoid plexus of veins
- mandibular division (V3)
- Otic Ganglion
to get to the deep infratemporal fossa what must be removed?
- zygomatic arch and part of the ramus
- lateral pterygoid removed
what is the attachment of the temporalis muscle?
temporal fossa to coronoid process
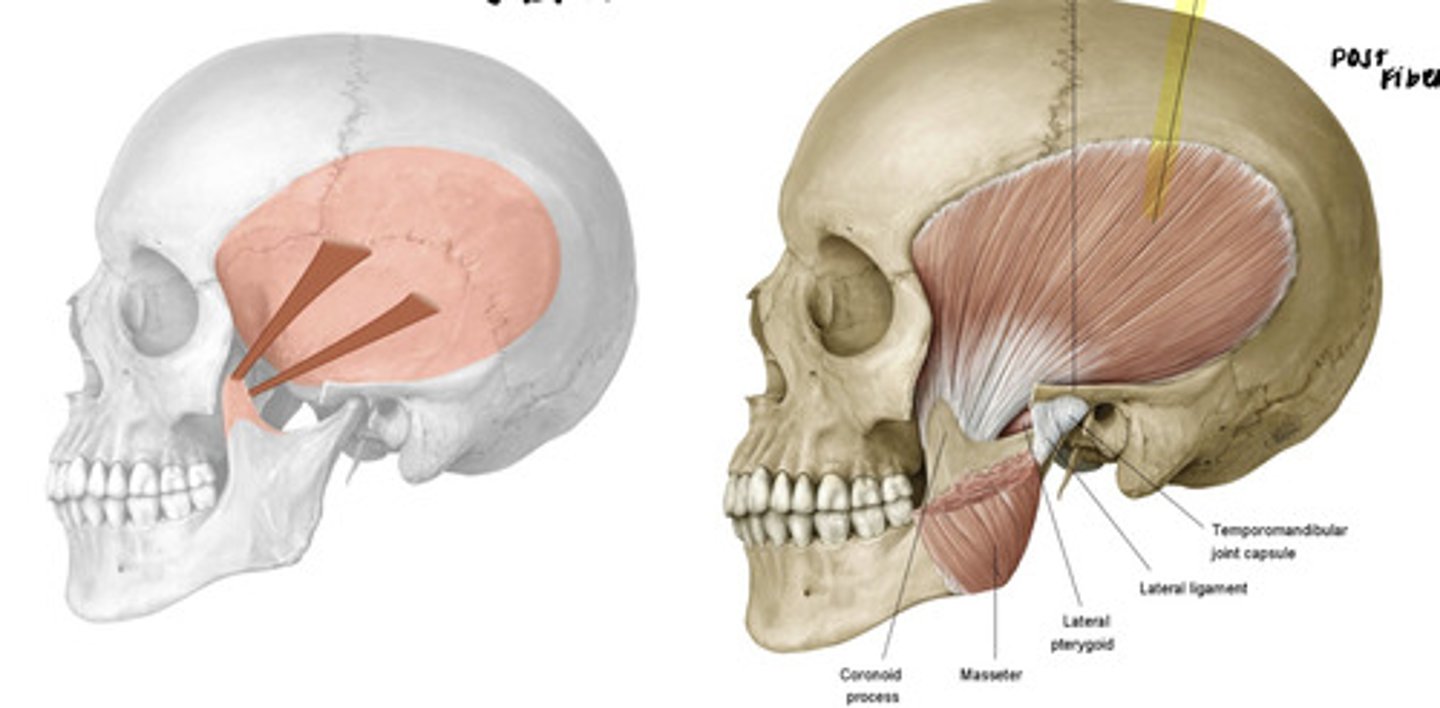
what is the action of temporalis on the mandible?
elevate and retract
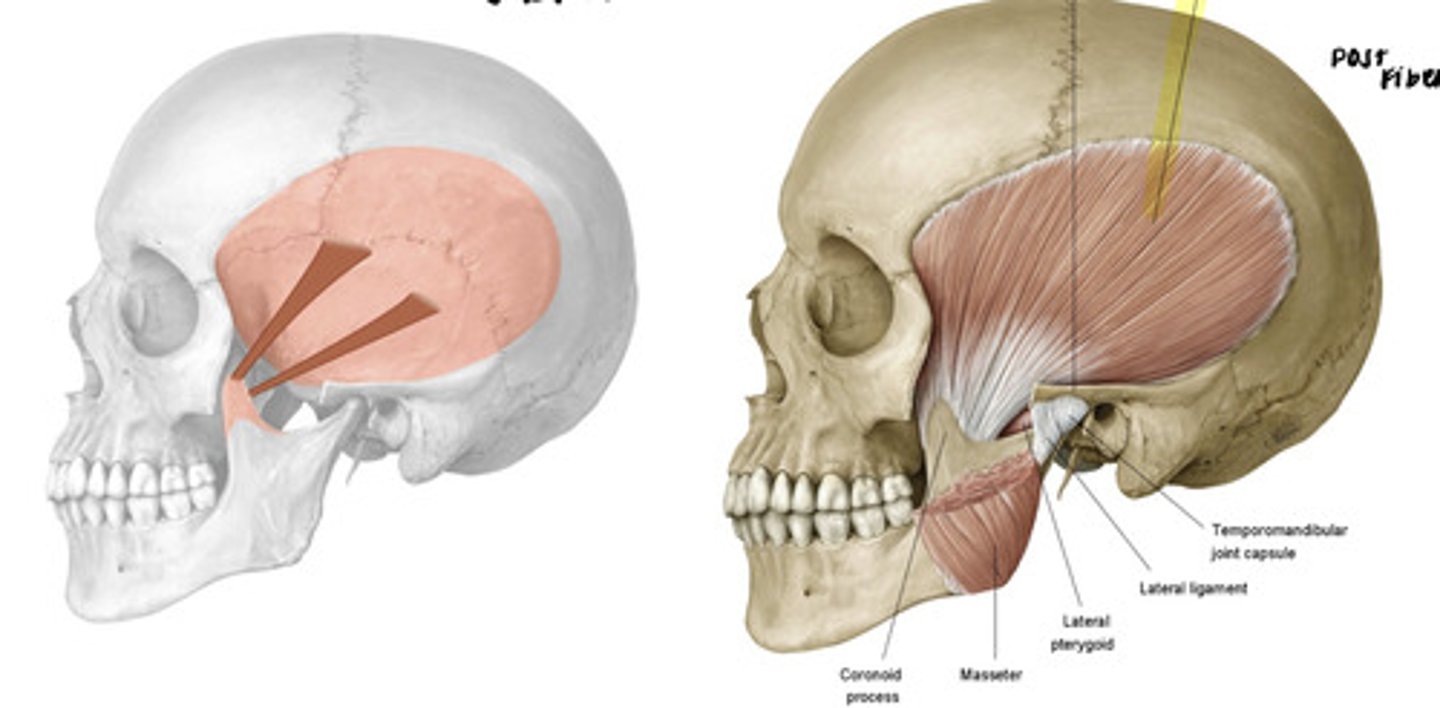
the posterior fibers of the temporalis are the ones responsible for what action?
retraction
to elevate the jaw means to do what?
close the jaw
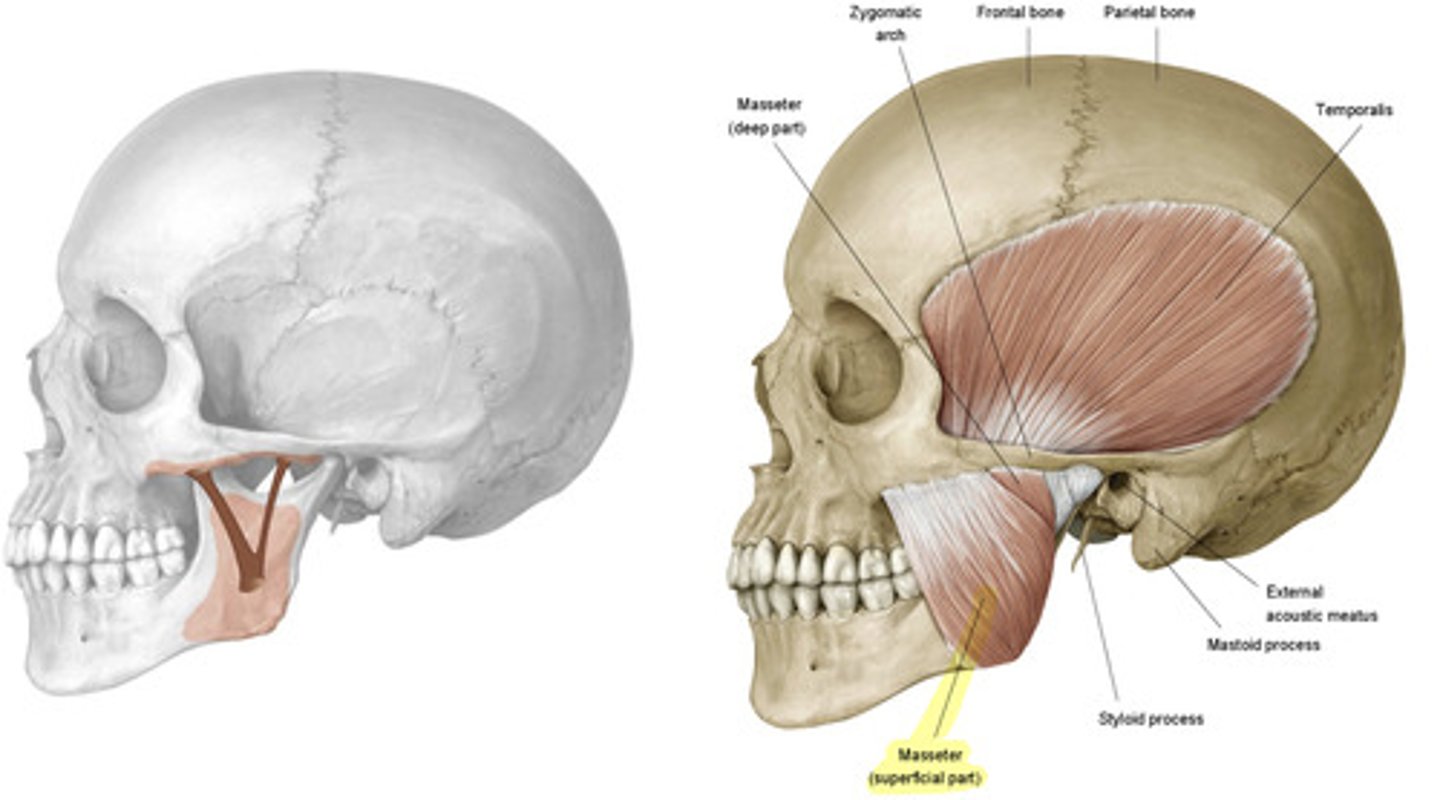
what is the attachment for the masseter?
zygomatic arch to the superficial side of the angle of the mandible
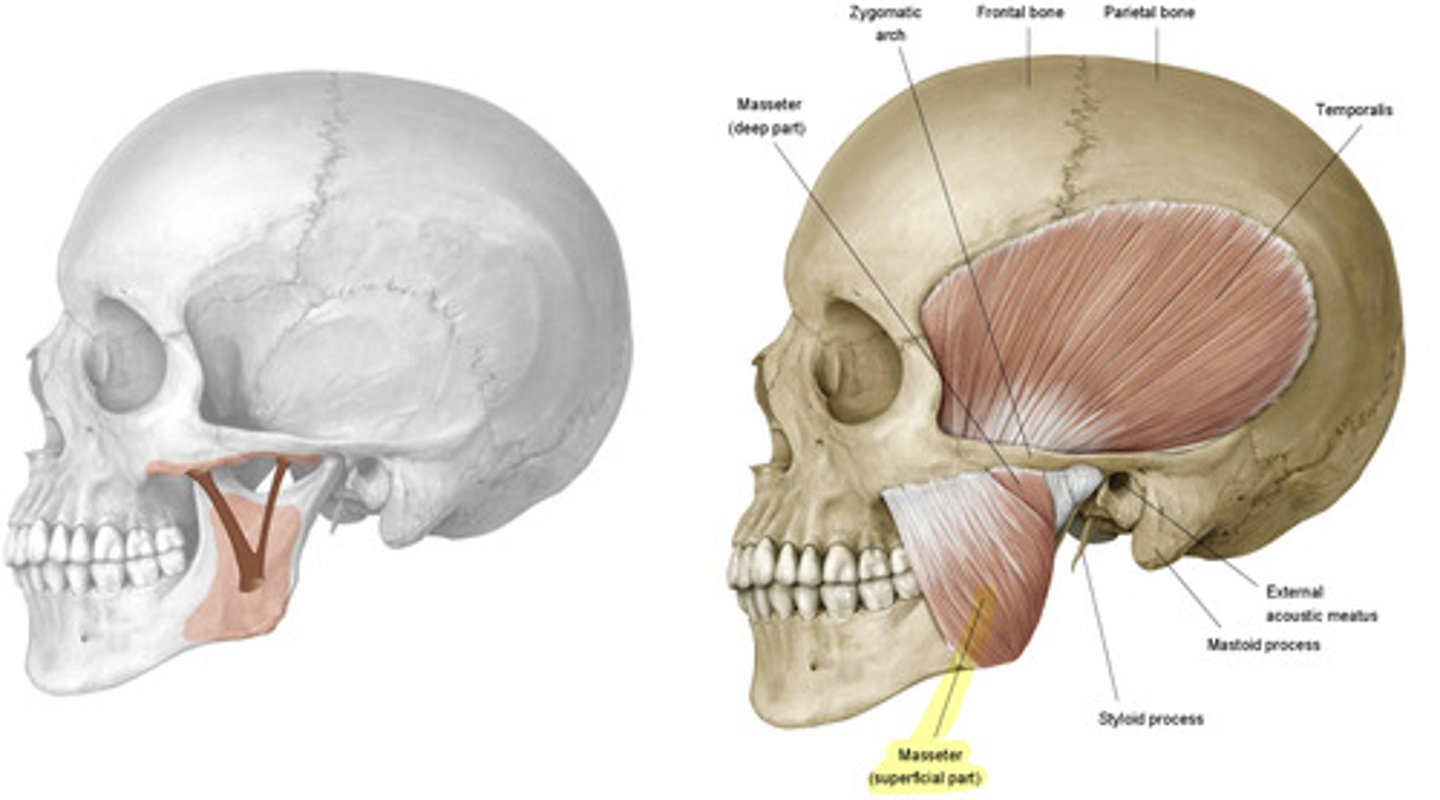
what is the action of the masseter on the mandible?
elevate
what is the attachment of the medial pterygoid?
- Superficial Head: maxilla to the deep side of the mandibular angle
- Deep Head: lateral pterygoid plate to the deep side of the mandibular angle
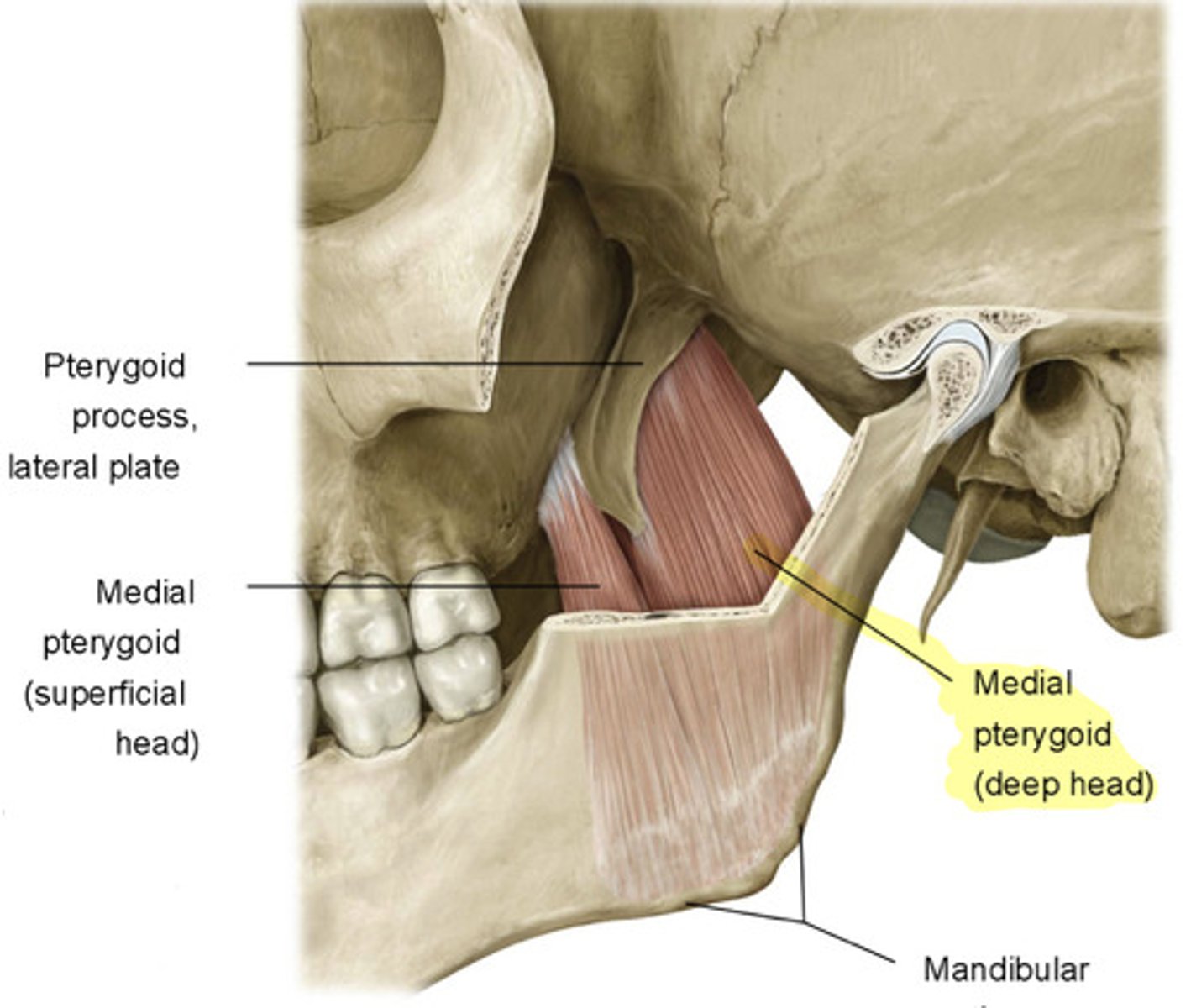
what is the action of the medial pterygoid?
elevates mandible
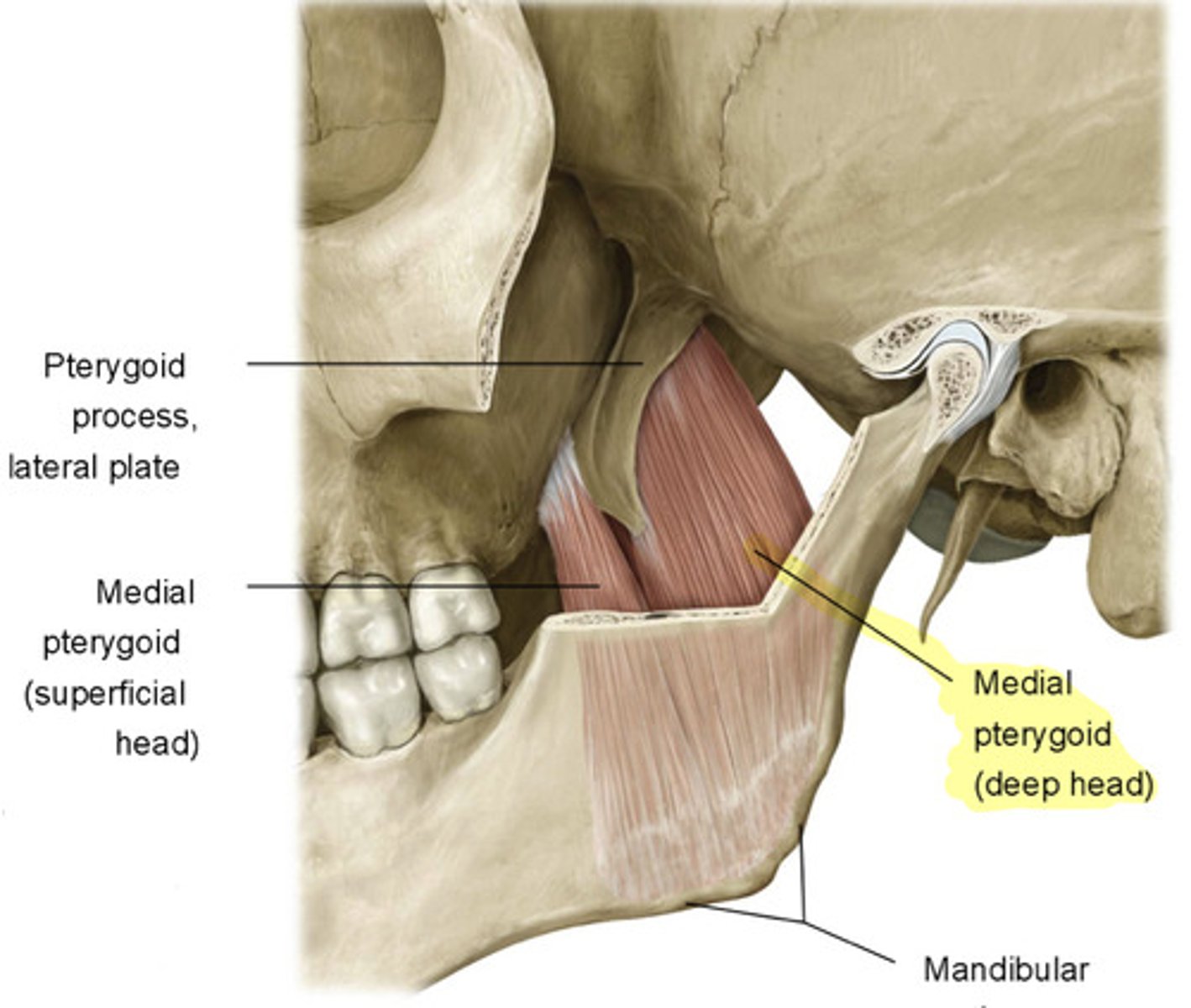
what is the attachment of the lateral pterygoid?
Superior Head: greater wing of sphenoid
Deep Head: lateral pterygoid plate
both attach to the condyloid process at the temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
what is the action of the lateral pterygoid?
protract and depress mandible (chin)
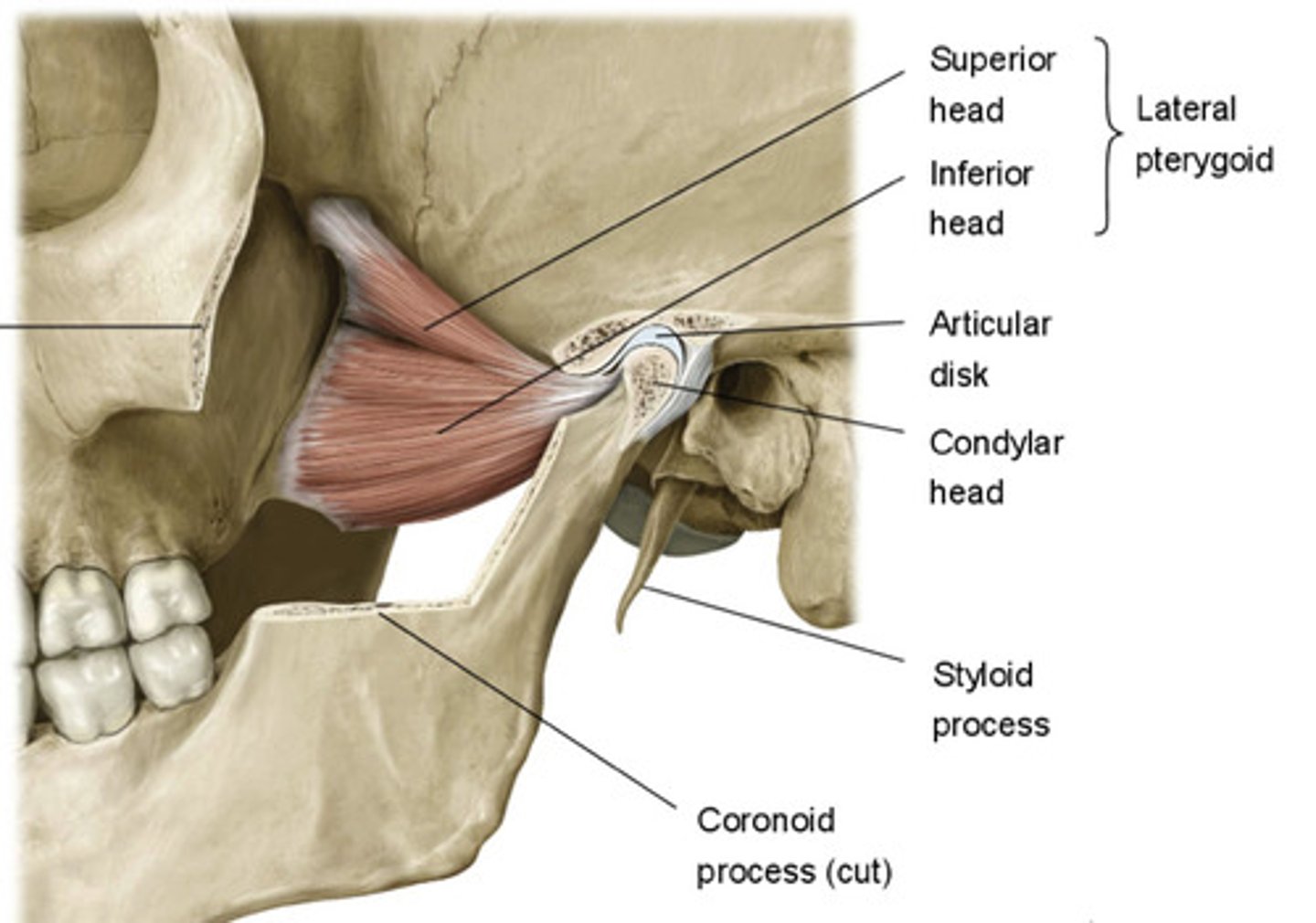
what type of joint is the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
a modified hinge joint divided into two cavities by an articular disc
What are the articular surfaces for the temporomandibular joint?
mandibular fossa and the articular tubercle of the temporal bone with the head of the mandible (Condylar process)
what type of glide occurs between the articular disc and the mandibular fossa at the superior joint cavity?
anterior gliding
what type of motion occurs between the mandibular condyle and the articular disc at the inferior joint cavity?
rotation
what are the important arteries of the infratemporal region?
- maxillary artery
- middle meningeal artery
- inferior alveolar artery
the maxillary artery can be divided into what 3 portions during its course?
1st: lies deep to the ramus of the mandible
2nd: lies anterior to the ramus (location of muscular branches)
3rd: begins at the entrance of the pterygopalatine fossa and continues into the fossa
what does the middle meningeal artery supply?
the meninges
what is the course of the middle meningeal artery?
it passes between the two roots of the auriculotemporal nerve to enter the foramen spinosum
how does the meningeal artery enter the cranium?
foramen spinosum
what does the inferior alveolar artery supply?
the teeth
how does the inferior alveolar artery get into the area to supply the teeth?
it enters the mandibular foramen (basically goes into the bone) and comes out of the jaw as mental artery
what are the V3 branches of the infratemporal fossa?
- inferior alveolar nerve
- lingual nerve
- buccal nerve
- auriculotemporal nerve
what are the V2 branches of the Pterygopalatine Fossa?
- infraorbital nerve
- zygomatic nerve
- posterior superior alveolar nerve
- sphenopalatine nerves
- descending palatine nerves
how does the mandibular nerve enter the infratemporal fossa?
through the foramen ovale
what are the branches of the mandibular nerve?
- inferior alveolar nerve
- auriculotemporal nerve
- lingual nerve
- buccal nerve
how does the inferior alveolar nerve enter?
mandibular foramen
what does the inferior alveolar nerve innervate?
mandibular teeth sensation
what is the termination of the inferior alveolar nerve?
mental nerve
which nerve has two roots surrounding the middle meningeal artery? (actually splits around this artery)
auriculotemporal nerve
what does the auriculotemporal nerve supply?
sensory to the skin anterior to the ear
what offers general sensory innervation to the tongue?
lingual nerve
what is the innervation to the inside of the cheek? (pierces through buccinator)
buccal nerve
nerves to the muscles of mastication are independent branches of what that travel to their respective muscles?
branches of V3
V3 is what nerve?
Mandibular Nerve which is a branch of Trigeminal
what branch of the mandibular nerve appears from between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid?
Buccal
what branches of the mandibular nerve are located at the inferior aspect of the inferior head of the lateral pterygoid muscle?
- lingual nerve
- inferior alveolar nerve
list inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve, and buccal nerve from lateral to medial:
inferior alveolar nerve, lingual nerve, buccal
the inferior alveolar nerve enters the bone of the mandible, does the nerve to the mylohyloid and lingual nerve enter the bone?
no! they travel just deep to the bone.
- inferior dives deep, goes into bone, and comes out mental
- the lingual is deep to bone going to the tongue
the mandibular division of trigeminal (V) has a large sensory and small motor component, which of the branches of the trigeminal are predominantly motor?
the branches from the stem and anterior division
the buccal nerve branches from the anterior division of the trigeminal, but what is important to note?
it is SENSORY to the inside of the cheek
the posterior division of the trigeminal nerve gives off what major sensory nerves?
- auriculotemporal nerve
- lingual nerve
- inferior alveolar
the lingual nerve accepts what as a hitch hiker? what is its role?
the chorda tympani from the facial nerve that carries the special fibers for taste
the chorda tympani carries sympathetics or parasympathetics for submandibular region?
parasympathetics
terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve exit as what? through where? supplying what?
the mental nerve through the mental foramen supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the mandible
the mental nerve gives off a small motor branch called what?
nerve to the mylohyoid
where does the nerve to the mylohyoid travel?
down superficial to the muscles of the floor of the mouth to innervate the mylohyoid and the anterior belly of the digastric
what are the parasympathetic pathways associated with the infratemporal fossa?
- innervation of the sublingual and submandibular glands
- innervation of the parotid gland
what are the innervations of the sublingual and submandibular glands?
- CN VII
- Preganglionic sympathetic neuron: superior salivary nucleus
- postganglionic sympathetic neuron: submandibular ganglion
what are the innervations of the parotid glands?
- CN IX
- preganglionic parasympathetic neuron: inferior salivary nucelus
- postganglionic parasympathetic neuron: Otic Ganglion
what is the continuation of the maxillary artery called after it passes through the pterygomaxillary?
sphenopalatine artery
what does the continuation of the maxillary artery, sphenopalatine artery, supply?
the nasal cavity
what are the 3 clinically important branches of the maxillary artery? what do they supply?
Inferior Alveolar: lower teeth
middle meningeal: dura and meninges
posterior superior alveolar: upper teeth and maxillary sinus
what are the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve from the stump of V3?
auriculotemporal
what are the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve anterior division?
- motor branches to muscles of mastication
- buccal
what are the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve posterior division?
- lingual
- inferior alveolar
which of the major sensory branches gives off a small root to the region under the mandible?
inferior alveolar
what is the motor root/nerve that inferior alveolar gives off? what is it supplying in this region?
nerve to the mylohyoid; its motor to the mylohyoid and anterior belly of digastric
how does the special sense of taste reach the tongue?
the fibers for special sensation of taste leave the facial nerve as it travels within the temporal bone in a branch called the chorda tympani.
the chorda tympani passes through the middle ear cavity and enters the back side of the lingual nerve within the infratemporal fossa.
taste fibers for the anterior 2/3 of the tongue are then distributed with the lingual nerve.