Protein Structure & Function and Globular & Fibrous Proteins
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
How do you identify a 4 alpha helical bundle?
4 helices
they have polar and non polar amino acids
usually have up to 6 non polar residues next to each other to create hydrophobic area inside the bundle
How can you identify a alpha/beta protein?
have a combination of alpha and beta secondary structures
How can you identify a beta-alpha-beta protein?
each beta strand twists to distort H bond
can be saddle shape or barrel shape
amphipathic helices outside
hydrophobic strands in middle
How can you identify a domain?
several proteins associated together
frequently linked or inserted within one another
Name and briefly describe 2 fibrous proteins
alpha keratin
2 polypeptide dimer that have a left handed twist
chains cross linked by disulfide
beta keratin
stacked anti-parallel beta sheets
alternating Gly & Ala/Ser residues
stacking makes it strong
dispersed among alpha helices to give some flex
What internal conformational change occurs when oxygen binds the heme Fe in hemoglobin?
A shift of the F-helix
histidine is in this helix
changes interactions
rotation of one alpha-beta dimer
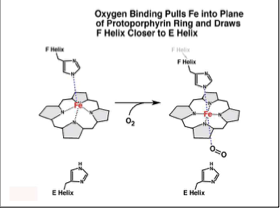
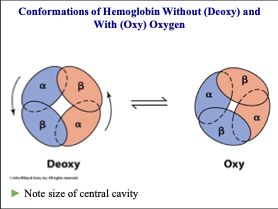
How is the quaternary structure changed when oxygen binds the heme Fe in hemoglobin?
The space between the alpha helices tightens with oxygen is bound (0.39 nm)
What is the Bohr effect and how does it facilitate CO2 transport?
The Bohr effect enhances oxygen delivery to tissues where CO₂ production is high
Does this by making Hb bound with O2 more acidic (lowering the pH)
helps CO₂ transport by promoting hemoglobin's release of oxygen and uptake of CO₂.
How does BPG affect the transport of oxygen by hemoglobin?
BPG binds to deoxy Hb (squeezed conformation)
lowers amount of O2 bound
lowering affinity of Hb for O2
What are globular protiens?
soluble in water
circular shape
alpha-helix and beta sheet stabilize structure
L-amino acids
What are 3 types of alpha helices?
amphipathic - one side hydrophobic & one side hydrophilic
hydrophobic - inside membrane/structure
polar - solvent exposed
Why can’t myoglobin be used to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues?
binds too tightly with oxygen
meant to drop off oxygen to mitochondria
used for tissues
Does BPG inhibit or enhance O2 binding?
inhibits binding to encourage the oxygenation of tissue