(openstax chapter 2) Campbell Biology Concepts & Connections Chapter 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Organic Compounds
Carbon-based molecules that usually contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon.
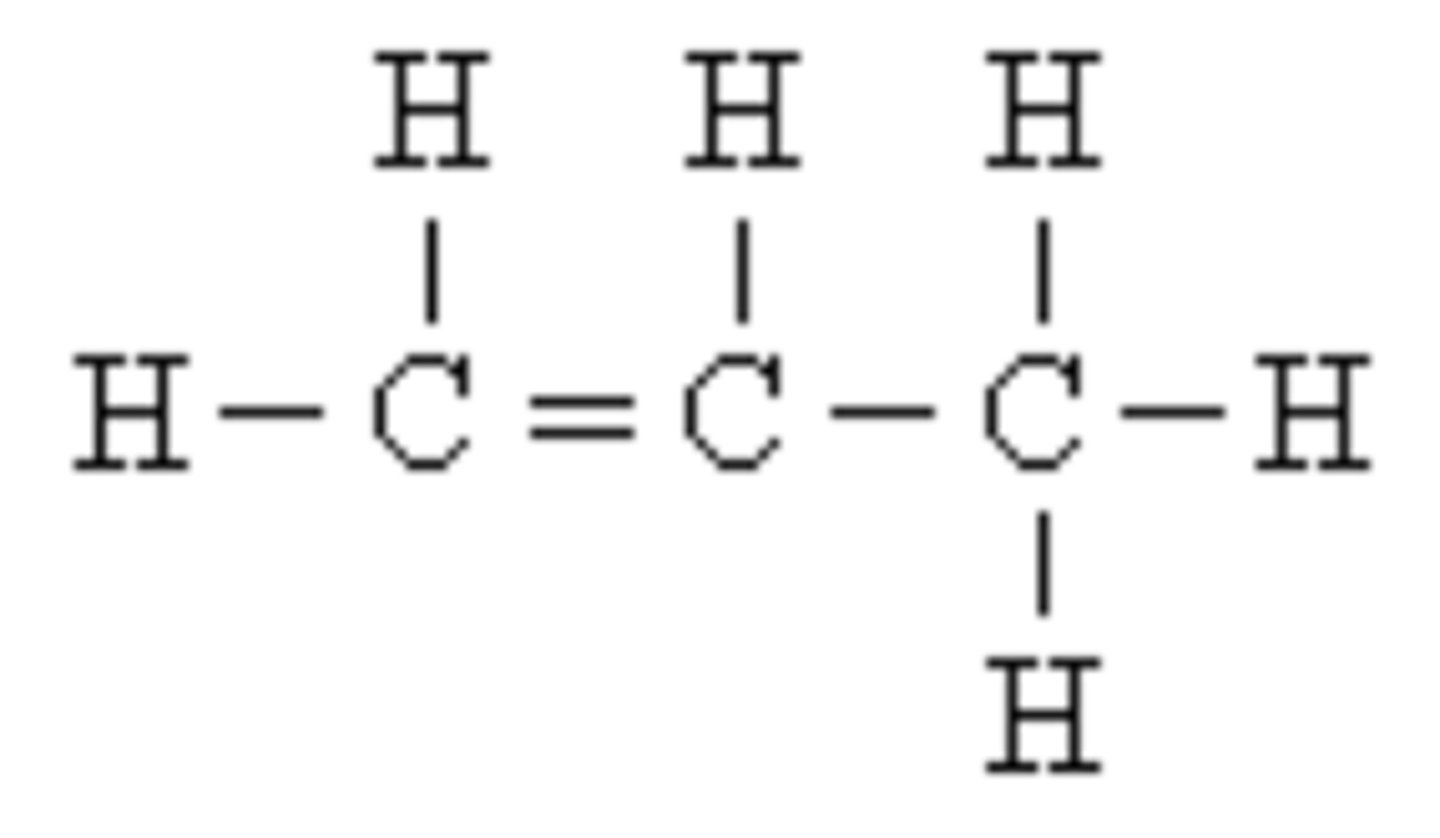
Hydrocarbons
An organic compound composed only of the elements carbon and hydrogen.
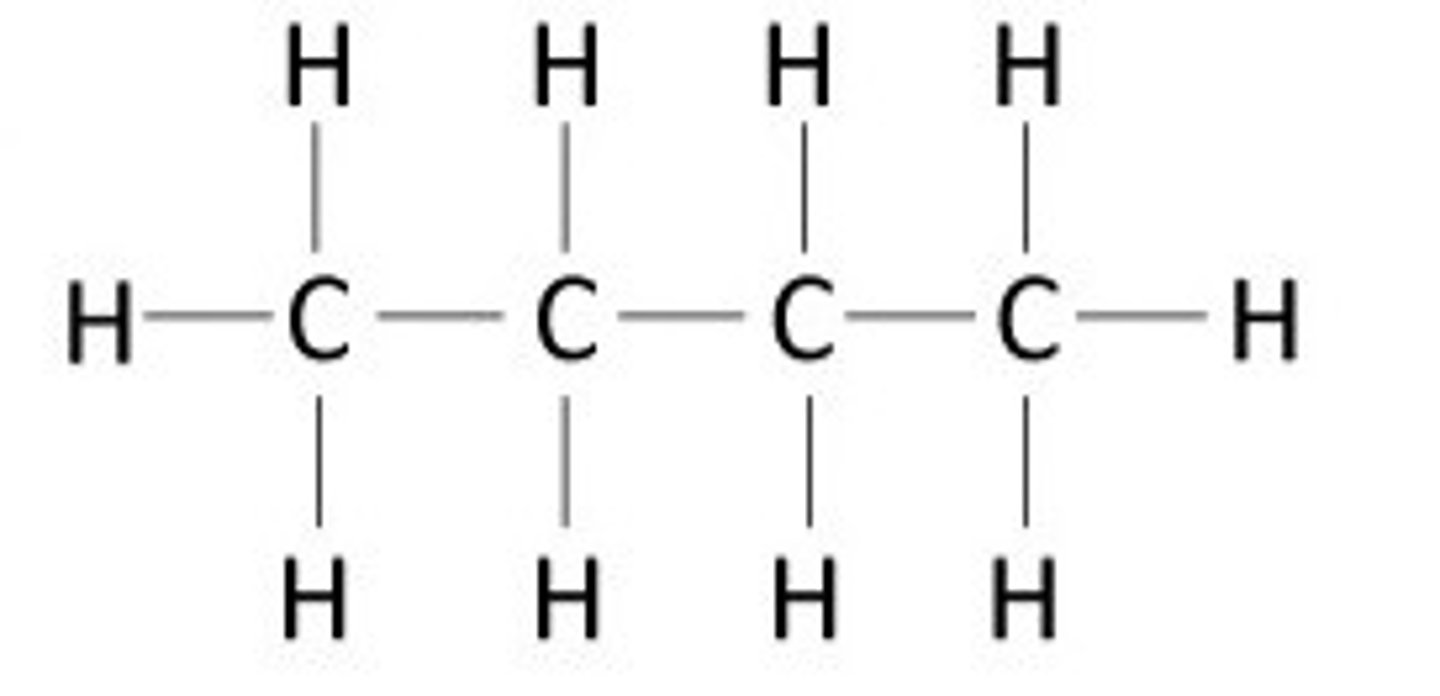
Carbon Skeleton
The chain of carbon molecules that forms the structural backbone of an organic molecule.
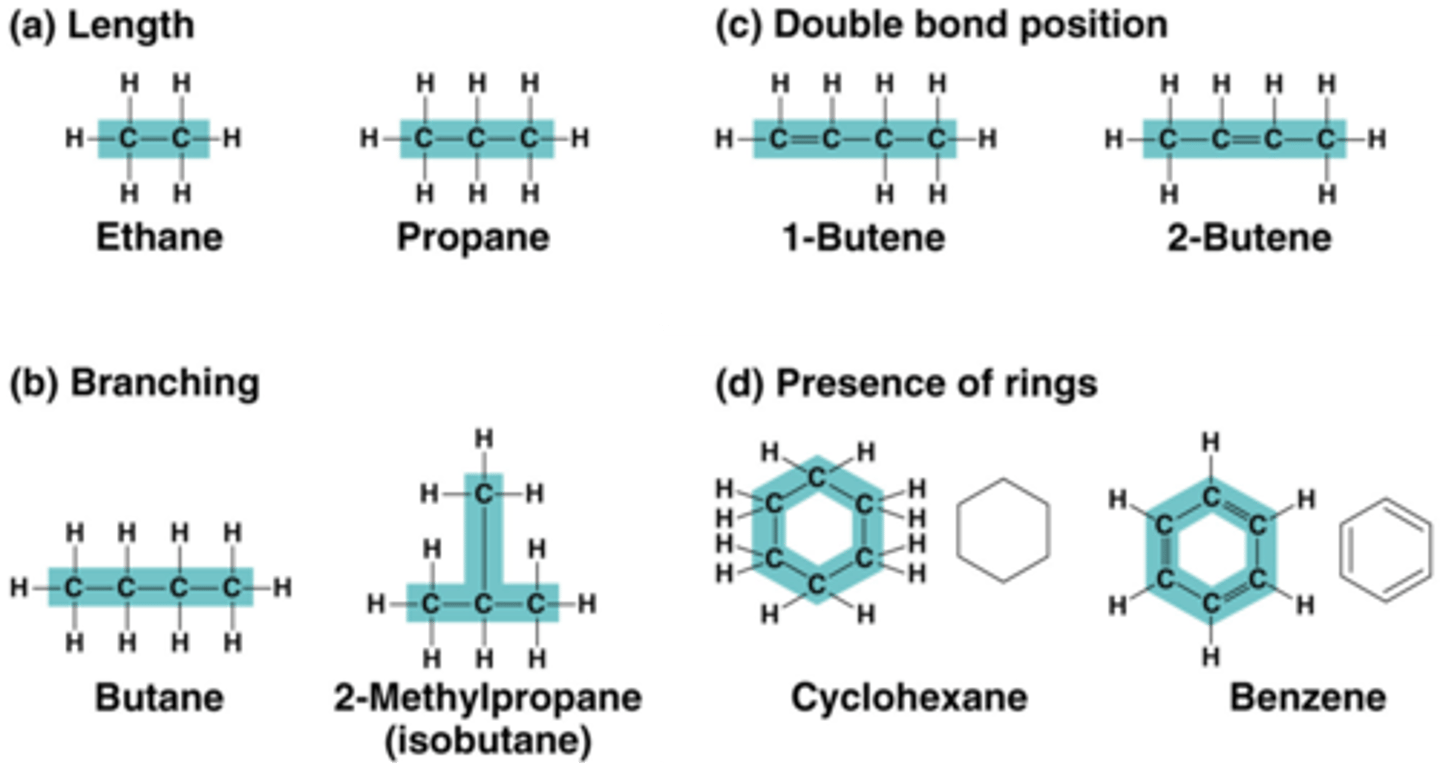
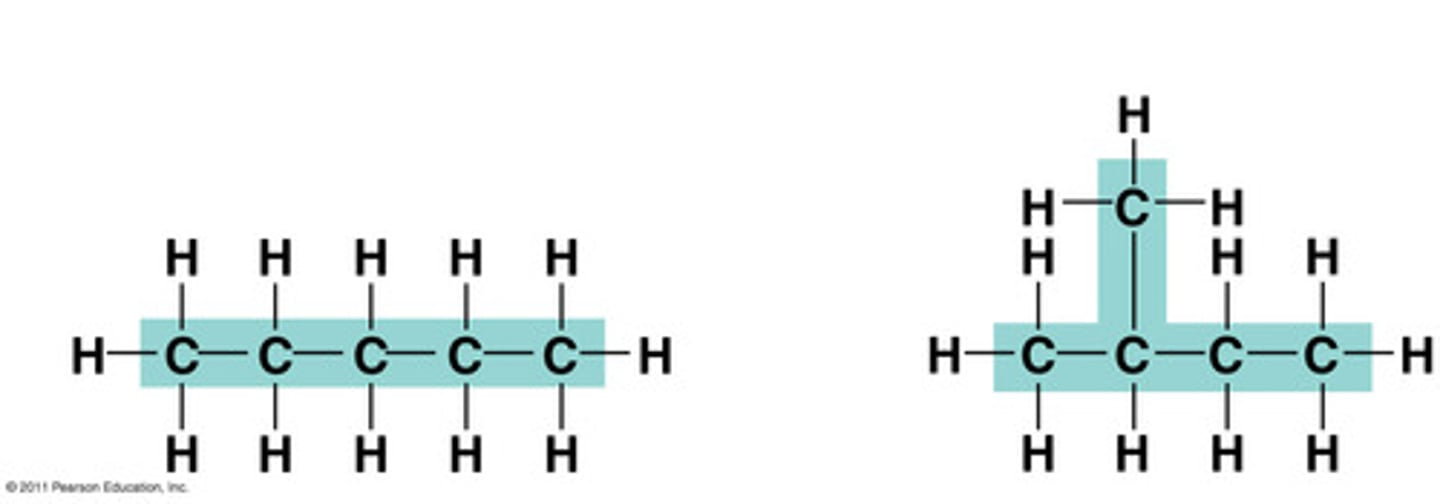
Isomers
Organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and, therefore, different properties.
Functional Groups
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
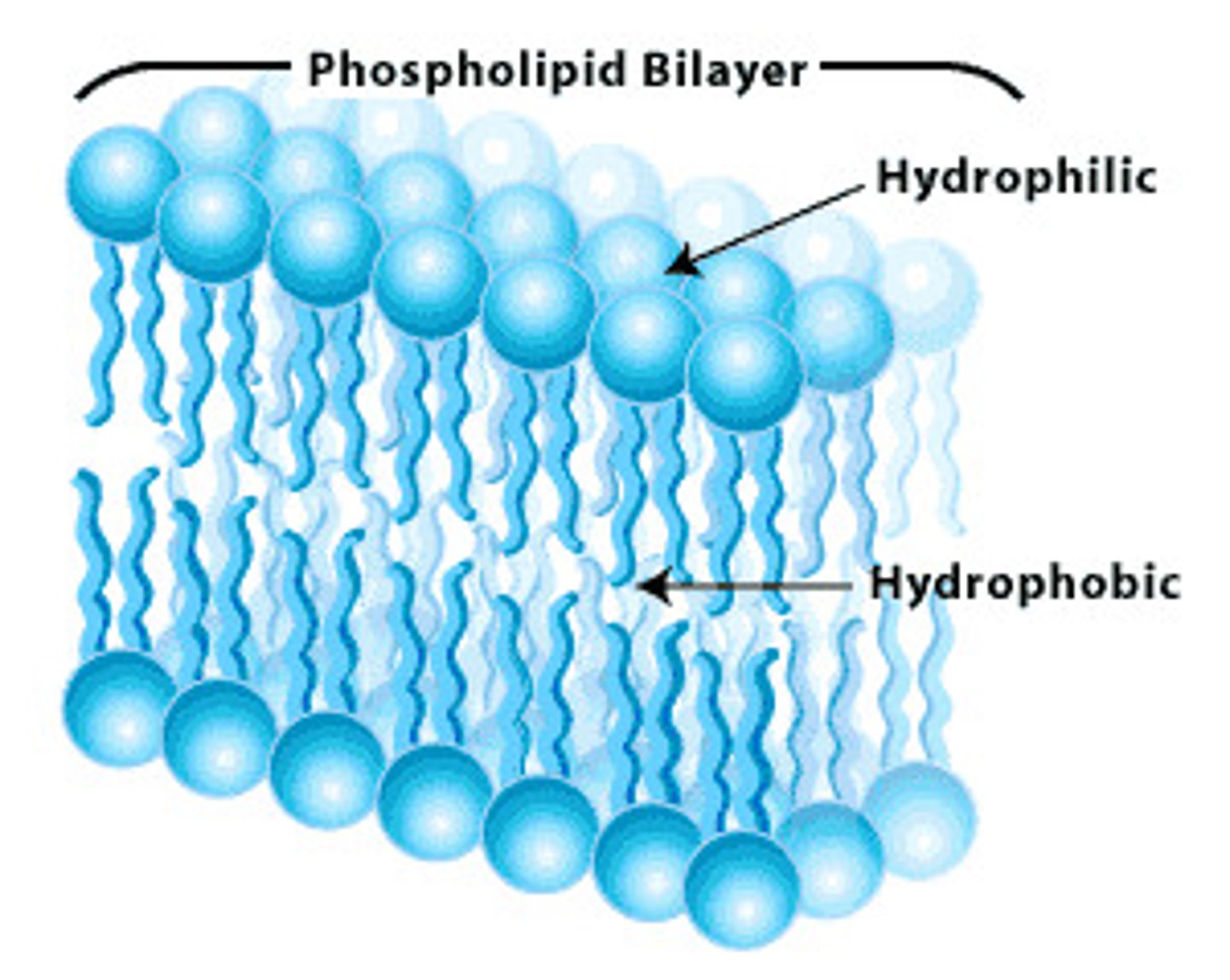
Hydrophilic
"Water-loving"; pertaining to polar or charged molecules (or parts of molecules) that are soluble in water.

Hydroxyl Group
(-OH) consists of a H atom bonded to an O atom which in turn is bonded to a C.
Macromolecules
A large molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules, usually by a dehydration reaction i.e. protein, carbohydrate, nucleic acids.
Polymers
A large molecule consisting of many identical or similar monomers linked together by covalent bonds.
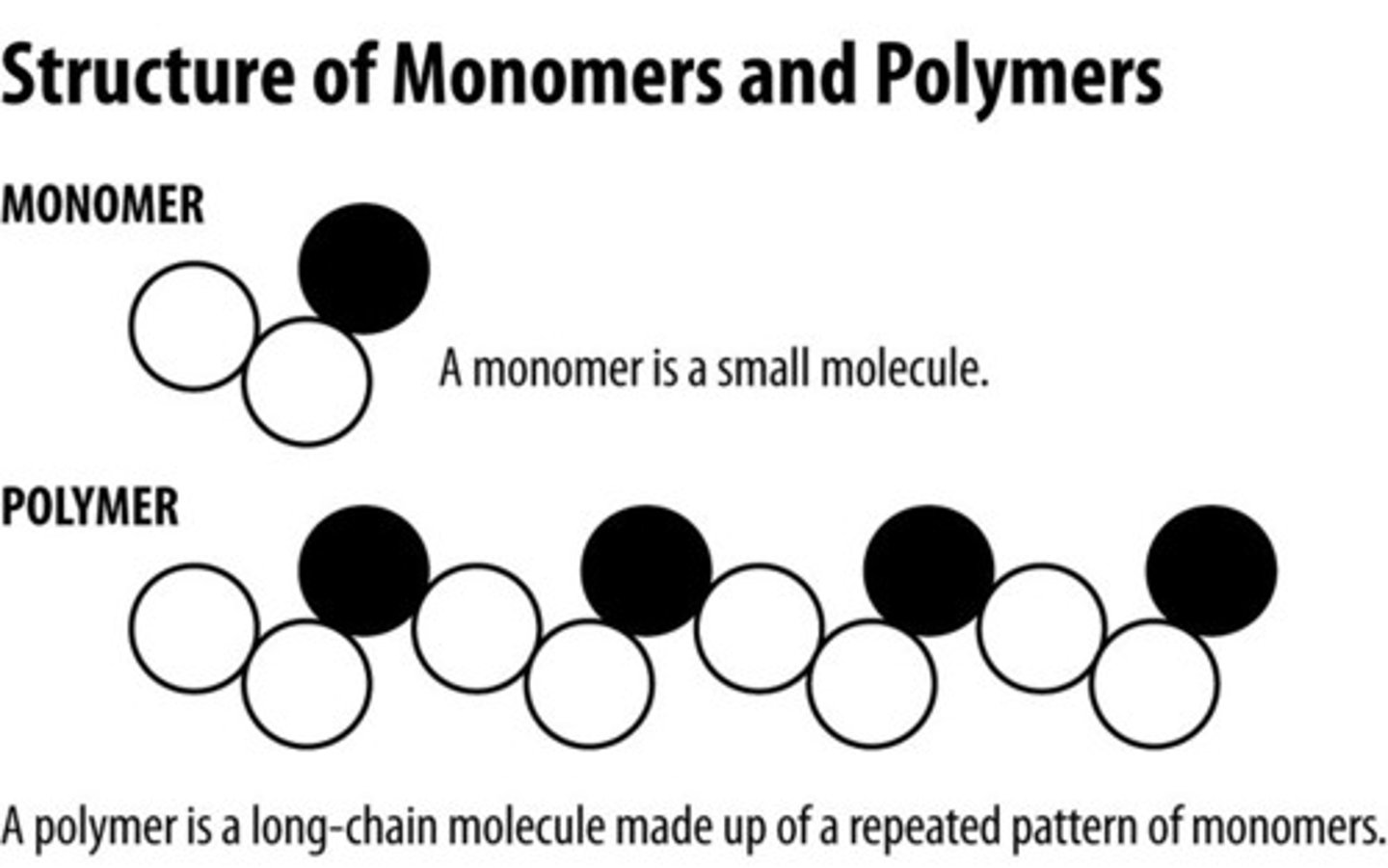
Monomers
The subunit that serves as the building block of a polymer.
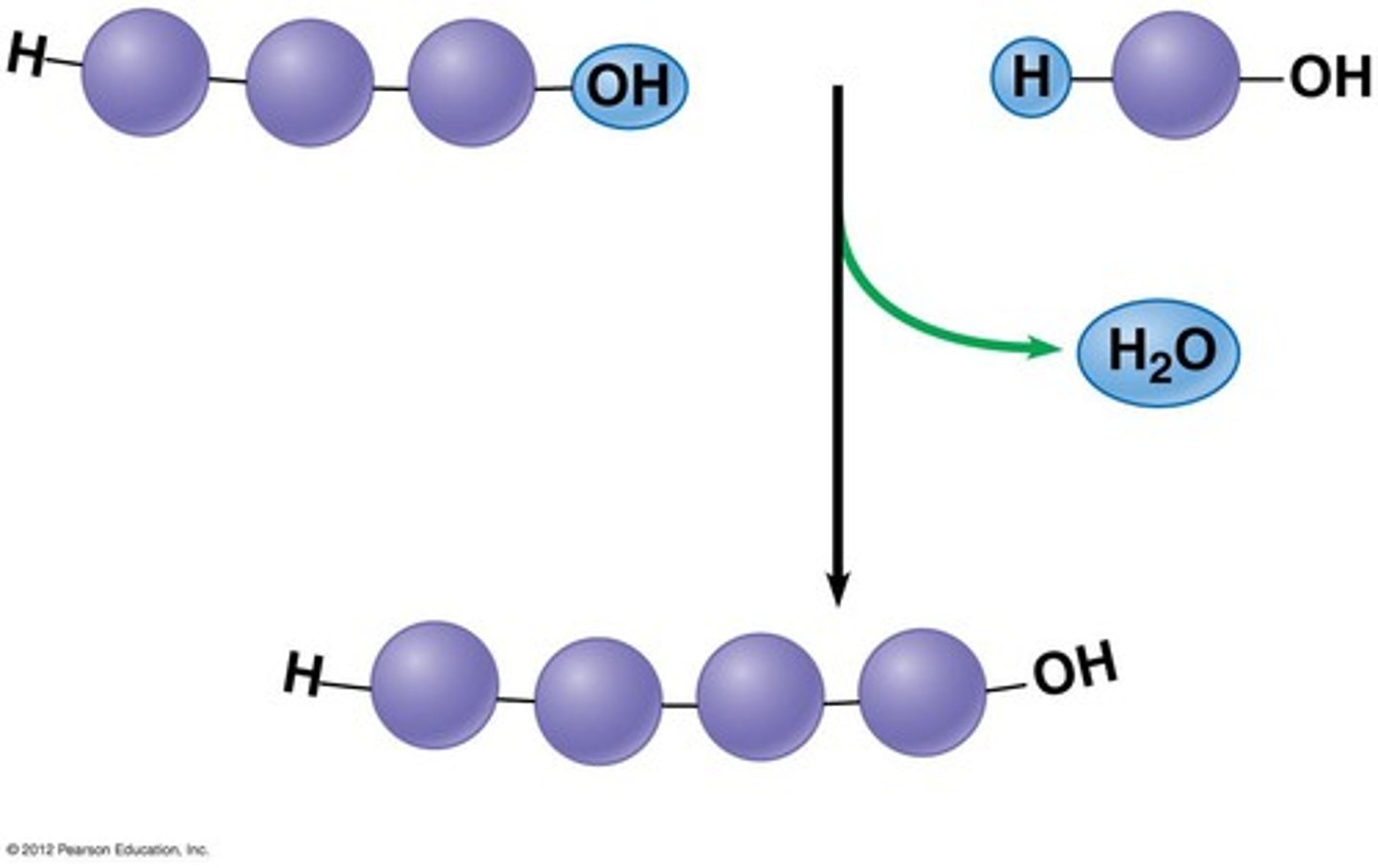
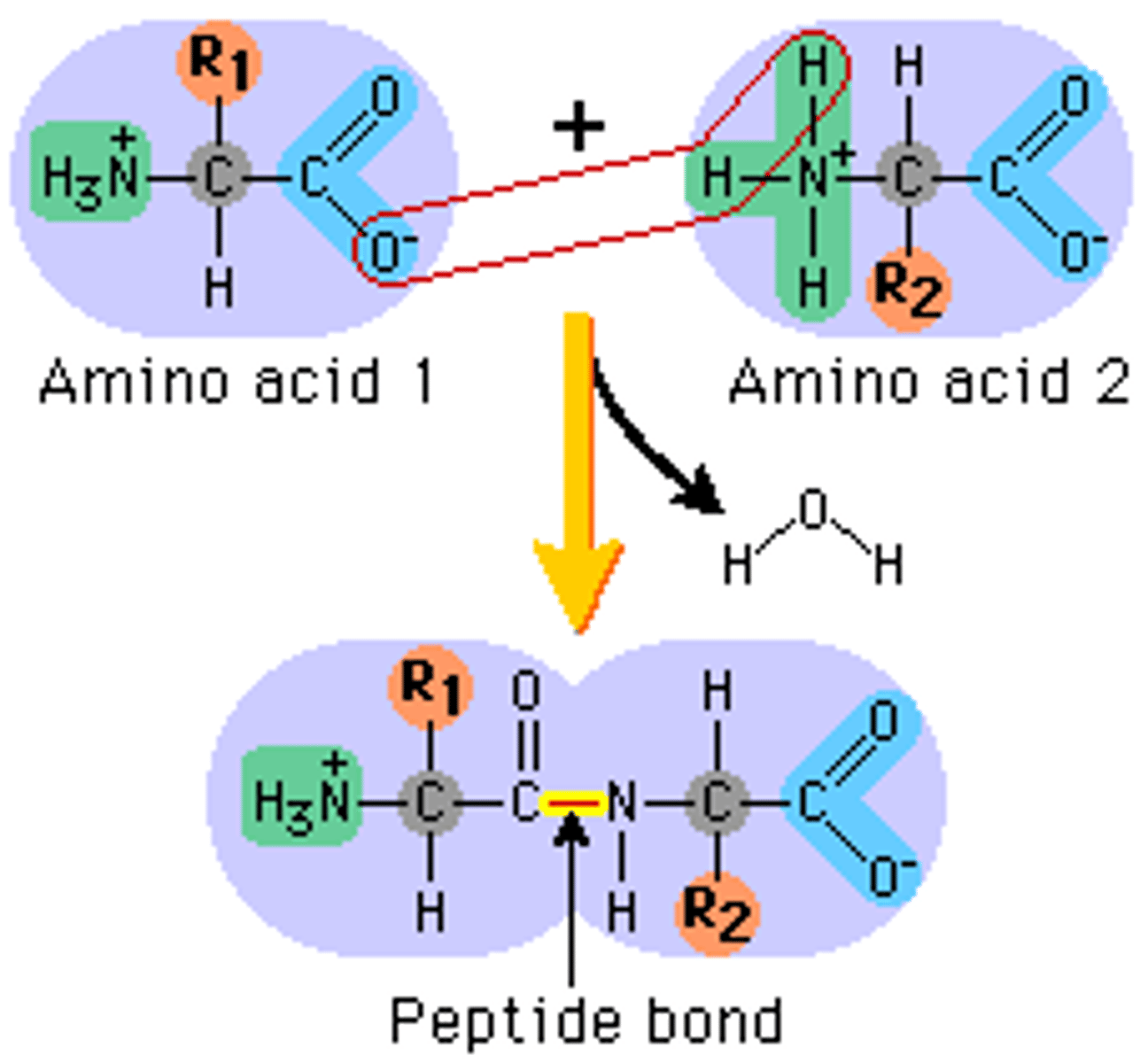
Dehydration Reaction
A chemical reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
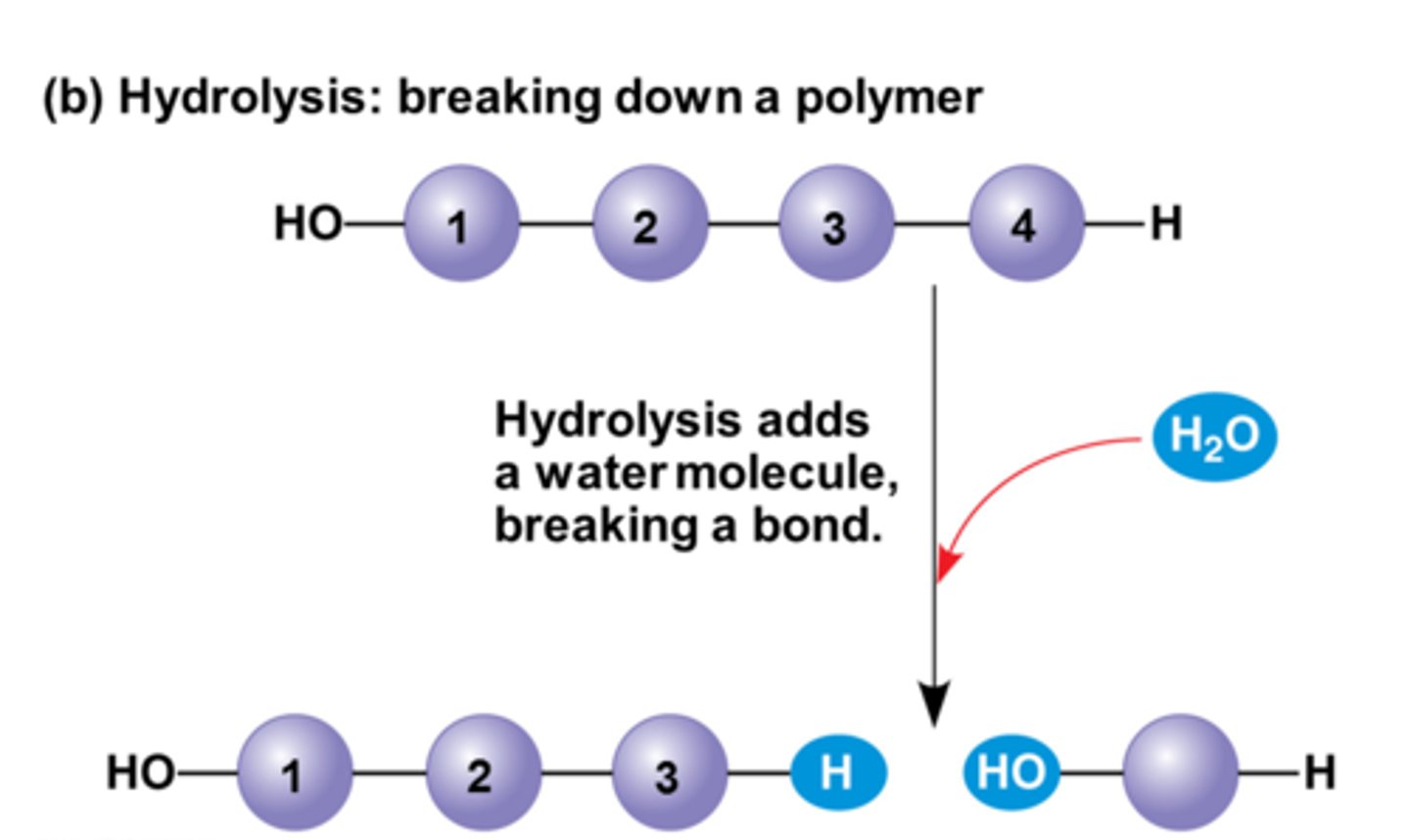
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water; process by polymers are broken down and an essential part of digestion.
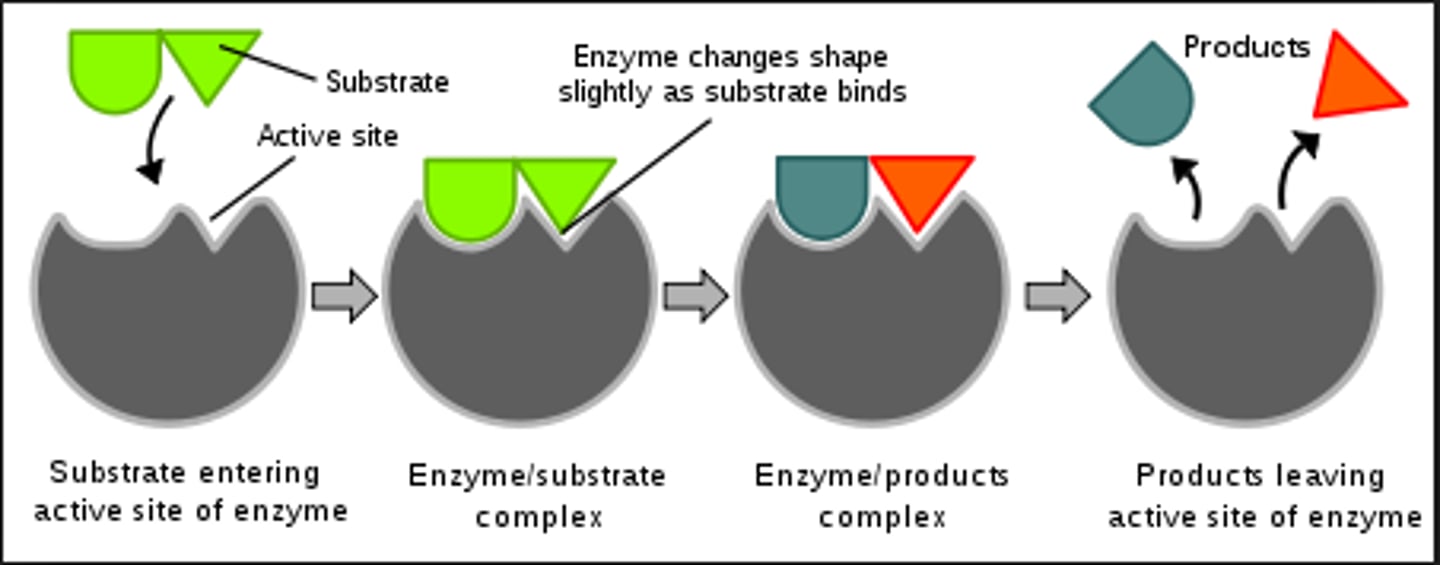
Enzyme
A macromolecule, usually a protein, that serves as a biological catalyst, changing the rate of chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
Carbohydrate
Member of the class of biological molecules consisting of single-monomer sugars (monosaccharides), two-monomer sugars (disaccharides), and polymers (polysaccharides).

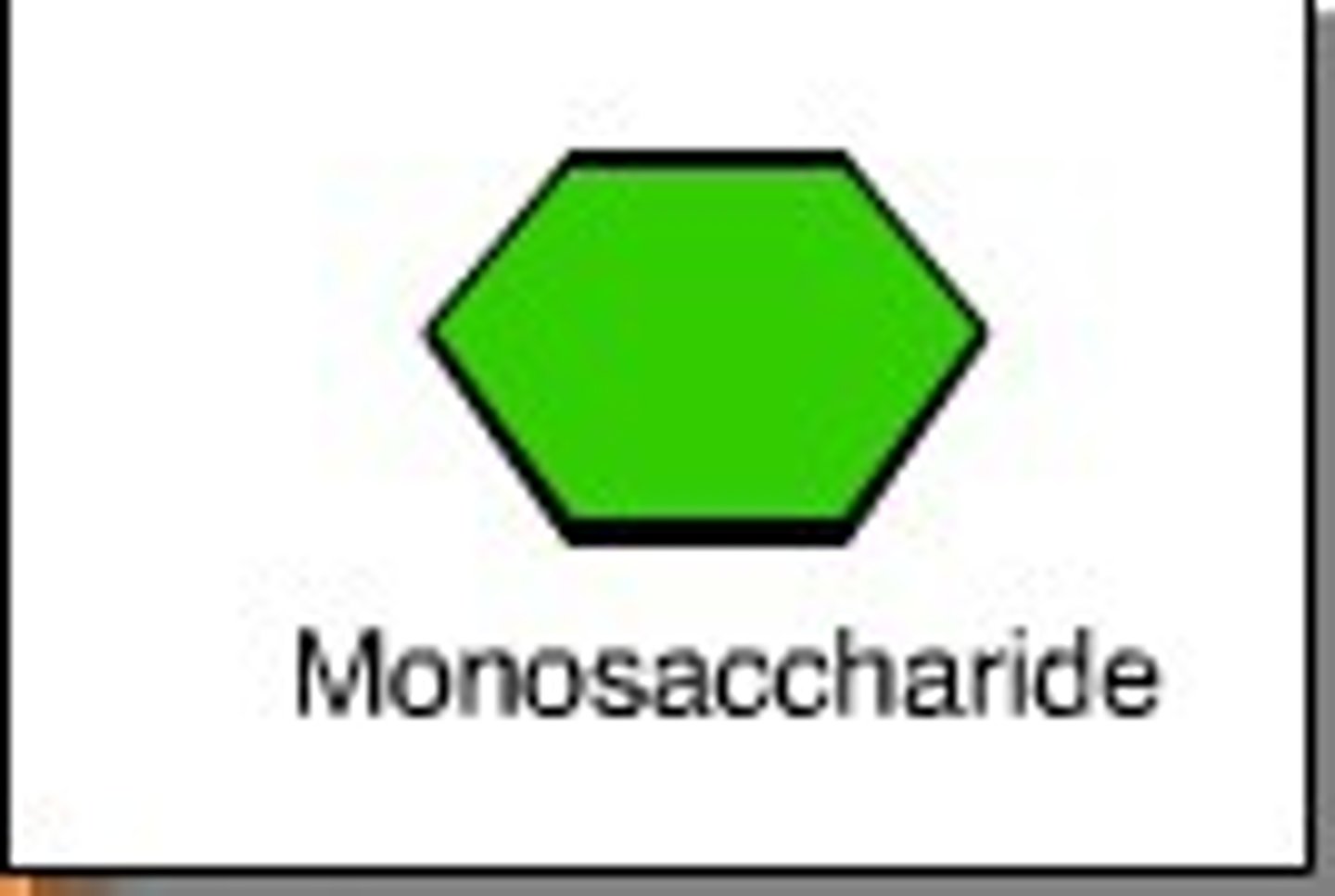
Monosaccharide
The simplest carbohydrate; a simple sugar with a molecular formula that is generally some multiple of CH2O. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides and polysaccharides.
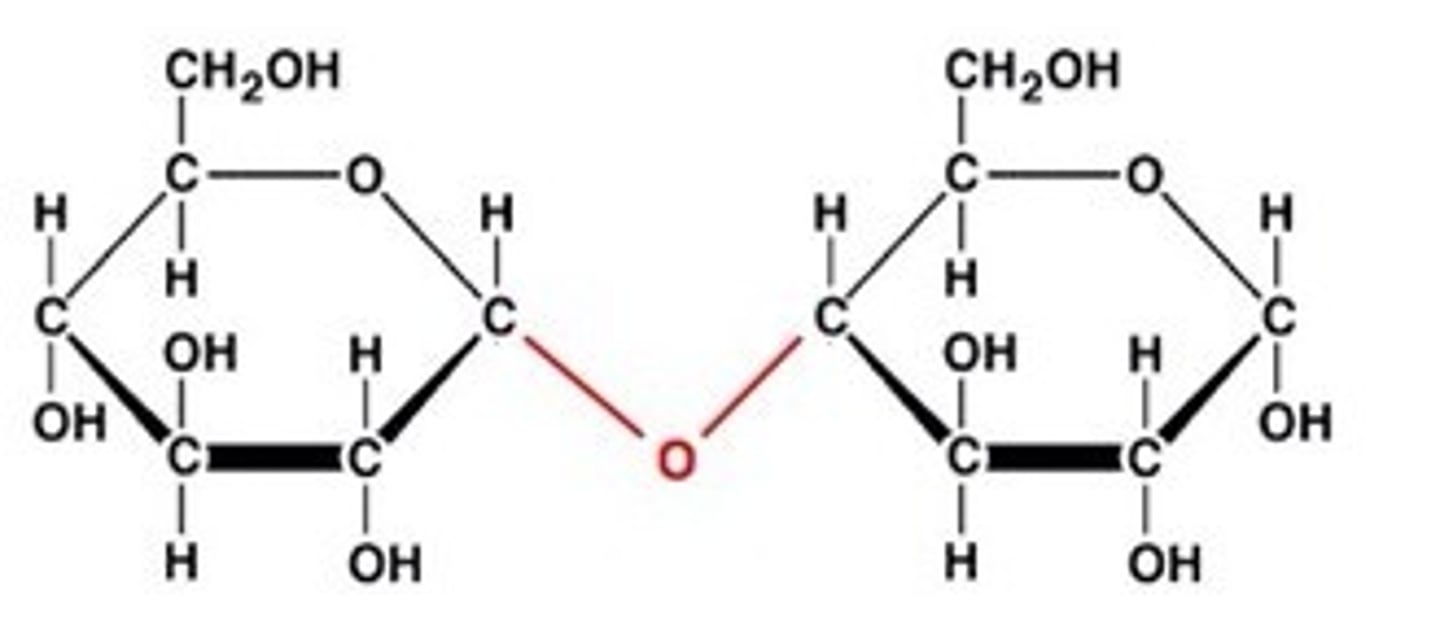
Disaccharide
A sugar molecule consisting of two monosaccharides linked by a dehydration reaction.
Starch
A storage polysaccharide found in the roots of plants and certain other cells; a polymer of glucose.

Cellulose
A large polysaccharide composed of many glucose monomers linked into cable-like fibrils that provide structural support in plant cell walls.

Chitin
A structural polysaccharide found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of arthropods.

Lipid
An organic compound consisting mainly of carbon and hydrogen atoms linked by nonpolar convalent bonds, making the compound mostly hydrophobic. Lipids include fats, phospholipids, and steroids and are insoluble in water.

Hydrophobic
"Water-fearing"; pertaining to nonpolar molecules (or parts of molecules) that do not dissolve in water.
Fat
A large lipid molecule made from an alcohol called glycerol and three fatty acids; a triglyceride. Most fats function as energy-storage molecules.

Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Pertaining to fats and fatty acids whose hydrocarbon chains lack the maximum number of hydrogen atoms and therefore have one or more double covalent bonds. Unsaturated fats and fatty acids do not solidify at room temperature.

Saturated Fatty Acid
Pertaining to fats and fatty acids whose hydrocarbon chains contain the maximum number of hydrogens and therefore have no double covalent bonds. Saturated fats and fatty acids solidify at room temperature.

Trans Fats
An unsaturated fat, formed artificially during hydrogenation of vegetable oils, which is linked to health risks.

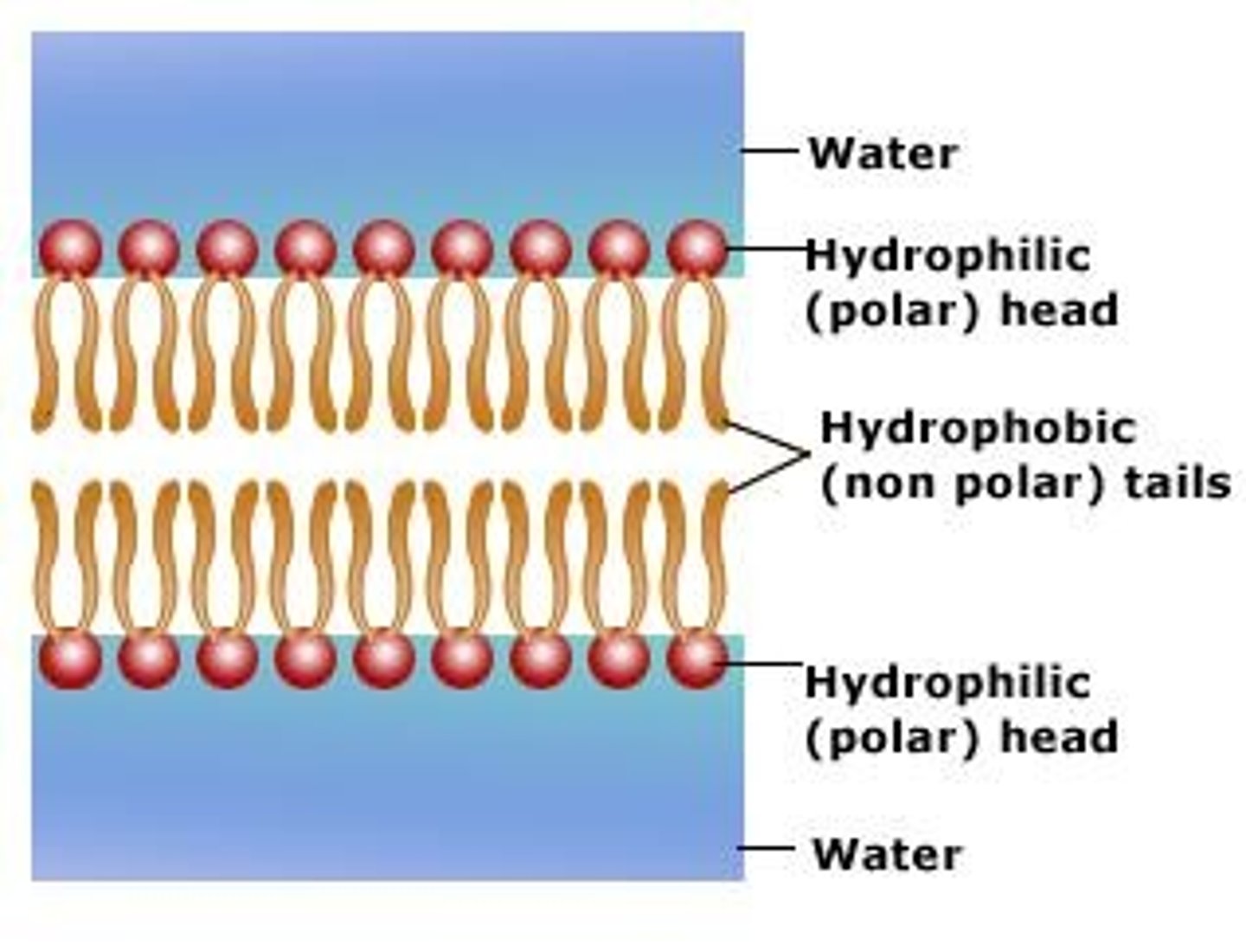
Phospholipid
A lipid made up of glycerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group, giving the molecule a nonpolar hydrophobic tail and a polar hydrophilic head. Phospholipids form bilayers that function as biological membranes.
Steroid
A type of lipid whose carbon skeleton is in the form of four fused rings with various chemical groups attached; examples are cholesterol, testosterone, and estrogen.

Cholesterol
A steroid that is an important component of animal cell membranes and that acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other steroids such as hormones.
Anabolic Steroids
A synthetic variant of the male hormone testosterone that mimics some of its effects.

Protein
A functional biological molecule consisting of one or more polypeptides folded into a specific three-dimensional structure.

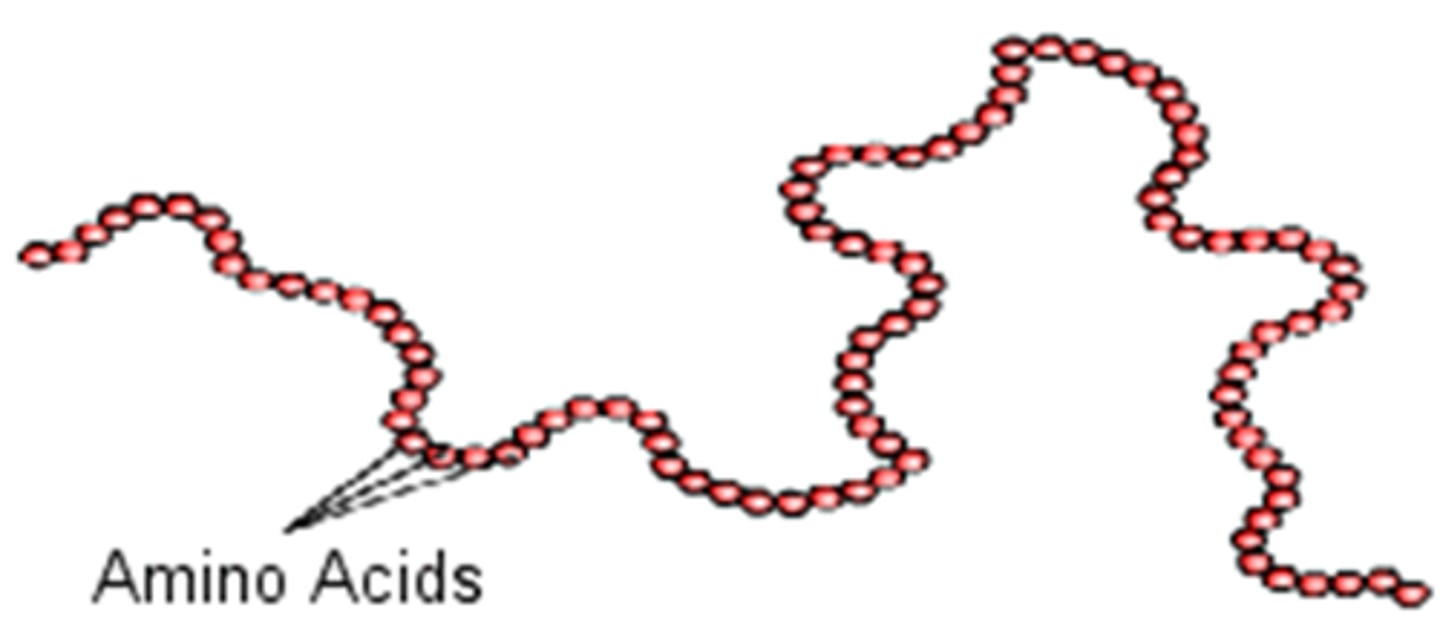
Amino Acid
An organic molecule containing a carboxyl group and an amino group; serves as the monomer of proteins.
Peptide Bond
The covalent linkage between two amino acid units in a polypeptide; formed by a dehydration reaction.
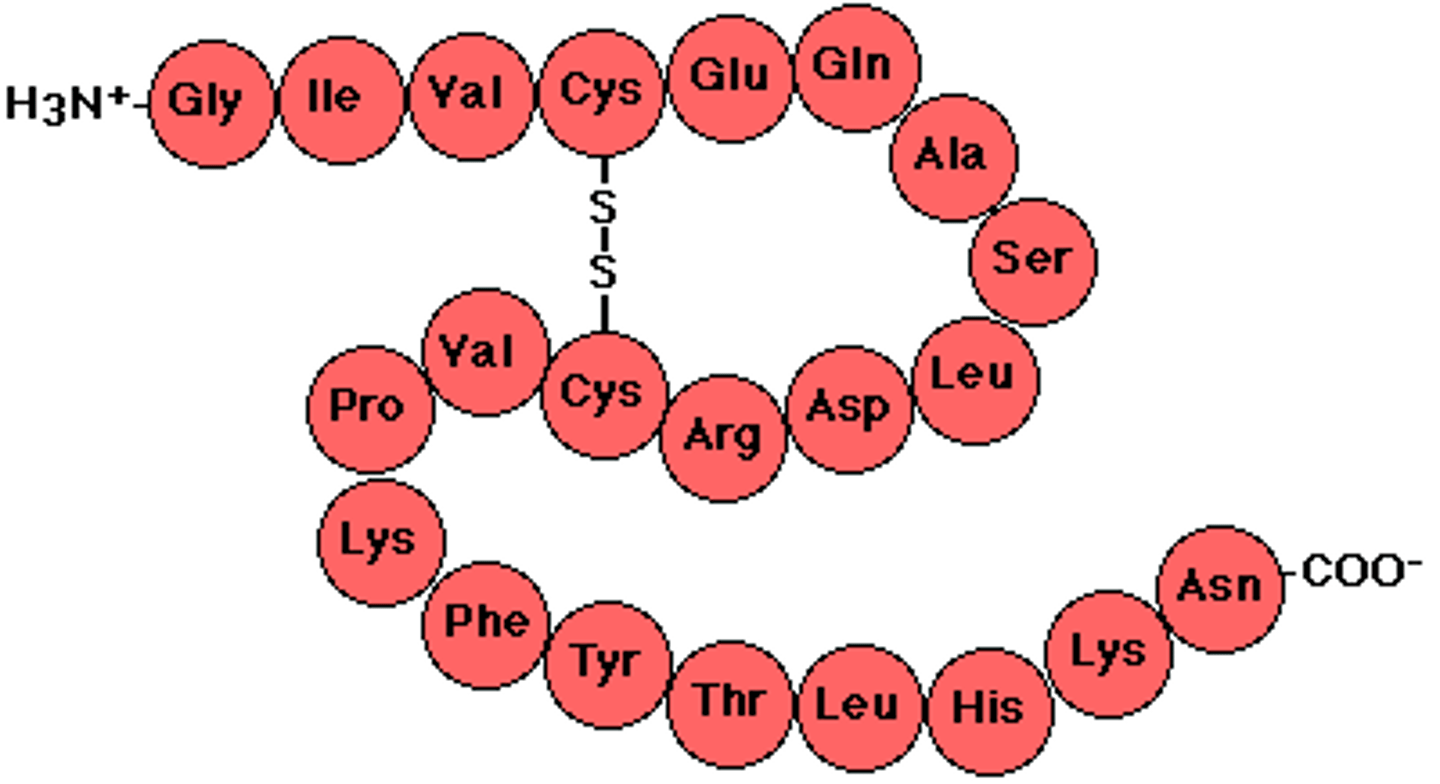
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Denaturation
A process in which a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and hence function; can be caused by changes in pH or salt concentration or by high temperature. Also refers to the separation of the two strands of the DNA double helix, caused by similar factors.
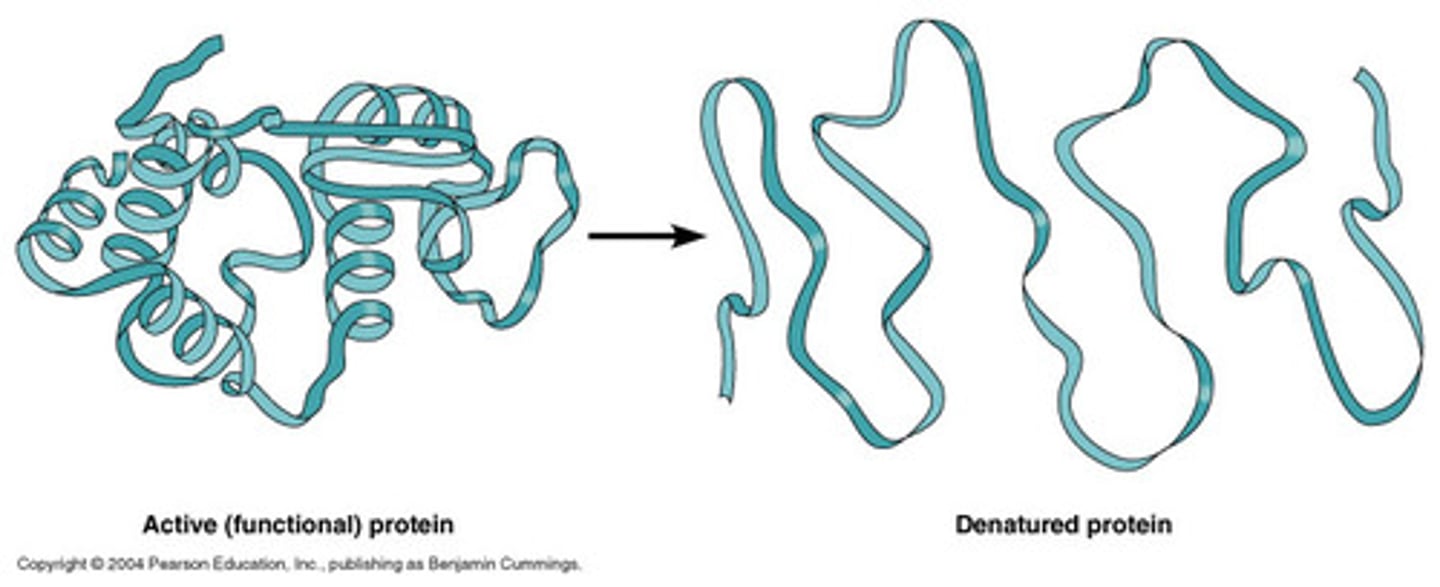
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.

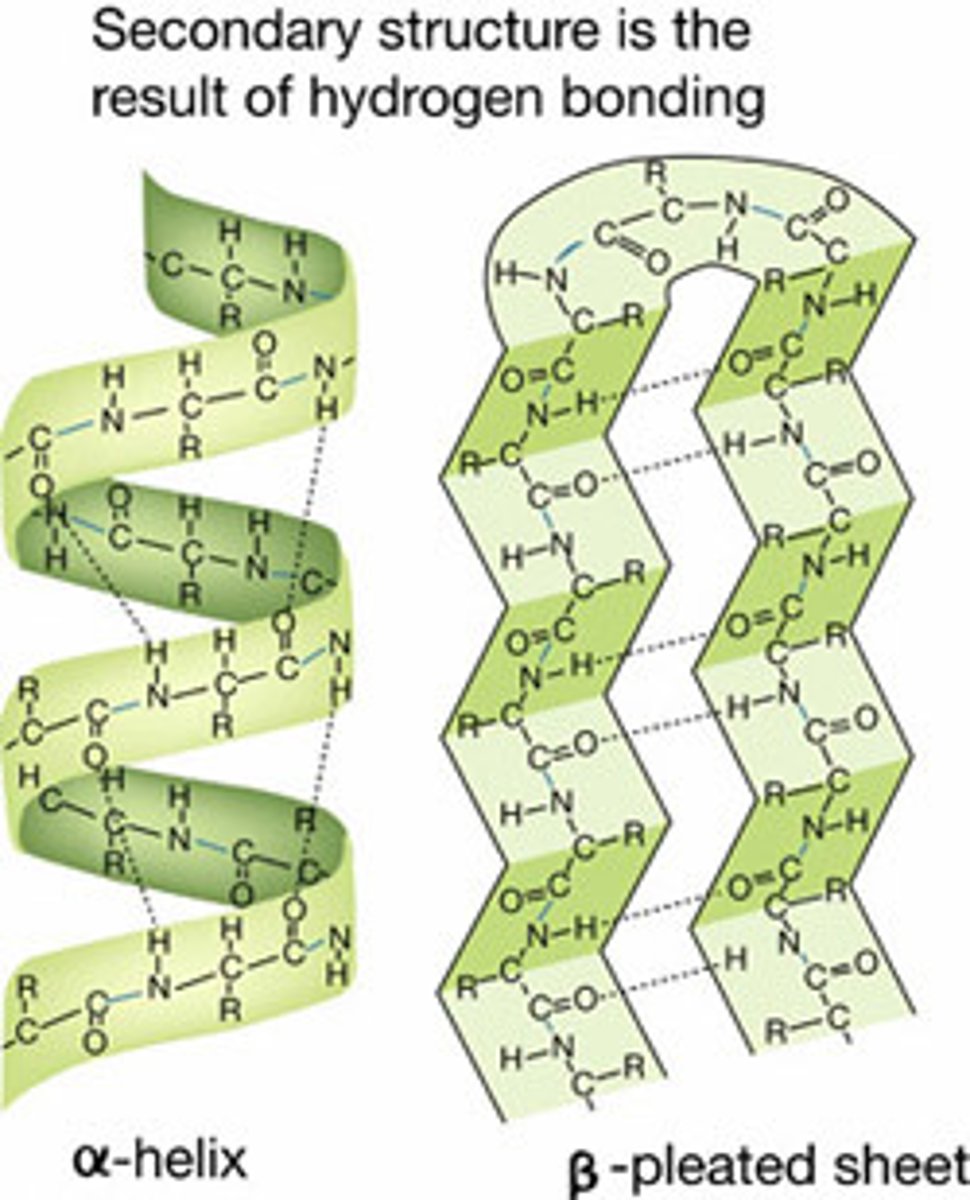
Secondary structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils or folds of a polypeptide chain.
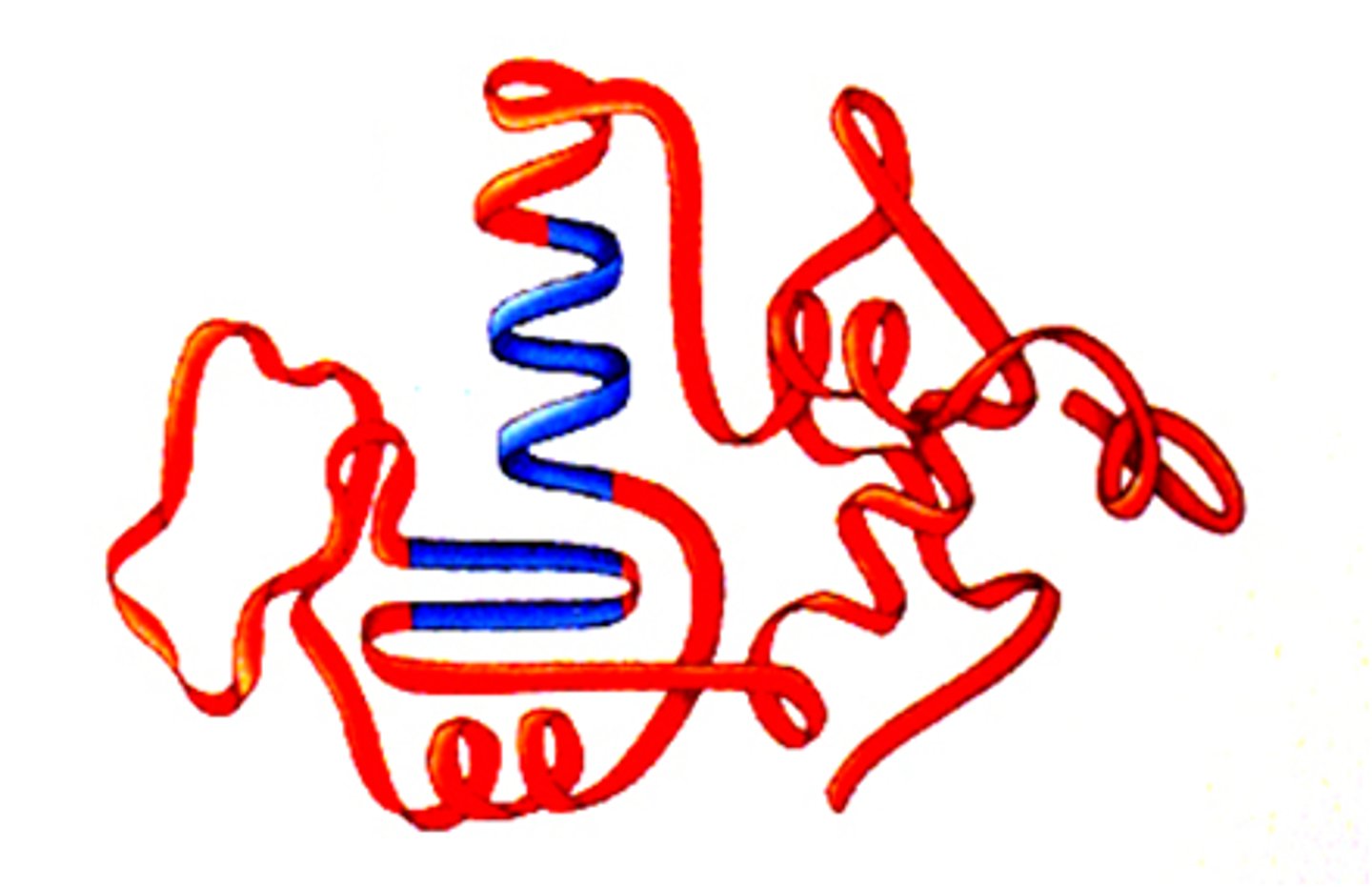
Tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
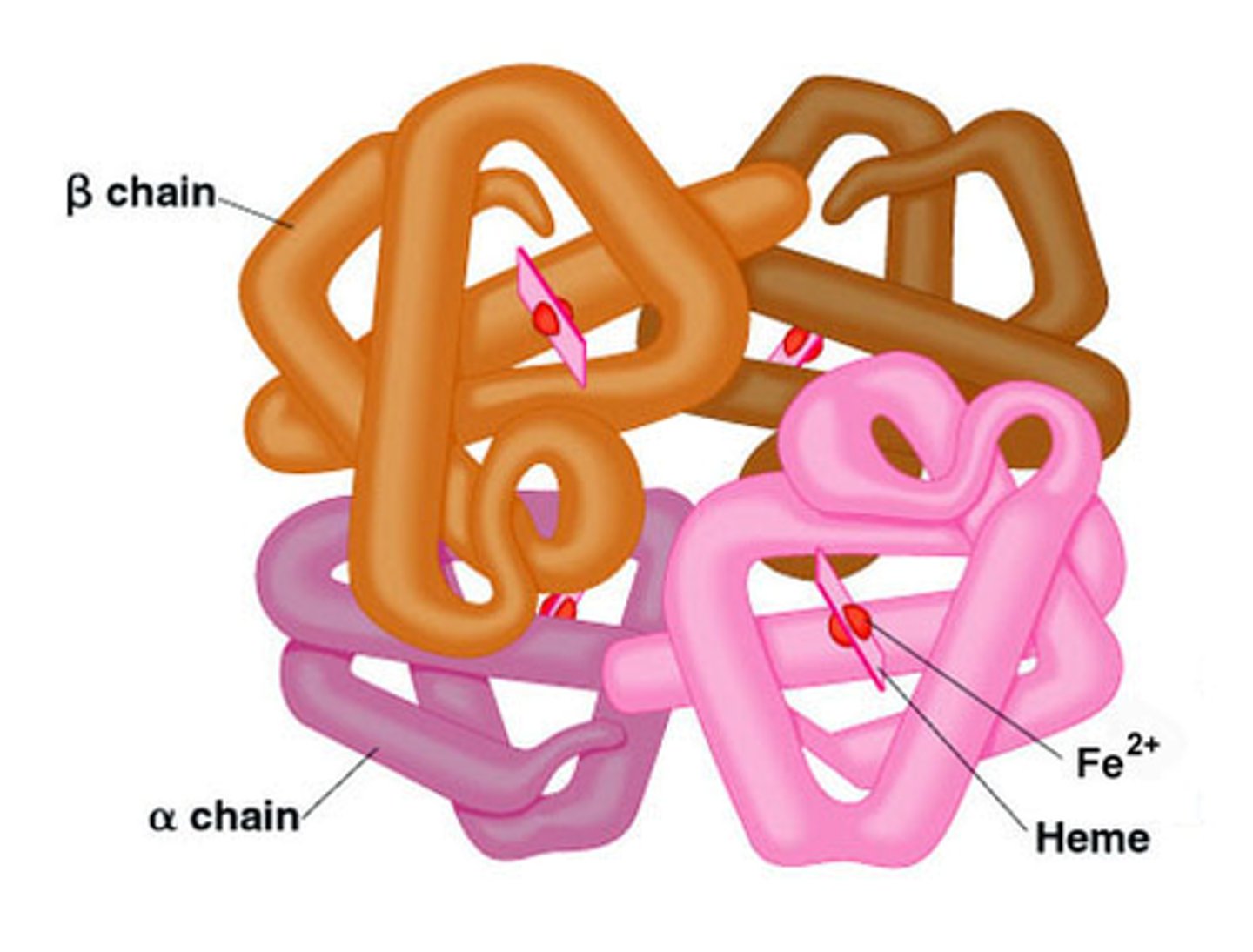
Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
Gene
A discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA (or RNA, in some viruses). Most of the genes of a eukaryote are located in its chromosomal DNA; a few are carried by the DNA of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
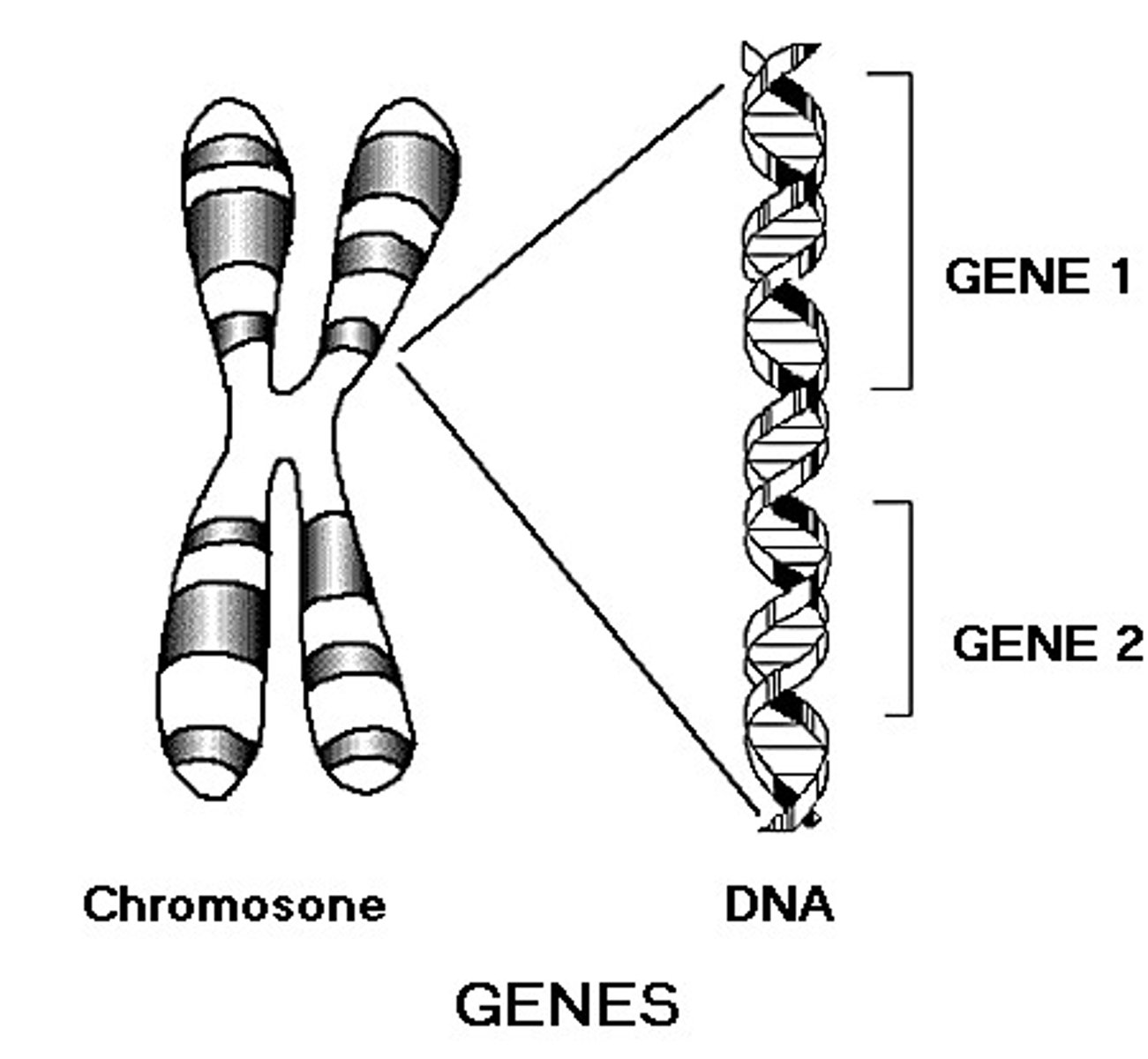
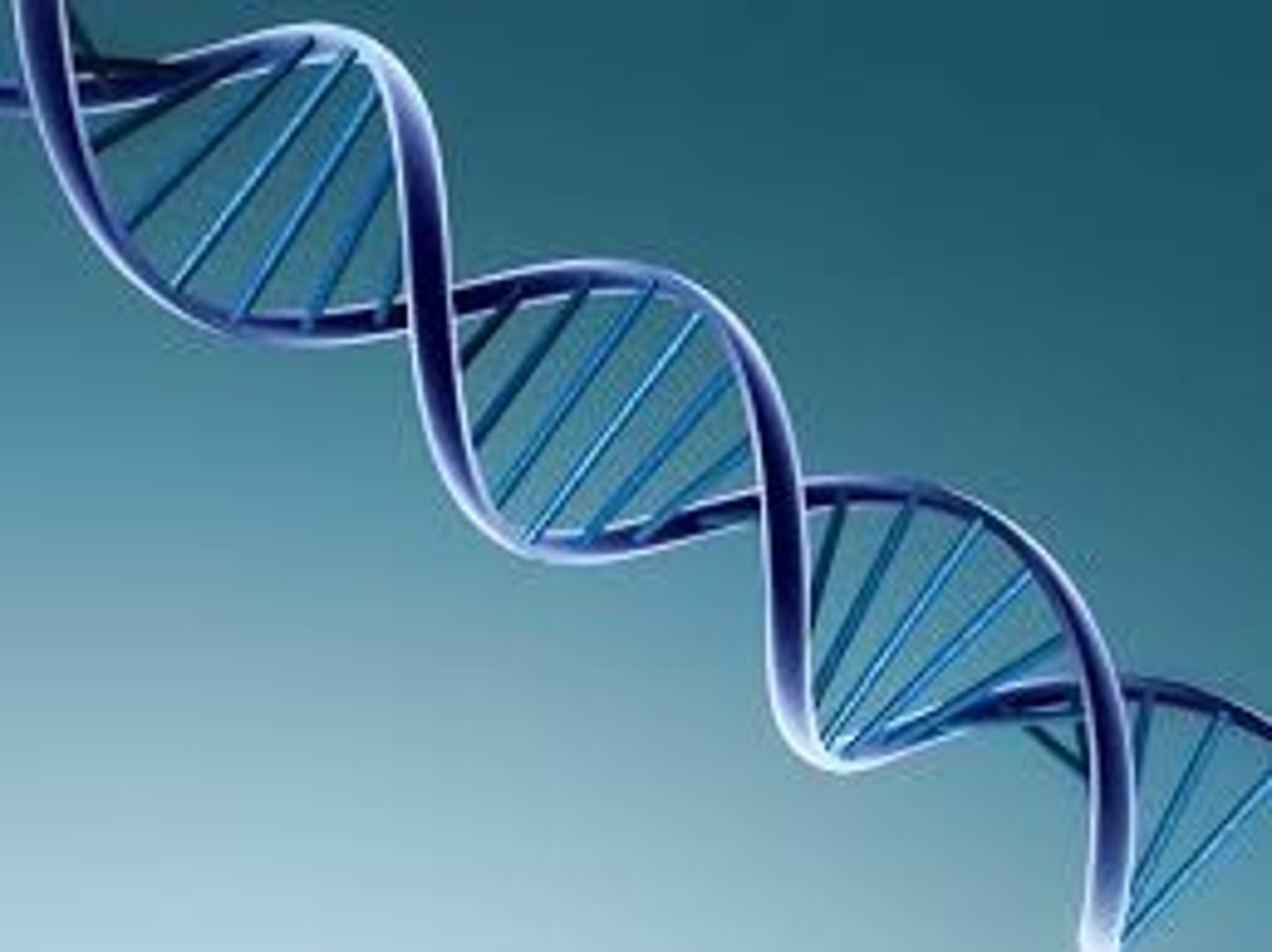
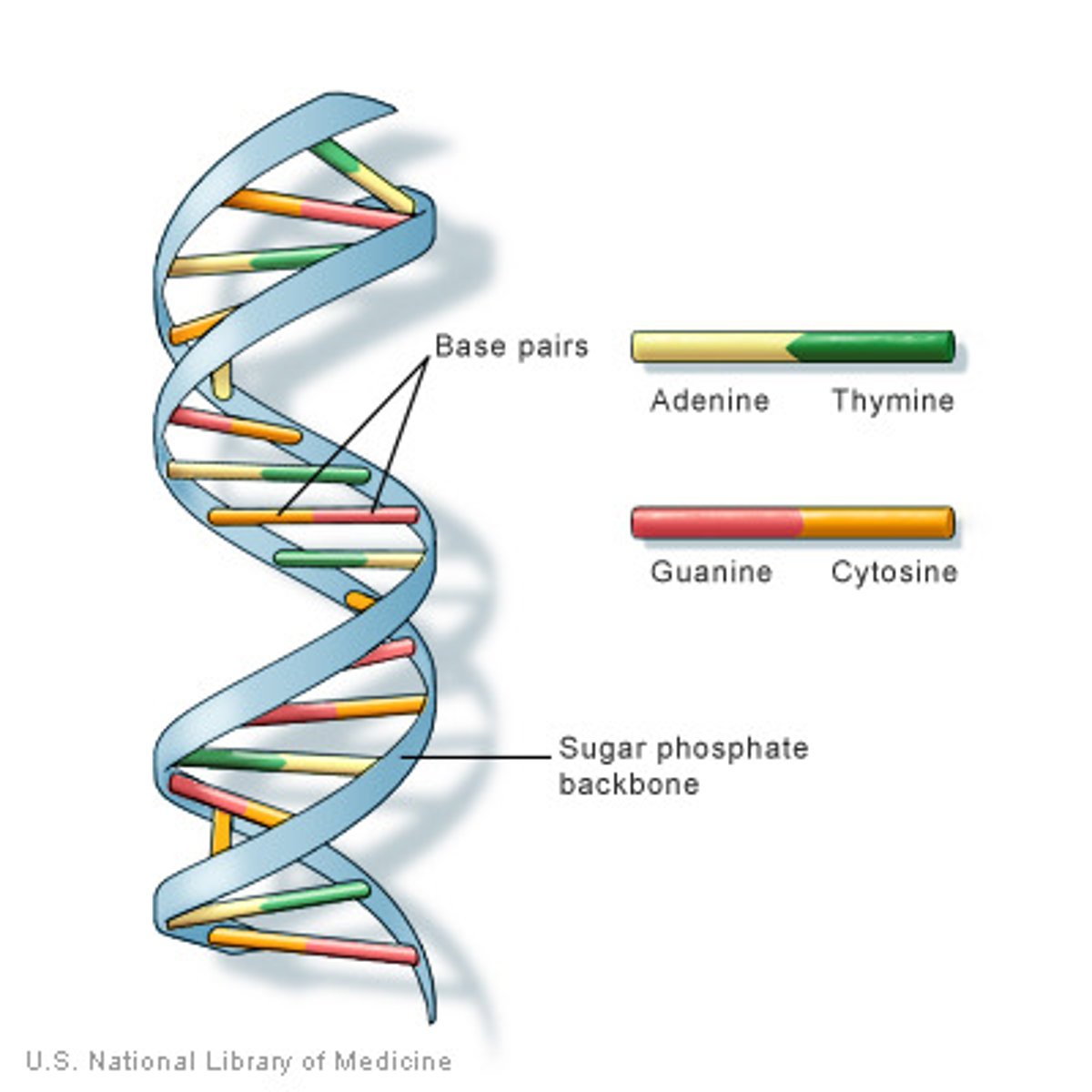
DNA
A double-stranded helical nucleic acid molecule consisting of nucleotide monomers with deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). Capable of replicating, is an organism's genetic material. See also gene.
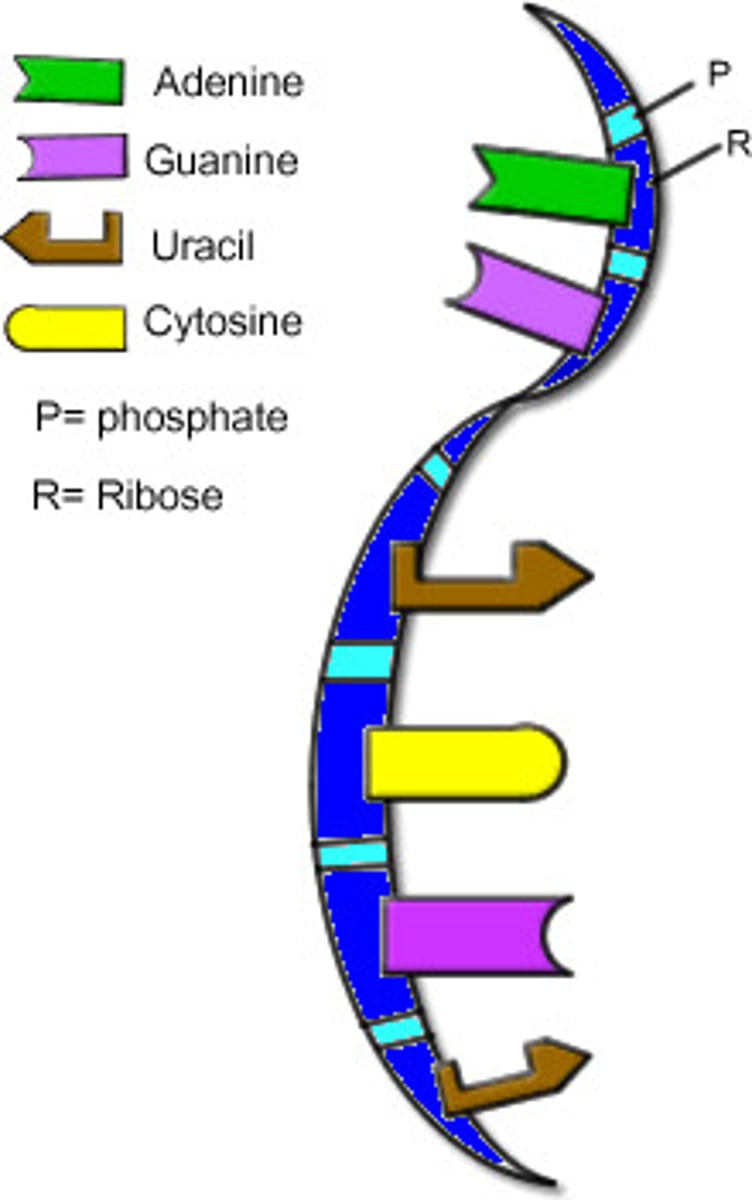
Nucleic Acid
A polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers; serves as a blueprint for proteins and, through the actions of proteins, for all cellular structures and activities. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA.
RNA
A type of nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses.
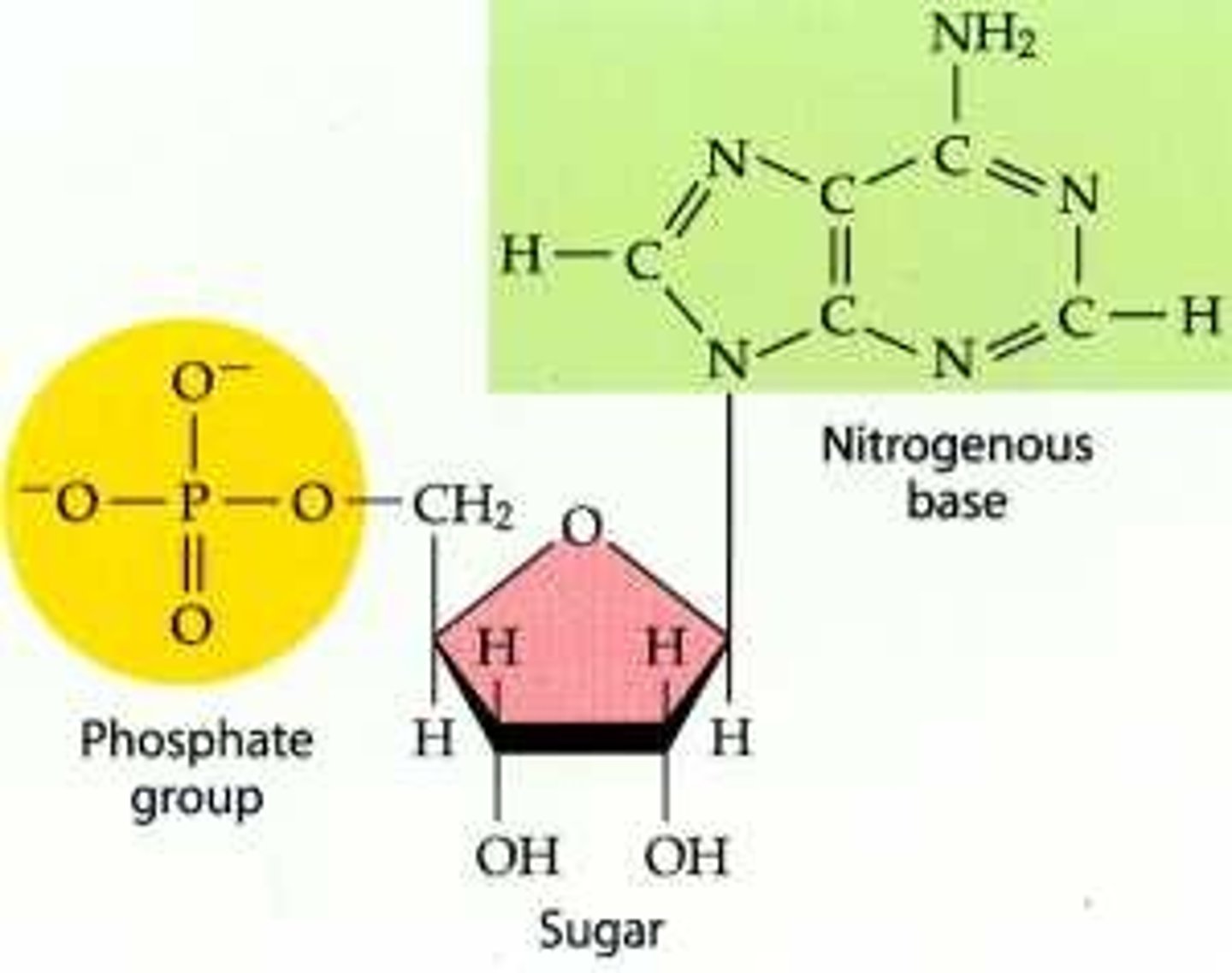
Nucleotides
An organic monomer consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids.
Double helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
