Week 6 - Nervous System - The Spinal Cord, The Peripheral Nervous System and Autonomic Nervous System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
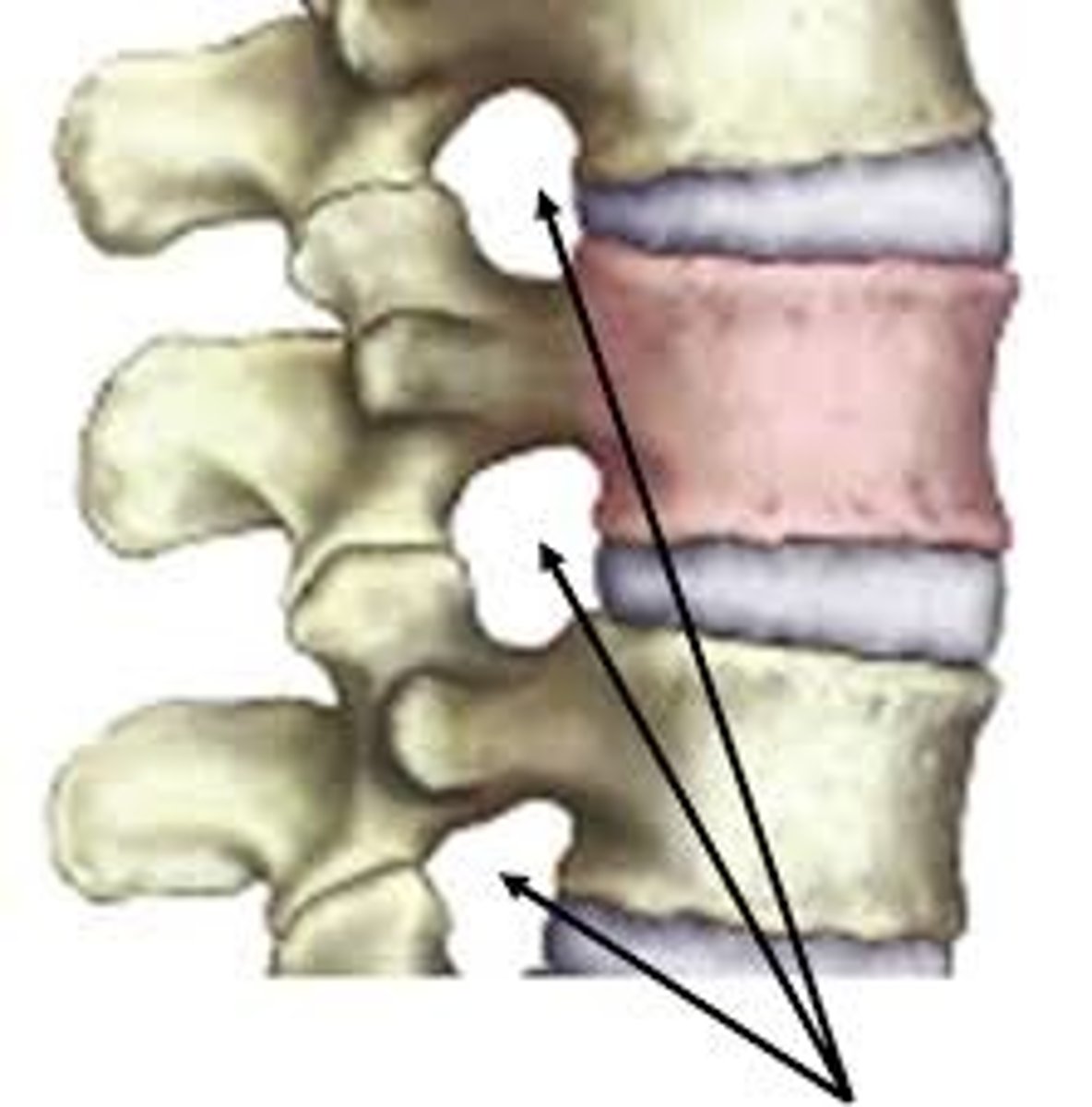
intervertebral foramina
lateral openings between adjacent vertebrae for spinal nerves
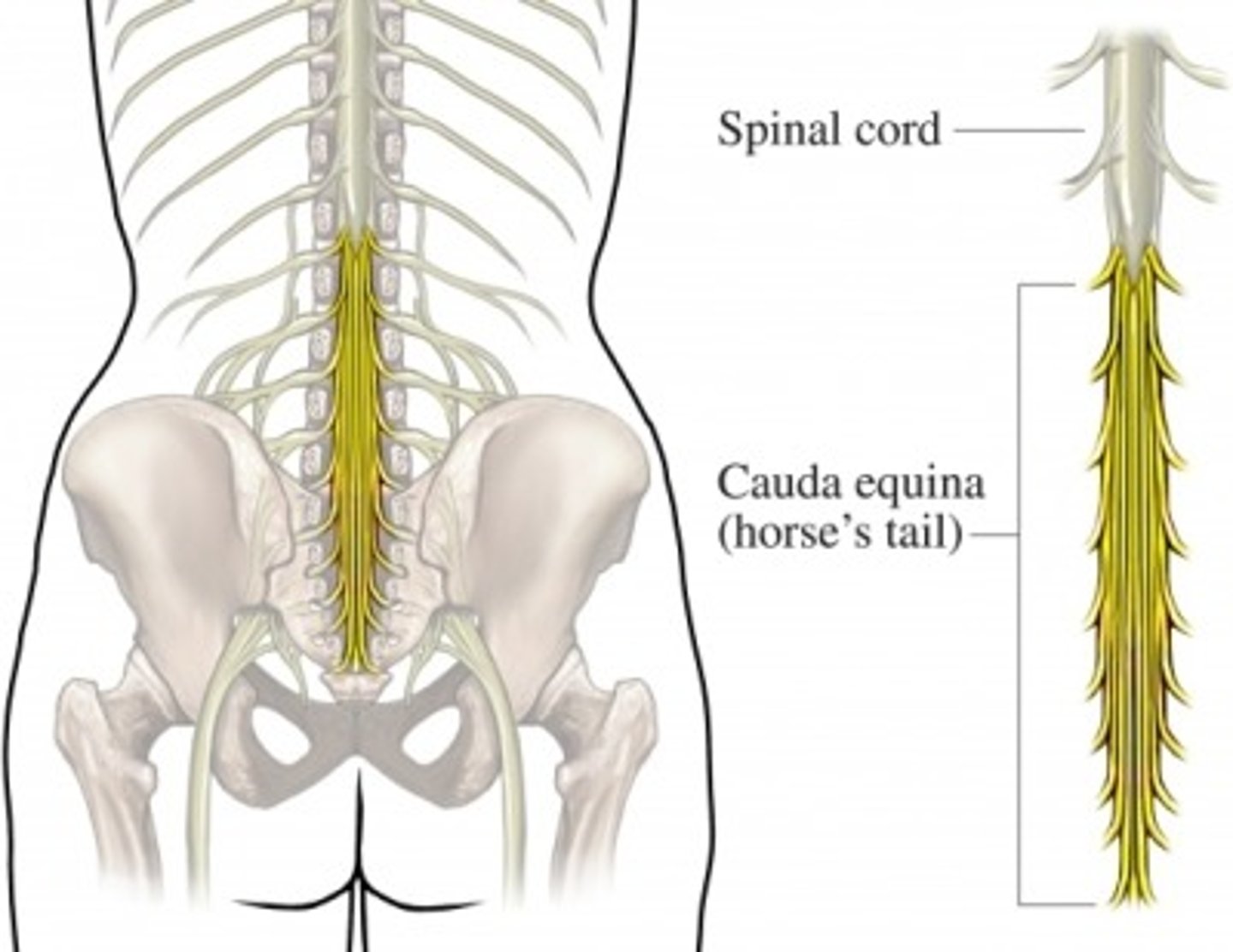
cauda equina
bundle of spinal nerve roots that descend from the inferior spinal cord inferior to the first lumbar vertebra and lie within the vertebral cavity; has the appearance of a horse's tail
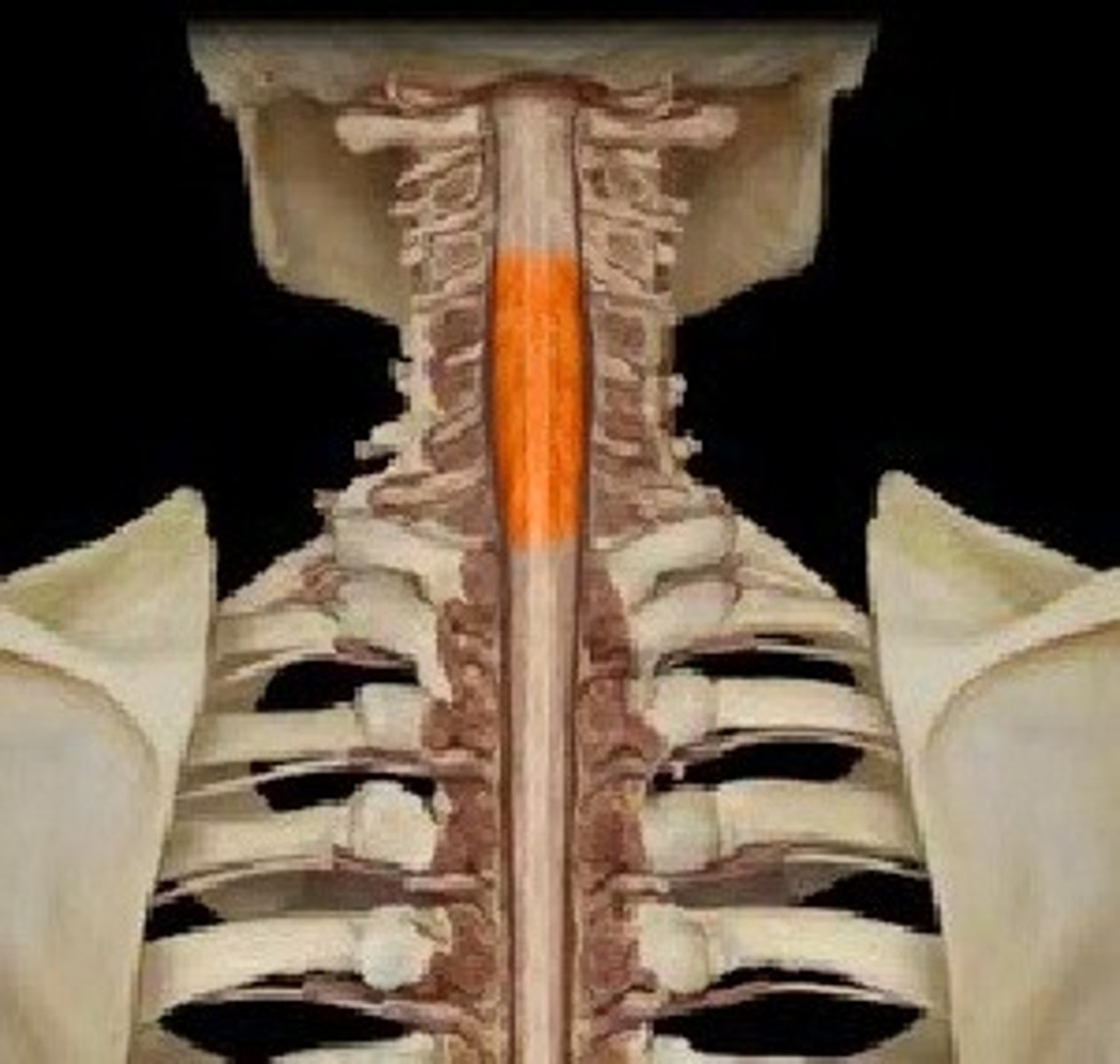
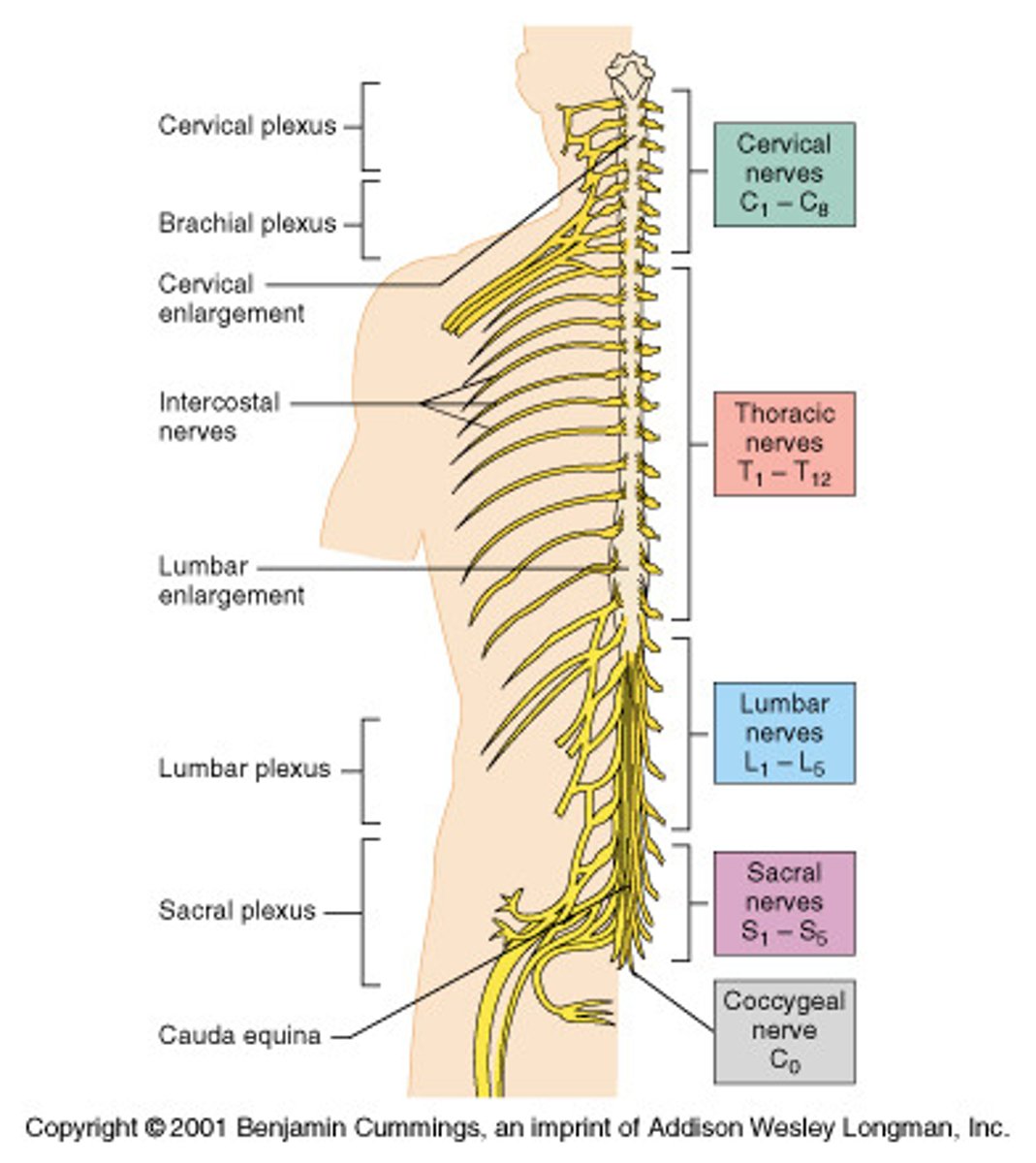
cervical enlargement
nerves of shoulders and upper limbs - associated with the brachial plexus and upper limb innervation
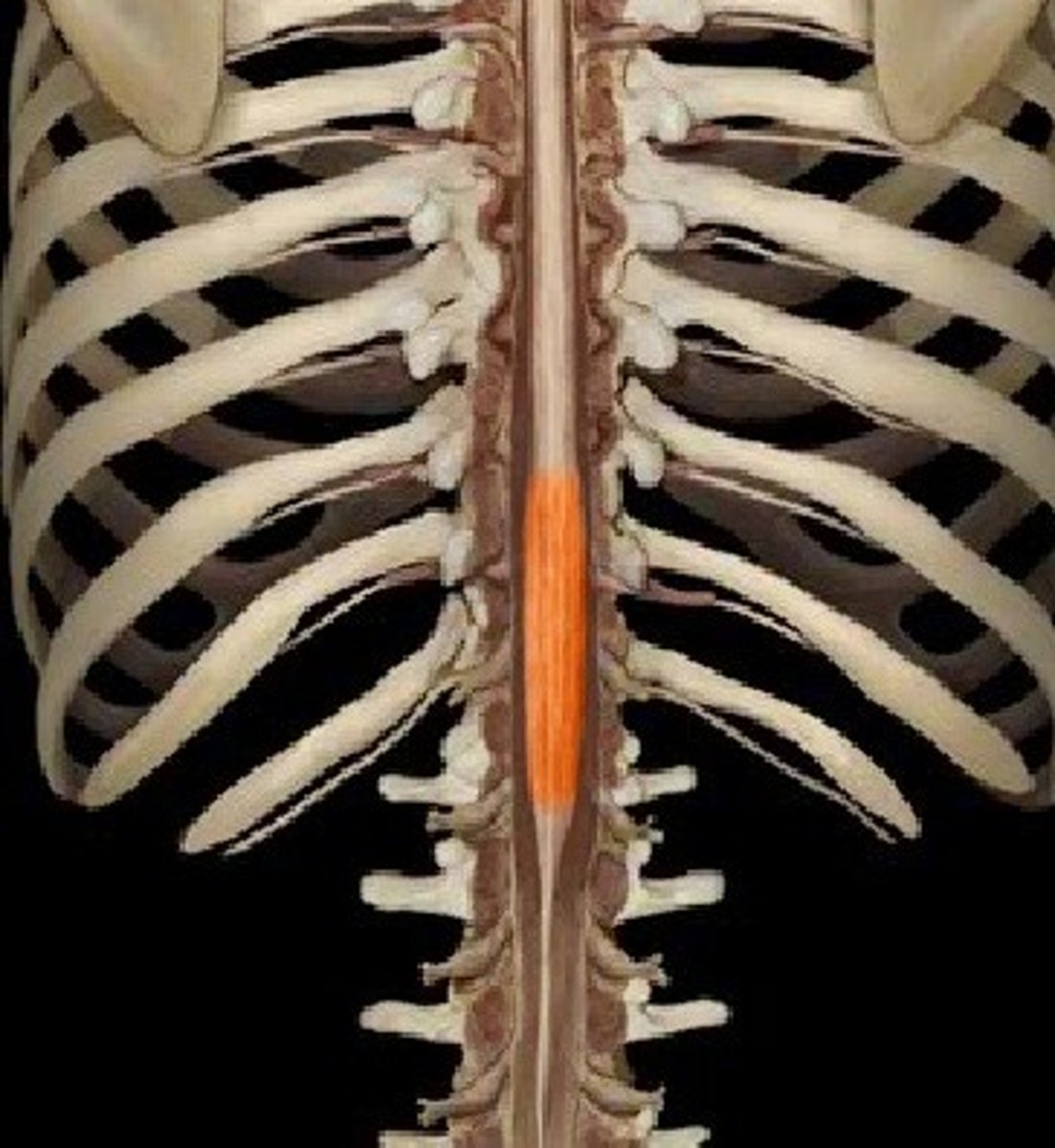
lumbar enlargement
nerves to pelvic region and lower limbs - associated with the lumbosacral plexuses and lower limb innervation
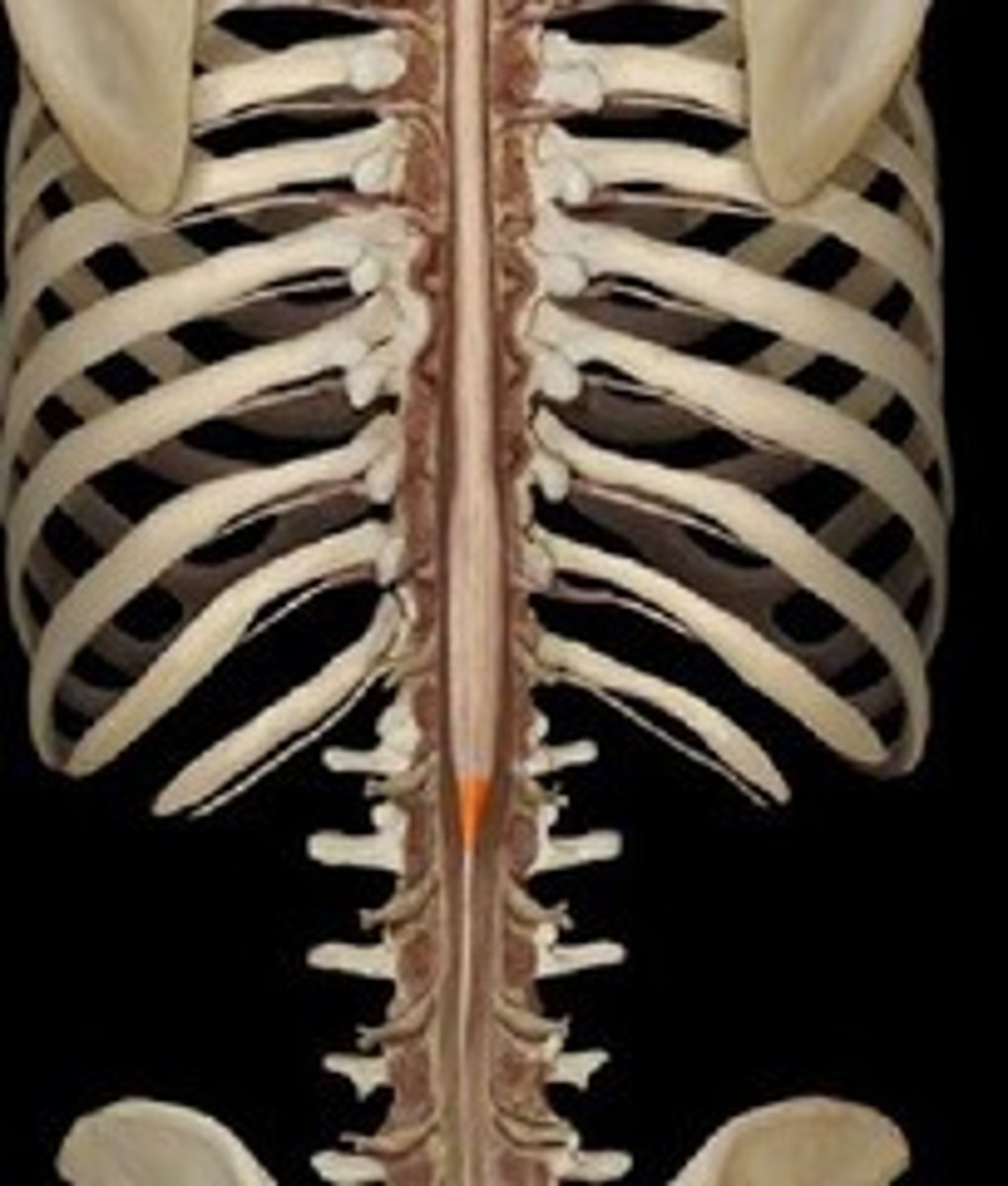
conus medullaris
terminal end of the spinal cord
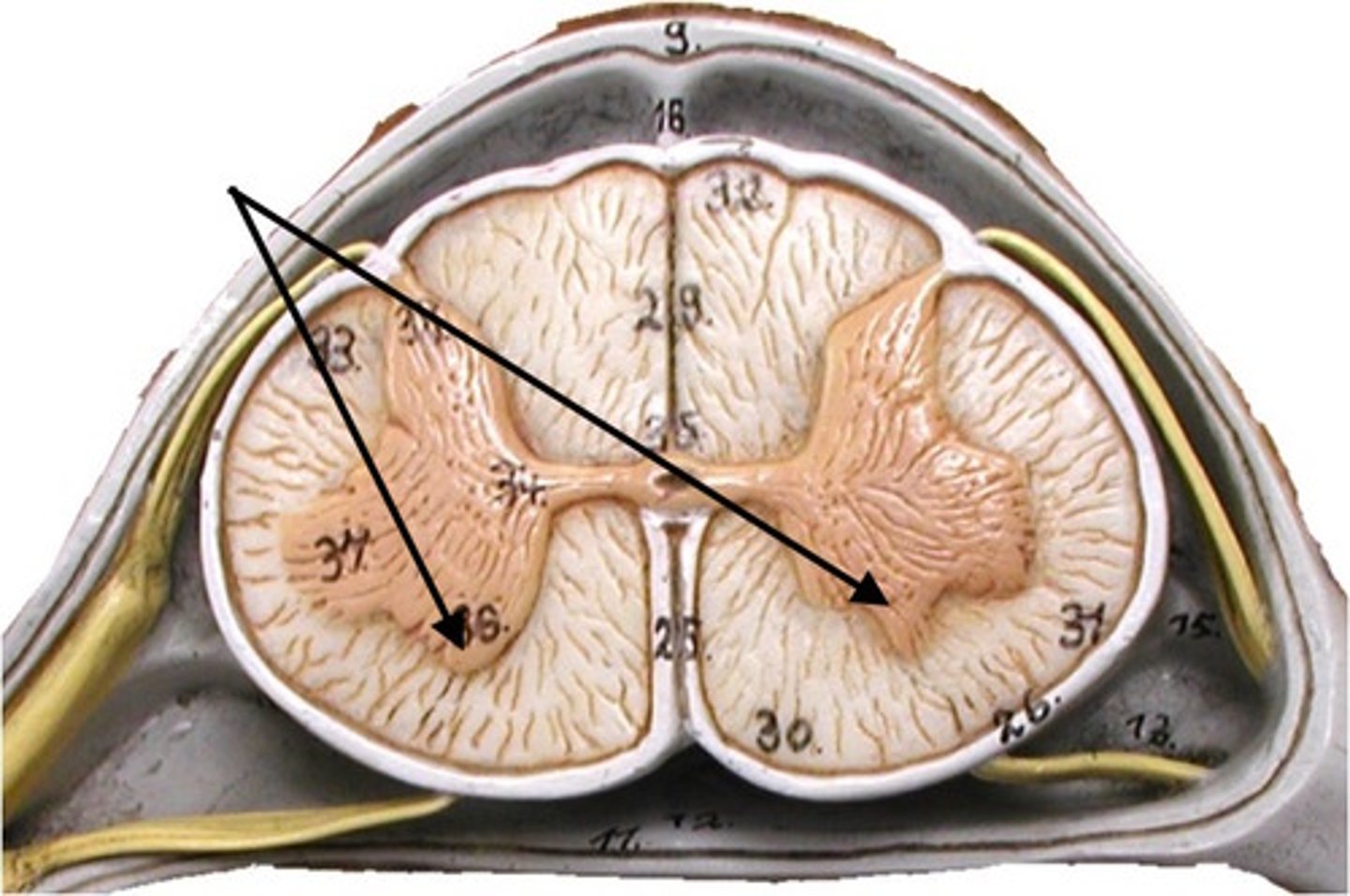
horn
grey matter of spinal cord
Posterior (dorsal) horn
gray matter region of the spinal cord in which sensory input arrives, sometimes referred to as the dorsal horn
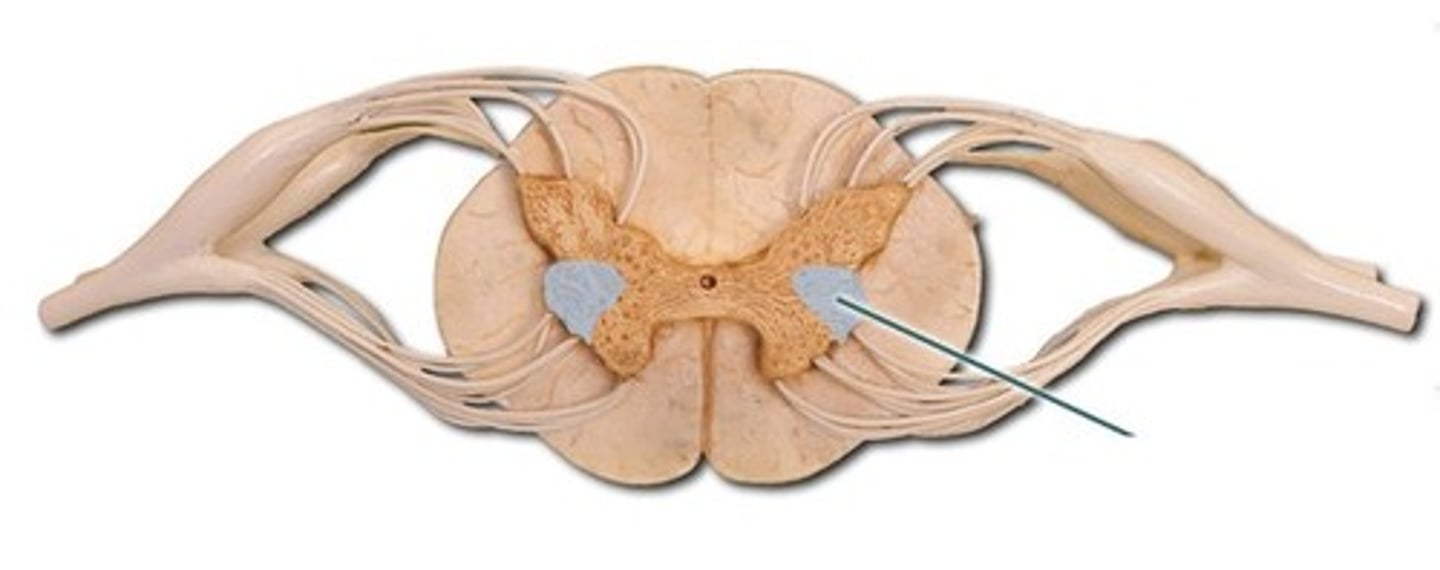
Anterior (ventral) horn
gray matter of the spinal cord containing multipolar motor neurons, sometimes referred to as the anterior horn
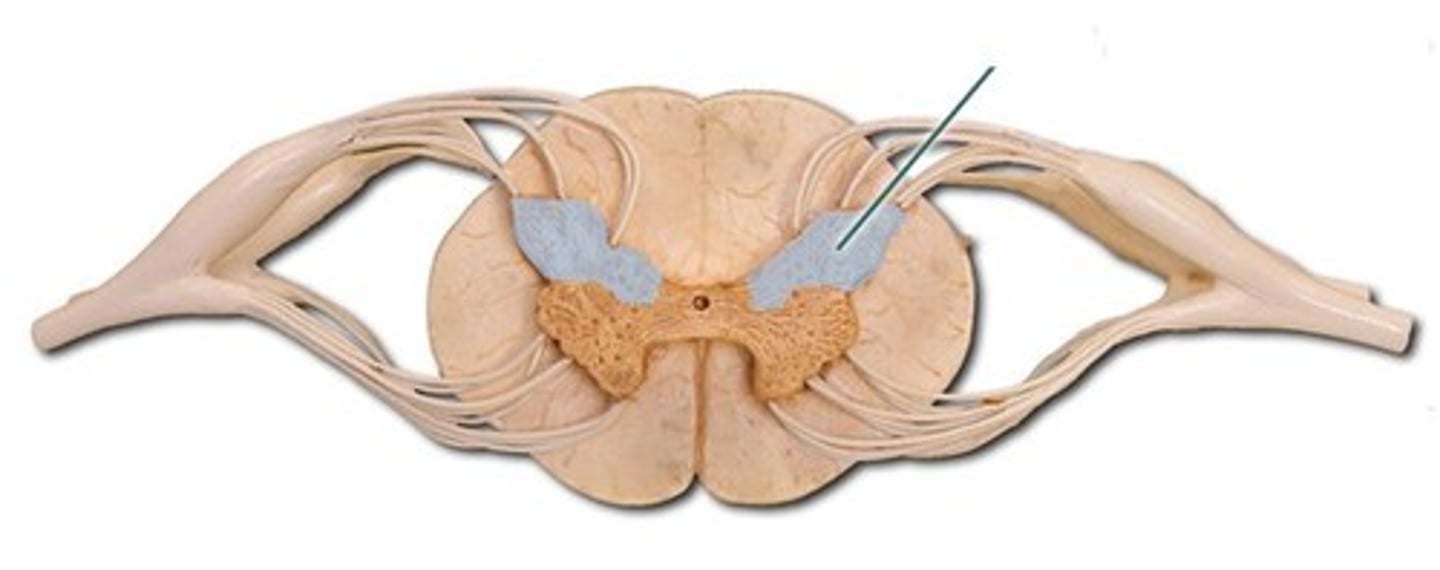
lateral horn
region of the spinal cord grey matter in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions that is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
posterior (dorsal) column
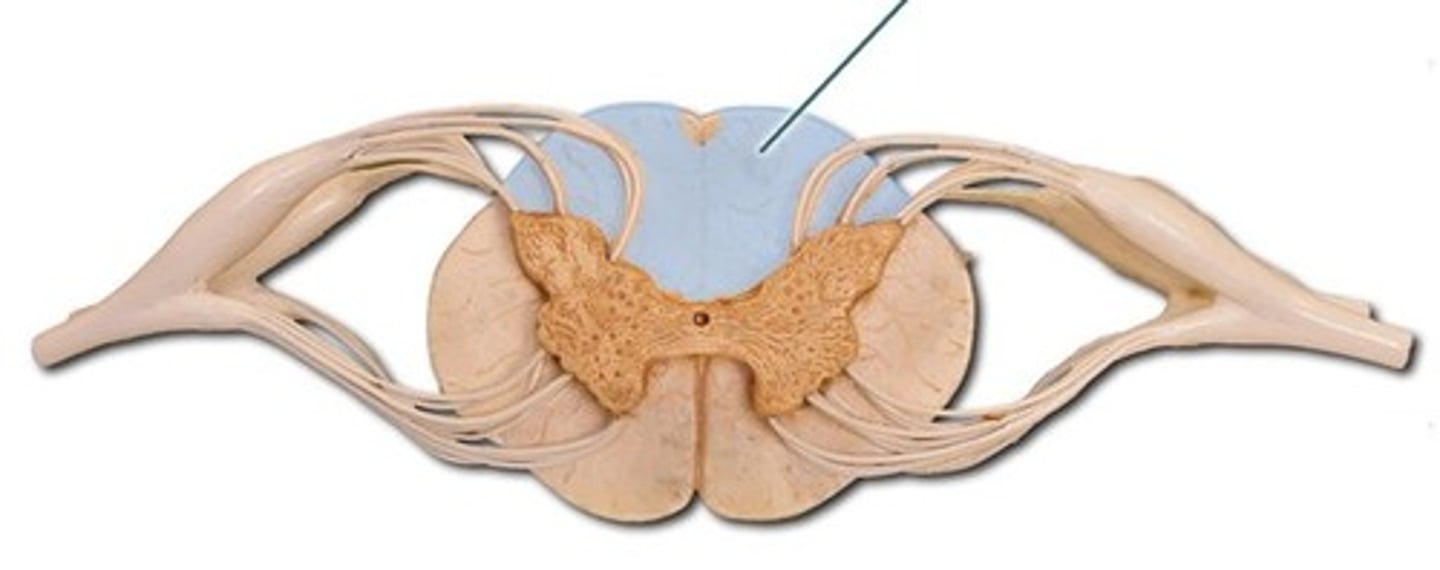
lateral column
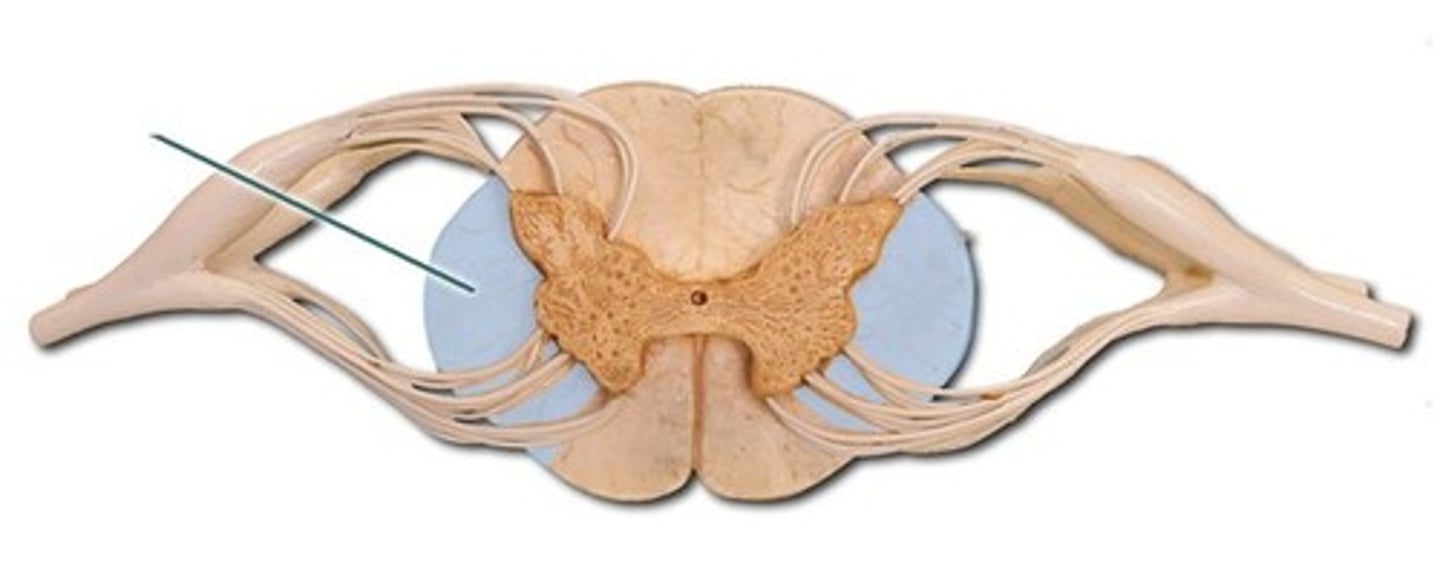
anterior (ventral) column
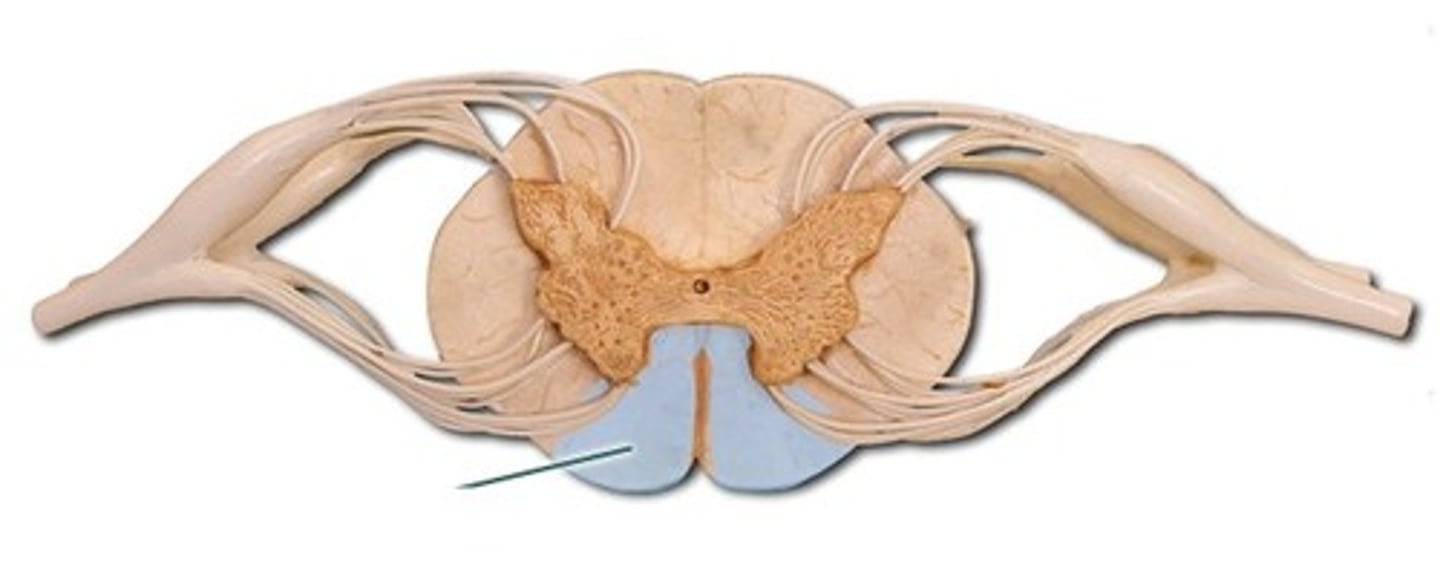
ascending tracts
central nervous system fibres carrying sensory information from the spinal cord or periphery to the brain
spinothalamic tract
an ascending nerve pathway from the spine to the thalamus along which pain impulses are carried to the brain - responsible for pain and temperature sensations
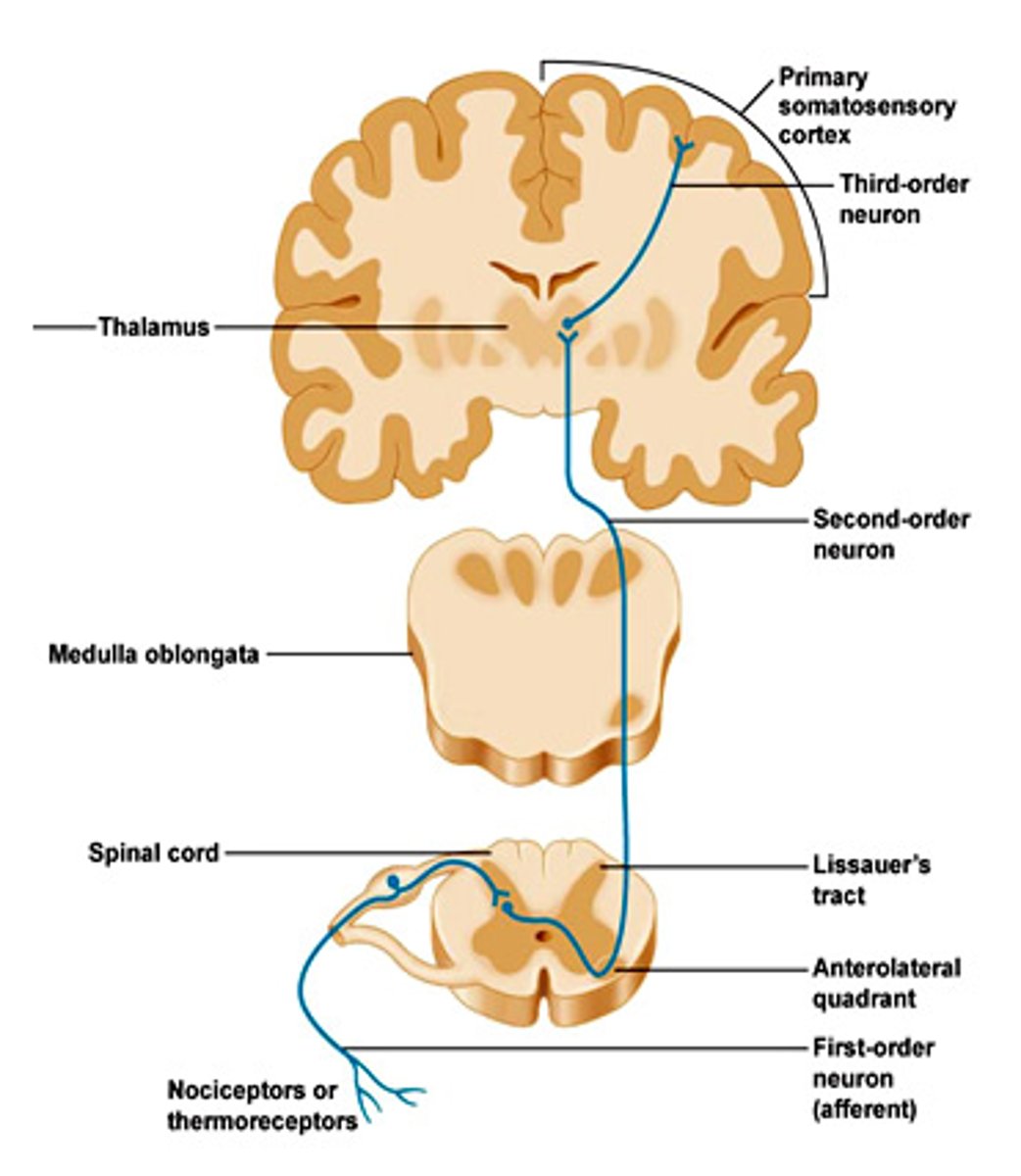
descending tracts
central nervous system fibres carrying motor commands from the brain to the spinal cord or to target organs in periphery
corticospinal tract
a descending tract that is responsible for the conscious or voluntary movements of skeletal muscles
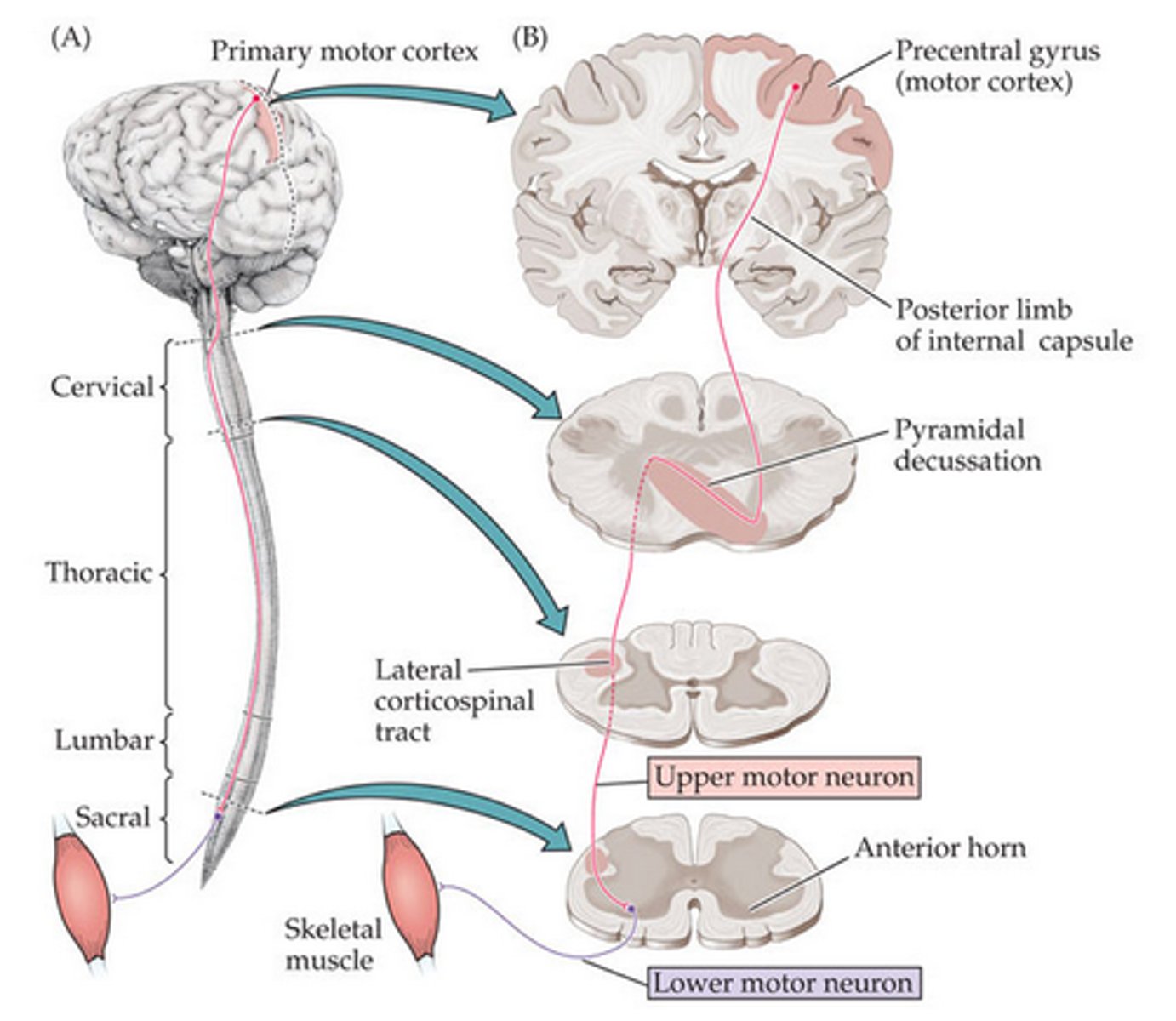
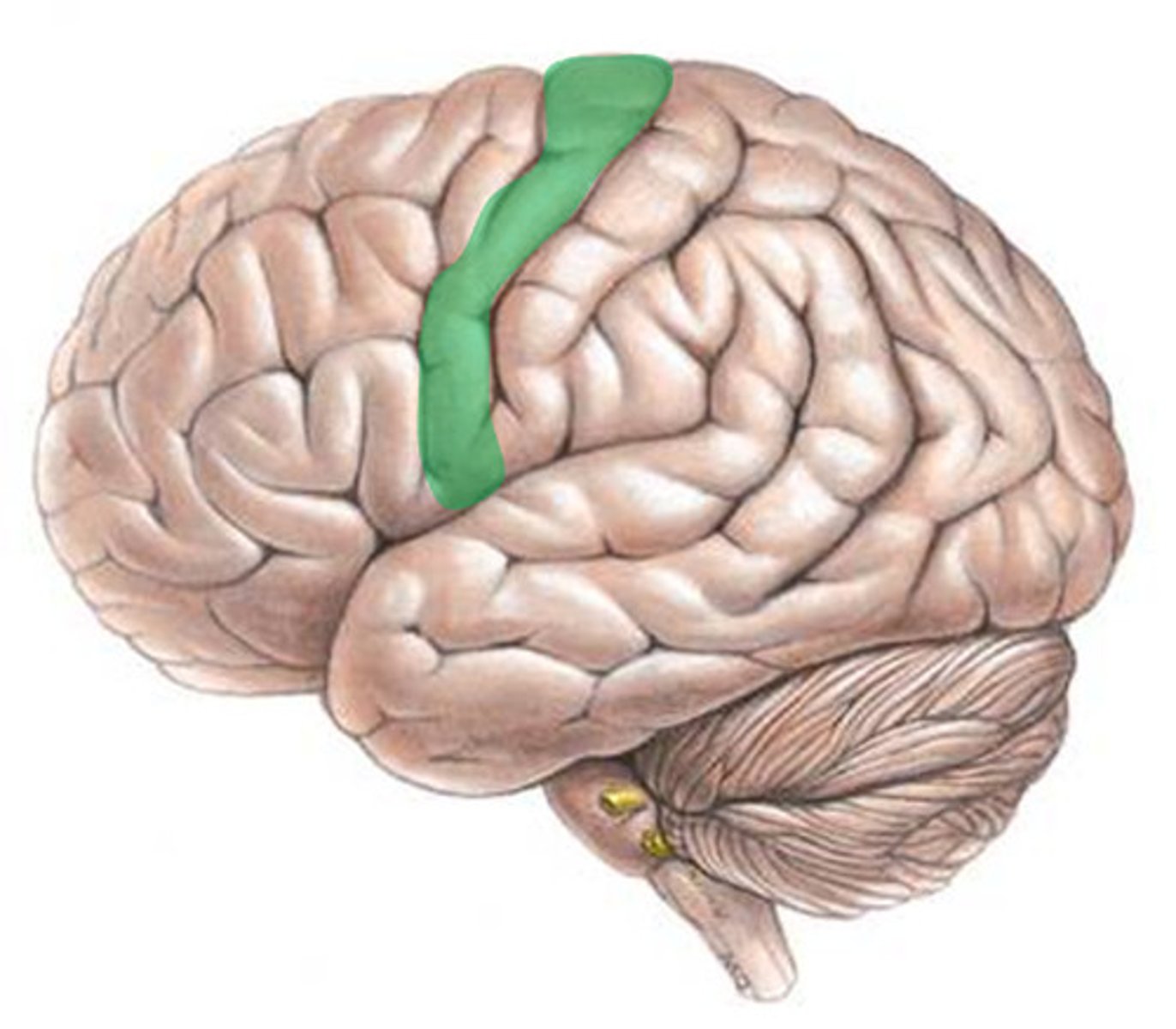
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
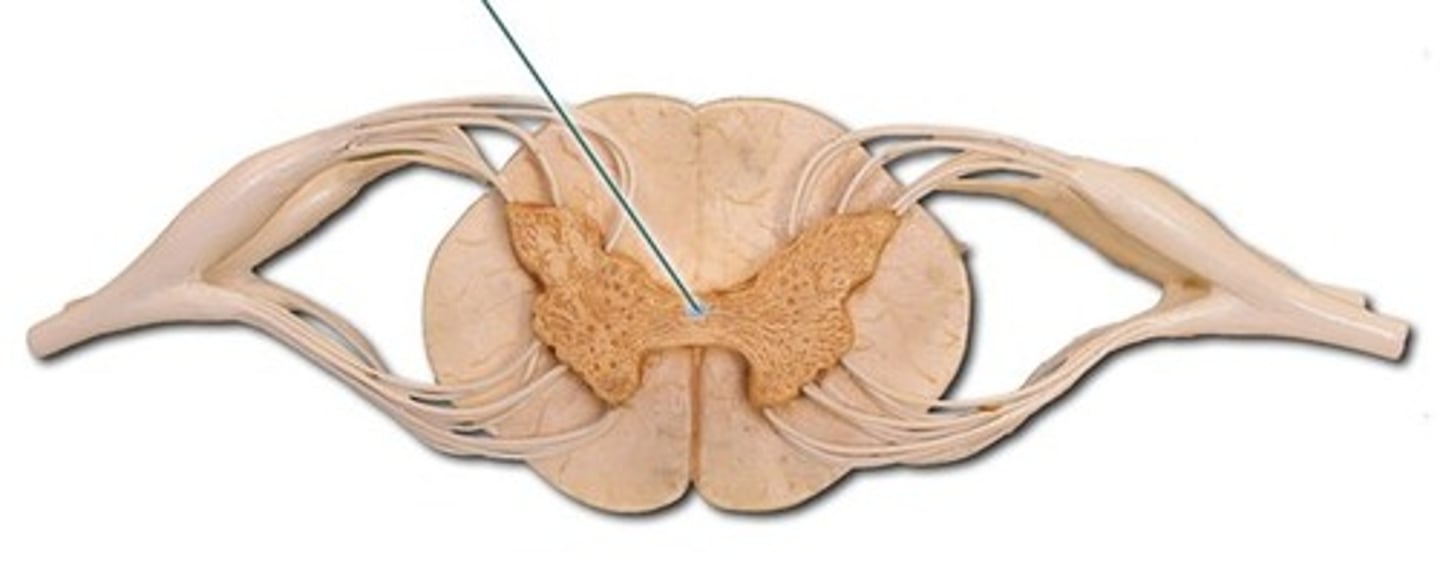
central canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata
cranial nerves
one of twelve nerves connected to the brain that are responsible for sensory or motor functions of the head and neck
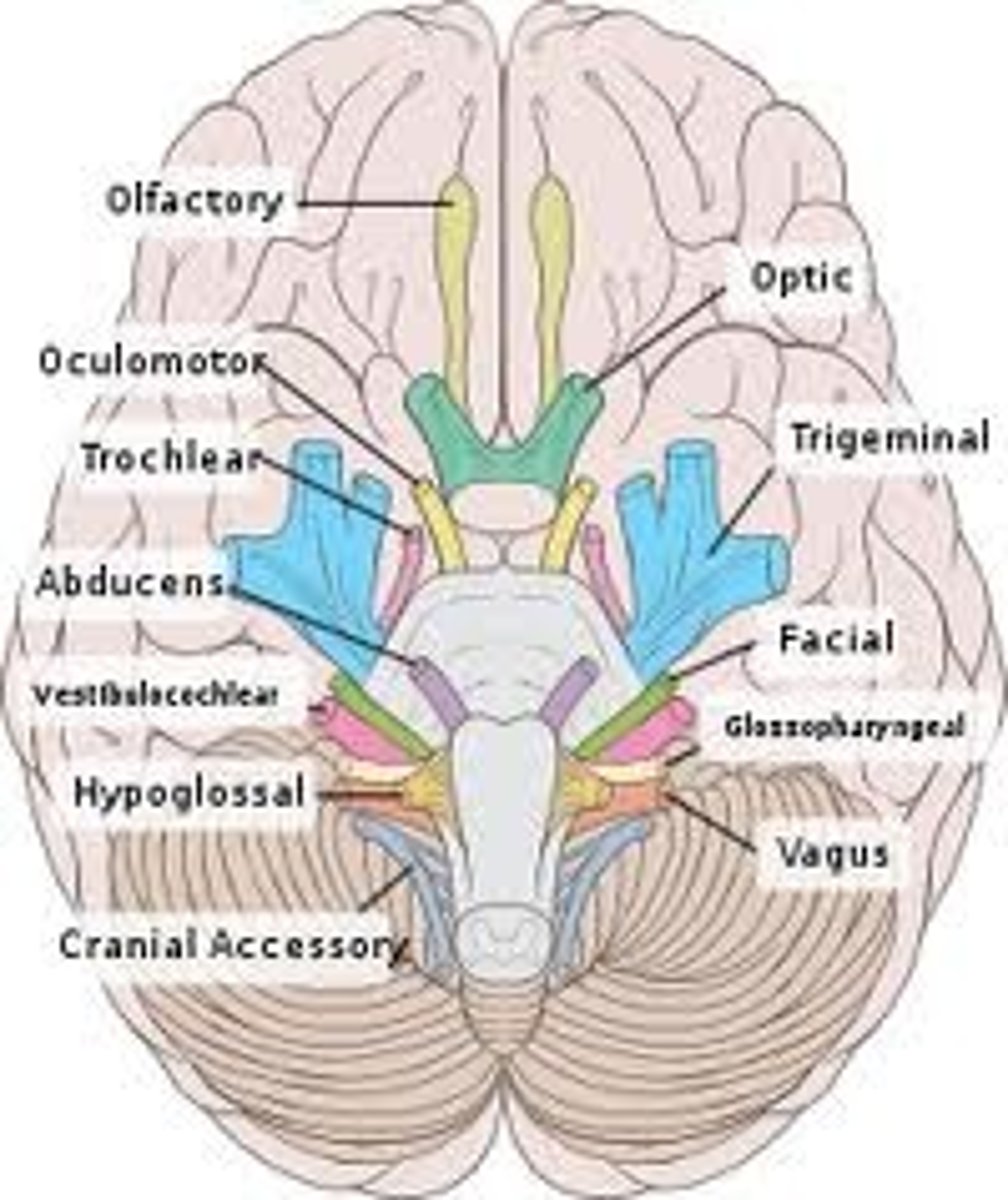
olfactory nerve (I)
first cranial nerve; responsible for the sense of smell
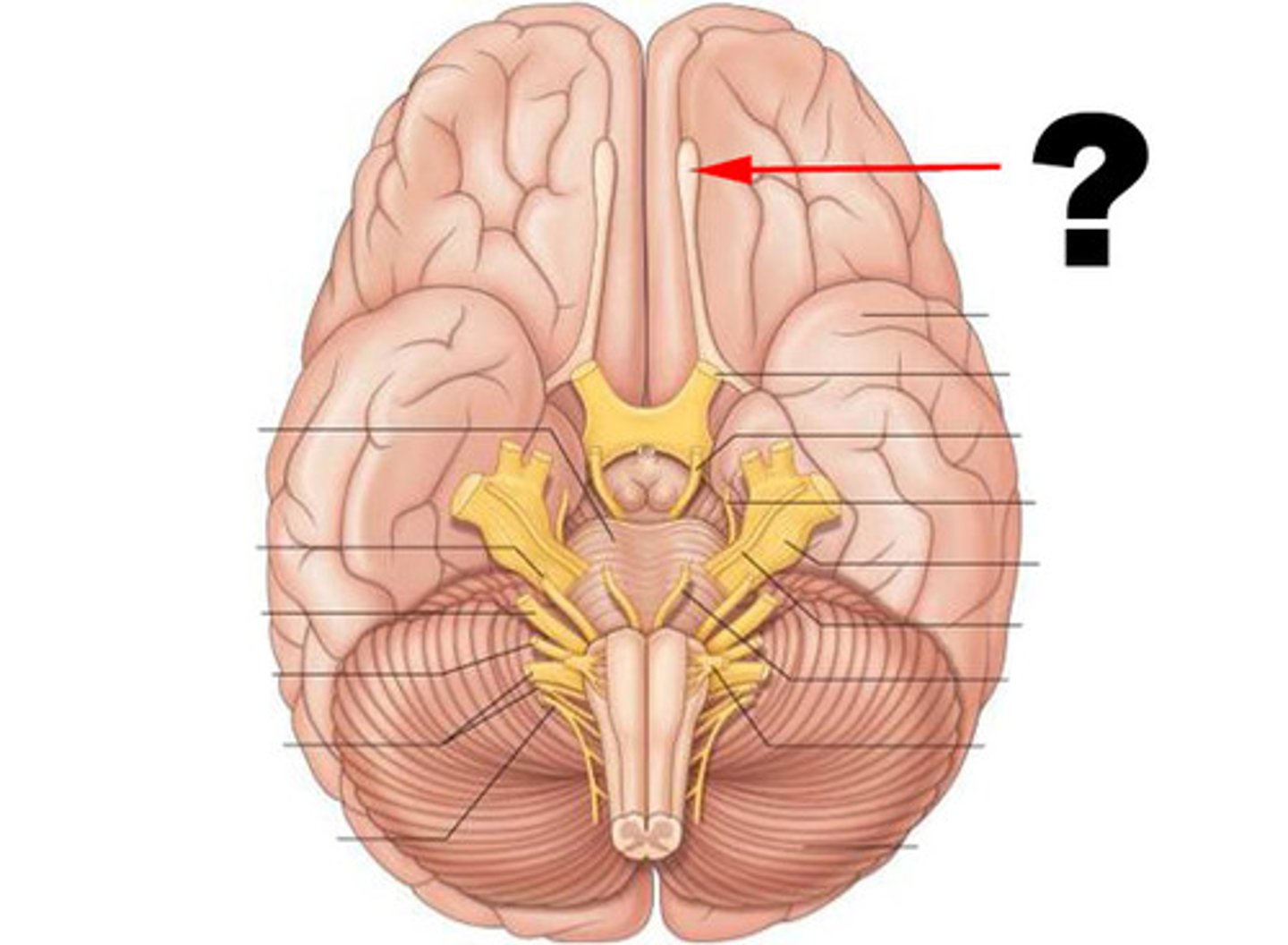
Optic Nerve (II)
second cranial nerve; responsible for visual sensation
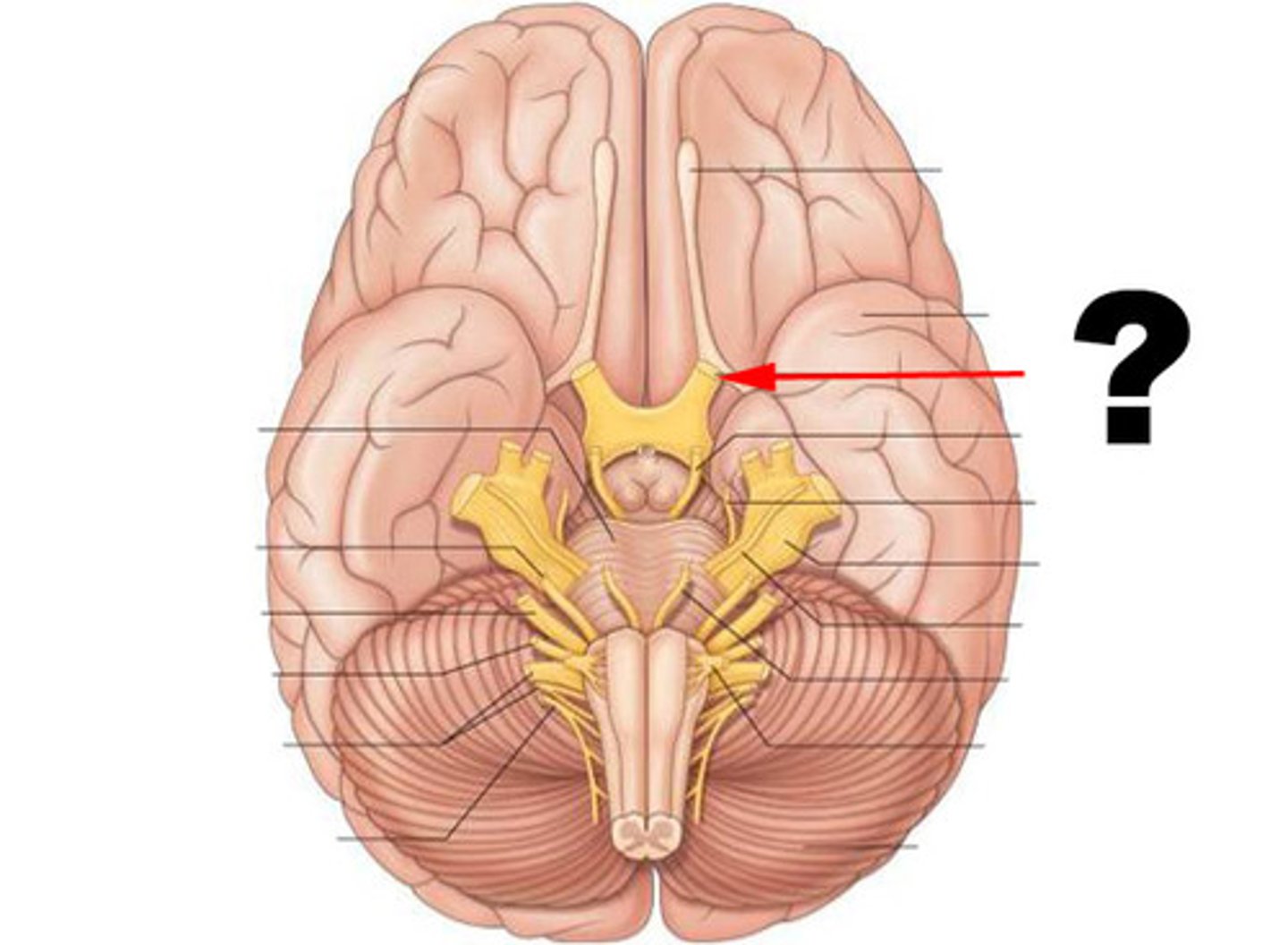
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
third cranial nerve; responsible for contraction of four of the extraocular muscles, the muscle in the upper eyelid, and pupillary constriction and the accommodation reflex
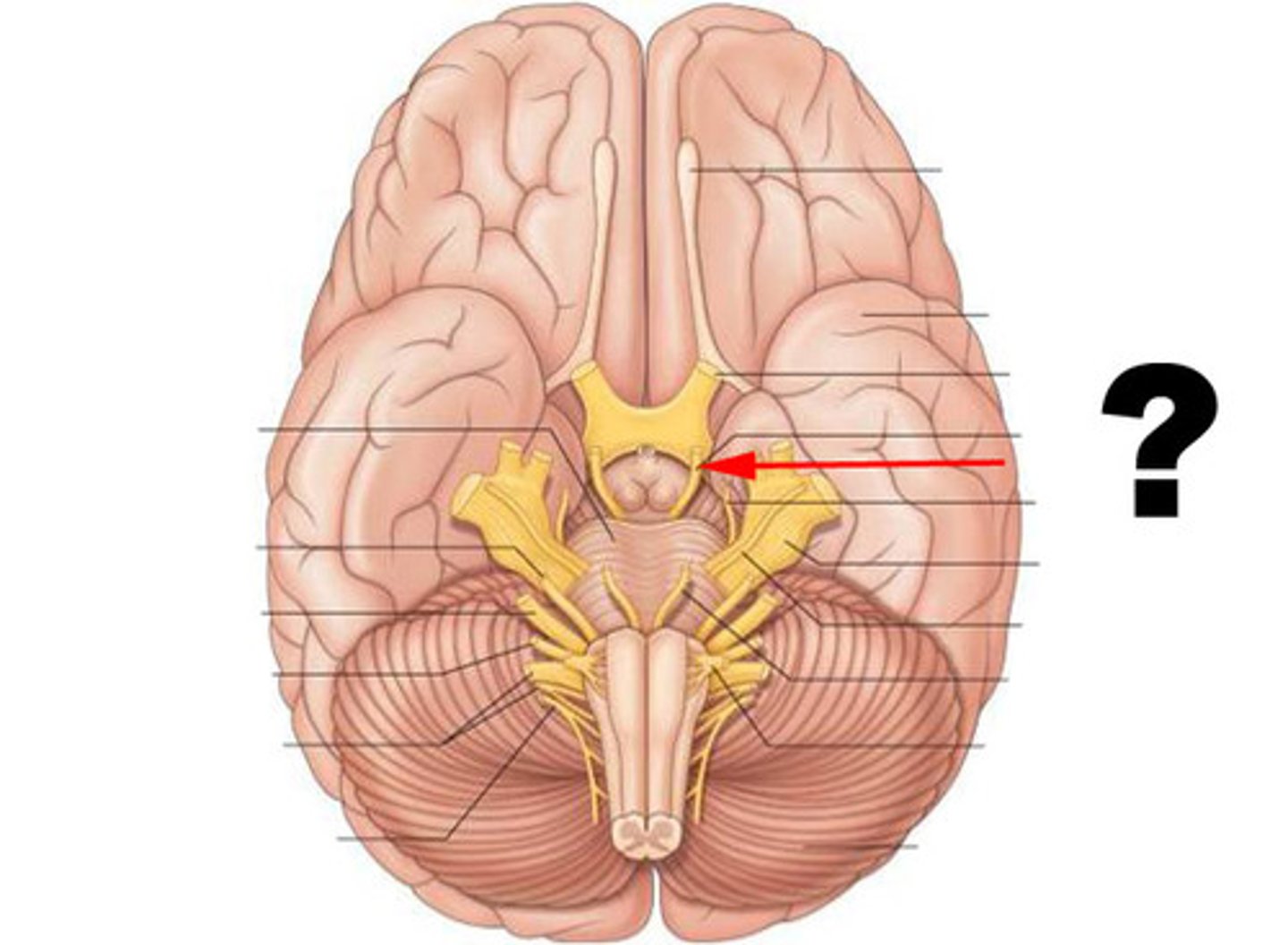
trigeminal nerve (V)
fifth cranial nerve; responsible for cutaneous sensation of the face and contraction of the muscles of mastication
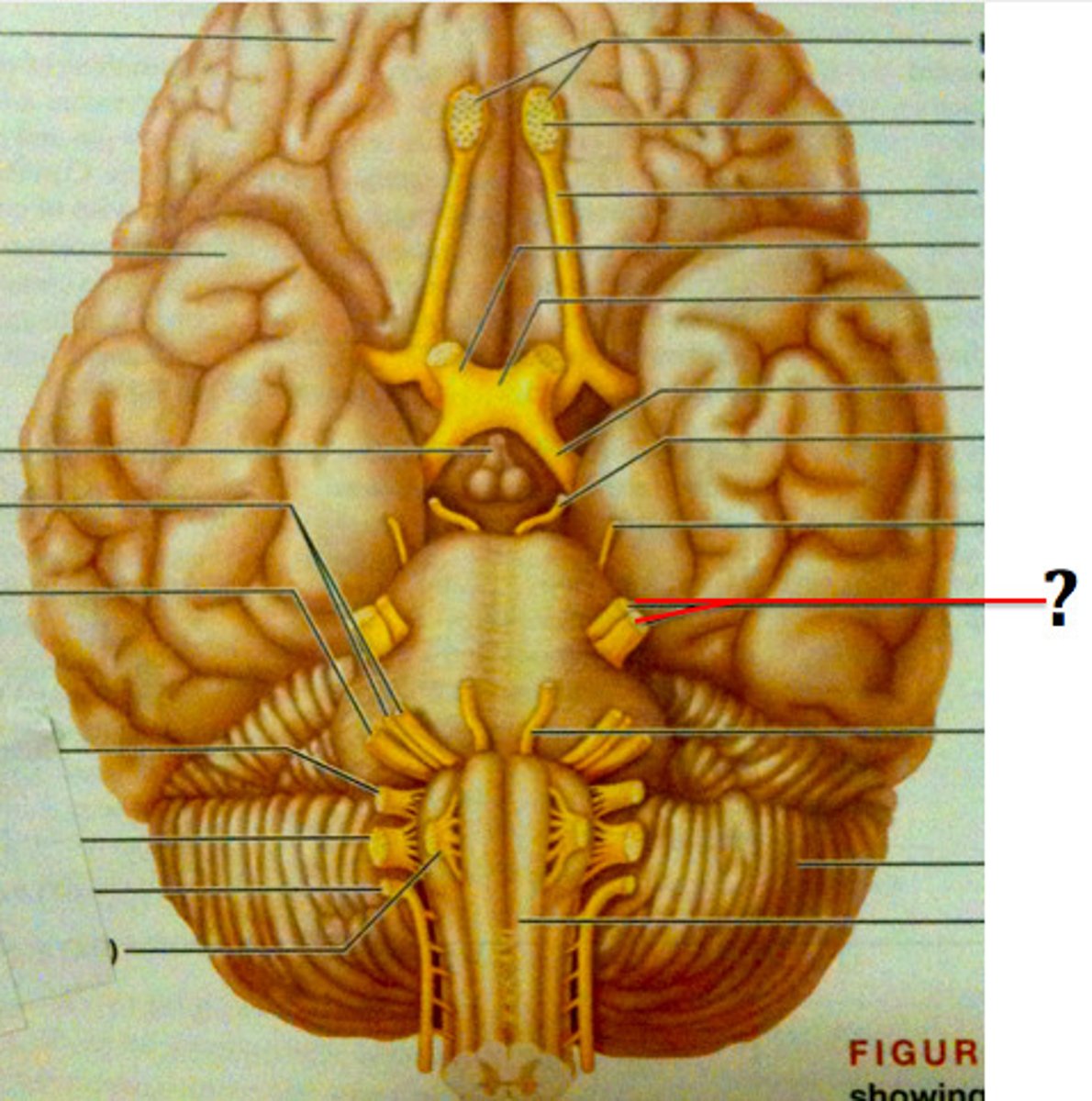
facial nerve (VII)
seventh cranial nerve; responsible for contraction of the muscles of facial expression and for part of the sense of taste, as well as causing saliva production
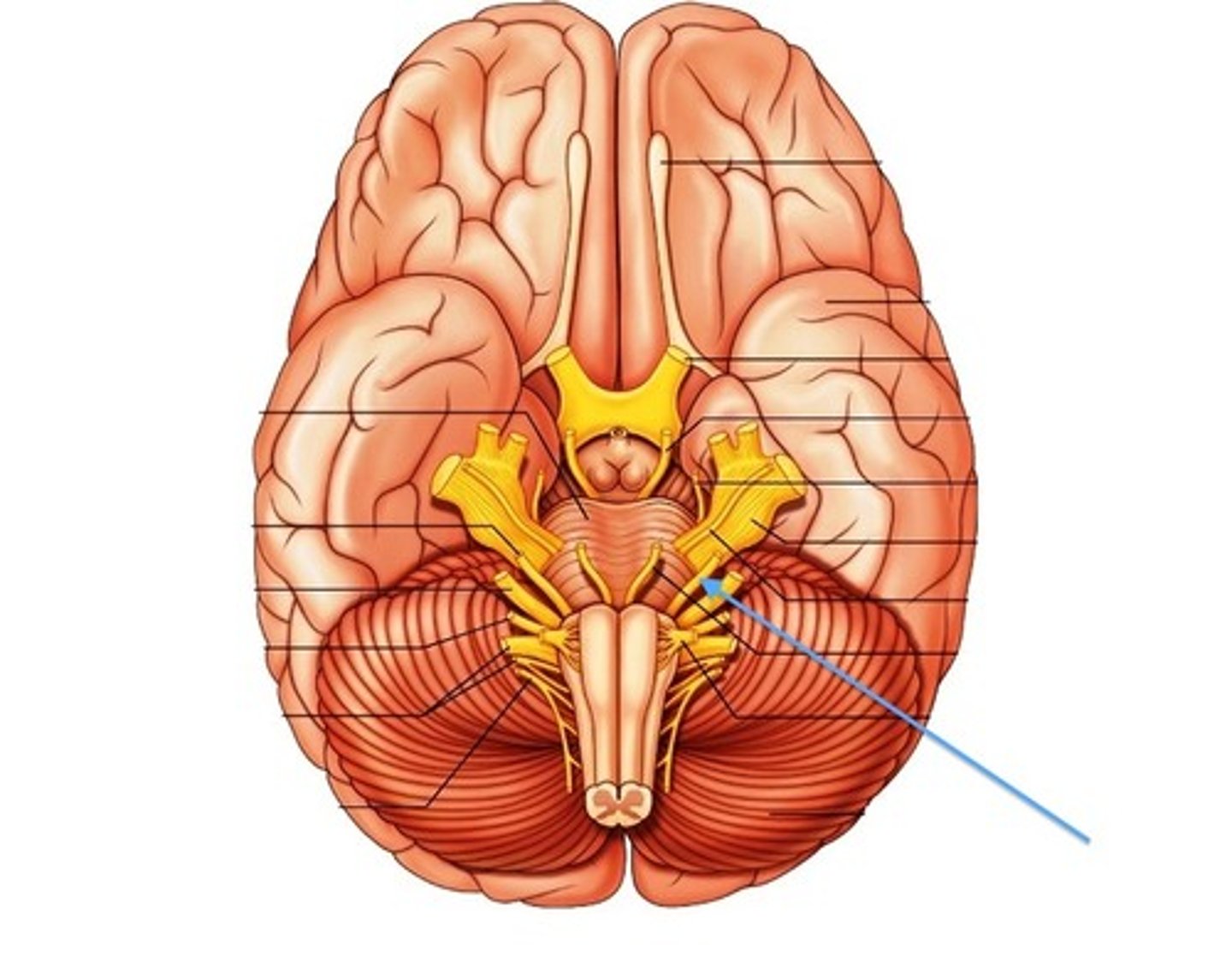
vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
eighth cranial nerve; responsible for the sensations of hearing and balance
vagus nerve (X)
tenth cranial nerve; responsible for the autonomic control of organs in the thoracic and upper abdominal cavities
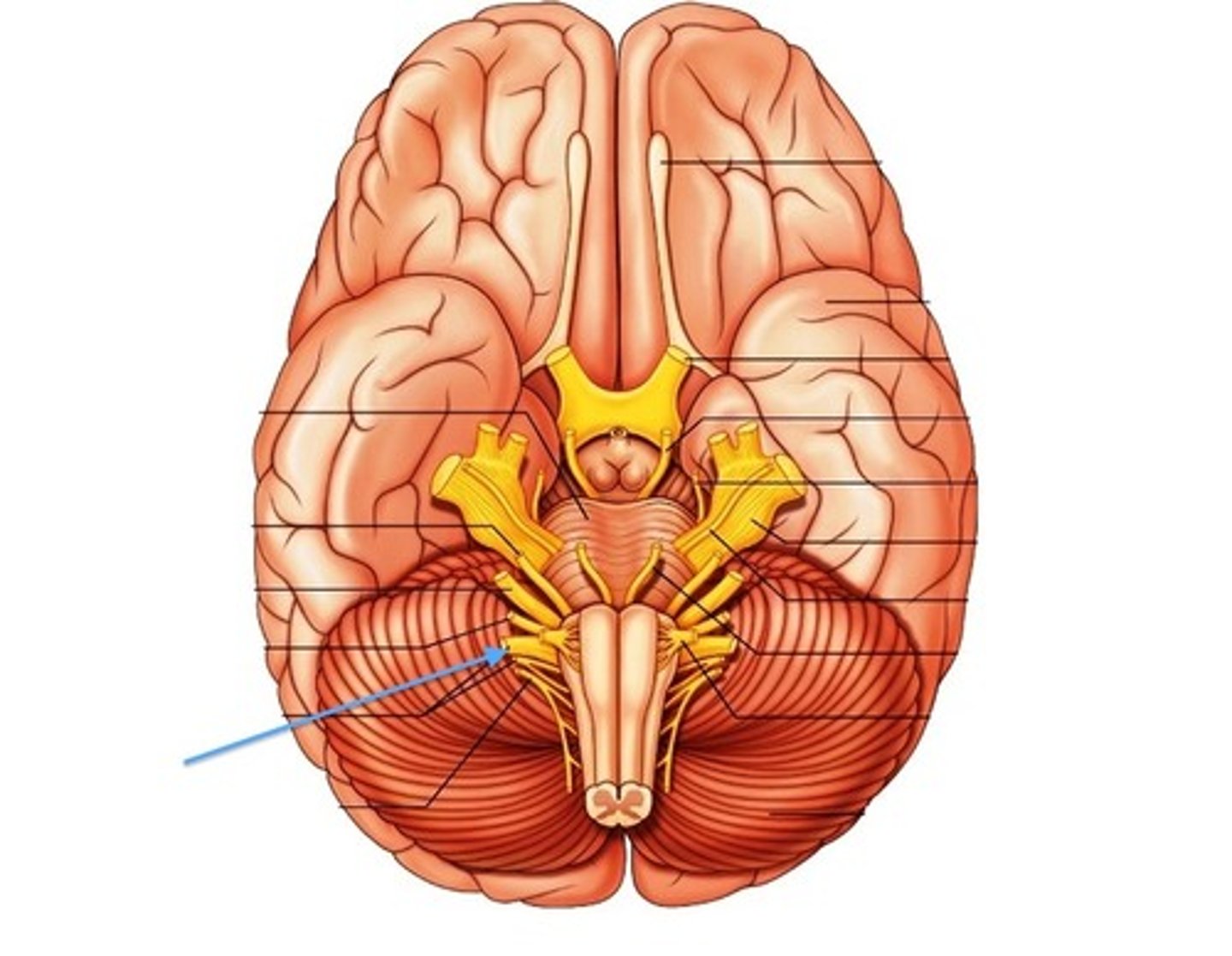
spinal nerves
one of 31 nerves connected to the spinal cord
dorsal (posterior) nerve root
axons entering the posterior horn of the spinal cord
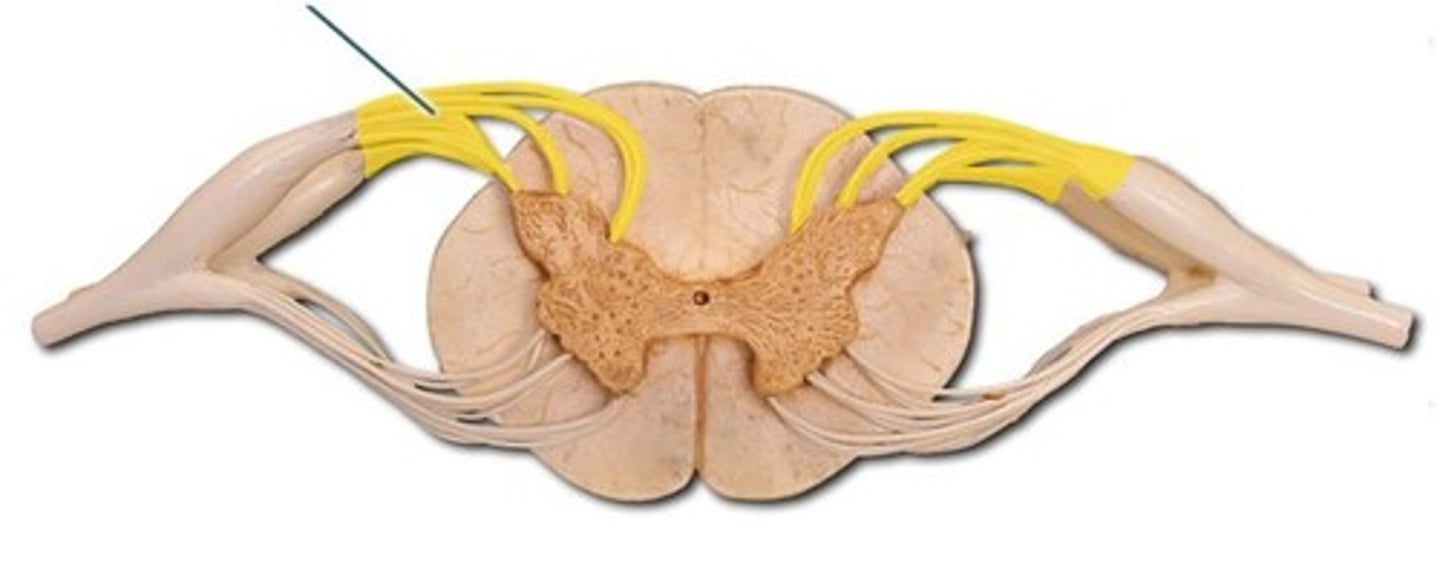
dorsal (posterior) root ganglion
sensory ganglion attached to the posterior nerve root of a spinal nerve; contains the cell bodies of sensory neurons
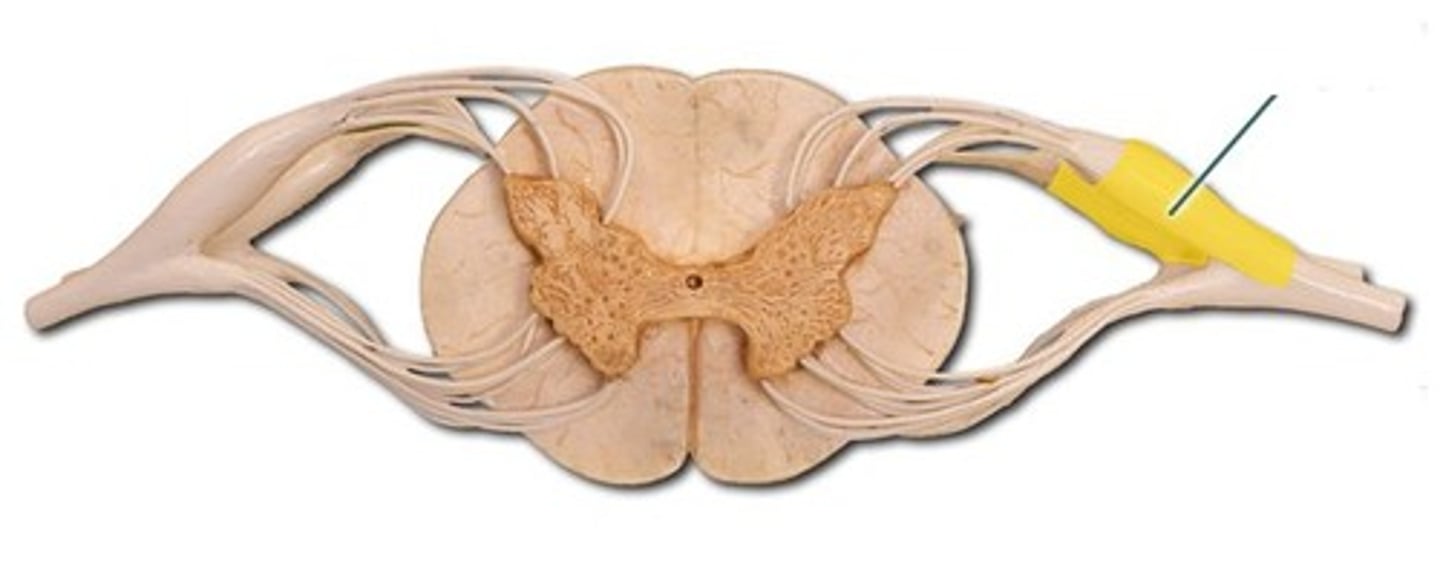
ventral (anterior) nerve root
axons emerging from the anterior or lateral horns of the spinal cord
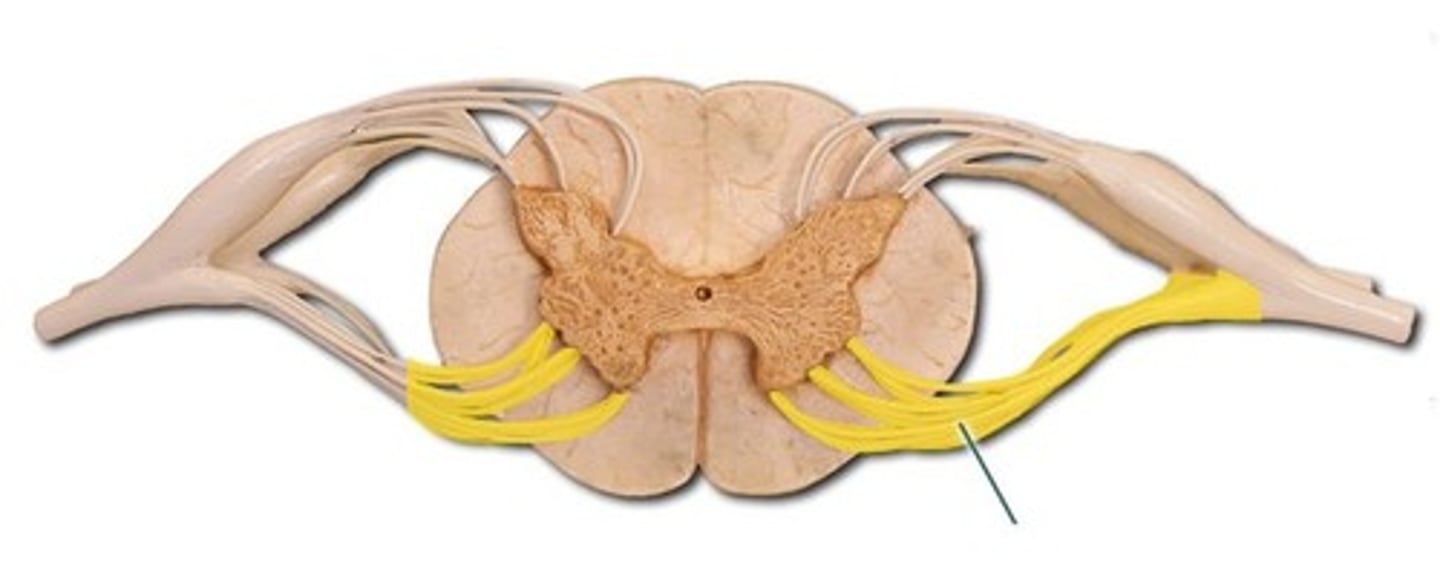
body of the spinal nerve
its body is relatively short; forms from the union of the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal nerve
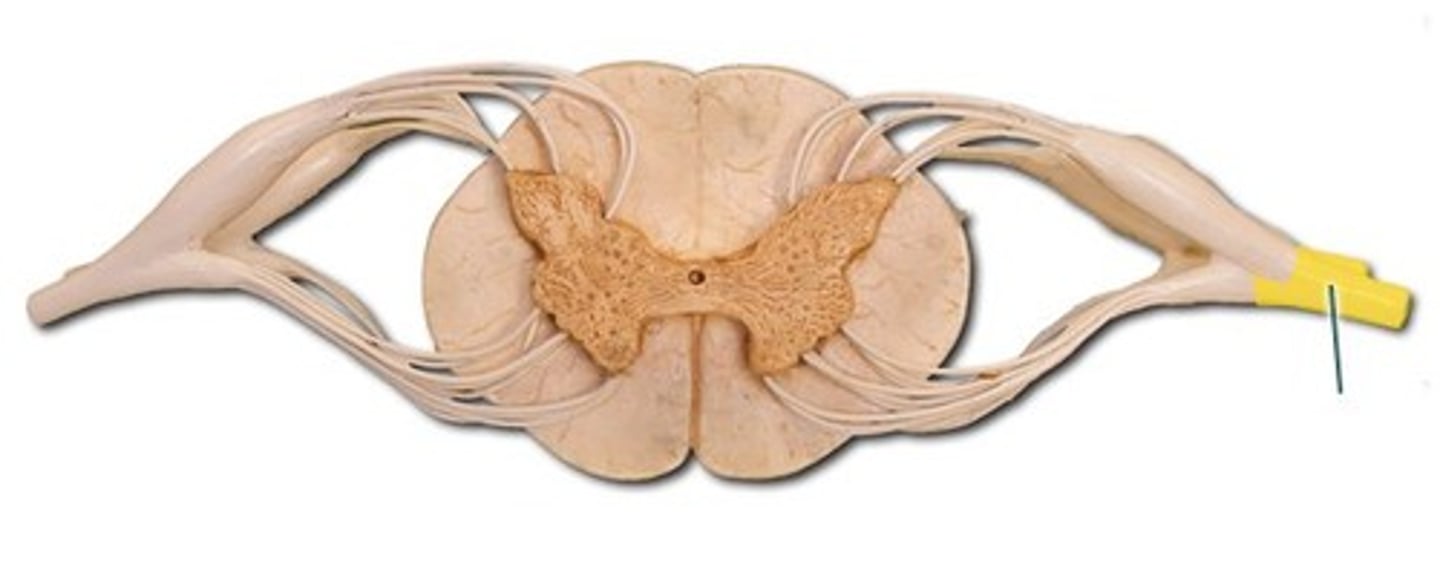
dorsal (posterior) ramus
smallest branch of the body of the spinal nerve; supplies largely organs of the back/dorsum
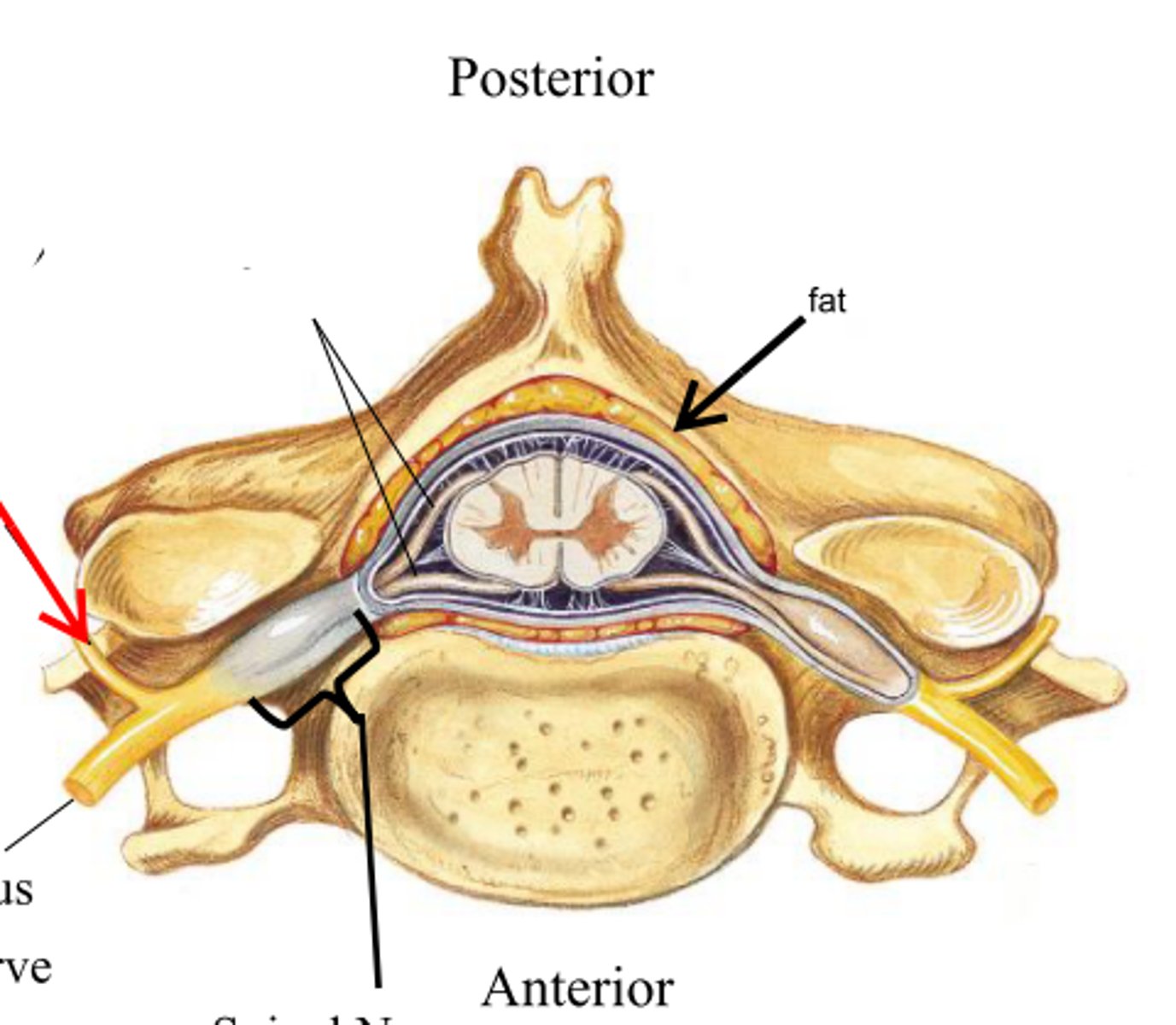
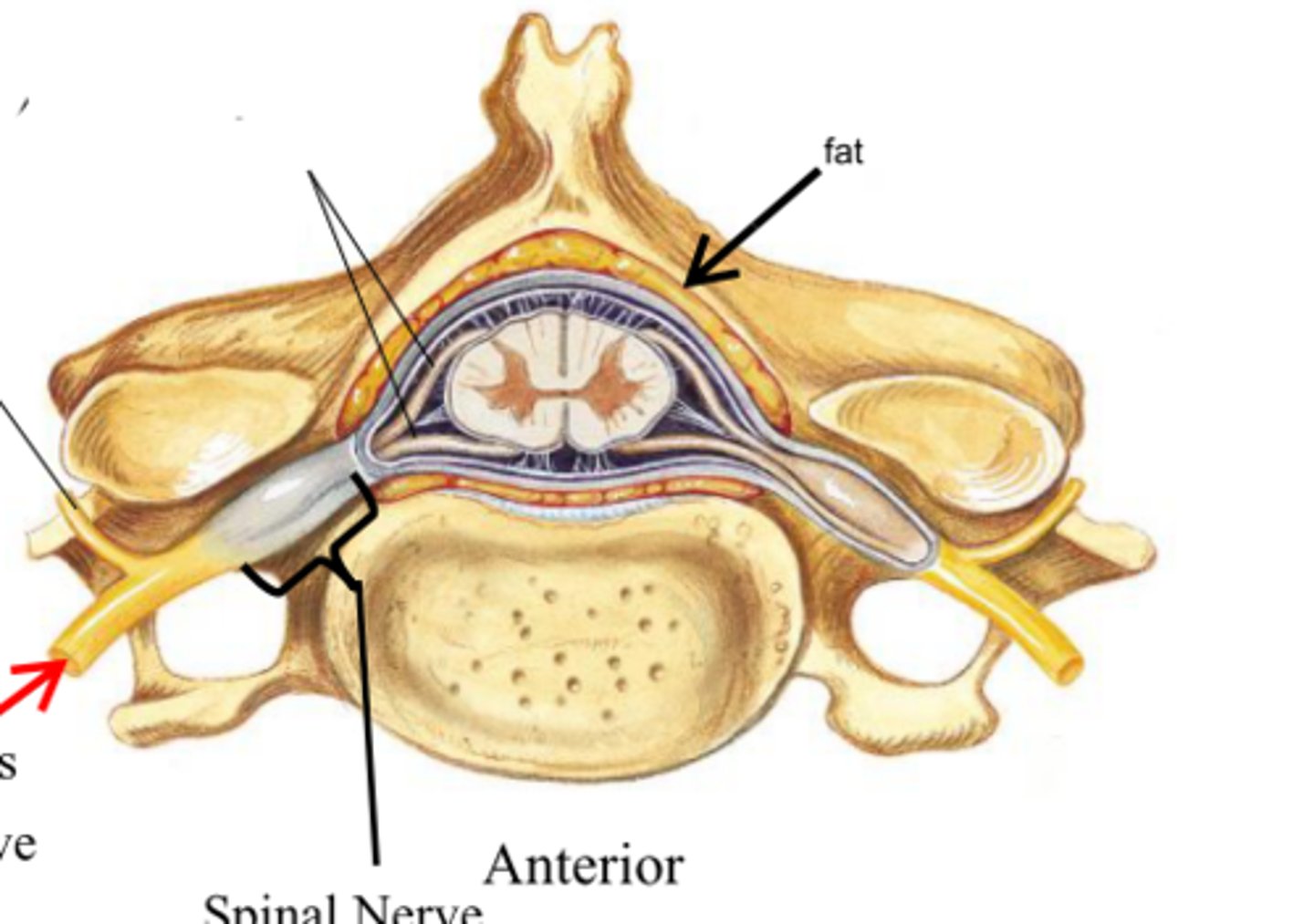
ventral (anterior) ramus
largest branch of the body of the spinal nerve; supplies most regions of the body anterior to the vertebral column
cervical nerves
C1-C8
thoracic nerves
T1-T12
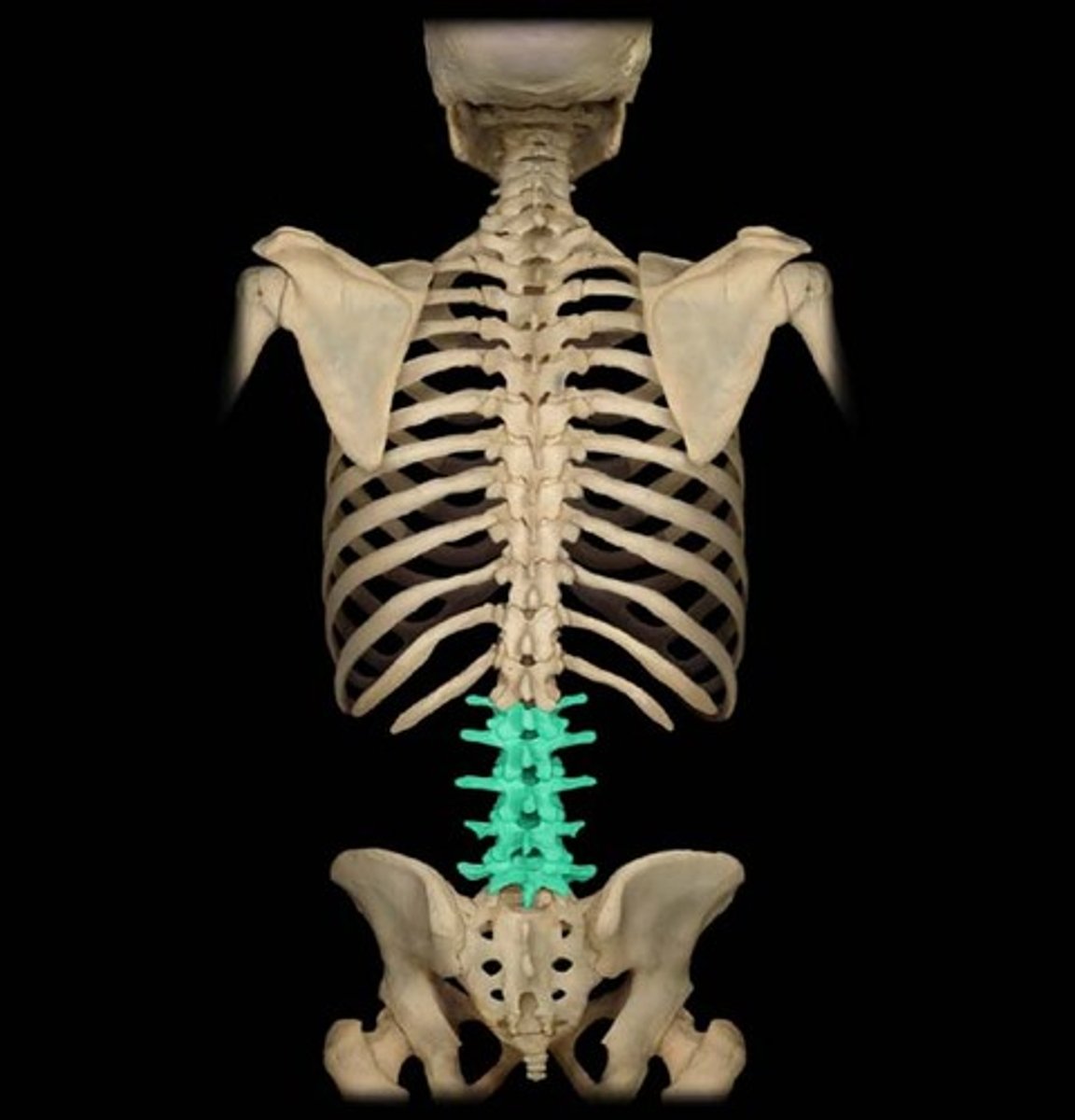
Lumbar nerves
L1-L5
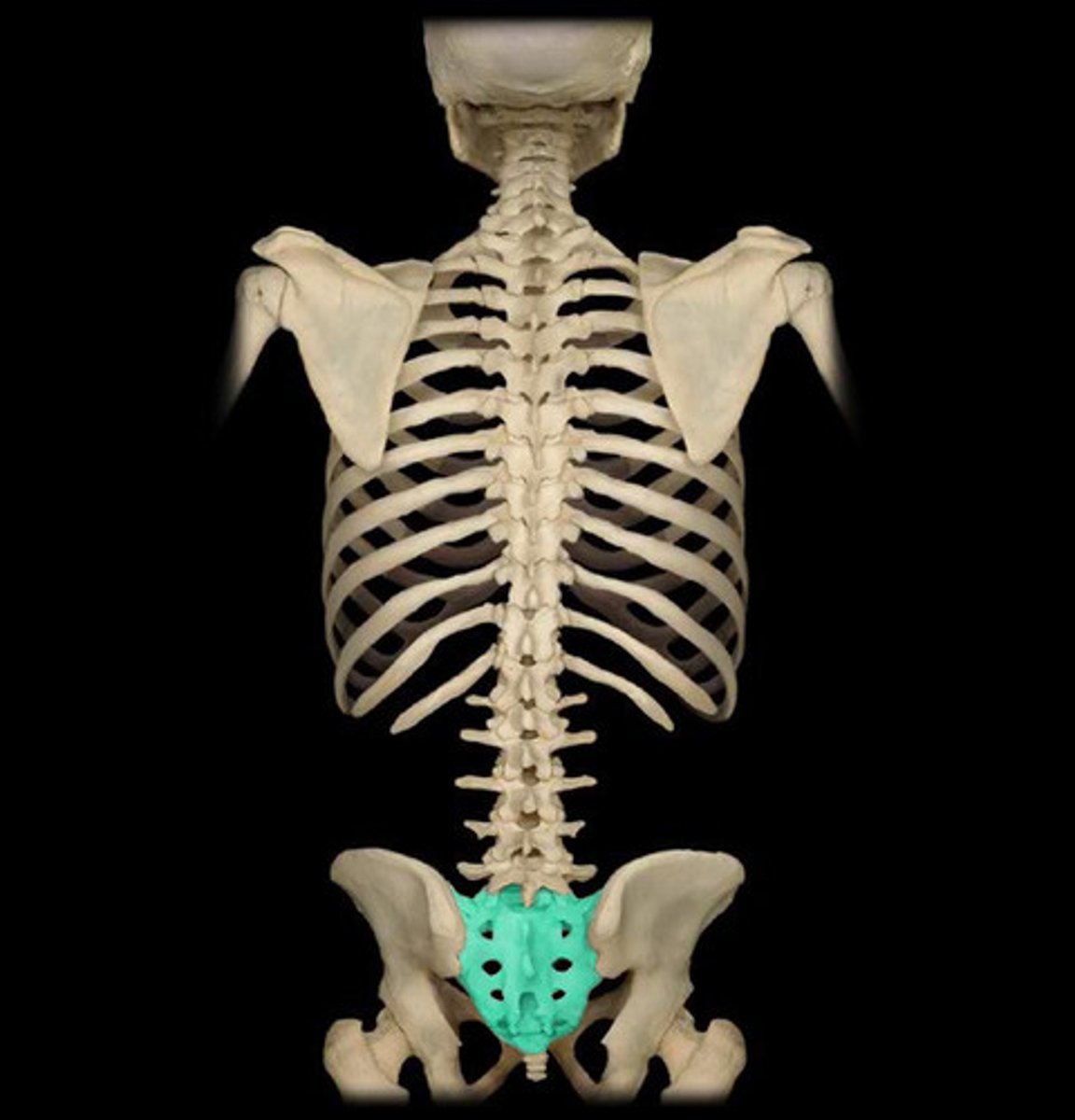
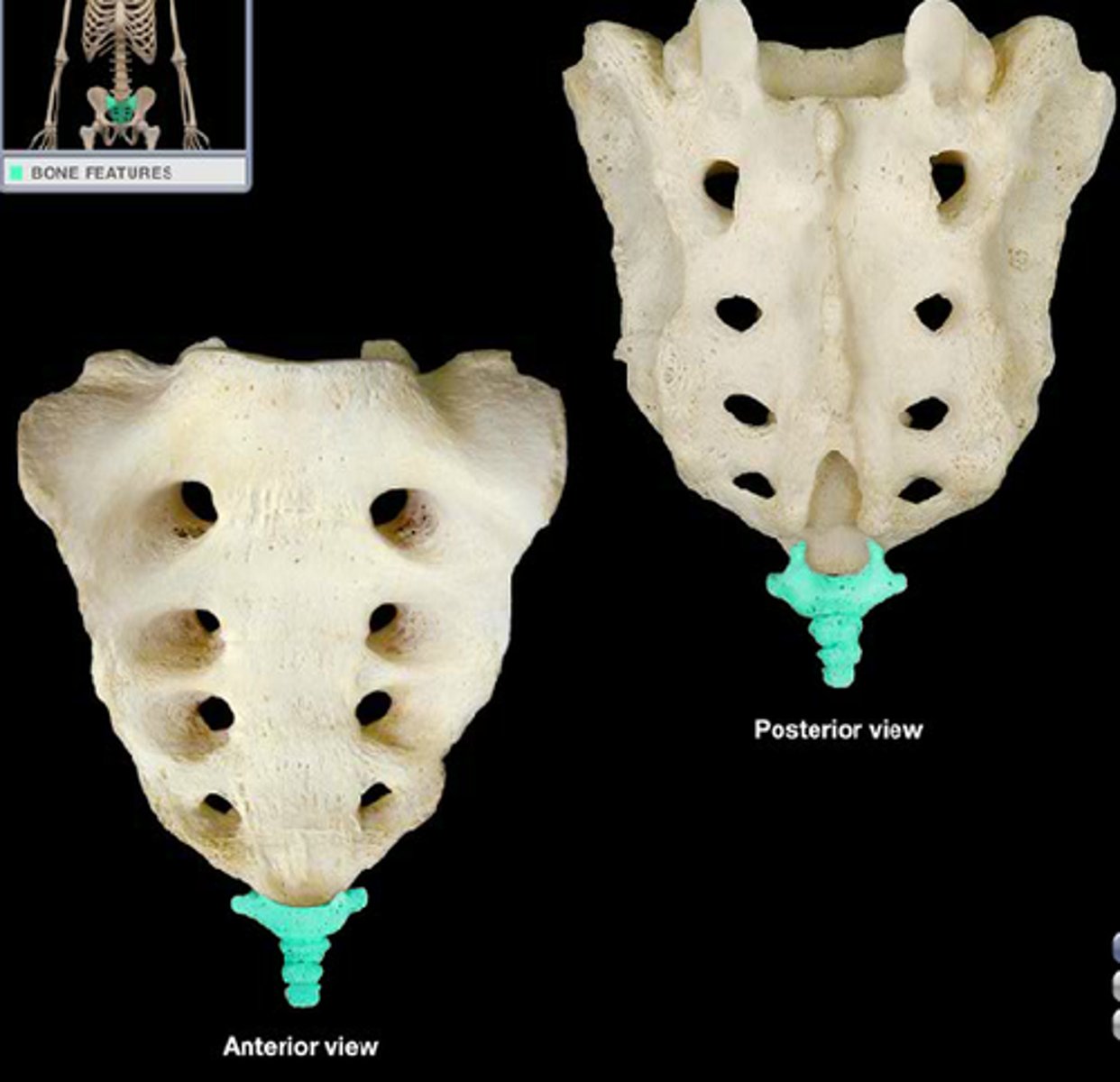
sacral nerves
S1-S5
coccygeal nerves
1 pair
peripheral nerve
nerve in the periphery distal to a nerve plexus or spinal nerve
nerve plexus
network of nerves in the PNS
cervical plexus
nerve plexus associated with the superior cervical spinal nerves (C1 through C5)
phrenic nerve
innervates the thoracic diaphragm
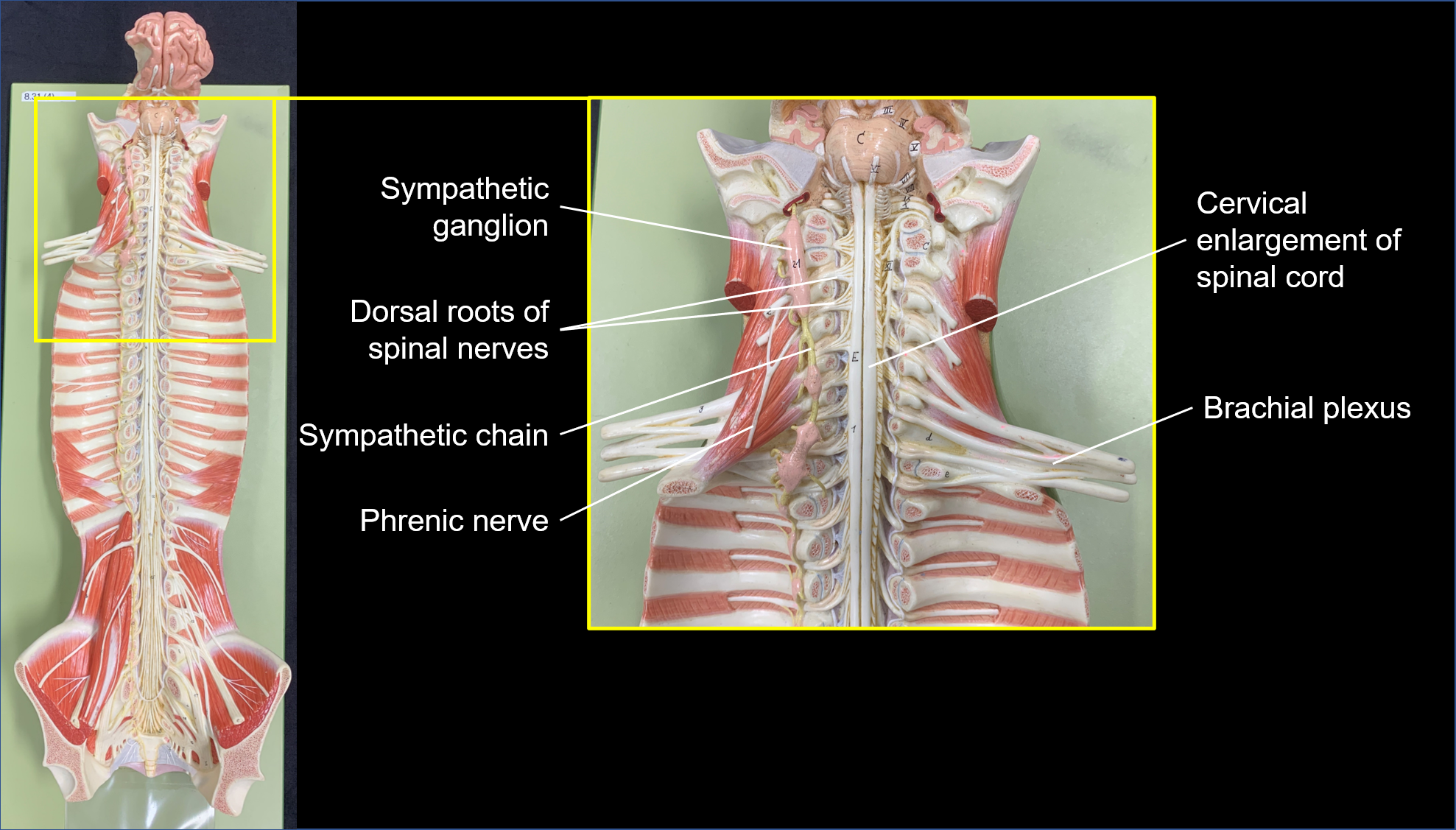
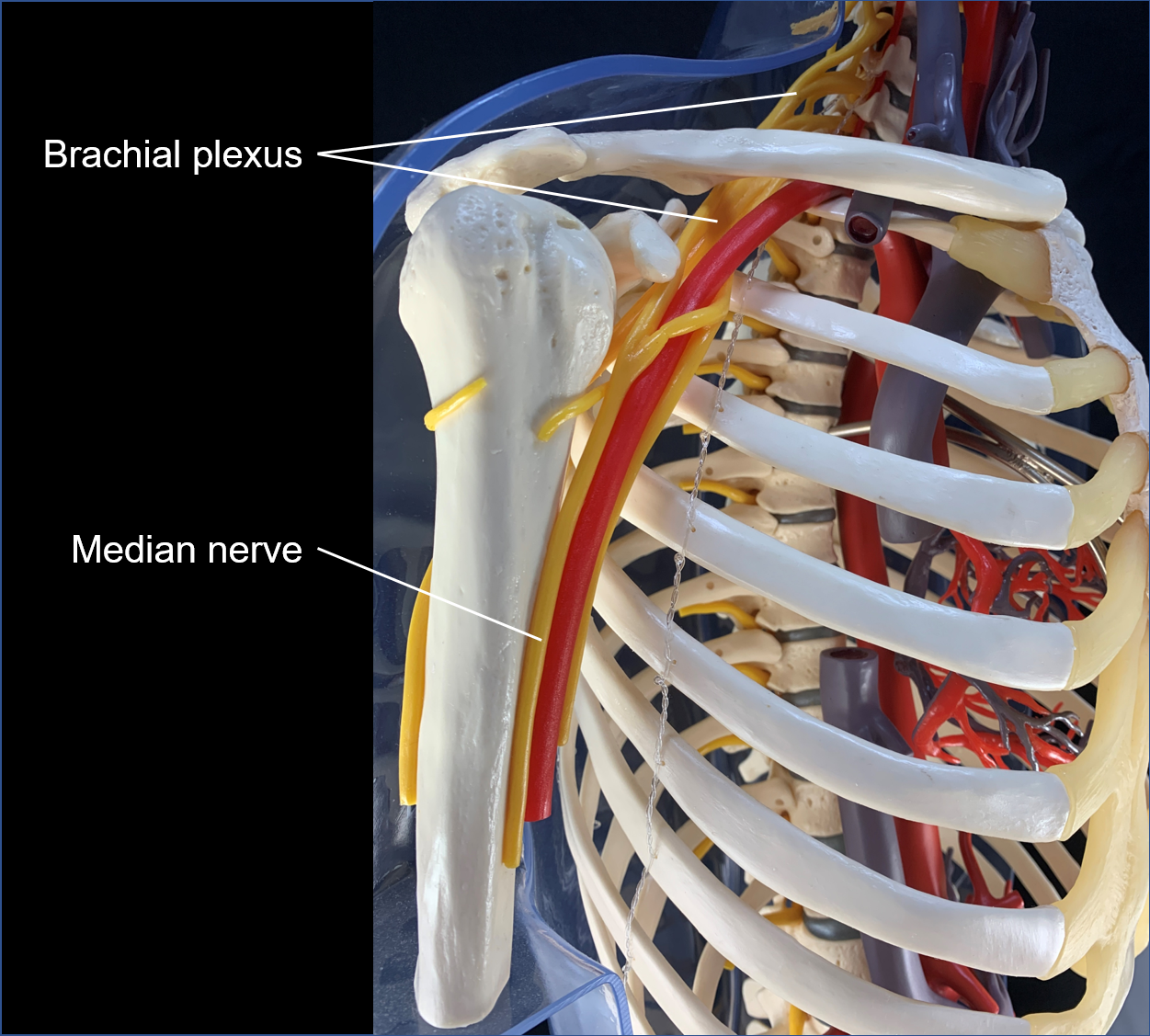
brachial plexus
nerve plexus associated with the inferior cervical spinal nerves and first thoracic spinal nerve (C4 through T1)
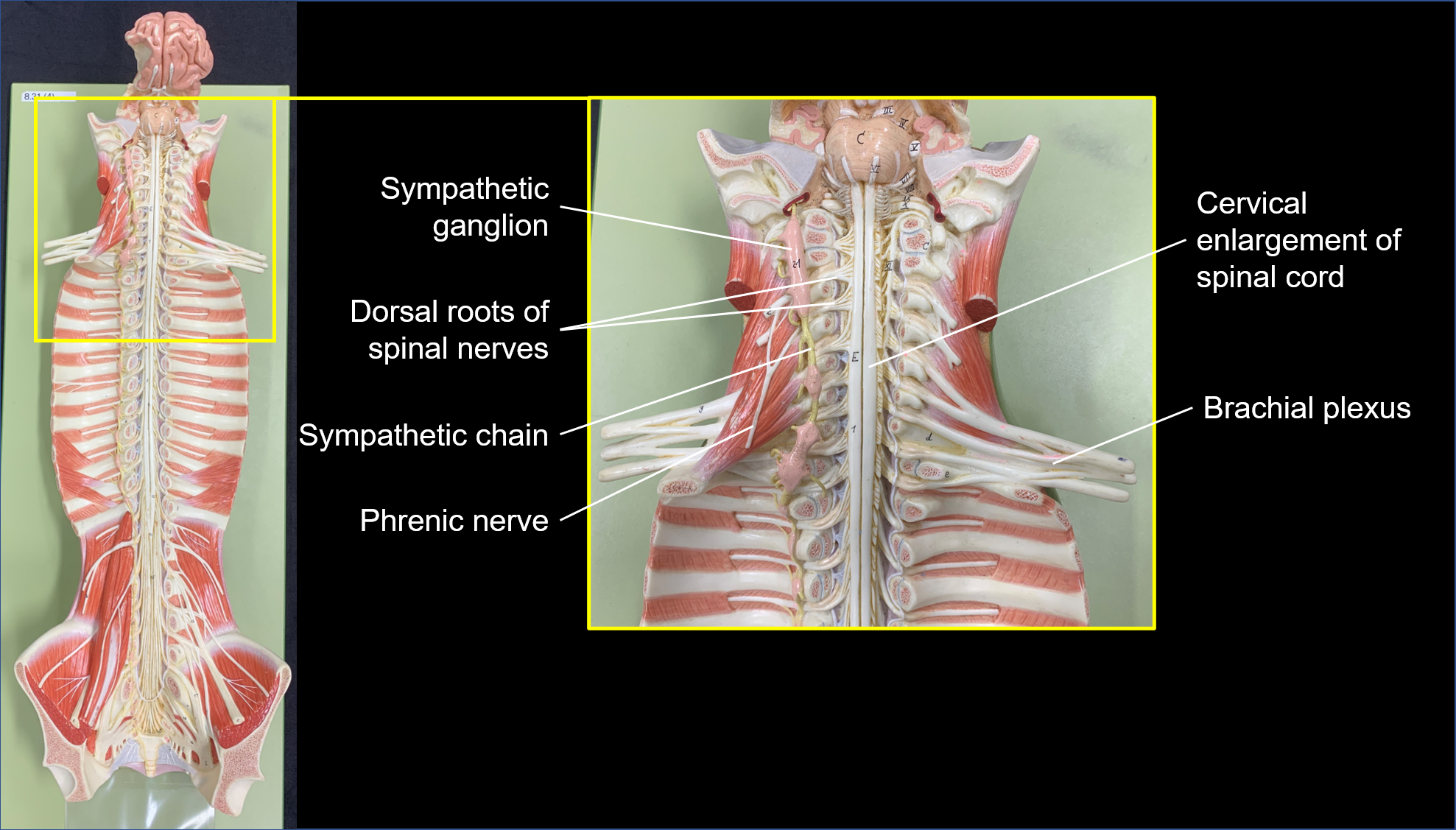
median nerve
innervate the majority of muscles in the anterior antebrachium and palmar region
lumbar plexus
nerve plexus associated with all the lumbar spinal nerves
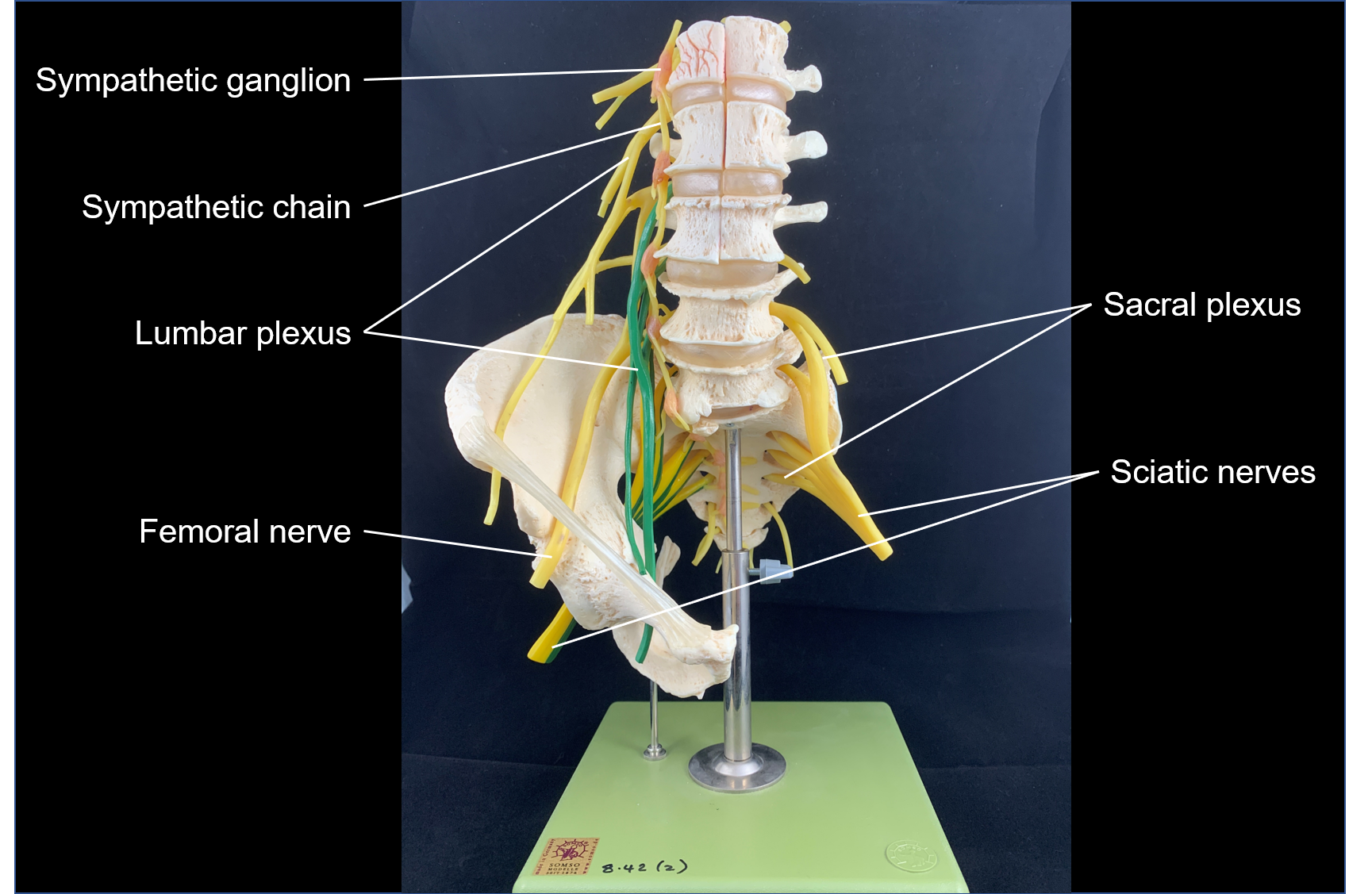
femoral nerve
systemic nerve of the anterior leg that arises from the lumbar plexus
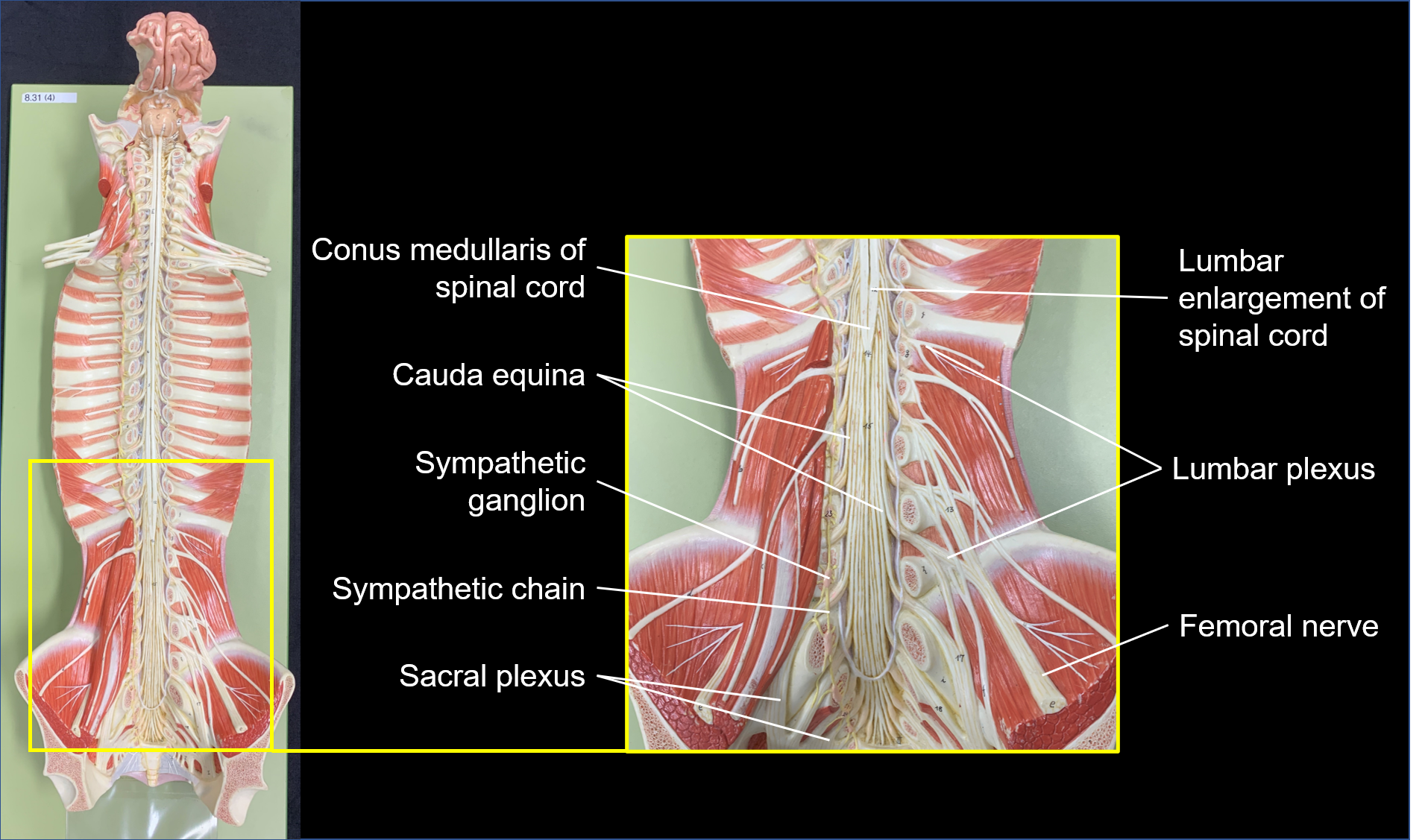
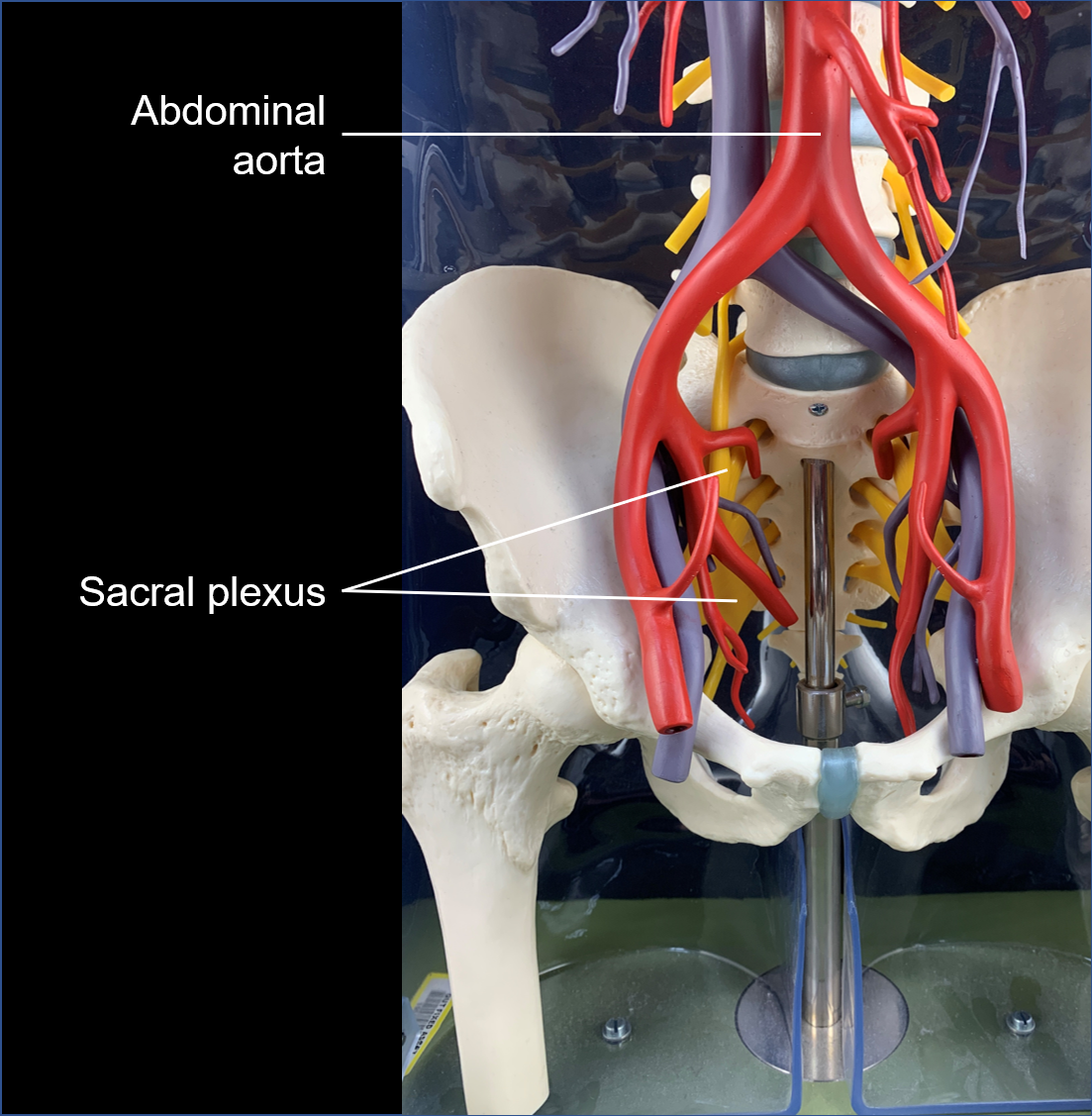
sacral plexus
nerve plexus associated with the inferior lumbar (L4 and L5) and sacral spinal nerves (S1 to S4)
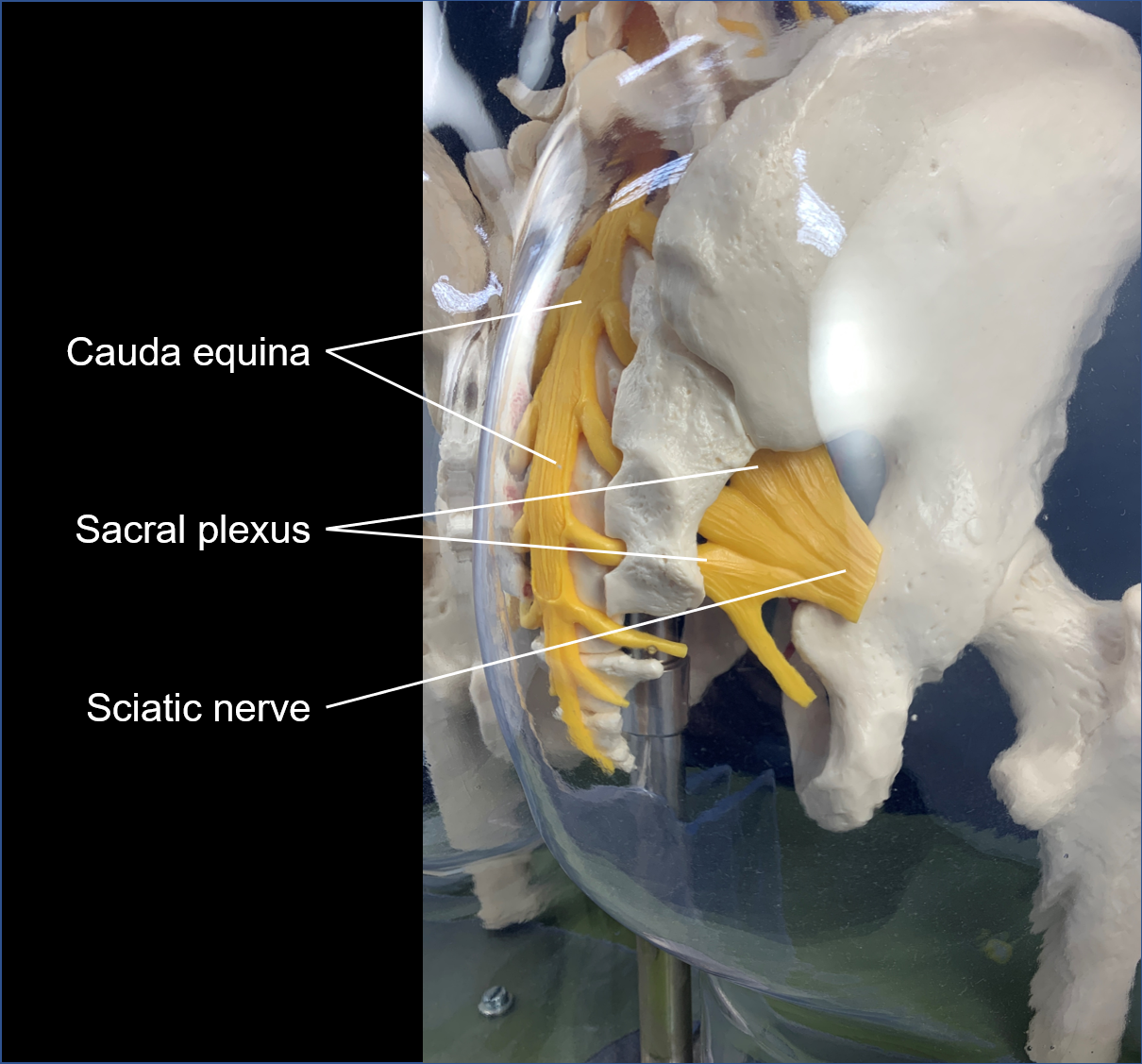
sciatic nerve
systemic nerve from the sacral plexus and extends across the hip joint and gluteal region into the posterior femoral region
kinesthesia
general sensory perception of movement of the body
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy (homeostasis) by by controlling involuntary functions like lowering heart rate, stimulating digestion, and constricting pupils
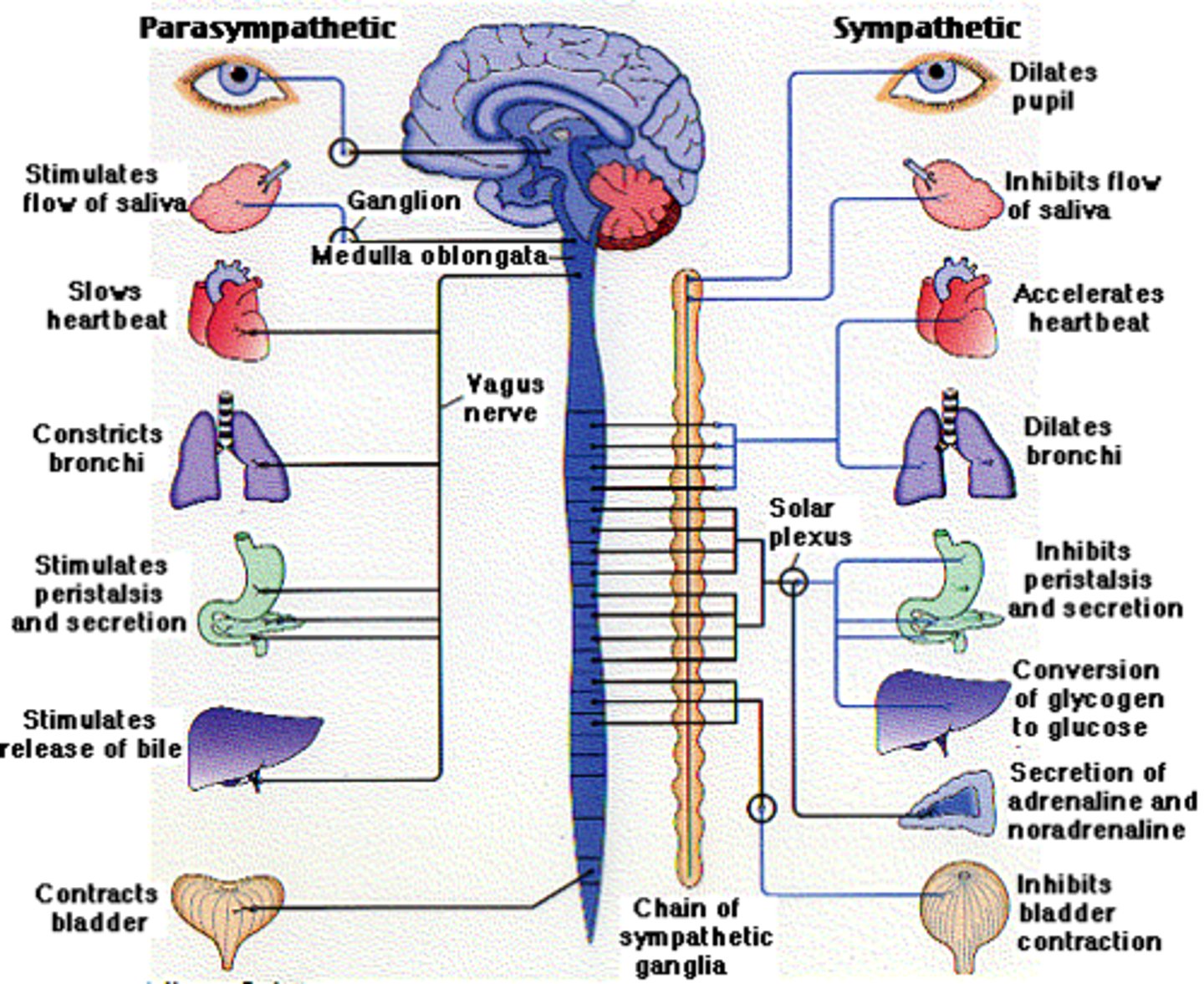
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
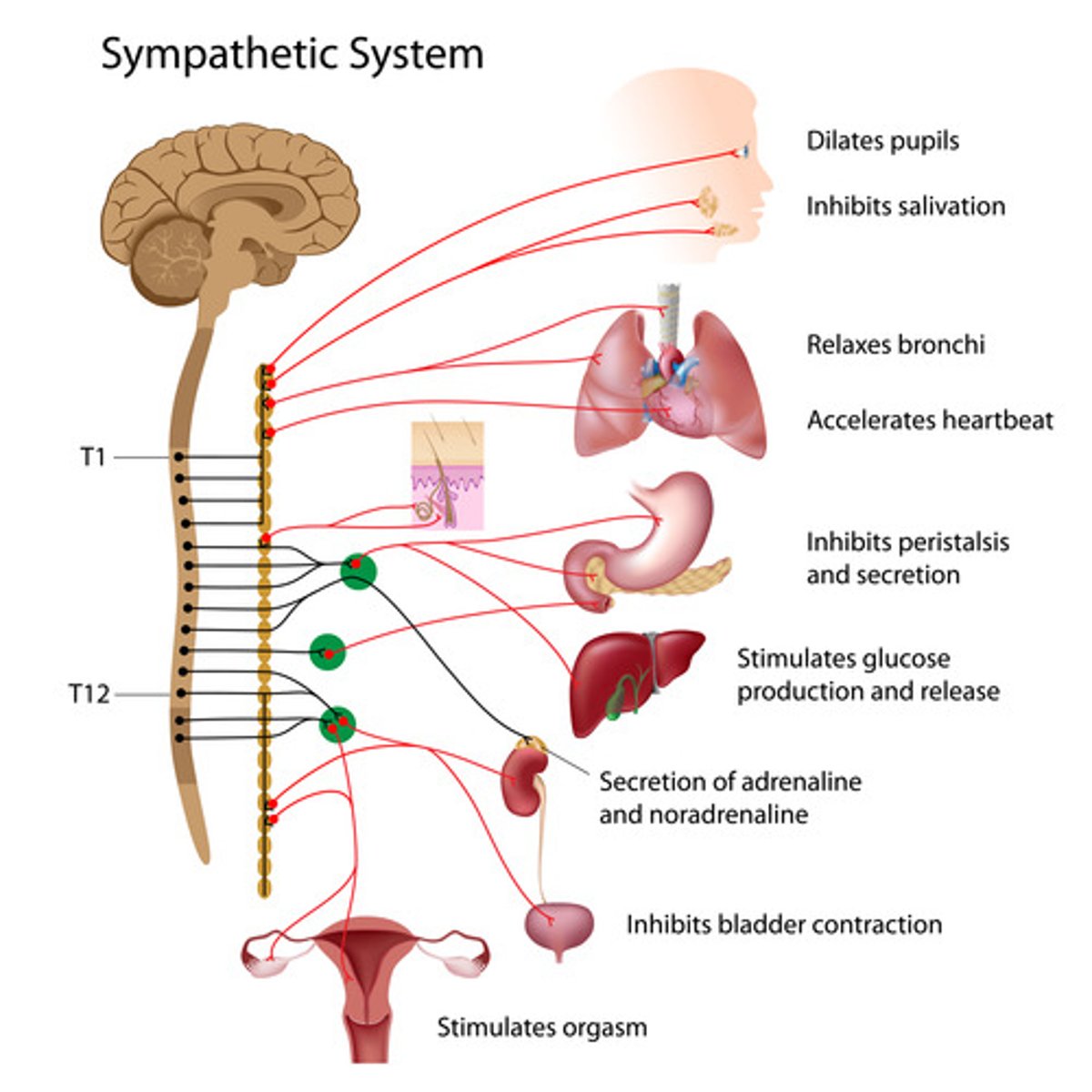
sympathetic ganglia
autonomic ganglia in a chain along the anterolateral aspect of the vertebral column that are responsible for contributing to homeostatic mechanisms of the autonomic nervous system