C/T medical screening
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
self-report questionnaires
Use ___ for pts w/ neck pain to id baseline status and monitor changes related to pain/func/disability/psychosocial funcing
red flag
warning sign that indicate need for reeval by a medical specialist
yellow flag
warning signs used to assess for pain-associated psychological distress
yellow flag
indicate higher risk for delayed recovery or development of chronic sxs
yellow flag
may require referral for psychological eval/counseling
viscerogenic
type of conditions: neoplasm, inflam or systemic disease, cardiopulm condition, C vascular pathology
neuromoskel
type of conditions: upper C lig instability, C myelopathy
98.6, 160/95, 100, 25
signs of inflam or systemic disease: temp >___°F, bp >___mmHg, resting pulse >___bpm, resting RR >___breaths/min, excessive fatigue
C neoplasm
type of conditions: metastatic lesions (leukemia, hodgkin’s disease), C bone/cord tumors, lung cancer, pancoast’s tumor, esophageal cancer, thyroid cancer
T neoplasm
type of conditions: mediastinal tumor, metastatic lesion, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, multi myeloma
pulm
types of conditions: tracheobronchial irritation, chronic bronchitis, pneumothorax, pleuritis involving the diaphragm
cardiac
types of conditions: angina, myocardial infarction, aortic aneurysm, occipital migraine, C A ischemia or dissection, arteritis
C vascular pathology
can present w/ neck pain and HA up to 30 days
internal carotid A
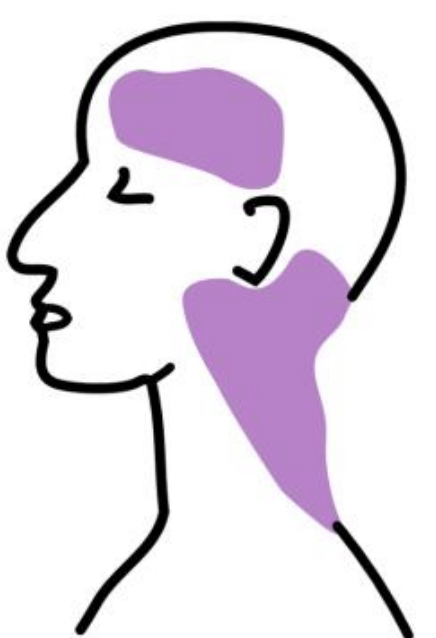

vertebral A
recent onset, mod/high severity, 1st and worst, 5D/3N
subjective exam hints for C vascular pathology
C vascular pathology
risk factors: current/past smoker, hypertension, high cholesterol, migraine, vascular anomaly, fam hx of stroke, taking oral contraception, recent infection, recent trauma
dizzy, diplopia, drop attack, dysphagia, dysarthria
5 D’s
numb, nystagmus, nausea
3 N’s
vitals (bp, hr, auscultation), neuro (CN, reflex, strength/sensation, gait), C A/PRoM
objective exam for C vascular pathology
canadian C-spine rules
screening tool for C spine fx; determines the need for C spine X-ray
65+, dangerous mechanism, paresthesia
canadian C-spine rules: high risk factors that mandates radiography
fall 3ft or 5 stairs, axial load to head, MVA w/ high speed or w/ rollover/eject; can’t rot neck 45° L/R
canadian C-spine rules: “dangerous mechanisms”
safe assess of RoM
canadian C-spine rules: simple rear-end MVA, sit/ambulatory, delayed onset of neck pain, no midline C-spine tenderness
5
C images should include ___-view x-ray
major trauma or minor if >50, osteoporosis, long-term corticosteroid use
red flags for T spinal fx
>52, BMI <22, no leg pain, no exercise, female
osteoporotic compression fx of T spine cluster
upper C lig instability
risk factors: recent trauma, throat infection, congenital collagenous compromise (down syndrome, ehlers-danlos), inflam arthritides (RA, ankylosing spondylitis), recent neck/head/dental surgery
C1
w/ lack of stability, ___ can slide forward
upper C lig instability
subjective findings: neck/head pain, feel unstable, constant need for support, sxs worsen, facial/limb paresthesia/overt LoB w/ AROM, lump in throat, metallic taste, limb weakness/coordination loss
sharp purser, alar lig, ant shear
3 tests for upper C lig instability
C myelopathy
UMN disorder where SC is compromised in C spine central canal
cook
name of cluster for C myelopathy
>45, gait deviation, hoffman, inverted supinator, babinski
cook cluster parts
C myelopathy
subjective findings: >45, gait unsteadiness, LoB/coordination, limb weakness/paresthesia, bowel/bladder dysfunc
spondylosis w/ stenosis, disc herniation, spondylolisthesis, tumor
4 ways of SC compression (C myelopathy)