Epithelial Tissue|4 Medical Histology
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test #2 Tissues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
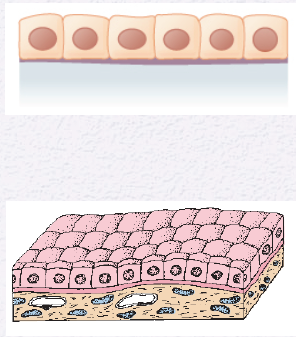
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal
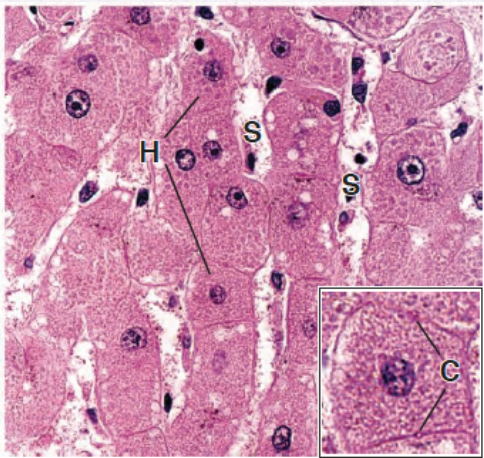
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal
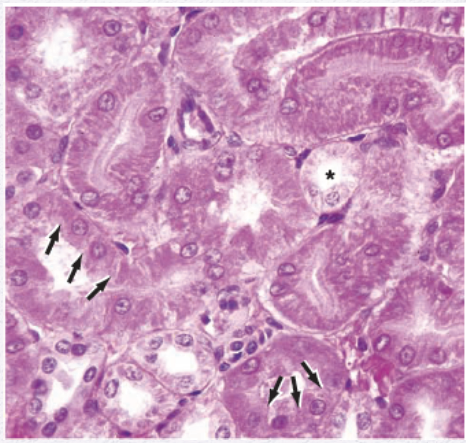
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal
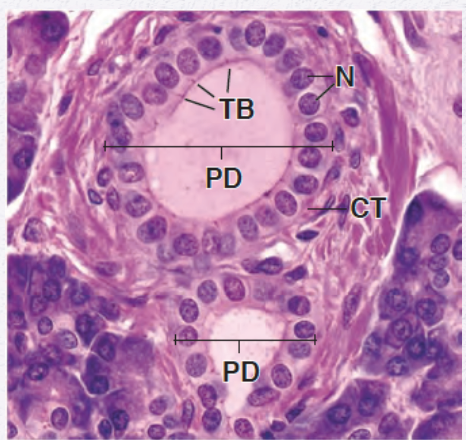
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal
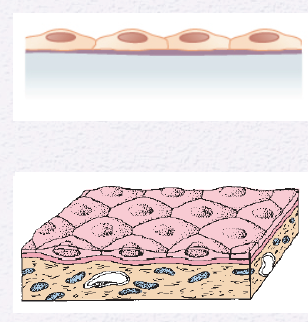
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Squamous
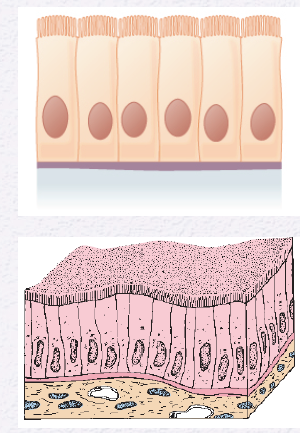
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Columnar
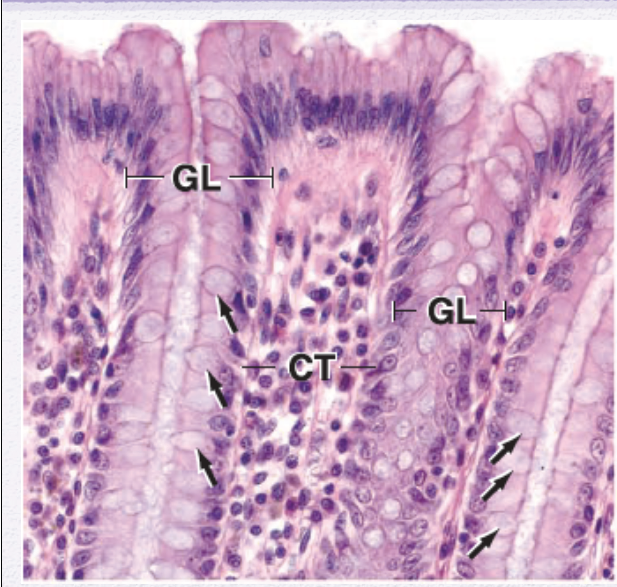
Identify the Epithelium
Simple Columnar (with goblet cells)
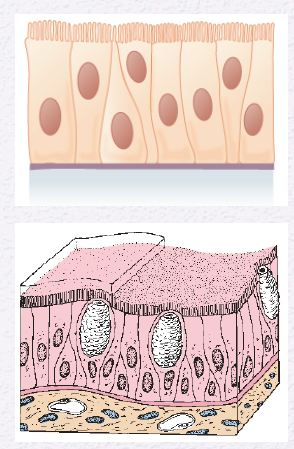
Identify the Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar
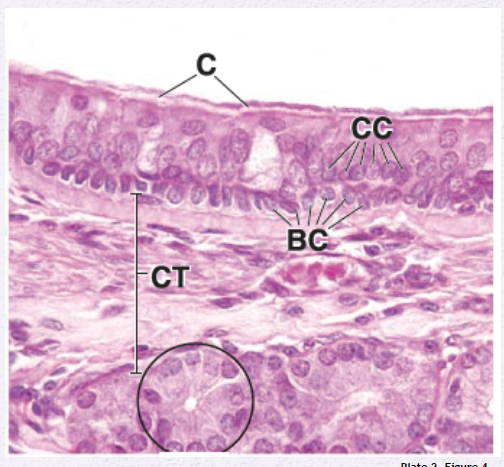
Identify the Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar
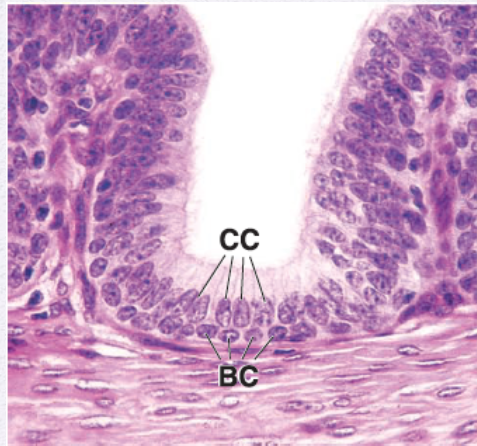
Identify the Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar
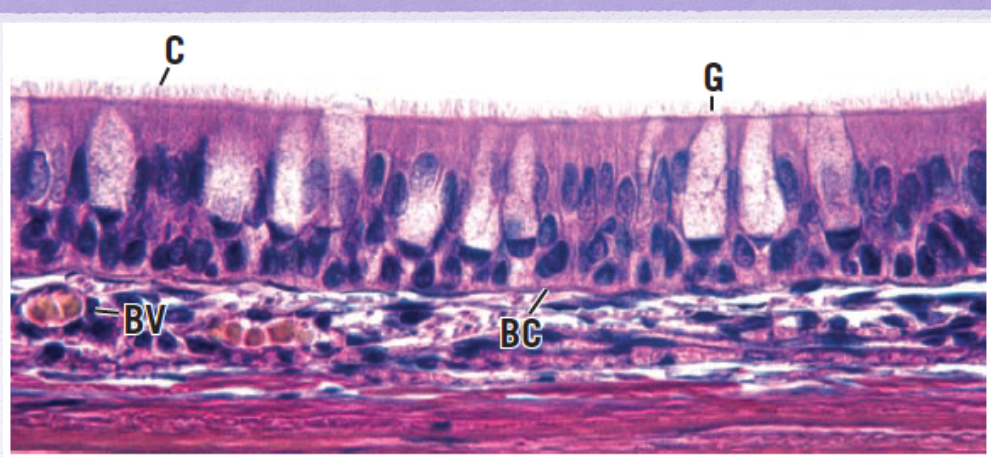
Identify the Epithelium
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Squamous
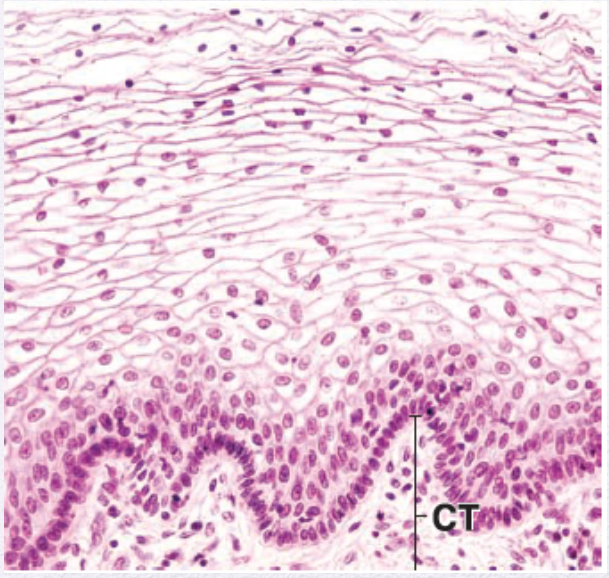
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Squamous
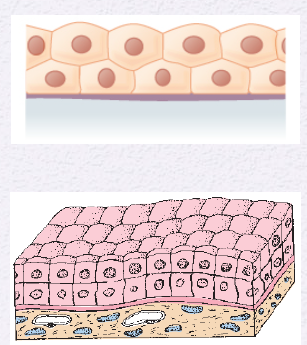
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal
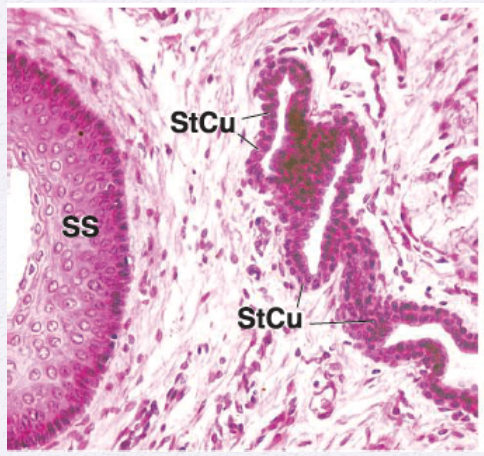
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal and Stratified Columnar
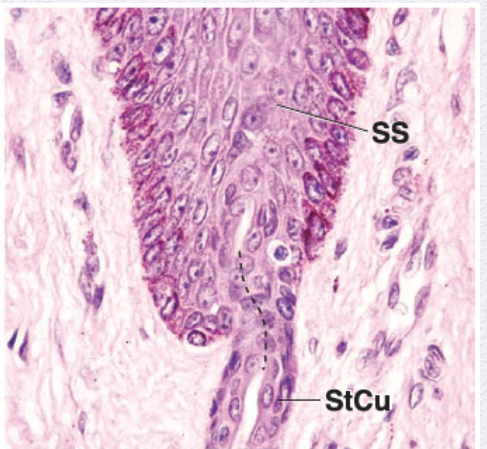
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal and Stratified Columnar
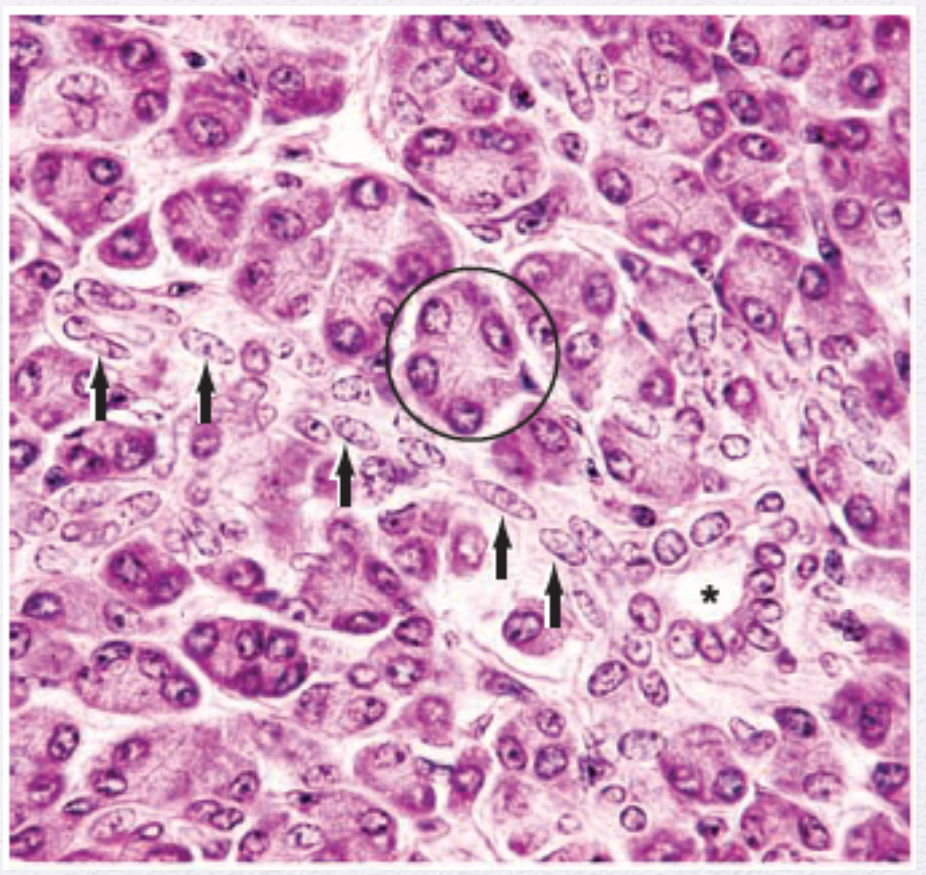
Identify the Epithelium (Circle)
Simple Columnar
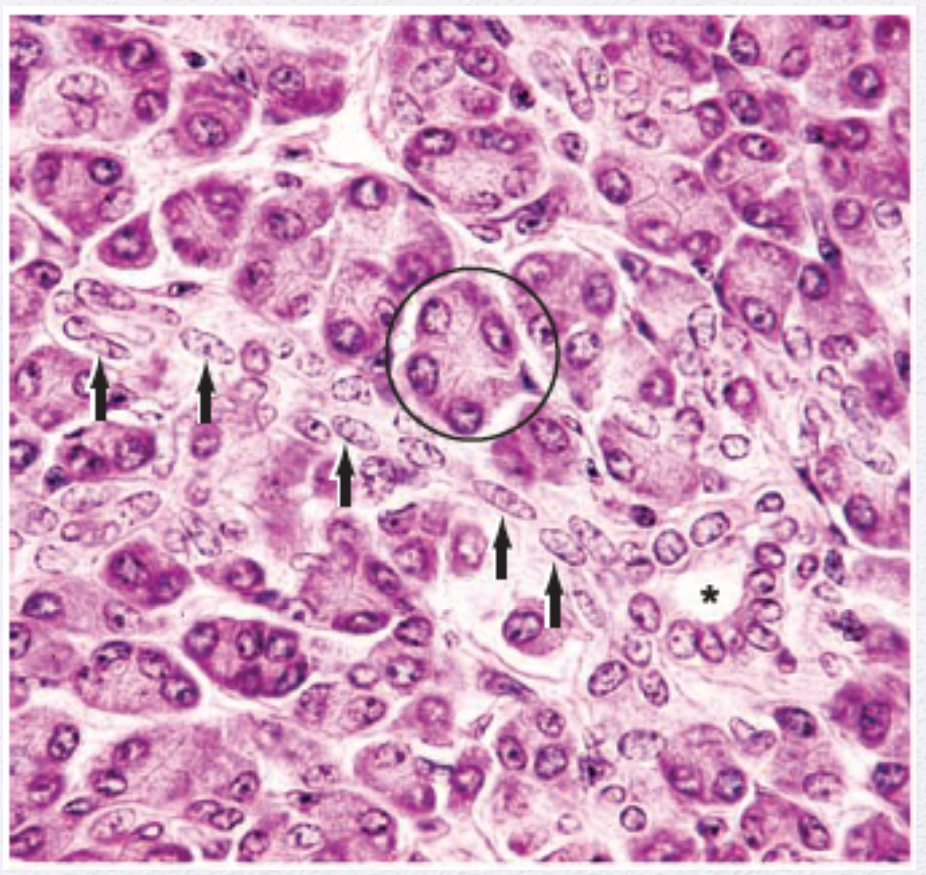
Identify the Epithelium (Arrows)
Simple Squamous
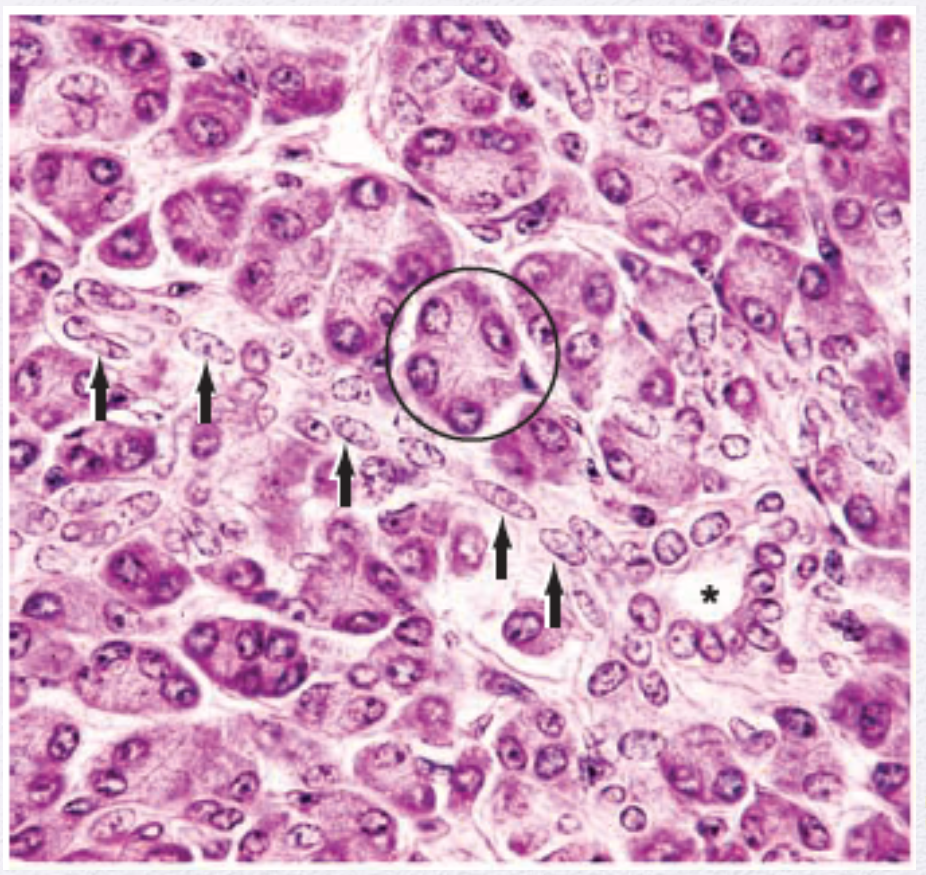
Identify the Epithelium (Asterisk)
Simple Cuboidal
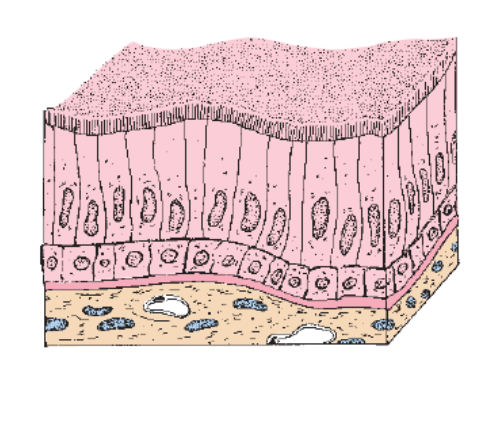
Identify the Epithelium
Stratified Columnar
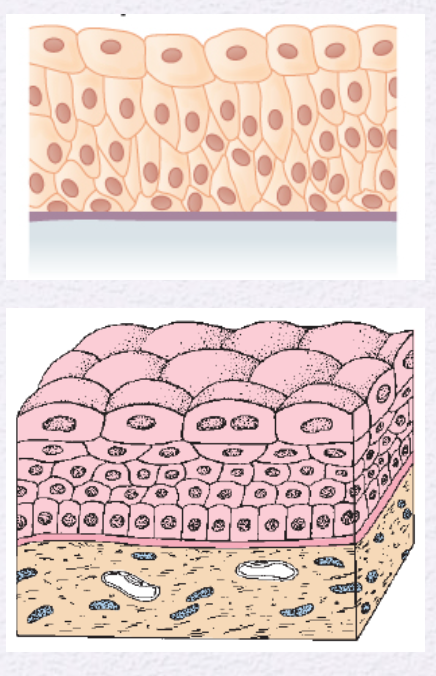
Identify the Epithelium
Transition Epithelium (Urothelium)
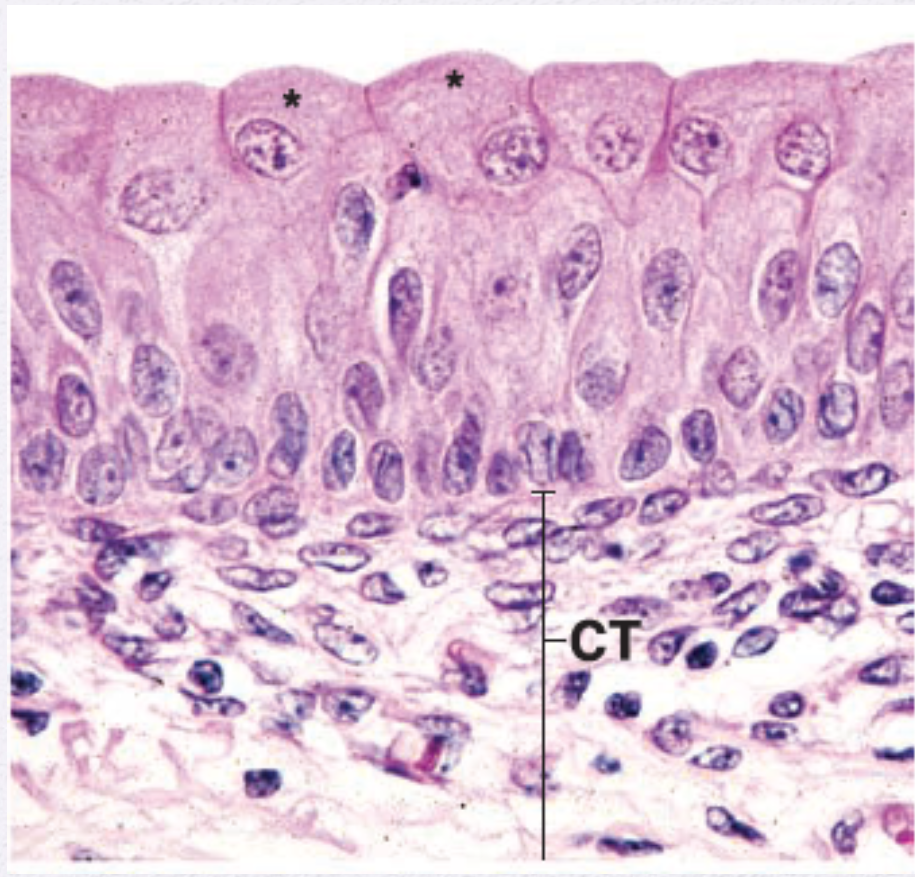
Identify the Epithelium
Transition Epithelium (Urothelium)
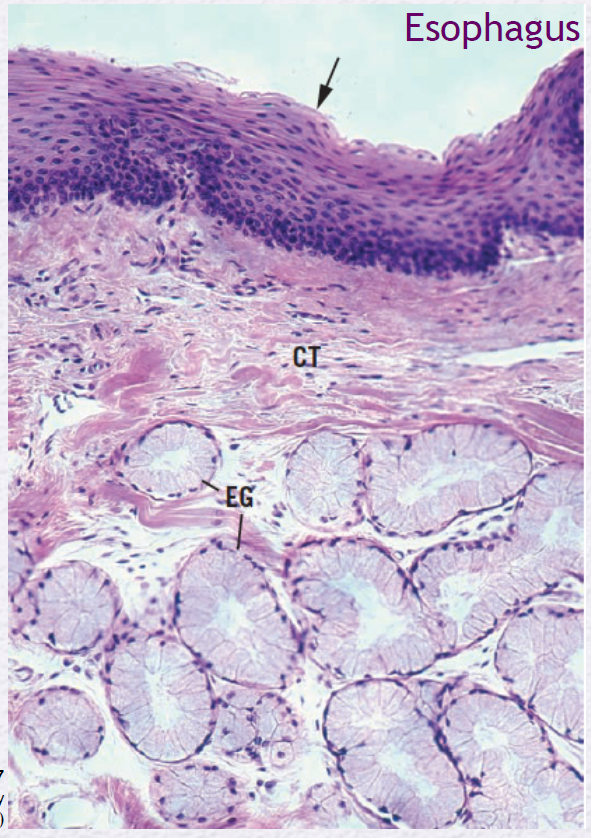
Identify the Epithelium (arrow)
Stratified Squamous
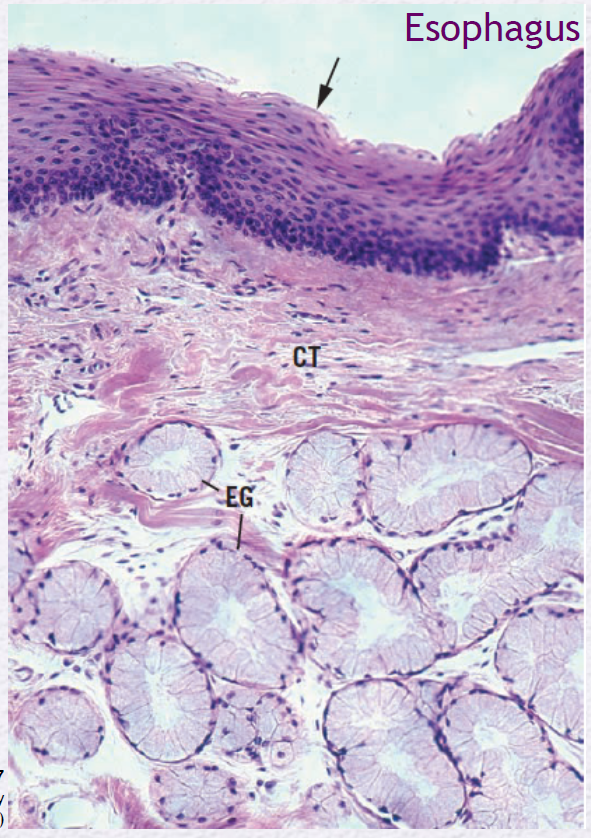
Identify the Epithelium (EG)
Esophageal Gland
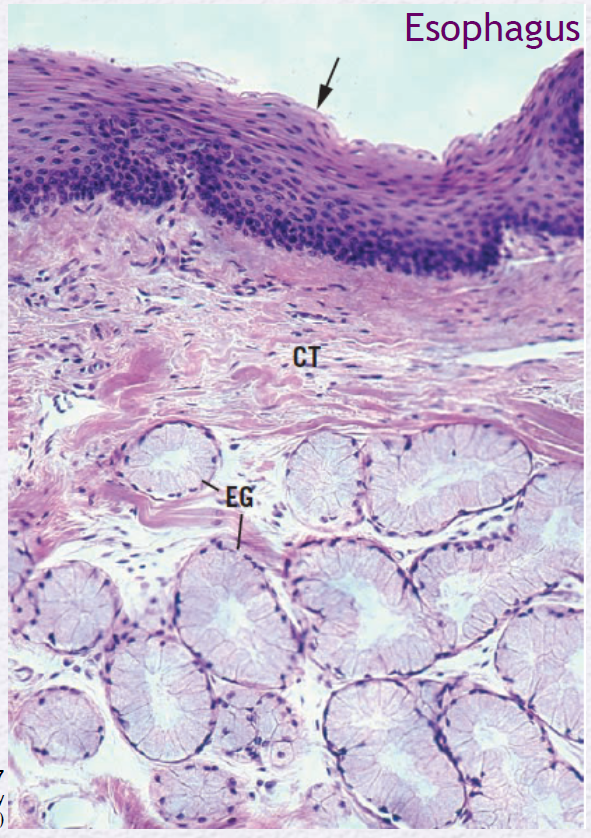
Mention the parts of a Gland
Parenchyma and Stroma
Parenchyma
Functional portion of secretory and ductal epithelial cells.
Stroma
Supporting CT, separated from parenchyma by a basal lamina.
Supporting CT, separated from parenchyma by a basal lamina.
Stroma
Functional portion of secretory and ductal epithelial cells.
Parenchyma
Mention the 4 types of Body Tissue (4)
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Simple Squamous Typical Locations (4)
vascular system (endothelium)
body cavities (mesothelium)
Bowman’s Capsule (kidney)
Respiratory Spaces in Lungs
Simple Squamous vascular system (endothelium) function
Exchange, barrier in CNS
Simple Squamous body cavities (mesothelium) function
Exchange & lubrication
Simple Squamous Bowman’s Capsule (kidney) function
Barrier
Simple Squamous Respiratory Spaces in Lungs function
Exchange
Simple Cuboidal Typical Locations (4)
small ducts of exocrine glands
surface of ovary (germinal epithelium)
kidney tubules
thyroid follicules
Simple Cuboidal small ducts of exocrine glands function
Absorption and counduit
Simple Cuboidal surface of ovary (germinal epithelium) function
Barrier
Simple cuboidal kidney tubules function
Absorption & secretion
Simple cuboidal thyroid follicules function
Absorption & secretion
Simple Columnar Typical Locations (3)
Small intestines and colon
Stomach lining and gastric glands
Gallbladder
Simple columnar Small intestines and colon function
Absorption & secretion
Simple Columnar lining and gastric glands function
Secretion
Simple Columnar gallbladder function
Absorption
Pseudostratified Columnar typical locations (3)
Trachea and branchial tree
ducts deferens
efferent ductules of epididymis
Pseudostratified columnar trachea and branchial tree function
Secretion & Conduit
Pseudostratified columnar ducts deferens function
Secretion & Conduit
Pseudostratified columnar efferent ductules of epididymis
Absorption & Conduit
Stratified Squamous typical locations (3)
Epidermis
Oral Cavity and esophagus
Vagina
Stratified Squamous Epidermis function
Barrier & Protection
Stratified Squamous Oral Cavity and Esophagus function
Barrier & Protection
Stratified Squamous vagina function
Barrier & Protection
Stratified Cuboidal Typical Locations (3)
Sweat Gland duct
Large duct of exocrine glands
anorectal junction
Stratified Cuboidal sweat gland duct function
barrier and conduit
Stratified Cuboidal large ducts of exocrine glands function
barrier and conduit
Stratified Cuboidal anorectal junction funtion
barrier and conduit
Stratified columnar typical locations (2)
large ducts of exocrine glands
anorectal junction
Stratified columnar large ducts of exocrine glands function
barrier and conduit
Stratified columnar anorectal junction function
barrier and conduit
Transition (Urothelium) Typical Locations (4)
Renal Calyces
Ureteres
Bladder
Urethra
Transition (Urothelium) Major Functions
Barrier, Distensible Porperty
Mention the Exocrine Glands (3)
Merocrine
Apocrine
Holocrine
where the exocrine glands secrete their contents
Into a duct or a surface
where the endocrine glands secrete their contents
into the blood
where the paracrine or autocrine glands secrete their contents
into the local extracellular space
An example of an unicelllular exocrine gland
Goblet Cell
What are the exocrine secretion of multicelullar glands? (3)
mucus
serous
mixed secretion (both mucus and serous)
Exocrine Glands mechanism of secretion for Merocrine
parotid gland
eccrine sweat gland
Exocrine Glands mechanism of secretion for apocrine
mammary gland
apocrine sweat glands
Exocrine Glands mechanism of secretion for holocrine
sebaceous gland
Identify the exocrine gland
Simple alveolar (acinar)
Identify the exocrine gland
Simpled branched alveolar
Identify the exocrine gland
Simple tubular
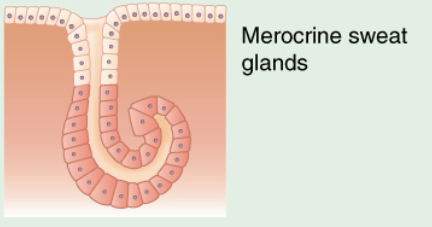
Identify the exocrine gland
simple coiled tubular
Identify the exocrine gland
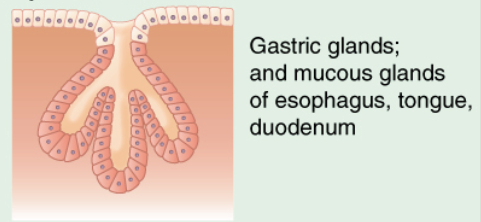
simple branched tubular
Identify the exocrine gland
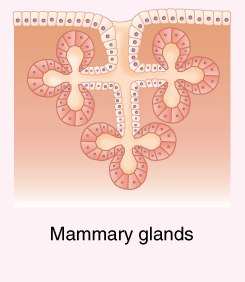
Compound alveolar (acinar)
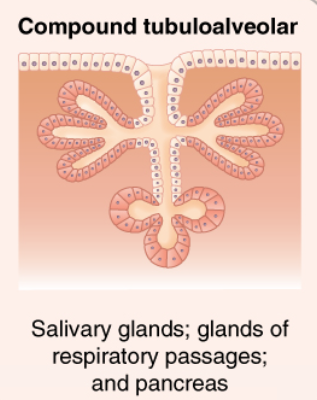
Identify the exocrine gland
Compound tubuloalveolar
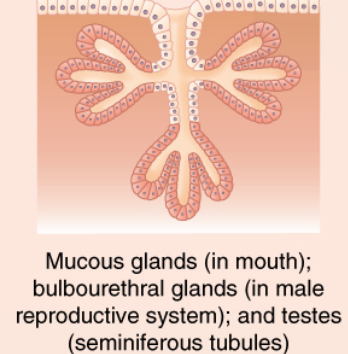
Identify the exocrine gland
compound tubular
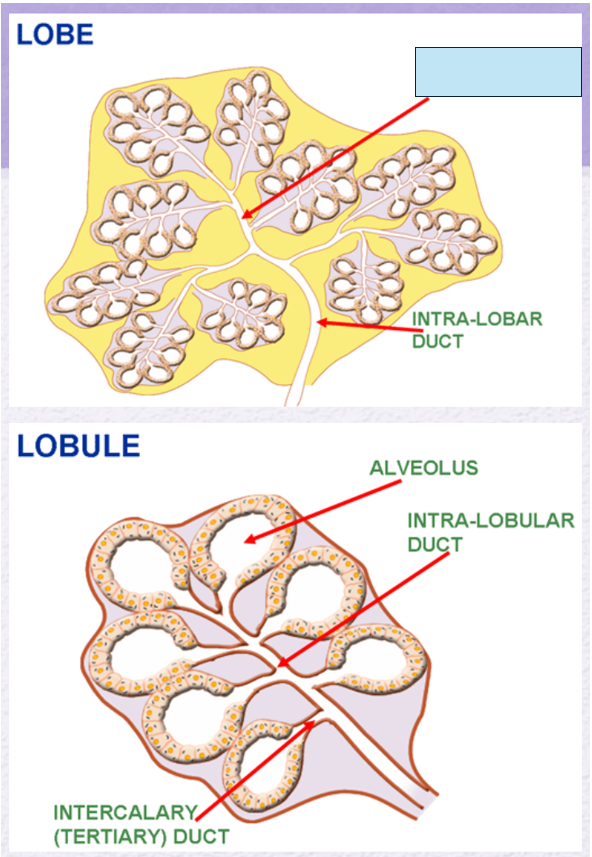
Name the gland’s duct (blue box)
Inter-lobular duct
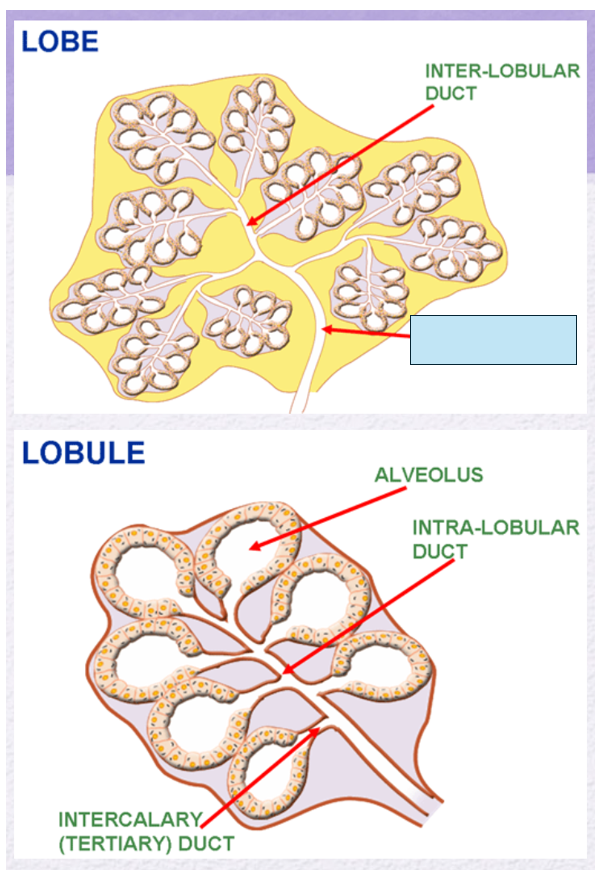
Name the gland’s duct (blue box)
Intra-lobar duct
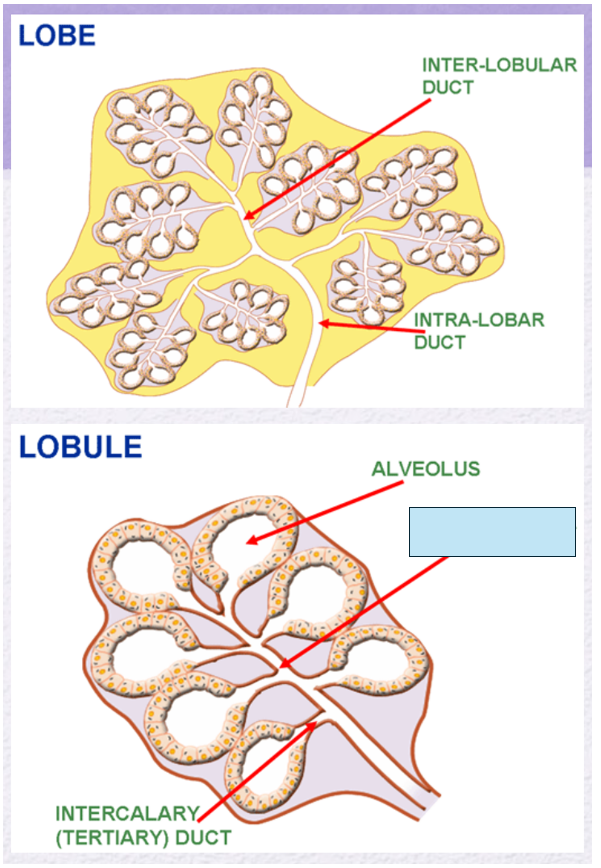
Name the gland’s duct (blue box)
intra-lobular duct
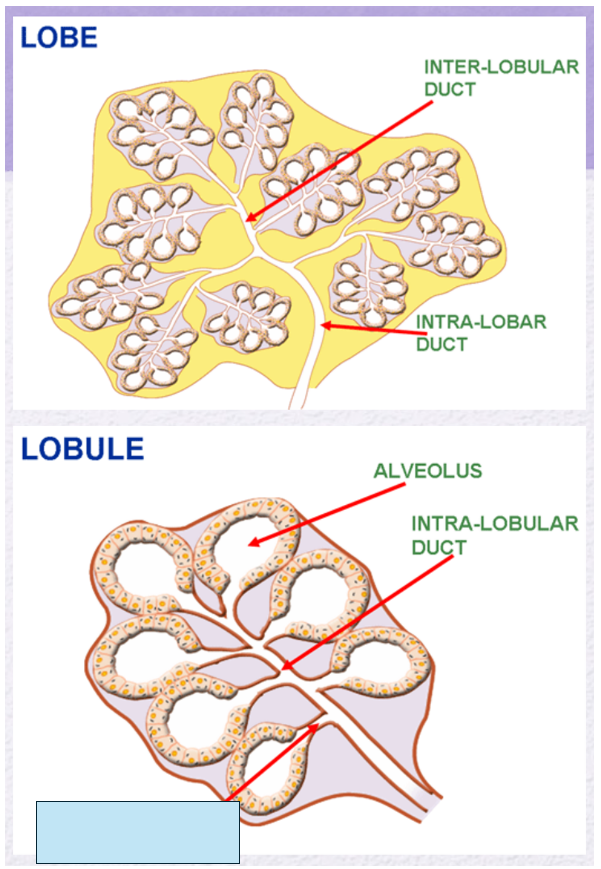
Name the gland’s duct (blue box)
intercalary (teriary duct)
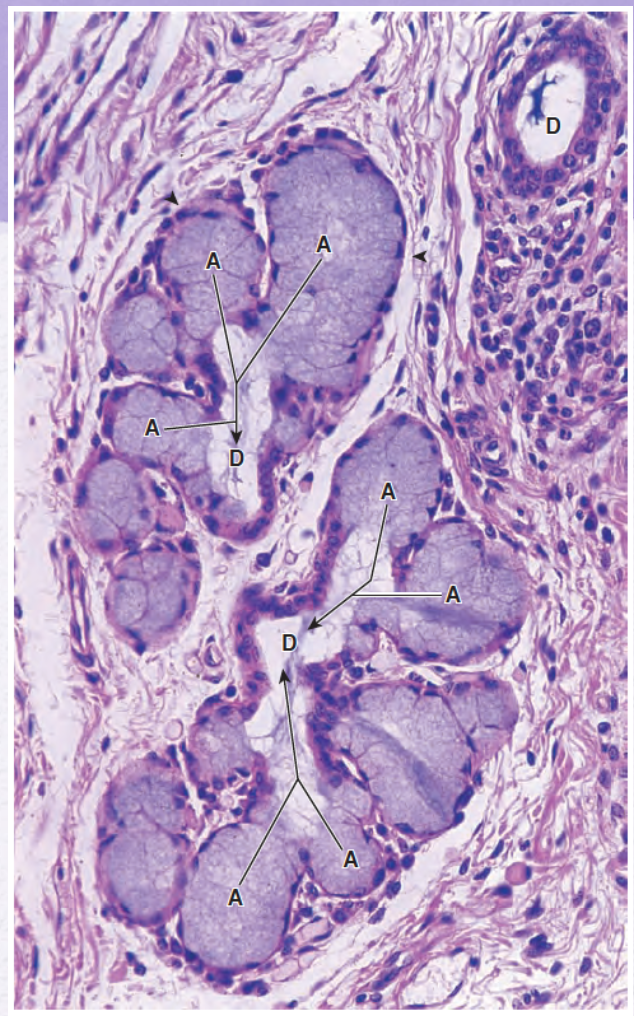
Identify the gland (mocus or serous secreting /simple or compound)
Mucus-secreting compound gland
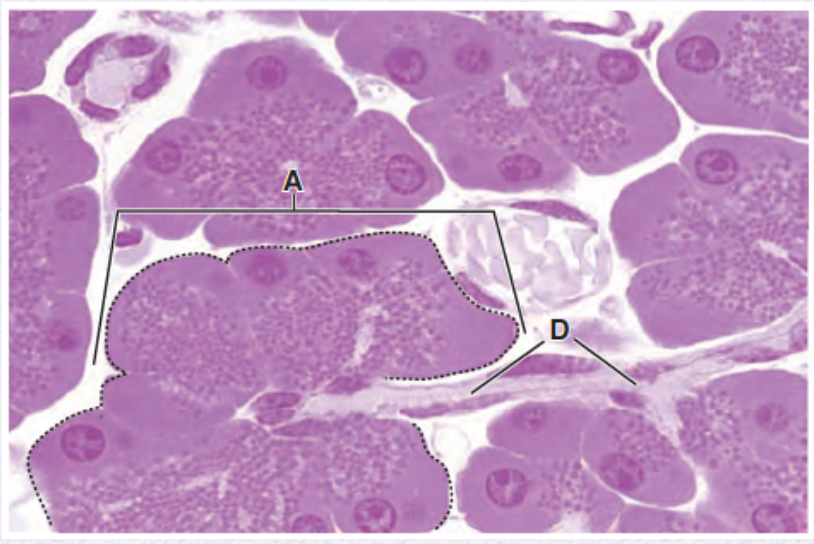
Identify the gland (mocus or serous secreting /simple or compound)
serous-secreting compoud gland
endocrine glands\unicellular gland typical locations (2)
GI epithelial
Respiratory epithelial
endocrine glands\multicellular gland typical location (1)
Adrenal Gland
endocrine glands\multicellular gland how the secretory material is released?
fenestThe secretory material is released into fenestrated capillaries, allowing hormones to rapidly enter circulation.
endocrine glands lacks?
Duct System
Where are fenestrated capillaries found in relation to the adrenal gland epithelium? (endocrine glands\multicellular)
They are abundant just outside the basal lamina of the glandular epithelium, facilitating hormone exchange between cells and blood.
What type of gland is the adrenal gland?
The adrenal gland is a multicellular endocrine gland composed of epithelial cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
What is metaplasia?
Metaplasia is the conversion of one type of differentiated epithelium into another in response to chronic irritation or stress.
What usually causes metaplasia to occur?
It often develops as a response to persistent injury or irritation, allowing tissue to better tolerate the stress.
What is the most common type of epithelial metaplasia?
The most common type is glandular columnar epithelium changing into stratified squamous epithelium.
What happens to the esophageal epithelium in chronic acid reflux?
The stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium is replaced by glandular mucus-secreting epithelium, known as Barrett epithelium.
Why is Barrett epithelium clinically significant?
Because it can progress to dysplasia and increase the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma if the chronic irritation continues.
What causes epithelial cell tumors to develop?
They occur when epithelial cells fail to respond to normal growth regulatory mechanisms, leading to uncontrolled proliferation.
What distinguishes a benign epithelial tumor from a malignant one?
Benign: Remains localized and does not invade nearby tissues.
Malignant: Invades neighboring tissues and may or may not metastasize to distant organs.
What is the general term for malignant epithelial tumors?
Carcinomas.
From where do carcinomas arise?
They arise from surface epithelia (such as skin or mucosal linings).