BIO 141 Exam 1
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Hardcastle's BIO Exam 1
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
Which is not an example of emergent property?
A.) the heart pumping blood through the body
B.) cities
C.) organ systems
D.) organisms cells
A.) the heart pumping blood through the body
B.) cities
C.) organ systems
D.) organisms cells
Organisms cells
2
New cards
What organelle is only found in plants?
Central vacuole
3
New cards
What is stored in central vacuoles?
Anthocyanin pigments, water, and crystals
4
New cards
What is biology?
The study of life
5
New cards
How many elements are essential to life?
25
6
New cards
What is hydrogen bonding?
1\.) a type of bond holding water molecules together
2\.) hydrogen bonded to either nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine
3\.) a weak bond
2\.) hydrogen bonded to either nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine
3\.) a weak bond
7
New cards
Mass number is…
protons + neutrons
8
New cards
Which is not an isotope of hydrogen?
A.) hydrogen
B.) deuterium
C.) tritium
D.) H-13
A.) hydrogen
B.) deuterium
C.) tritium
D.) H-13
H-13
9
New cards
What is covalent bonding?
Sharing of electrons between two atoms
10
New cards
What percent of cells are made up of water?
70-95%
11
New cards
What is tetravalency?
4 valence electrons, the ability to form 4 bonds
12
New cards
What are the emergent properties of water?
cohesion/adhesion, moderation of temperatures, insulation of bodies of water by floating ice, solvent of life
13
New cards
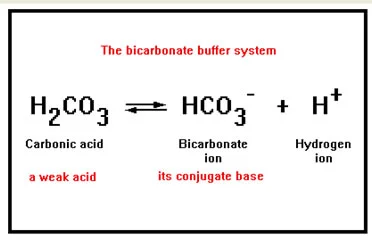
What happens in the bicarbonate buffer system when H+ ions are added to the system?
rxn shifts to the left and the bicarbonate ion accepts more H+
14
New cards
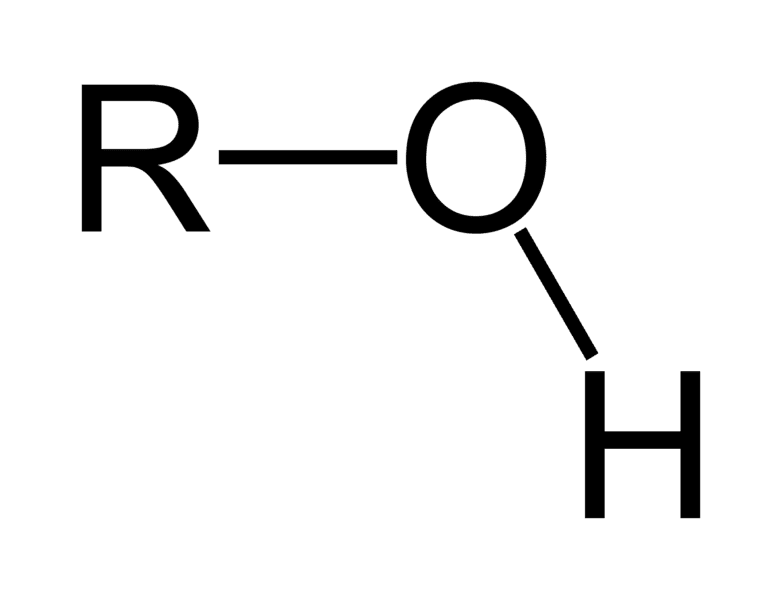
Name the functional group
hydroxyl
15
New cards
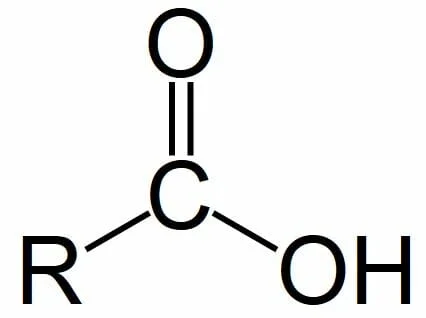
Name the functional group
carboxyl
16
New cards
what are macromolecules?
large molecules essential for life
17
New cards
17 T/F: Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids are macromolecules?
17 True
18
New cards
What type of bond is a glycosidic linkage?
covalent bonds
19
New cards
what is the primary function of cellulose?
cell wall structural support
20
New cards
what is dehydration synthesis?
removing a water molecule to bind two molecules together
21
New cards
What is the main function group present in carbohydrates?
carbonyl
22
New cards
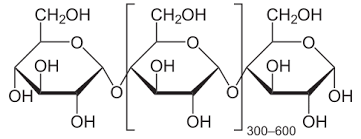
identify this structures primary function
plant food storage
23
New cards
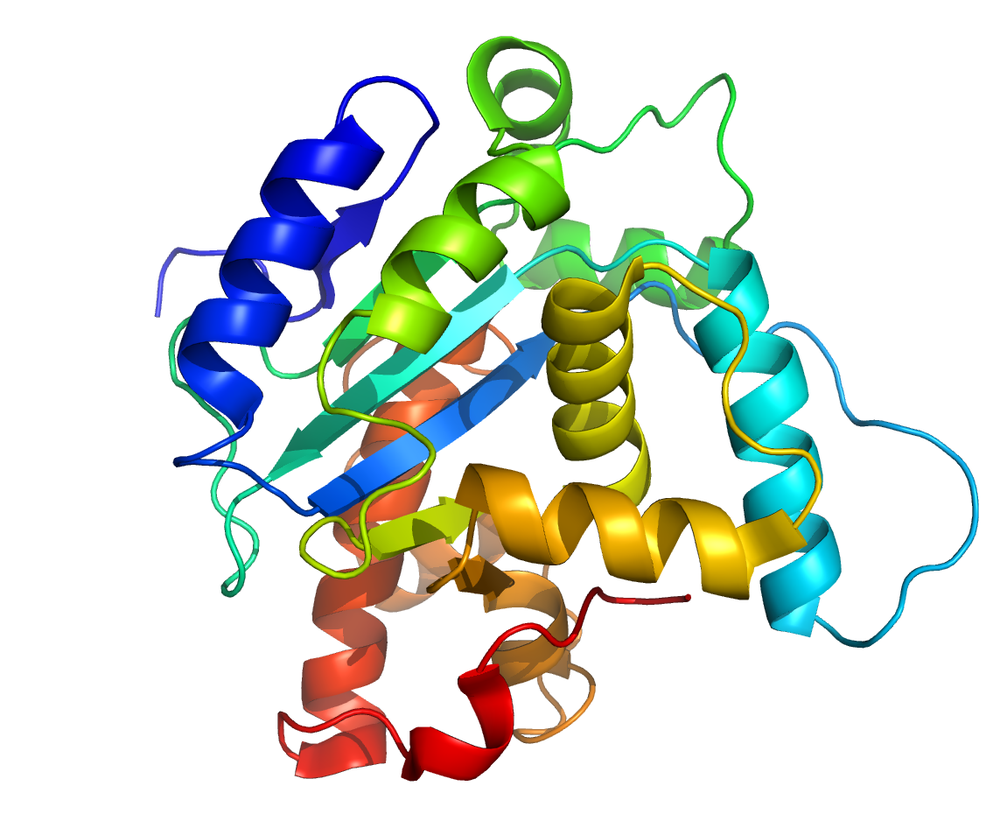
what type of structure is this protein displaying?
tertiary
24
New cards
T/F denaturing a protein is reversible.
False
25
New cards
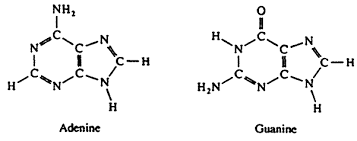
Is this structure purine or pyrimidine?
purine
26
New cards
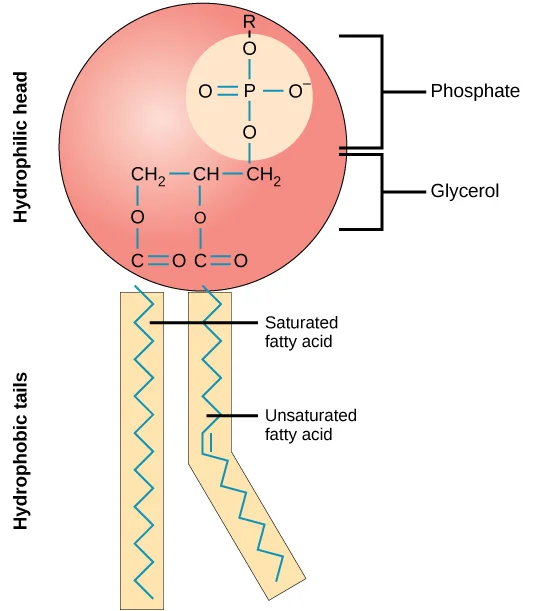
what is unique about this structure?
A.) it contains 3 fatty acids
B.) it forms hydrogen bonds
C.) found in hormones
D.) it is an amphipathic molecule
A.) it contains 3 fatty acids
B.) it forms hydrogen bonds
C.) found in hormones
D.) it is an amphipathic molecule
it is an amphipathic molecule
27
New cards
what type of microscope produces a 3-D image?
scanning electron microscope
28
New cards
T/F Hypothesis are concrete (non-changeable) answers to questions.
false
29
New cards
what electrons are most important in creating chemical bonds?
valence electrons
30
New cards
what does chemical equilibrium mean? (two answers)
A.) the reaction is balanced
B.) the amount of reactants and products are always equal
C.) the rates of both the forward and backward rxn are equal
D.) the chemicals are the same in both the reactants and products
A.) the reaction is balanced
B.) the amount of reactants and products are always equal
C.) the rates of both the forward and backward rxn are equal
D.) the chemicals are the same in both the reactants and products
the amount of reactants and products are always equal, and the rates of both the forward and backward rxn are equal.
31
New cards
what type of microscope is used most often in lab?
light microscope
32
New cards
why do humans sweat and dogs pant to cool themselves on hot days?
the warmest molecules turn to gas first and lowers body temperature.
33
New cards
which is not found in prokaryotic cells (two choices)
A.) nucleus
B.) DNA
C.) cell membrane
D.) endoplasmic reticulum
A.) nucleus
B.) DNA
C.) cell membrane
D.) endoplasmic reticulum
nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum
34
New cards
Function of nucleolus
ribosome synthesis
35
New cards
How does DNA spend 95% of its time in the nucleus?
A.) chromatin (relaxed state)
B.) supercoiled/ condensed
A.) chromatin (relaxed state)
B.) supercoiled/ condensed
chromatin (relaxed state)
36
New cards
Which is not a function of central vacuoles?
A.) storage
B.) support
C.) metabolism
D.) transportation
A.) storage
B.) support
C.) metabolism
D.) transportation
transportation
37
New cards
Why do organisms enter endosymbiotic relationships?
both organisms benefit from it
38
New cards
What process does mitochondria go through?
Cellular respiration
39
New cards
What is the function of chloroplast?
photosynthesis
40
New cards
How many separate sets of genes do plants have?
3 sets
41
New cards
How many sets of genes do animals have?
2 sets
42
New cards
What is the cytoskeleton?
fibers running through the cytoplasm
43
New cards
Wat is the function of microtubules during cell division?
Make spindle fibers that pull chromosomes apart
44
New cards
What protein makes microfilaments?
A.) actin
B.) tubulin
A.) actin
B.) tubulin
actin
45
New cards
How do plant cell walls stick to each other?
middle lamella