Lecture 64 & 65: Ocular Pathology
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
What forms the fibrous tunic of the ocular globe?
cornea and sclera
What is the vascular tunic of the ocular globe?
uvea
What is the uvea composed of?
anteriorly: the iris and ciliary body
posteriorly: the choroid
What are the functions of the tear film that covers the cornea?
preventing desiccation
removal of debris and microorganisms
providing oxygen, nutrition, growth factors and inflammatory chemokines
migration of leukocytes to the ocular surface
structured to allow light penetration with minimal scattering
What is the tear film composed of?
superficial lipid layer and underlying aqueous and mucin components
What is the difference in thickness of corneal epithelium in small animals vs large animals?
dogs and cats: 5-7 layers thick in health
ruminants and horses: 8-12 layers thick
What is the fibrous layer with vasculature which opposes choroid (opaque white)?
sclera
What is the iris composed of?
a surface of fibrocytes and melanocytes
deeper smooth muscle, blood vessels and nerves
posterior epithelium continuous with the ciliary body
How do large animal irises differ?
contains cystic structure
corpora nigra in horses (helps reduce glare)
granula iridica in ruminants
What extends from base of iris to the junction with the choroid and retina, forming the iridocorneal angel which aids in drainage of aqueous humor?
ciliary body
What is the ciliary body composed of?
connective tissue with blood vessels and nerves
smooth muscle (ciliary muscle) - aids in lens position and changes
What are the two layers of the ciliary body?
inner layer: ciliary epithelium (aqueous humor production)
outer layer: pigmented ciliary epithelium
What is the funciton of the iridocorneal angle?
allow aqueous humor to drain from eye
What is the function of the lens?
a biconvex, avascular structure that refracts light on retina and provides focus, also separates anterior chamber from posterior chamber (along within iris and ciliary body)
What is the lens composed of?
lens epithelium (only on anterior surface of lens)
lens capsule (basement membrane)
lens nucleus composed of lens fibers (epithelial cells which migrate inward)
What is vitreous?
an optically clear elastic hydrogel composed of collagen, hyaluronic acid, and widely dispersed hyalocytes
What is the photoreceptor layer which converts light into electrical impulses?
retina
Number of photoreceptors associated with a ________ is associated with visual acuity.
ganglion cell
What is the benefit of a tapetum lucidum?
choroidal adaptation utilized in low light to stimulate photoreceptors a second time
What is the continuation of the nerve fiber (ganglion) layer of the retina, and is composed of axons, myelin, and glial cells?
optic nerve
What is anophthalmia?
complete failure of development of the eye, typically bilateral
What is microphthalmia?
small disorganized globe in an orbit of normal size
What usually causes microphthalmia?
most often results from traumatic injury to the globe:
in utero trauma
ischemic injury
infection
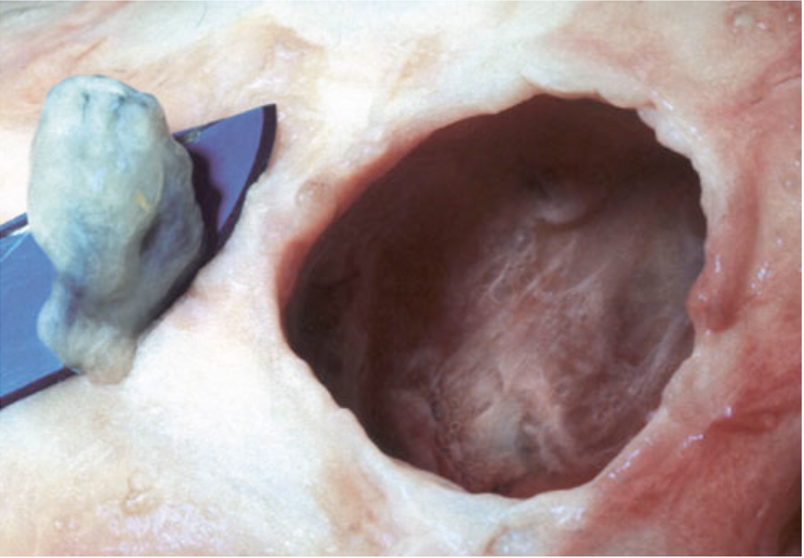
What ocular developmental abnormality is shown here?
microphthalmia
What is cyclopia and synophthalmia?
failure of division of the ocualr primordium into paired optic stalks forming a single midline ocular structure
cyclopia = one set of structures
synophthalmia = two sets of structures
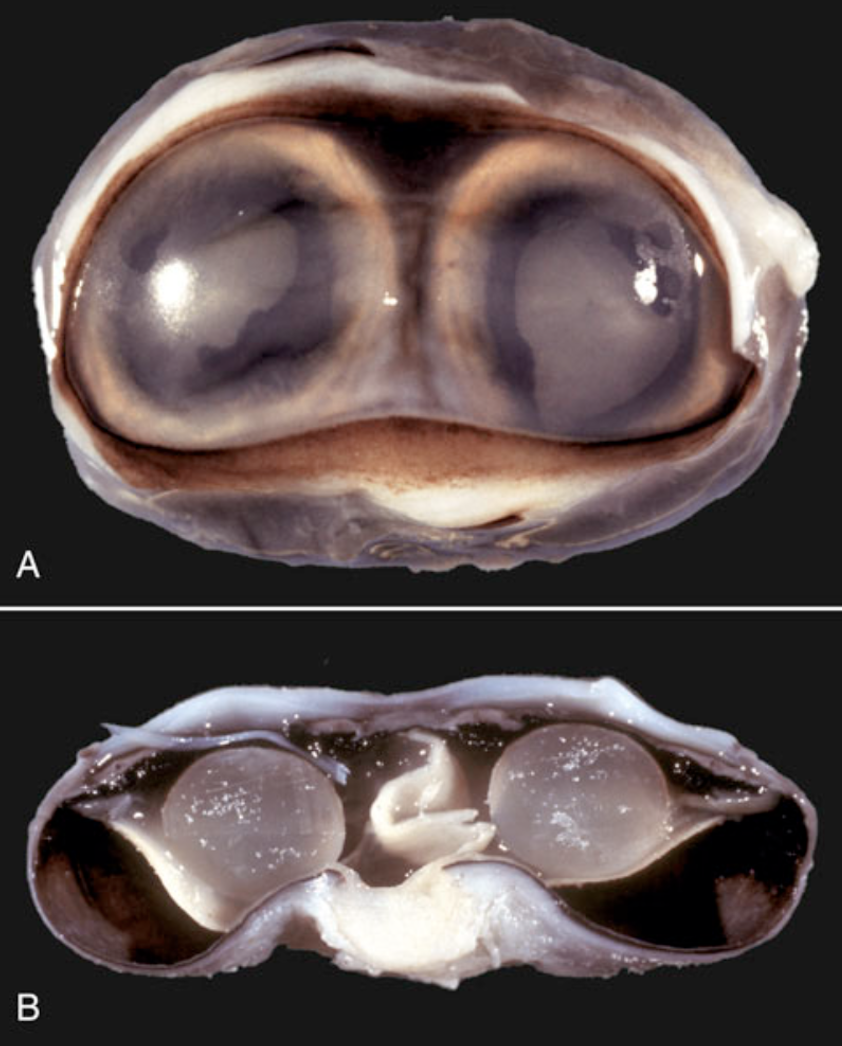
What ocular developmental abnormality is seen here?
synophthalmia
What is coloboma?
failure of the optic fissure to close (in the last 3rd of gestation) resulting in an outgrowth of the retina through the defect → concurrent choroidal and scleral hypoplasia most often seen adjacent to the optic nerve
What breeds are predisposed to coloboma?
charolais cattle (often bilateral)
australian shepherd dogs
What is the collie eye anomaly?
bilateral, congenital, recessively inhereted syndrome with:
choroidal hypoplasia + hypopigmentation
segmental tapetal hypoplasia/aplasia
posterior coloboma
± retina detachment (impaired vision), retinal dysplasia, and intraocular hemorrhage

What abnormality is seen in this dog?
collie eye anomaly

What has occurred here?
retinal detachment due to collie eye anomaly
What is glaucoma?
a diverse group of diseases which share physiologic and structural characteristics and affects every part of the globe → sustained increase in intraocular pressure → ocular hypertension → pain → loss of vision → blindness
What is the difference between primary and secondary glaucoma?
primary: occurs without any known acquired intraocular disease to explain the increase in intraocular pressure → developmental defect in the structure and function of the iridocorneal angle and aqueous humor drainage pathway → goniodysgenesis
secondary: acquired lesions responsible for impairment of aqueous humor outflow (ex. lens luxation, inflammation etc)
What is goniodysgenesis?
developmental defect in the structure and function of the iridocorneal angle and aqueous humor drainage pathway
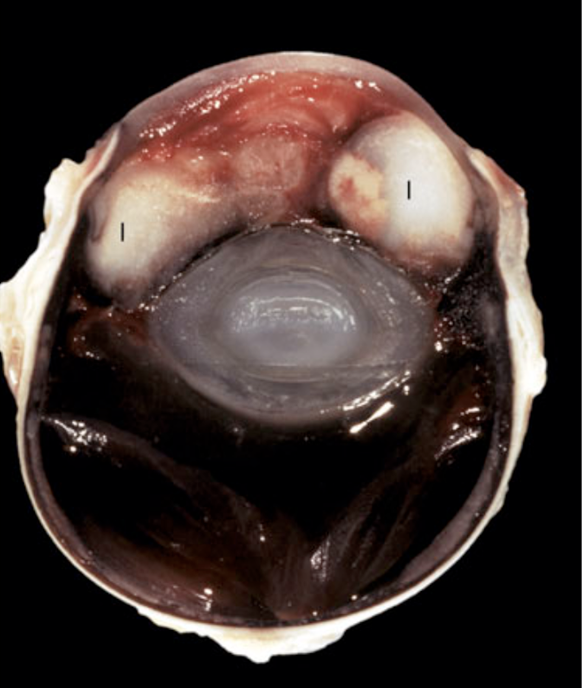
What has occurred here?
secondary glaucoma (from metastatic lymphoma)

What has occurred here? Note the hydropic swelling of the lens secondary to diabetes mellitus causing iritic compression.
secondary glaucoma from intumescent cataract
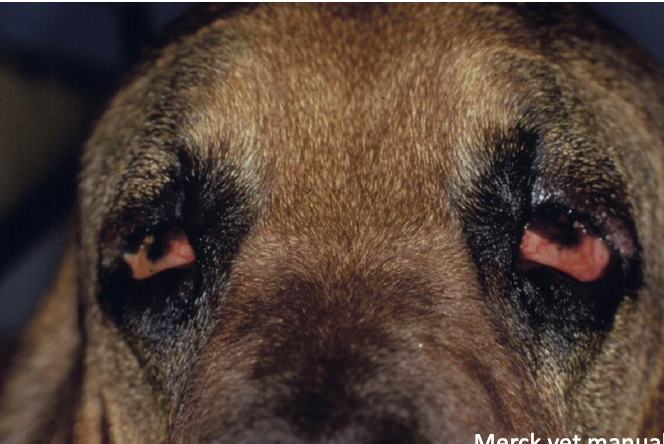
What is entropion and what does it result in?
inward rolling of eyelid margin due to inadequate eyelid length which results in irritation of the cornea by eyelid hair → nonspecific keratitis → corneal ulceration → blepharospasms
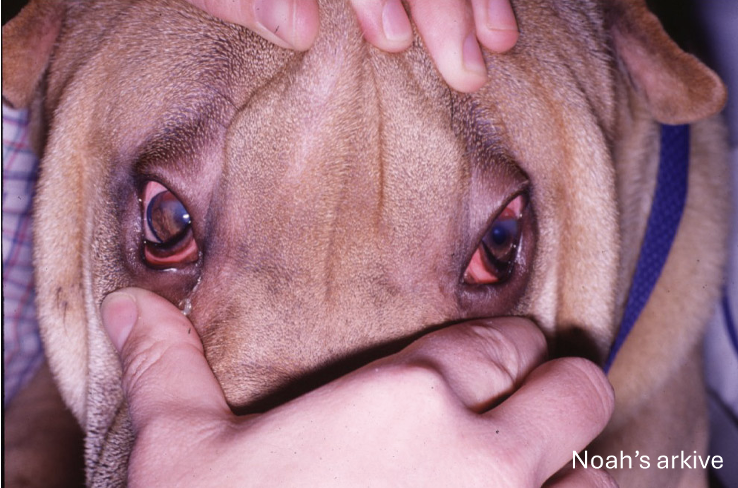
What developmental anomaly is shown?
entropion
What developmental anomaly is shown?
ectropion
What is ectropion?
undue laxity of an excessively long eyelid resulting in eversion of eyelid margin, usually affecting the lower eyelid »» upper eyelid with no direct corneal irritation but can result in chronic keratitits
What is chalazion?
(sterile process) leakage of meibomian gland secretory material into the surrounding dermis → granulomatous inflammation; can occur with meibomian gland disease, inflammation, or neoplasia
What are the three types of conjunctivitis?
eosinophilic: allergic or hypersensitivity response, parasitic
lymphoplasmacytic: chalmydophila or nonspecific
suppurative: often bacterial
What parasitic disease of the conjunctiva and orbit of dogs, cats and horses is caused by the filarial worm containing Wolbachia spp. transmitted by black flies (simulium spp.) and gnats/midges (cullicoides spp.)?
onchocerciasis
How does onchocerciasis present?
off white nodules within the conjunctiva or episcleral
What is the pathogenesis of thelazia spp.?
nematode affecting domestic animals is transmitted by flies and results in lymphofollicular conjunctivitis
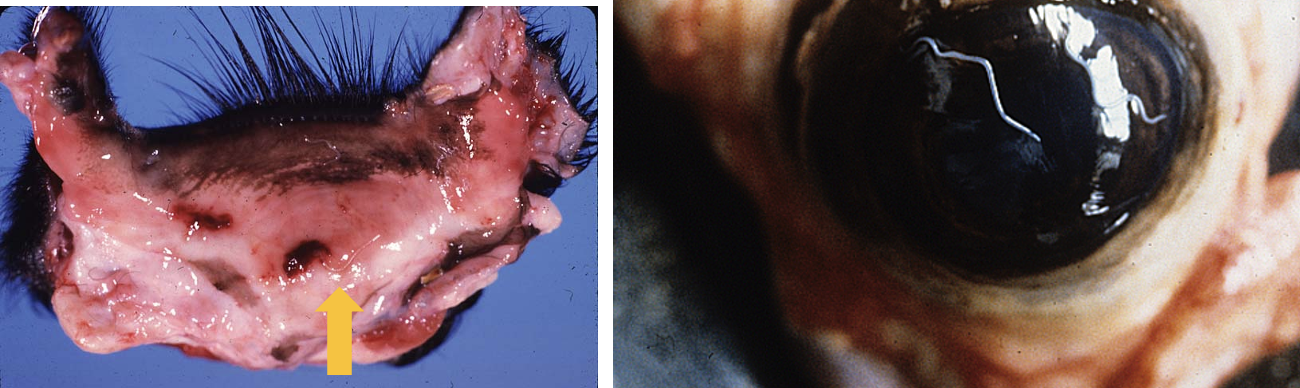
What is affecting this eye?
thelazia spp.
What is habronemiasis?
summer sores in horses
eosinophilic granulomas in response to migration of nematode larvae (Draschia megastoma, Habronema muscae, Habronema majus)
nematodes migrate to the stomach, penetrate the lumen, and excrete larvae in feces → ingested by maggots → transferred to horse via fly bites → firm nodule with caseous center
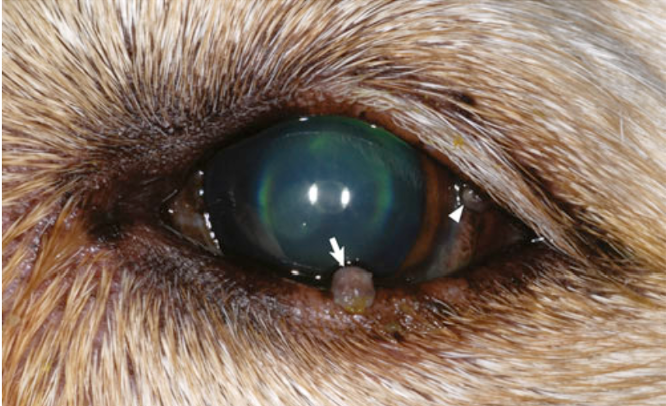
What is this?
meibomian gland adenoma (sebaceous gland of eyelid)
What is this?
squamous cell carcinoma
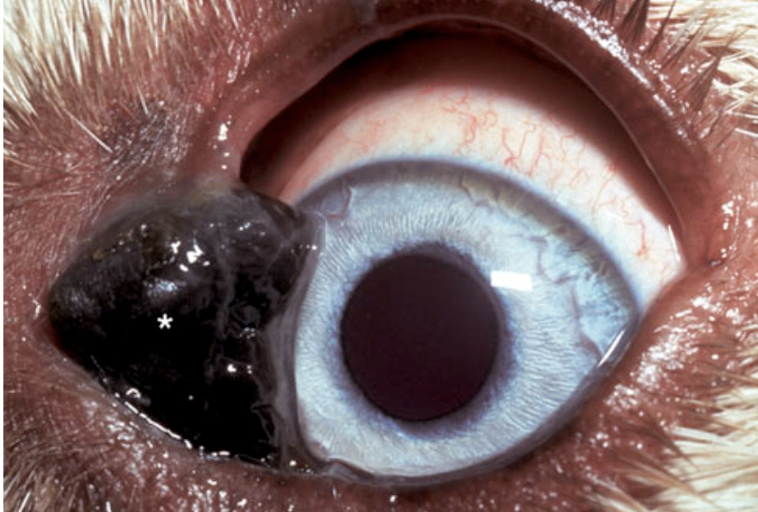
What is this?
cutaneous melanocytoma on the eyelid
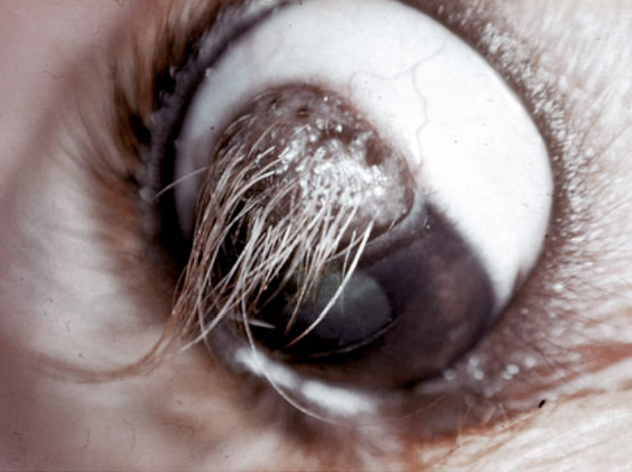
What is this?
corneal dermoid: a type of choristoma with ectopic hair follicles and adnexal glands within the cornea
What is keratoconjunctivitis sicca and what can it result in?
dry eye, common in dogs, or inadequate tear film resulting in:
corneal edema
suppurative keratitis
squamous metaplasia
neovascularization
stromal fibrosis
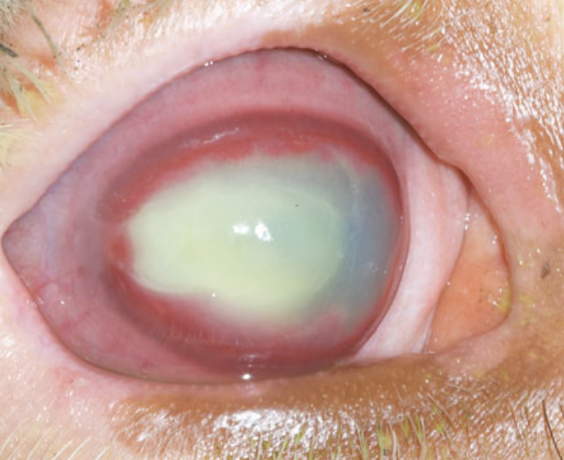
What is affecting this cow?
infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis
What commonly causes infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (pink eye)?
most commonly a gram negative coccobacillus, Moraxella bovis, transmitted by mechanical vectors (face fly = musca autumnalis) in the summer
UV damage, BHV-1 can predispose or increase severity
What species is most commonly affected by eosinophilic keratitis?
cats
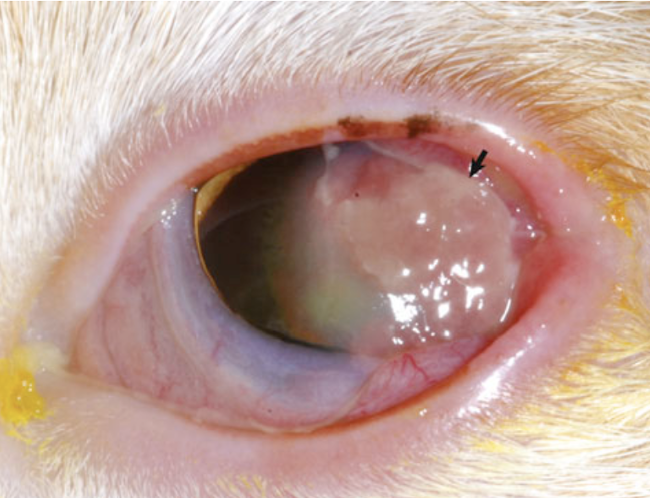
What is this? note the white to pink proliferative plaques involving the lateral cornea and conjunctiva.
eosinophilic keratitis
What is the most commonly isolated species from fungal keratitis in horses?
aspergillus
What is a keratomalacia “melting ulcer”?
neutrophils fom the tear film release lytic enzymes which results in necrosis/malacia of the cornea, can progress rapidly and esult in descemetocele and/or corneal perforation
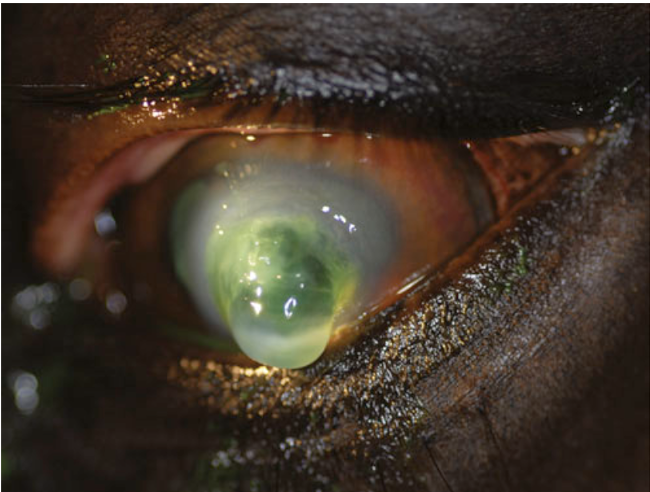
What is this?
keratomalacia
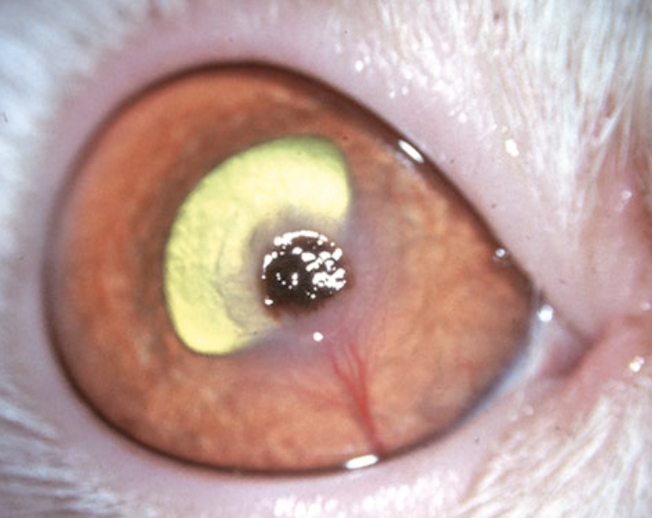
What is this and what species is it most commonly seen in?
corneal sequestrum, most often occurs in cats after chronic ulceration
What is persistent pupillary membrane?
abnormal persistence of the perilenticular vascular meshwork, common in dogs
anterior chamber: persistent pupillary membrane
vitreous chamber: persistent primary vitreous
When are persistent pupillary membranes clinically significant?
if they contact the lens (cataract) or the cornea (fibrous dysplasia and opacity) where they can interfere with proper development

What is this?
persistent pupillary membrane
What is the most common cause of glaucoma and blindness in horses?
equine recurrent uveitis
What is uveodermatologic syndrome?
immune mediated condition targeting a protein involved in melanin production within melanocytes causing dermal depigmentation and bilateral uveitis → blindness; breeds predisposed = akitas, siberian huskies, samoyeds, and australian shepherds
What are the two subcategories of lens induced uveitis?
phacolytic uvities: mild lymphoplasmacytic anterior uveitis as a result of cataracts and leakage of lens proteins
phacoclastic uveitis: immune mediated disease resulting in the release of large amoutns of lens protein → foreign body reaction → granulomatous inflammation
What causes phacoclastic uveitis in rabbits?
encephalitozoon cuniculi
How does FIP cause ocular disease?
replication in macrophages → type III and type IV hypersensitivity response → vasculitis → pyogranulomatous to lymphoplasmacytic panophthalmitis to uveitis
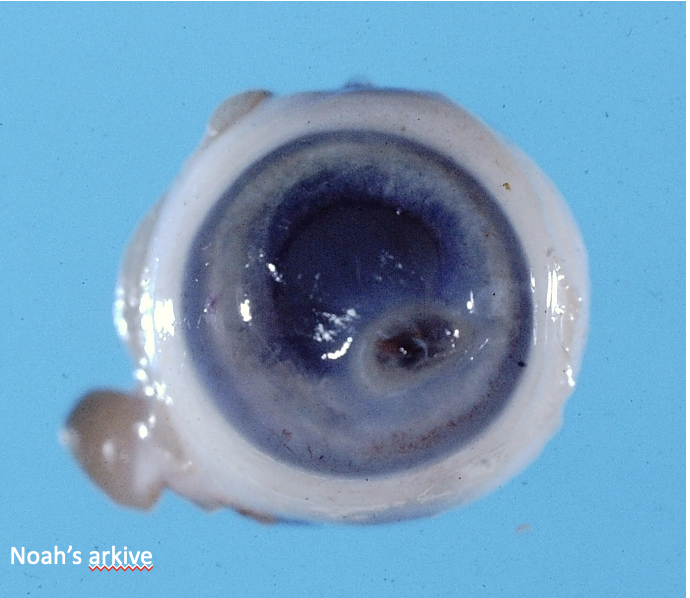
What is affecting this feline eyeball?
FIP
How does blastomycosis cause ocular disease in dogs?
systemic fungal infection that causes severe pyogranulomatous endopthlamitis to panophthalmitis
What is the most common type of uveal neoplasia?
melanocytic neoplasia
What are some characteristics of ocular melanosis?
Carin terriers predisposed
slow progressive infiltration of the uvea by melanophages and melanocytes without mass formation
extends along the choroid and into the optic meninges
often unilateral at presentation, can progress to bilateral
What is a melanocytoma/malignant melanoma?
tumor in dogs most commonly found on the iris or ciliary body
What is the most reliable indicator of malignancy of a melanocytoma?
mitotic count > 4 per 10 HPF differentiates a benign melanocytoma from a malignant
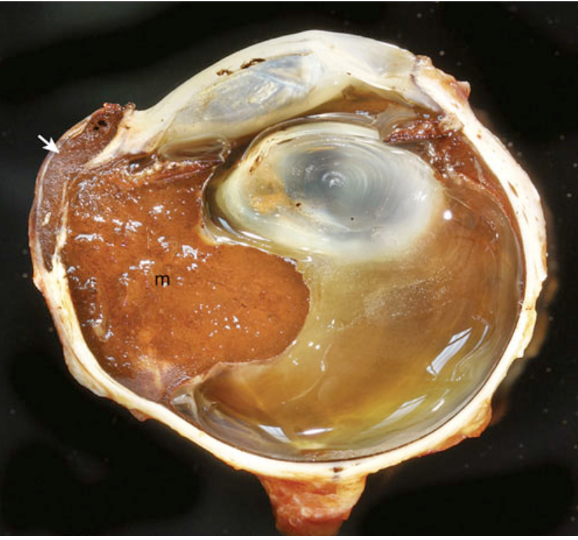
What is this?
melanocytoma
What is the common ocular neoplasm in cats?
feline diffuse iris melanoma
What are the characteristics of feline diffuse iris melanoma?
focal or multifocal to coalescing regions of iris hyperpigmentation which coincides with collections of neoplastic melanocytes
initially affects iris → infiltration of ciliary body which increases risk of metastatic spread
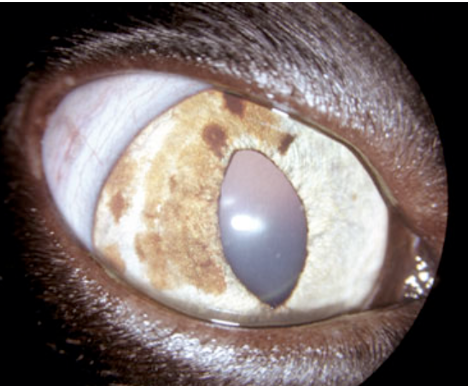
What is this?
feline diffuse iris melanoma
What ocular disease is associated with the iris in gray horses with cutaneous melanomas?
equine intraocular melanocytic neoplasia (EIMN)
What is the difference between primary or secondary lens luxation?
primary:
no known trauma or ocular disease
congenital vs. spontaneous
may be bilateral
associated with abnormal or insufficent lens zonules
secondary:
due to excessive stretching of zonular ligaments due to glaucoma (with bupthalmos), space occupying mass, or severe cataracts
What can happen if a lens luxates into the anterior chamber?
pain and glaucoma

What has occurred here?
anterior lens luxation
How does diabetic cataracts occur (usually in dogs)?
high levels of glucose within aqueous humor → excessive glucose absorbed by lens → transformed by aldose reductase enzyme into sorbitol → accumulation of sorbitol → hyperosmotic effect → influx of fluid → opacity and apoptosis of lens epithelial cells
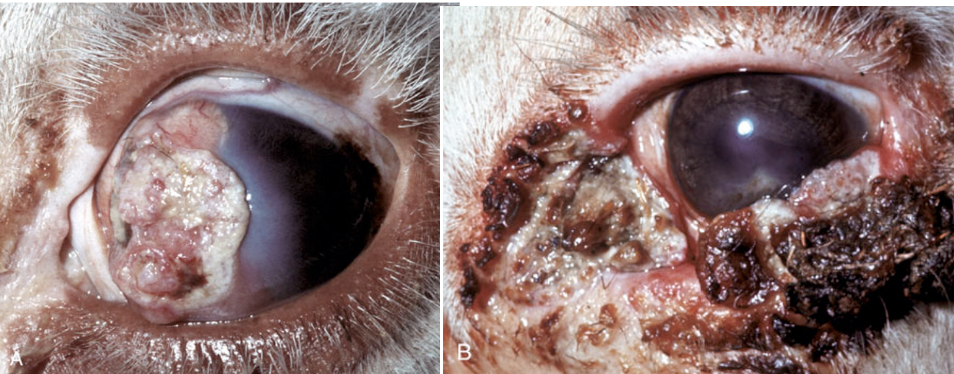
What is feline posttaumatic ocular sarcoma?
2nd most common primary ocular neoplasm in cats
ocular trauma → period of dormancy → neoplastic transformation to a sarcoma
lens capsule rupture present in all causes and neoplasms are centered around the lens
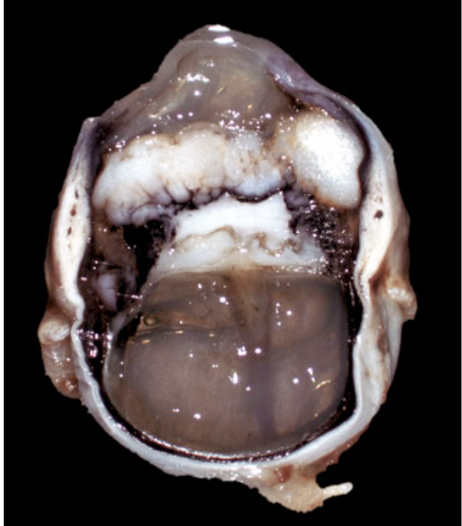
What is this? (feline)
feline posttraumatic ocular sarcoma