PT 606 FINAL
1/349
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
350 Terms
job of the bursae
prevent rubbing between supraspinatus and superior acromion
- reduce friction
- non-contractile tissue
Causes of adhesions
Collagen loses its elasticity and ability to glide due to adhering to surrounding structures
- not mobilized in a timely manner and cause adhesions in a nearby structure
Contracture
adhesive tissue shortening, long-term, ADAPTIVE, permanently shortened
- hypOmobility
Synvitis
inflammation of a joint
Hemarthrosis
bleeding within a joint
Contusion
capillary rupture, bleeding due to direct blow
- present in soft tissue
- SEVERE tissue compression
Ganglion
fluid-filled cyst; along a tendon
NON-contractile
capsule, ligaments, bursa, labrum
Contractile
muscle and muscle-tendon unit
Capsular pattern
predictable loss of ROM; proportional
NON-capsular pattern
no pattern, no predictable loss
Contents of the subacromial space
Supraspinatus tendon
Infraspiantus tendon
Teres minor tendon
subscapularis tendon
biceps tendon
transverse humeral ligament
subacromial burse
Primary impingement
> 35 years old
structural, anatomical
Fault or abnormality
Example of primary impingement
- altered acromial shape
- thick coraci-acromial ligament
- inflammation/thickening of tendons
- inflamed RC tendons
Secondary impingement
late teens- 20s
vigorous overhead activities
biomechanical, muscular weakness, altered muscle timing, postural impairment
Example of secondary impingement
-rotator cuff weakness
-scapular muscle weakness
- altered force couples
- postural impairment
- posterior capsule tightness
- excessive thoracic flexion
Prognostic factors that impact healing (negative)
Age >70
Tear size
Fatty deposits
low bone mineral density
high physical activity
Comborbid factors impacting healing
CVD, smoking, diabetes
Circulation of lymph
secrete fluid into the interstitial space (Start)
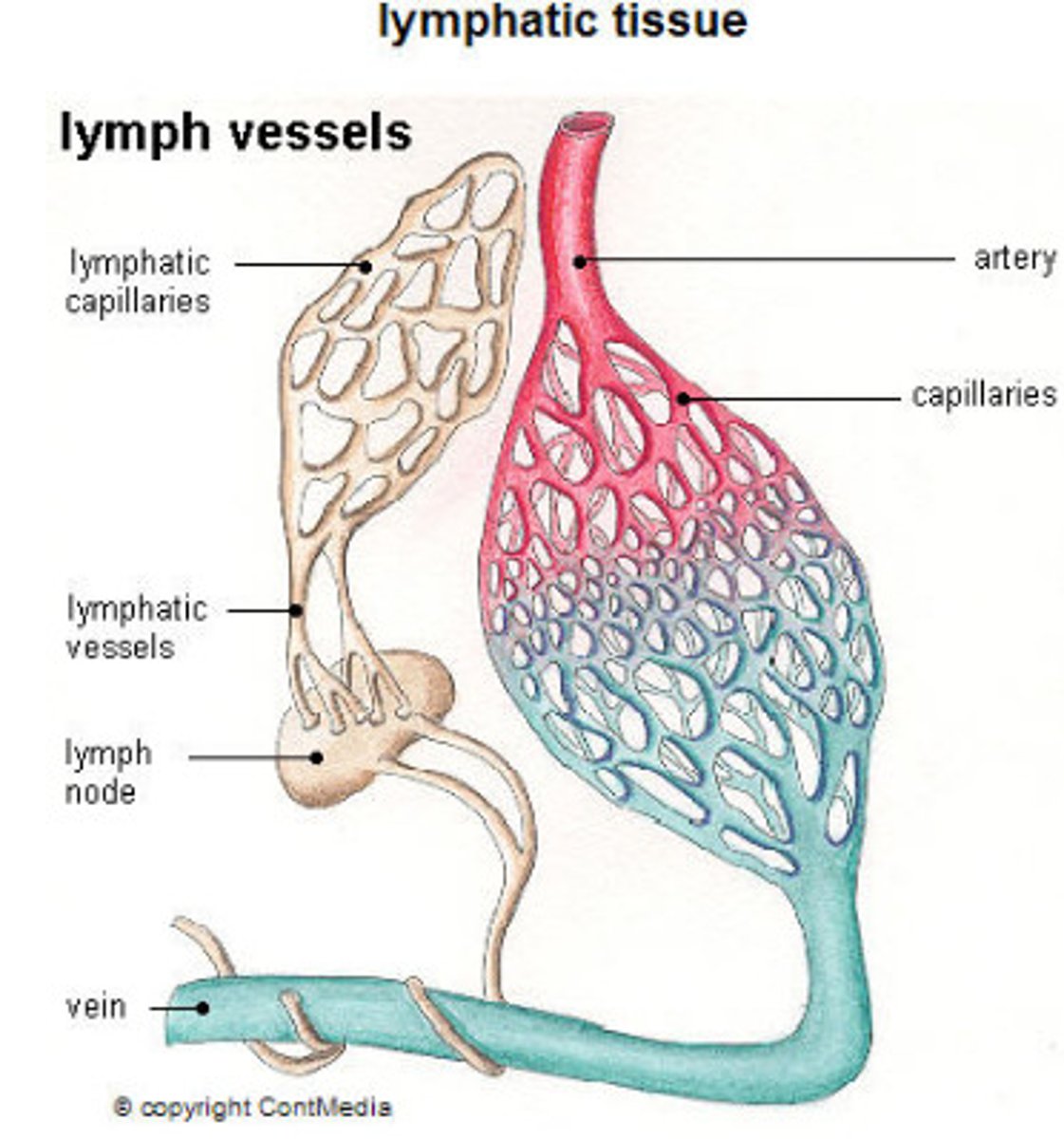
Once fluid enters the lymphatic vessels, it is known as _____
lymphatic fluid or lymph
Composition of lymph
rich in
- protein
- white blood cells
- fat
- metabolites
- waste products
________% of fluid from the arteries into the interstitium is reabsorbed by the venous system, the remaining _____% returns via the lymphatic system
90% is reabsorbed by the venous system
10% returns via the lymphatic system
Lymph moves both ways or just one way?
ONE WAY! from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck
The pathway of lymph
lymphatic capillaries --> collectors --> lymph nodes --> trunks --> lymphatic ducts -->subclavian vein
What does lymphatic flow rely on?
Intrinsic muscle contractions (within the vessel walls)
- occurs at a rate of 6-10 times per minute
what increases lymphatic flow
heat, exercise, inflammation
Circulation of lymph
Arterial blood -->
supplies nutrients and O2
-->
tissues and organs -->
excess fluid + waste + protein + fats -->
interstitium --> lymph vessels --> lymph --> veins
Functions of lymph
maintains healthy connective tissue
removes fluid, foreign particles, proteins, and fats from tissue (return to blood stream)
protects the body from infection and disease
Lymphedema
abnormal accumulation of protein-rich fluid in the interstitial tissues (leading to swelling)
- most common in the extremities
Lymphedema occurs when ______ exceeds ______
when lymphatic load (LL) exceeds the transport capacity (TC)
lymph time volume
the amount of lymph transported per unit of time
transport capacity (TC)
the maximum lymph time volume
Pathology of lymphedema
impaired lymphatic system = buildup of protein molecules in the interstitium = too large to pass = physiological changes in the tissue (overtime) = fibrosis and continuous pull of water into the interstitum
Dynamic insufficiency
when a healthy lymphatic system is overladed
dynamic insufficiency examples
sprained ankle, DVT, cardiac edema resulting in low protein edema
Mechanical insufficiency
when the lymphatic system is diseased, resulting in a high-protein edema
primary lymphedema
hereditary, congenital
- too few or abnormal lymph vessels
Secondary lymphedema
caused by damage, inflammation, or blockage of lymph vessels
- surgery
- infections
- tumors
- radiation
- filariasis
stages of lymphedema
Subclinical (stage 0)
Stage I
Stage II
Stage III
Subclinical, stage 0 (lymph)
feeling of heaviness in the limb without visible swelling
Stage I (lymph)
pitting edema is present, high water content, swelling reduced with elevation; it is reversible
Stage II (lymph)
non-pitting edema is present, not reduced by elevation, with moderate to severe clinical fibrosis
Stage III
Elephantiasis, skin changes, and lobules are present
Venous edema
hemosiderin staining, fibrosed/brawning subcutaneous tissue, pitting, atrophic skin, malleolar ulcerations
Cardiac edema
swelling greatest distally, sudden weight gain, bilateral nad symmatrical pitting, decrease with elevation
lipedema
occurs in women, bilateral symmetrical swelling from iliac crest to ankles
(Dorsum of foot NEVER involved; little to no pitting, painful to palpation and bruises easily)
Diagnosis of lymphedema
Lymphography
Doppler ultrasound
CT
MRI
- must rule out DVT, malignancy, cardiac issues
Compression garments
custom made garments (similar to short-stretch bandages)
- worn during the day
- recommended 20 hours per day
Classes of compression garments
Class I: 20-30 mmHg
Class II: 30-40 mmHg
Class III: 40-50 mmHg
Class IV: 50-60 mmHg
Complex Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
Phase I = reductive phase
Phase II = maintenance phase
Pneumatic compression
- inflates from distal to proximal (wave of pressure to move fluid)
- 80-110 mmHg for 4-8 hours
pros and cons of pneumatic compression
P
- used for patients unable to attend treatment or bandage, minimal fibrotic changes, use is controversial
C:
- can cause fibrotic bands, does not address truncal edema, can cause genital edema, patient is inactive
Contraindications for CDT
General
- acute infection
- cardiac edema
- malignant disease
Compression
- arterial disease
- CHF
- HTN
- Diabetes
- sensory neuropathy
MLD
- pregnancy
- recent surgery
- cardiac arrhythmias
- Congestive heart failure
General precautions for lymphedema
- avoid extreme hot (climates, showers, baths, saunas)
- no BP cuffs on affected side
- mani/pedi at salon
- insect bites, needle punctures, cuts, deep massage
Decongestive exercise
walking/cycling
arm ergometer
the limb must be wrapped
Sensitivity
ability of the test to obtain a positive test when the target condition is present (true positive)
Sensitivity calculation
Sensitivity = A / A+C
(LEFT column)
Specificity
ability of the test to obtain a negative test when the condition is absent (true negative)
Specificity calculation
D / B + D
(right column)
Specificity/sensitivity table
Left column = sensitivity
Right column = specificity
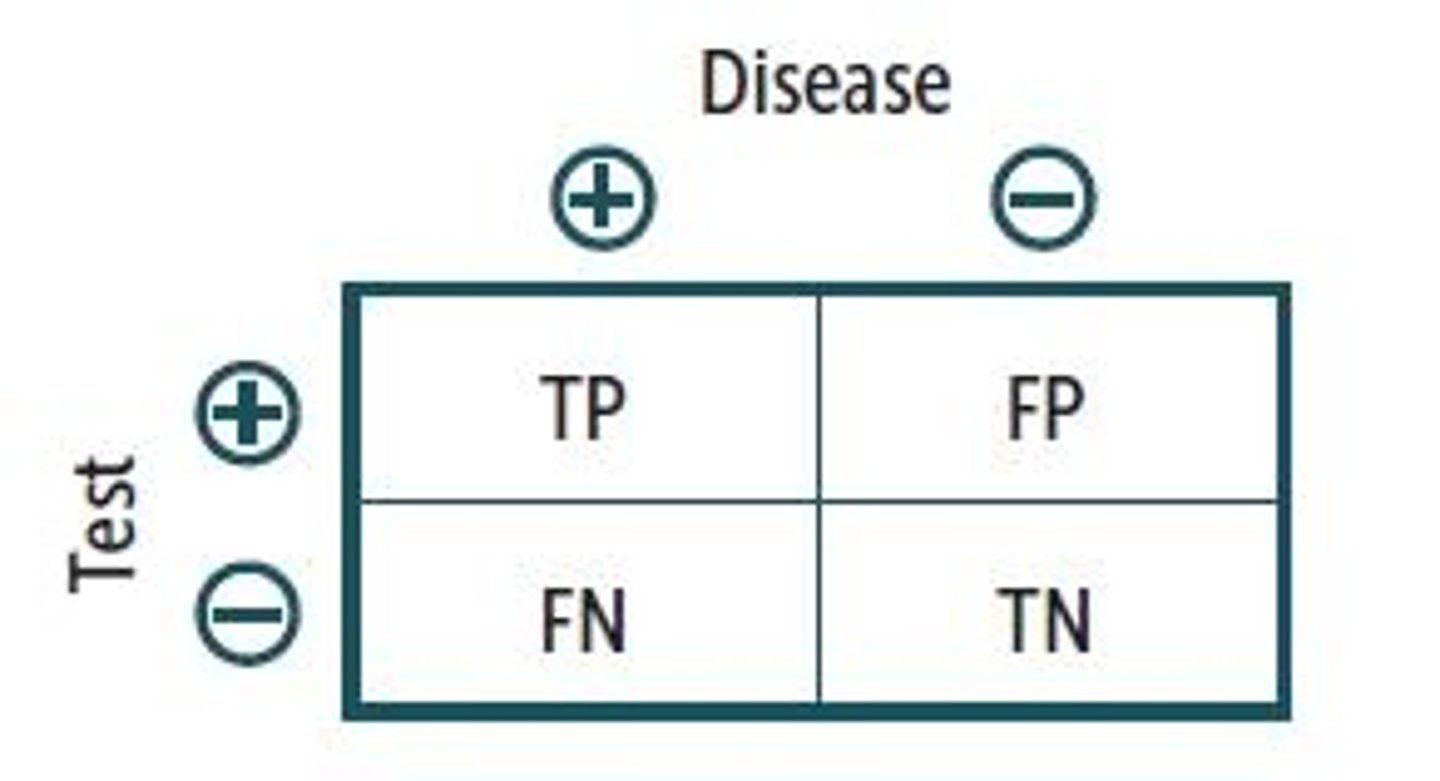
PPV =
A/A+B
(true positive / true positive + false positive)
NPV =
D/C+D
(true negative / true negative + false negative)
Prevalence calculation
A+C/A+B+C+D
Likelihood ratios
Large +LR = ruling in the condition (+LR>1)
Small -LR= ruling out the condition (-LR<1)
Close to 0 = no diagnostic value (LR=1)
"SPIN"
Spin = specificity = rule IN
"SNOUT"
Snout = sensitivity = rule out
AROM
stresses contractile and non-contractile tissues
PROM
stresses non-contractile tissue
Resisted ISO
assess the neuromuscular system
joint play
stresses non-contractile tissue
Weak and painful
Contractile
Strong and painful
minor contractile
Weak and painless
neurological impairment, complete contractile tissue rupture
Pain with repitition
vascular insufficiency
Strong and painless
Normal
"itis"
inflammation
"opathy"
degenerative
Arthrokinematics
Roll
Glide/Slide
Spin
Convex on Concave
Gliding/sliding in the OPPOSITE direction as the movement of the bone
Concave on convex
sliding/sliding in the SAME direction as the angular movement of the bone
Glide/slide
applied parallel to the treatment plane
- unweight joint (grade I distraction) prior
Distraction technique
applied perpendicular to treatment plant
GH joint Arthrokinematics
CONVEX humeral head
CONCAVE glenoid fossa
GH resting position
55 ABD
30 Horiz. ADD
Slight ER
GH posterior glide
IR
Flexion
Horizontal ADD
GH anterior glide
ER
Extension
Horizontal ABD
GH inferior glide
ABD
flex
GH Distraction
all motions, entire joint capsule
Contraindication/precautions for joint mobilization
-unstable/hypermobile
-recent fracture
- open epiphyseal plates
- joint effusion
- weakened skin
- weak bone
- local infection
- inability to relax
Joint mob assessment
Quality (crepitus, edema)
Quantity (hypomobile, hypermobile, normal)
Symptoms (pain, stiff, apprehension)
End feel (firm, hard, empty)
treatment grades
Resistance free range
tissue resistance range
R1
R2
Anatomical limit
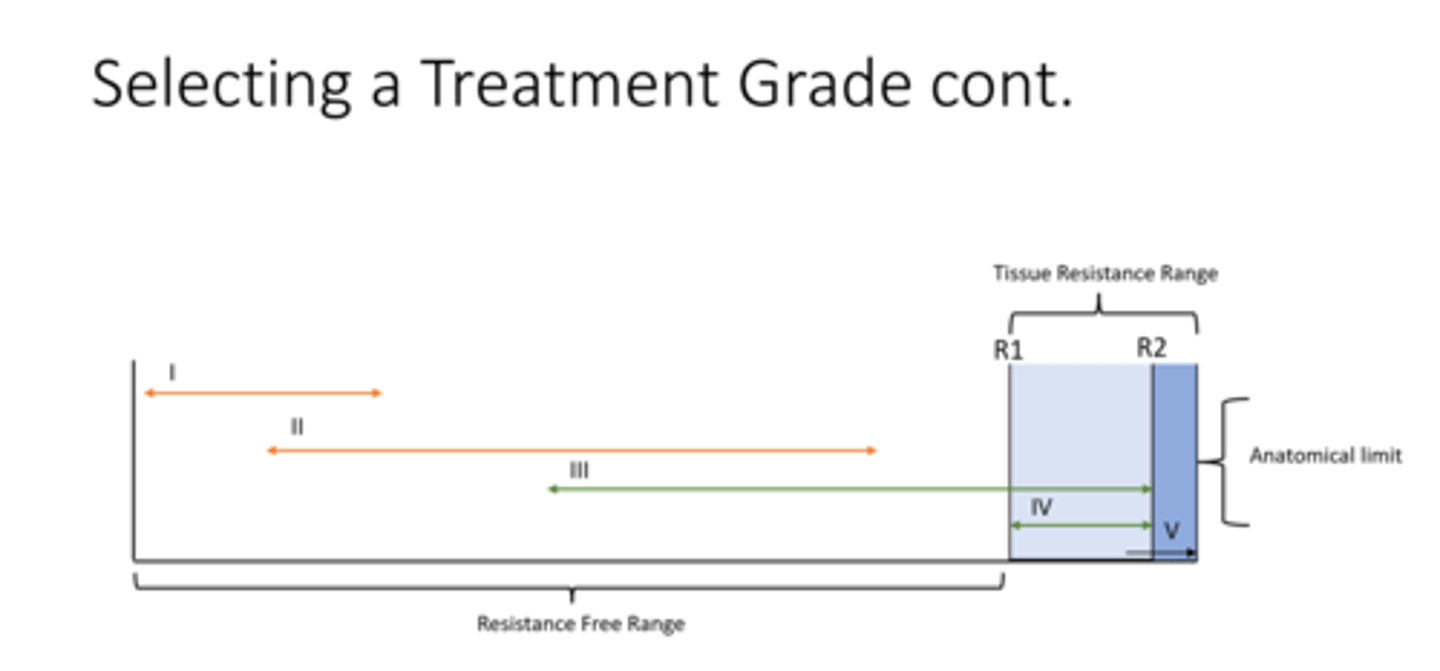
resistance free range
no tissue resistance
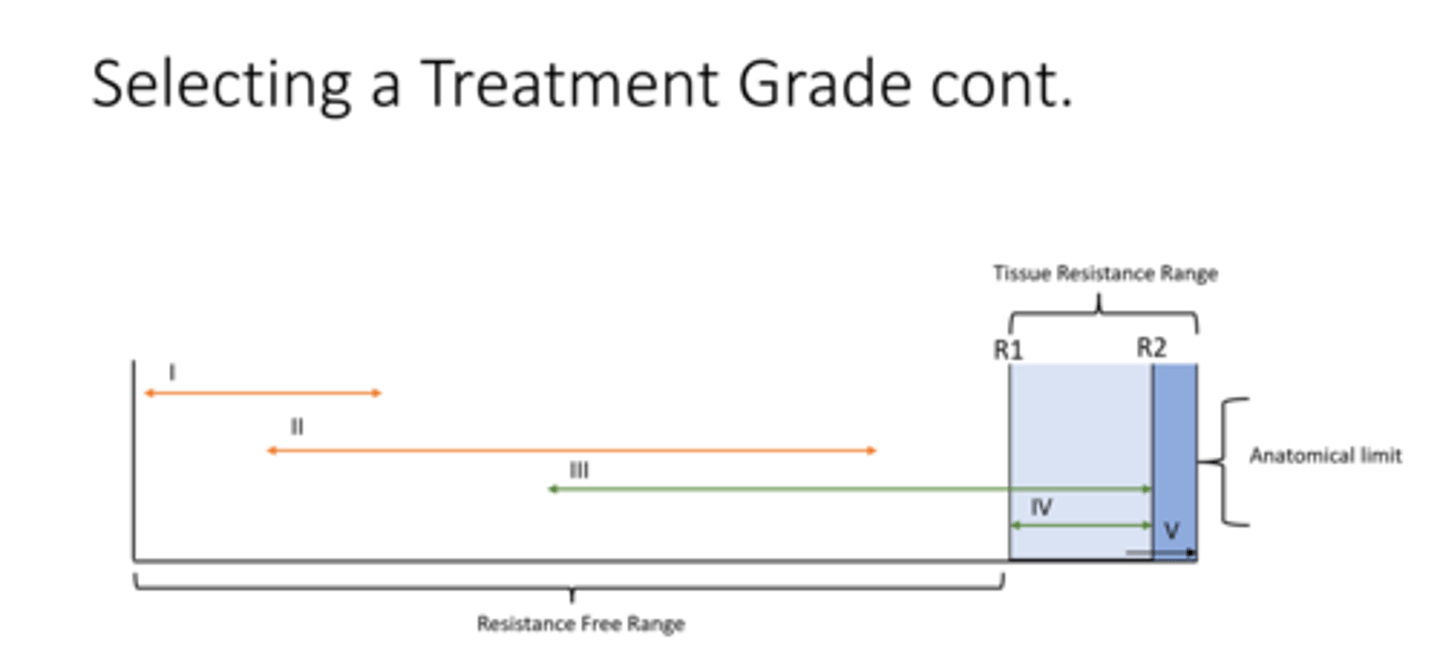
tissue resistance range
the range where there is limtation to movement for the articular surface
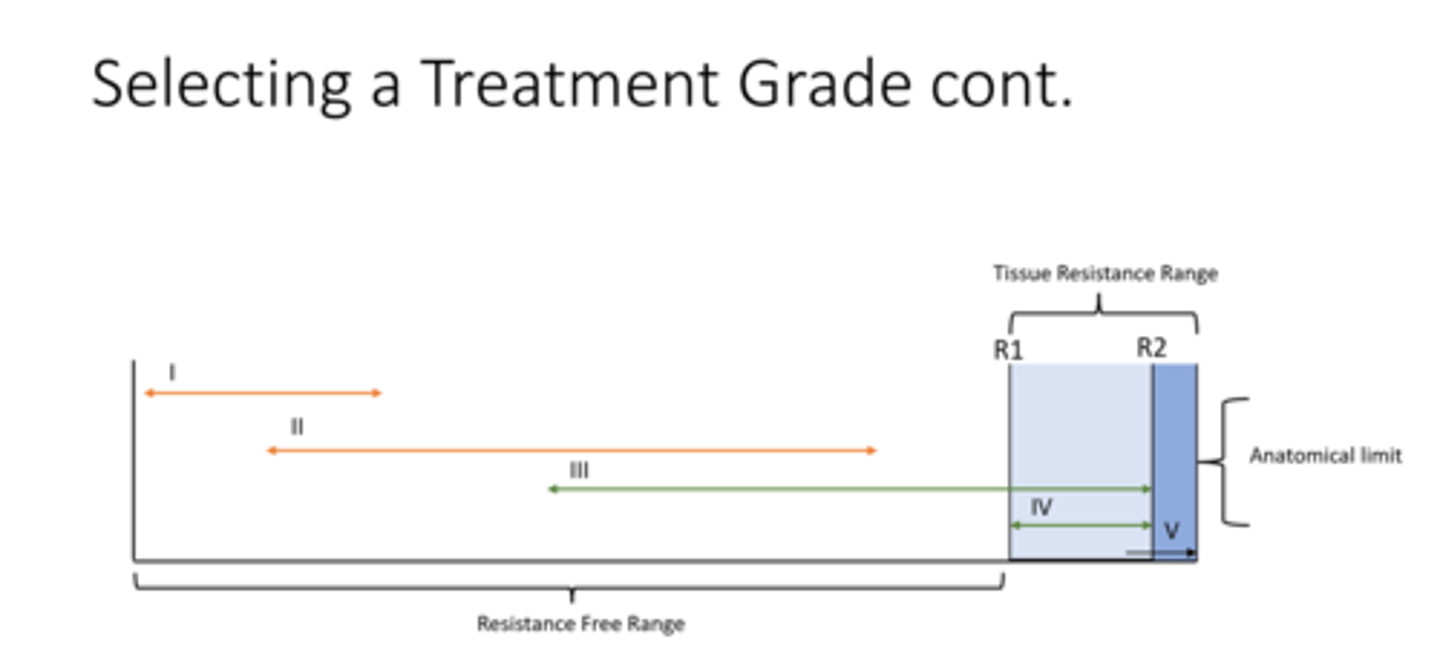
R1
initial tissue resistance (take up slack)
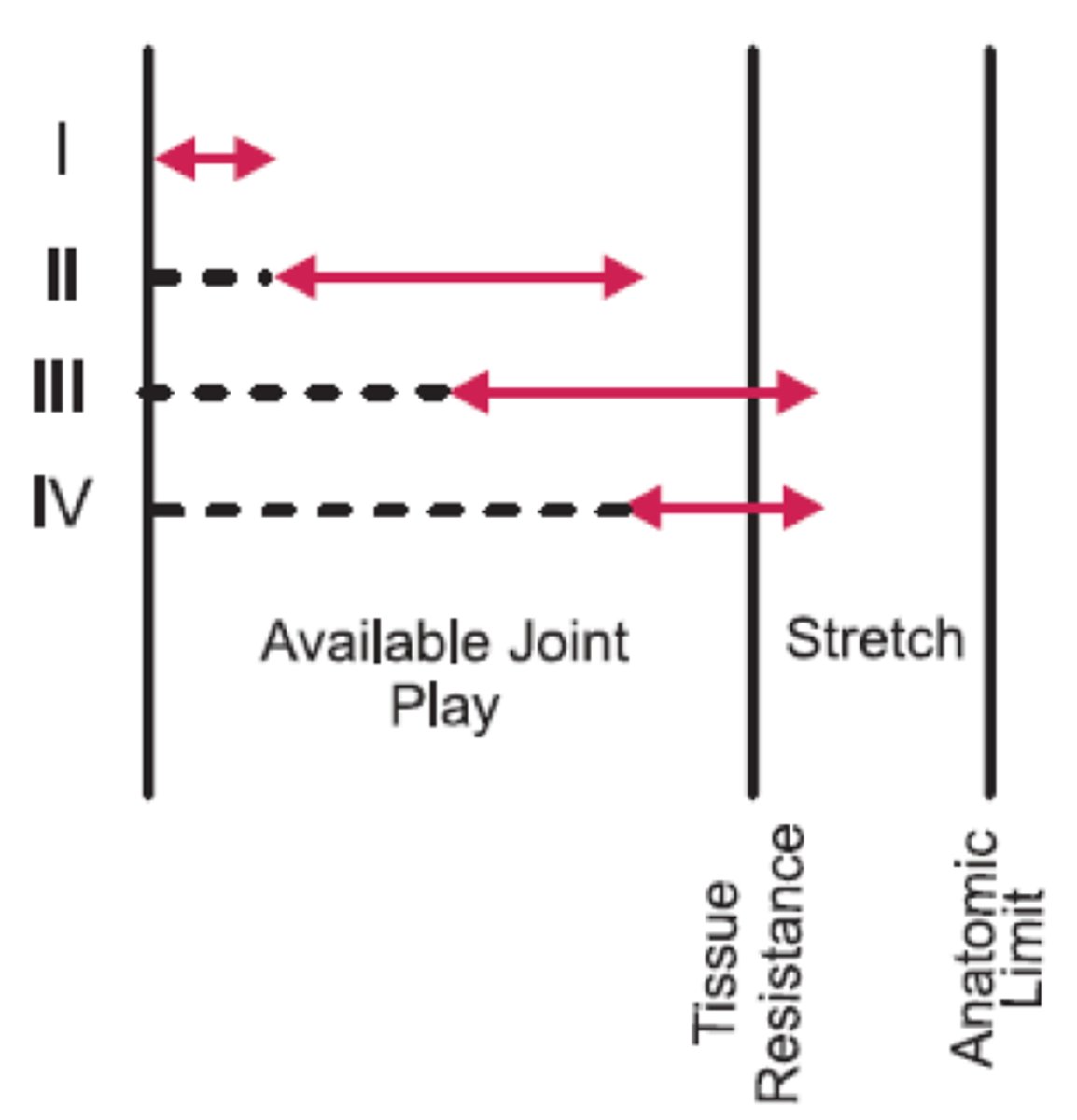
R2
tissue resistance
Anatomical limit
articular end point
pain dominant
loose packed position
grades I and II
Sustained or oscillatory
stiffness dominant
end ROM (before pain)
Grades III or IV (oscil)
Grades II or III (sustained)
effects of joint mobilization intervention
- promotes synovial fluid movement
- mechanical stretch/distension
- stimulates mechanoreceptors
- incr. blood composition
- change in alpha motor neuron activity
- change in automatic response
Static/passive stability
NON-contractile tissue
- ligaments, joint capsule, labrum