Cons Gen -- Final Exam
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
list one proximate cause, or driver, of genetic erosion
reduced population size
because of their resolution and ability to capture fine-scale structure, population delineation should be conducted with genetic/genomic data to the exclusion of other data types (e.g., demographic, behavioural, etc.)
false
the earliest stages of speciation often begin with gradual genetic differentiation (the sundering of a gene pool), but the entire process typically takes hundreds of thousands or millions of years
true
over time, hybrid zones change in three ways. what are they?
reinforcement, fusion, stability
genetic rescue can occur when two inbred populations are crossed if outbreeding depression goes down and overall genetic relatedness goes up.
false
genetic erosion refers to the overall loss of genetic diversity, which includes the loss of individual genes and their combinations
true
genetic rescue can affect the community through all of the following except
- increasing individual niche partitioning
- adapting to the current habitat and reducing dispersal
- reversing the direction of genetic Allee effect
- higher resilience to demographic stochasticity
- reinforcing predator-prey dynamics
adapting to the current habitat and reducing dispersal
peripheral populations are generally more prone to extinction than are core populations. Which of the following statements about populations is untrue?
peripheral populations may contain important genetic variants that are not present in core populations
peripheral populations are often subject to reduced gene flow
core populations usually contain unique genetic variants that are deleterious
peripheral populations are often subject to reduced efficiency of selection because of small population sizes
peripheral populations always have higher genetic diversity
peripheral populations always have higher genetic diversity
the ___ defines species to include “any species of fish or wildlife or plants and any ___ of any species of fish or wildlife which interbreeds when mature.”
Endangered Species Act, distinct population segment
hybridization can be assessed with genetic markers, and such marker data are commonly used to define new subspecies irregardless of geography
false
genetic tools reflect evolutionary timescales (millenia) whereas environmental niche modeling reflects ecologicla timescales (tens or hundreds of years)
true
as long as a founding captive population is large enough, captive breeding and subsequent reintroduction programs will be successful as the effects of inbreeding, drift and selection ill be mitigated
false
greater habitat connectivity can decrease the odds of outbreeding depression and local adaptation by increasing gene flow, thus decreasing genetic differentiation between and among populations
true
adaptations to captivity can be maladaptive in the wild because captive animals will dominate when released/reintroduced into the natural population
false
habitat loss can occur even without a concomitant loss in its geographic footprint if barriers to movement (powerlines) emerge
true
which of the following is the least likely outcome of vertebrate road mortality?
reduced gene flow
decreased genetic diversity
decreased hybridization
reduced effective population size
increased genetic structure
decreased hybridization
zoos contribute to conservation in several ways, including (choose all that apply):
sustaining captive individuals to increase genetic diversity
recovery of endangered species
exhibition of animals not locally common
research (animal husbandry)
conservation policy insights
recovery of endangered species
exhibition of animals not locally common
research (animal husbandry)

For the associated Figure, pick the 3 plots (i.e., from choices a, b, c, d, e, and/or f) that best correspond to the answer choices below:
isolated by distance
random mating population
fragmented cline
b, a, e
Which statement best describes A) heterozygote(s), B) homozygote(s), and C) genotype(s)? (1 point each)
The alleles a person has are called (Blank 1) ____________.
(Blank 2) ___________ have two identical alleles at a gene locus.
(Blank 3) ____________ have two different alleles at a gene locus.
genotypes; homozygotes; heterozygotes
What is the ultimate source of genetic diversity in every population?
Mutation
There are exceptions to most, if not all, scientific Laws. For example, Newton's Law of Gravity (describing the force of gravitational attraction between two bodies as the product of the masses and inversely as the square of the distance between them) breaks down at the quantum level. Pick two of Mendel's three laws and describe how they are often violated in nature (in the future, provide explanation).
Law of Dominance: incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, multifactorial traits)
Law of Independent Assortment: linked genes
Explain the "semi-conservative" process of DNA replication.
Each new DNA molecule comprises one original strand and one newly synthesized strand that complements the original.
Which of the following statement is NOT true about dosage compensation in mammals?
Dosage compensation accounts for the observation that the amount of product formed by two copies of a gene is the same as that formed by having only one copy of that gene.
The X-chromosome displays dosage compensation.
One of the two X chromosomes in each cell is randomly inactivated early in development.
Females heterozygous for X-linked traits are the homogametic sex.
Females heterozygous for X-linked traits are the homogametic sex.
Allelic variation among loci is "shuffled" through independent assortment of chromosomes. Using a single word, how else is allelic variation shuffled within a chromosome?
Recombination
Eukaryotic genes consist of introns (A), exons (B) and regulatory sequences (C). Choose the correct answers. (1 point each).
(Blank 1)__________ are coding sequences that specify a polypeptide or protein.
(Blank 2)_________ are non-coding sequence that serve in part as spacers to facilitate copying/cutting/pasting new forms of genes or gene products (i.e., RNA or proteins).
(Blank 3)_________ are molecular tuning knobs that are used to increase or decrease gene expression.
exons; introns; regulatory sequences
Which of the following statements is correct?
Edwin Chargaff found that the amount of A and C are proportional to G and T, respectively, and this empirical fact helped scientists elucidate the double-helical structure of DNA.
Multifactorial traits are the same as quantitative traits and such traits are influenced by multiple genes.
Genes can assort independently among gametes even if they are on the same chromosome.
There are so few Y-linked traits because the Y chromosome contains a very small number of genes, far fewer than any autosome or the X chromosome.
There are so few Y-linked traits because the Y chromosome contains a very small number of genes, far fewer than any autosome or the X chromosome.
Gaucher's disease, an autosomal recessive condition, is much more common in Ashkenazi Jews than in the general population. Charles, a Jewish man without the disease, has a sister with Gaucher's as does his father. His mother is unaffected. Charles's wife, Rachel, does not show the disease but knows she carries a disease allele. What is the probability that the first child of Charles and Rachel will not show Gaucher's disease, but has a disease allele?
1/4
Polydactyly (extra fingers) is a rare, monogenic condition inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. A man with six fingers on each hand and his unaffected wife seek genetic counseling. Their first son has six fingers on each hand, but the second son has five fingers. What is the probability that their next child will have polydactyly?
1/2
More than 98% of genomic DNA codes for proteins
False
If your favorite species' genome has a (high) mutation rate of 1 x 10-4 per gene per generation then, on average, a mutation at any given gene occurs once every generations.
10,000
During (Blank #1)__________, the information encoded in DNA is copied into mRNA (i.e., from nucleic acid to nucleic acid). The process of (Blank #2)__________ then converts the mRNA sequences into a sequence of amino acids called a polypeptide (i.e., from a nucleic acid to a protein). This information flow, from DNA->RNA->protein, is the basis of the (Blank #3)__________ of molecular biology.
transcription; translation; central dogma
The eminent evolutionary biologist, Theodosius Dobzhansky, said "nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." List two pieces of scientific evidence from molecular biology that support this contention.
(any of the following)
Homology of genes from bacteria to man
common informational macromolecule (DNA)
functional macromolecules (proteins)
mutation as driving force for natural selection
The phenomenon termed (Blank #1)__________ silences the great majority of genes on one of the two X chromosomes. In contrast, (Blank #2)__________ silences one gene at a time across many different autosomes. (Blank #1)__________ is random in that either the paternally derived chromosome or the maternally derived chromosome is affected. In (Blank #2)__________, either the allele transmitted by the father or the one transmitted by the mother will be silenced in an ordered non-random fashion from one generation to the next.
X-inactivation; imprinting
Which of the following statement is incorrect about mutation in protein-coding genes?
A nucleotide substitution could be silent if it produces no change in the amino acid sequence (i.e., a silent substitution).
A nucleotide substitution could produce a change in the amino acid, but this single amino acid change could be neutral (e.g., an exchange of two similar amino acids like a valine for an alanine).
A synonymous nucleotide substitution in an exon could produce a functional change in the resulting protein.
A nucleotide substitution could occur in an intron and therefore be removed during splicing of the primary transcript.
A synonymous nucleotide substitution in an exon could produce a functional change in the resulting protein.
It is reported that the human genome has ~25,000 protein-coding genes that have the capacity to produce several hundred thousand gene products. What can directly account for the vast difference in gene number and product number? Choose all that apply.
tRNA transformation
Alternative promoters
Post-translational modification
Alternative splicing of immature mRNA
mRNA editing
Alternative promoters
Post-translational modification
Alternative splicing of immature mRNA
mRNA editing
A spontaneous mutation is a heritable alteration in the nucleotide sequence (or structure) of the genome of an organism. Which of the following does not represent a causative mechanism underlying a spontaneous mutation? Choose all that apply.
Proofreading errors associated with DNA polymerase
Replication slippage
Base misincorporation errors associated with DNA polymerase
Diet (e.g., aflatoxins)
Replication slippage
Base misincorporation errors associated with DNA polymerase
Diet (e.g., aflatoxins)
The base sequence of the template DNA strand is 5'-AATCAGACATGCGTC-3'. What is the base sequence of the primary transcript of this template DNA strand?
5'-GACGACUGUCUGAUU-3'
(Blank #1) of the genetic code means that the same amino acid can be encoded by more than one codon. It occurs most often due to changes in the (Blank #2) position of codons.
degeneracy; third
What type of mutation should (in general) be the most deleterious in terms of the probability of "protein" change?
Frameshift mutation
In a screening program to detect a-thalassemia in Sri Lanka, the heterozygote "carrier" frequency was 4%. What is the fraction of Sri Lankan population that does not show a-thalassemia? Assume that there are three alleles including a normal allele, a dominant mutant allele, and a recessive mutant allele, and the recessive mutant allele's frequency is a half of the normal allele's frequency.
0.08
A population cannot have low heterozygosity and high allelic diversity at the same time.
False
(Blank)__________ is one of three levels of biodiversity—the others being species diversity and ecosystem diversity--recommended for conservation by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as well as the Convention on the Biological Diversity.
genetic diversity
Inbreeding changes genotype frequencies by increasing homozygosity, but it does not change allele frequencies.
True
The rate of mutation exceeds the rate of genetic drift in the absence of gene flow.
False
Sexual selection, including male-male competition and female choice, can lead to deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for reasons such as nonrandom mating.
True
Positive assortative mating for a given trait increases homozygosity at the loci responsible for the trait.
True
Because natural selection favors well-adapted genotypes, it always acts to decrease genetic diversity.
False
Which of the following best describes the relationship among population size, drift, inbreeding, fixation, and fitness decline?
The harmful alleles that ultimately contribute to inbreeding depression are less likely to be fixed by mutation and drift in smaller populations.
The harmful alleles that ultimately contribute to inbreeding depression are more likely to be fixed by mutation and drift in larger populations.
The harmful alleles that ultimately contribute to inbreeding depression are less likely to be fixed by mutation and drift in larger populations.
The harmful alleles that ultimately contribute to inbreeding depression are less likely to be fixed by mutation and drift in larger populations.
In a field study by Meagher et al. (2000), the reproductive success of field mice was measured in part by survival of weaned offspring. In outdoor enclosures, the male inbred mice showed a weaned offspring survival rate of 22%, while the outbred male mice had a weaned offspring survival rate of 50%. Using the equation from the lecture notes and/or the textbook, what is the general measure of inbreeding depression (δ)?
δ = 0.56
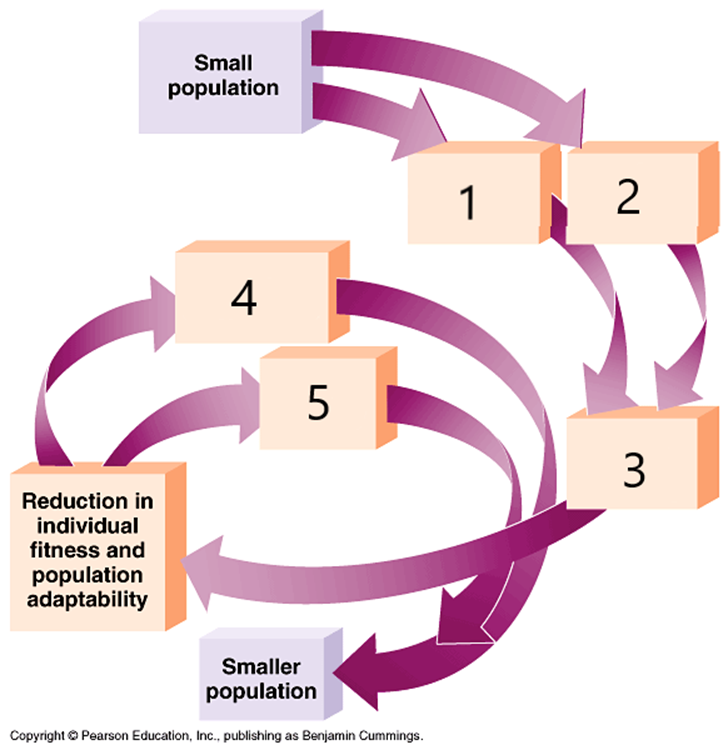
In the following graphic of the extinction vortex, match each number to the correct word or phrase below:
Inbreeding (1 or 2), Loss of genetic variability (3), Random genetic drift (1 or 2), Higher mortality (4 or 5), Lower reproduction (4 or 5).
(Blank)__________ describes the proportion of total phenotypic variation in a population due to genetic factors.
heritability
What principle is a null model for population genetics and states that populations following idealized conditions will have the same allele frequencies from one generation to the next?
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Among the options below, which are the correct assumptions necessary for Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium? Select all that apply.
Allelic frequencies may not be the same in males and females
No genotype provides any advantages for viability and fertility
Mating is not random
The population is sufficiently large that allele frequencies do not change across generations
The number of alleles per locus should not exceed four
Mutation regularly occurs to generate new alleles
Immigration exceeds emigration
No genotype provides any advantages for viability and fertility
The population is sufficiently large that allele frequencies do not change across generations
A diploid, sexual organism has a locus with 4 alleles: the frequency of the A allele is f(A) = 0.3, the frequency of the B allele is f(B) = 0.2, the frequency of the C allele f(C) = 0.1, and the frequency of the D allele f(D) = 0.4. What are the expected genotype frequencies for AB, BC, CD, and AD?
f(AB) = 0.12; f (BC) = 0.04; f (CD) = 0.08; f(AD) = 0.24
(Blank #1): a change from one allele to another resulting from additions, deletions, or substitutions of nucleotides in the original DNA sequence. Increases variation in a population.
(Blank #2): the effective exchange of genetic material from one population to another via migration; homogenizes the two populations.
(Blank #3): Nature's "preference" for/against phenotypes through the process of differential survival and reproduction due to heritable characteristics.
(Blank #4): sampling error resulting from the random change in allele frequencies from one generation to the next; greater effect in small populations, which may cause alleles to be more rapidly fixed or lost; decreases genetic variation.
mutation; gene flow; natural selection; genetic drift
Go to the AlleleA1 web site (https://faculty.washington.edu/herronjc/a1/) and simulate a single population with a starting A1 frequency of 0.7, a finite population of size = 50, no migration, no selection, unidirectional mutation rate from A1 to A2 = 0.001, and an inbreeding coefficient = 0.7. What happens to the allele A1 over 5000 generations?
decreasing to nearly zero
Repeated generations of self-fertilization can increase autozygosity to the theoretical maximum of 100%.
True
In any given species, the potential severity of outbreeding depression is generally higher than inbreeding depression.
False
Individuals polymorphic at functional Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) loci usually suffer more seriously from pests, parasites, and infectious diseases than do inbred individuals.
False
Compared to a single large population of the same total size, completely isolated and fragmented populations experience all of the following except:
Inbreeding depression
Increased inbreeding
Elevated extinction risk
Loss of genetic diversity over generations
Increased ability to evolve
Increased ability to evolve
In a hypothetical study on five Canadian populations of moose (Alces alces), the average observed heterozygosity for 21 microsatellite loci was 0.42. The average of expected heterozygosity within these populations was 0.63. The expected heterozygosity across all five populations was 0.75. Provide the answers below to two decimal places.
A) Calculate the inbreeding within populations
B) Calculate the inbreeding due to population differentiation
C) Calculate the total inbreeding due to both inbreeding within populations and differentiation among them.
A) 0.33
B) 0.16
C) 0.49
Fill in the blanks regarding zygosity and fitness.
The (Blank #1) hypothesis posits that a heterozygote advantage is specifically due to the assayed loci.
The (Blank #2) hypothesis claims that marker loci are closely linked to fitness loci.
The (Blank #3) hypothesis claims that a heterozygote advantage is conveyed not by the scored loci or tightly linked loci but by genome-wide effects (heterosis).
direct effect; local effect; general effect
The genetic effects of habitat fragmentation depend upon (choose all that apply):
distribution of individuals in fragments
time since fragmentation
effective migration rates
geographic distribution of fragments
All of the choices
predator-prey dynamics
distribution of individuals in fragments
time since fragmentation
effective migration rates
geographic distribution of fragments
What is not a common mechanism underlying Outbreeding Depression?
Maladaptation
Genetic compatibility
Physiological incompatibility
Chromosomal inversions
Reproductive isolation
Genetic compatibility
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Genetic rescue effects typically persist to at least the F3 generation and, in outbreeding species, are expected to stabilize by this time
Genetic rescue is not impacted by the mating system
Use of augmented gene flow between populations of outbreeding species is recommended when the risk of outbreeding depression is low
The beneficial effects of genetic rescue generally far outweigh the negative effects of outbreeding depression (which are often predictable)
Crossing of an inbred population to an unrelated population reduces inbreeding, and increases genetic diversity
Genetic rescue is not impacted by the mating system
Among vertebrates, an individual's sex can be determined genetically (by XY chromosomes or ZW chromosomes), by environmental conditions such as embryo incubation temperature, or by behavioral factors (e.g., dominance or agonistic interactions).
True
The number of different proteins of a species is strictly determined by the number of genes whereby there is a 1:1 relationship between an individual gene and its singular protein product.
False
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that genic information moves from DNA to RNA to protein in the direction of DNA replication -> translation -> transcription.
False
Using a hypothesis testing statistical framework, scientists can reject the null model based on goodness-of-fit tests with empirical data but doing so does not prove the alternative hypothesis.
True
Homologous sequences are orthologous if they are derived from a speciation event.
True
Microsatellites, often used as genetic markers in conservation efforts, occur in tens of thousands of locations in eukaryotic genomes and consist of di-, tri-, or tetra- nucleotide tandem repeats in DNA sequences.
True
Genetic distance (i.e., recombination rate) is equivalent to physical distance at a chromosome level such that 1Megabase (Mb) = 1centiMorgan (CM).
False
In eutherian mammals, small portions of the X and Y chromosomes can cross-over because they share a homologous region
True
The term "genome" includes protein-coding genes, intergenic regions (i.e., gene deserts), non-functional pseudogenes, and repetitive regions such as telomeres, satellite DNA, and transposable elements.
True
Eukaryotic genes consist of exons, introns, and associated regulatory sequences such as promoters and enhancers.
True
List two characteristics of RNA which indicate it could be considered as the earliest replicator molecule.
RNA can encode information
RNA molecules can function as enzymes
Genome size does not correlate with organismal complexity; this phenomenon is called the (Blank) and is illustrated by the fact that some salamanders have genomes >10x the size of the human genome.
C-value paradox
A(n) is any specific physical location in the genome, in a gene or chromosome.
A(n) is a part of the genome sequence that encodes an RNA or protein product.
A(n) is a particular variant at a locus that may or may not result in phenotypic differences.
locus; gene; allele
The (Blank) Theory of Inheritance states that inherited traits are controlled by genes residing on chromosomes and are transmitted through gametes.
Chromosomal
During replication, the enzyme (Blank #1)____________ elongates the daughter strand in the 5' to 3' direction and the enzyme (Blank #2)____________ fuses the replicated DNA fragments into a contiguous molecule.
DNA polymerase; DNA ligase
The (Blank #1) can be described as an organism's (Blank #2) DNA content, which refers to the information in a single set of chromosomes.
genome; haploid
Which of the following is NOT a cost/problem associated with sexuality?
Physiological and/or energetic expenses associated with rearing offspring of two different sexes
Physiological and/or energetic expenses associated with finding a mate
Physiological and/or energetic expenses associated with aggressive intrasexual competition
Sexually transmitted diseases
Physiological and/or energetic expenses associated with rearing offspring of two different sexes
The nitrogenous bases (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine) in DNA molecules are arranged in complementary pairs. Which nucleotide pairs with ADENINE in DNA? Which nucleotide pairs with it in RNA? If 22% of the DNA extracted from a shark genome is found to be ADENINE, what percentage will be represented by guanine, cytosine and thymine respectively?
thymine, uranine, 33, 33, 22 %
How many DNA duplex molecules are obtained from an initial single DNA duplex after 7 cycles of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
128
A geneticist found that a specific mutation—a nucleotide substitution--has no effect on the polypeptide encoded by a given gene. Fill in the blanks for all possible reasons.
The substitution could be (Blank #1) , meaning that it produced no change in the amino acid sequence.
The substitution could produce a change in the amino acid, but this single amino acid change would be (Blank #2) .
The substitution could occur in an (Blank #3) and therefore would be removed during splicing of the primary transcript.
synonymous; neutral; intron
If a trait is polygenic, determined by three biallelic genes with equally additive contributions to the phenotypic trait, what is the probability of the offspring phenotype having two dominant and four recessive alleles when the parental genotypes are AaBbCc and AaBbCc?
15/64
Which of the following terms is incorrectly matched with the definition?
linkage: the co-inheritance of two genes because they are in close proximity on a chromosome and have little or no recombination between them
none of them
charged tRNA: a tRNA molecule to which an amino acid has been attached
polygenic: One phenotypic trait influenced by many genetic loci
transversion: substitution of one purine for another purine
a and c are incorrect
genotype: the alleles intrinsic to an individual
transversion: substitution of one purine for another purine
Is Mendel's law of independent assortment true for all pairs of genes? Why or why not?
No, not all pairs of genes follow the law of independent assortment because genes near each other (i.e., linked) on the same chromosome do NOT assort independently
Color blindness is a common X-linked recessive trait. Assume a female with a color blindness allele mates with a normal male. Denote the color blindness allele as Xb, and the normal allele as XB. What are the possible genotypes of the offspring? What is the probability that the offspring is color blind?
XBXB, XbXB, XBY, XbY. The probability the offspring is color blind is 0.25.
Among the following choices, which is usually organized in a single circular haploid chromosome and inherited maternally?
Mitochondrial DNA
Autosomal chromosomes
The mammalian Y chromosome
The mammalian X chromosome
Mitochondrial DNA
In the context of "genotype x environment interaction", what will happen if a crop strain from A region is planted in B region where the environment varies?
The crop strain may maintain a constant genotype, but its phenotype may differ due to varying environmental conditions.
Sarah and Ben have two children (Christopher, and Sue). Sarah and Sue suffer from an allergic response to caffeine characterized by hives and facial swelling. Ben and Christopher do not have this problem. The two children grow up and some have children of their own. One out of Sarah's three daughters is affected, whereas all of Christopher's two sons are not. What is the most likely mode of inheritance of this condition by a recessive mutation?
Autosomal inheritance
The genetic code is degenerate, which means
Multiple codons correspond to one amino acid
For DNA replication, cells must solve at least three problems. Select 3 of these problems from the 5 choices below.
addition of the RNA primers
manage coiling stress generated during unwinding
unwinding of the helix
post-translational modification of the nascent DNA chain
ligation of Okazaki fragments
manage coiling stress generated during unwinding
unwinding of the helix
ligation of Okazaki fragments
Which of the following terms is not matched properly with the definition?
Spontaneous mutation: A mutation due to an internal mutagen
Missense mutation: Nucleotide change that results in a single amino acid substitution
Synonymous mutation (substitution): A mutation that has a phenotypic effect on the protein.
Nonsense mutation: Nucleotide change that results in a premature stop codon
Synonymous mutation (substitution): A mutation that has a phenotypic effect on the protein.
DNA is organized into chromatin, a nucleoprotein structure of eukaryotic chromosomes. Histon octamers facilitate this process by making nucleosomes. Which one is not a member of histones that participated in the histone octamer?
H4
H3
H2A
H1
H2B
H1
A coding/sense strand has the sequence 5' AGCATTTCGACG 3'. What is the template/anti-sense strand that matches this DNA sequence (label the 5' and 3' ends)? What is the resulting mRNA sequence (label the 5' and 3' ends)?
5'-CGTCGAAATGCT-3', 5'- AGCAUUUCGACG-3'.
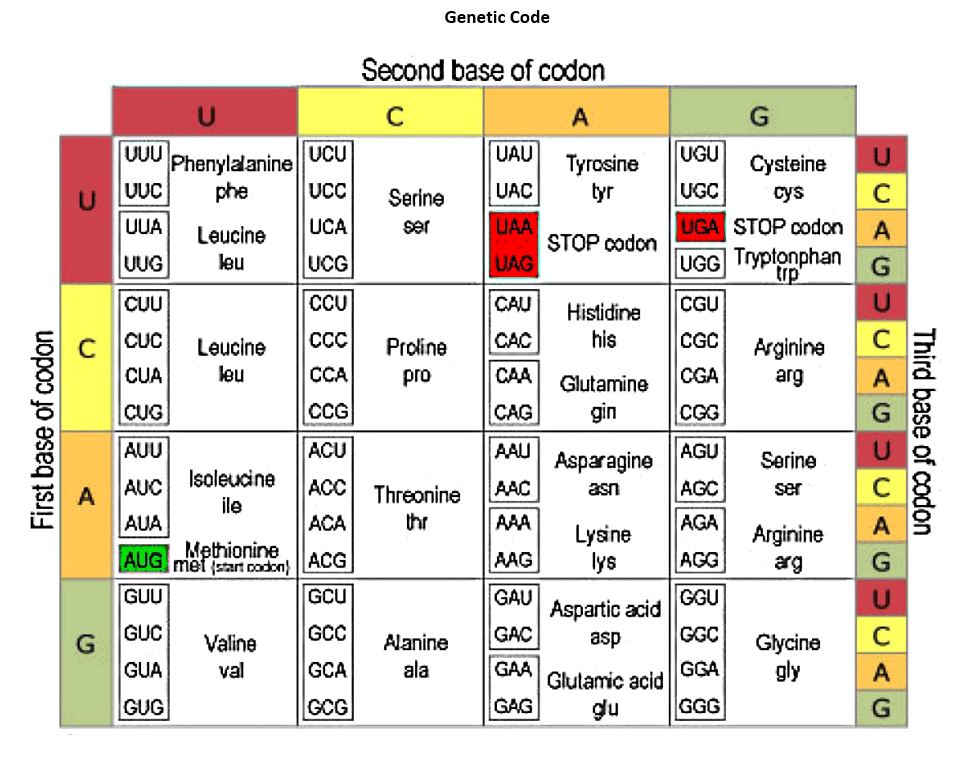
A coding/sense strand has the sequence 5' AGCATTTCGACG 3'. After translation, assuming a start codon is immediately upstream of the given sequence, what will be the resulting amino acid sequence?
Ser-Ile-Ser-Thr
![<p><span>What is the amino acid sequence if "CG" is inserted like so: 5' AGGAA[CG]AACTTTAG 3'. What is the name for this type of mutation?</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/adba6788-edea-444c-b6b9-4457d5355904.jpg)
What is the amino acid sequence if "CG" is inserted like so: 5' AGGAA[CG]AACTTTAG 3'. What is the name for this type of mutation?
Arg-Asn-Glu-Leu-Stop, frameshift mutation
Select "three" proper descriptors of each type of RNA molecule from the five options below. tRNA (Blank #1) , rRNA (Blank #2) , mRNA (Blank #3) .
A. is generally a single-stranded molecule
B. is a template for protein synthesis
C. is one component of the ribosome
D. can carry one type of amino acid per molecule
E. is the product of RNA polymerase.
AED; AEC; AEB