membrane transport
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Small non polar molecules do/don’t what
Do not need ion channels/transporters to go through membrane. They are simple diffusion
Small uncharged polar molecules do/don’t what
They can go across membrane bc it’s small,uncharged. They diffuse more easily
Larger uncharged polar molecules do/don’t what
They’re more difficult to get across the membrane bc they’re fat. Some are even prohibited. Ex. Glucose
Ions do/don’t what
They are charged and large so they CANNOT pass through membrane on their own. Need transporter or channel to go through
whats consists in passive transport
NO ATP
channels,- needs to be specific to it
transporter - only fits specific molecule
whats the term when were considering concentration + charge of molecule
electrical concentration gradient
whats resting membrane potential
when there is no charge diff across membrane (on both sides ? )
when plasma membrane potential is 0 the leak channels are closed.
whats the energy source for glucose na+
the natural concentration gradient of na+ (they are cooperative binding )
in voltage gated sodium channels what makes the sensor regions to open
the membrane potential outside of cell turn negative, pulling the positively charged sensors up.
what occurs in the inactivated part of sodium voltage gated blah
the plug stops sodium from entering but channel is still open until inner membrane potential becomes negative again
what the branches at the end of the neuron cell called
nerve terminals
in the neuron what do dendrites do
bring in signals to cell body
whats patch clamp recording
(CHOPSTICKS) method used to tell whether channels are open or not
in calcium channels whats the 2 cells called and the space between them
pre synaptic cell—> post synaptic
inbwtween is SYNAPTIC CLEFT
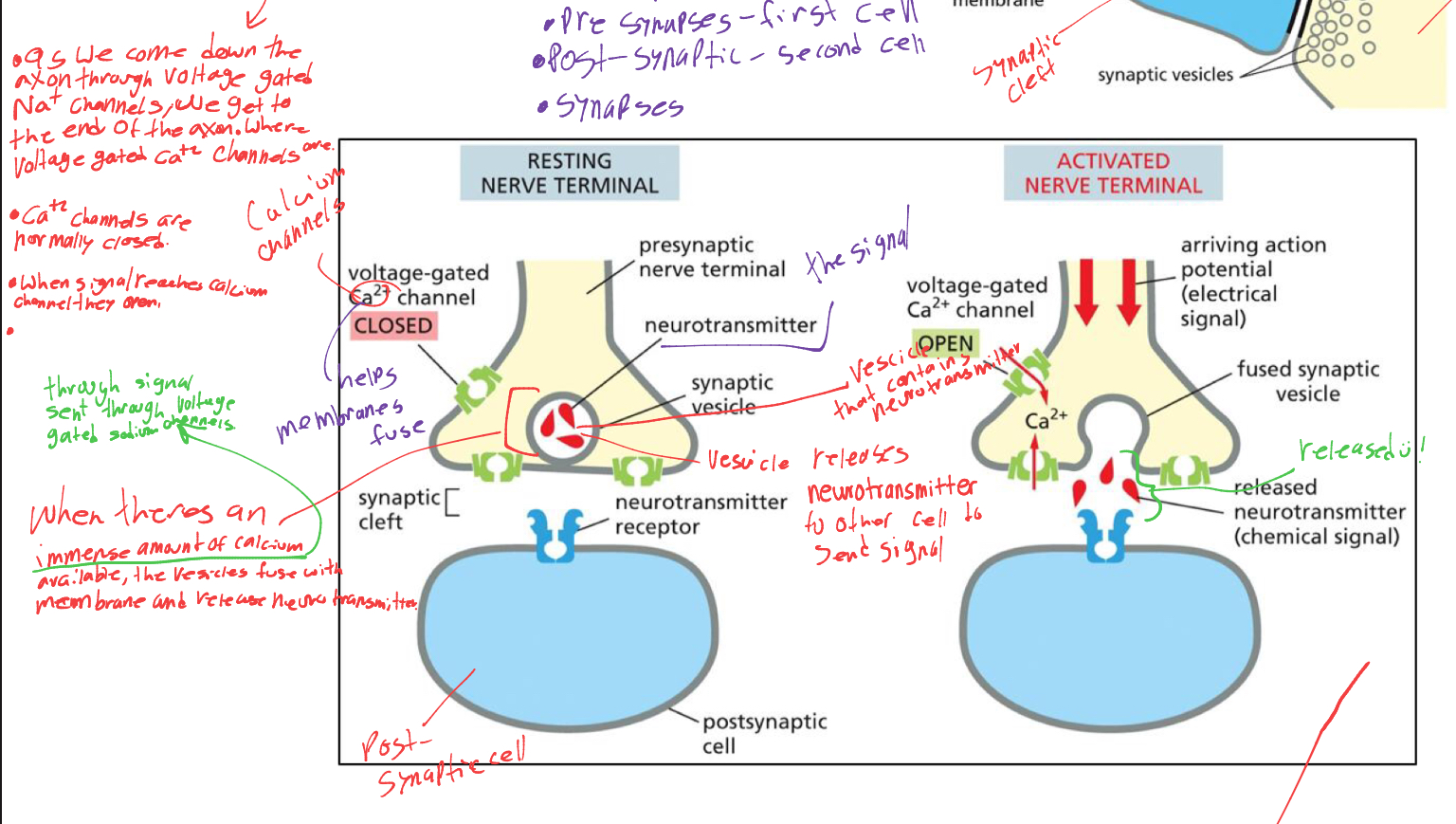
when a signal reaches the calcium channels what happens
they open, signaling the vesicle to fuse with membrane and release neurotransmitter to neurotransmitter receptor.
what happens in transmitter gated ion channels
neurotransmitter binds. to receptor and activate the post synaptic cell
what are all the pumps and channels
sodium potassium pump,- pumps sodium out of cell and potassium inside, through the shape change
glucose sodium pump- uses support(binding together) to enter. glucose rides sodium.
potassium leak channels- natural. concentration gradient
voltage gated sodium channels- the action potential.
calcium channels (nerve cell signaling)- neuronal