Chem 642 Exam 4
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
RNA polymerase: can synthesize RNA chains without a primer.
True
RNA polymerase from E. coli (core enzyme alone) can recognize specific start signals in DNA.
False; It recognizes the Promoter
The sigma factor of E. coli RNA polymerase: combines with the core enzyme to confer specific binding to a primer.
False; binding to a promoter.
Termination of transcription is a known function of TFIIH.
False; (Any of the following) DNA helicase activity, Hydrolysis of ATP, Formation of an open complex, Nucleotide excision repair
Processing of a primary mRNA transcript in a eukaryotic cell normally involve: conversion of normal bases to modified bases, such as inosine and pseudouridine.
False; 5' cap, 3' polyA tail, and splice out intron.
The 5'-terminal cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs is a(n): 7-methylguanosine joined to the mRNA via a 5' to 5' triphosphate linkage.
True
Compared with DNA polymerase, reverse transcriptase: makes more errors because it lacks the 3' to 5' proofreading exonuclease activity.
True
Telomerase consists of RNA only.
False; RNA and protein.
Several different codons may encode the same amino acid.
True
The large subunit of Ribosome contains rRNA molecules; the small subunit does not.
False; Both have rRNA.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (amino acid activating enzymes): "recognize" specific tRNA molecules and specific amino acids.
True
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (amino acid activating enzymes): "recognize" any tRNA molecules and specific amino acids.
False; Specific tRNA and specific amino acids
Since introns are largely genetic 'junk,' they do not have to be removed precisely from the primary transcript during RNA splicing.
False; They must, otherwise you get wrong coding sequences
All Eukaryotic cells use one type of RNA polymerase to transcribe all classes of RNA.
False; Eukaryotic cells have three types
The large and small subunits of ribosomes undergo association and dissociation during each cycle of translation.
True
RNA polymerase:
can synthesize RNA chains without a primer.
3 multiple choice options
RNA polymerase from E. coli (core enzyme alone) has all of the following properties except that it:
recognizes specific start signals in DNA.
3 multiple choice options
The sigma factor of E. coli RNA polymerase:
combines with the core enzyme to confer specific binding to a promoter.
3 multiple choice options
After binding by E. coli RNA polymerase, the correct order of events for transcription initiation is:
closed complex formation, open complex formation, start of RNA synthesis, promoter clearance.
3 multiple choice options
Processing of a primary mRNA transcript in a eukaryotic cell does not normally involve:
conversion of normal bases to modified bases, such as inosine and pseudouridine.
3 multiple choice options
The 5'-terminal cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs is a(n):
7-methylguanosine joined to the mRNA via a 5' − 5' triphosphate linkage.
3 multiple choice options
The excision (splicing) of many group I introns requires, in addition to the primary transcript RNA:
a guanine nucleoside or nucleotide (only).
3 multiple choice options
The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is an example of a(n) ___________ reaction.
condensation
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following are features of the wobble hypothesis?
The "wobble" occurs only in the first base of the anticodon.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is not part of miRNA formation?
Pseudouridine
3 multiple choice options
Which one of the following statements about the elongation phase of protein synthesis is true?
Peptidyl transferase is a ribozyme.
3 multiple choice options
Eukaryotic cells have three distinct RNA polymerases.
True
Eukaryotic cells mRNAs are generally synthesized by RNA polymerase I.
False; RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II synthesizes only rRNAs. (eukaryotic cells)
False; RNA Polymerase I
The 5S rRNA is synthesized by RNA polymerase II. (eukaryotic cells)
False; RNA polymerase I
Eukaryotic cells RNA polymerases initiate transcription at specific promoter sites on the DNA
True
Describe in words (not using structures) the important features of the structures present on the 5' and 3' ends of mature (processed) eukaryotic mRNAs.
At the 5' end, there is a cap made up of a 7-methylguanosine joined to the 5'-terminal nucleotide through a 5' to 5' triphosphate group, This guanine nucleotide is methylated on N-7. At the 3' end is the poly(A) tail consisting of a run of 80-250 adenosine nucleotides.
mRNA
codes for proteins
rRNA
components of ribosome
snRNA
splicing of RNA transcripts
tRNA
adaptor for protein synthesis
Initiation factor 2 (IF-2)
a protein factor that, when bound to GTP, brings the fMet-tRNAfMet to the initiation complex.
Shine-Dalgarno (16S RNA, complementary)
a component of the small (30S) subunit. It contains a sequence complementary to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the mRNA, and helps to line up the mRNA initiation AUG codon on the ribosome
Peptidyl transferase
a ribozyme in the 50S ribosomal subunit. It catalyzes formation of each peptide bond as the ribosome moves along the mRNA.
Release factors
proteins that bring about the release of the finished polypeptide when the ribosome encounters a termination codon in the mRNA.
Elongation factor G (EF-G)
participates in the translocation of the ribosome down the mRNA by one codon after each peptide bond is formed.
N10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate
the cofactor that donates a methyl group in the conversion of tRNA-bound Met to fMet.
ATP
the substrate for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; it donates an AMP residue in the formation of aminoacyl adenylate, which donates the aminoacyl group to tRNA.
tRNAfMet
tRNAfMet is the transfer RNA that initiates protein synthesis by inserting the first amino acid (fMet) in every prokaryotic protein.
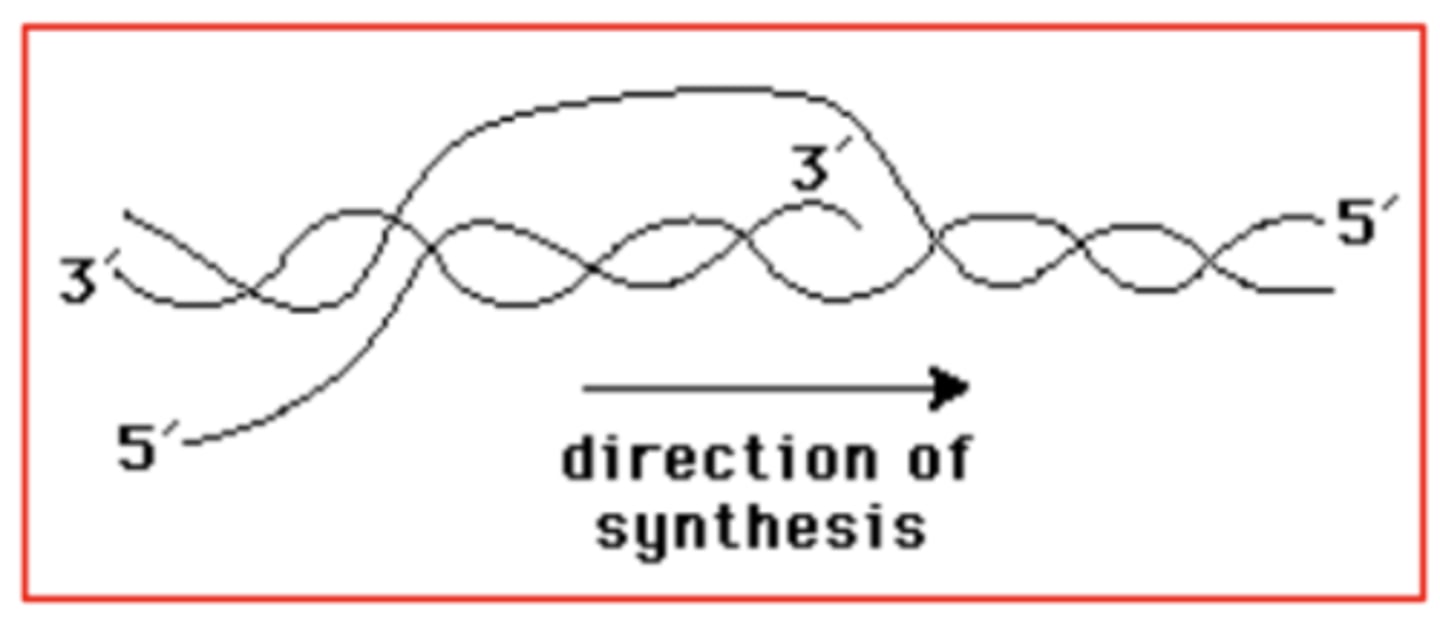
Below, an RNA molecule is being transcribed from a strand of DNA. Indicate the 5' and 3' ends of the RNA molecule and of the strand of DNA that is complementary to the RNA molecule. In which direction is synthesis occurring?
Which of the following is not known to be involved in initiation by eukaryotic RNA polymerase II?
DNA polymerase activity
3 multiple choice options
Splicing of introns in nuclear mRNA primary transcripts requires:
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs).
3 multiple choice options
Differential RNA processing may result in:
the production of two distinct proteins from a single gene.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is not usually essential for the catalytic activity of ribozymes?
Correct interaction with protein
3 multiple choice options
AZT (3'-azido-2',3 -dideoxythymidine), used to treat HIV infection, acts in HIV-infected cells by:
inhibiting reverse transcriptase.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is not true about telomerase?
Telomerase utilizes a tRNA template.
3 multiple choice options
Which one of the following statements about ribosomes is true?
There are two major ribosomal subunits, each with multiple proteins.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements about the tRNA that normally accepts phenylalanine is false?
The tRNA must contain the sequence UUU
3 multiple choice options
It is possible to convert the Cys that is a part of Cys-tRNACys to Ala by a catalytic reduction. If the resulting Ala-tRNACys were added to a mixture of (1) ribosomes, (2) all the other tRNAs and amino acids, (3) all of the cofactors and enzymes needed to make protein in vitro, and (4) mRNA for hemoglobin, where in the newly synthesized hemoglobin would the Ala from Ala-tRNACys be incorporated?
Wherever Cys normally occurs
3 multiple choice options
First step of protein synthesis
The 50S subunit binds to the initiation complex of the 30S subunit and mRNA.
Second step of protein synthesis
Aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A site.
Third step of protein synthesis
Peptide bond formation shifts the growing peptide from the P to the A site.
Fourth step of protein synthesis
Deacylated tRNA is released from ribosome.
Bacterial mRNA is broken down within a few minutes of its formation in E. coli.
True
Bacterial mRNA consists only of the bases that code for amino acids.
False; also has non-coding regions that are not translated at the beginning and end of the sequence
Polysomes do not necessarily contain mRNA.
False; they are clusters of ribosomes translating a strand of mRNA into peptide chains
Bacterial mRNA normally occurs as a double-stranded structure, with one strand containing codons, the other containing anticodons.
False; single-stranded structure containing base pairs that is complementary to the template strand and matches the coding strand
Bacterial mRNA can be translated while it is still being synthesized.
True
In eukaryotes, the 3' end of the mRNA is associated with the 5' end during initiation, whereas in prokaryotes, it is not.
True
In prokaryotes, it is initiated at an AUG near a Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the mRNA, whereas in eukaryotes, it is initiated at an AUG near the 3' end of the mRNA.
False; the opposite is true
In prokaryotes, it is initiated with Met, whereas in eukaryotes, it is initiated with fMet.
False; the opposite is correct
In prokaryotes, translation and transcription are coupled, whereas in eukaryotes, they are not.
True
The template strand of a segment of double-stranded DNA contains the sequence:
(5)-CTT TGA TAA GGA TAG CCC TTC-(3')
(a) What is the base sequence of the mRNA that can be transcribed from this strand?
(b) What amino acid sequence could be coded by the mRNA base sequence in (a),
using only the first reading frame starting at the 5' end? (Fig. 27-7, p. 1107 shown)
(c) Suppose the other (complementary) strand is used as a template for transcription.
What is the amino acid sequence of the resulting peptide, again starting from the 5'
end and using only the first reading frame?
(a) (5)GAA GGG CUA UCC UUA UCA AAG(3')
(b) Glu-Gly-Leu-Ser-Leu-Ser-Lys
(c) The codons translate to Leu-Stop-Stop. No peptide would be produced because of the stop codons.
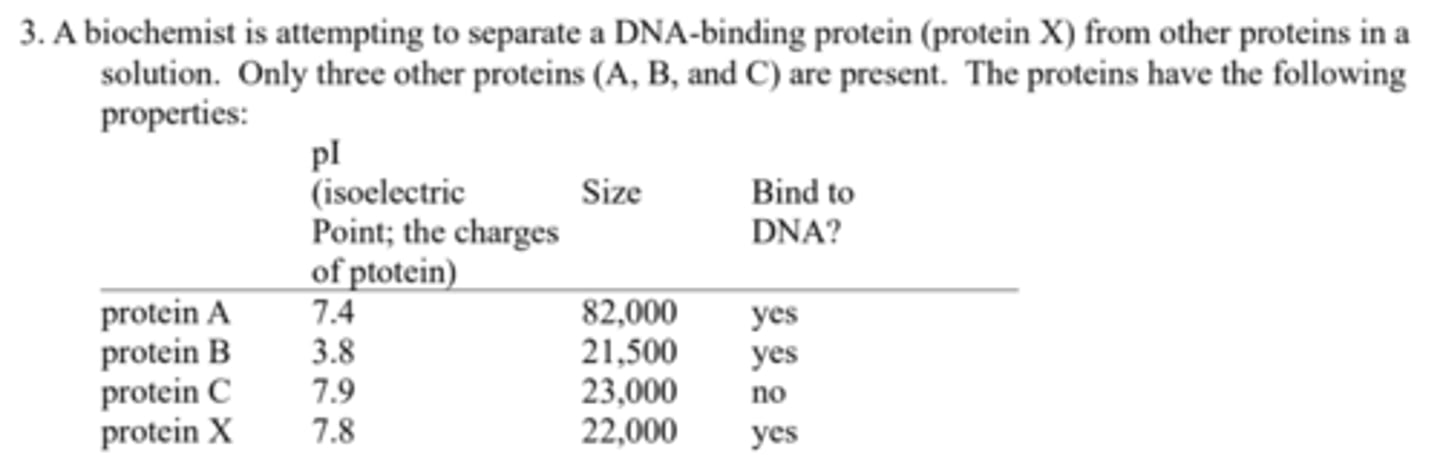
What type of protein separation techniques might she use to separate: (a) protein X from protein A?
Size-exclusion (gel filtration) chromatography to separate on the basis of size;
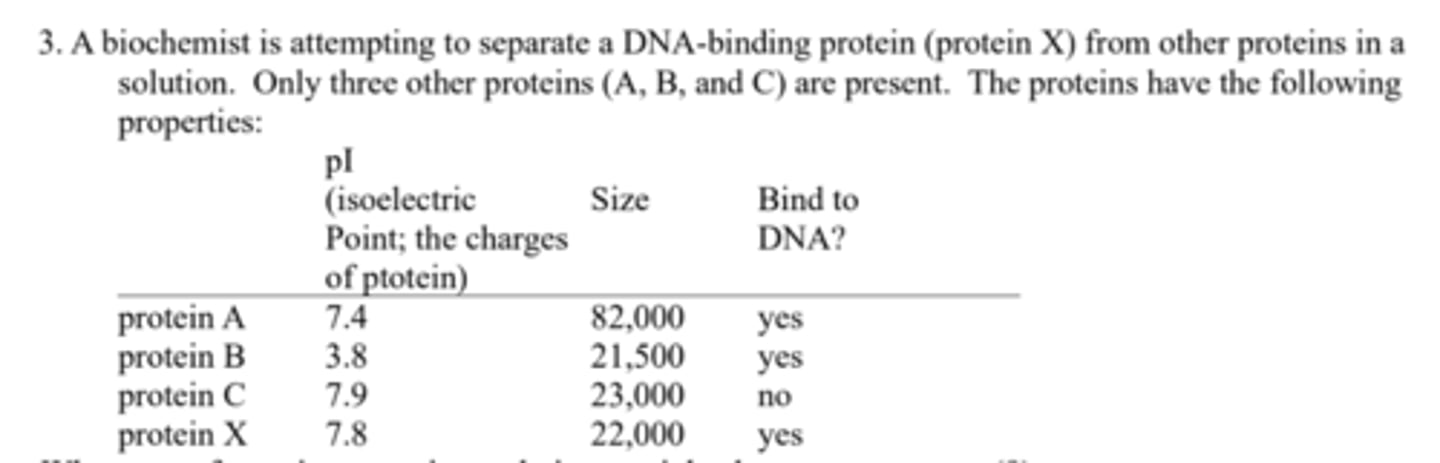
What type of protein separation techniques might she use to separate: (b) protein X from protein B?
ion-exchange chromatography or isoelectric focusing to separate on the basis of charge;
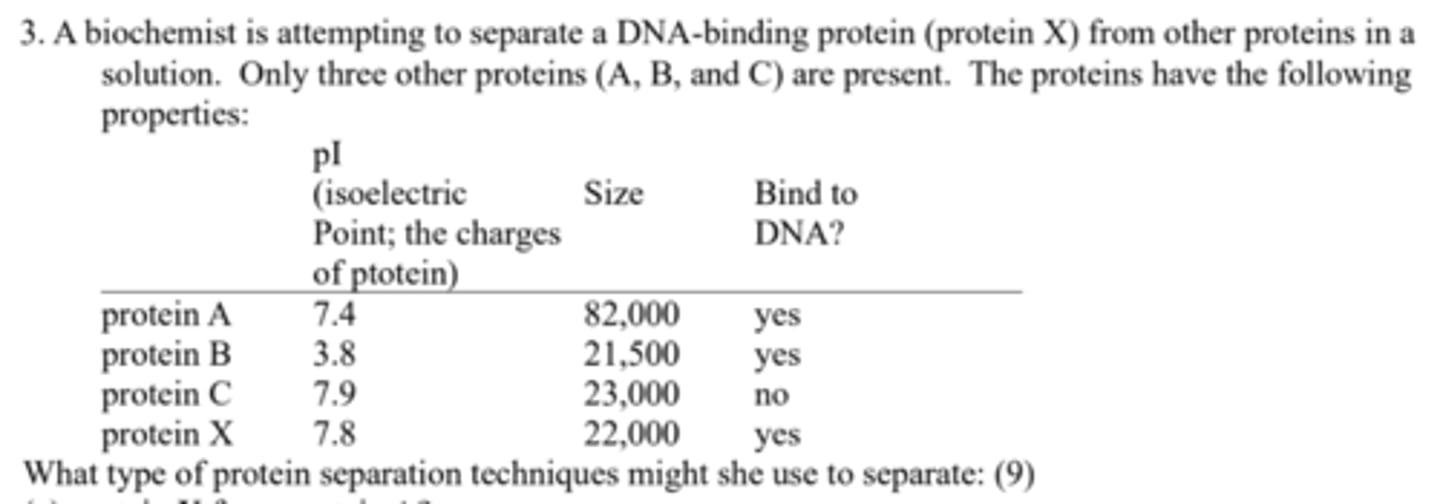
What type of protein separation techniques might she use to separate: (c) protein X from protein C?
specific affinity chromatography, using immobilized DNA.