ap bio u4
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
ligand
molecule that can produce signals
receptor
protein that the ligand binds to and can receive signals
4 steps of communication btwn signal & target cell
1. signaling cell receives stimulus
2. cell produced & releases signaling molecules (ligands)
3. ligands bind to receptor proteins
4. target cell responds
endocrine signaling
long distance, but slow
(ex. hormones)
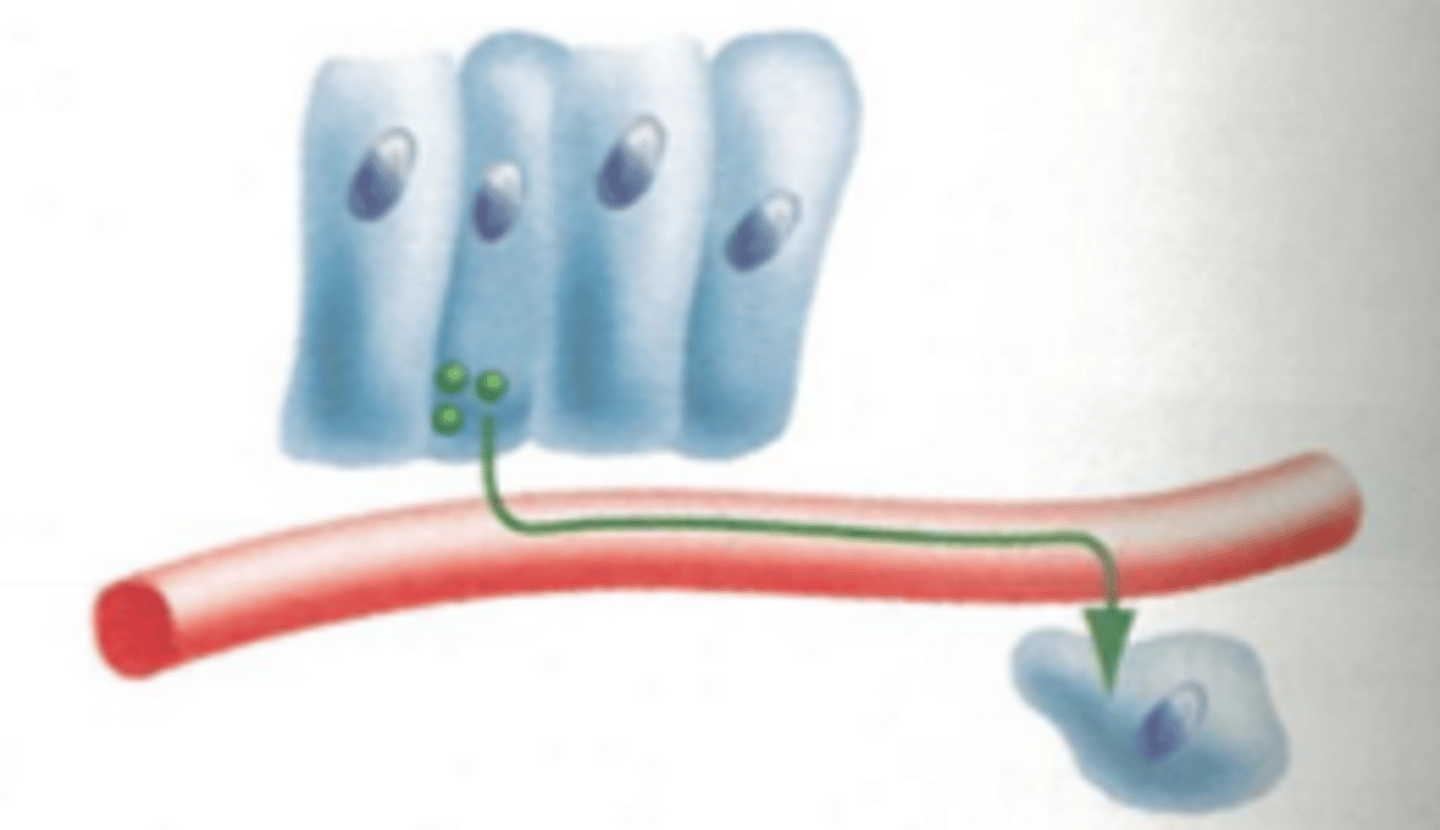
paracrine signaling
faster method, but must be close together
(ex. nerve cells)
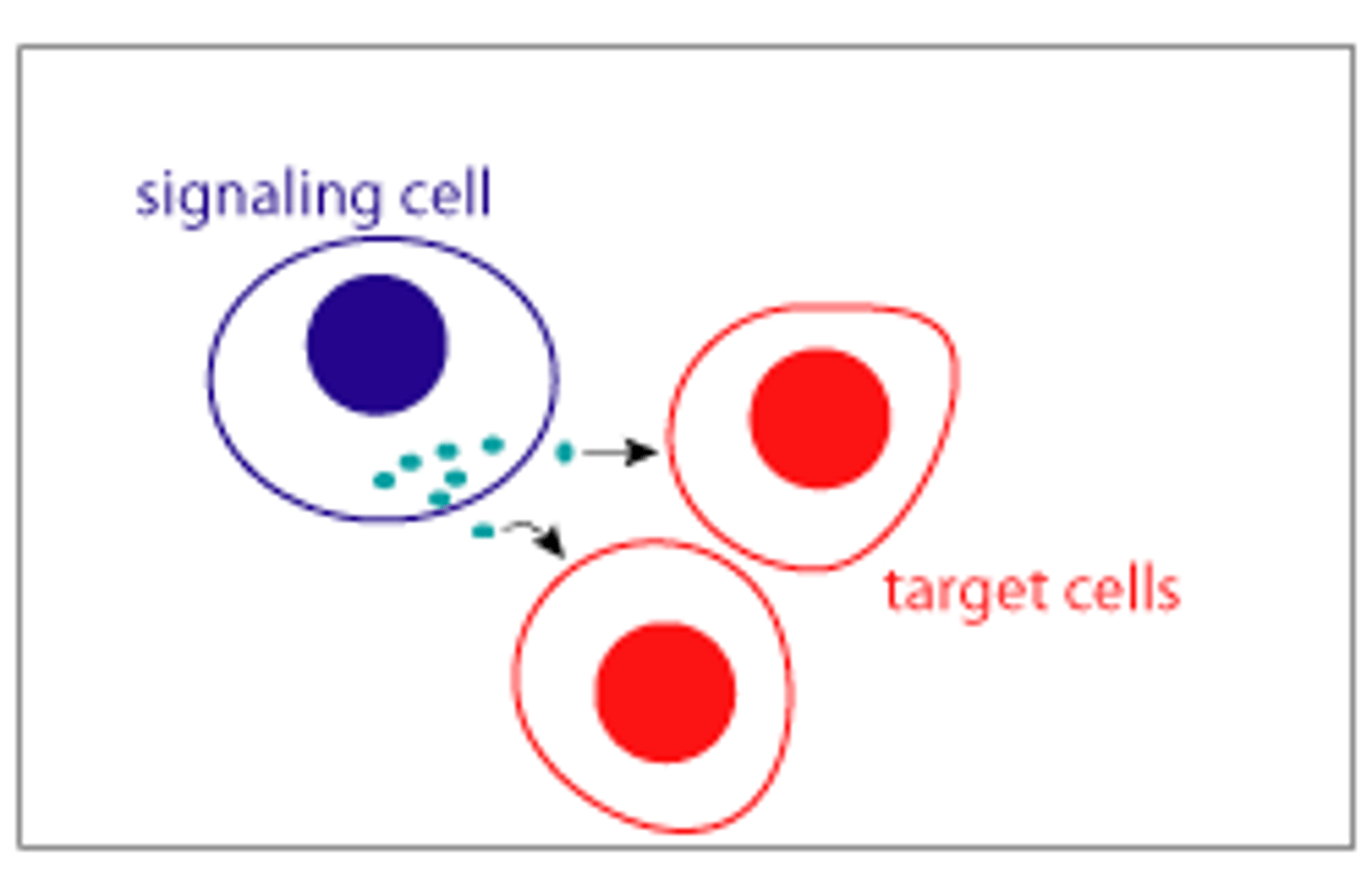
autocrine signaling
within the same cell, cells must produce both receptor & signal
(immune cells)
plasmodesmata
channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent PLANT cells
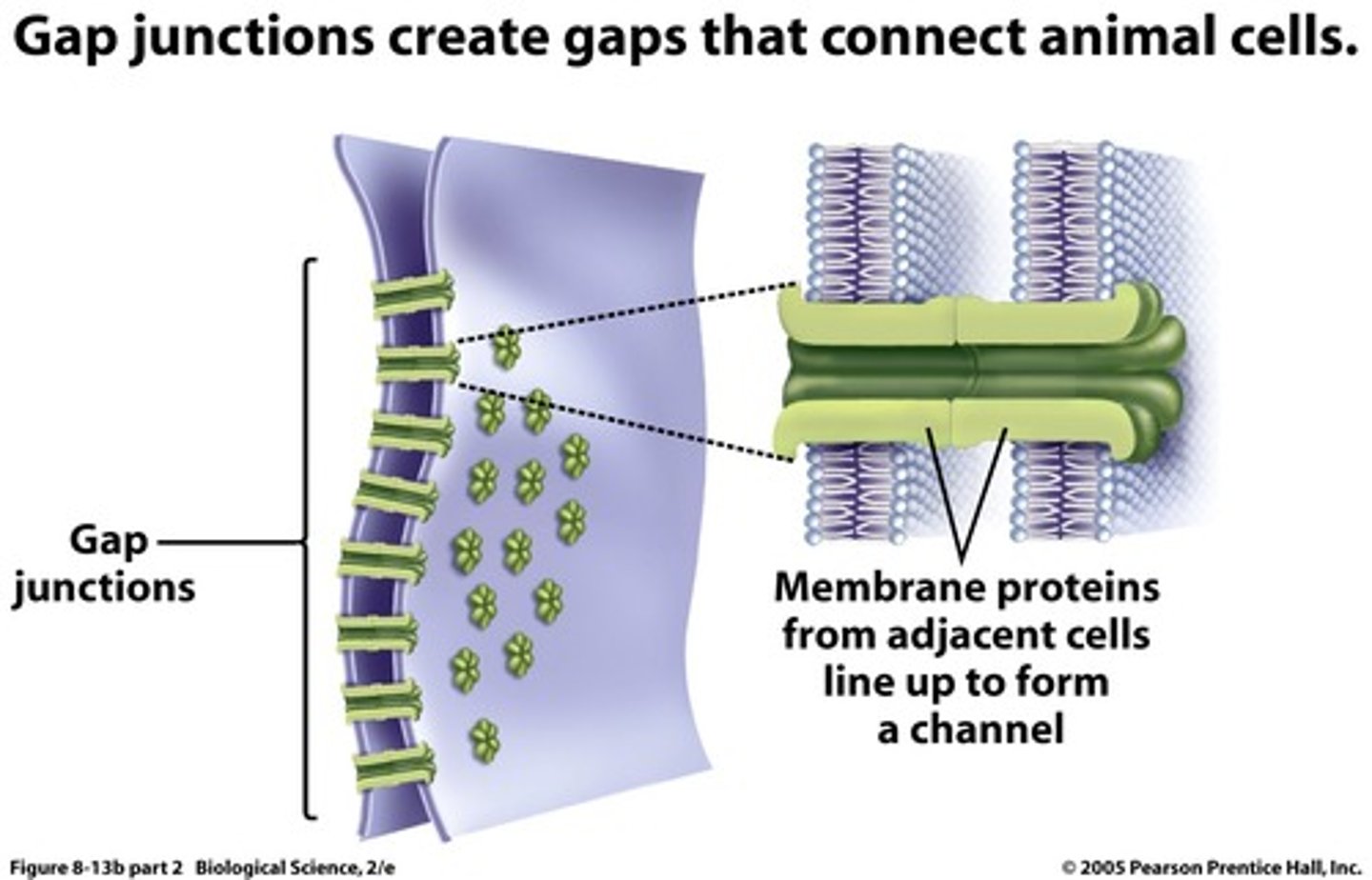
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent ANIMAL cells
positive feedback loop
causes a system to change further in the same direction/change is amplified
(eg. contractions)
negative feedback loop
causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving/goes back to original state
ligand receptor complex
the structure formed when a ligand and its receptor noncovalently bind (weak interaction)
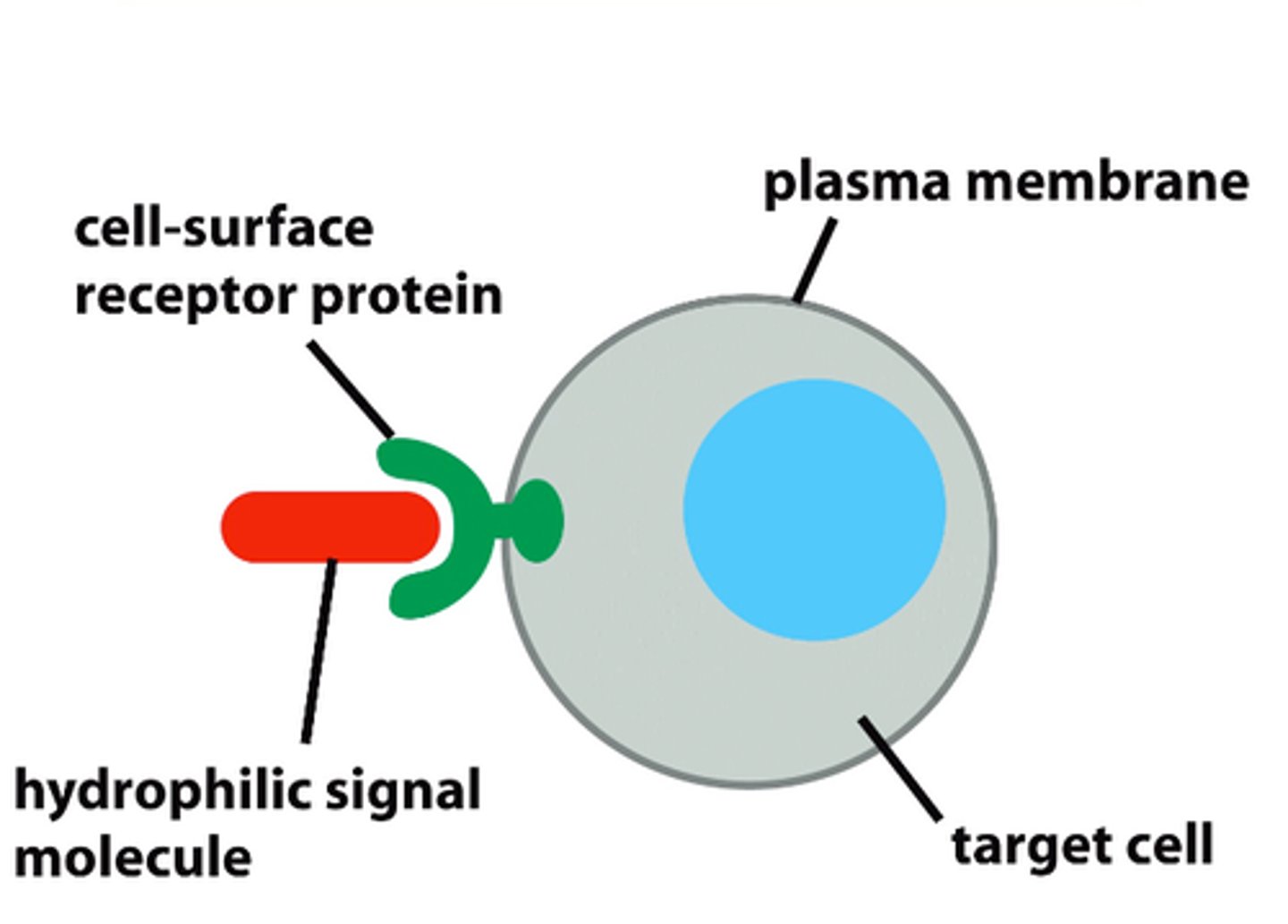
hydrophilic & polar signaling molecules
- can dissolve and are easily transported in extracellular fluid
- binds to receptor proteins on surface of cell
3 types of receptor proteins (hydrophilic molecules)
g protein-coupled receptors
receptor-protein kinases
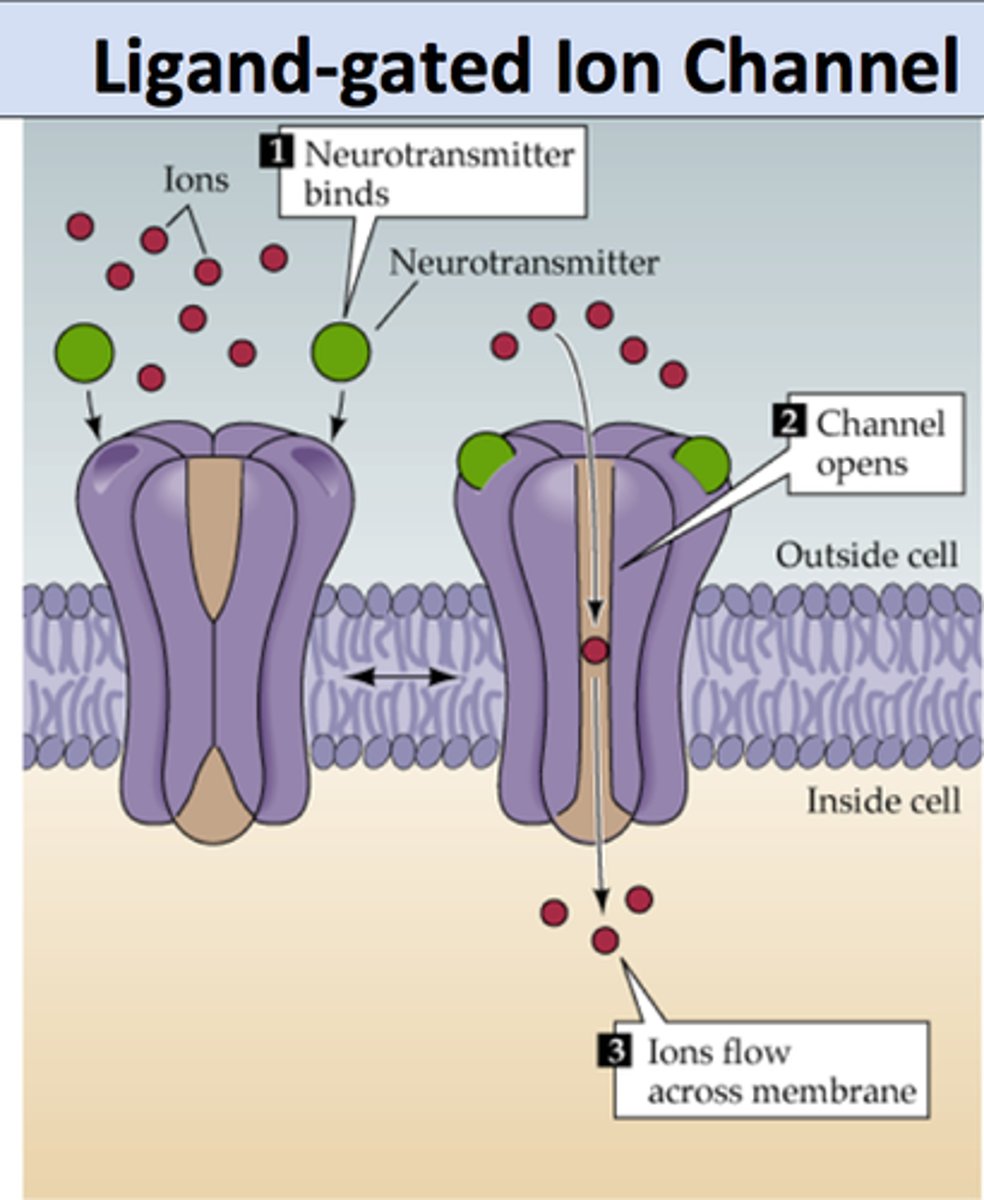
ligand-gated ion channels
*all water soluble
*located on plasma membrane as embedded proteins
*responses from target cells are rapid but brief
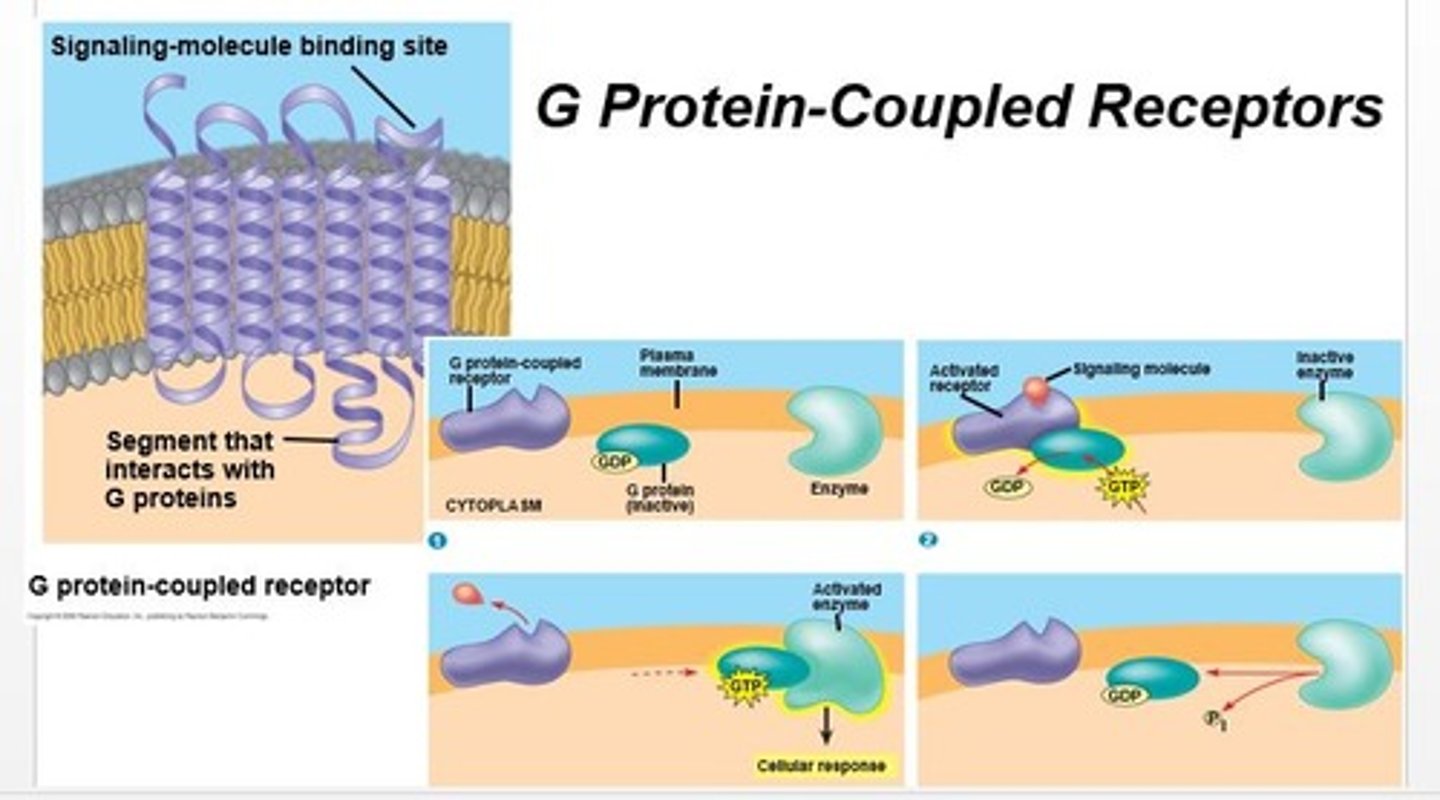
g protein-coupled receptors
membrane receptors with G protein
- if GDP is bound to G protein, the protein is inactive
- when Gp binds to ligand receptor, forms GTP
- activates second messenger
second messenger
usually small molecules that move quickly to help signal amplify thru cell
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
produced when hormone binds to receptor protein
second messenger: it activates protein kinases
adenylyl cyclase
target protein and converts ATP to cAMP (activating protein kinases)
kinase
enzyme that catalyzes addition of P groups to protein, activating them
(the phosphate groups come from ATP)
signaling cascade
small amt of signal amplified to produce large cellular response
termination of signaling pathway (4 steps)
1. adrenaline (ligand) detaches from receptor, inactivating it
2. G protein deactivates itself (GTP => GDP) & detaches
3. cAMP not produced, stops activation of target proteins
4. P groups are removed from protein
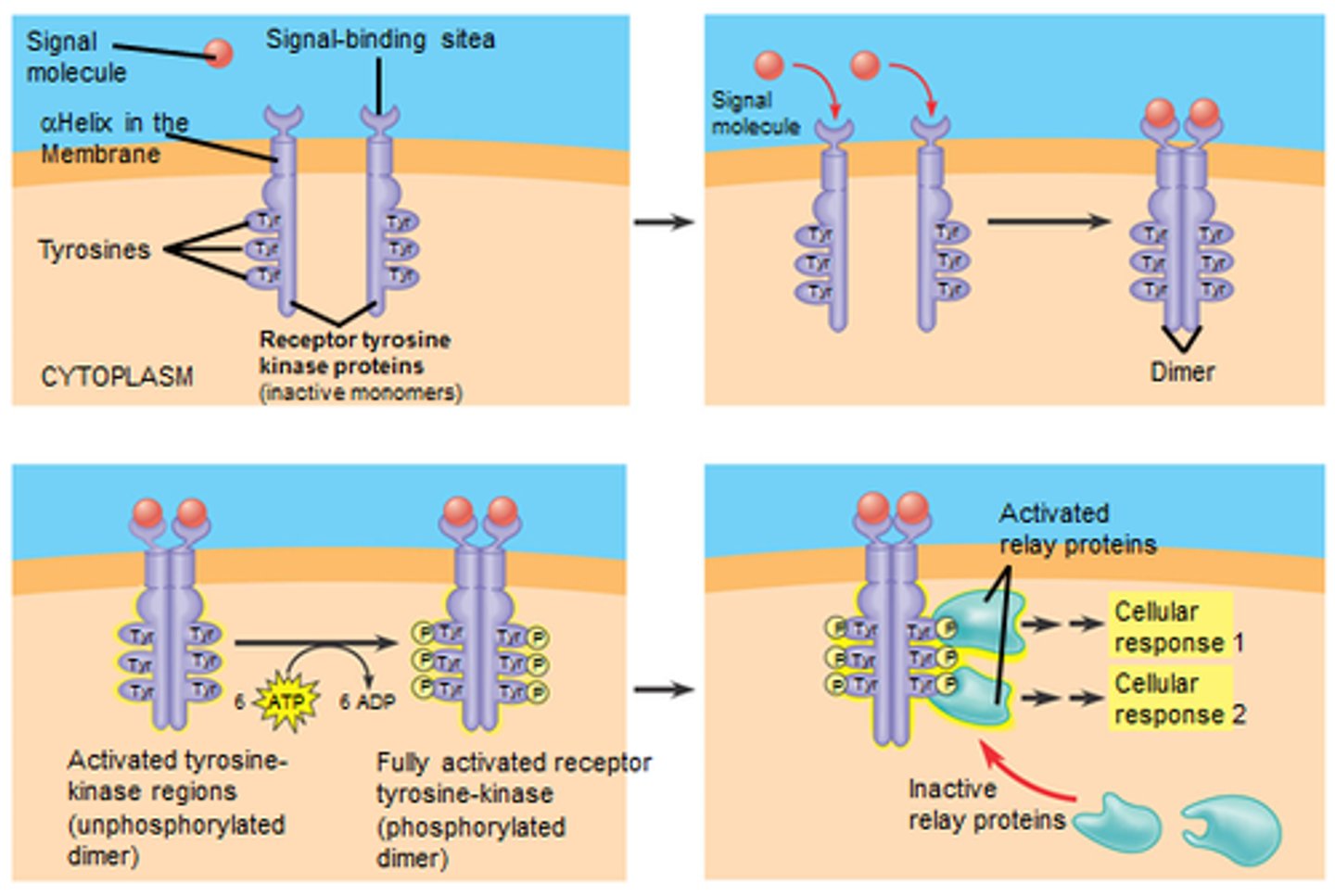
receptor protein kinases (3 steps)
1. signaling molecule binds to domain which brings two halves of the receptor together
2. this activates kinase activity, phosphates are attached
3. replay proteins bind to phosphates and send out cellular responses
ligand-gated ion channels
membrane ion channels that open when specific ligands are bound to it
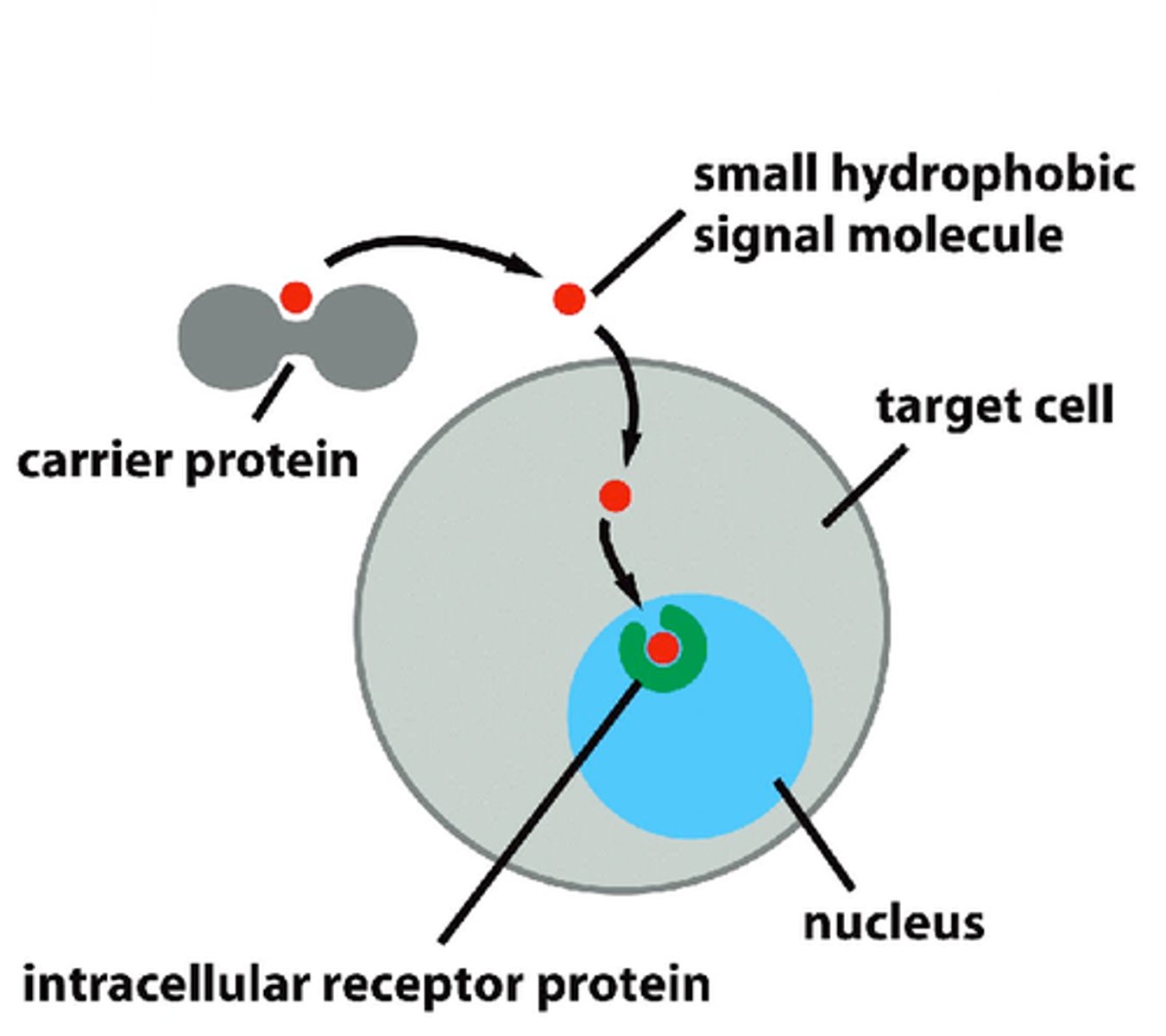
hydrophobic, nonpolar signaling molecules
1. diffuse into target cells and activates receptor proteins
2. activated ligand-receptor complexes control gene expression/protein synthesis inside nucleus
*slow to start, but usually sustained
process for how G protein-coupled receptors are activated
When a signal binds to the extracellular part of the receptor protein (top), the G protein binds to the signal-receptor complex inside the cell (middle). As a result of binding to the complex, the G protein's GDP is exchanged for GTP. The G protein then binds to and activates a target protein (bottom). The active target protein produces intracellular events, leading to a cellular response.
endo/exogenous ligands
endo: produced by body
exo: produced by outside body
agonists vs antagonists
agonist: stimulates receptors/produces a response
antagonist: inhibits responses
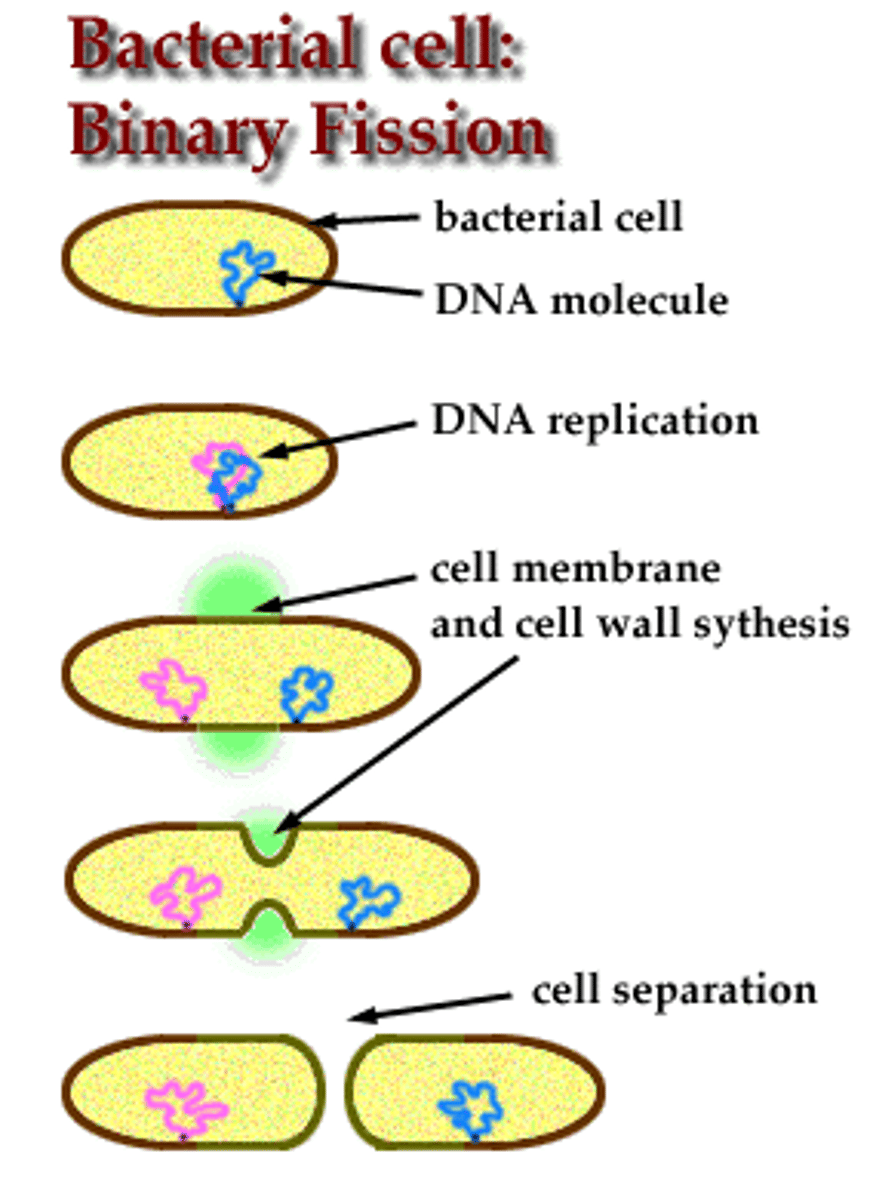
binary fission
form of asexual reproduction in which one cell divides to form two identical cells
mitochondria & chloroplast performs this form of cell division
steps of binary fission
1. circular DNA is copied
2. both DNA loops attach to membrane
3. cell elongates and separates
4. new cell membrane & cell wall are synthesized
5. 2 daughter cells are formed
chromosome
complex of DNA/RNA/chromatin proteins
allows DNA to be accurately copied during cell division
interphase
period of the cell cycle between successive M phases
G1 phase
directly after M phase, preparations to copy DNA
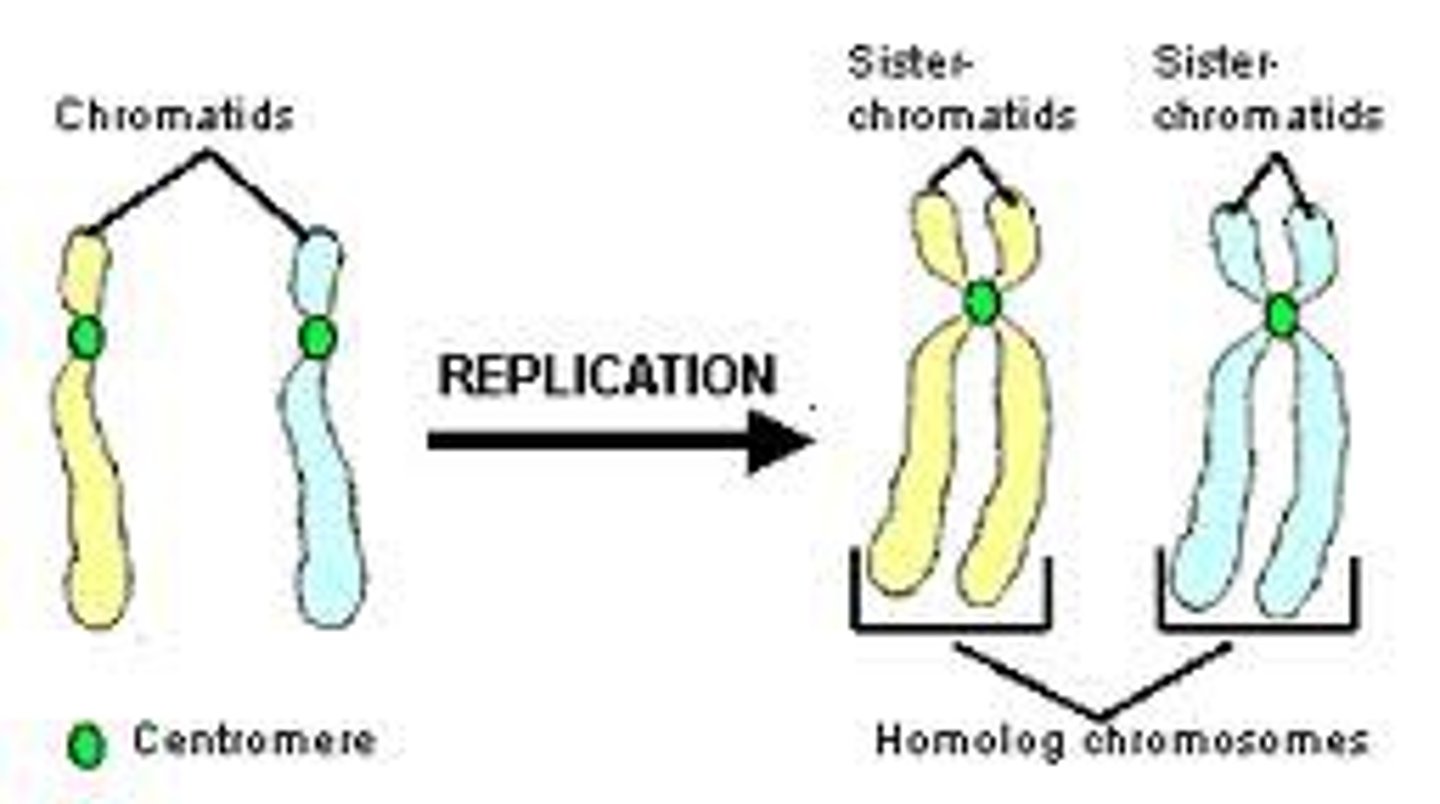
S phase
DNA replication (chromosomes are duplicated into sister chromatids held together by the centromere)
G2 phase
directly after S phase & prep for M phase
GROWTH PHASE aka size & protein content increases
G0 phase
a nondividing state in which a cell has left the cell cycle
mitosis
division of nucleus in eukaryotic cell
mitotic spindle
group of fibers made up of microtubules
pulls the chromosomes to opposite ends of the dividing cell
centrosome
microtubule organizing center (duplicated in S phase on opposite sides of the nucleus)
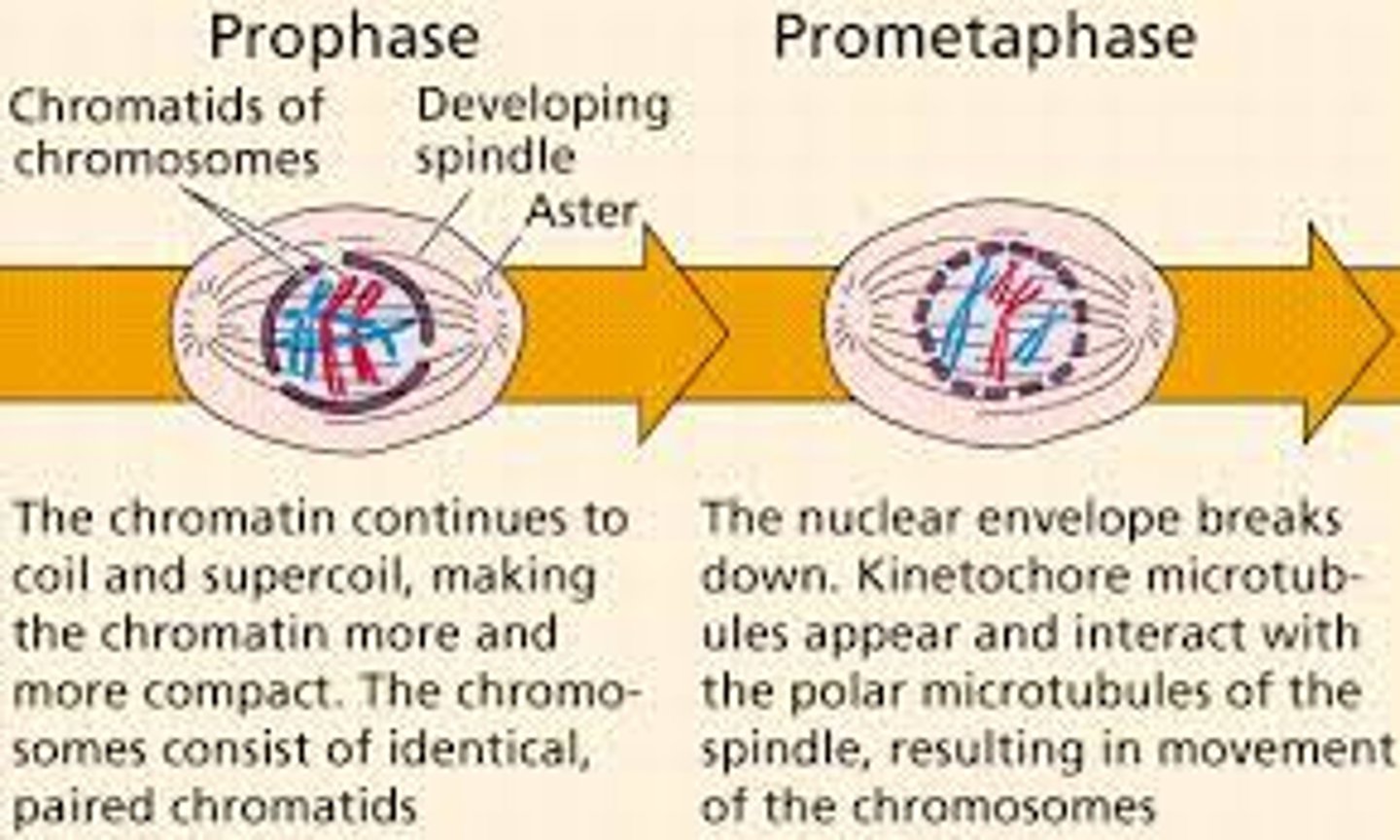
prophase
chromatin fibers => chromosomes (they are condensed and become visible)
microtubules extend from centrosomes (mitotic spindle)
centrosomes migrate to opposite sides
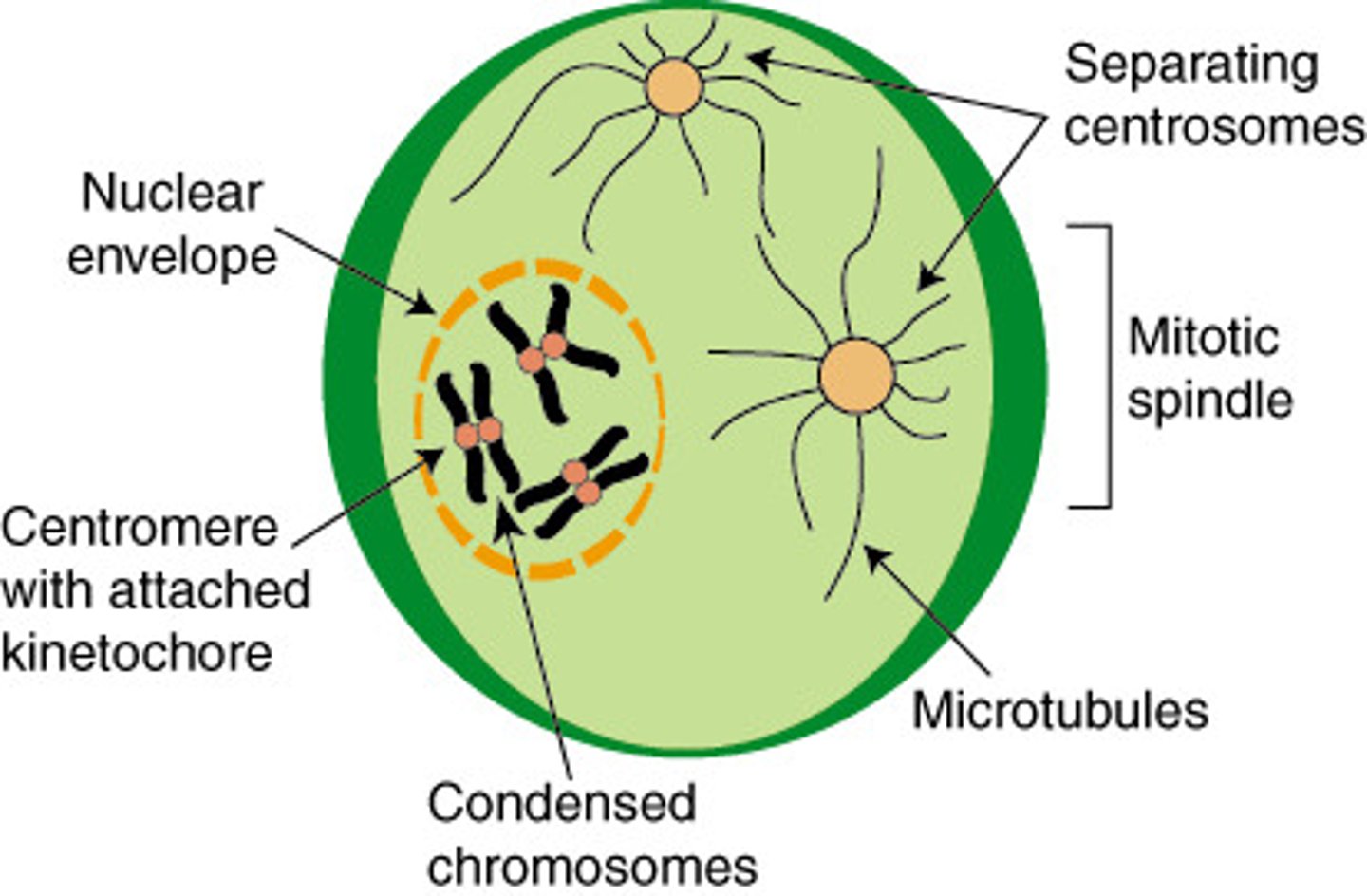
prometaphase
nuclear envelope breaks down and the mitotic spindle attaches to the chromosomes
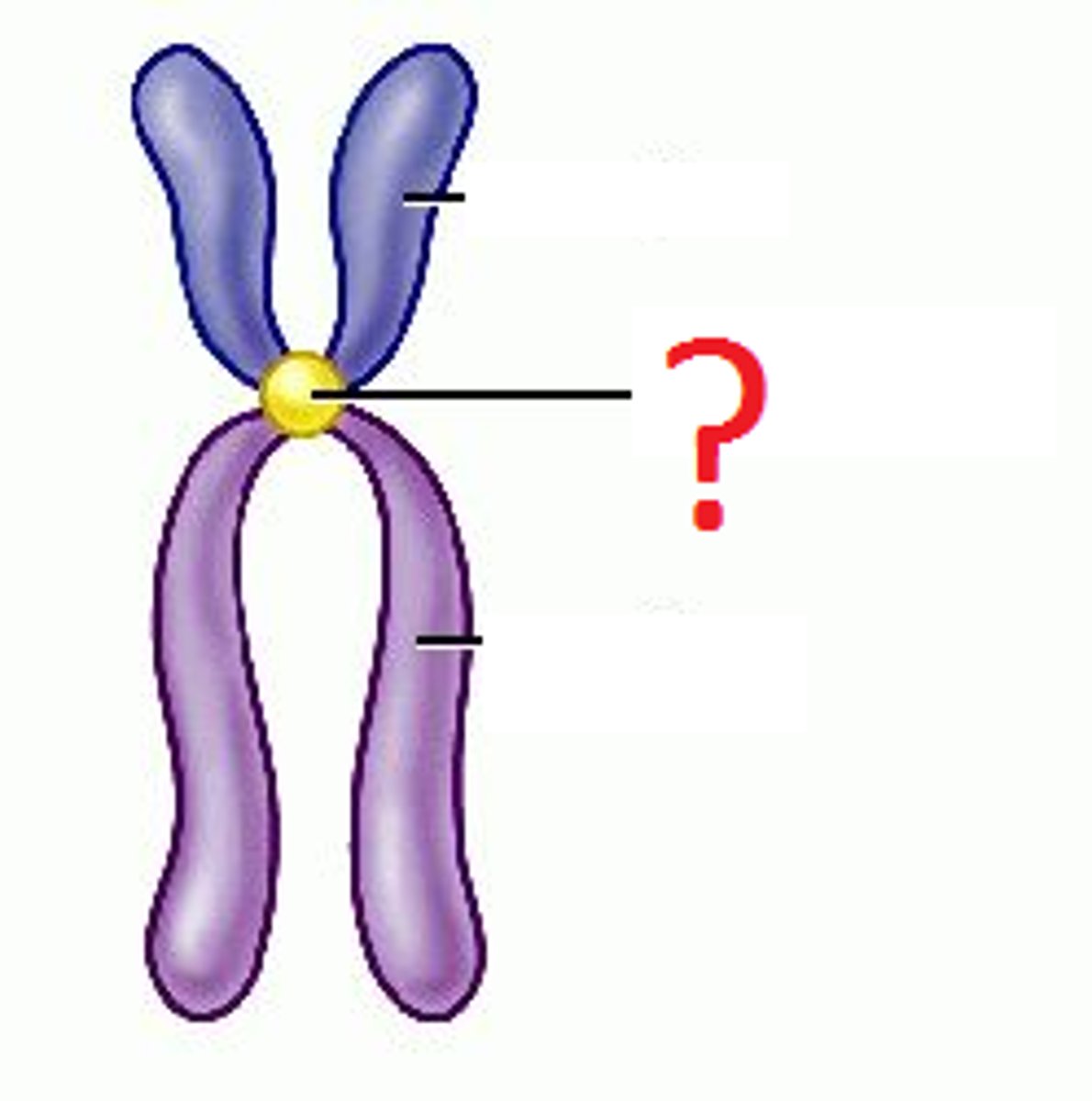
centromere
spindle attaches to chromosome here
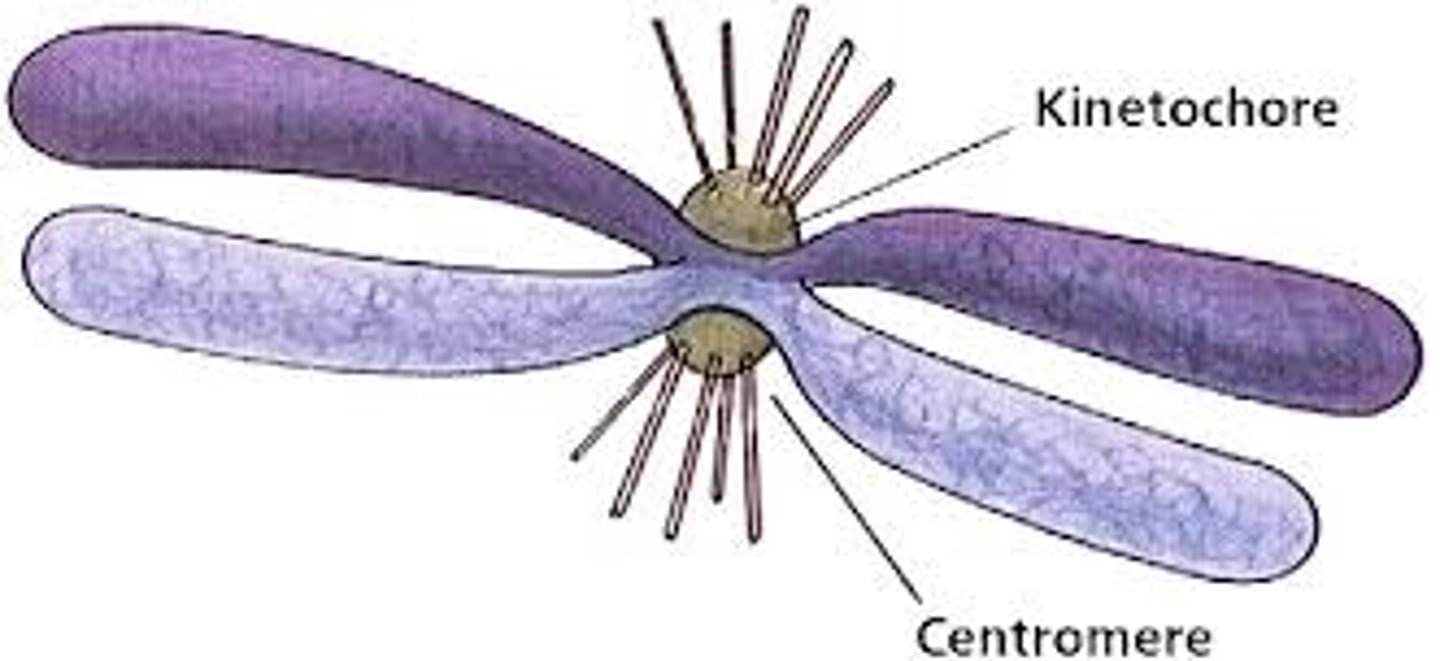
kinetochore
sites of spindle attachment, allows spindle to guide chromosomes
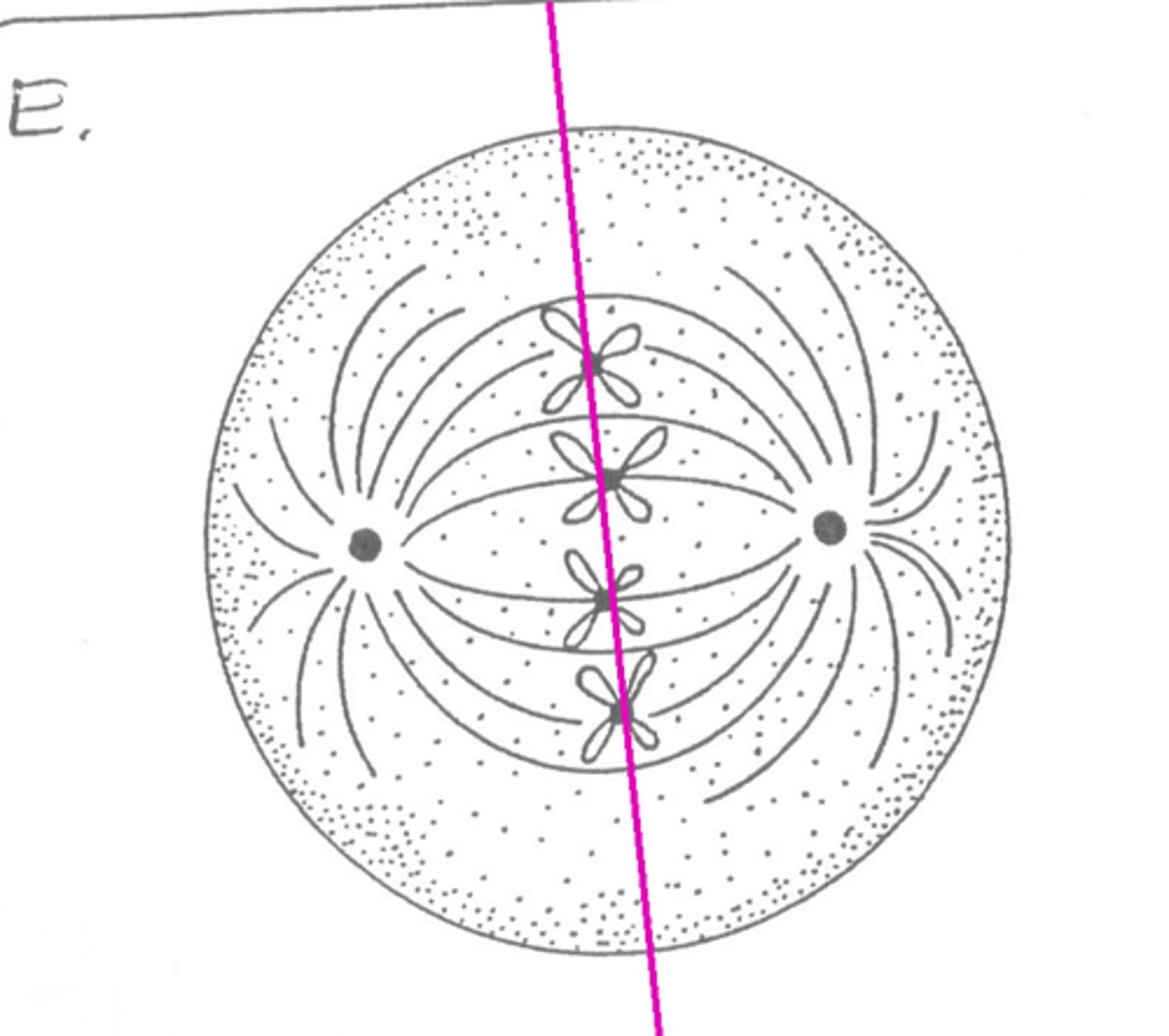
metaphase
the mitotic spindles lengthen or shorten to move the chromosomes to the middle of the cell
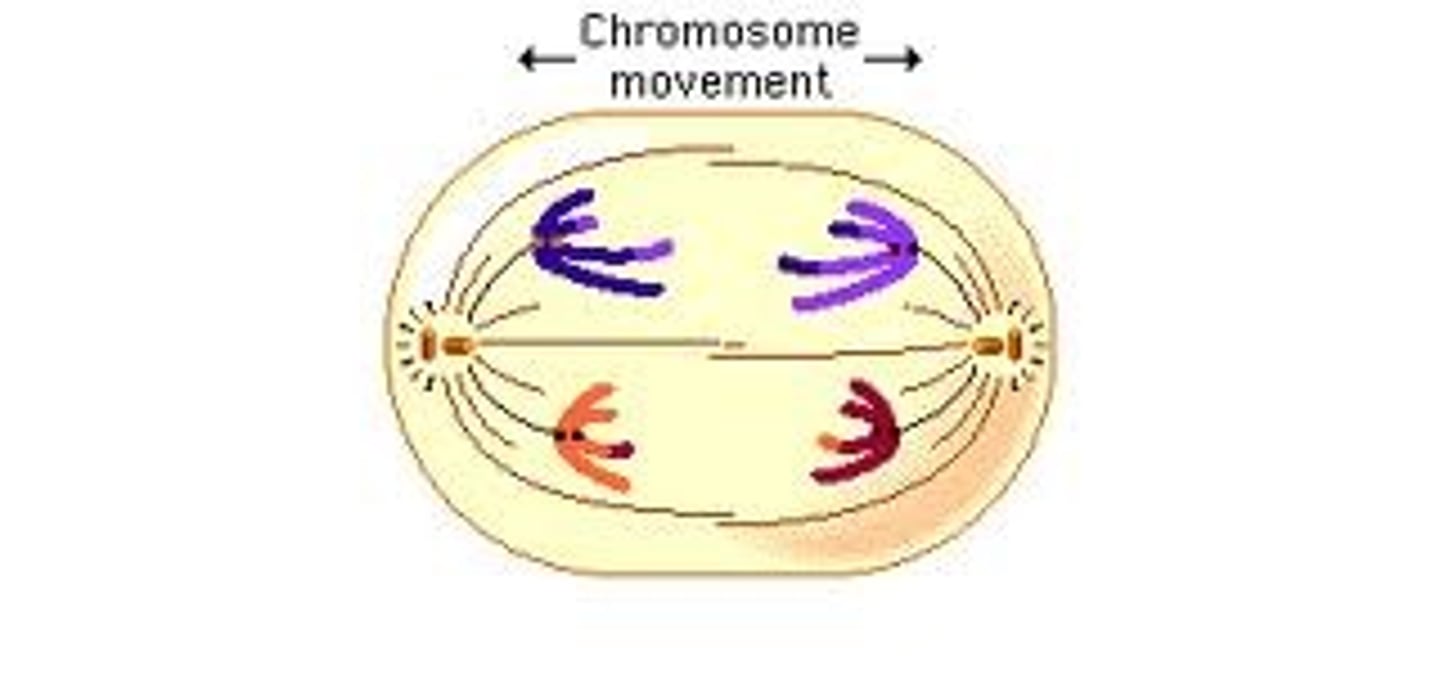
anaphase
centromere separates -> sister chromatids separate & move to opposite poles
*each chromatid is now a chromosome
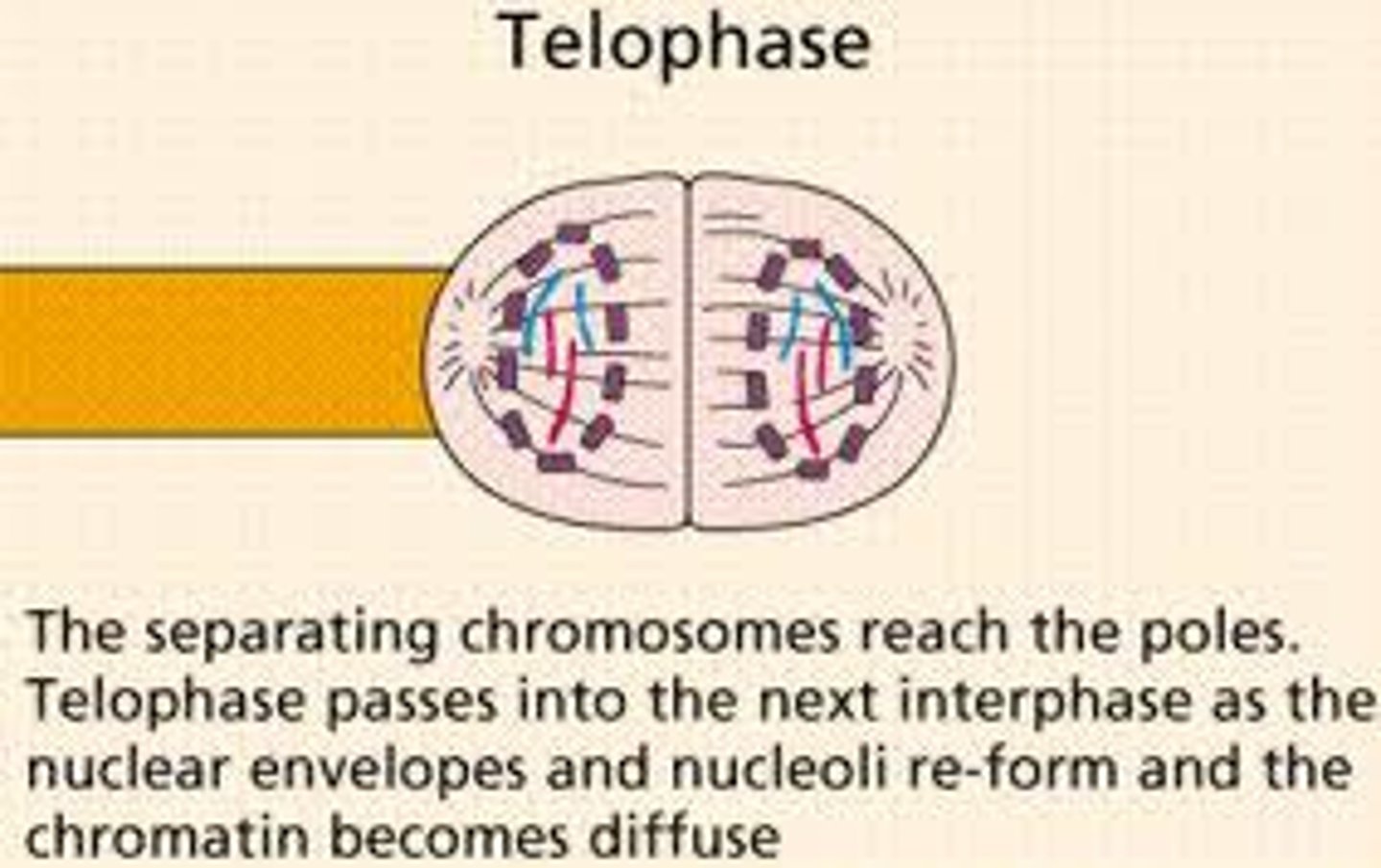
telophase
nuclear envelope forms and chromosomes decondense (become less visible)
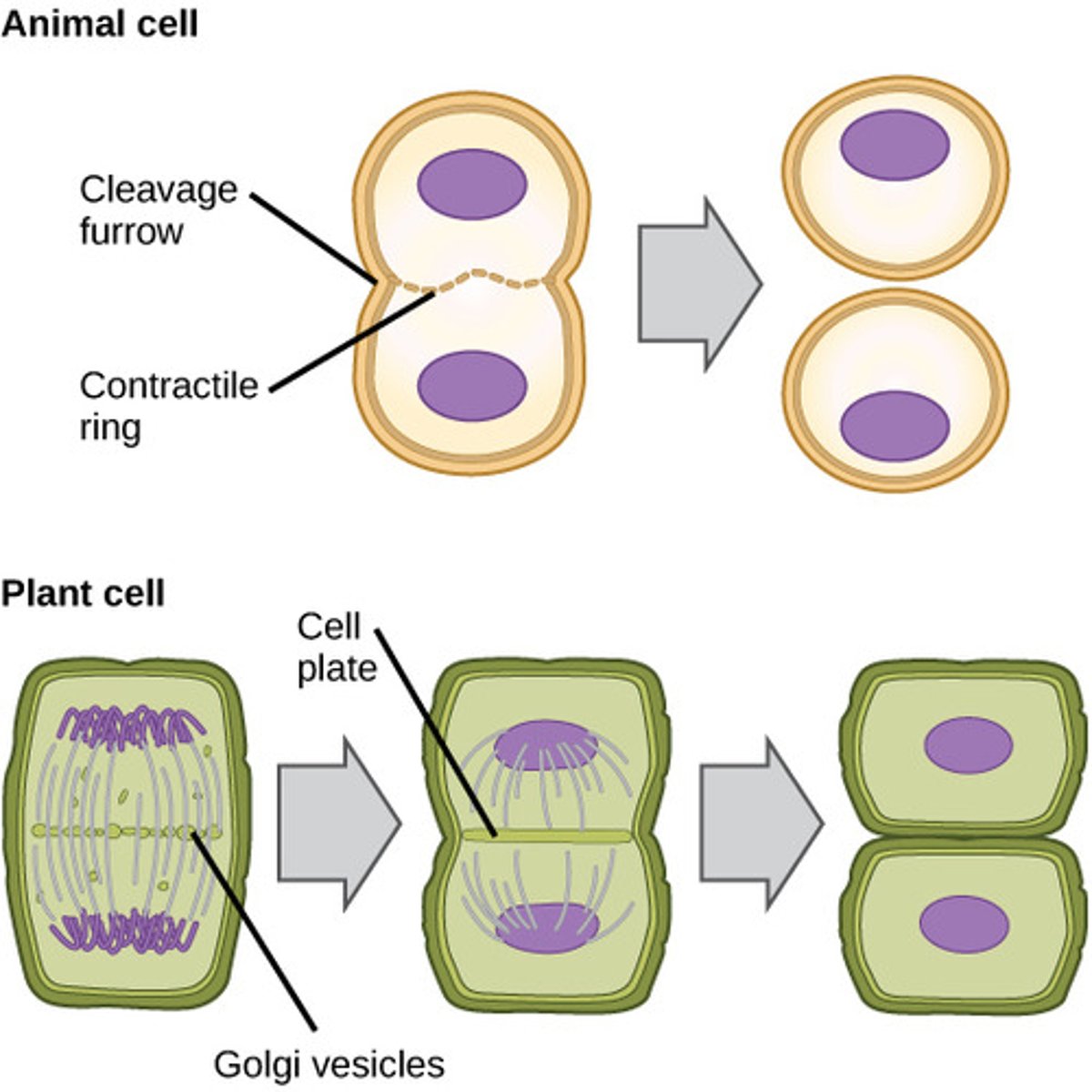
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
cytokinesis in animal cells
cell membrane is drawn inward until the cytoplasm is pinched into two nearly equal parts
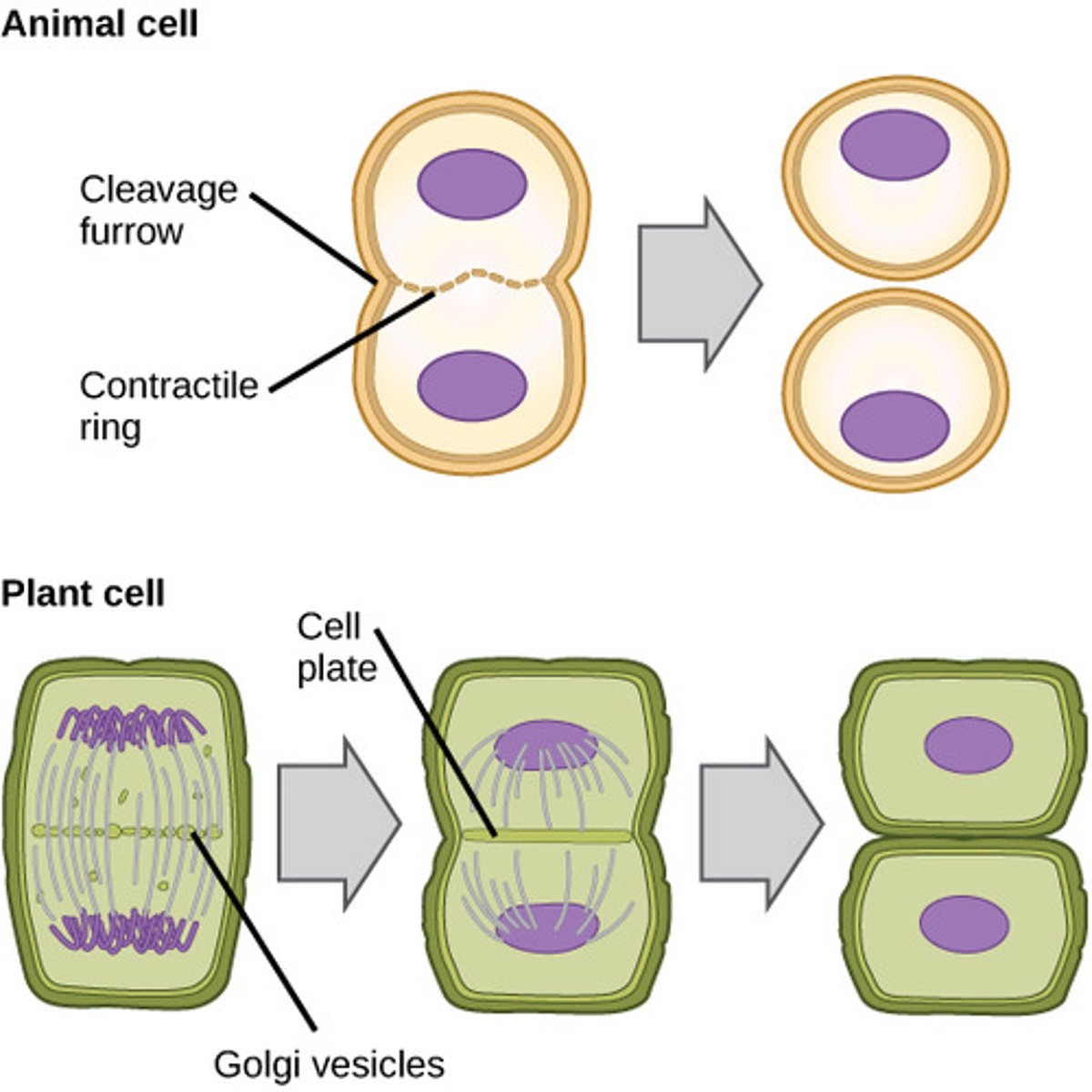
cytokinesis in plant cells
cell wall splits into two and vesicles fuse together to form a new cell wall
cyclins
proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells
cyclin dependent kinases
a protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin
- cyclin binds to CDK and kinase function is activated
- cyclin-CDK complex transfer P groups to target proteins (promotes cell division)
- cyclin degrades
DNA damage checkpoint
before its copied in the S phase, is DNA damaged?
if so, delay cyclin-CDK function
DNA replication checkpoint
at the end of G2, is all DNA replicated?
spindle assembly checkpoint
before anaphase, are all chromosomes attached to the spindle?
disruption of cell cycle checkpoints can lead to what
cell death or cancer
necrosis
contents of the cell leak out and potentially damage neighboring cells
apoptosis
cells die thru distinct set of cellular changes (specific enzymes are released)
cancer
a group of diseases characterized by uncontrollable cell division
carcinogens
chemicals that cause cancer
p53
when a DNA is damaged by radiation, protein kinase phosphorylates p53
- p53 binds to DNA and turns on several genes
- one of these genes guides production of protein which blocks cyclin-CDK complex formation
- gives the cell time to repair DNA
p53 behavior in cancer
1. inactivation of p53 allows cell to divide in presence of DNA damage
2. second mutation might accelerate this faulty cell division
3.benign cancer might interfere with cell cycle checkpoint
4. malignant cancer might allow these cells to migrate thru body