CSD: Speech and Hearing Science- Chpt. 1, 8, & 9 Test
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Energy
ability to do work
elasticity
property of a material that returns it to its orginal shape
power
rate of work done or energy used in a period of time
speed
distance traveled at any given time
pressure
force acting on a specific surface are
velocity
distance traveled in a given unit of time in a specific direction
volume
quantity of a 3D space occupied
mass
amount of matter in an object
force
any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, direction, or shape
scientific measurement systems are based on __________ system
metric
the main function of this part of the ear is to help channel sound waves in the ear canal
outer ear
a type A tympanogram indicates
normal middle ear function
This part of the inner ear is important for hearing
cochlea
a sound with one single frequency
pure tone
individuals with high-frequency hearing loss have particularly have difficulty perceiving
consonants
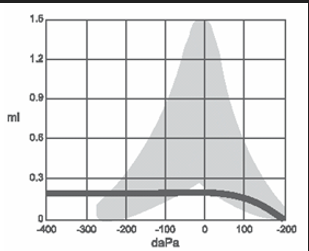
what type of tympanogram is this and what would it typically suggest
abnormal type B
suggests very little or no movement of the tympanic membrane
could be caused by pressure in the middle ear or cerumen preventing a proper test
Amplitude corresponds to loudness and frequency corresponds to pitch (T/F)
true
an electronic device designed to directly stimulate the auditory nerve and is typically used for persons with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss
cochlear implant
diagnostic test of the middle ear system
tympanogram
what is the unit of measurement for frequency
hertz
What separates the outer and middle ear
tympanic membrane
What is an otoacoustic emission (OAE) and what type of patient demographic might we use this test for? What is the difference between how an audiologist might use this test vs. how a speech language pathologist might use this test?
OAE measures the sounds the inner ear, specifically the cochlea, sends back through the ossicles
can be used on any patient as the patient does not need to be conscious
most likely used on someone suspected of severe hearing loss to show whether the inner and middle parts of the ear are working correctly
Audiologist: see where damage could be
SLP: extent of hearing damage and how this could affect speech perception or production
length of time it takes to complete one cycle of a vibration
period
the semicircular canals and vestibule are important for
balance
tympanometry tests three main properties of the middle ear…
pressure
compliance
volume
what does Eustachian tube do?
keeps middle ear space ventilated
equalizes pressure between middle ear and atmosphere
runs from the nasopharynx into the middle ear
Threshold
the maximum or minimum frequency of a sound a person can hear at a certain amplitude
if someone has normal tympanometry results, we cannot assume that they have normal hearing (T/F)
true
a combination of biology and acoustics in the study of sound production and perception in animals including humans
bioacoustics
know where malleus, pinna/auricle, tympanic membrane, cochlea, eustachian tube/auditory tube, semicircular canals, stapes, and incus are on diagram
four major parts of the auditory system
outer ear
middle ear
inner ear
auditory nerve
three types of hearing loss
conductive
sensorineural
mixed
graph that represents an individual’s hearing threshold at selcted frequencies
audiogram
on an audiogram hearing loss is documented by
decibels and frequency
This test is one of the objective hearing measures discussed in class. It uses electrodes to measure the response from the 8th cranial nerve
auditory brainstem response (ABR)
Which of the following statements is NOT true of otitis media?
can result from upper respiratory infection
can result from build-up in the middle ear
common in young children
results in a mixed hearing loss
results in a mixed hearing loss
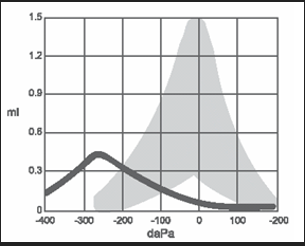
What type of tympanogram is this and what would it typically suggest
abnormal type C
suggests extremely negative pressure in the middle ear
primarily caused by stiffening of the ossicles