Excipients for Immediate-Release Tablets
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What are the two Types of oral tablets?
Immediate release
Modified release
What are the types of immediate release oral tablets?
Disintegrating tablets
Chewable tablets
What are the types of modified release oral tablets?
Extended/prolonged release tablets
Delayed release/gastro-resistant tablets
What defines an immediate-release tablet in terms of drug release?
Majority of the drug is released in a short time, typically 70% or Q = 75% in 45 minutes as per BP dissolution test.
Are immediate-release tablets usually coated or uncoated?
They can be either uncoated or coated.
What materials are typically used for coating immediate-release tablets?
Coatings are typically made of sucrose
or hydrophilic polymeric films.
What are some excipients used as process aids in tablet manufacturing?
Lubricants,
anti-adherents,
and glidants.
Which excipients aid in tablet formation?
Fillers/diluents
and binders.
What excipients enhance the organoleptic properties of tablets?
Coating polymers/sugar,
colourants,
flavourings.
Organoleptic properties refer to the sensory attributes of a product mainly taste, smell, color, texture, and appearance.
organoleptic properties are important because they affect patient acceptability and compliance.
Which excipients are involved in drug release and absorption?
Disintegrants,
dissolution enhancers,
absorption enhancers.
What is the primary function of a filler (diluent) in tablet formulation?
Bulk up the tablet to a minimum size
Usually >50 mg necessary for handling
Important for low-dose drugs
Name 3 common fillers (diluents) used in tablet formulation.?
Starch
Lactose
Microcrystalline cellulose
What is the role of a binder in tablet formulation?
Acts as an adhesive that makes particles stick
Increases compactability of powder mixture and tablet hardness
What is a potential downside of using excessive binder?
May hinder tablet disintegration and drug dissolution
Name common binders used in tablet formulations.
Lactose
Microcrystalline cellulose
Excipients that prevent particles from sticking
> lubricant
> anti-adherent
> glidant
What is the function of a lubricant
Reduces friction between tablet and die during tablet ejection
What is the role of an anti-adherent?
Prevents powder/tablet adhesion to punches
What does a glidant do?
Reduces powder cohesion
Improves powder flowability
Enhances mixing and content uniformity
Name 3 common lubricants, anti-adherents, and glidants.?
Magnesium stearate
Talc
Colloidal silica
What causes friction in boundary lubrication, and how do lubricants reduce it?
Friction between particles and equipment or other particles inhibits particle movement.
Small, adherent lubricant molecules coat particle surfaces in multiple layers that slide easily past one another.
Lubricants reduce particle-equipment and particle-particle interactions, lowering friction.

Which excipients commonly function as lubricants in boundary lubrication?
Magnesium stearate
Stearic acid
Talc
What additional roles can lubricants play besides lubrication?
Often act as anti-adherents and glidants.
Why can excessive amounts of hydrophobic lubricants be problematic?
They impair wetting and thus reduce dissolution of the tablet.
Excipients that break up a disintegrating tablet?
> disintegrant
> super disintegrant
> effervescent disintegrant
What is the primary function of a disintegrant in tablets?
Break up the tablet into smaller particles
Increase specific surface area and dissolution rate
Follows the principle of the Noyes-Whitney equation
Usually materials that swell upon hydration
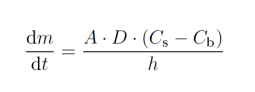
What is a superdisintegrant?
A high-performance disintegrant
Promotes more rapid disintegration compared to regular disintegrants
What is an effervescent disintegrant?
Produces a fizzing reaction on contact with water
Common in effervescent tablets for rapid disintegration and better taste masking
What is the Noyes-Whitney equation"?
The Noyes-Whitney equation describes the rate at which a solid dissolves in a liquid. It says that the dissolution rate increases when:
The surface area of the solid increases
The concentration gradient (difference between drug at the surface and in the surrounding liquid) is higher
The diffusion layer is thinner
The solvent is stirred or agitated

Excipients that enhance organoleptic properties
> coating excipients
> colourant
> flavouring
What are the functions of coating excipients?
Mask unpleasant taste
Improve ease of swallowing
Reduce friability or powdery feel of the tablet
What is the role of colourants in tablets?
Aid in tablet identification
Can be dispersed throughout the tablet, in the coating, or used as printing
What is the purpose of flavouring agents in tablets?
Enhance the taste of the tablet
Typically used in chewable tablets, not in tablets meant to be swallowed whole
Do all immediate-release (IR) tablets contain the same excipients?
No, not all IR tablets will contain all of the common excipients
Some may include other excipients not listed
What makes excipient selection complex in tablet formulation?
Many excipients are multifunctional
Some formulations include excipients with opposite effects
The same excipient can behave differently depending on its concentration
How does excipient selection impact drug release?
The formulation dictates the release profile
Different formulations can produce equivalent release profiles (bioequivalence)
What is disintegration?
first step in tablet dissolution and drug release
larger particle surface area means higher dissolution rate
it is accelerated by disintegrants
what are the 6 mechanisms of tablet disintegration?
1 swelling
2 wicking (capillary effect)
3 strain recovery
4 heat of interaction (wetting)
5 interruption of bonding forces
6 repulsion
What is the swelling mechanism of tablet disintegration? step 1
Involves hydrophilic but water-insoluble polymers
Water uptake causes the polymer to swell, increasing volume
Swelling creates internal pressure that breaks the tablet apart
Degree of swelling depends on:
• Particle size
• Degree of crosslinking
What is the wicking mechanism of tablet disintegration? step 2?
Involves the capillary effect
Creates hydrophilic pathways within the tablet
Water is drawn rapidly into the tablet through these channels
What is the strain recovery mechanism of tablet disintegration? step 3?
Particles undergo elastic deformation during compression
They become interlocked before they can relax (strain)
Water penetrates the tablet, allowing particles to relax and recover their shape
This expansion pushes other particles apart, causing disintegration
: What is the heat of interaction mechanism of tablet disintegration? step 4
Heat energy is released when particles interact with water (exothermic reaction)
Entrapped air inside the tablet absorbs this energy and expands
The expanding air pushes particles apart, leading to tablet disintegration
What is the "interruption of bonding forces" mechanism of tablet disintegration? step 5
Tablets are held together by interlocking particles and solid bridges
In the presence of water, these bonds are weakened or interrupted
Water dissolves bonding agents or forms new bonds with particles
What is the repulsion mechanism of tablet disintegration?
Water uptake causes electrostatic repulsion between particles due to ionisation of ingredients in water
Particles of the same charge are pushed apart, leading to disintegration
What are superdisintegrants and how do they work?
Cross-linked polymers
Swell extensively upon contact with water
Promote rapid tablet disintegration

How do effervescent disintegrants work?
Contain carbonate and bicarbonate salts
Under acidic conditions, these break down into CO₂ and water
Carbonate and bicarbonate must first dissociate in water before reacting
The released CO₂ causes fizzing, helping tablet disintegration
Identify the tablet type from excipients