RAD 152: Unit 4
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Anode Heat
electrons in the outer shell are raised to an excited or higher energy level, electrons then immediately drop back to their normal energy level and emit (heat) infrared radiation
Anode Heat
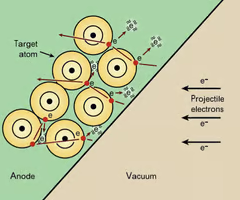
Heat & mA have what type of relationship?
direct relationship
Heat & kVp have what type of relationship?
direct relationship
Binding Energy
holds an electron in its orbit
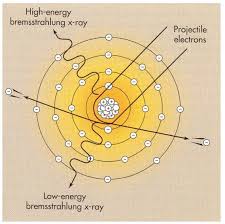
Bremsstralung Radiation
the closer the projectile electron gets to the nucleus, the more it is influenced by the nuclear electric field
as the projectile electron passes by the nucleus, it is slowed down and its course changes
Bremsstrahlung Radiation
“braking” of projectile electrons
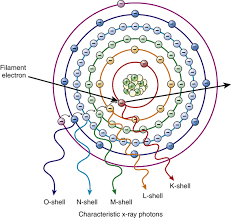
Characteristic Radiation
occurs in the inner shell electron
characteristic photons are emitted when an outer- shell electron drops to fill an inner shell
Characterisitc Cascade
after an outer shell electron has been dropped to fill the”hole” another electron will drop to fill the “hole” it left 7 so on until only the outer most shell is missing an electron
K-Shell photons
binding energy of 69.5 KeV
L,M,N Shell Photons
have energy of 12 KeV
Characteristic Radiation
Continuous Emission Spectrum
measures any type of x-ray emission occuring
Discrete Emission Spectrum
measuring one type of x-ray emission
characteristic x-rays have precisely fixed energies
Efficiency & kVp
the efficiency of x-ray production increases with increasing kVp
Efficiency & mA
efficiency of the x-ray production is independent of the tube current
Incident (projectile) Electron
accelerated electrons that comprise the x-ray tube current
K- Characteristic X-rays
require tube potential of at least 70 kVp to be produced
X- Ray Emission Spectrum
a measurement tool used to determine the approximate frequency with which each x-ray interaction occurs
Emission Spectrum Shifts to the Right
the higher the effective energy or quality of the x-ray beam
kVp
Emission Spectrum Shifts to the Left
the lower the effective energy of the x-ray beam
Emission Spectrum (large under the curve)
higher the intensity or quantity of the x-ray beam
Emission Spectrum (small under the curve)
lower the intensity of the x-ray beam
15% Rule (Part 1)
increasing or decreasing the kVp by 15% has the same effect as doubling or halving the mAs
15% Rule (Part 2) (Altering or adjusting image exposure)
Increase kVp 15%, the same mAs must be utilized—→ double mAs, the same kVp must be utilized
decrease kVp 15%, the same mAs must be used—→ ½ mAs the same kVp must be used
15% (Part 3) (Maintaining Optical Density)
Increase kVp by 15% with a reduction in mAs by ½
Decrease kVp by 15% with doubing the mAs
Added Filtration
Aluminum Sheets
decreases intensity of x-ray beam & increases average energy (HVL)
Compensating Filtration
Provides uniform image density for parts of varing thickness
Density
the degree of blackening on the image
Filtration
remove low energy (soft) x-rays from beam
Increasing Filtration:
increases quality of an x-ray
decreases the quanity of an x-ray beam
Grid
improves image contrast by absorbing scatter radiation produced in the pt before its able to reach the IR
As grid ratio increases, the number of photons reaching the IR decreases
Half- Value Layer
the thickness of absorber material necessary to reduce an x- beam to half of its original intensity
describes x-ray quality
Inherent Filtration
Window
Dielectric Oil
Prime Factors
kVp
mA
Exposure Time
Distance
mAs Reciprocity
the same radiographic density will result from different mA and time selections, provided that the mAs totals are equal
Total Filtration
the total of both inherent and added filtration
Quality
determined by kVp
Quantity
determined by mAs and kVp
Three Primary Anose Target Interactions
Anode Heat
Characteristic Radiation
Brems Radiation
What produces low energy brems?
created the projectile electron is barely influenced by the nucleus
at larger distances from the nucleus (very little energy is lost)
What produces high energy brems?
occurs when projective electron loses most if not all of its kinetic energy & drifts away from the nucleus
at closer distances more energy is lost
Emission Spectrum (added filtration)
causes spectrum to shift to the right
decreases amplitude
The Discrete Portion of the Spectrum changes with?
different target materials
mAs, kVp, and added filtration affect what on the emission spectrum?
amplitude
kVp
potential difference applied across the tube at the time the exposure is initiated
mA
unit measuring tube current
Time
determines the length of time tube produces x-rays
Distance
affects the amount of radiation reaching the patient
Factors Affecting X-ray Quantity
mAs (directly related)
kVp(directly related)
distance (inversely related )
filtration (inversely related)
Factors Affecting X-ray Quality
filtration (directly related)
kilovolt peak (directly related)
Describe X-ray Quantity
intensity of beam
number of photons in a beam
measured in milligray
Describe X-ray quality
penetrability of the beam
how many photons will penetrate the anatomy
represented by HVL
kVp Controls what?
beam quality
amount of scatter
Increase in kVP
more parts are penetrated
longer scale of contrast
Decrease kVp
more photons are absorbed in patient
shorter scale of contrast
As SID increases
beam intensity decreases
As SID decreases
beam intensity increases
Monoenergetic
beam that contains x-rays that all have the same energy
Heterogeneous
beams that have different energy
Why is Aluminum a good filtration choice?
efficiently removes low energy x-ray
inexpensive
readily available
easily shaped
Purpose of Grid
improve image contrast by absorbing scatter
as grid ratio increases, the number of photons reaching the IR decreases