Bones Quiz: Biomed
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What are the 4 functions of the skeletal system?
Support, mineral storage, fat storage, blood cell production
Describe support in the skeletal system
Assists with posture and protects internal organs
Describe mineral storage in skeletal system
Intercellular matrix, stores phosphate, supplies calcium to muscles and neurons
Describe fat storage in the skeletal system
Yellow marrow as a energy source
Describe blood cell production in skeletal system
red marrow, produces RBCs, WBC, and platelets
Tendons
Connects bone-to-bone
Ligaments
Connects muscle-to-bone
Orbicularis Oris
A sphincter that encloses the mouth - causes lips to close and pucker
Orbicularis Oculi
Surrounds eye and allows us to blink
Temporalis
Side of head attached to mandible allows for chewing
Facial muscles are _____ _____ _____ that connect the bones of the skull to the skin. They’re used for chewing, facial expressions, etc.
Striated Skeletal Muscle
Striations are caused by proteins called ____ & ____. These proteins allow for muscle ____.
Actin; Myosin; Contraction
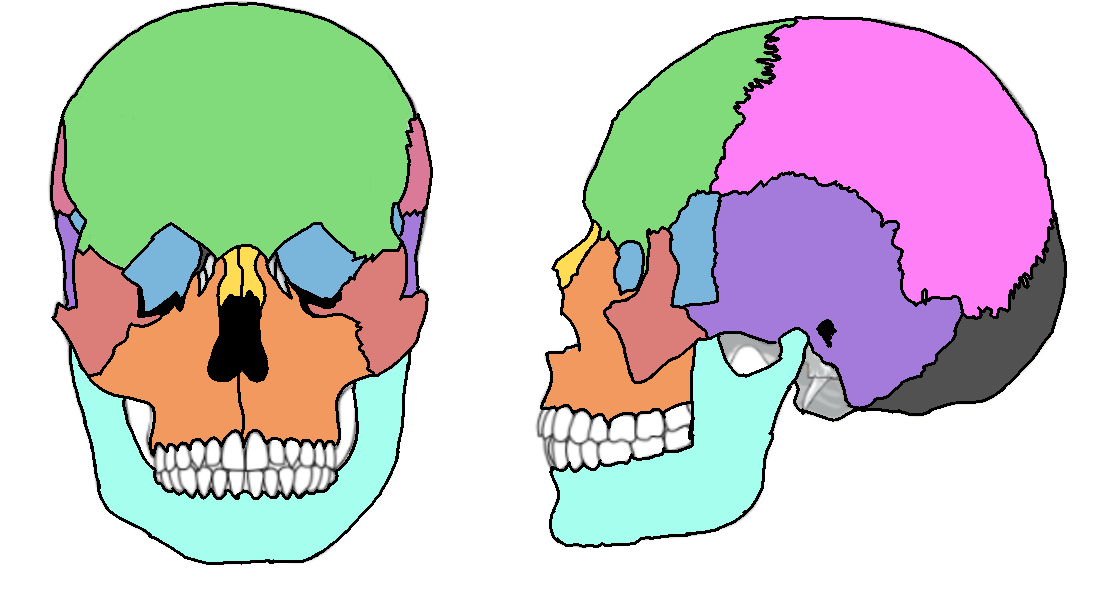
What color is the parietal?
Pink (skull)
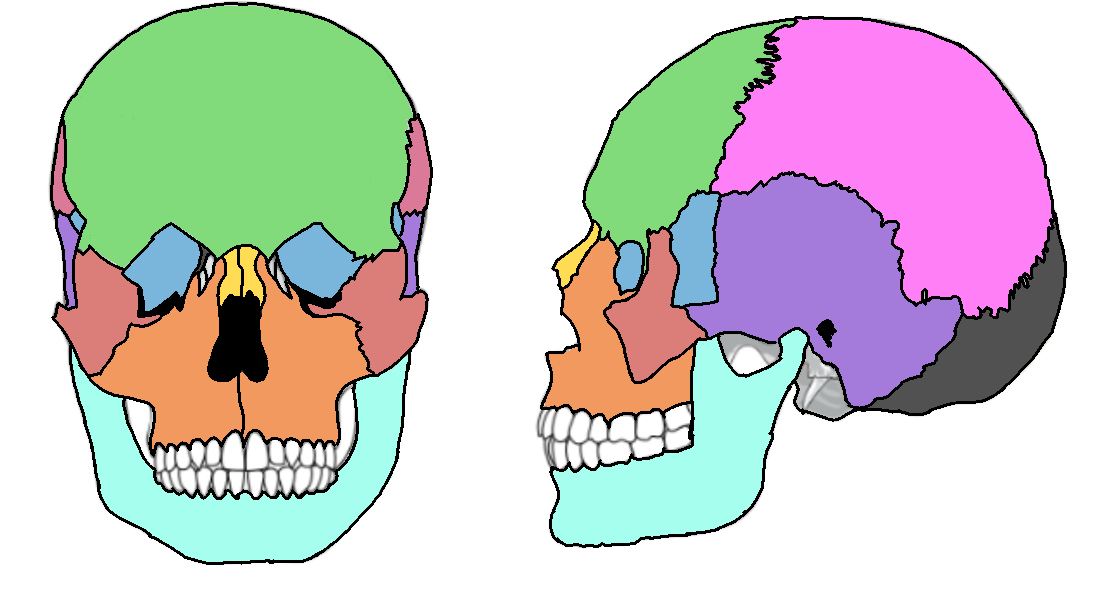
What color is the mandible?
Teal(skull)
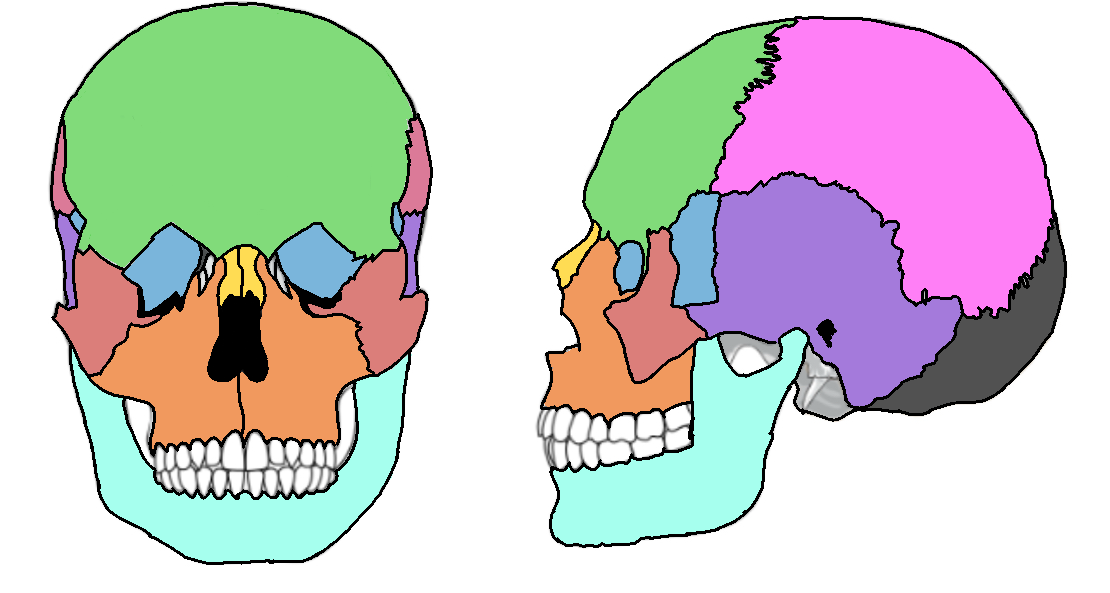
What color is the zygomatic?
Light red(skull)
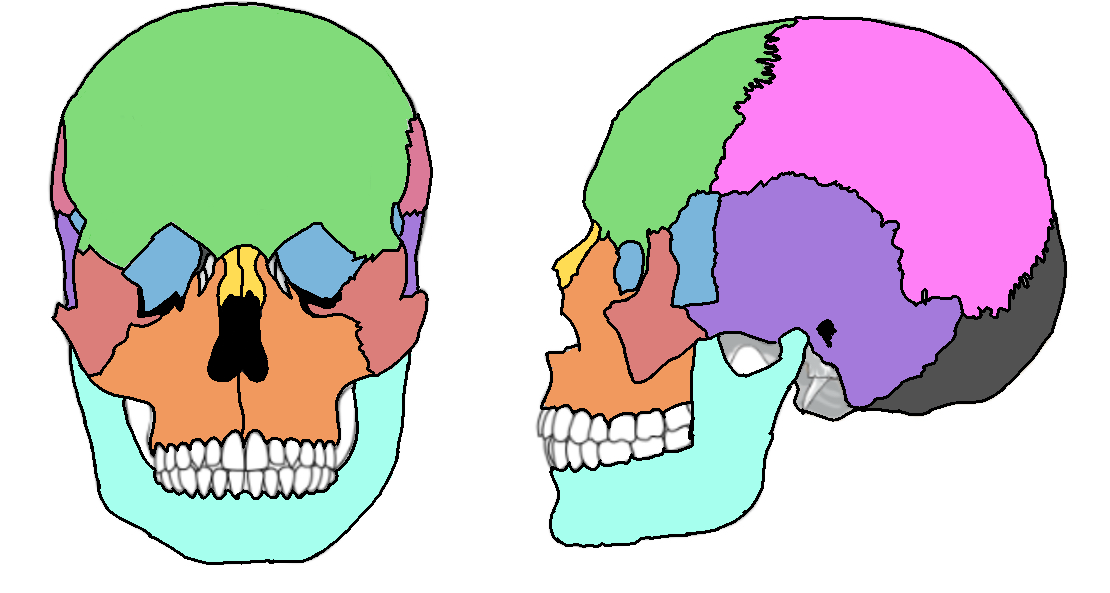
What color is maxilla?
Orange(skull)
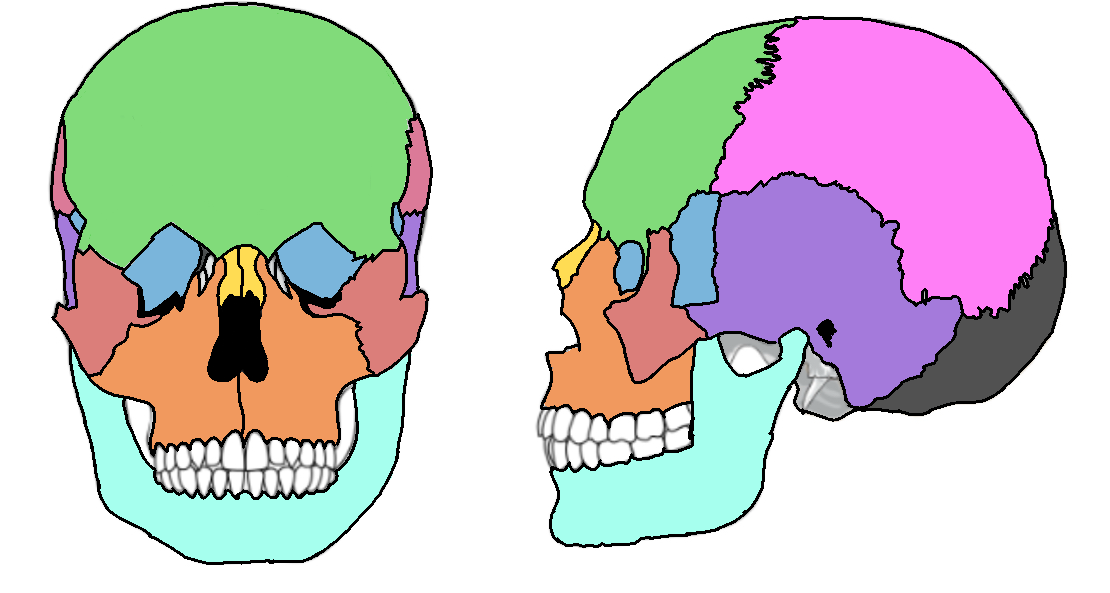
What color is the frontal bone?
Green(skull)
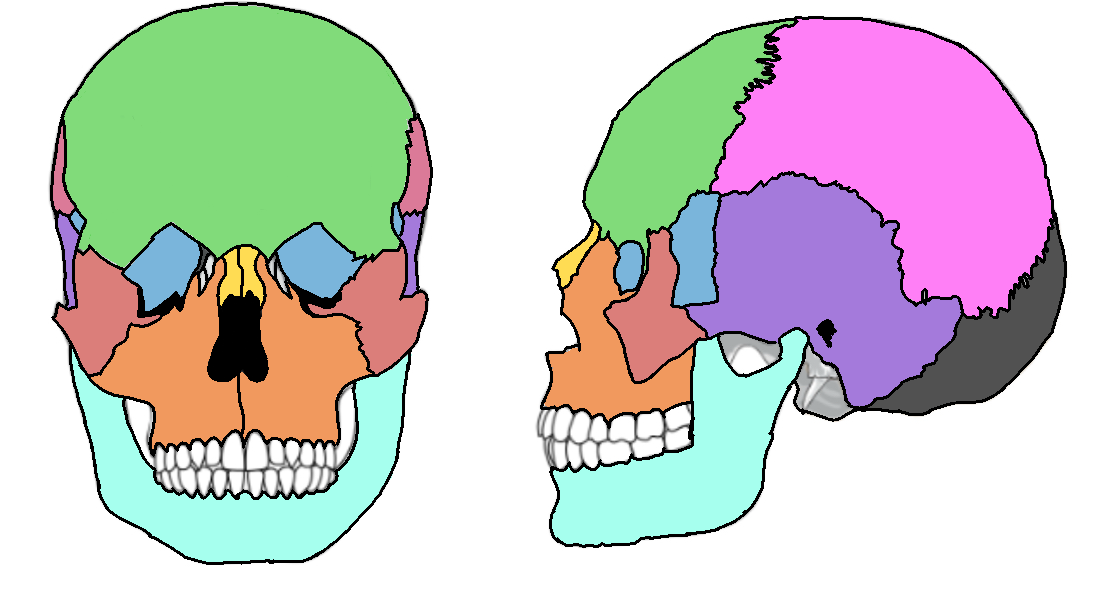
What color is the temporal bone?
Purple(skull)
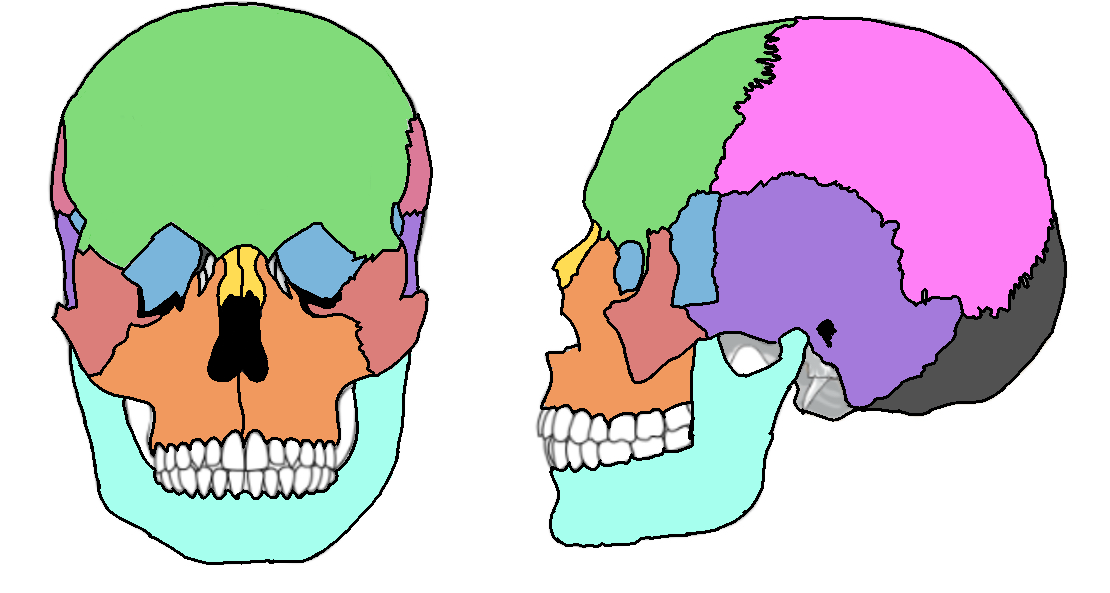
What color is the sphenoid bone?
Blue(skull)
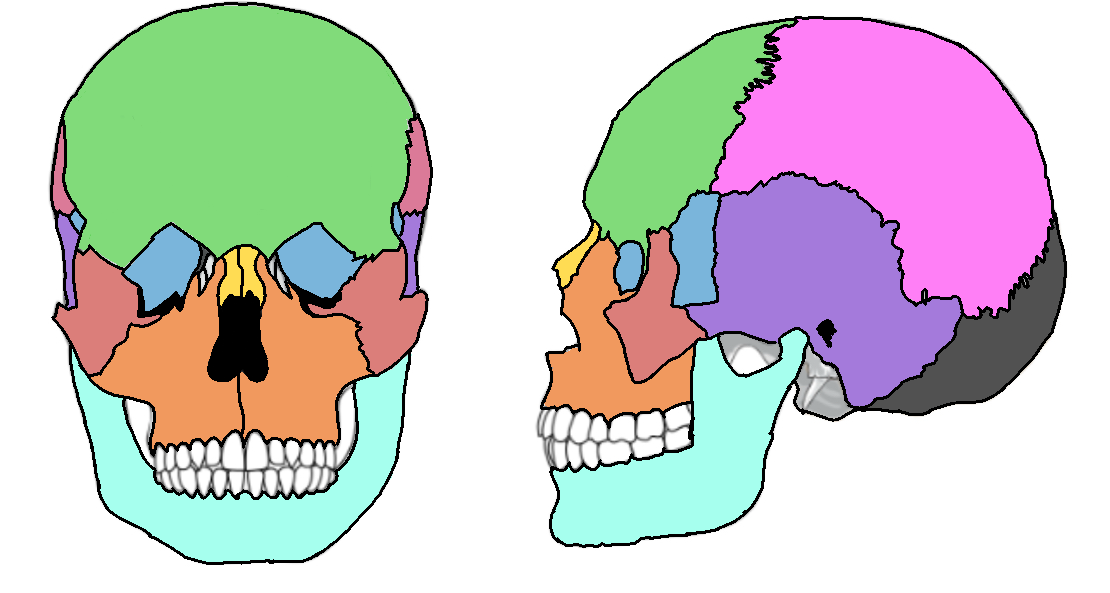
What color are the nasal bones?
Yellow(skull)
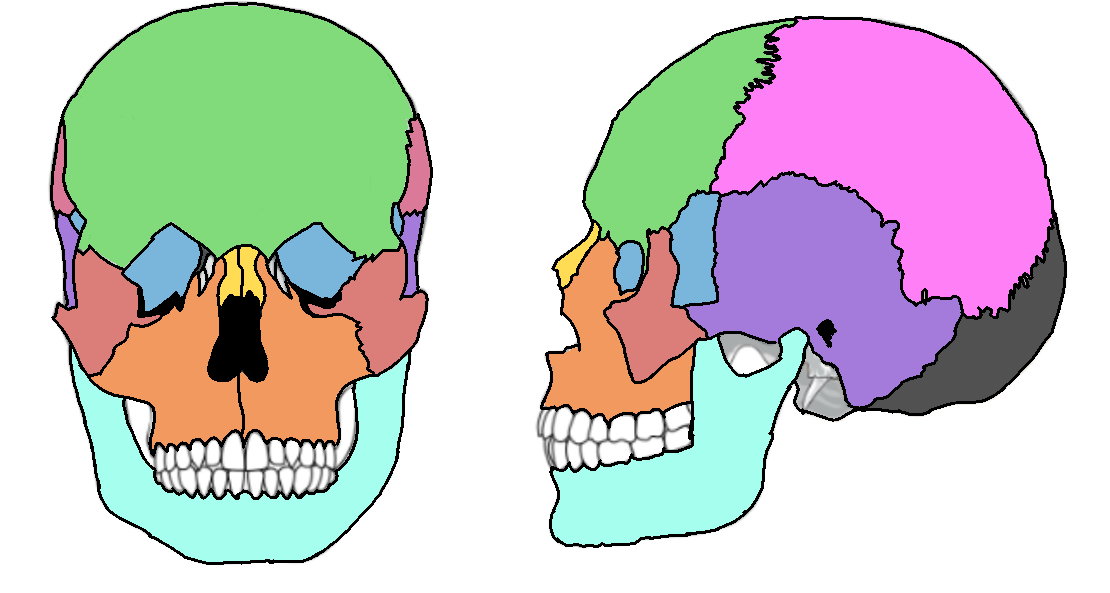
What color is the occipital bone?
Dark grey(skull)
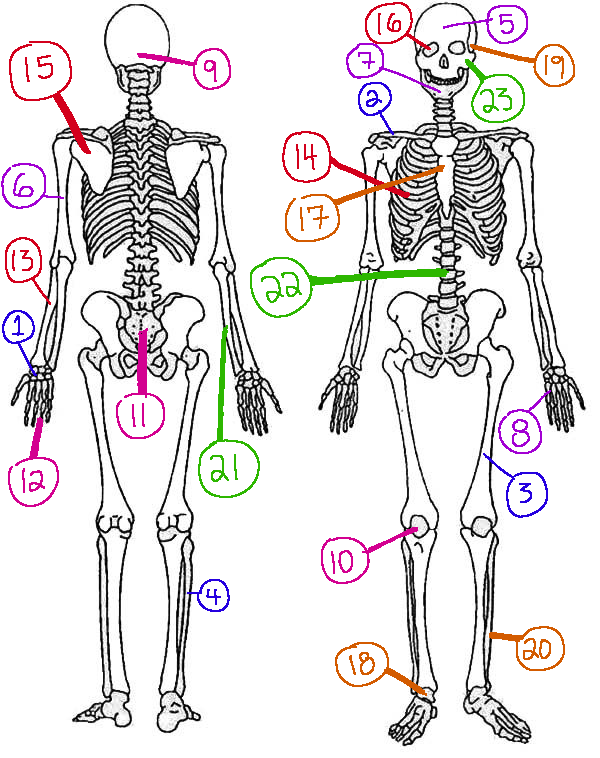
What # is the sphenoid
16 (skeletal)
What # are the carpals
1(skeletal)
What # is the sternum
17(skeletal)
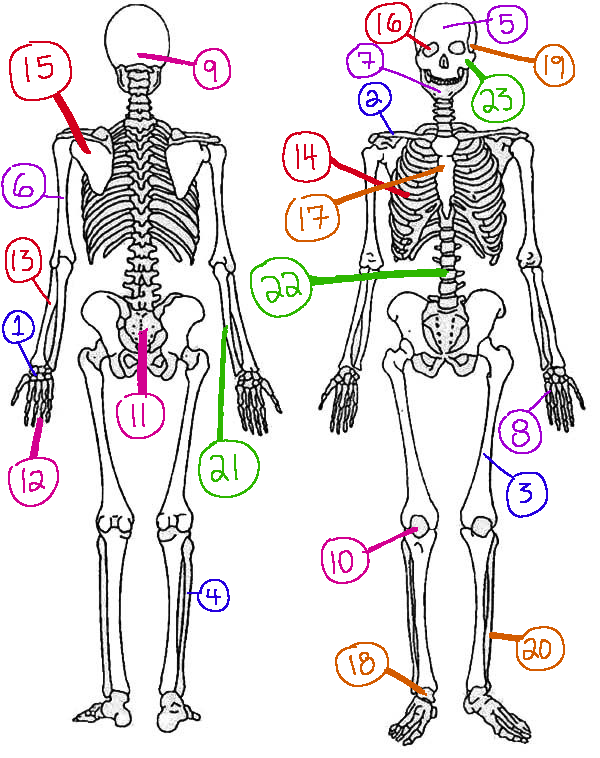
What # is the occipital bone
9(skeletal)
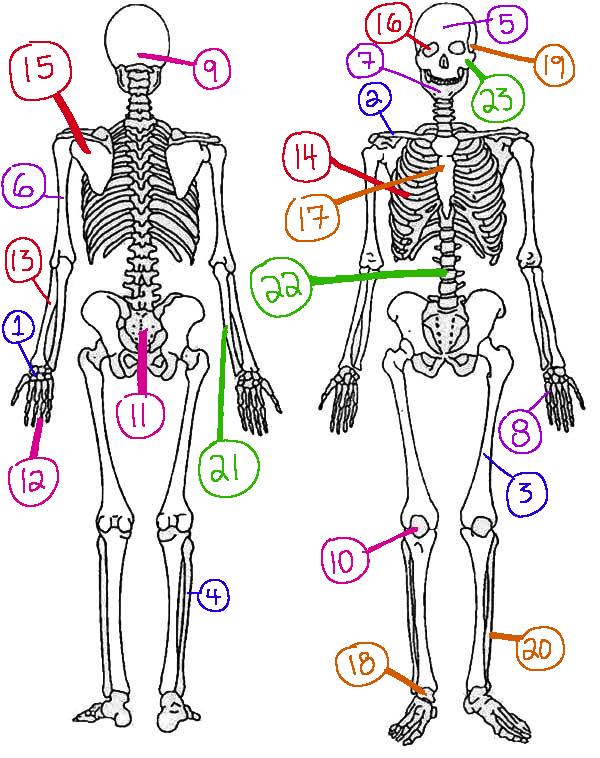
What # is the clavicle
2(skeletal)
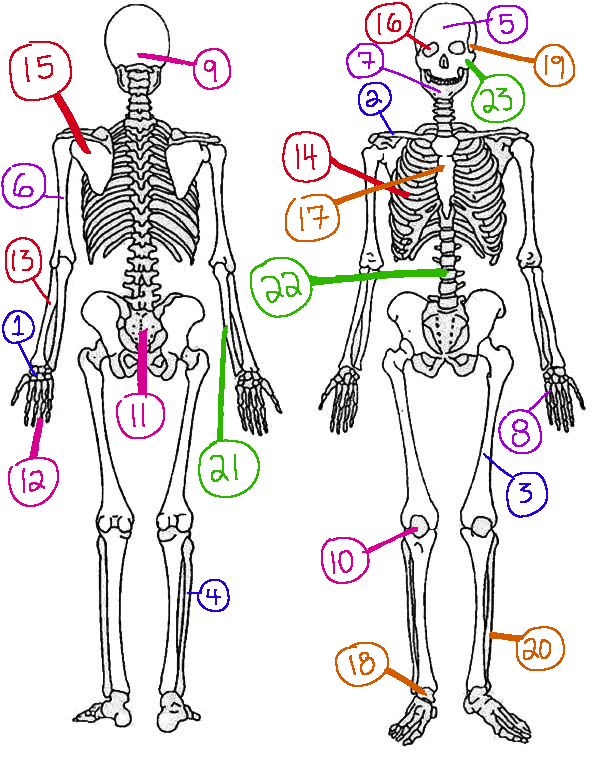
What # are the tarsals
18(skeletal)
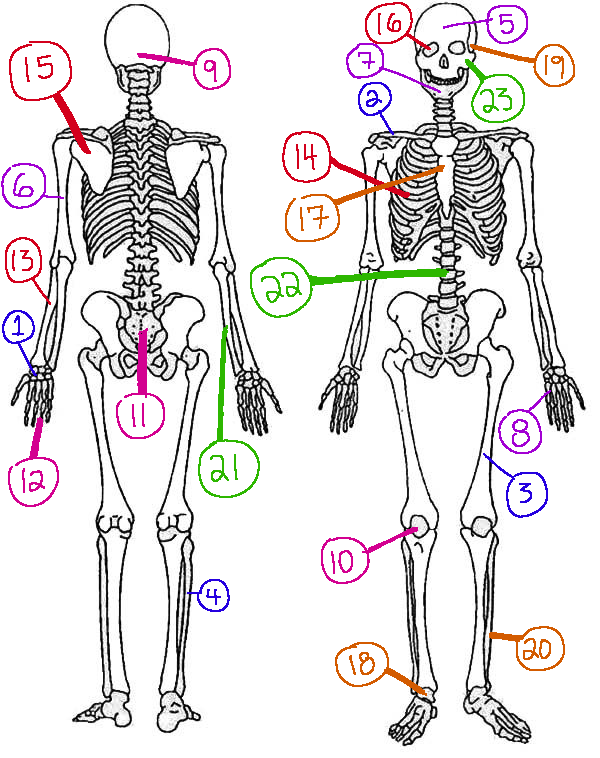
What # is the patella
10(skeletal)
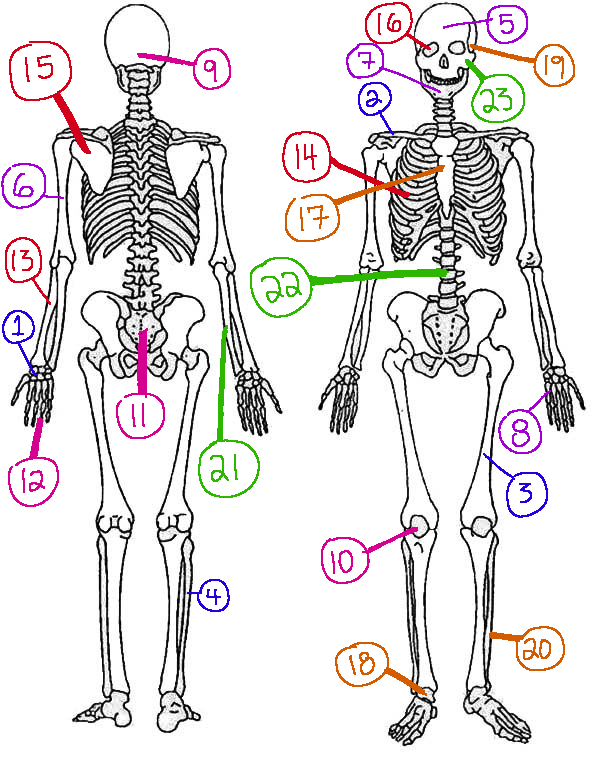
What # is the femur
3(skeletal)
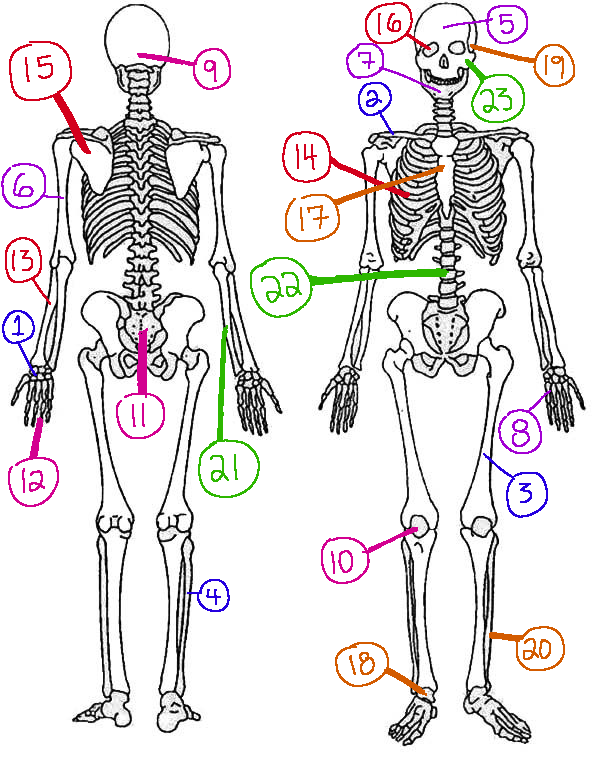
What # is the temporal bone
19(skeletal)
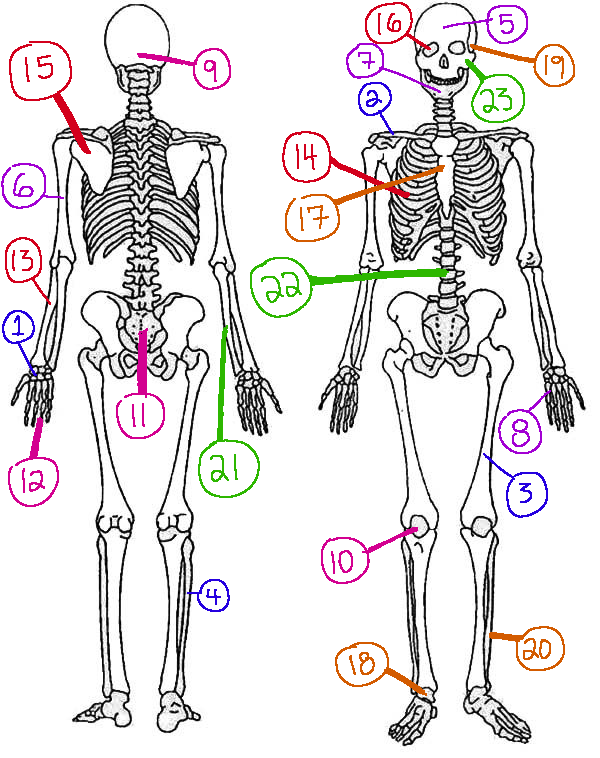
What # is the pelvic girdle
11(skeletal)
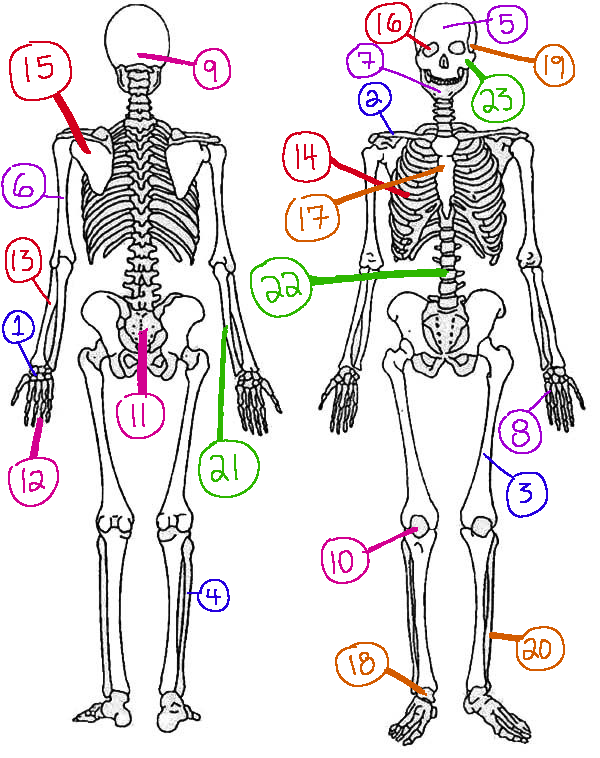
What # is the fibula
4(skeletal)
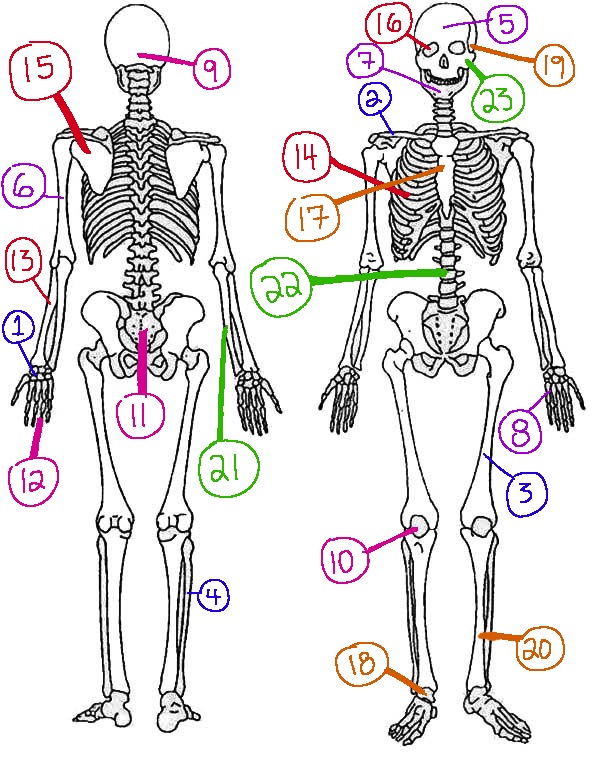
What # is the tibia
20(skeletal)
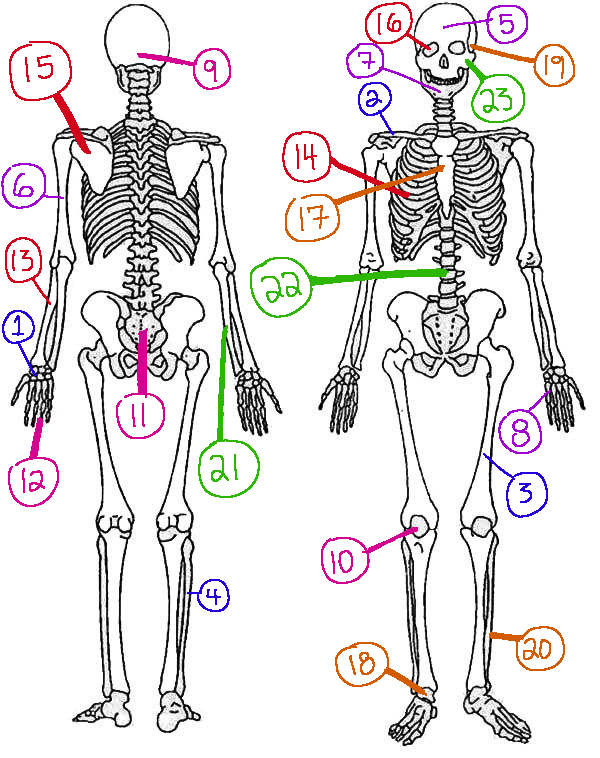
What # are the phalanges
12(skeletal)
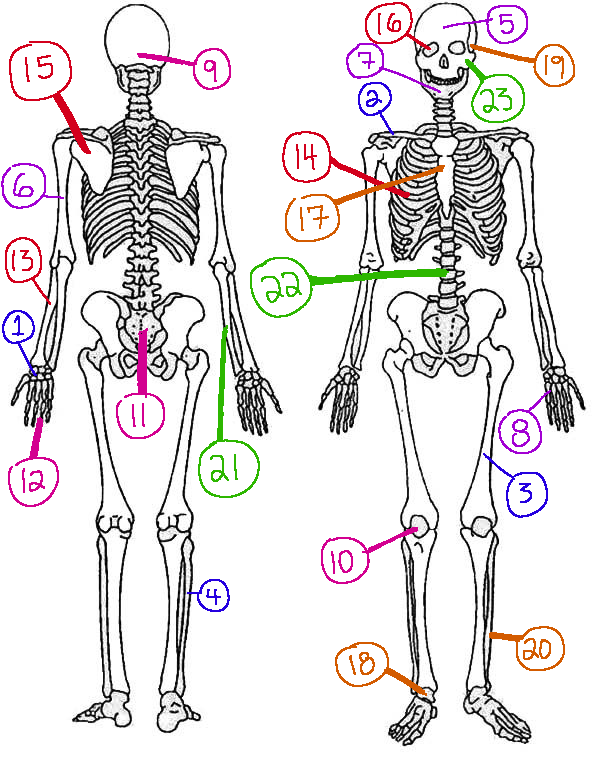
What # is the frontal bone?
5(skeletal)
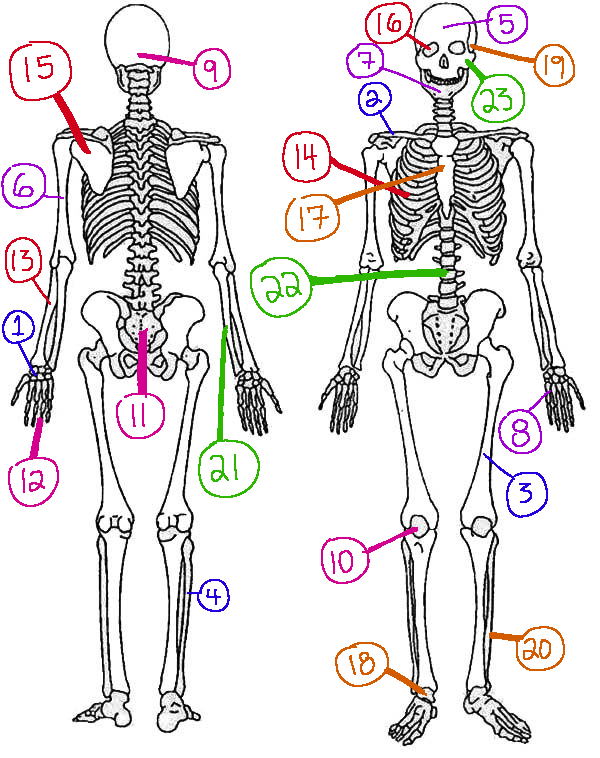
What # is the ulna
21(skeletal)
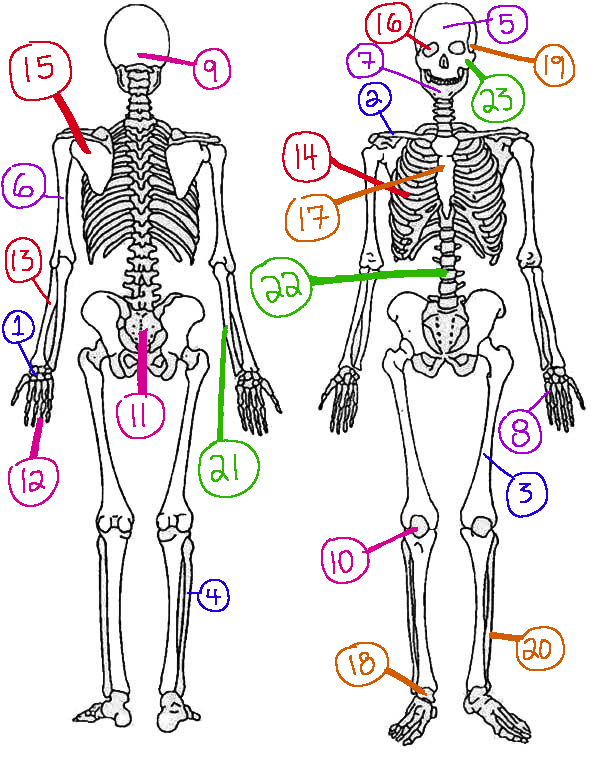
What # is the radius
13(skeletal)
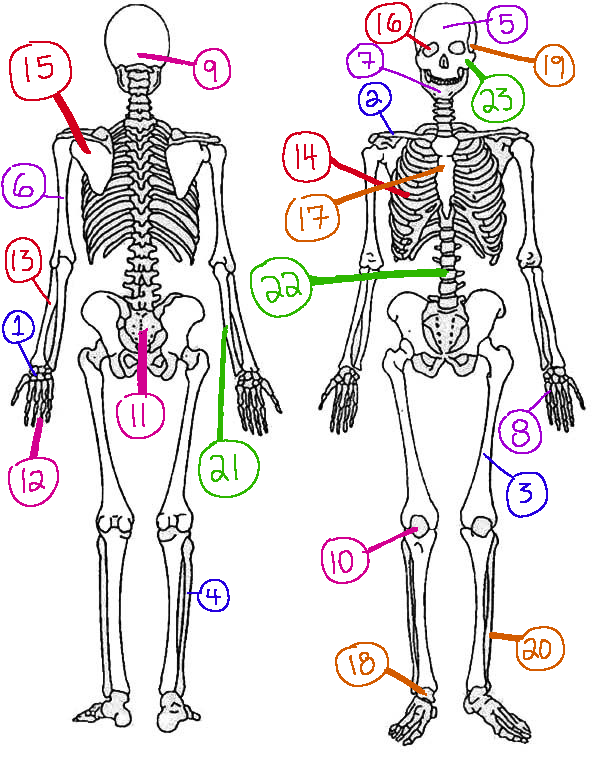
What # is the humerus
6(skeletal)
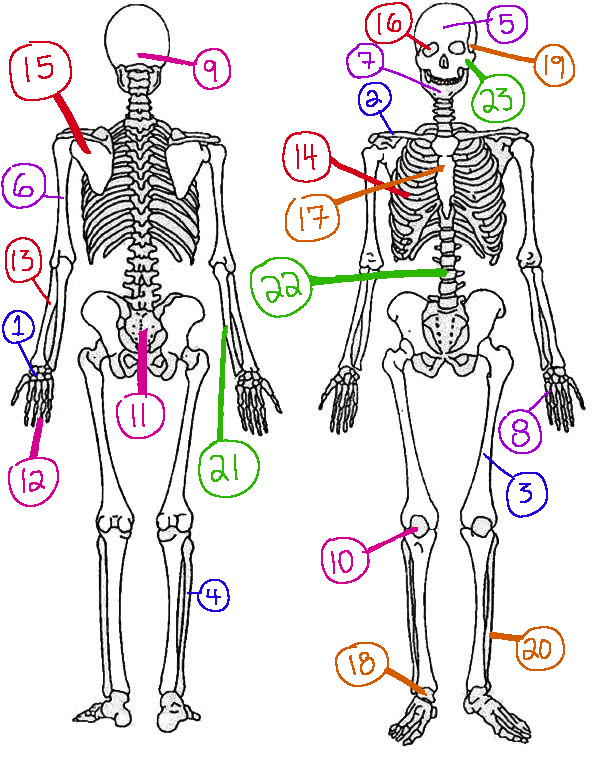
What # is the vertebral column
22(skeletal)
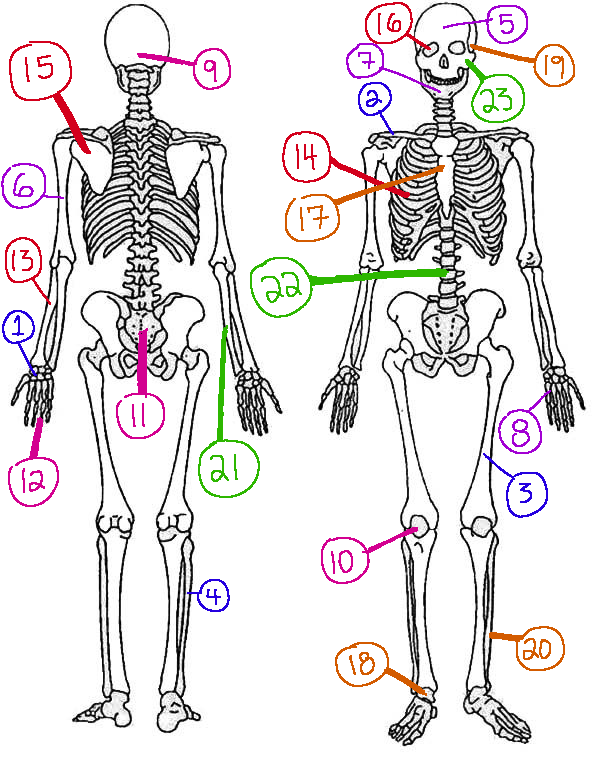
What # is the rib cage
14(skeletal)
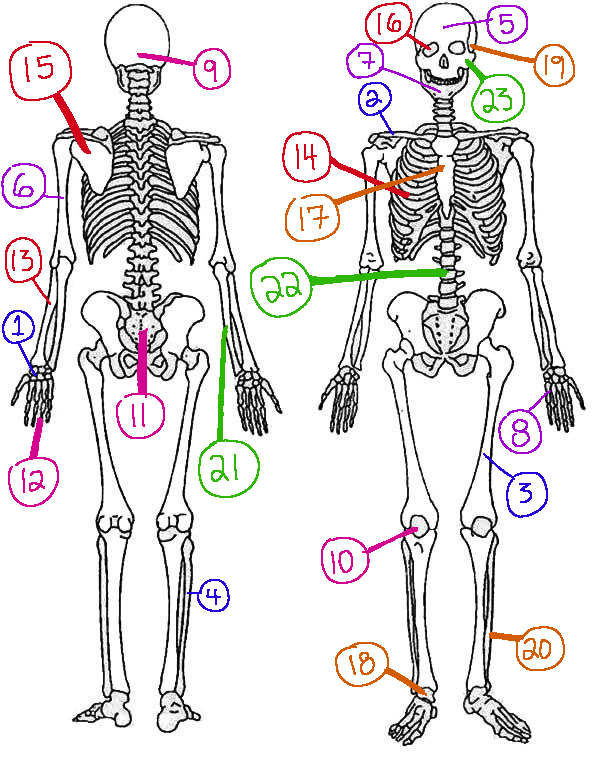
What # is the mandible
7(skeletal)
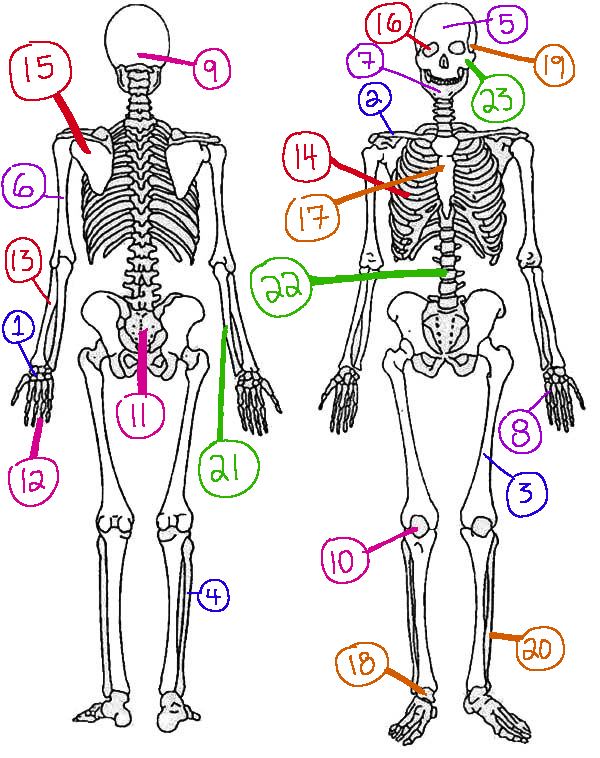
What # is the scapula
15(skeletal)
What # is the zygomatic
23(skeletal)
What are long bone classification rules
Longer than wide; attachment sites for muscles
What are short bone classification rules
Length=width; cube shaped; glide over one another
What are flat bone classification rules
Flat and curved; organ protection
What are irregular bone classification rules
Oddly shaped; protection
What are sesamoid bone classification rules
Seed shaped
What bone type is the mandible
flat
What bone type are the ribs
Flat
What are the only two bones that are classified short
Carpals and tarsals
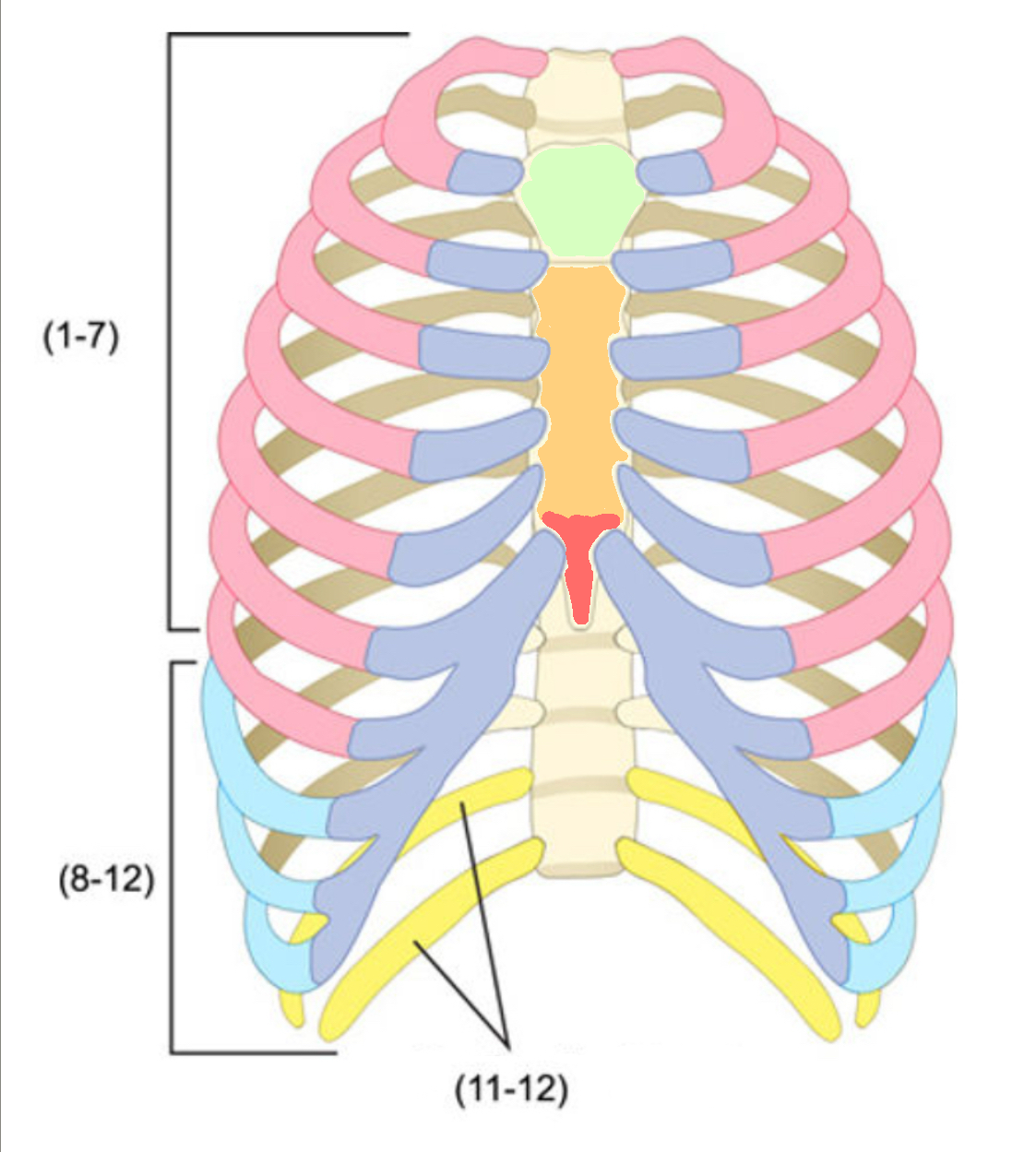
What color is cartilage
purple (ribs)
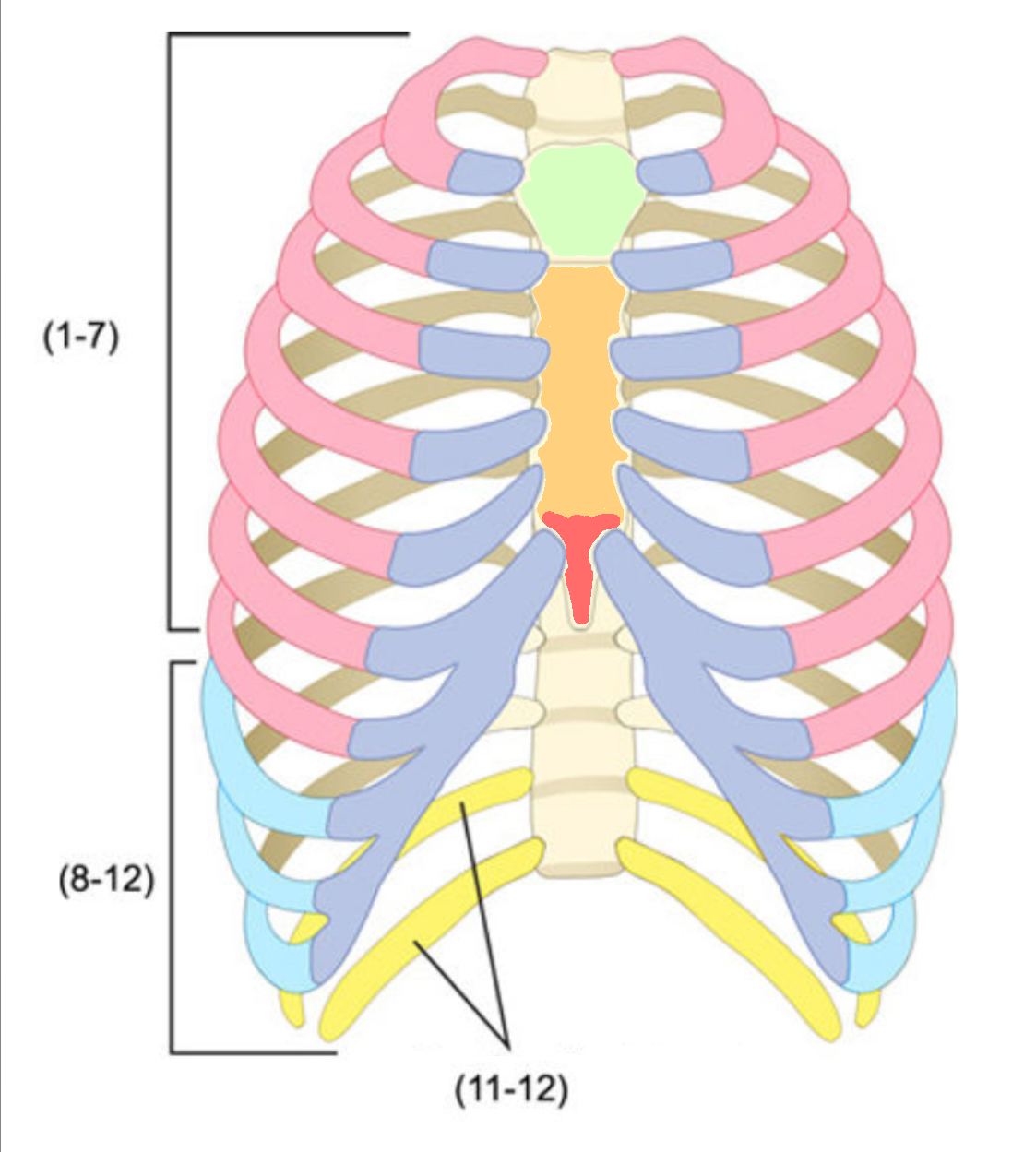
What color are false ribs
Blue(ribs)
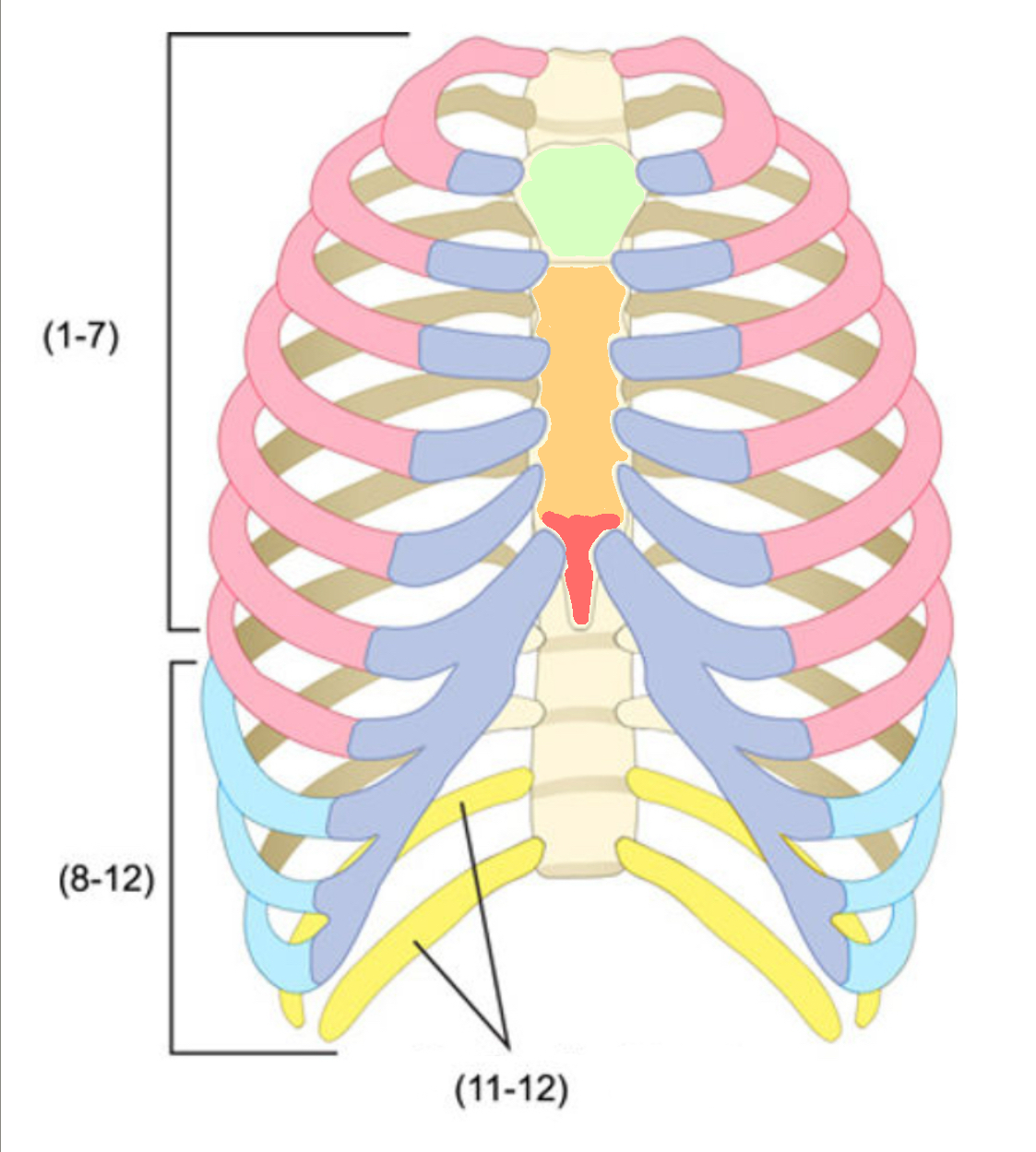
What color is the body of the sternum
Orange(ribs)
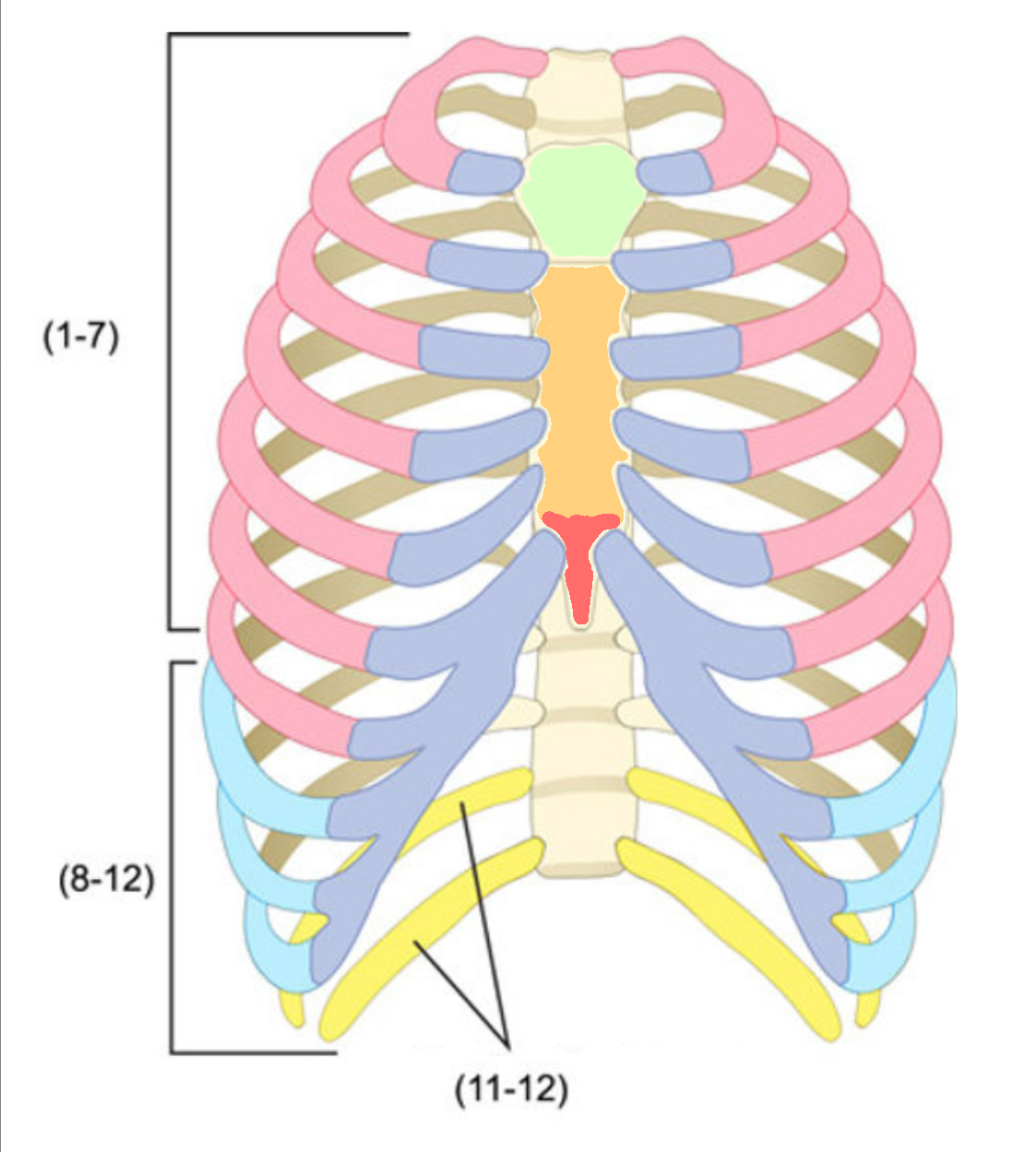
What color are the true ribs
Pink(ribs)
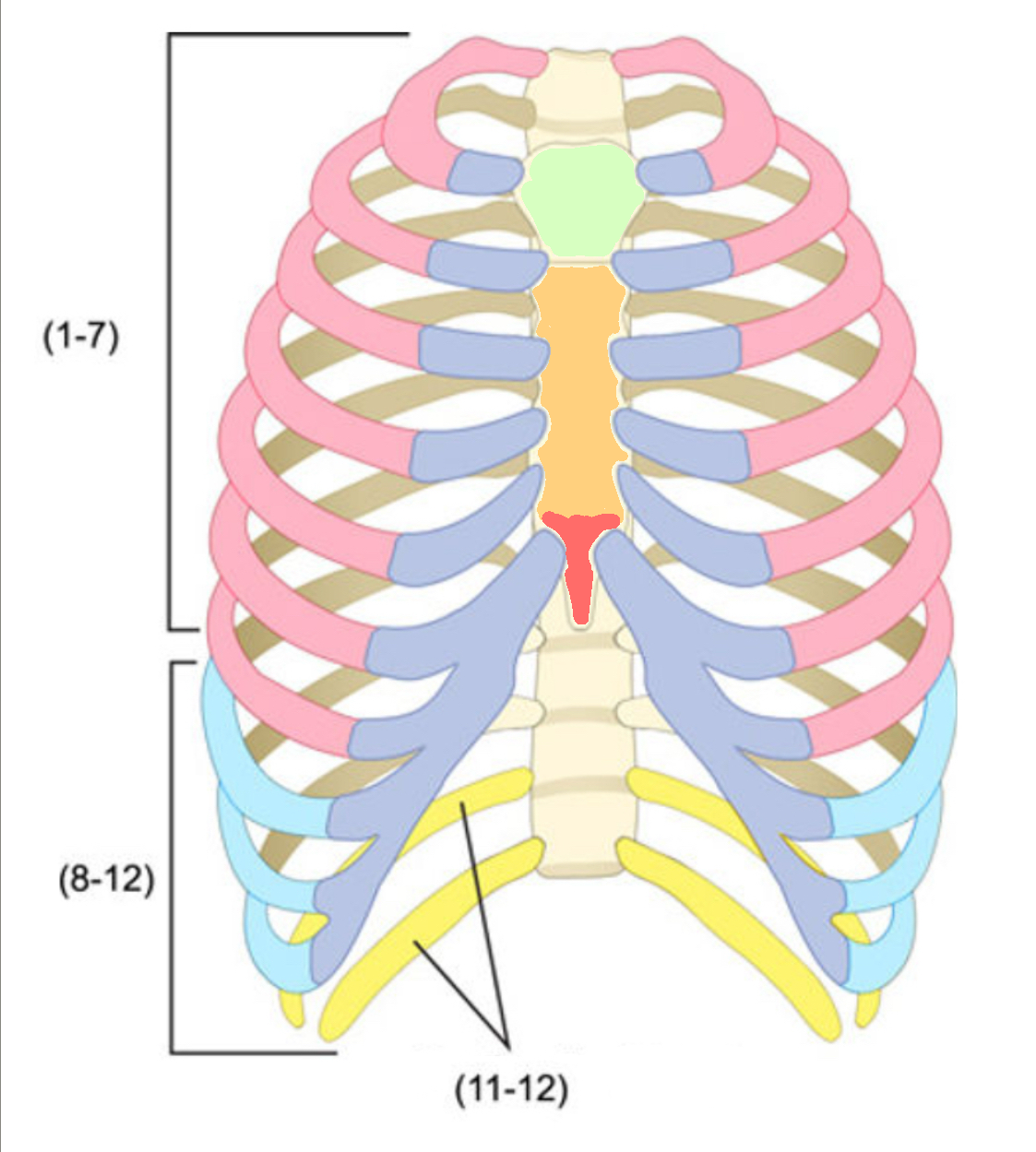
What color are the floating ribs
Yellow(ribs)
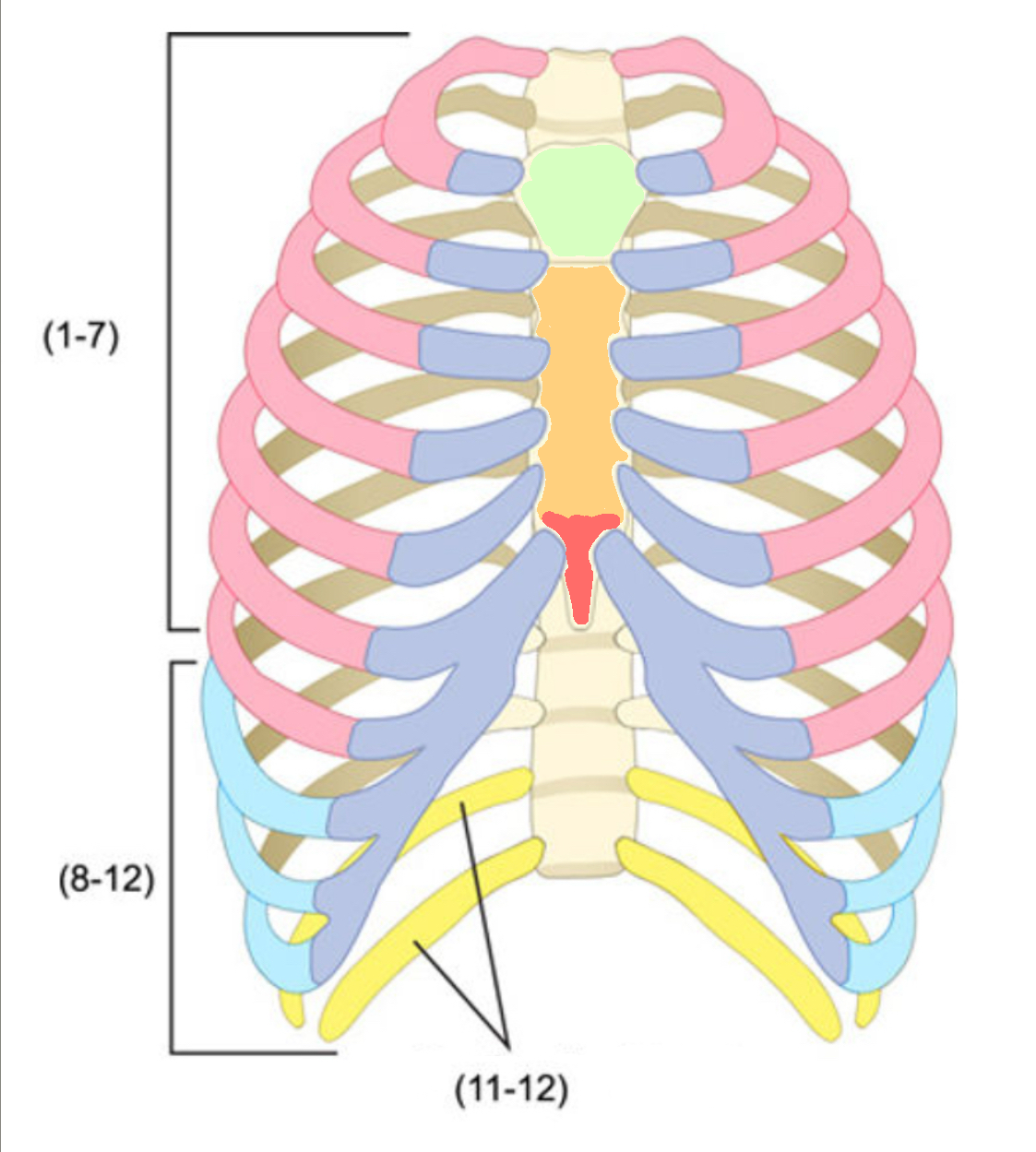
What color is the manubrium
Green(ribs)
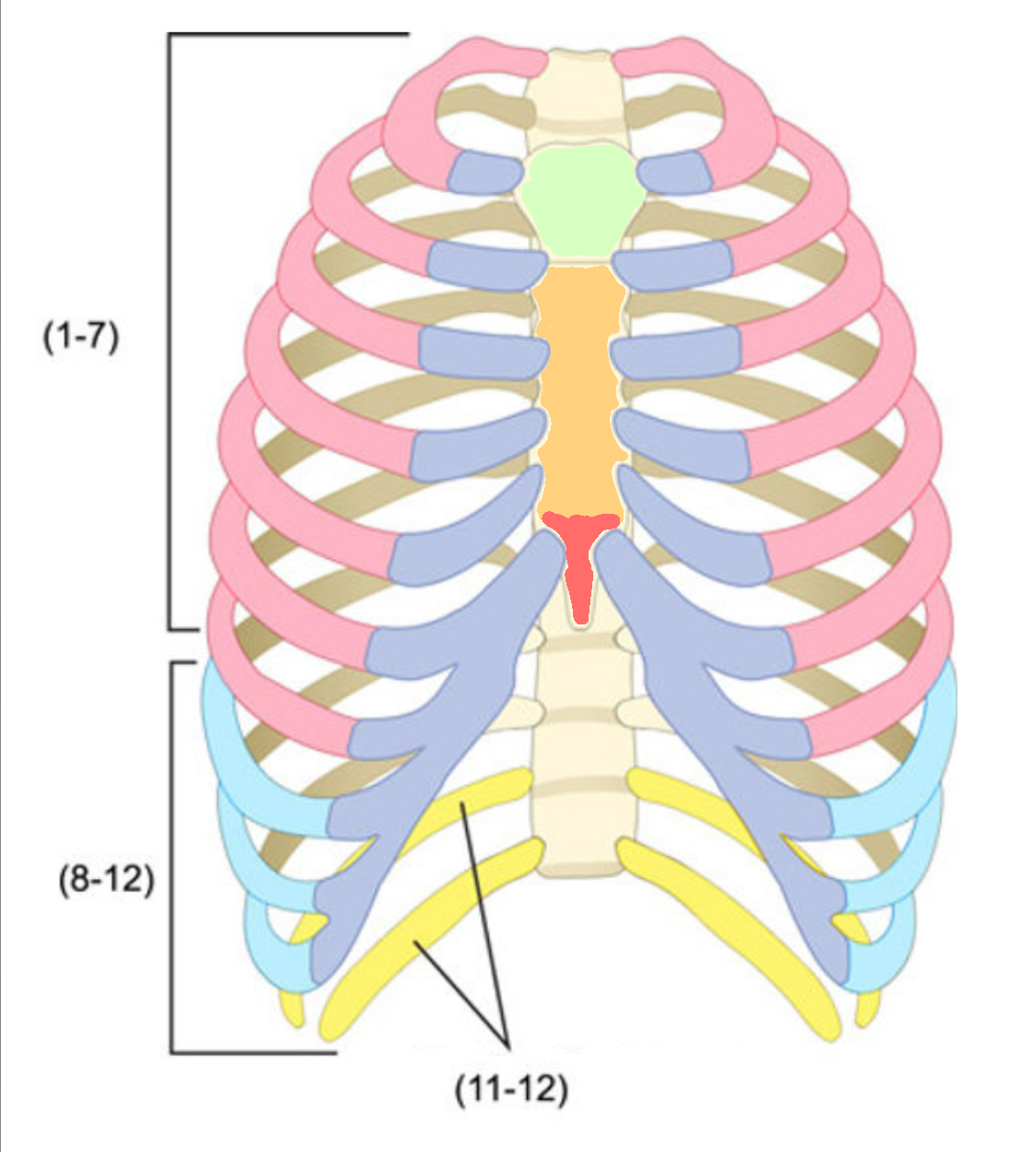
What color is the xiphoid process
Red(ribs)

What color is thoracic?
Blue (vertebral column)
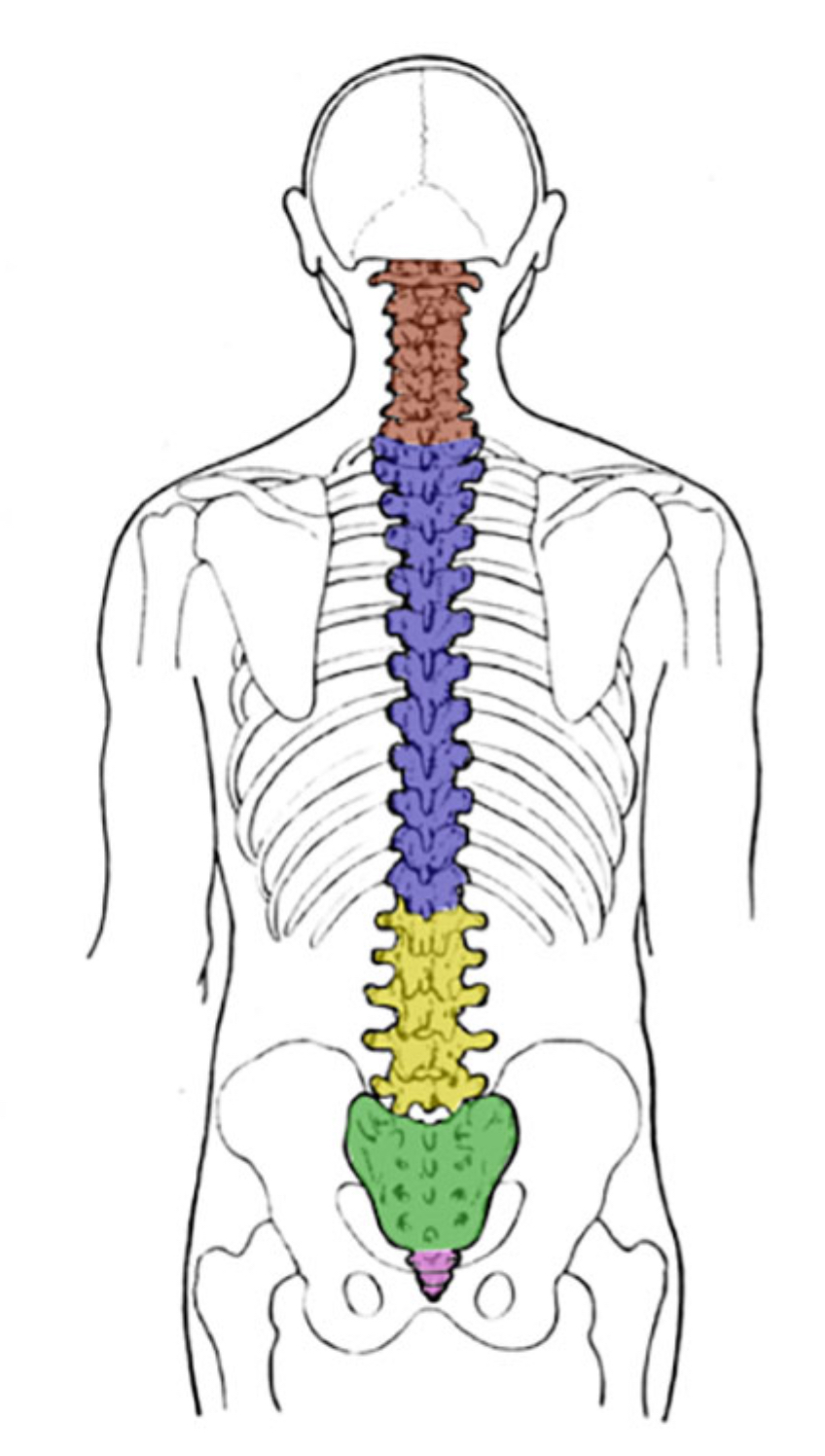
What color is coccyx
Pink (vertebral column)
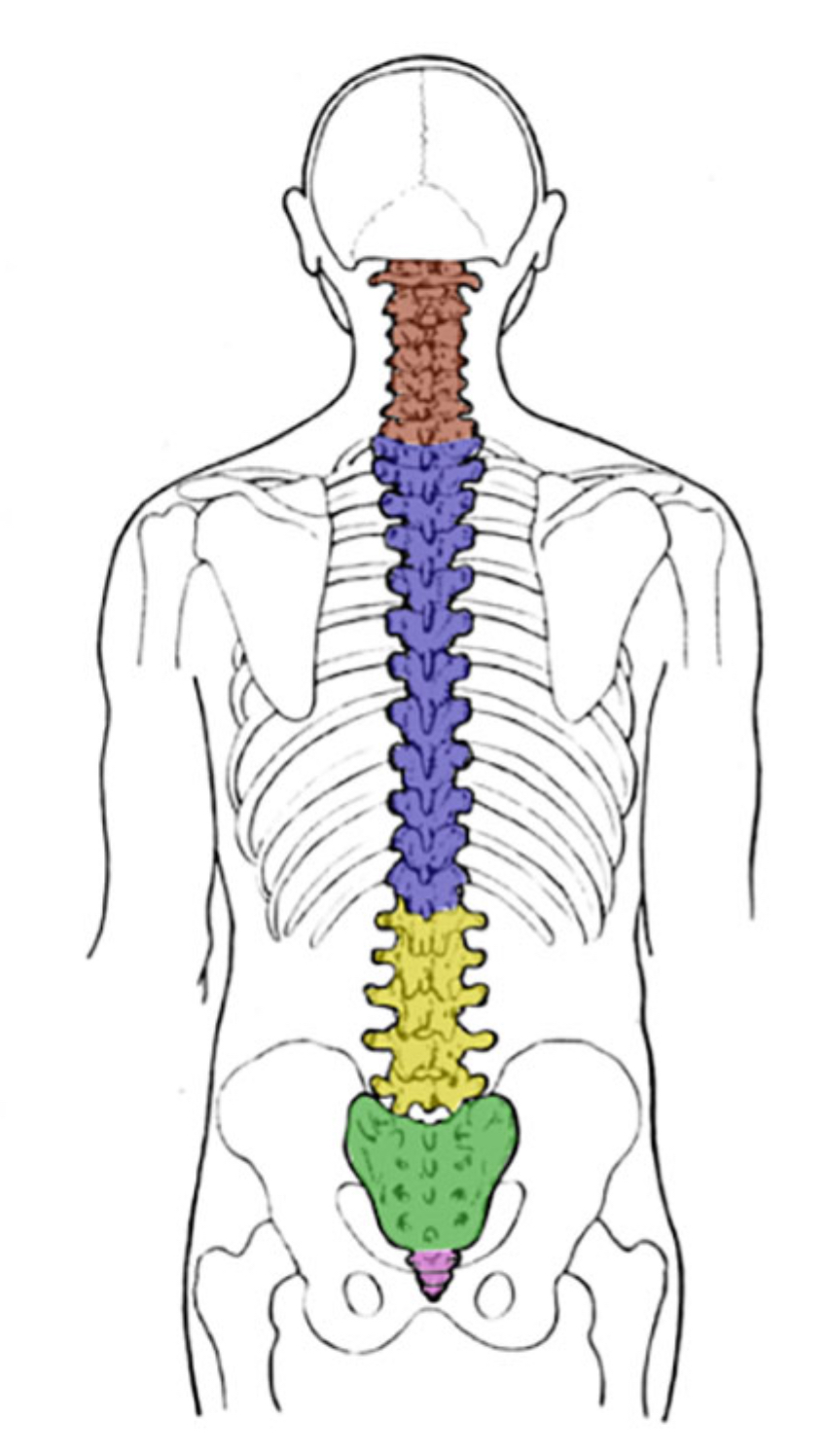
What color is sacral
Green (vertebral column)
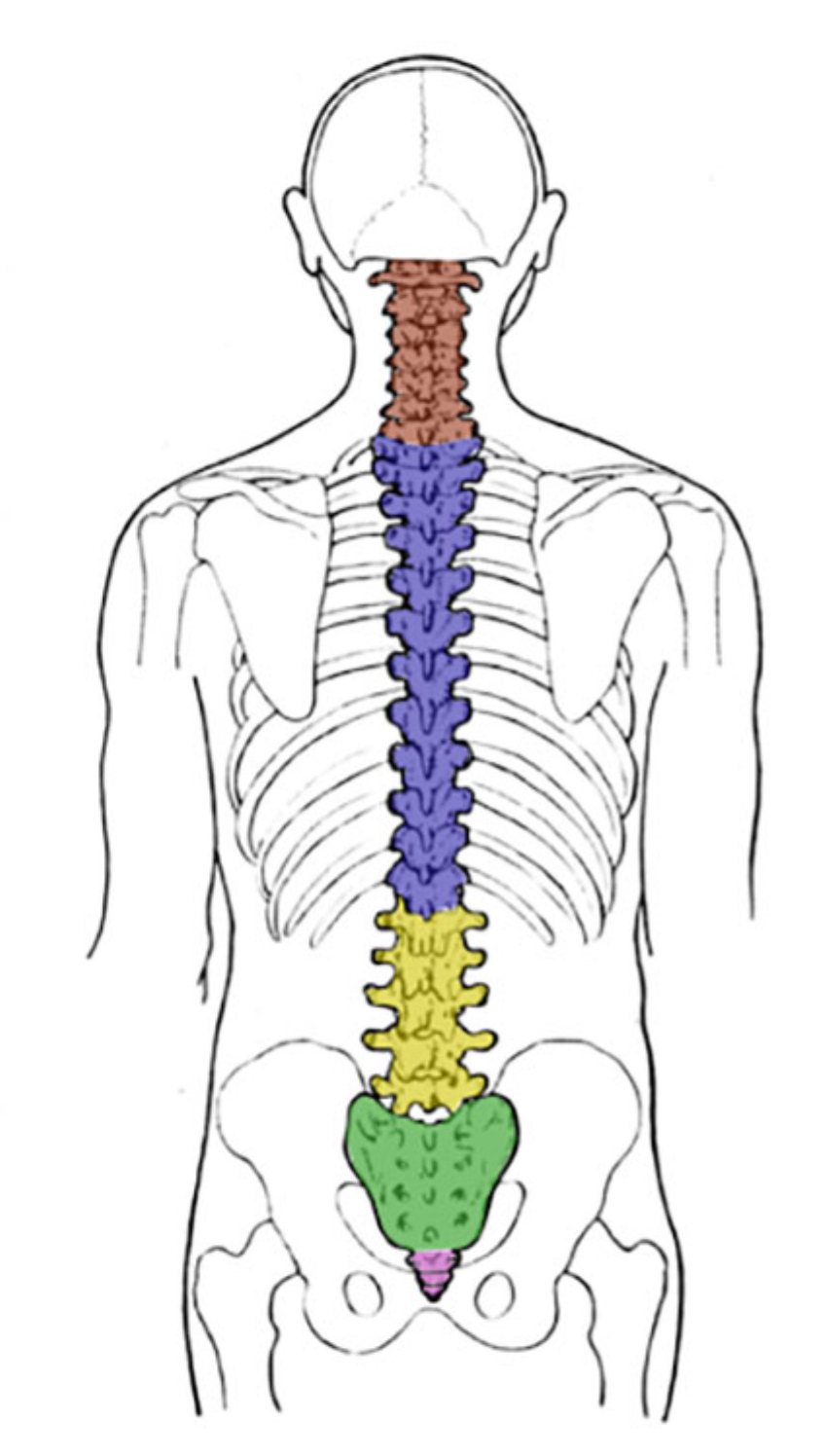
What color is cervical
Red (vertebral column)
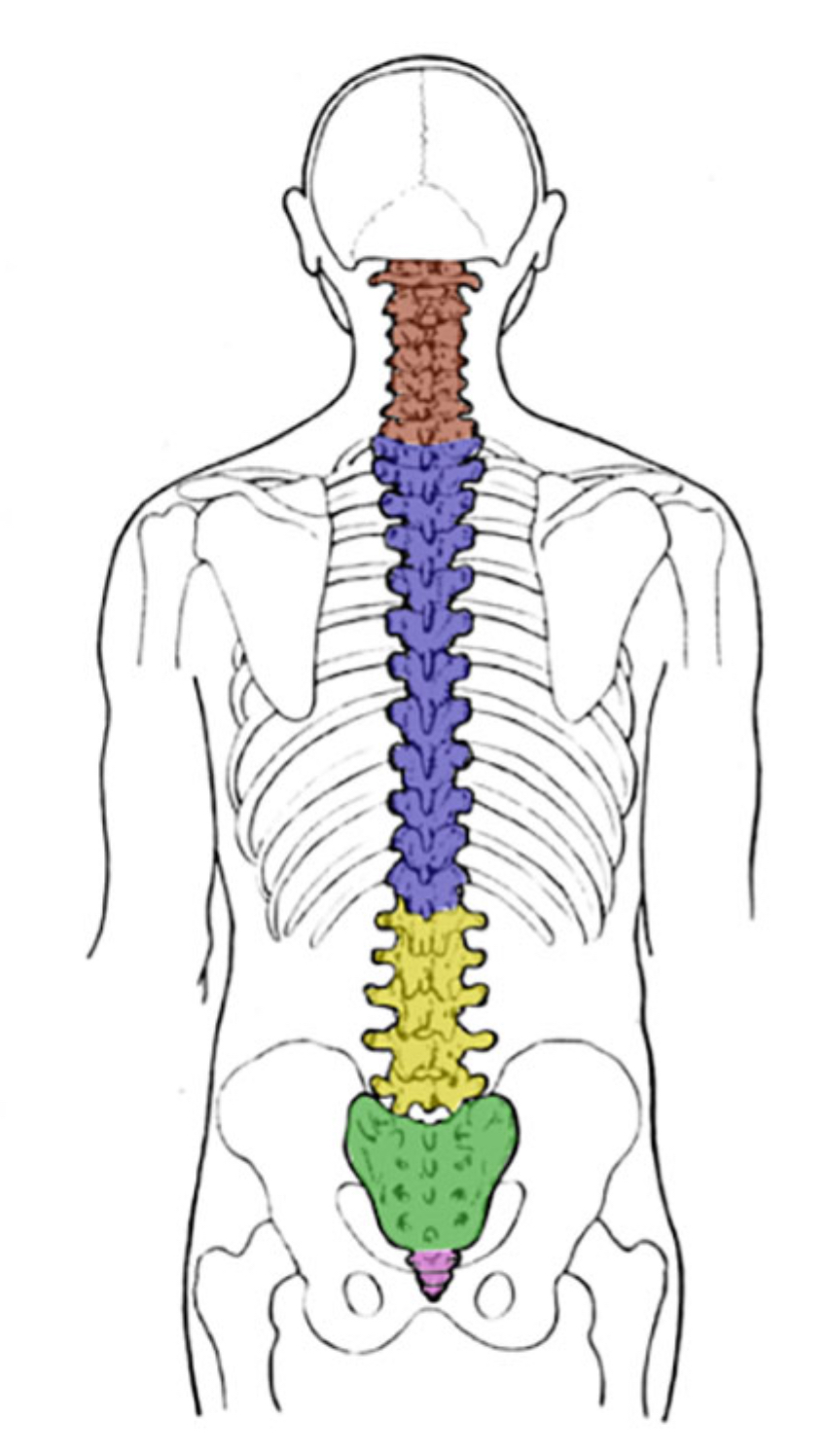
What color is lumbar
Yellow (vertebral column)
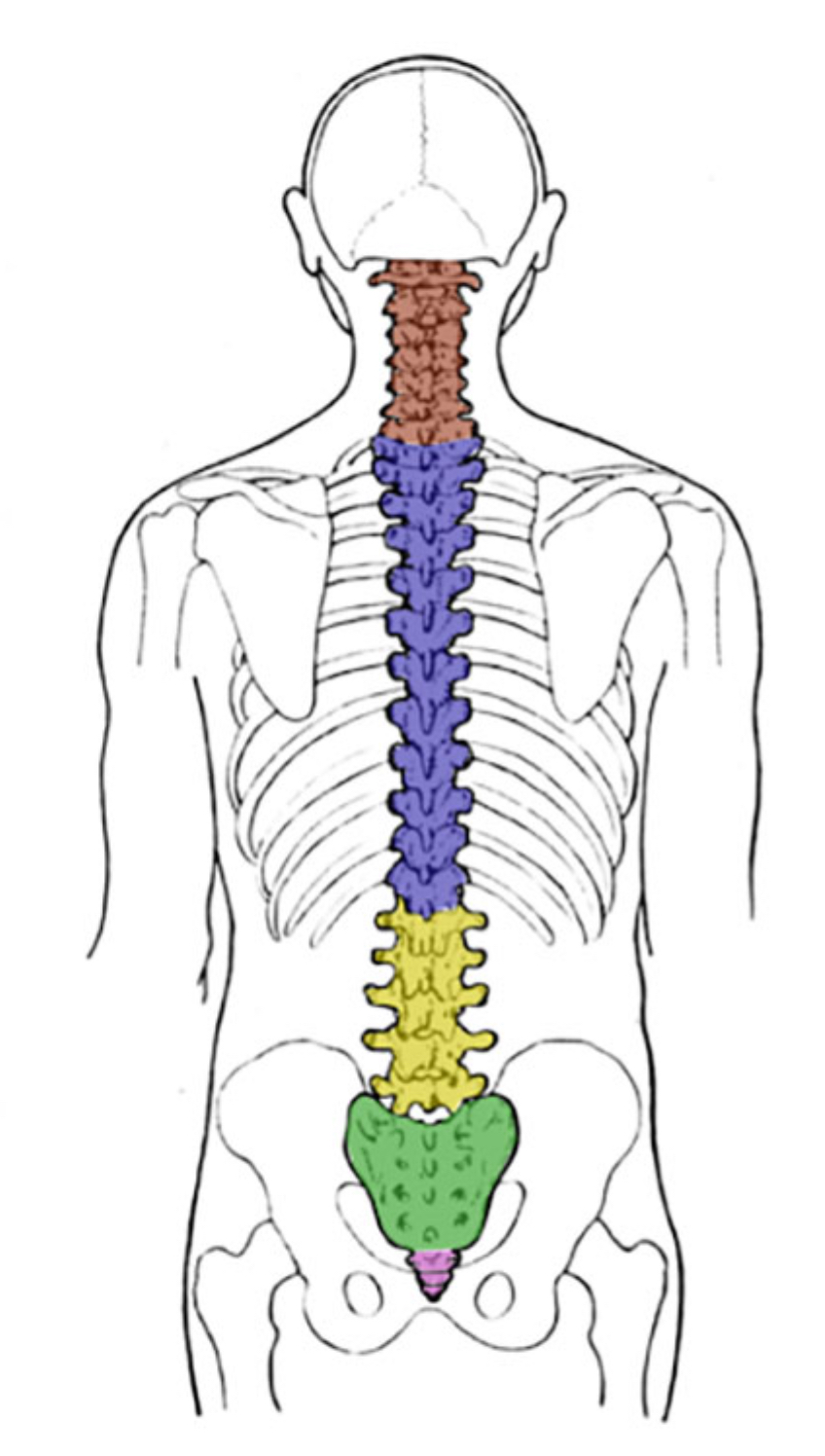
What is the breakfast (7)?
Cervical
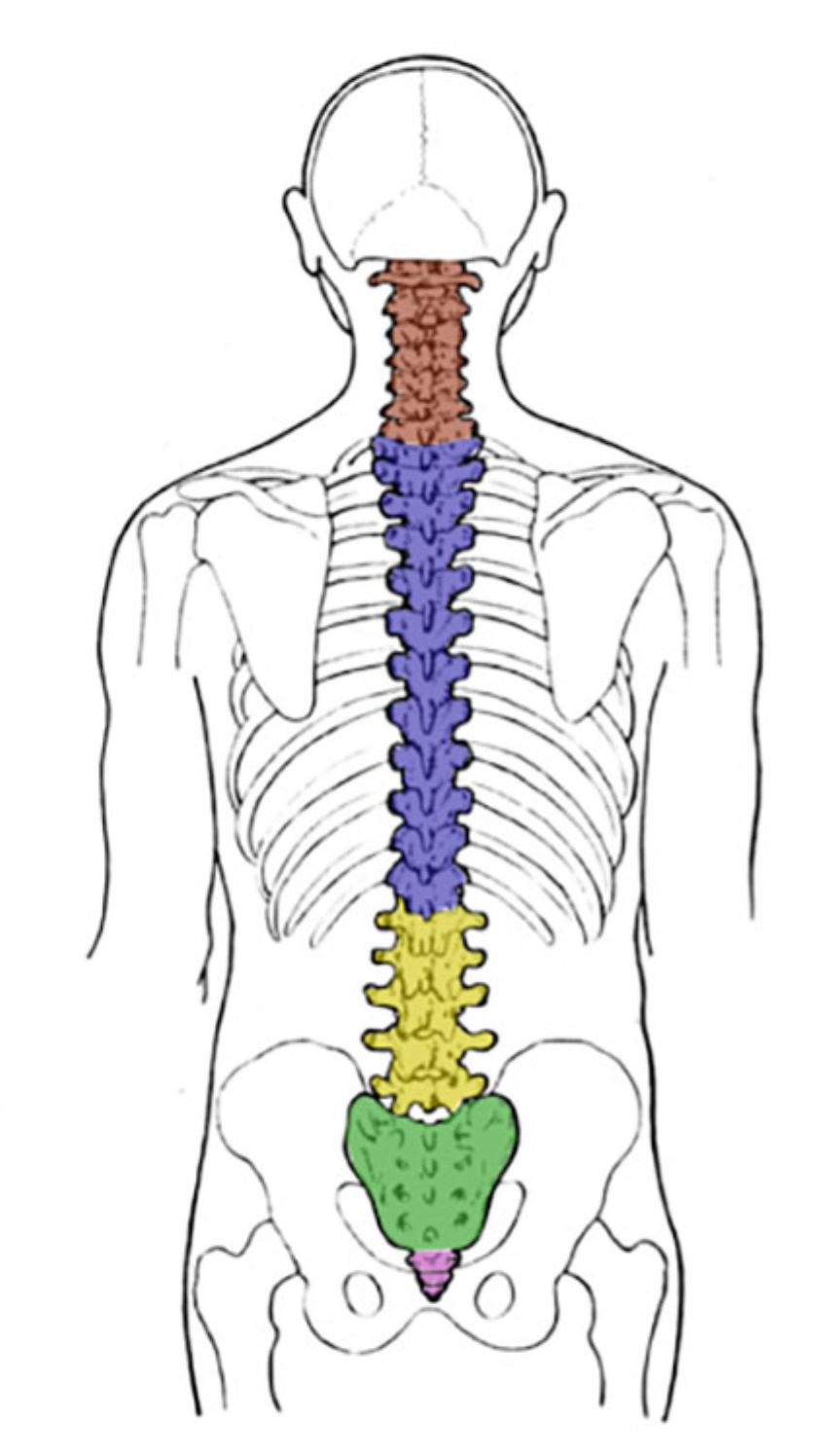
What is lunch (12)?
Thoracic
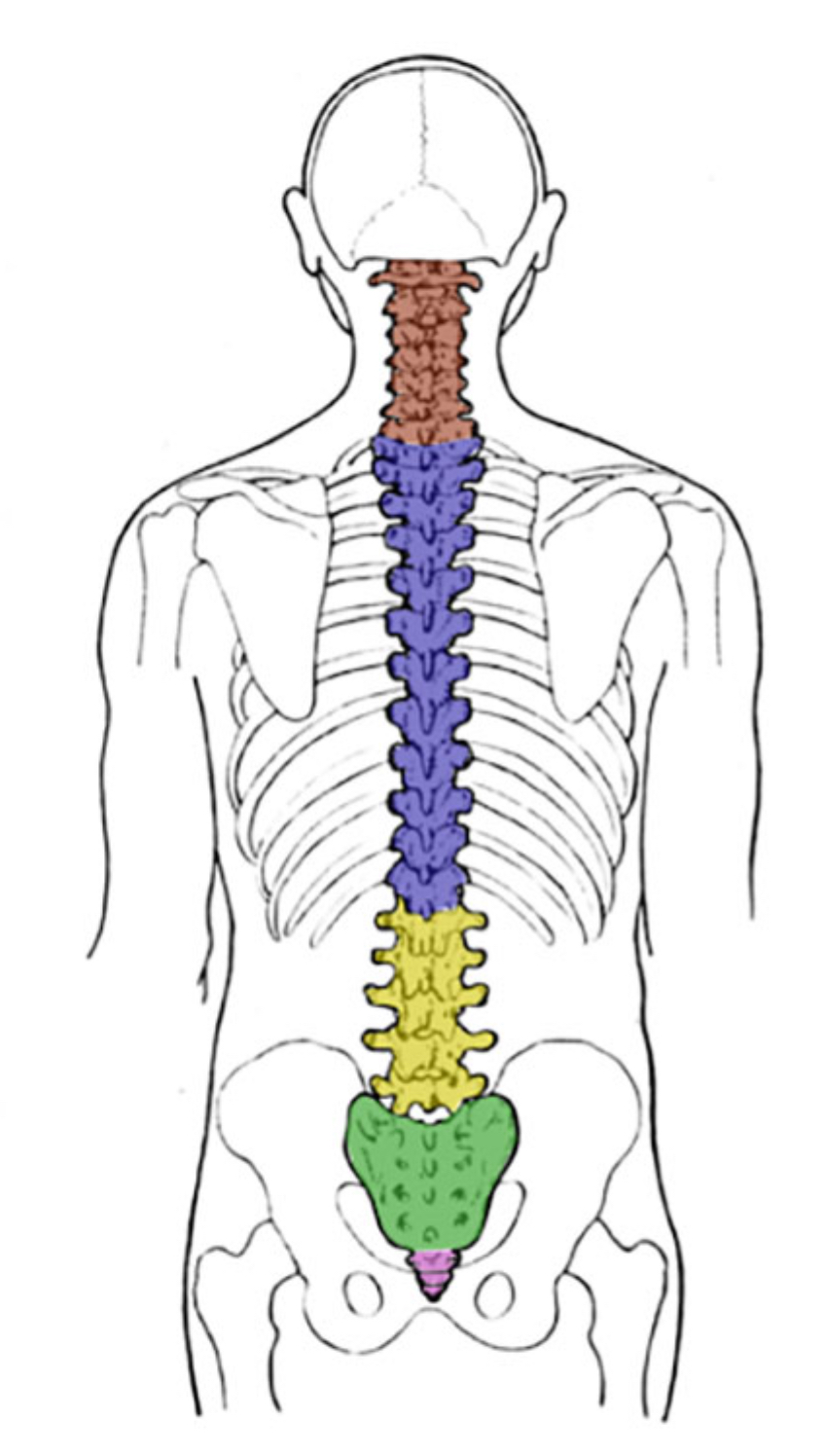
What is dinner (5)?
Lumbar
How many total vertebra are there
33
What kind of tissue is found between each vertebra
Intervertebral disc (acts as a shock absorber)
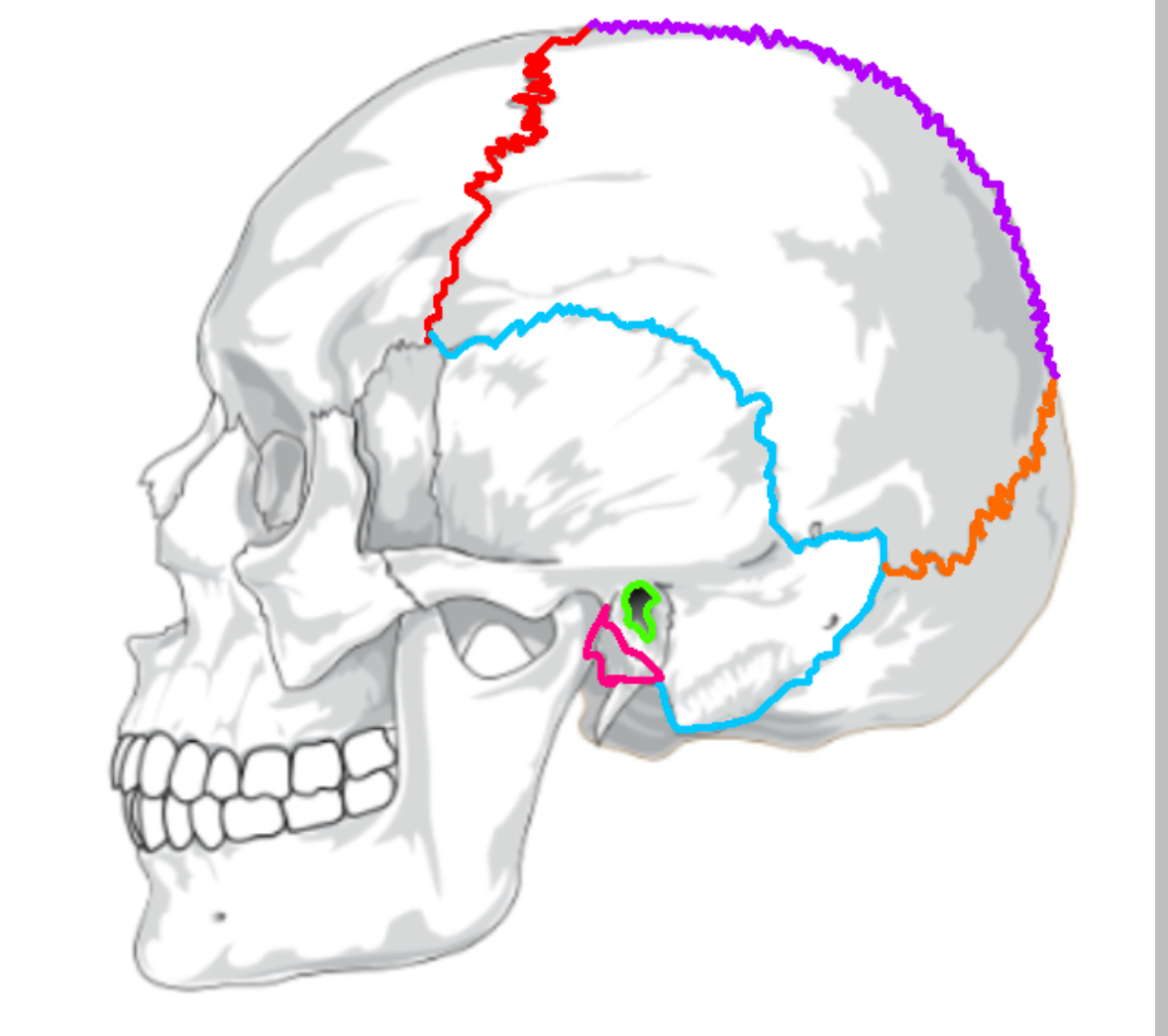
What color is the coronal suture
Red (sutures)
What color is lamboid
Orange(sutures)
What color is the saggital suture?
Purple(sutures)
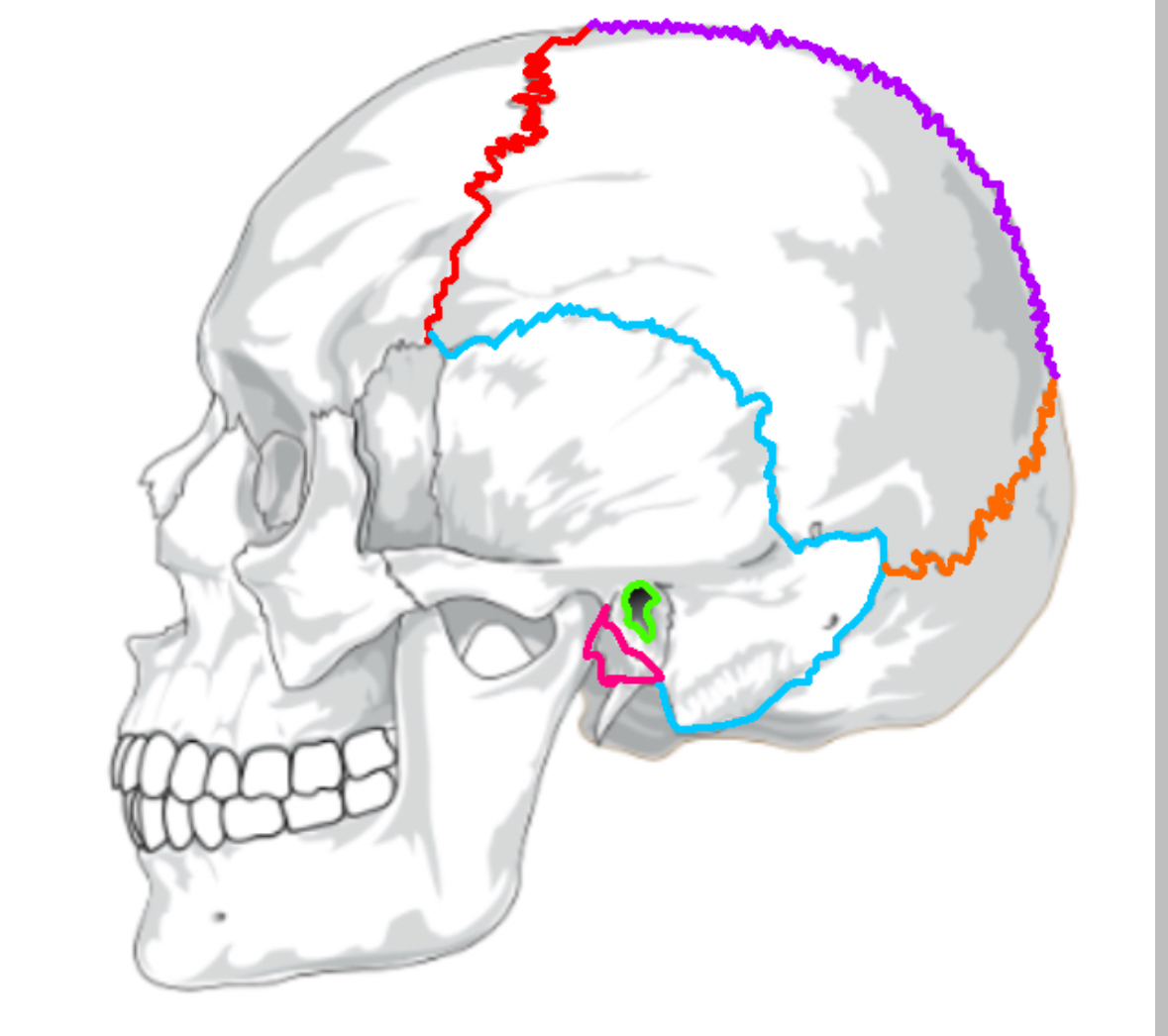
What color is the squamous suture?
Blue(sutures)
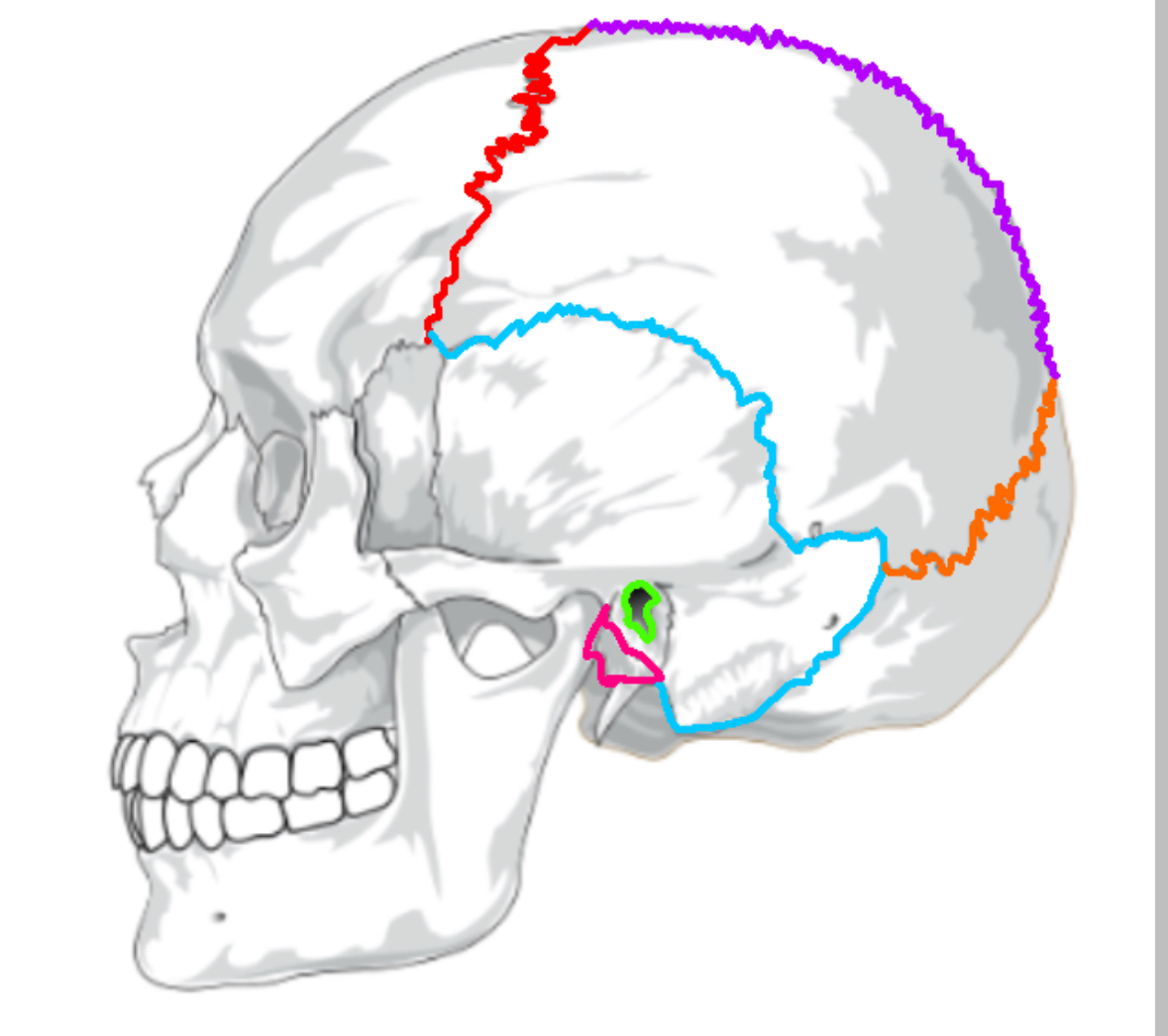
What color is the mastoid process
Pink(sutures)
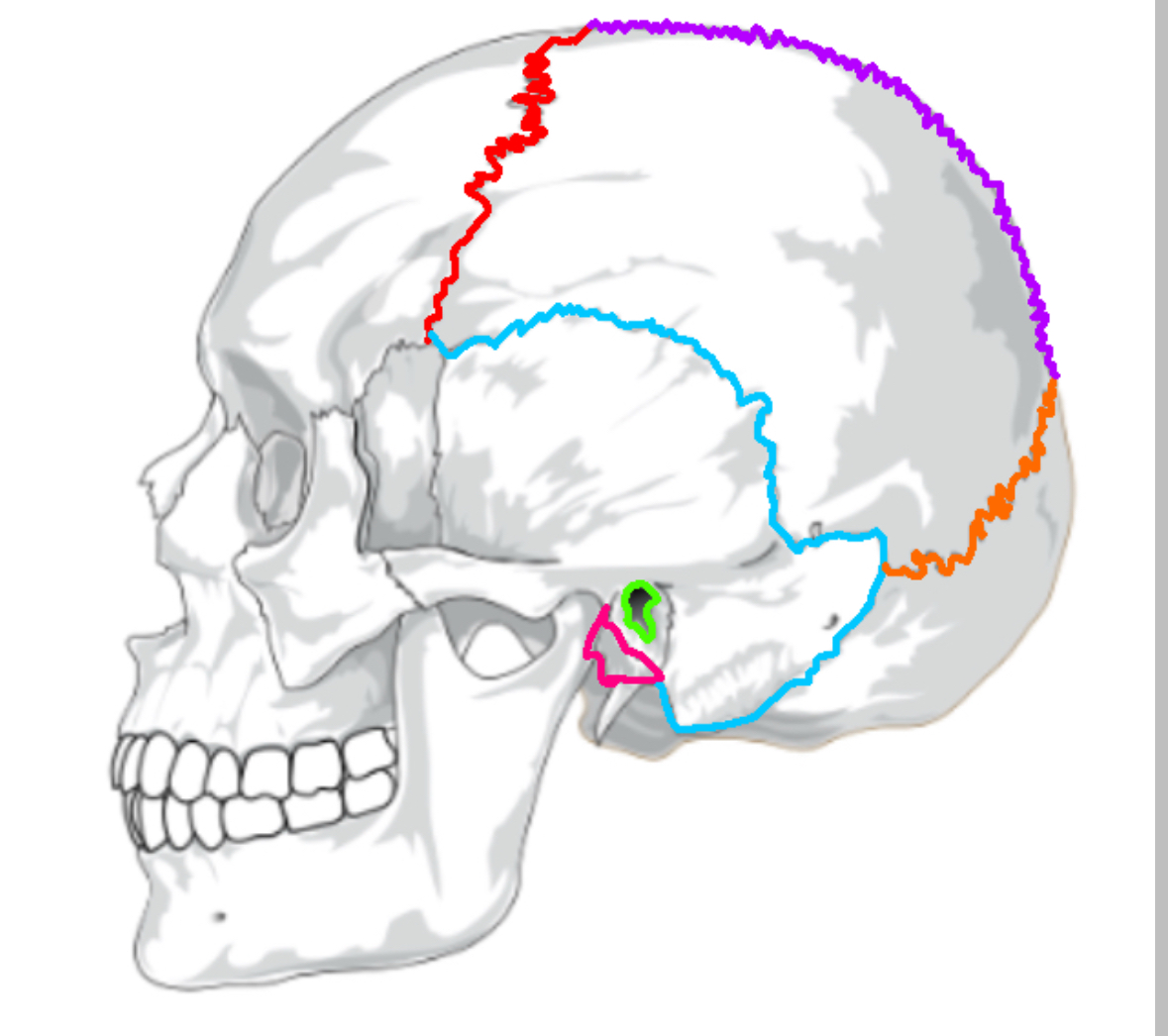
What color is the external acoustic process
Green(sutures)
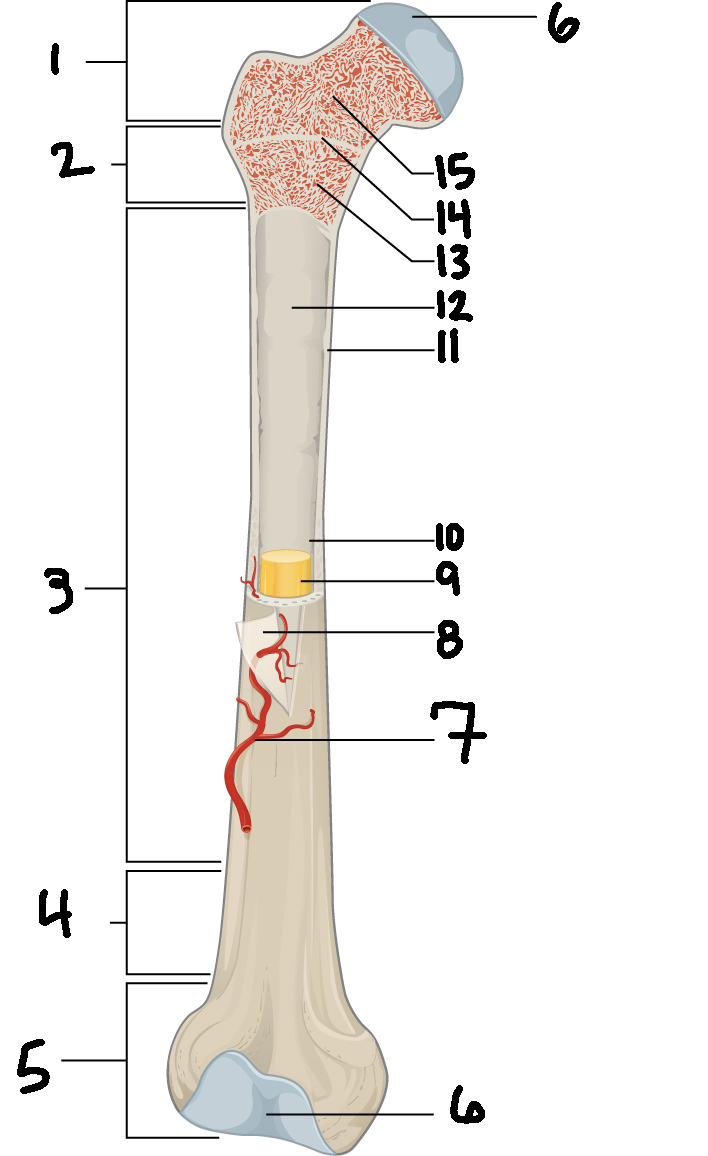
#3
Diaphysis
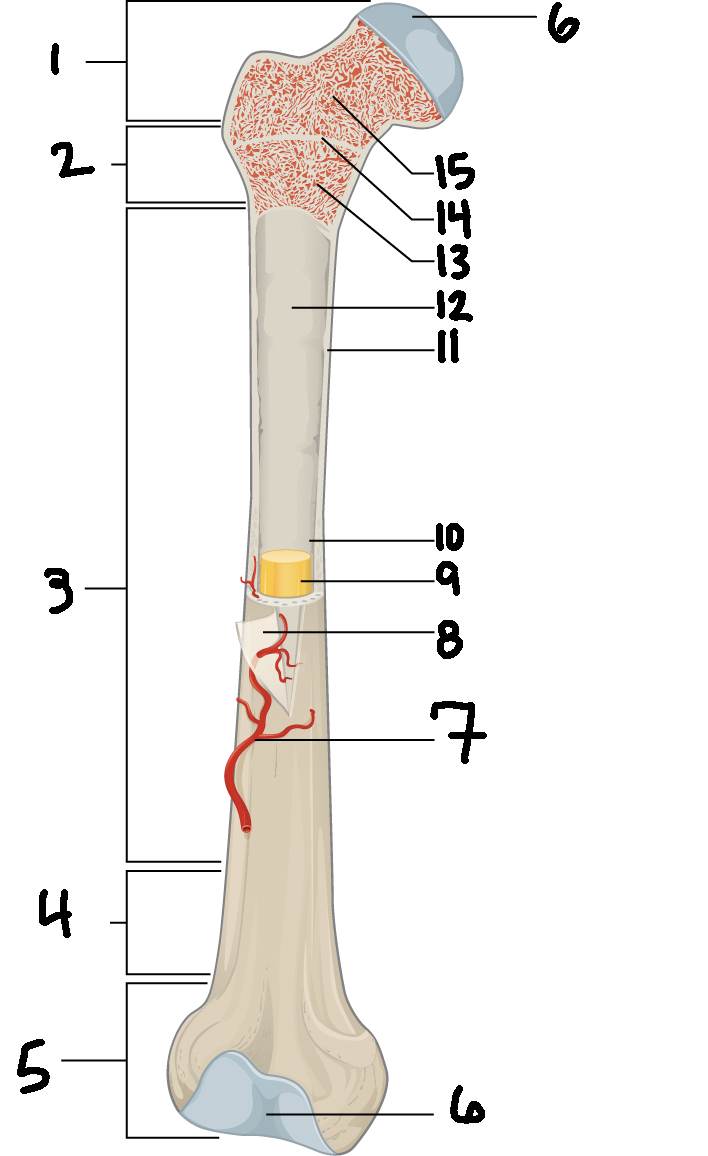
#10
Medullary cavity
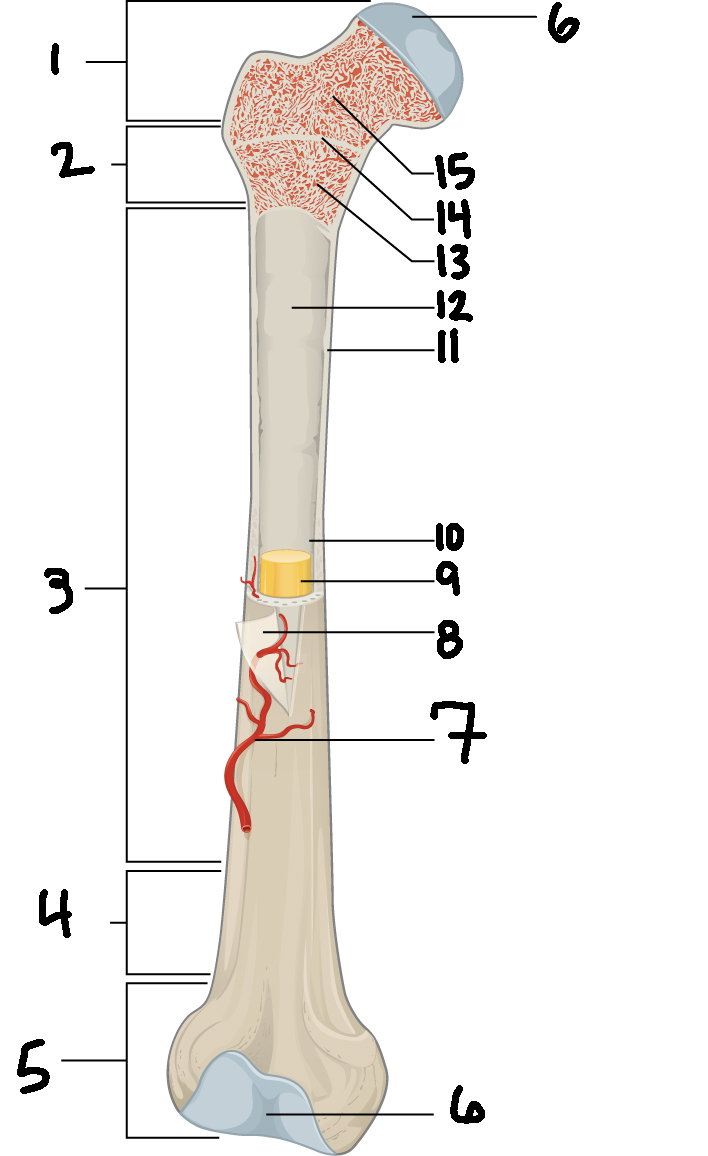
#6
Articular cartilage
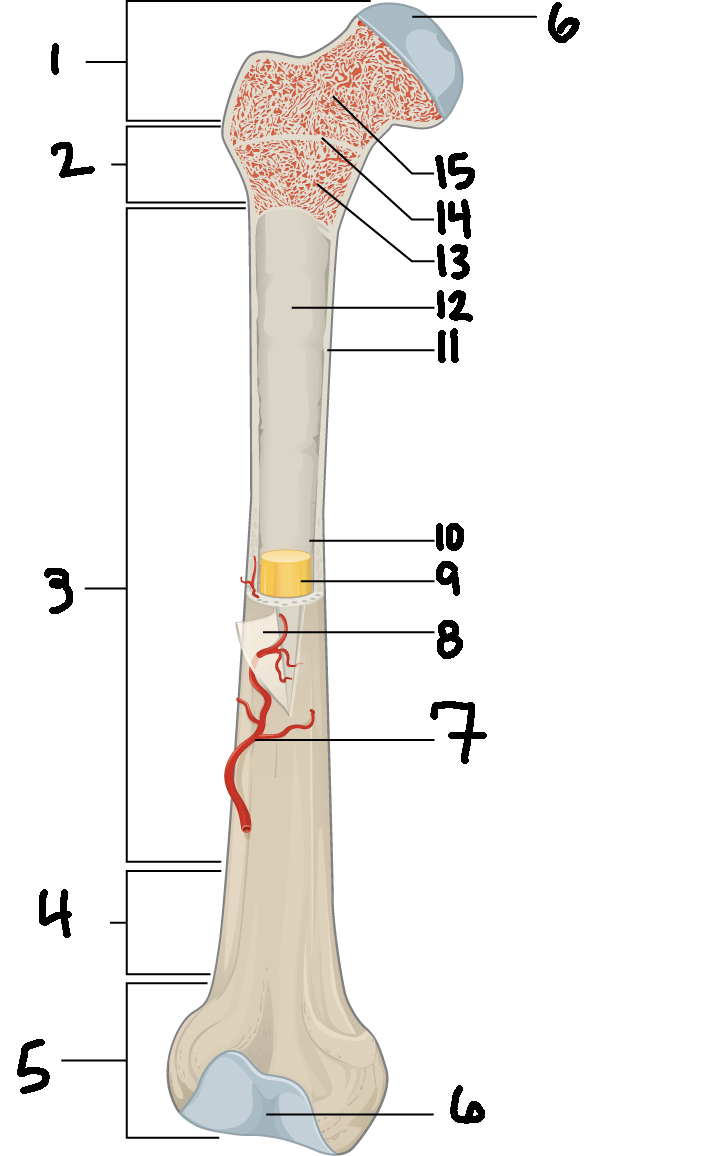
#8
Periosteum
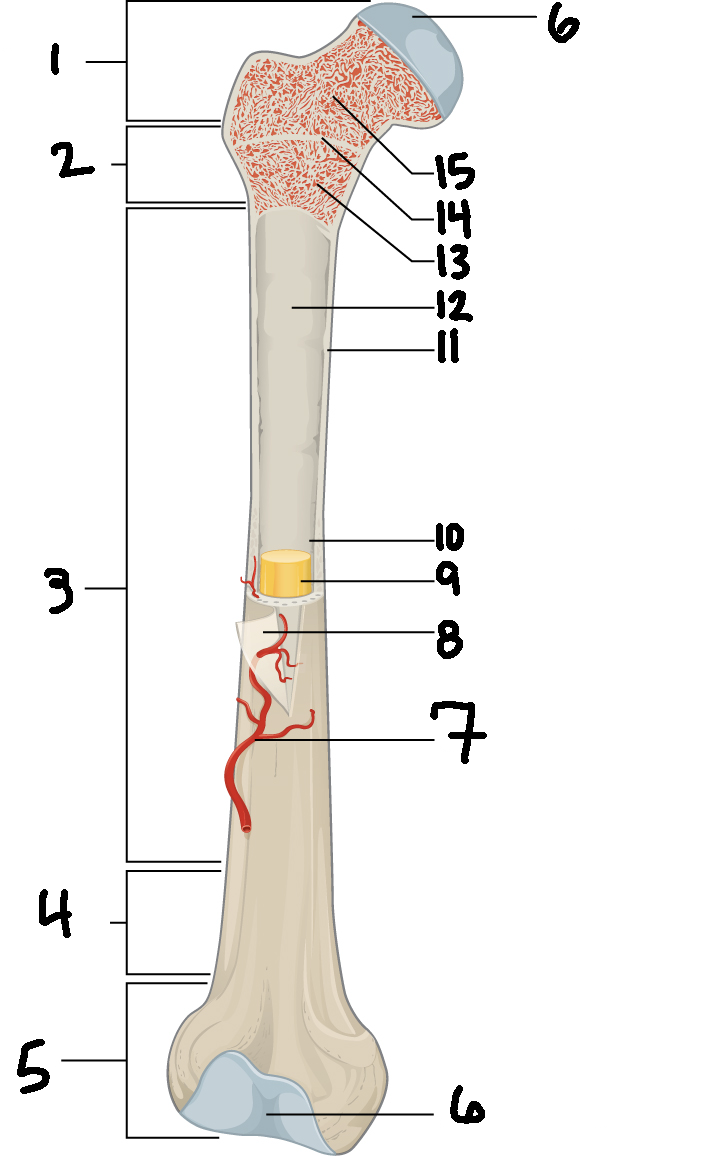
#9
Yellow bone marrow
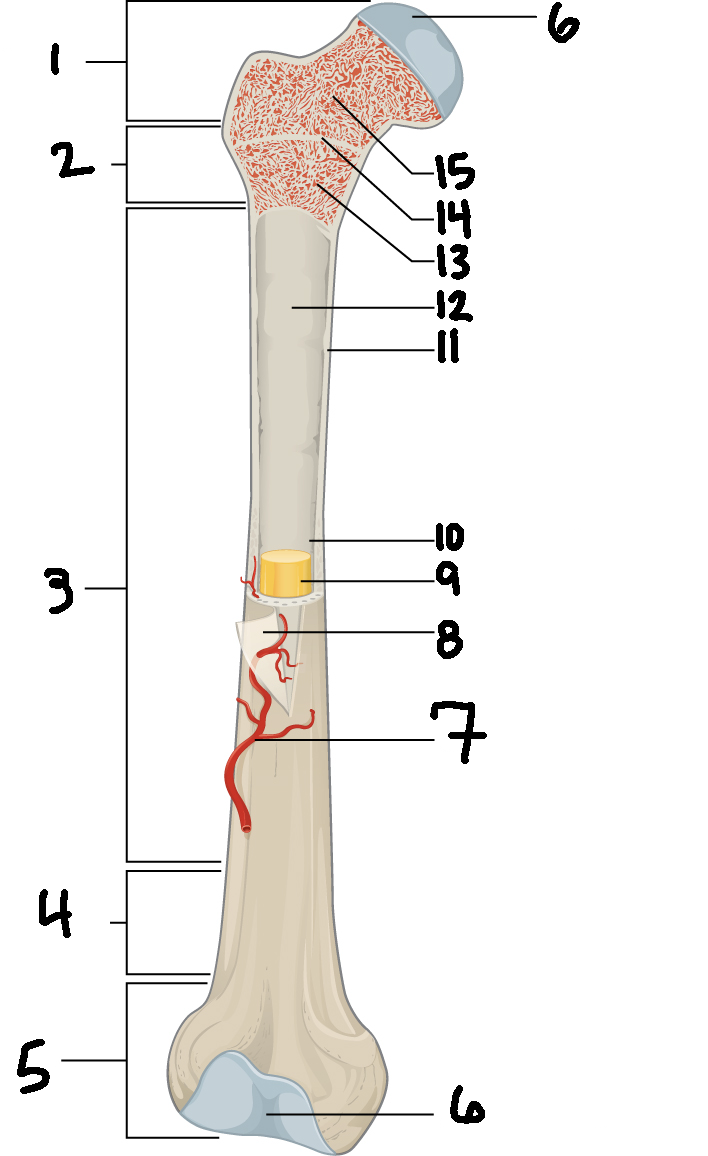
#11
Compact bone
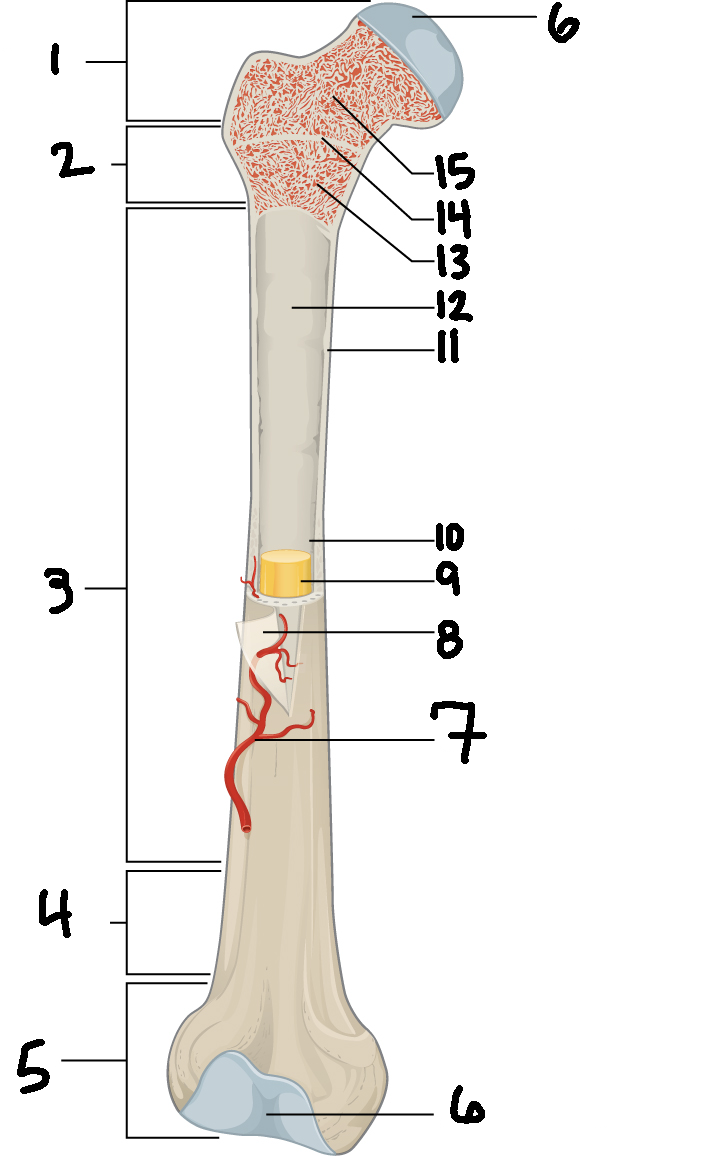
#7
Blood vessel
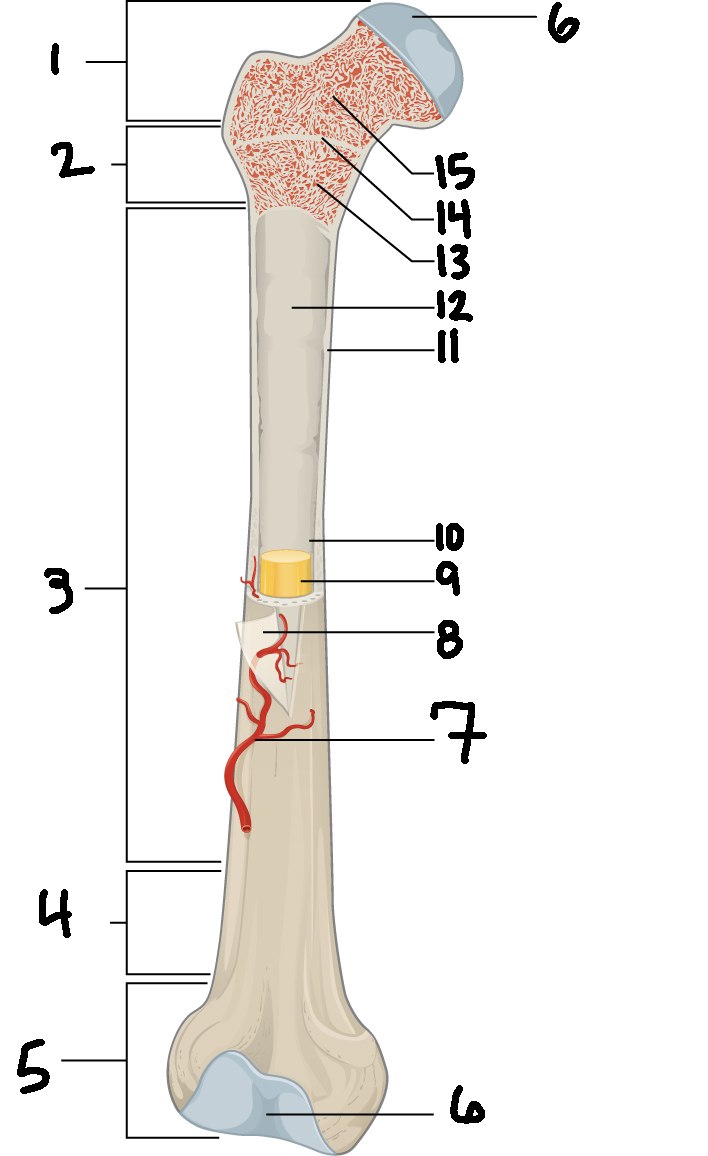
#5
Distal epiphysis
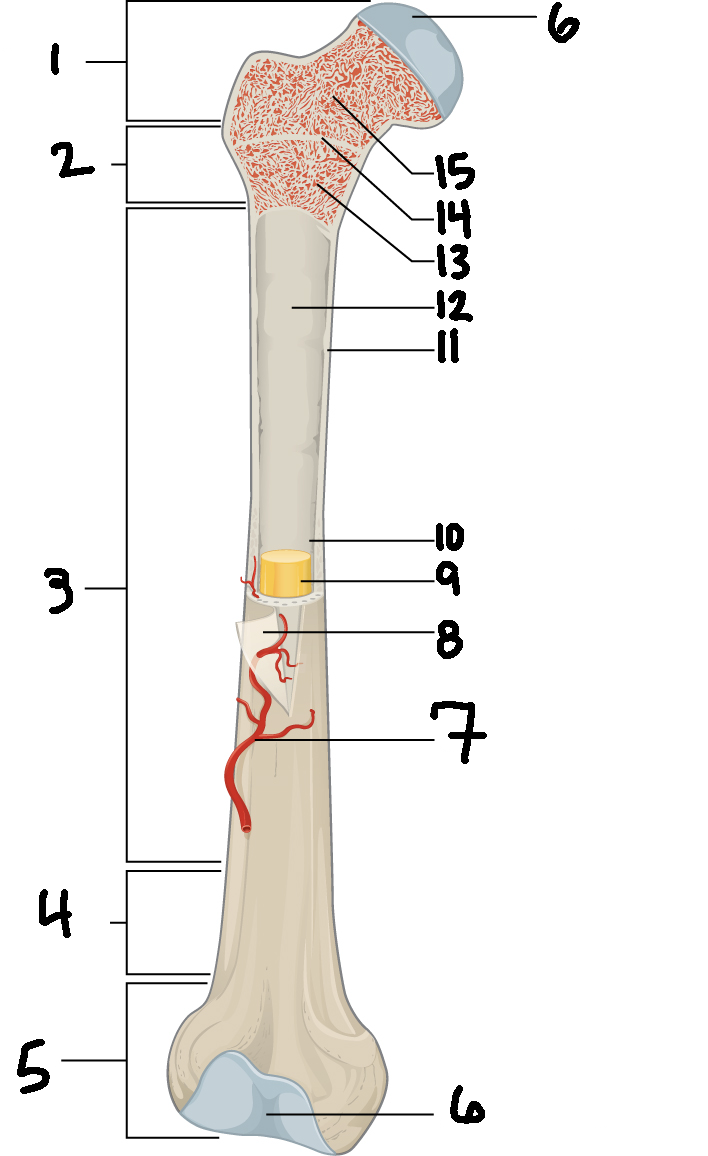
#13
Red bone marrow
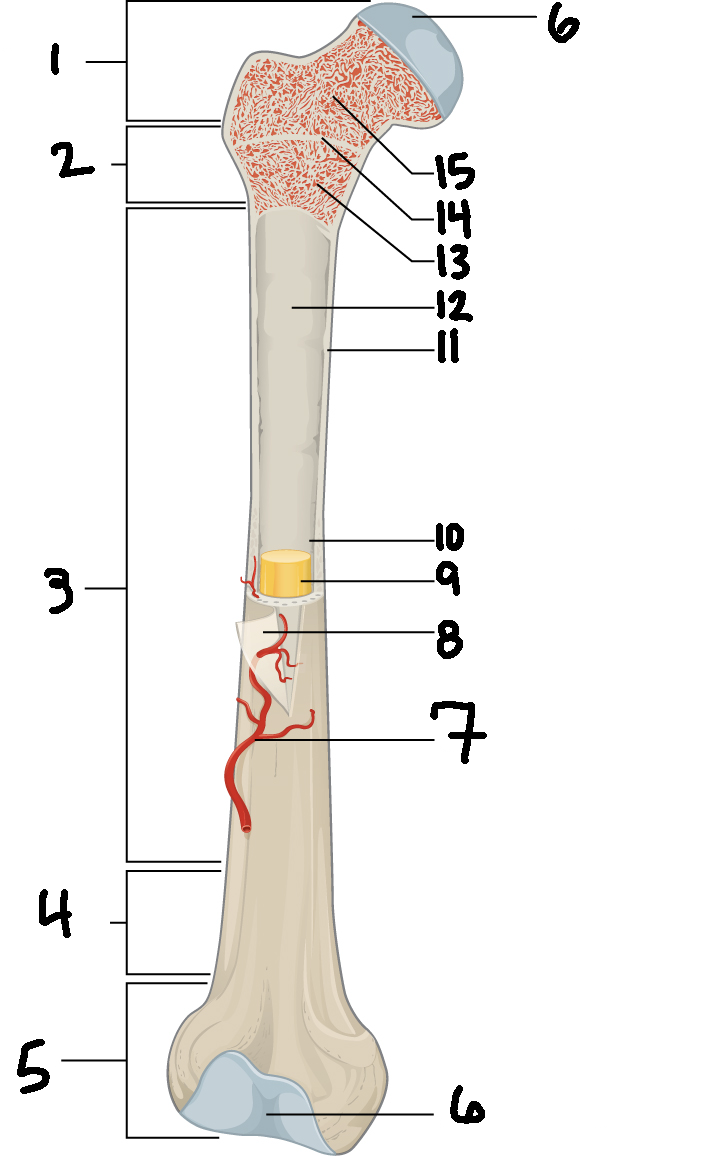
#2
Proximal metaphysis
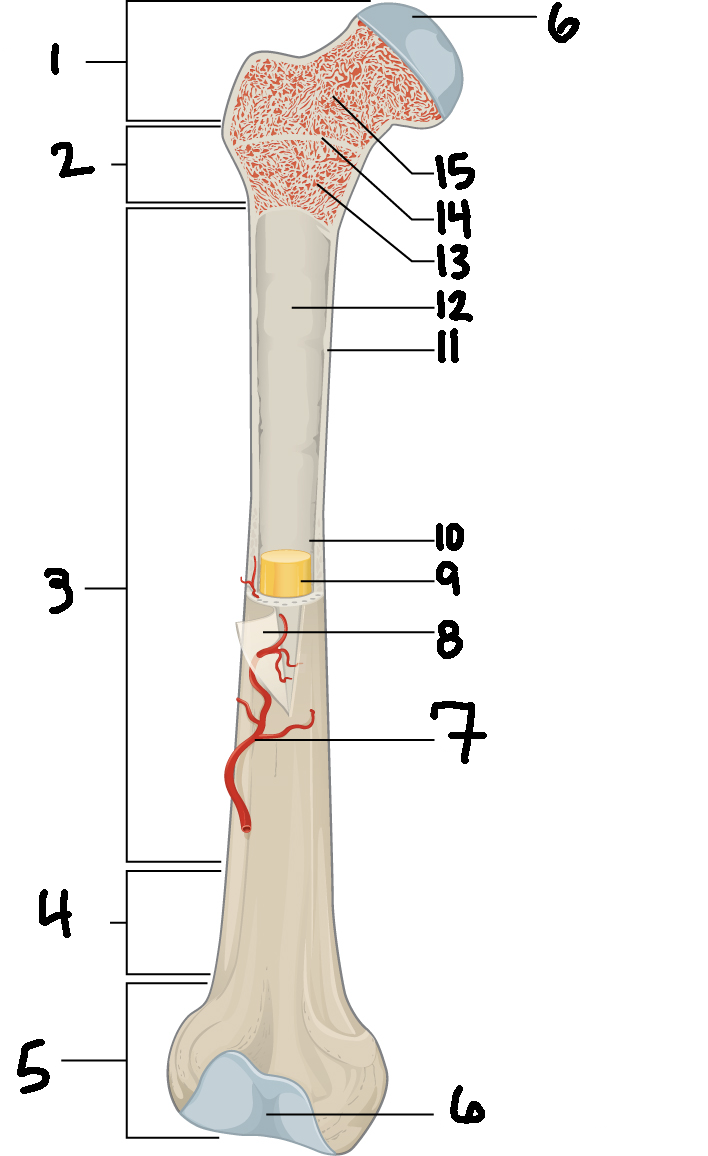
#15
Spongy bone
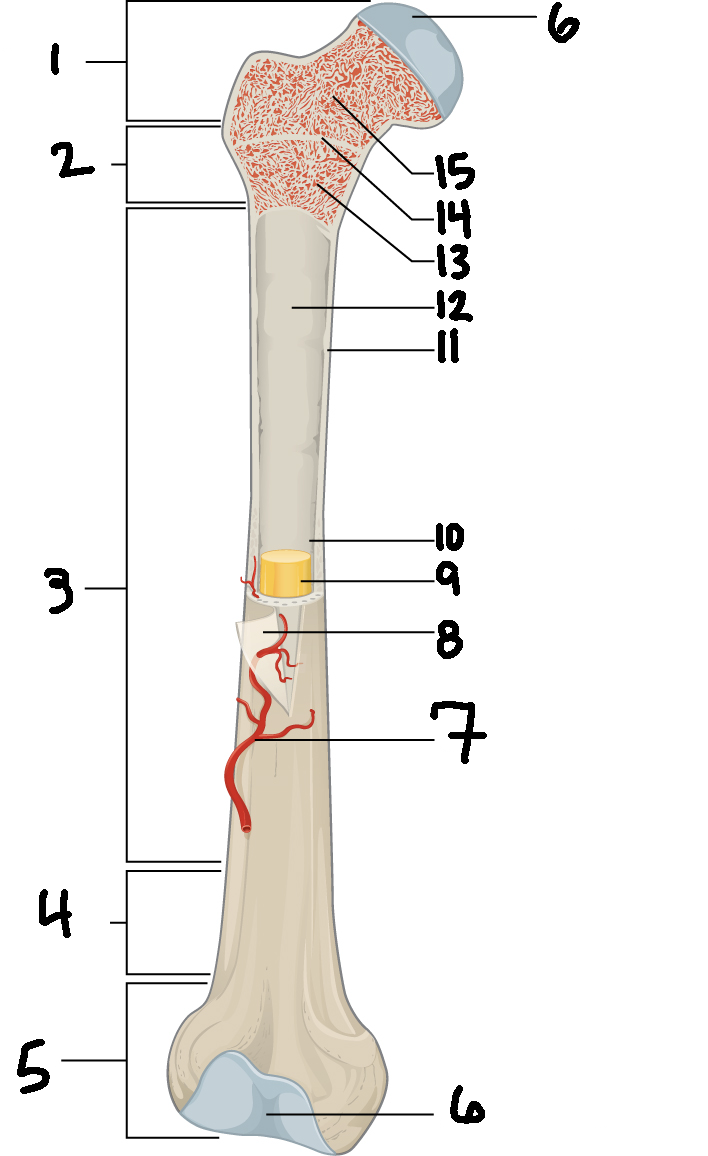
#14
Epiphyseal line
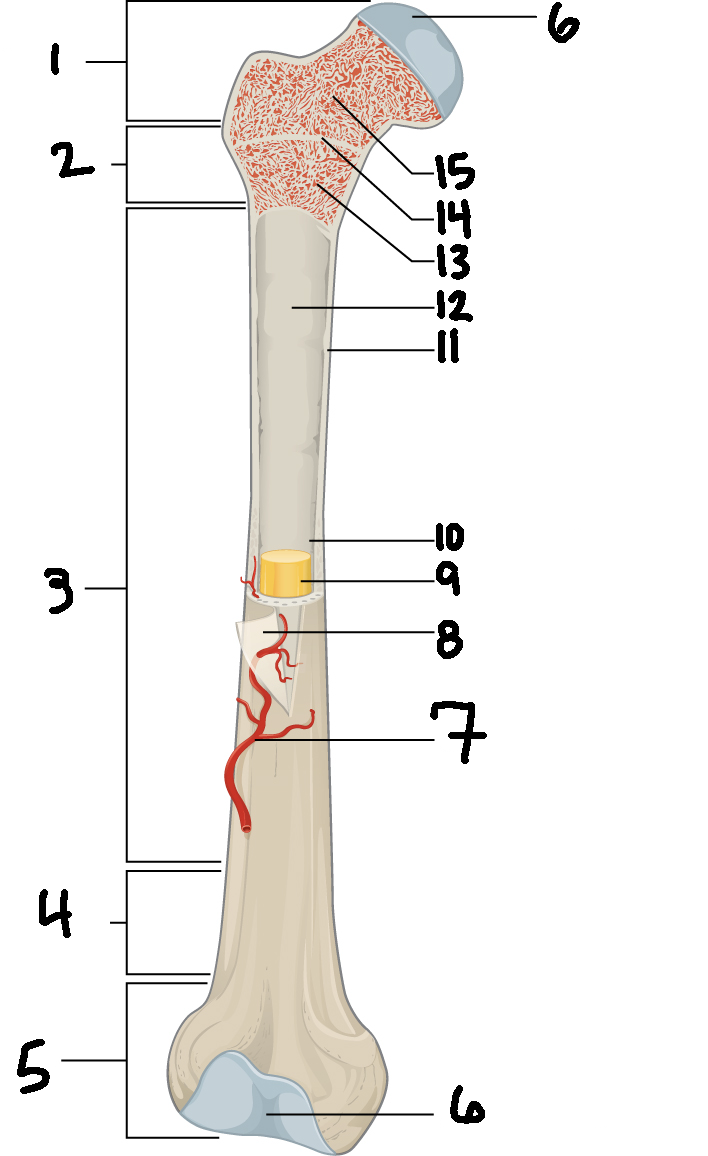
#4
Distal metaphysis
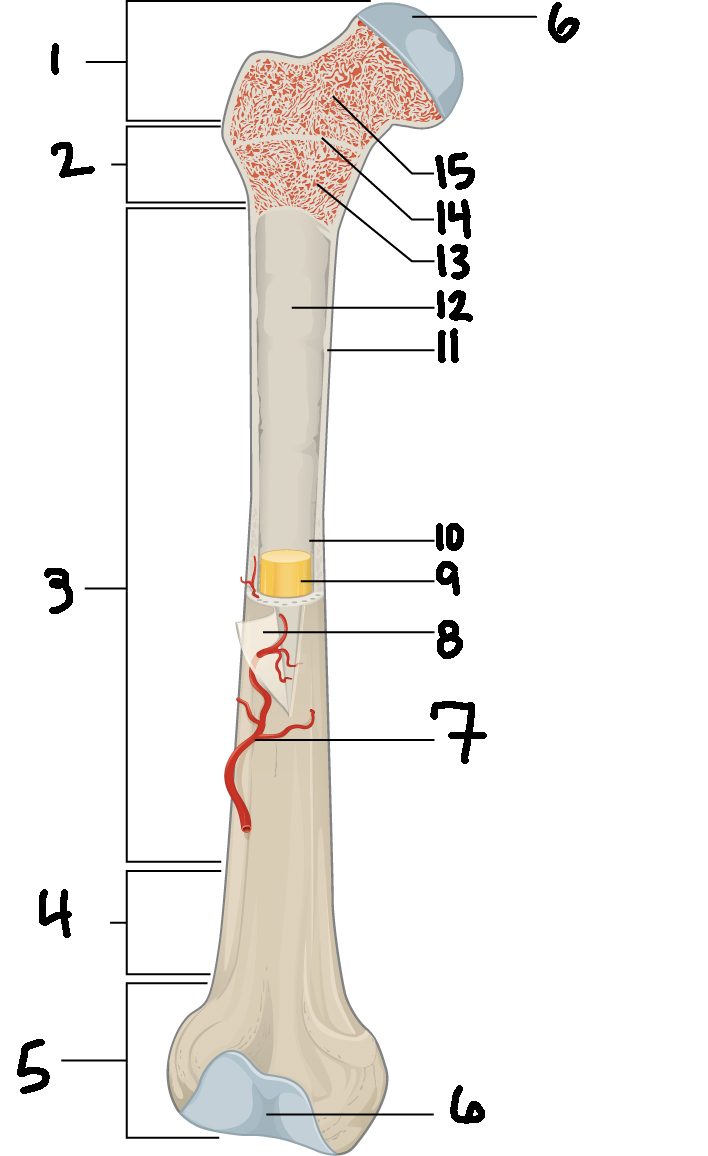
#1
Proximal epiphysis
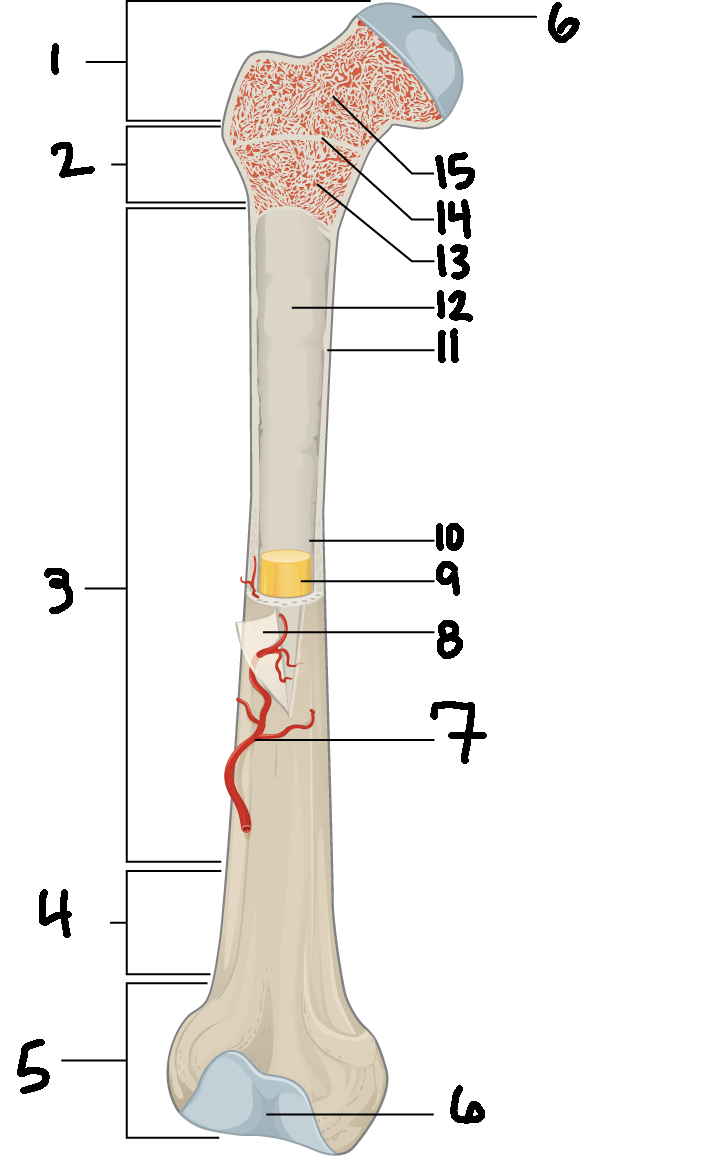
#12
Endosteum
Function of mastoid process
Attachment for head muscles; contains air cells that regulate ear pressure; protect the temporal bone
Function of external acoustic process (ear canal)
Channels sound to the eardrum; uses earwax to trap foreign objects
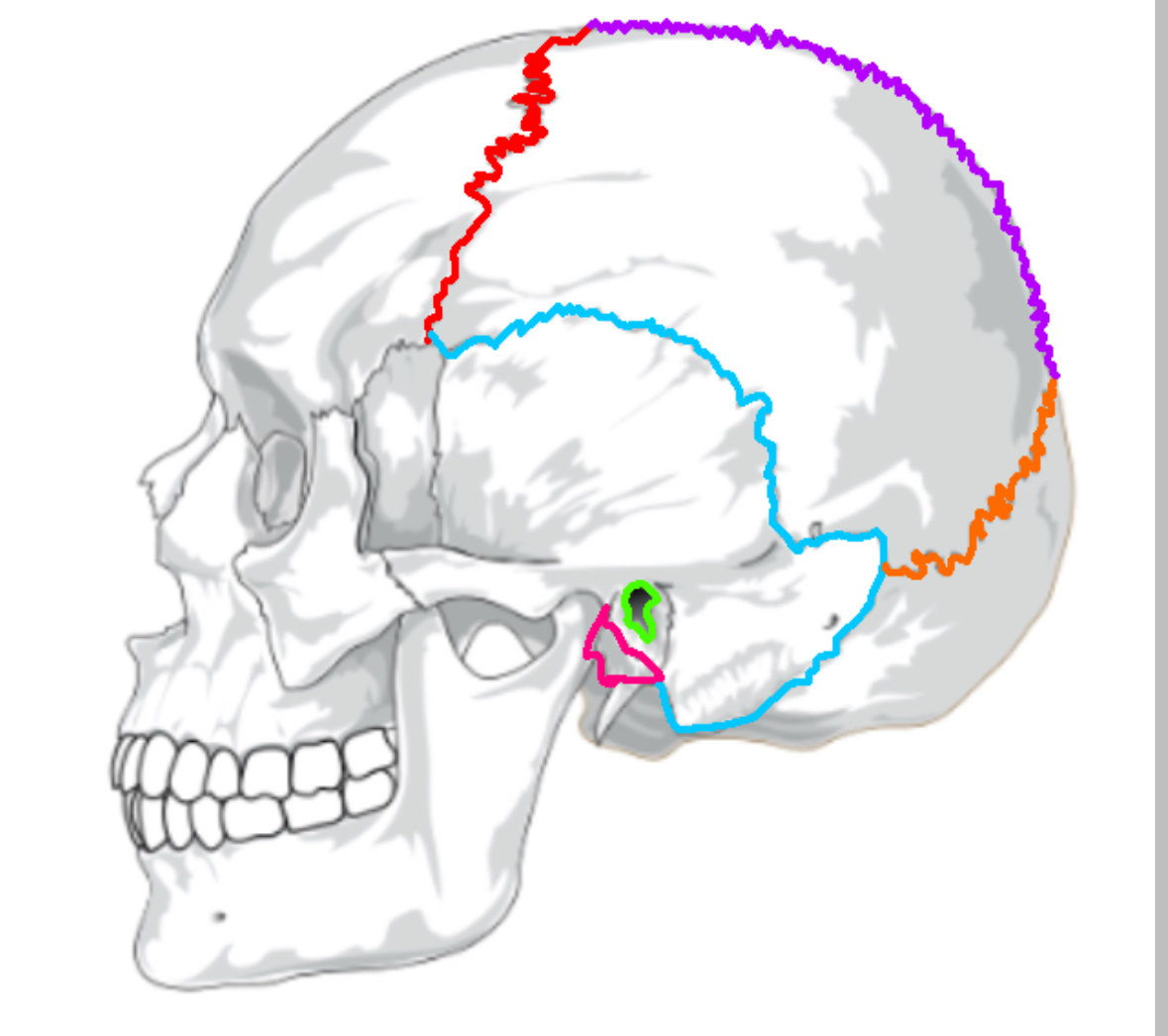
What does the coronal suture separate
frontal:parietal
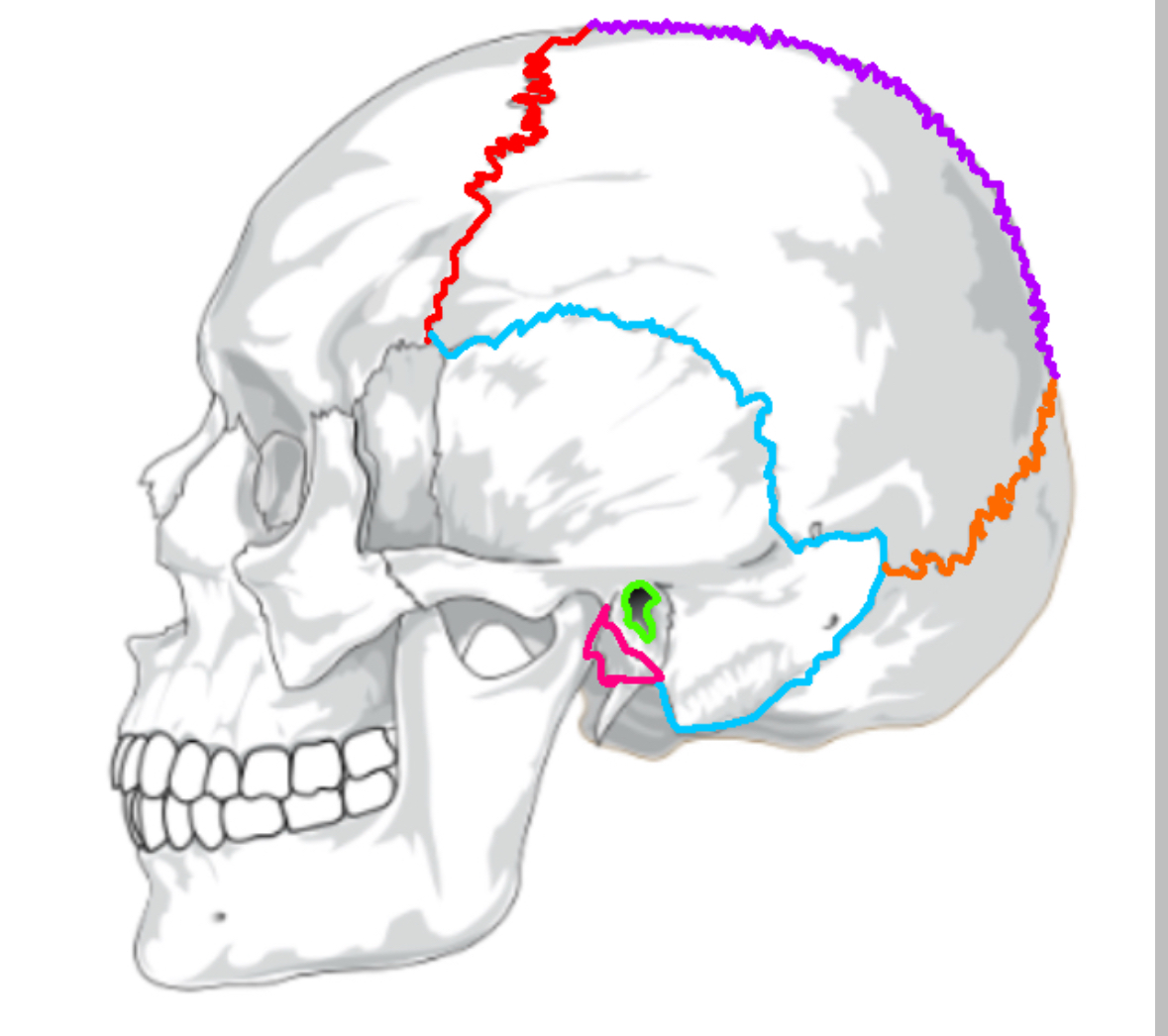
What does the squamous suture separate
temporal:parietal
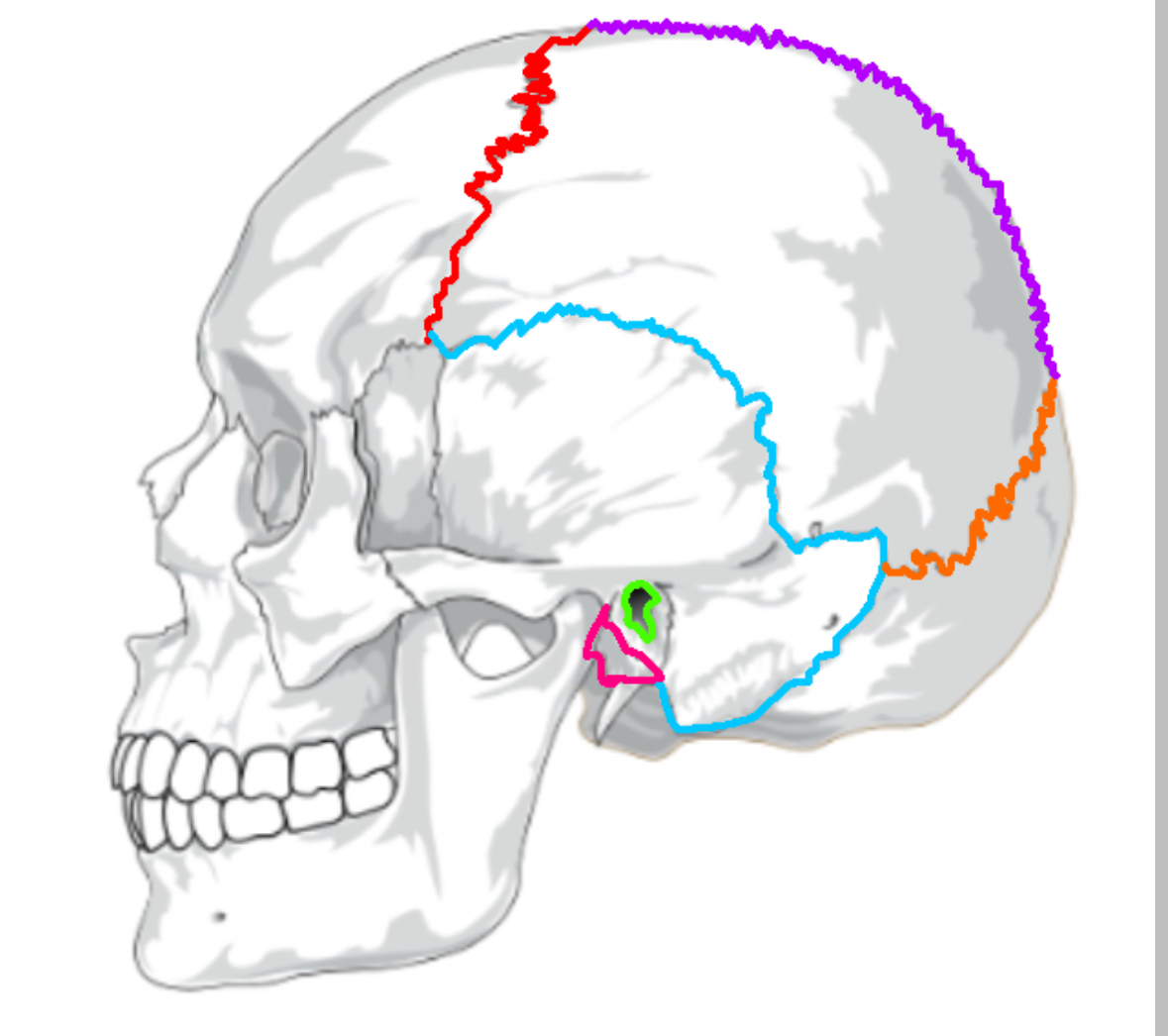
What does the lamboid suture separate
occipital:parietal
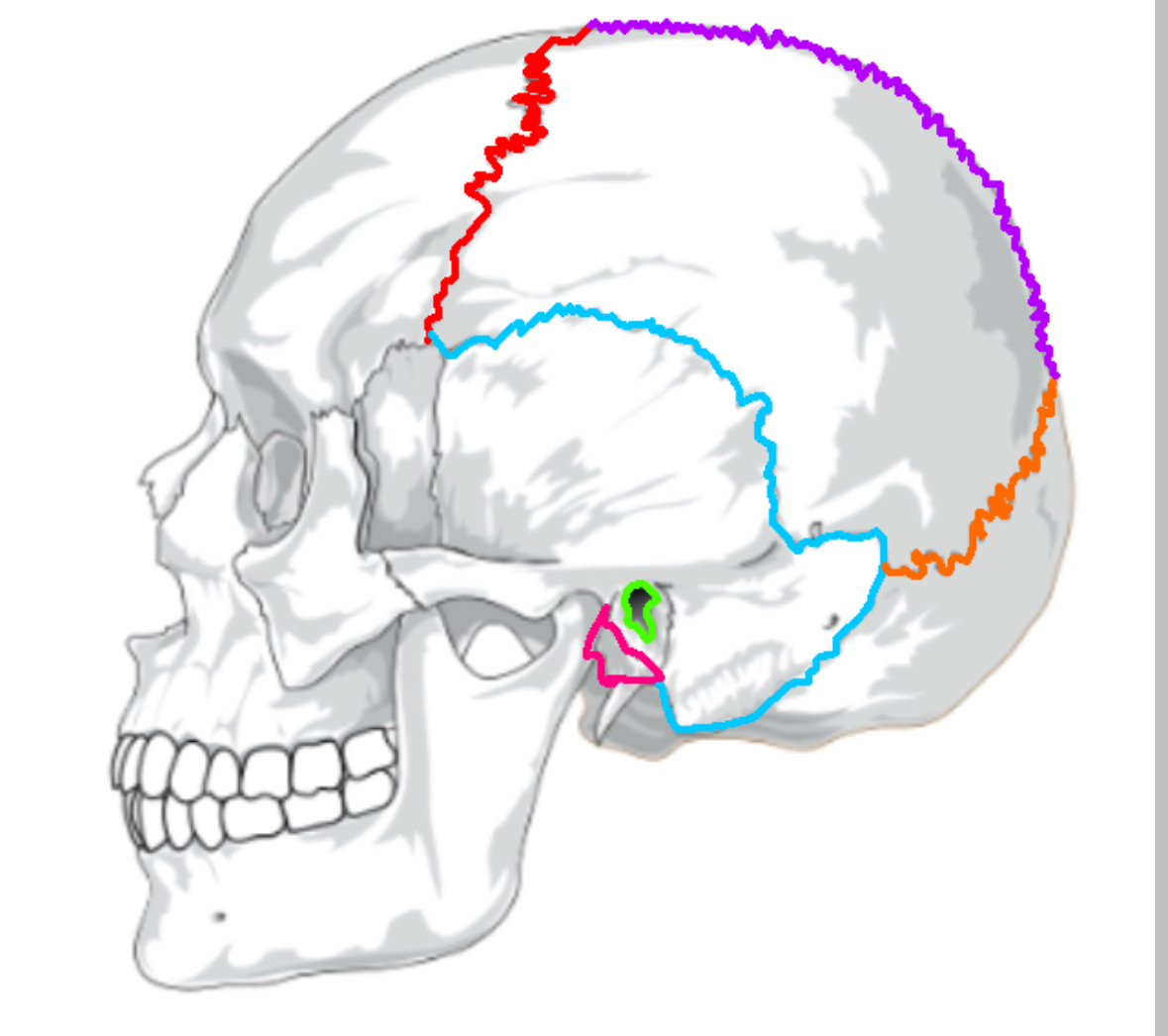
What does the saggital suture separate
parietal
Function of diaphysis
central part of bone - supports muscles (attachments); stores minerals like calcium and fat
Function of epiphysis
Ends of a long bone; forms joints w/ adjacent bones; covered w/ cartilage: location of spongy bone and red bone marrow
Function of articular cartilage
Connective tissue - covers epiphysis; decrease friction and absorb energy
Function of periosteum
Layer of vascular tissue that covers the bone - supplies blood and allows bone to grow and heal
Function of compact bone
Dense outer layer=strength and protection