The rate and extent of chemical change
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is collision theory?
Chemical reactions can only occur when the reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy
Define activation energy
The minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur
How do you calculate the mean rate of reaction?
Mean rate of reaction = quantity of reactant used/time taken
OR
Mean rate of reaction = quantity of product formed/time taken
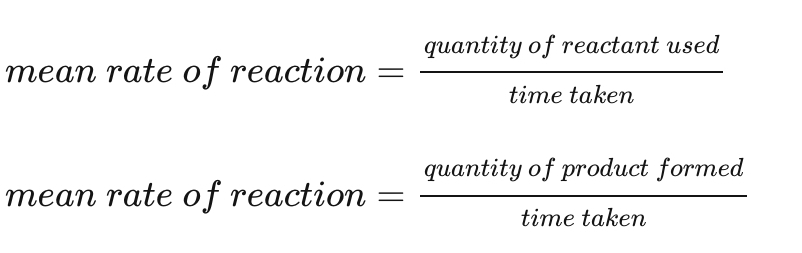
How do you calculate the rate of reaction on a graph?
By calculating the gradient → draw a tangent if the line is curved
What can increase the rate of reaction?
Increased concentration (or pressure for gases)
Increased temperature
Increased surface area
Catalysts
How does a catalyst increase the rate of reaction?
Catalysts offer an alternate reaction pathway which uses less activation energy
↳ This dosen't change the number of collisions but increases the number of sucessful collisions → particles has more energy
If the forward reaction is exothermic, what will the backwards reaction be?
Endothermic → same amount of energy transferred will be the same
What is dynamic equilibrium? What happens at equilibrium?
When a reversible reaction in a closed system reaches equilibrium
so when the:
Forward and backward reactions are still happening
Forward and backward reactions have the same rate of reaction
Concentrations of all the reacting substances remain constant
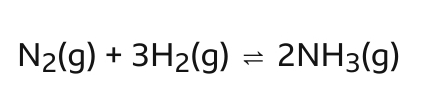
What is this process called? Where is the equilibrium position?
To the left if the concentration of N2 and H2 is greater than NH3
and vice versa
What is Le Chatelier's principle?
That if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in conditions, the system will respond by shifting the position of equilibrium to counteract the change
what happens to the position of equilibrium when the concentration of reactants are increased?
Increasing the concentration of reactants will shift the position of equilibrium to the products and favour the backwards reactions which will increase the amount of products produced
What will happen to the position of equilibrium if the temperature of exothermic reaction is increased?
Increasing the temperature of the exothermic reaction will cause the position of equilibrium to shift to the right, favouring the endothermic reaction and decrease the amount of products produced
What will happen to the position of equilibrium if the pressure of the reaction is increased?
If the pressure of the reaction is increased, the equilibrium position will shift to the side with the fewest molecules of gas to reduce the pressure