Week 1 - Databases
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
what is a database?
a group of related data
what is data?
piece of information that has some meaning associated with it
what is a mini-world?
some part of the real world about which data is stored in the data base
what is a database management system (DBMS)?
a software that will manage our database
what is a flat file?
one line of it is a record; each thing separated by a comma is data; a group of flat files is a database
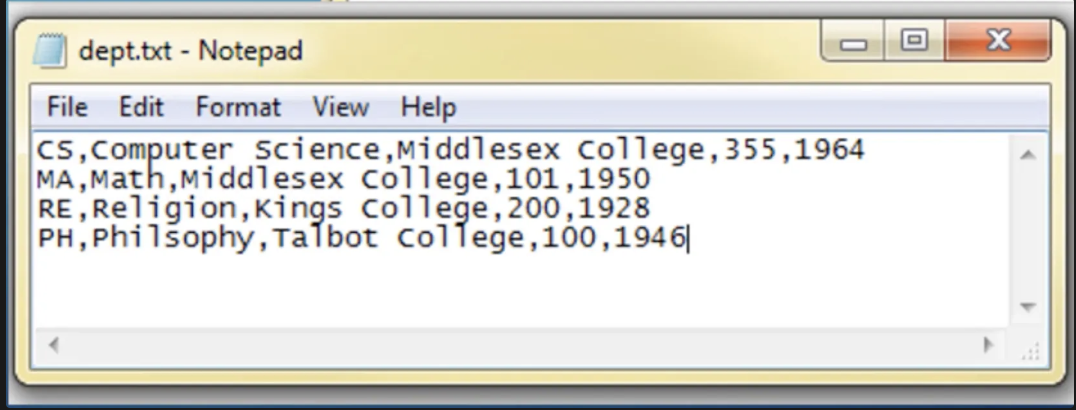
why is a DBMS better than using the flat file system?
Data redundancy/inconsistency is reduced
Isolates the program from the data
Provides persistent storage of data
Multiple users can use it
Data is abstracted
Security, integrity and backups
Generalized query tools
Provides multiple user interfaces
Possible to enforce standards since data is centralized
Reduced development time
Up to date information managed centrally
what are the disadvantages of DBMS?
Flat Files are cheap (are free)
DBMS requires maintenance
DBMS are initially complex
what does a database administrator do?
Give and revoke access to the database for new people
Installing and upgrading the DBMS
Monitor and improve the performance
Backing up and restoring databases
what does a database designer do?
dentify and collect all data that is to be stored
Identify relationships between data
Create model of the data
Structure the data
Communicate with end users to identify their needs
what does a system analysis and application programmer do?
Determine needs of end users
Develop spec for the system
Develop software that communicates to the database
Test implementation too
what do end users do?
Access database
Using the database
what is a schema?
a description of the database but NOT the data itself (kind of like types in programming languages)
what is a state/snapshot?
The data in the database at a moment in time — so every time we delete or add or change a value of a data item we change the state
what is the schema of the schema?
meta data — like what tables and columns exist
what are the 3 levels of the 3 schema architecture?
internal level, conceptual level, and external level
what is the Internal level?
the internal level describes the data storage and indices to get to the data; hard disk
what is the conceptual level?
the data in the database is stored in tables
what is the external level
shows the data that each end user is interested in and hides the other data
what is logical data independence?
the capacity to change the conceptual schema without affecting the external schema or views
what is physical data independence?
the ability the change the internal schema without changing the conceptual schema
where and how do we start building the DBMS?
start with DATA and not the code
Narrow your scope as much as possible and figure out what data you need to store/save by:
Gather reposts your customers use/print/generate
Look at any screens where the customer enter/modify data
Find the requirements of your customers/stakeholders
Figure out how they view the data
Integrate the views to get the minimal data that you need to store
what is an entity?
a single “THING” that exists — has independent existence; it is any object in our mini-world that we want to model and store information about
what is an entity type?
a set of entities that have the same set of attributes
what is an attribute?
describes a “thing”; it defines the information about the entity that needs to be store; an entity has a domain
what is a composite attribute?
an attribute that can be broken down further (eg. name = Bart Simpson; can be broken down into last name and first name)
what is an atomic/simple attribute?
and attribute that cannot be broken down any further eg. age = 45
what is a single-valued attribute?
an attribute that can only take one value (eg. age)
what is a multivalued attribute?
an attribute that can take on multiple values (eg. college degrees)
what is a derived attribute?
an attribute that can be derived from other data — doesnt have to physically exist in the database (eg. age can be derived from birthdate)
what is a stored attribute?
an attribute that the database stores and keeps (eg. birthdate is permanently stored instead of age because age changes every year)
what is a key attribute?
has uniqueness (eg. student number)
what is a value?
is taken on by an attribute
what is a domain?
the type of values that an attribute can take (eg. string, integer, real)
what are null values?
used for information that is not applicable or unknown (eg. Apartment number — maybe the person lives in a house. Or phone number — maybe we don’t know the phone number)
what is the ER diagram notation for entity type

what is the ER diagram notation for attribute?

what is the ER diagram notation for a key attribute

what is the ER diagram notation for a multivalued attribute?

what is the ER diagram notation for a composite attribute?

what is the ER diagram notation for a derived attribute?

what is a relationship?
a named grouping of entites
what is a relationship set?
an ordered list of entity sets
what a relationship type R
among n entity types E1, E2…En defines a set os associations among entities. So R is a set of relationship instances ri, where each ri associates n entities (e1, e2,…,en) and each entity ej in ri is a member of entity type Ej, 1≤ j ≤ n. Hence a relationship type is a mathematical relation on E1, E2, ..En
eg (”Reid”, “CS3319”) is a relationship set of (Prof, Course); relationship type would be “teaches”

what is a recursive (unary) relationship?
an entity of one entity type that has a relationship with other entities of that same entity
what are attributes on relalationships?
describes some pieces of information about the relationship ((eg. A Student takes a Course, the Grade would be attributed to that relationship)
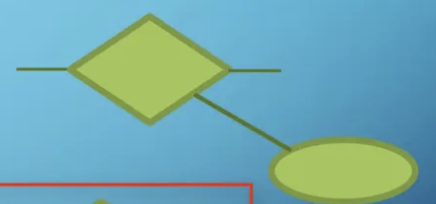
what is a cardinality ratio?
number of relationships instances that entity can participate in
what are the different types of cardinality ratios?
One-to-one
One-to-Many
Many-to-many

what is a participation constraint?
specifies whether the existence of an entity depends on it being related to another entity via the relationship type
what is total (mandatory) participation?
every entity in the entity set must be related to the other entity set via the relationship (eg. every employee must Work_For a department)
denoted as double line
what is partial (optional) participation?
some or part of the entity set are related to the other entity set but not necessarily all (eg. some employees manage a department but not all)
denoted as a single line
what is (min, max) notation?
where 0 ≤ min ≤ max and max ≥ 1; each entity must participate in at least min and at most max relationships; so a min of 0 implies partial participation
what is a weak entity?
If an entity’s key attribute is not a true key that does not uniquely identify the entity, the entity type might be a Weak Entity
If one Entity cannot exist without the existence of the other Entity (its Owner) which it has a relationship with, that Entity Type might be a Weak Entity
Have no key attribute of their own
Cannot exist without its identifying owner
Always has total participation with its identifying owner
Always has a double line around the relationship with its identifying owner
The identifying owner does not have to have 1 weak entity
Can sometimes be represented as composite, multi-valued attributes
Use a dashed underline to show the partial key of the weak entity
Use a double outlined diamond to show the relationship with the owner entity
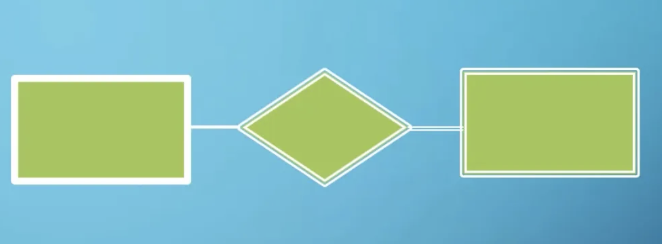

what does this represent
zero or more

what does this represent
one or more

what does this represent
one and only one

what does this represent?
zero or 1