Ch 15 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
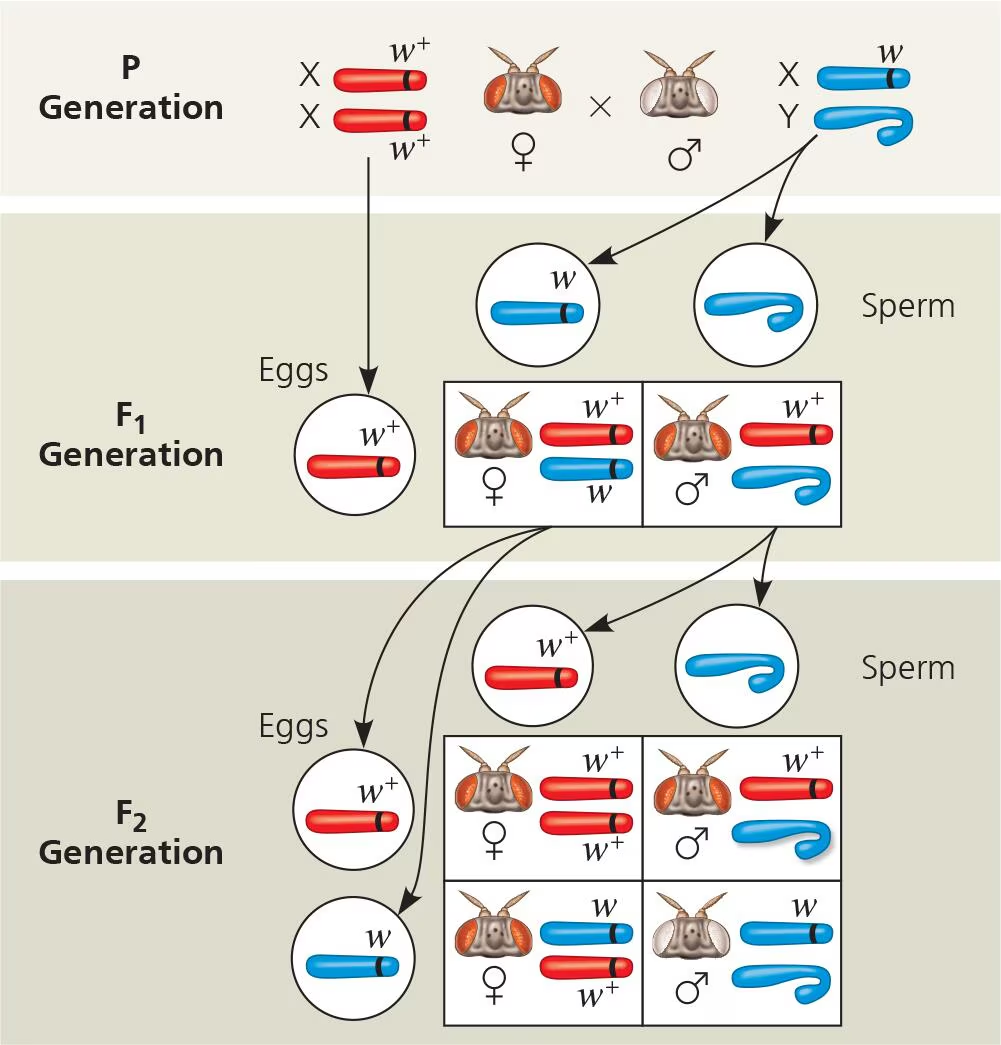
Thomas Morgan Discovery
1.) mated male flies with white eyes (mutant type) with female with red eyes (wild type) (P generation)
2.) F1 generation has all red eyes; Morgan breeds F1 female to F1 male
3.) F2 generation has typical ratio of 3:1, but notes only males have white eyes
4.) determines that the eye color allele must be located on X-chromosome since recessive trait (white eyes) only expressed in males with XY vs females with XX
5.) refers to discovery as X-linked inheritance
Fruit Flies Use in Genetics
good organisms for genetic studies because: prolific breeders/breed at high rate; generation can be bred every two weeks; only four easily distinguishable pairs of chromosomes
Wild Type vs Mutant Alleles
wild: phenotype most commonly observed in natural populations; also refers to the individual with that phenotype
mutant: traits alternative to the wild type
X-Linked Gene
gene located on the X-chromosome; such genes show a distinctive pattern of inheritance
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance Pattern
fathers pass X-linked alleles to all daughters but none of their sons
mothers can pass X-linked alleles to both sons and daughters
ex: color-blindness; hemophilia
X-Linked Conditions in Males
higher frequency due to only having one X-chromosome; if males inherits recessive X-linked condition, it will be expressed as there’s no second X chromosome to provide healthy copy
Pedigree
diagram of family tree with conventional symbols, showing the occurrence of heritable characters in parents and offspring over multiple generations; can be tool for identifying modes of inheritance and calculating probability of inheritance
How to Read a Pedigree
blank circle/square: female/male
filled circle/square: female/male expresses trait
half-filled circle/square: female/male carrier of trait (does not express trait)
crossed out circle/square: dead female/male
diamond: unspecified sex
vertical line: generation
horizontal line: partners
connected little vertical and horizontal lines: siblings
double horizontal line: consanguinity (inbreeding)
Dosage Compensation
females have two X chromosomes, males have one; yet the amount of gene product is the same
mechanism that regulates the expression of sex-linked gene products
Lyon Hypothesis of X-Inactivation
hypothesis about dosage compensation in female mammals: random inactivation of one X chromosome in females equalizes the activity of X-linked genes in males and females
Tortoiseshell Cat Supports Lyons Hypothesis
Barr body chromosomes are reactivated in cell that give rise to eggs, resulting in every female gamete having an active X after meiosis
two cell populations in adult cat from each parent: allele for black fur and allele for orange fur both active
Examples of X-Inactivation in Females
“mosaic” of two types of cells: those with active X derived from male parent and those with active X from female parent
half of cells will express one allele, while other expresses the other
ex: patches of normal skin and patches of skin lacking sweat glands
Barr Bodies & Formation
dense object/staining mass inside somatic nuclei/nuclear envelope in cells of female mammals; represents a highly condensed, inactivated X chromosome
formed due to dosage compensation, which balances expression of X-linked genes in cells
Active Gene on Inactivated X-Chrom
XIST (X-inactive specific transcript); the one active gene expressed on a Barr body; results in a chromosome covered in RNA
Cell Cycle Stages of Nondisjunction
error in meiosis in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes or a pair of sister chromatids fail to separate properly from each other
during meiosis I: results in copies of both homologs in one gamete
during meiosis II: results in both sister chromatids in one gamete
Polyploidy
chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets; cells have extra chromosome sets; result of an accident of cell division
Aneuploidy
chromosomal aberration in which cells have additional or missing chromosomes; not missing entire sets
Deletion
deficiency in a chromosome resulting from the loss of a fragment through breakage
missing genetic segment from a chromosome
Duplication
aberration in chromosome structure due to fusion with a fragment from a homologous chromosome, such that a portion of a chromosome is duplicated;
present of an extra genetic segment on a chromosome
Inversion
aberration in chromosome structure resulting from a reattachment of a chromosomal fragment in a reverse orientation to the chromosome from which it originated
chromosome segment is flipped in orientation
Translocation
aberration in chromosome structure resulting from attachment or a chromosomal fragment to a nonhomologous chromosome
where two non-homologous chromosomes exchange segments
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
genetic disease caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21; characterized by developmental delays and heart and other defects that are generally treatable or non-life threatening
Turner Syndrome (XO)
syndrome in females caused by monosomy (missing one X chromosome); features include short stature, webbing at back of neck, infertility due to incomplete sexual development, and impaired hearing
Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)
syndrome in males caused by aneuploidy (extra X chromosome); features incomplete sexual development, long limbs, large hands and feet, some breast tissue development; is the most common genetic cause of male infertility
XYY (Jacobs Syndrome)
syndrome in males caused by aneuploidy (extra Y chromosome); features great height, acne, speech and reading disabilities