Honors Biology Final Study Guide - Unit 2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Atom
The basic unit of a chemical element.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together.
Organelle
Specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions.
Cell
A cell is the smallest living unit.
Tissue
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organ
A structure composed of different tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to perform complex functions.
Organism
An individual living entity.
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area.
Community
A group of different populations that live together in a defined area.
Ecosystem
A community of living organisms and their interactions with their environment.
Biosphere
The global sum of all ecosystems, where life exists.
Cytology
The study of cellular structure and function.
Cell Theory
Cells are the building blocks of all organisms.
Homeostasis
The ability of a cell to maintain a stable internal environment.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
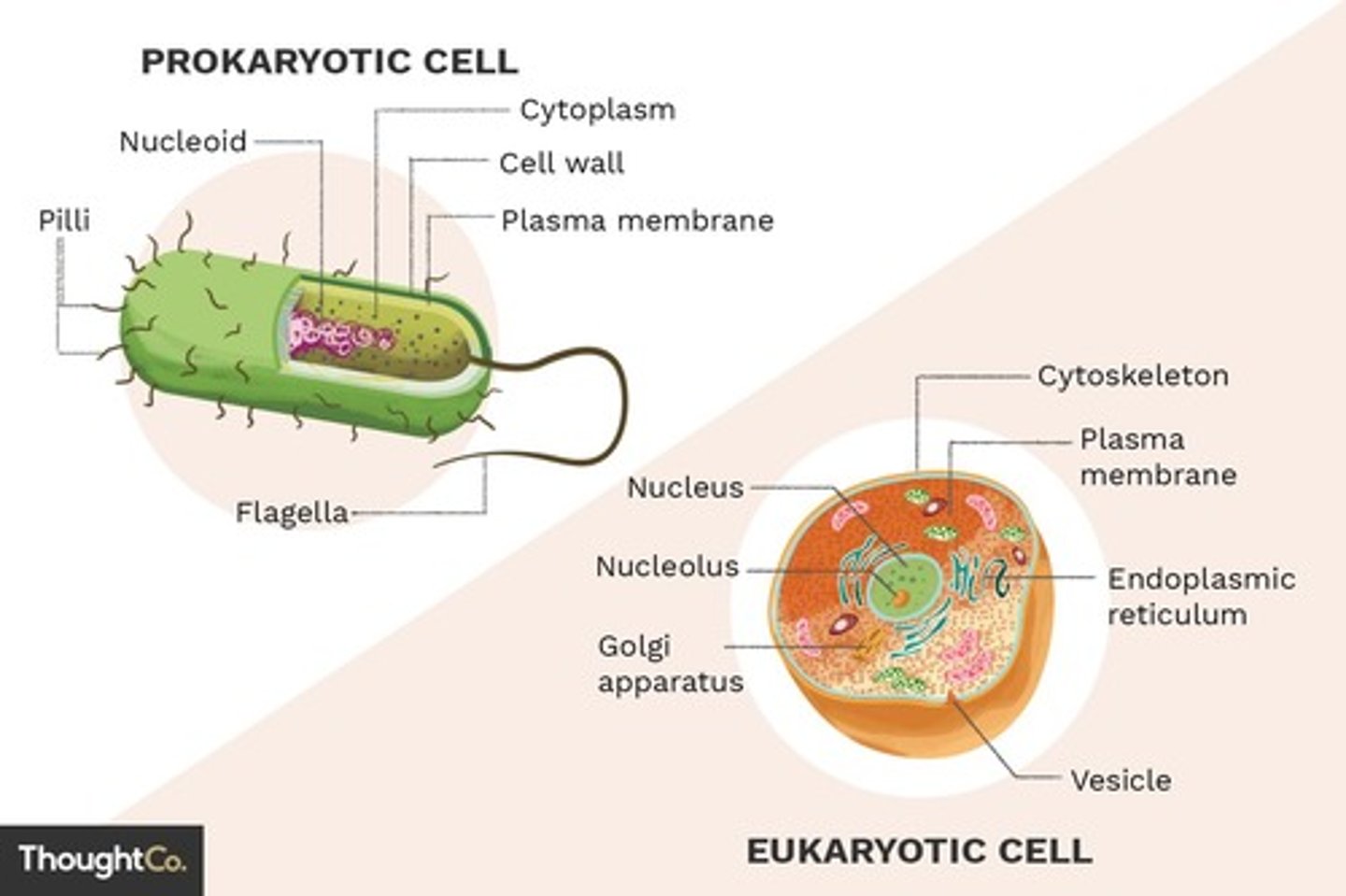
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Cell Wall
A rigid outer layer found in plant cells, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea.
Cell Membrane
A semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cell, separating the interior from the external environment.
Cytoplasm
The gel-like fluid inside the cell membrane that contains all the organelles.
Nucleus
The control center of the cell, containing the cell's genetic material (DNA).
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of membranes studded with ribosomes that synthesizes and transports proteins.
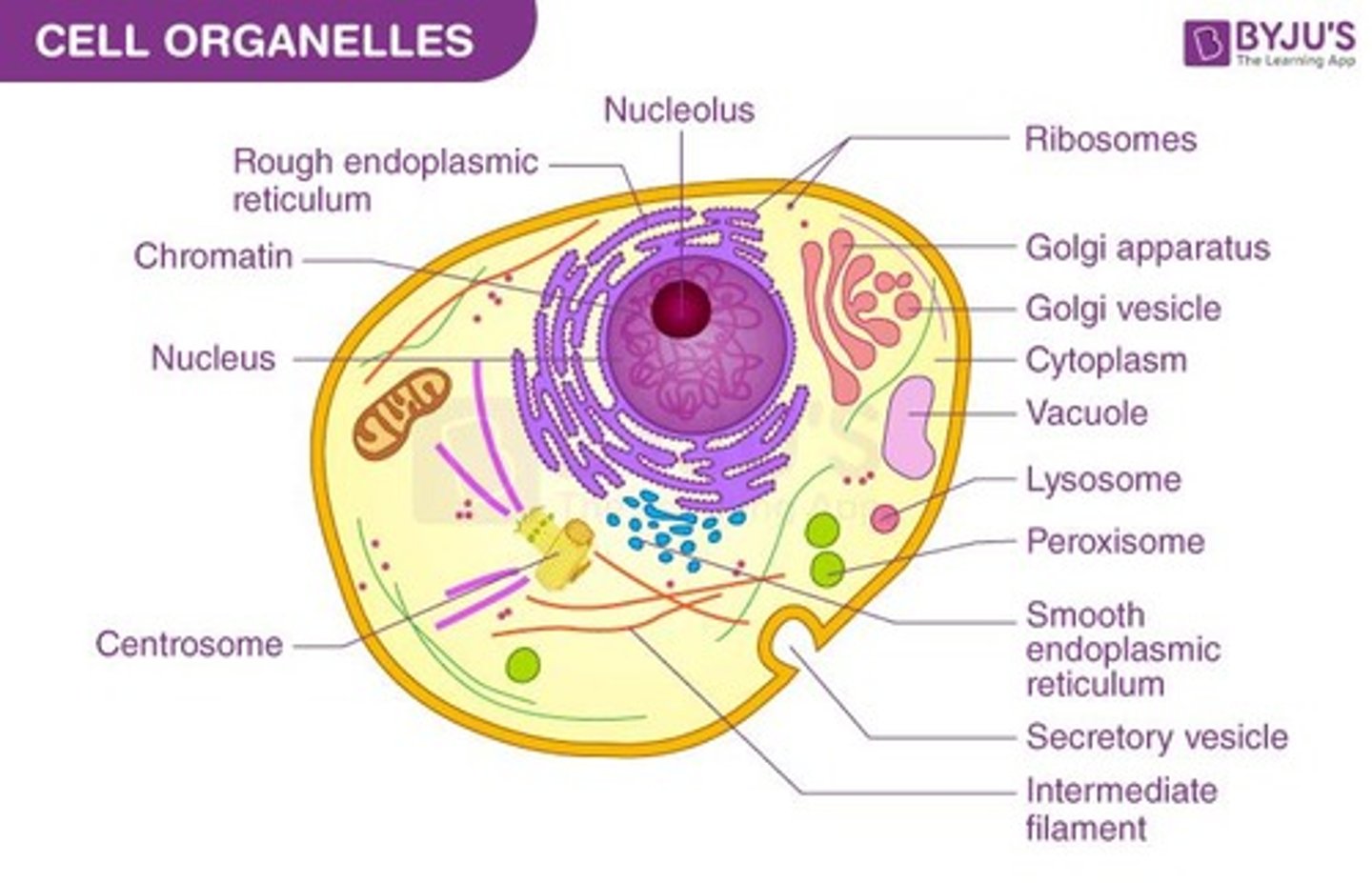
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of membranes without ribosomes that synthesizes lipids and detoxifies harmful substances.
Ribosome
Small, spherical structures that are the sites of protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
Double-membrane bound organelles that generate energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
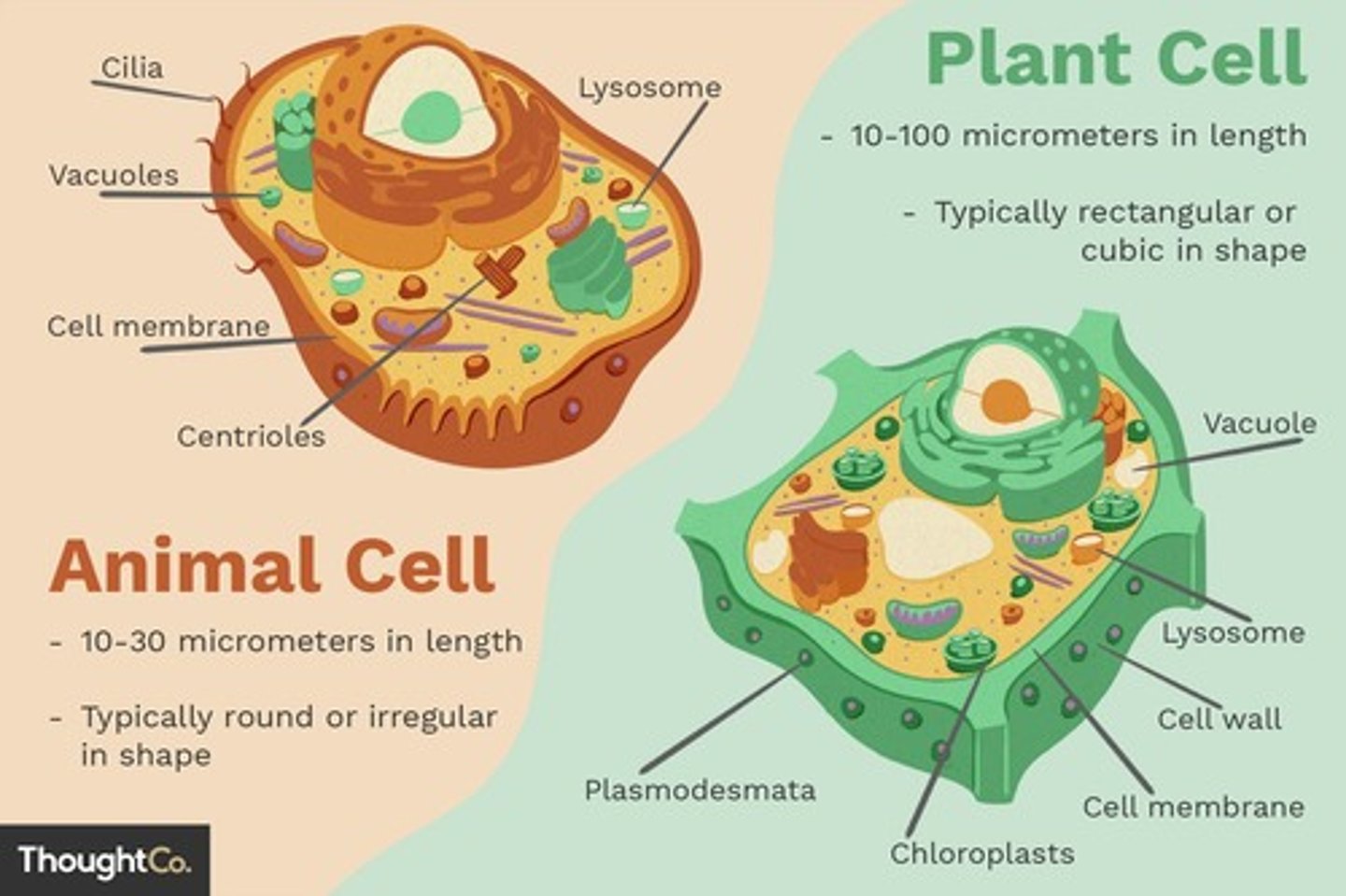
Vacuole
A membrane-bound sac within the cytoplasm of a cell that maintains turgor pressure and stores substances.
Plant Cells
Maintains turgor pressure (water pressure that keeps the cell firm). Stores water, nutrients, and waste products. Provides structural support.
Animal Cells
Stores waste products and can be involved in protein synthesis.
Chloroplast
Description: Double-membrane-bound organelle primarily found in plant and algal cells. Location: Found in the cytoplasm of plant and algal cells. Function: Photosynthesis: Converts light energy into chemical energy (sugars). Contains chlorophyll for light absorption.
Golgi Body
Description: A series of flattened, membrane-bound sacs (cisternae). Location: Found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Function: Protein Modification and Sorting: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport. Lysosome Formation: Involved in the formation of lysosomes.
Centriole
Description: Cylindrical structures composed of microtubules. Location: Found in animal cells and some other eukaryotes. Function: Cell Division: Involved in organizing microtubules during cell division.
Lysosome
Description: A membrane-bound sac containing digestive enzymes. Location: Found in the cytoplasm of animal cells and some plant cells. Function: Digestion: Digests cellular waste, debris, and foreign invaders.
Cytoskeleton
Description: A network of protein fibers that provides structure and support. Location: Found in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells. Function: Cell Shape: Maintains cell shape and provides support. Movement: Involved in cell movement, intracellular transport, and cell division.
Peroxisome
Description: A membrane-bound vesicle containing enzymes. Location: Found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Function: Breakdown of Fatty Acids: Breaks down fatty acids and detoxifies the cell. Hydrogen Peroxide Production: Produces and then breaks down hydrogen peroxide.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
A Dutch draper and scientist, and one of the pioneers of microscopy. In the late 17th century, he became the first man to make and use a real microscope.
Light Microscope
Compound light microscope has more than one lens. Light is focused through lenses and magnifies the specimen.
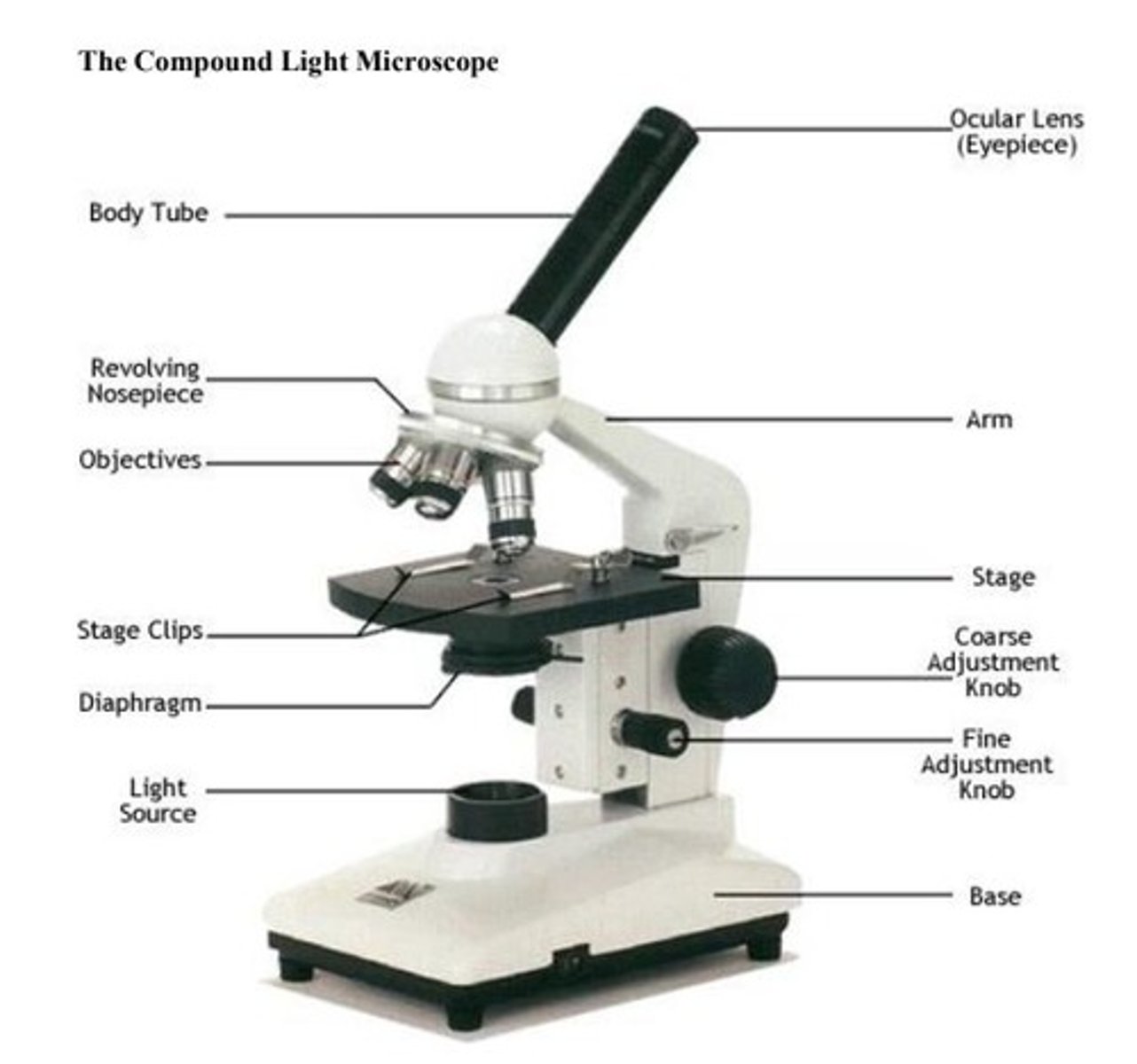
Electron Microscope
Uses a beam of electrons to create an image of a specimen. Capable of much higher magnification (over 1 million times) than a light microscope. Can see much smaller objects in finer detail. Large, expensive pieces of equipment.
Eyepiece
Where you look through to see the specimen. The magnification power is 10x.
Objectives
The smallest is 4x, the medium is 10x, the highest is 40x and 100x and helps magnify the specimen.
Coarse focus knob
Used to bring the specimen into approximate focus.
Fine focus knob
Used to fine tune the focus on the specimen.
Light source
To illuminate the specimen on the slide.
Neck/arm
To support the microscope head when it is carried.
Base
Serves as a support for microscopes.
Revolving Nosepiece
Holds two or more objective lenses and rotates to change power.
Stage
Positions the specimen, either for preparation prior to examination for rapid scans or for precise alignment in the beam path.
Stage clips
Hold the slides in place.
Diaphragm
Controlling the amount of light that passes through the specimen.
Total Magnification
Calculated by multiplying the objective lens magnification by the eyepiece magnification.
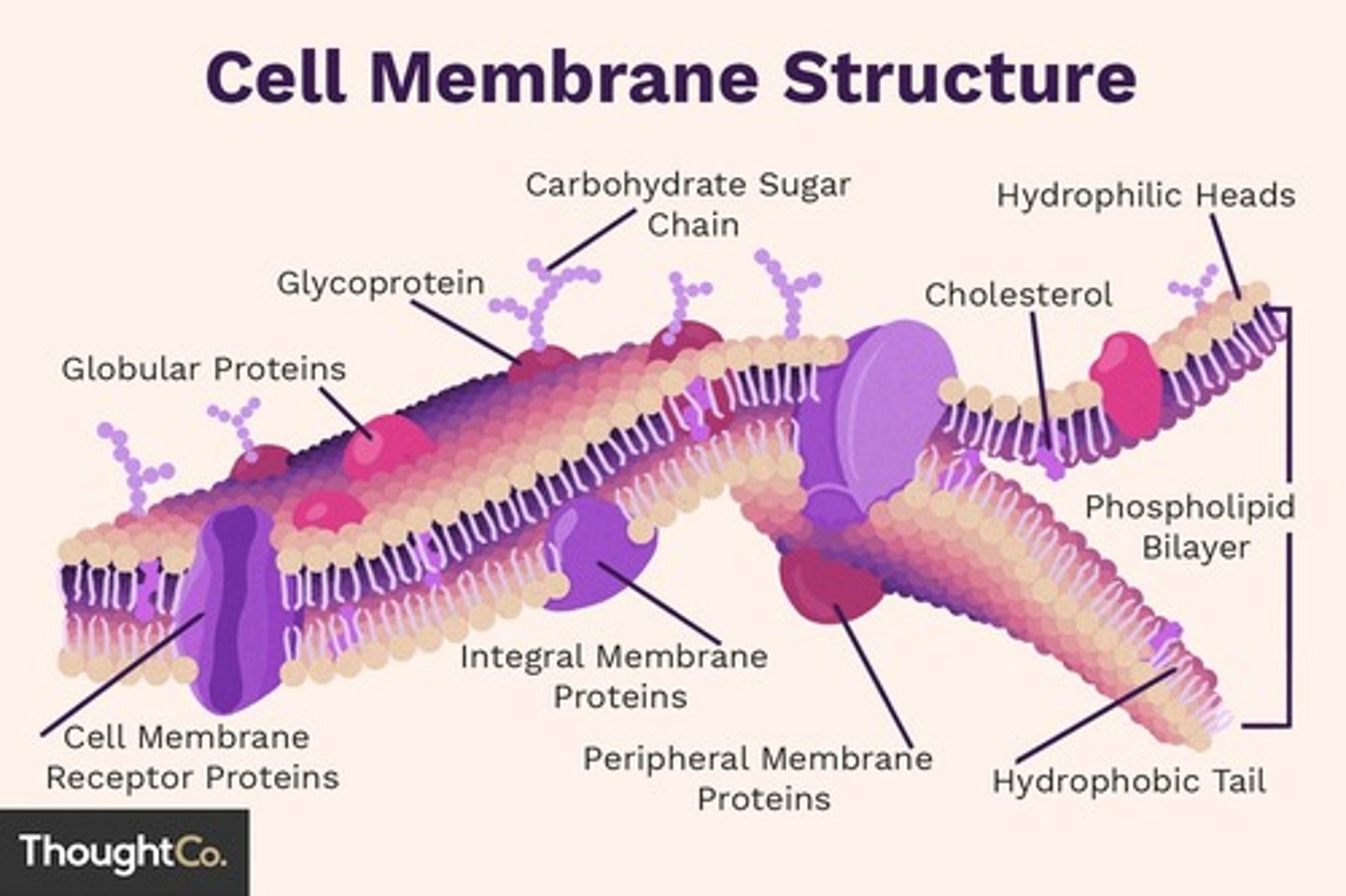
Fluid Mosaic Model
Phospholipids are free to move sideways, so the membrane also appears to be very fluid, like currents in a lake. Cholesterol is also found in the membrane, stabilizing the membrane flexibility.
Phospholipid Bilayer
This double layer of phospholipids forms the basic structure of the membrane.
Integral Proteins
These proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and can span the entire membrane or only part of it.
Peripheral Proteins
These proteins are loosely attached to the outer or inner surface of the membrane, often interacting with integral proteins.
Cholesterol
Interspersed among the phospholipids, cholesterol helps to maintain membrane fluidity at different temperatures.
Glycolipids
These lipids have a carbohydrate chain attached, and they are located on the outer surface of the membrane.
Channel Proteins
These are specific types of integral proteins that allow certain molecules or ions to pass through the membrane.
Marker Proteins
These integral proteins have carbohydrates attached to them, forming glycoproteins, which serve as markers for cell identification and recognition.
Osmosis
Movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion
Movement of solutes from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
Hypertonic Solution
The solution outside the cell has the higher concentration of solute than the solution inside the cell.
Hypotonic Solution
The solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of solute than the solution inside the cell.
Isotonic Solution
The solutions inside and outside of the cell have the same concentration of solute.
Concentration Gradient
Exists when solutes are not at equilibrium; area of high concentration vs. area of low concentration.
Passive Transport
Movement of particles into or out of the cell WITHOUT required energy.
Result of Isotonic Solution
Water moves equally in both directions and the cell remains the same size! (Equilibrium)
Result of Hypertonic Solution
Water moves out of the cell by osmosis, into the solution; cell shrinks (Plasmolysis).
Result of Hypotonic Solution
Water moves from the solution into the cell by osmosis: cell swells and bursts open (cytolysis).
Solute
A substance dissolved in a solvent (ex. sugar).
Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving (ex. water).
Solution
The homogeneous mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent.