Secondary structure
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what is Secondary structure
it is the local spatial arrangement of backbone ignoring side chains. Usually B pleated sheets and a helicalase
what bonds are important in α-helices and β-sheets
Hydrogen bonds
in hydrogen bonds which group is Donner and which is acceptor
The group that provides the hydrogen atom is referred to as the hydrogen bond donor (e.g. N-H) ; the group that provides the lone pair is referred to as the hydrogen bond acceptor (e.g. N)
what is stronger covalent or hydrogen bonds?
Covalent
what is the bond dissociation energy for a hydrigen bond?
2-40 KJ/mol
what is bond dissociation energy for a covalent bond?
359 KJ/mol
which is a longer bond hydrogen or covalent bonds?
hydrogen bonds are longer
Bond length for hydrogen bond
~ 2 Å
bond length for a single covalent bond
~ 1 Å
how does H bonding work in alpha helix
x + 4 rule
a carbonyl group forms a hydrogen bond with an anime group 4 positions down
this patters stabilizes the alpha helix structure
where do teh side chains face in the chain
face outwards so steric interference (when atoms are too close together form repulsion) is avoided with backbone or other side chains
Each residue is related to the next one by a rise of.. and a rotation of…
1.5 Å
100 degree rotation
how many amino acid residues per turn
3.6 amino acid residues per turn
what is the pitch
the vertical distance the helix rises by each turn
it is the rise between 2 amino acids x the amount of residues per turn
for alpha helix what is the pitch
5.4 Å
what is the screw sence
the direction in which the helicase twists
alpha helicase can be
right handed (twists clockwise N→C, most common)
or
Left handed (twists anticlockwise)
in B -sheets …
neighboring stands H bonds together between C=O and N-H groups
in parallel β-sheet…
stands run in the same direction
NH group of one stand is HB to a C=O of adjacent stand , this C=O is also HB to a amine group 2 residues down the chain
in antiparallel β-sheet
stands run in opposite directions
the C=O groups and NH groups are hydrogen bonded to NH and C=O groups on adjacent stand

what is the distance between 2 adjacent amino acids
3.5 Å
side chains of adjacent amino acids….
point in opposite directions
what can loops and turns do
they connect α-helices and β-sheets and can also cause a change in the polypeptide direction
Loops
Can vary in length and shape
located on the surface of proteins, usually on polar AA
Turns
when have a loop that is 3-6 AA, a regular hydrogen bond pattern, and specific dihedral angles are called β-turn
β-turn
or also called reverse turn
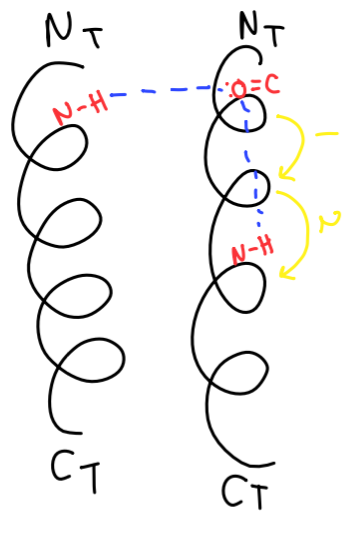
turn 180 dregrees involving 4 amino aicd resiudes
the C=O at point x is HB to NH group on residue x+3
this interaction stabilized ppt chain from any abrupt changes in direction
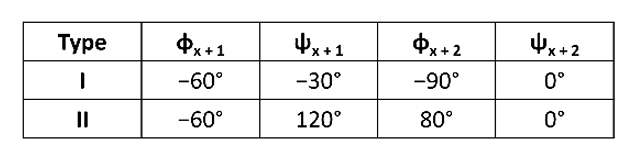
different classes of β-turns depedning on Psi and Pie angles at x+1 and x+2
there are TI and TII
φ and ψ angles of the residues at positions x + 1 and x + 2
The x + 2 residue of the type II turn can only be occupied by glycine
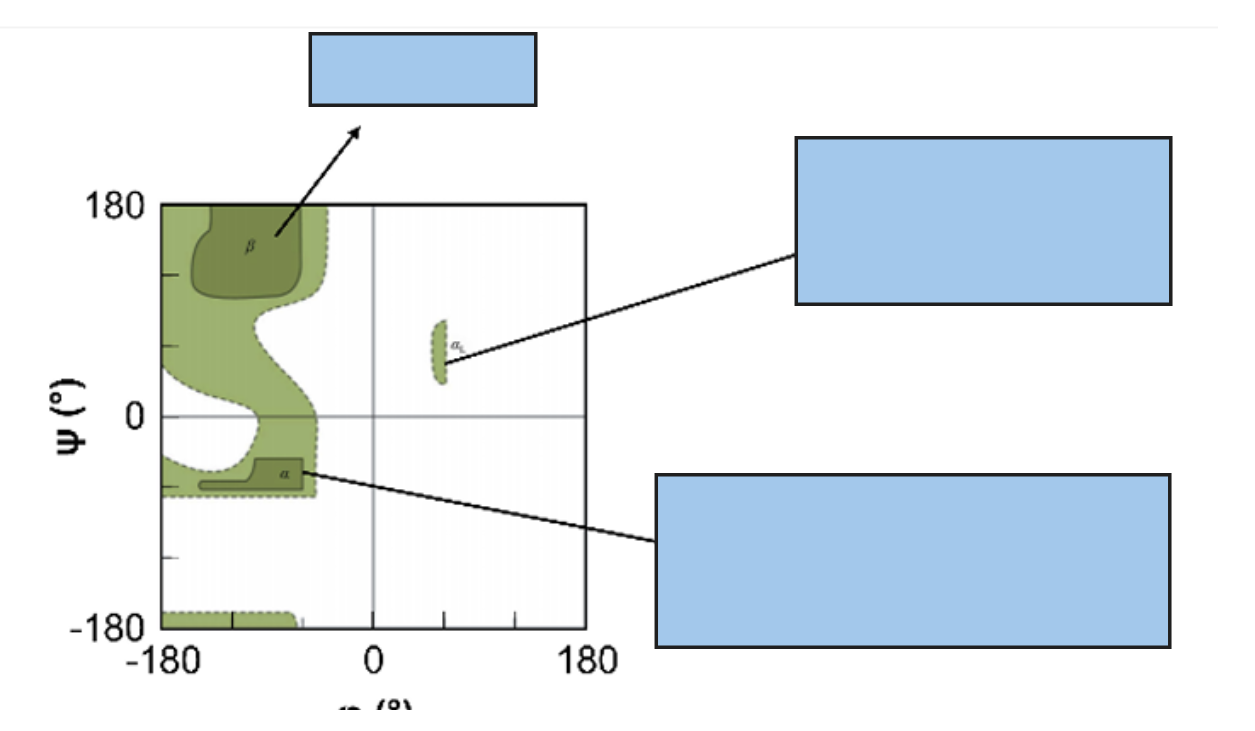
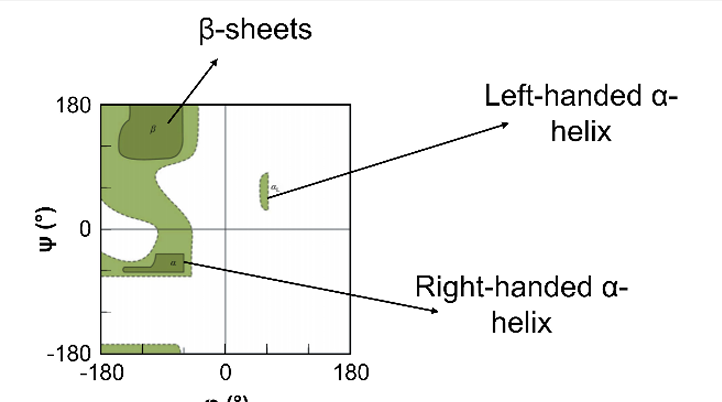
which amino acids are most likely to be α-helix former’s
Alanine
Glutamic acid
Methionin
Which amino acids are β-sheet formers
Isoleucine
Valine
Tyrosine
whic amino acids are most likely β-turns
Asparganine
Glycine
Proline
when Proline is involed
60% of bonds are in cis configuration
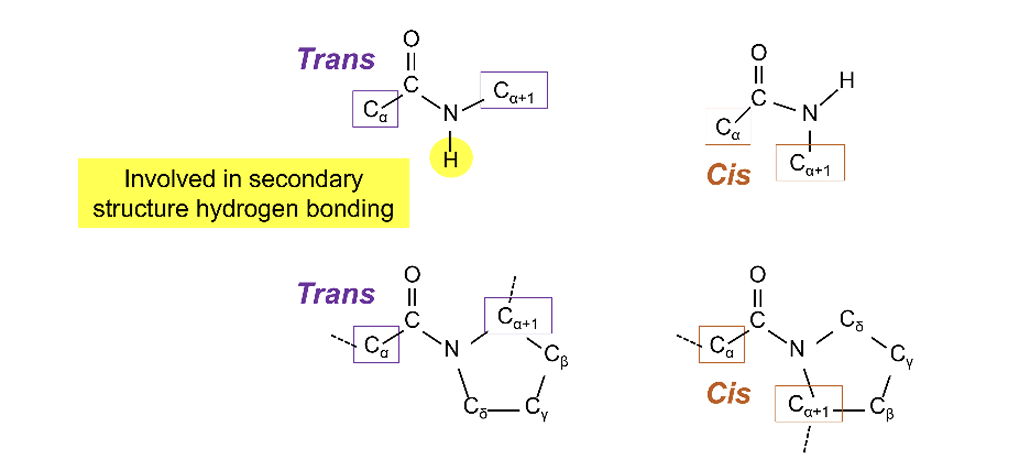
why does Prolines are rarely found in α-helices and β-sheets
doensnt really ahve H to take part in HBC
no rotation aroudn C-N bond so produced destabilizing kink in an α-helix